Lecture 20 Topic Modelling
目录
- Topic Modelling
- A Brief History of Topic Models
- LDA
- Evaluation
- Conclusion
Topic Modelling
-
makeingsense of text
- English Wikipedia: 6M articles
- Twitter: 500M tweets per day
- New York Times: 15M articles
- arXiv: 1M articles
- What can we do if we want to learn something about these document collections?
-
questions
- What are the less popular topics on Wikipedia?
- What are the big trends on Twitter in the past month?
- How do the social issues evolve over time in New York Times from 1900s to 2000s?
- What are some influential research areas?
-
topic models to the rescue
- Topic models learn common, overlapping themes in a document collection
- Unsupervised model
- No labels; input is just the documents!
- What’s the output of a topic model?
- Topics: each topic associated with a list of words
- Topic assignments: each document associated with a list of topics
-
what do topics look like
-
A list of words
-
Collectively describes a concept or subject
-
Words of a topic typically appear in the same set of documents in the corpus(words overlapping in documents)

-
Wikipedia topics(broad)

-
Twitter topics(short,conversational)

-
New York Times topics

-
-
applications of topic models
- Personalised advertising(e.g. types of products bought)
- Search engine
- Discover senses of polysemous words(e.g. apple: fruit, company, two different clusters)
A Brief History of Topic Models
-
latent semantic analysis

-
LSA: truncate

-
issues
- Positive and negative values in the U U U and V T V^T VT
- Difficult to interpret(negative values)

-
-
probabilistic LSA
-
based on a probabilistic model to get rid of negative values

-
issues
- No more negative values!
- PLSA can learn topics and topic assignment for documents in the train corpus
- But it is unable to infer topic distribution on new documents
- PLSA needs to be re-trained for new documents
-
-
latent dirichlet allocation(LDA)
- Introduces a prior to the document-topic and topicword distribution
- Fully generative: trained LDA model can infer topics on unseen documents!
- LDA is a Bayesian version of PLSA
LDA
-
LDA
- Core idea: assume each document contains a mix of topics
- But the topic structure is hidden (latent)
- LDA infers the topic structure given the observed words and documents
- LDA produces soft clusters of documents (based on topic overlap), rather than hard clusters
- Given a trained LDA model, it can infer topics on new documents (not part of train data)

-
input
- A collection of documents
- Bag-of-words
- Good preprocessing practice:
- Remove stopwords
- Remove low and high frequency word types
- Lemmatisation
-
output
-
Topics: distribution over words in each topic

-
Topic assignment: distribution over topics in each document

-
-
learning
-
How do we learn the latent topics?
-
Two main family of algorithms:
- Variational methods
- Sampling-based methods
-
sampling method (Gibbs)
-
Randomly assign topics to all tokens in documents

-
Collect topic-word and document-topic co-occurrence statistics based on the assignments
-
first give some psudo-counts in every cell of two matrix(smoothing,no event is 0)

-
collect co-occurrence statistics

-
-
Go through every word token in corpus and sample a new topic:
-
delete current topic assigned to a word

-
update two matrices

-
compute the probability distribution to sample: P ( t i ∣ w , d ) ∝ P ( t i ∣ w ) P ( t i ∣ d ) P(t_i|w,d) \propto P(t_i|w)P(t_i|d) P(ti∣w,d)∝P(ti∣w)P(ti∣d) ( P ( t i ∣ w ) → P(t_i|w) \to P(ti∣w)→ topic-word, P ( t i ∣ d ) → P(t_i|d) \to P(ti∣d)→ document-topic)

- P ( t 1 ∣ w , d ) = P ( t 1 ∣ m o u s e ) × P ( t 1 ∣ d 1 ) = 0.01 0.01 + 0.01 + 2.01 × 1.1 1.1 + 1.1 + 2.1 P(t_1|w,d)=P(t_1|mouse)\times{P(t_1|d_1)}=\frac{0.01}{0.01+0.01+2.01}\times{\frac{1.1}{1.1+1.1+2.1}} P(t1∣w,d)=P(t1∣mouse)×P(t1∣d1)=0.01+0.01+2.010.01×1.1+1.1+2.11.1
-
sample randomly based on the probability distribution
-
-
Go to step 2 and repeat until convergence
- when to stop
- Train until convergence
- Convergence = model probability of training set becomes stable
- How to compute model probability?
- l o g P ( w 1 , w 2 , . . . , w m ) = l o g ∑ j = 0 T P ( w 1 ∣ t j ) P ( t j ∣ d w 1 ) + . . . + l o g ∑ j = 0 T P ( w m ∣ t j ) P ( t j ∣ d w m ) logP(w_1,w_2,...,w_m)=log\sum_{j=0}^TP(w_1|t_j)P(t_j|d_{w_1})+...+log\sum_{j=0}^TP(w_m|t_j)P(t_j|d_{w_m}) logP(w1,w2,...,wm)=log∑j=0TP(w1∣tj)P(tj∣dw1)+...+log∑j=0TP(wm∣tj)P(tj∣dwm)
- m = #word tokens
- P ( w 1 ∣ t j ) → P(w_1|t_j) \to P(w1∣tj)→ based on the topic-word co-occurrence matrix
- P ( t j ∣ d w 1 ) → P(t_j|d_{w_1}) \to P(tj∣dw1)→ based on the document-topic co-occurrence matrix
- infer topics for new documents
-
Randomly assign topics to all tokens in new/test documents

