AsyncTask使用及源码查看Android P
AsyncTask
AsyncTask用于处理耗时任务,可以即时通知进度,最终返回结果。可以用于下载等处理。
使用
实现类继承三个方法
1. doInBackground后台执行,在此方法中进行延时操作
/*** Override this method to perform a computation on a background thread. The* specified parameters are the parameters passed to {@link #execute}* by the caller of this task.** This method can call {@link #publishProgress} to publish updates* on the UI thread.** @param params The parameters of the task.** @return A result, defined by the subclass of this task.** @see #onPreExecute()* @see #onPostExecute* @see #publishProgress*/@WorkerThreadprotected abstract Result doInBackground(Params... params);
2. onProgressUpdate刷新UI
/*** Runs on the UI thread after {@link #publishProgress} is invoked.* The specified values are the values passed to {@link #publishProgress}.** @param values The values indicating progress.** @see #publishProgress* @see #doInBackground*/@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})@MainThreadprotected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values){}
3. onPostExecute结果返回,此结果即为后台执行方法返回的结果。
/*** <p>Runs on the UI thread after {@link #doInBackground}. The* specified result is the value returned by {@link #doInBackground}.</p>* * <p>This method won't be invoked if the task was cancelled.</p>** @param result The result of the operation computed by {@link #doInBackground}.** @see #onPreExecute* @see #doInBackground* @see #onCancelled(Object) */@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})@MainThreadprotected void onPostExecute(Result result) {}
Result,Progress,Params三者是AsyncTask的泛型,从代码可以看出,Result为返回结果类型,Progress是刷新进度的类型,Params是处理耗时任务时需要传入的类型。
public abstract class AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result>
4. execute启动方法
/*** Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns* itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it.* * <p>Note: this function schedules the task on a queue for a single background* thread or pool of threads depending on the platform version. When first* introduced, AsyncTasks were executed serially on a single background thread.* Starting with {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#DONUT}, this was changed* to a pool of threads allowing multiple tasks to operate in parallel. Starting* {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#HONEYCOMB}, tasks are back to being* executed on a single thread to avoid common application errors caused* by parallel execution. If you truly want parallel execution, you can use* the {@link #executeOnExecutor} version of this method* with {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR}; however, see commentary there for warnings* on its use.** <p>This method must be invoked on the UI thread.** @param params The parameters of the task.** @return This instance of AsyncTask.** @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either* {@link AsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link AsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}.** @see #executeOnExecutor(java.util.concurrent.Executor, Object[])* @see #execute(Runnable)*/@MainThreadpublic final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) {return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);}
分析
相关知识点:
- 线程池
- Android Handler
1. 构造器
/*** Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.*/public AsyncTask() {this((Looper) null);}/*** Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.** @hide*/public AsyncTask(@Nullable Handler handler) {this(handler != null ? handler.getLooper() : null);}/*** Creates a new asynchronous task. This constructor must be invoked on the UI thread.** @hide*/public AsyncTask(@Nullable Looper callbackLooper) {mHandler = callbackLooper == null || callbackLooper == Looper.getMainLooper()? getMainHandler(): new Handler(callbackLooper);mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() {public Result call() throws Exception {mTaskInvoked.set(true);Result result = null;try {Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);//noinspection uncheckedresult = doInBackground(mParams);Binder.flushPendingCommands();} catch (Throwable tr) {mCancelled.set(true);throw tr;} finally {postResult(result);}return result;}};mFuture = new FutureTask<Result>(mWorker) {@Overrideprotected void done() {try {postResultIfNotInvoked(get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {android.util.Log.w(LOG_TAG, e);} catch (ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException("An error occurred while executing doInBackground()",e.getCause());} catch (CancellationException e) {postResultIfNotInvoked(null);}}};}
1.1 Handler
使用getMainHandler()返回的Handler。消息处理部分可以看到完成处理与进度更新。
private static Handler getMainHandler() {synchronized (AsyncTask.class) {if (sHandler == null) {sHandler = new InternalHandler(Looper.getMainLooper());}return sHandler;}}private static class InternalHandler extends Handler {public InternalHandler(Looper looper) {super(looper);}@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"})@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {AsyncTaskResult<?> result = (AsyncTaskResult<?>) msg.obj;switch (msg.what) {case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT:// There is only one resultresult.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]);break;case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS:result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData);break;}}}private void finish(Result result) {if (isCancelled()) {onCancelled(result);} else {onPostExecute(result);}mStatus = Status.FINISHED;}@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})@MainThreadprotected void onProgressUpdate(Progress... values) {}
1.2 WorkerRunnable实现对象mWorker
使用Callable接口。
private static abstract class WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> implements Callable<Result> {Params[] mParams;}1.3 FutureTask实现对象 mFuture