-
Update document-topic matrix based on the assignments; but use the trained topic-word matrix (kept fixed)

-
Go through every word in the test documents and sample topics: P ( t i ∣ w , d ) ∝ P ( t i ∣ w ) P ( t i ∣ d ) P(t_i|w,d) \propto P(t_i|w)P(t_i|d) P(ti∣w,d)∝P(ti∣w)P(ti∣d)
-
Go to step 2 and repeat until convergence
-
- hyper-parameters
-
T T T: number of topic

-
β \beta β: prior on the topic-word distribution
-
α \alpha α: prior on the document-topic distribution
-
Analogous to k in add-k smoothing in N-gram LM
-
Pseudo counts to initialise co-occurrence matrix:

-
High prior values → \to → flatter distribution

- a very very large value would lead to a uniform distribution
-
Low prior values → \to → peaky distribution

-
β \beta β: generally small (< 0.01)
- Large vocabulary, but we want each topic to focus on specific themes
-
α \alpha α: generally larger (> 0.1)
- Multiple topics within a document
-
-
-
Evaluation
- how to evaluate topic models
- Unsupervised learning → \to → no labels
- Intrinsic(内在的,固有的) evaluation:
- model logprob / perplexity(困惑度,复杂度) on test documents
- l o g L = ∑ W ∑ T l o g P ( w ∣ t ) P ( t ∣ d w ) logL=\sum_W\sum_TlogP(w|t)P(t|d_w) logL=∑W∑TlogP(w∣t)P(t∣dw)
- p p l = e x p − l o g L W ppl=exp^{\frac{-logL}{W}} ppl=expW−logL
- issues with perlexity
- More topics = better (lower) perplexity
- Smaller vocabulary = better perplexity
- Perplexity not comparable for different corpora, or different tokenisation/preprocessing methods
- Does not correlate with human perception of topic quality
- Extrinsic(外在的) evaluation the way to go:
- Evaluate topic models based on downstream task
- topic coherence
-
A better intrinsic evaluation method
-
Measure how coherent the generated topics (blue more coherent than red)

-
A good topic model is one that generates more coherent topics
-
- word intrusion
- Idea: inject one random word to a topic
- {farmers, farm, food, rice, agriculture} → \to → {farmers, farm, food, rice, cat, agriculture}
- Ask users to guess which is the intruder word
- Correct guess → \to → topic is coherent
- Try guess the intruder word in:
- {choice, count, village, i.e., simply, unionist}
- Manual effort; does not scale
- Idea: inject one random word to a topic
- PMI ≈ \approx ≈ coherence?
- High PMI for a pair of words → \to → words are correlated
- PMI(farm, rice) ↑ \uparrow ↑
- PMI(choice, village) ↓ \downarrow ↓
- If all word pairs in a topic has high PMI → \to → topic is coherent
- If most topics have high PMI → \to → good topic model
- Where to get word co-occurrence statistics for PMI?
- Can use same corpus for topic model
- A better way is to use an external corpus (e.g. Wikipedia)
- High PMI for a pair of words → \to → words are correlated
- PMI
- Compute pairwise PMI of top-N words in a topic
- P M I ( t ) = ∑ j = 2 N ∑ i = 1 j − 1 l o g P ( w i , w j ) P ( w i ) P ( w j ) PMI(t)=\sum_{j=2}^N\sum_{i=1}^{j-1}log\frac{P(w_i,w_j)}{P(w_i)P(w_j)} PMI(t)=∑j=2N∑i=1j−1logP(wi)P(wj)P(wi,wj)
- Given topic: {farmers, farm, food, rice, agriculture}
- Coherence = sum PMI for all word pairs:
- PMI(farmers, farm) + PMI(farmers, food) + … + PMI(rice, agriculture)
- variants
- Normalised PMI
- N P M I ( t ) = ∑ j = 2 N ∑ i = 1 j − 1 l o g P ( w i , w j ) P ( w i ) P ( w j ) − l o g P ( w i , w j ) NPMI(t)=\sum_{j=2}^N\sum_{i=1}^{j-1}\frac{log\frac{P(w_i,w_j)}{P(w_i)P(w_j)}}{-logP(w_i,w_j)} NPMI(t)=∑j=2N∑i=1j−1−logP(wi,wj)logP(wi)P(wj)P(wi,wj)
- conditional probability (proved not as good as PMI)
- L C P ( t ) = ∑ j = 2 N ∑ i = 1 j − 1 l o g P ( w i , w j ) P ( w i ) LCP(t)=\sum_{j=2}^N\sum_{i=1}^{j-1}log\frac{P(w_i,w_j)}{P(w_i)} LCP(t)=∑j=2N∑i=1j−1logP(wi)P(wi,wj)
- Normalised PMI
- example (PMI tends to favor rarer words, use NPMI to relieve this problem)
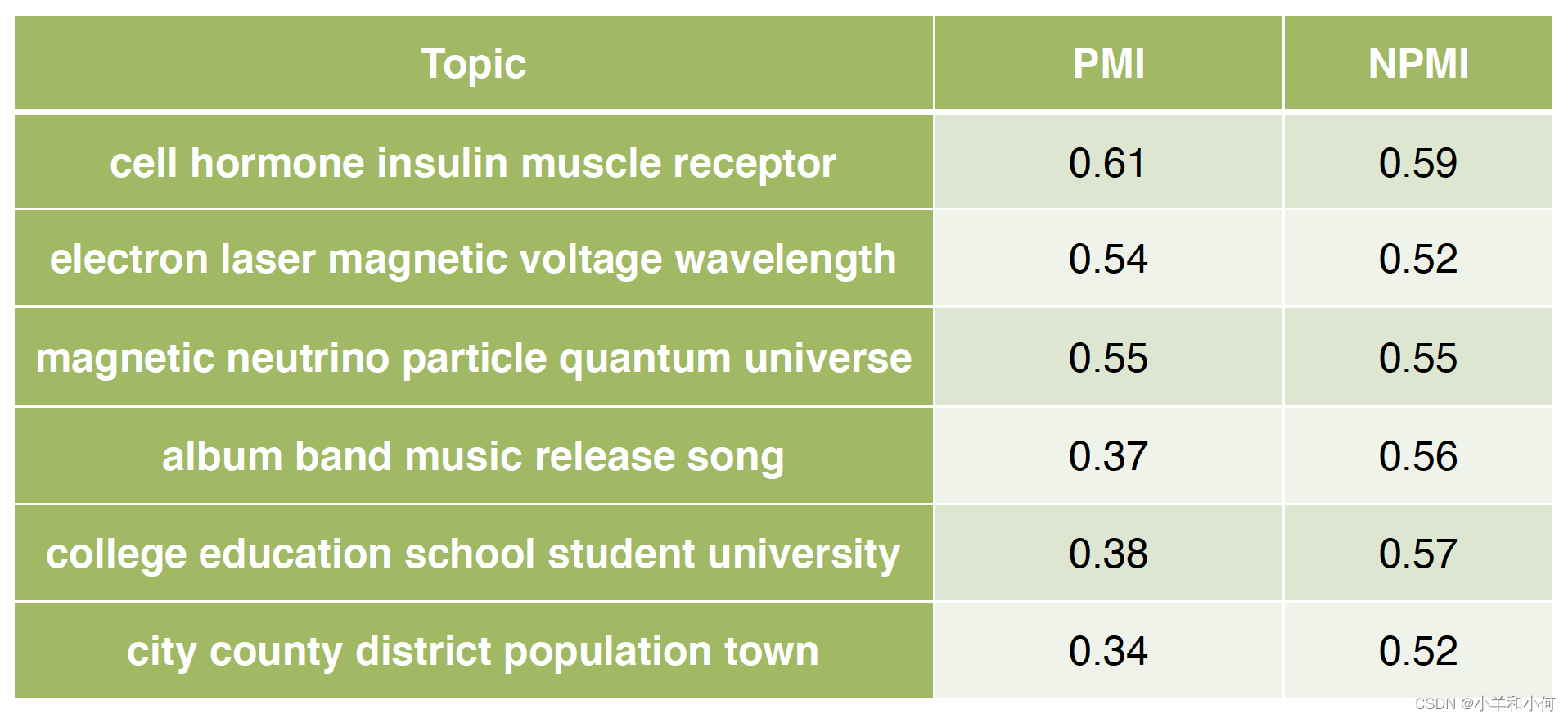
- Compute pairwise PMI of top-N words in a topic
Conclusion
- Topic model: an unsupervised model for learning latent concepts in a document collection
- LDA: a popular topic model
- Learning
- Hyper-parameters
- How to evaluate topic models?
- Topic coherence
相关文章:

Lecture 20 Topic Modelling
目录 Topic ModellingA Brief History of Topic ModelsLDAEvaluationConclusion Topic Modelling makeingsense of text English Wikipedia: 6M articlesTwitter: 500M tweets per dayNew York Times: 15M articlesarXiv: 1M articlesWhat can we do if we want to learn somet…...
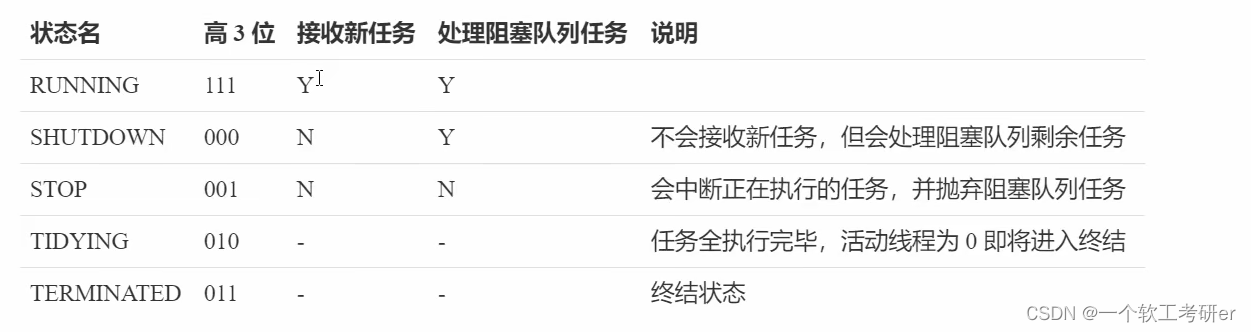
ThreadPoolExecutor线程池
文章目录 一、ThreadPool线程池状态二、ThreadPoolExecutor构造方法三、Executors3.1 固定大小线程池3.2 带缓冲线程池3.3 单线程线程池 四、ThreadPoolExecutor4.1 execute(Runnable task)方法使用4.2 submit()方法4.3 invokeAll()4.4 invokeAny()4.5 shutdown()4.6 shutdownN…...