FutureTask其中保存了Callable接口。
public FutureTask(Callable<V> var1) {if (var1 == null) {throw new NullPointerException();} else {this.callable = var1;this.state = 0;}}
2. exectue执行操作开始
@MainThreadpublic final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> execute(Params... params) {return executeOnExecutor(sDefaultExecutor, params);}/*** Executes the task with the specified parameters. The task returns* itself (this) so that the caller can keep a reference to it.* * <p>This method is typically used with {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR} to* allow multiple tasks to run in parallel on a pool of threads managed by* AsyncTask, however you can also use your own {@link Executor} for custom* behavior.* * <p><em>Warning:</em> Allowing multiple tasks to run in parallel from* a thread pool is generally <em>not</em> what one wants, because the order* of their operation is not defined. For example, if these tasks are used* to modify any state in common (such as writing a file due to a button click),* there are no guarantees on the order of the modifications.* Without careful work it is possible in rare cases for the newer version* of the data to be over-written by an older one, leading to obscure data* loss and stability issues. Such changes are best* executed in serial; to guarantee such work is serialized regardless of* platform version you can use this function with {@link #SERIAL_EXECUTOR}.** <p>This method must be invoked on the UI thread.** @param exec The executor to use. {@link #THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR} is available as a* convenient process-wide thread pool for tasks that are loosely coupled.* @param params The parameters of the task.** @return This instance of AsyncTask.** @throws IllegalStateException If {@link #getStatus()} returns either* {@link AsyncTask.Status#RUNNING} or {@link AsyncTask.Status#FINISHED}.** @see #execute(Object[])*/@MainThreadpublic final AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result> executeOnExecutor(Executor exec,Params... params) {if (mStatus != Status.PENDING) {switch (mStatus) {case RUNNING:throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"+ " the task is already running.");case FINISHED:throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot execute task:"+ " the task has already been executed "+ "(a task can be executed only once)");}}mStatus = Status.RUNNING;onPreExecute();mWorker.mParams = params;exec.execute(mFuture);return this;}
2.1 进行status判断:
- 正在运行的对象调用此方法会抛出异常,正在运行的设置在此方法中。
- 已经完成的对象调用此方法会抛出异常,已经完成的设置在InternalHandler中调用。
private void finish(Result result) {if (isCancelled()) {onCancelled(result);} else {onPostExecute(result);}mStatus = Status.FINISHED;}
2.2 调用onPreExecte()方法
子类实现此方法会在耗时操作前执行一些操作。
/*** Runs on the UI thread before {@link #doInBackground}.** @see #onPostExecute* @see #doInBackground*/@MainThreadprotected void onPreExecute() {}
2.3 执行exec.execute(mFuture)
2.3.1 exec是什么?
通过调用链可看出是sDefaultExecutor。在代码中可以看到是SerialExecutor静态内部类对象。
public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = new SerialExecutor();private static final int MESSAGE_POST_RESULT = 0x1;private static final int MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS = 0x2;private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR;private static class SerialExecutor implements Executor {final ArrayDeque<Runnable> mTasks = new ArrayDeque<Runnable>();Runnable mActive;public synchronized void execute(final Runnable r) {mTasks.offer(new Runnable() {public void run() {try {r.run();} finally {scheduleNext();}}});if (mActive == null) {scheduleNext();}}protected synchronized void scheduleNext() {if ((mActive = mTasks.poll()) != null) {THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR.execute(mActive);}}}
2.3.2 execute(final Runnable r)传是mFuture这里是Runnable
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V>{}
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {void run();
}
2.3.3 调用mFuture的run方法
刚才1.3futuretask实现对象-mfuture可以看出
this.callable = var1;,即此处调用了mWorker的call()方法
public void run() {if (this.state == 0 && UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, (Object)null, Thread.currentThread())) {boolean var9 = false;try {var9 = true;Callable var1 = this.callable;if (var1 != null) {if (this.state == 0) {Object var2;boolean var3;try {var2 = var1.call();var3 = true;}....}....}....}....}}
2.3.4 mWorker调用doInBackground
mWorker = new WorkerRunnable<Params, Result>() {public Result call() throws Exception {mTaskInvoked.set(true);Result result = null;try {Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);//noinspection uncheckedresult = doInBackground(mParams);Binder.flushPendingCommands();} catch (Throwable tr) {mCancelled.set(true);throw tr;} finally {postResult(result);}return result;}};
2.3.5 doInBackground返回result,调用postResult(result)
这里发送了结果,见1.1处理
private Result postResult(Result result) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Message message = getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result));message.sendToTarget();return result;}
3. 进度刷新
进度刷新可以调用如下方法。大多在doInBackground中使用。
/*** This method can be invoked from {@link #doInBackground} to* publish updates on the UI thread while the background computation is* still running. Each call to this method will trigger the execution of* {@link #onProgressUpdate} on the UI thread.** {@link #onProgressUpdate} will not be called if the task has been* canceled.** @param values The progress values to update the UI with.** @see #onProgressUpdate* @see #doInBackground*/@WorkerThreadprotected final void publishProgress(Progress... values) {if (!isCancelled()) {getHandler().obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS,new AsyncTaskResult<Progress>(this, values)).sendToTarget();}}
4. 如何暂停/取消
直接在doInBackground方法中返回Result即可,Result是泛型,可以自定义各种类型的返回值。
相关文章:

AsyncTask使用及源码查看Android P
AsyncTask AsyncTask用于处理耗时任务,可以即时通知进度,最终返回结果。可以用于下载等处理。 使用 实现类继承三个方法 1. doInBackground后台执行,在此方法中进行延时操作 /*** Override this method to perform a computation on a back…...
花2个月面过华为测开岗,拿个30K不过分吧?
背景介绍 美本计算机专业,代码能力一般,之前有过两段实习以及一个学校项目经历。第一份实习是大二暑期在深圳的一家互联网公司做前端开发,第二份实习由于大三暑假回国的时间比较短(小于两个月),于是找的实…...

JAVA练习51-最大子数组和
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 目录 前言 一、题目-最大子数组和 1.题目描述 2.思路与代码 2.1 思路 2.2 代码 总结 前言 提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容: 2月15日练…...

Inception Transformer
paper链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12956v2 code链接: https://github.com/sail-sg/iFormer Inception Transformer一、引言二、实现细节三、实验一、分类二、检测三、分割四、消融实验一、引言 最近的研究表明,Transformer具有很强的建立远程依赖关系的能力…...
10分钟学会数据库压力测试,你敢信?
目录 前言 查看数据库版本 下载驱动: 菜单路径 配置 Variable Name Bound to Pool模块配置 Connection pool configuration模块配置 Database Connection Configuration模块配置 菜单路径 Variable Name Bound to Pool 脚本结构 脚本(执行查询…...

论文阅读 | Video Super-Resolution Transformer
引言:2021年用Transformer实现视频超分VSR的文章,改进了SA并在FFN中加入了光流引导 论文:【here】 代码:【here】 Video Super-Resolution Transformer 引言 视频超分中有一组待超分的图片,因此视频超分也经常被看做…...

7-6 带头节点的双向循环链表操作
本题目要求读入一系列整数,依次插入到双向循环链表的头部和尾部,然后顺序和逆序输出链表。 链表节点类型可以定义为 typedef int DataType; typedef struct LinkedNode{DataType data;struct LinkedNode *prev;struct LinkedNode *next; }LinkedNode;链…...

npm publish 、 npm adduser 提示 403 的问题
0. 查看使用的源:npm config get registry1. 如果使用的不是官方的源,切换:npm config set registry https://registry.npmjs.org/2. 登录:npm adduser3. 查看是否登录成功:npm whoami4. 执行发布命令:npm …...