chatgpt赋能python:Python实践:如何升级pip
Python实践:如何升级pip Python作为一门高效的脚本语言,被广泛应用于数据分析、人工智能、Web开发等领域。而pip则是Python的包管理工具,是开发Python应用的必备工具。但是pip在使用过程中,有时候会出现版本不兼容或者出现漏洞等…...
【JavaEE进阶】mybatis
目录: 一、Mybatis是什么 三个映射关系如下图: 二、mybatis的使用(前置工作简单案例) 第一步:导入MAVEN依赖 第二步: 在spring项目当中新建数据源 第三步:新建一个实体类,是和…...
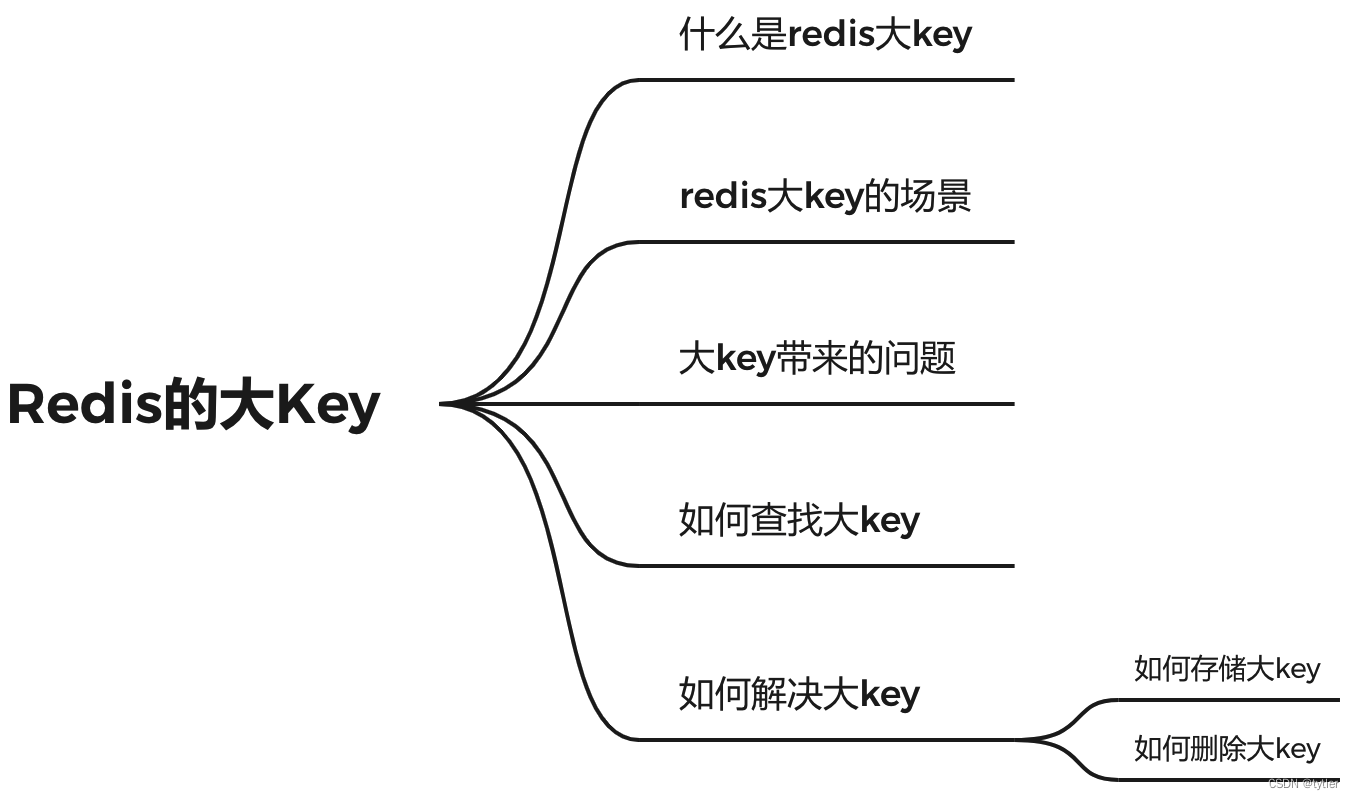
Redis的大key
什么是 redis 的大 key redis 的大 key 不是指存储在 redis 中的某个 key 的大小超过一定的阈值,而是该 key 所对应的 value 过大对于 string 类型来说,一般情况下超过 10KB 则认为是大 key;对于set、zset、hash 等类型来说,一般…...
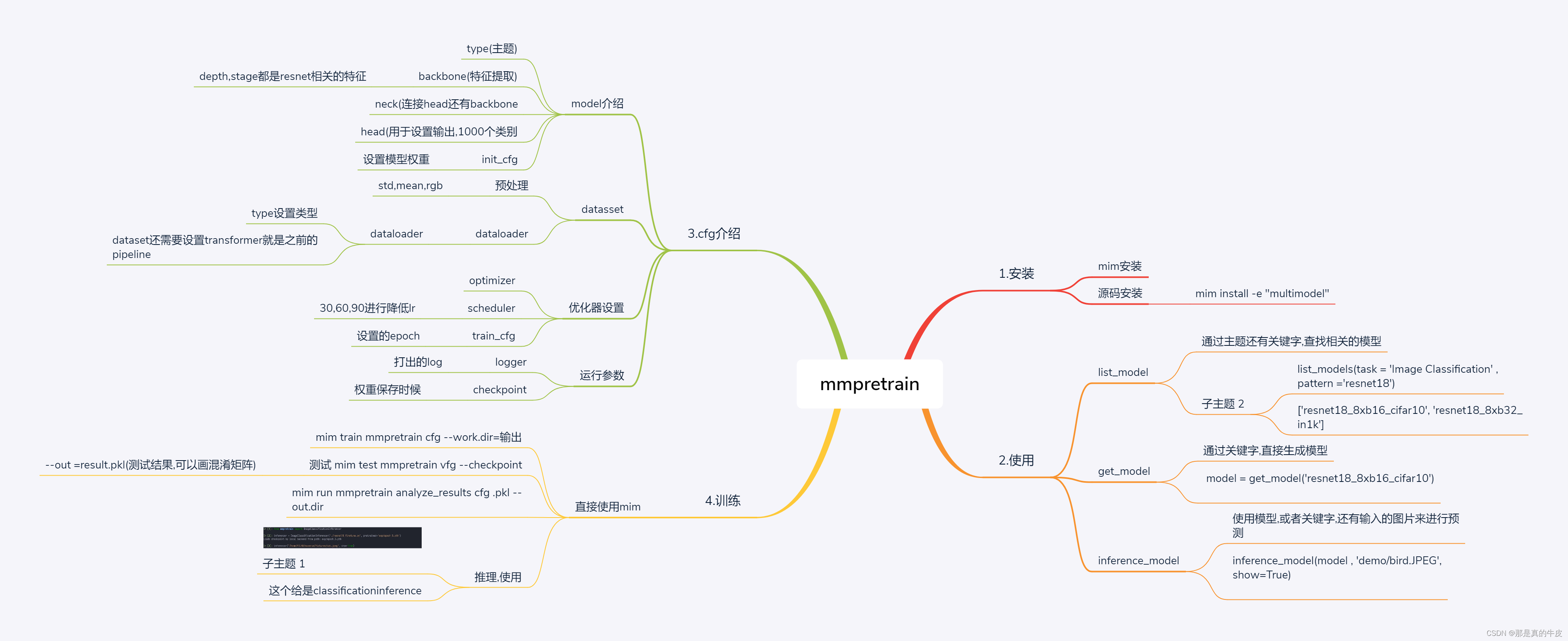
MMPretrain
title: mmpretrain实战 date: 2023-06-07 16:04:01 tags: [image classification,mmlab] mmpretrain实战 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ccTl9bOl-1686129437336)(null)] 主要讲解了安装,还有使用教程.安装教程直接参考官网.下面讲…...
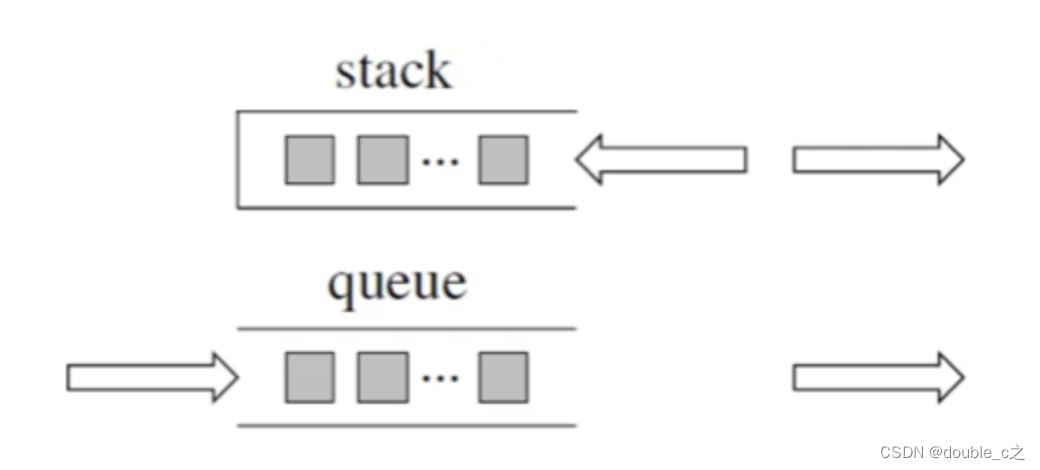
栈和队列(数据结构刷题)[一]-python
文章目录 前言一、原理介绍二、用栈实现队列1.操作2.思路 三、关于面试考察栈里面的元素在内存中是连续分布的么? 前言 提到栈和队列,大家可能对它们的了解只停留在表面,再深入一点,好像知道又好像不知道的感觉。本文我将从底层实…...
【备战秋招】JAVA集合
集合 前言 一方面, 面向对象语言对事物的体现都是以对象的形式,为了方便对多个对象 的操作,就要 对对象进行存储。 另一方面,使用Array存储对象方面具有一些弊端,而Java 集合就像一种容器,可以动态地把多…...