Java 8的函数式接口使用示例
什么是函数式接口 有且只有一个抽象方法的接口被称为函数式接口,函数式接口适用于函数式编程的场景,Lambda就是Java中函数式编程的体现,可以使用Lambda表达式创建一个函数式接口的对象,一定要确保接口中有且只有一个抽象方法&…...

2023年企业如何改善员工体验?为什么员工体验很重要?
什么是员工体验?大约 96% 的企业领导者表示,专注于员工体验可以更轻松地留住顶尖人才。[1] 这还不是全部。令人震惊的是,87%的企业领导者还表示,优先考虑员工的幸福感将给他们带来竞争优势。尽管有这些发现,但只有19%的…...
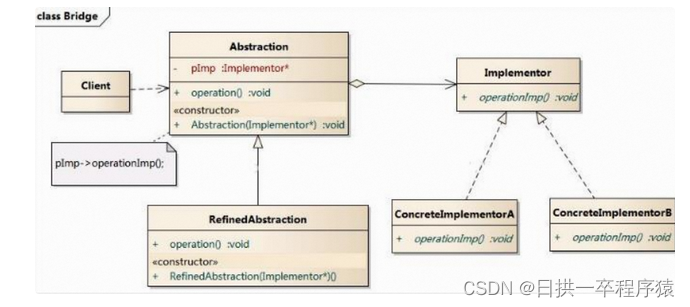
设计模式:桥接模式让抽象和实现解耦,各自独立变化
一、问题场景 现在对”不同手机类型“的 “不同品牌”实现操作编程(比如: 开机、关机、上网,打电话等) 二、传统解决方案 传统方案解决手机使用问题类图: 三、传统方案分析 传统方案解决手机操作问题分析 1、扩展性问题(类爆炸),如果我们…...