setState详解
this. setState( [partialState], [callback]) 1.[partialState] :支持部分状态更改 this, setState({ x:100 //不论总共有多少状态,我们只修改了x,其余的状态不动 });callback :在状态更改/视图更新完毕后触发执行,也可以说只要执行了setS…...

Qt5.12.6配置Android Arm开发环境(windows)
1. 安装jdk1.8 2.安装Android Studio 并安装 SDK 与NDK SDK Tools 选择 26.0.3 SDK Platform 选择 Android SDK Platform 26 NDK选择19版本 安卓ARM环境配置成功如下: JDK1.8 , SDK 26 , NDK 19 在安装QT时要选择 ARMv7(32位CPU)与ARM64-v8a(64位CPU) 选择支持android平台…...
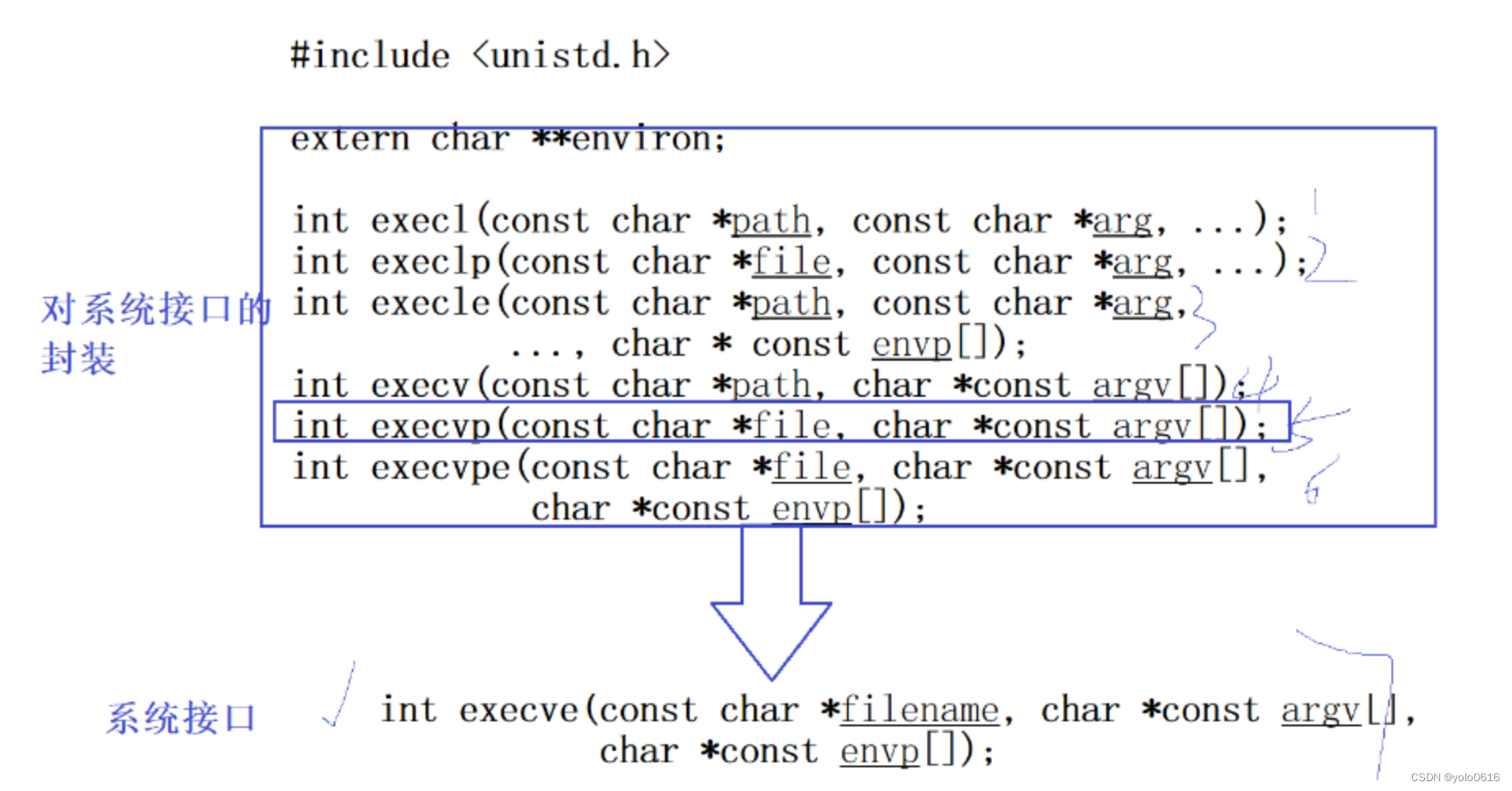
七、进程程序替换
文章目录 一、进程程序替换(一)概念(二)为什么程序替换(三)程序替换的原理(四)如何进行程序替换1. execl2. 引入进程创建——子进程执行程序替换,会不会影响父进程呢? &…...
C++核心编程——详解运算符重载
文章目录💬 一.运算符重载基础知识①基本概念②运算符重载的规则③运算符重载形式④运算符重载建议 二.常用运算符重载①左移(<<)和右移(>>)运算符重载1️⃣重载后函数参数是什么?2️⃣重载的函数返回类型是什么?3️⃣重载为哪种…...
2023年前端面试汇总-CSS
1. CSS基础 1.1. CSS选择器及其优先级 对于选择器的优先级: 1. 标签选择器、伪元素选择器:1; 2. 类选择器、伪类选择器、属性选择器:10; 3. id 选择器:100; 4. 内联样式:1000&a…...

Java调用Pytorch实现以图搜图(附源码)
Java调用Pytorch实现以图搜图 设计技术栈: 1、ElasticSearch环境; 2、Python运行环境(如果事先没有pytorch模型时,可以用python脚本创建模型); 1、运行效果 2、创建模型(有则可以跳过…...
【EasyX】实时时钟
目录 实时时钟1. 绘制静态秒针2. 秒针的转动3. 根据实际时间转动4. 添加时针和分针5. 添加表盘刻度 实时时钟 本博客介绍利用EasyX实现一个实时钟表的小程序,同时学习时间函数的使用。 本文源码可从github获取 1. 绘制静态秒针 第一步定义钟表的中心坐标center&a…...
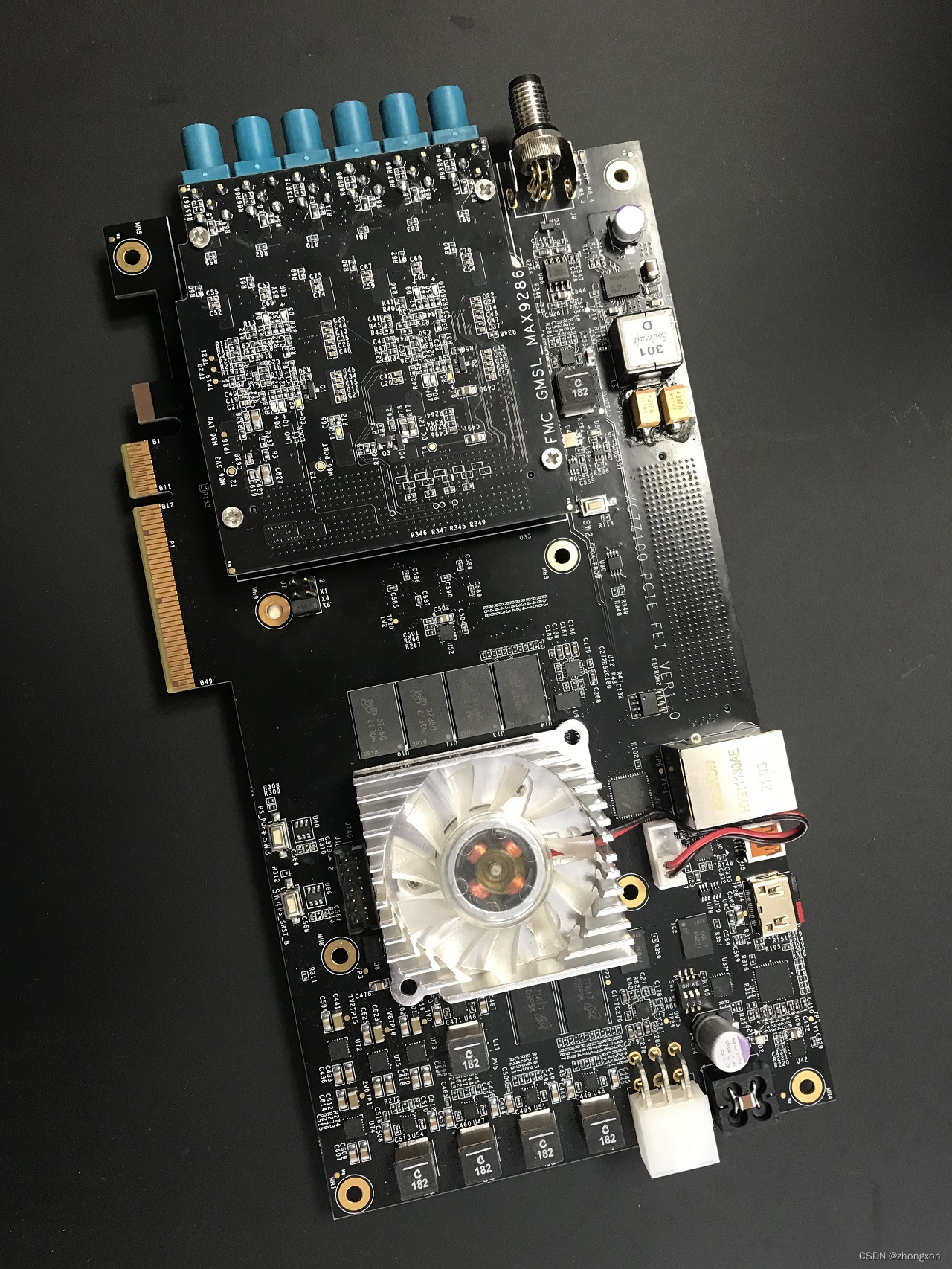