C++学习记录——십 STL初级认识、标准库string类
文章目录1、什么是STL2、STL简介3、什么是string类4、string类的常用接口说明1、常见构造函数2、容量操作3、迭代器4、其他的标准库的string类关于string类的内容,可以在cplusplus.com查看到。 1、什么是STL STL是C标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复…...
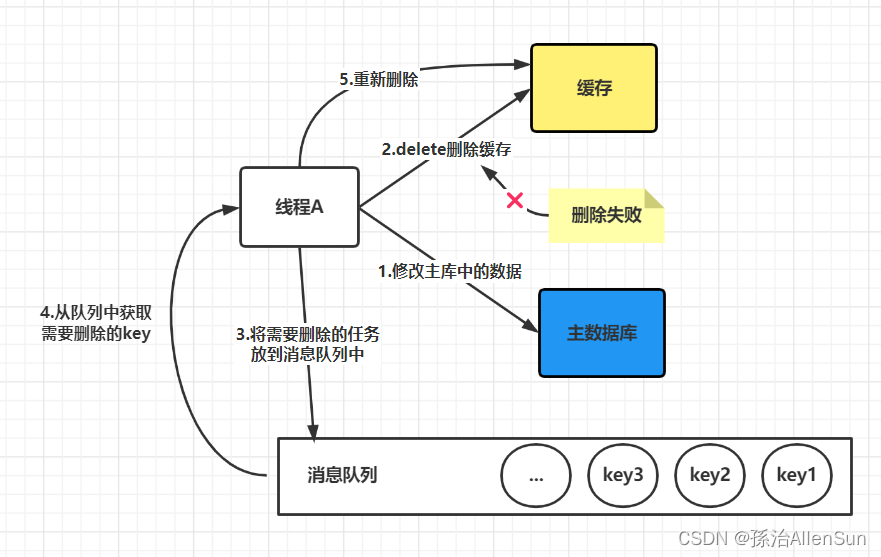
【redis】redis缓存与数据库的一致性
【redis】redis缓存与数据库的一致性【1】四种同步策略【2】更新缓存还是删除缓存(1)更新缓存(2)删除缓存【3】先更新数据库还是先删除缓存(1)出现失败时候的情况1-先删除缓存,再更新数据库&…...
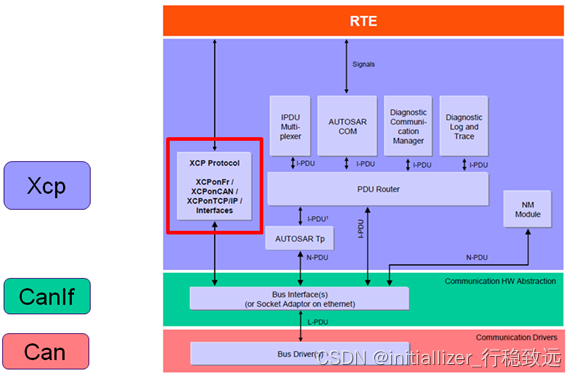
XCP实战系列介绍12-基于Vector_Davinci工具的XCP配置介绍(一)
本文框架 1.概述2. EcuC配置2.1 Pdu添加步骤2.2 配置项说明3. Can 模块配置4. CanIf 模块配置4.1 接收帧的Hardware Receive Object配置4.2 接收帧和发送帧的Pdu配置1.概述 在文章《看了就会的XCP协议介绍》中详细介绍了XCP的协议,在《XCP实战系列介绍01-测量与标定底层逻辑》…...
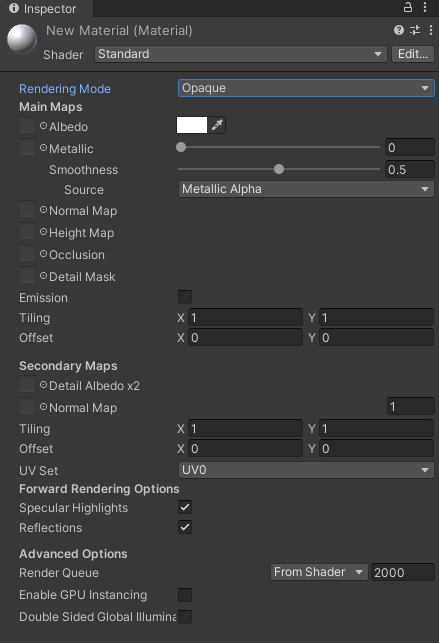
Unity Material详解
一、创建 二、属性 1.Shader:Unity内置了一些shader,用户自定义的shader也在这里出现. Edit: 可以编辑一些shader可编辑的内容,如一些属性. 2.Rendering Mode:渲染模式 Opaque-不透明-石头适用于所有的不透明的物体Cutout-镂空-破布透明度只有0%和100…...

碰撞检测算法分类
包围形法粗糙检测, 包含以下两种类检测外接圆法轴对齐包围矩形, AABB 碰撞检测算法之包围形法分离轴精细检测 BOX vs PolygonOBBseparating Axis Theorem碰撞检测算法之分离轴定理GJKGJK(Gilbert–Johnson–Keerthi), 相比 SAT 算法ÿ…...

代码随想录第十二天(
文章目录232. 用栈实现队列补充知识——Deque232. 用栈实现队列 答案思路: 在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来࿰…...
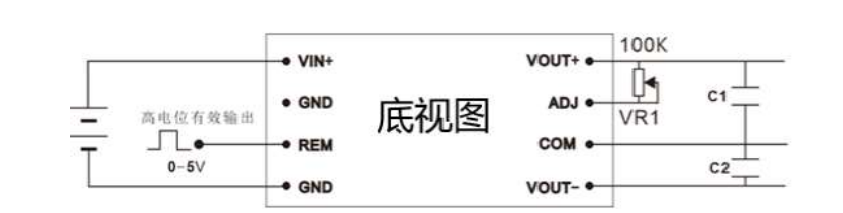
电源模块 DC-DC直流升压正负高压输出12v24v转±110V±150V±220V±250V±300V±600V
特点效率高达80%以上1*2英寸标准封装电源正负双输出稳压输出工作温度: -40℃~85℃阻燃封装,满足UL94-V0 要求温度特性好可直接焊在PCB 上应用HRA 1~40W系列模块电源是一种DC-DC升压变换器。该模块电源的输入电压分为:4.5~9V、9~18V、及18~36VDC标准&…...
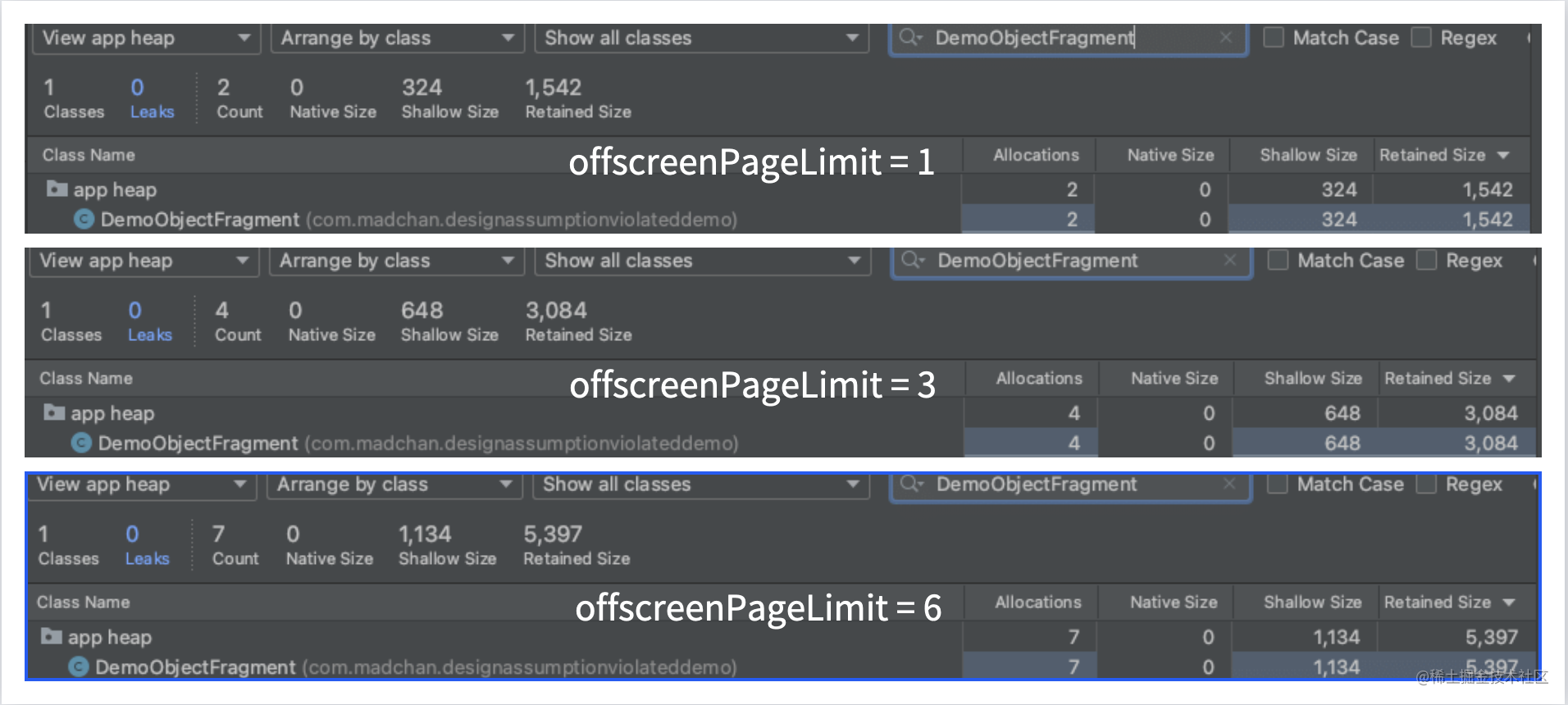
【动画图解】这个值取对了,ViewPager2才能纵享丝滑
前言 在前两篇文章中,我们通过一张张清晰明了的「示意图」,详细地复盘了RecyclerView「缓存复用机制」与「预拉取机制」的工作流程,这种「图解」创作形式也得到了来自不同平台读者们的一致认可。 而从本文开始,我们将正式进入Vi…...
CSDN每日一练:小豚鼠搬家
题目名称:小豚鼠搬家 时间限制:1000ms内存限制:256M 题目描述 小豚鼠排排坐。 小艺酱买了一排排格子的小房子n*m,她想让k只小豚鼠每只小豚鼠都有自己的房子。 但是为了不浪费空间,她想要小房子的最外圈尽量每行每列都有…...
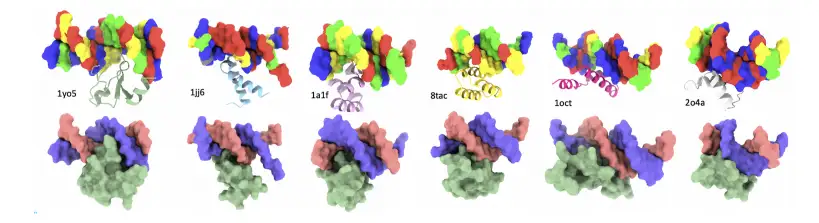
8k长序列建模,蛋白质语言模型Prot42仅利用目标蛋白序列即可生成高亲和力结合剂
蛋白质结合剂(如抗体、抑制肽)在疾病诊断、成像分析及靶向药物递送等关键场景中发挥着不可替代的作用。传统上,高特异性蛋白质结合剂的开发高度依赖噬菌体展示、定向进化等实验技术,但这类方法普遍面临资源消耗巨大、研发周期冗长…...

sqlserver 根据指定字符 解析拼接字符串
DECLARE LotNo NVARCHAR(50)A,B,C DECLARE xml XML ( SELECT <x> REPLACE(LotNo, ,, </x><x>) </x> ) DECLARE ErrorCode NVARCHAR(50) -- 提取 XML 中的值 SELECT value x.value(., VARCHAR(MAX))…...

三体问题详解
从物理学角度,三体问题之所以不稳定,是因为三个天体在万有引力作用下相互作用,形成一个非线性耦合系统。我们可以从牛顿经典力学出发,列出具体的运动方程,并说明为何这个系统本质上是混沌的,无法得到一般解…...

鸿蒙DevEco Studio HarmonyOS 5跑酷小游戏实现指南
1. 项目概述 本跑酷小游戏基于鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5开发,使用DevEco Studio作为开发工具,采用Java语言实现,包含角色控制、障碍物生成和分数计算系统。 2. 项目结构 /src/main/java/com/example/runner/├── MainAbilitySlice.java // 主界…...

Pinocchio 库详解及其在足式机器人上的应用
Pinocchio 库详解及其在足式机器人上的应用 Pinocchio (Pinocchio is not only a nose) 是一个开源的 C 库,专门用于快速计算机器人模型的正向运动学、逆向运动学、雅可比矩阵、动力学和动力学导数。它主要关注效率和准确性,并提供了一个通用的框架&…...

高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数
高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数 在软件开发中,单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常见的设计模式,确保一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。在多线程环境下,实现单例模式时需要注意线程安全问题,以防止多个线程同时创建实例,导致…...
论文笔记——相干体技术在裂缝预测中的应用研究
目录 相关地震知识补充地震数据的认识地震几何属性 相干体算法定义基本原理第一代相干体技术:基于互相关的相干体技术(Correlation)第二代相干体技术:基于相似的相干体技术(Semblance)基于多道相似的相干体…...

代码随想录刷题day30
1、零钱兑换II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。 请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。 假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。 题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带…...
在Mathematica中实现Newton-Raphson迭代的收敛时间算法(一般三次多项式)
考察一般的三次多项式,以r为参数: p[z_, r_] : z^3 (r - 1) z - r; roots[r_] : z /. Solve[p[z, r] 0, z]; 此多项式的根为: 尽管看起来这个多项式是特殊的,其实一般的三次多项式都是可以通过线性变换化为这个形式…...

解读《网络安全法》最新修订,把握网络安全新趋势
《网络安全法》自2017年施行以来,在维护网络空间安全方面发挥了重要作用。但随着网络环境的日益复杂,网络攻击、数据泄露等事件频发,现行法律已难以完全适应新的风险挑战。 2025年3月28日,国家网信办会同相关部门起草了《网络安全…...