基于XC7Z100的PCIe采集卡(GMSL FMC采集卡)
GMSL 图像采集卡 特性 ● PCIe Gen2.0 X8 总线; ● 支持V4L2调用; ● 1路CAN接口; ● 6路/12路 GMSL1/2摄像头输入,最高可达8MP; ● 2路可定义相机同步触发输入/输出; 优势 ● 采用PCIe主卡与FMC子…...
Kibana:使用 Kibana 自带数据进行可视化(一)
在今天的练习中,我们将使用 Kibana 自带的数据来进行一些可视化的展示。希望对刚开始使用 Kibana 的用户有所帮助。 前提条件 如果你还没有安装好自己的 Elastic Stack,你可以参考如下的视频来开启 Elastic Stack 并进行下面的练习。你可以开通阿里云检…...
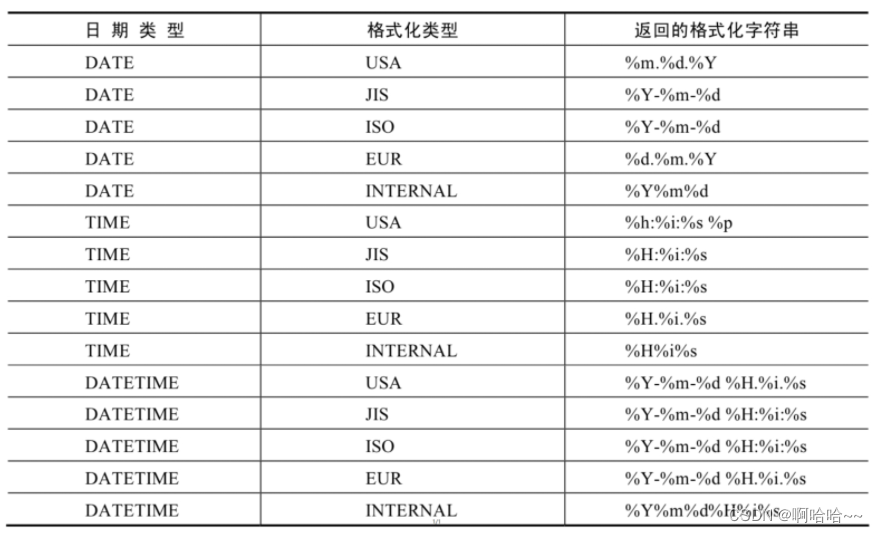
MySQL数据库基础 07
第七章 单行函数 1. 函数的理解1.1 什么是函数1.2 不同DBMS函数的差异1.3 MySQL的内置函数及分类 2. 数值函数2.1 基本函数2.2 角度与弧度互换函数2.3 三角函数2.4 指数与对数2.5 进制间的转换 3. 字符串函数4. 日期和时间函数4.1 获取日期、时间 4.2 日期与时间戳的转换 4.3 获…...

JVM | JVM垃圾回收
JVM | JVM垃圾回收 1、堆空间的基本结构2、内存分配和回收原则2.1、对象优先在 Eden 区分配2.2、大对象直接进入老年代2.3、长期存活的对象将进入老年代2.4、主要进行 gc 的区域2.5、空间分配担保3、死亡对象判断方法3.1、引用计数法3.2、可达性分析算法3.3、引用类型总结3.4、…...

avive零头撸矿
Avive 是一个透明的、自下而上替代自上而下的多元网络,旨在克服当前生态系统的局限性,实现去中心化社会。 aVive:一个基于 SBT 和市场的 deSoc,它使 dapps 能够与分散的位置 oracle 和 SBT 关系进行互操作。您的主权社交网络元宇宙…...
)
第178章 星际殖民的伦理(墨子)
弦光研究院星际殖民伦理委员会的圆形会议厅内,空气凝重得仿佛能够拧出水来。椭圆形的会议桌中央,全息投影展示着"神谕"提出的火星殖民方案细节,那些闪烁的基因图谱和生理改造示意图像一把把钥匙,试图打开通往人类进化新…...

互联网大数据环境下 MySQL 迁移至国产底座的技术实践与路径观察
互联网大数据环境下 MySQL 迁移至国产底座的技术实践与路径观察 在当前互联网大数据应用持续深化的背景下,企业对关系型数据库的性能稳定性、安全合规性及运维可控性提出了更高要求。随着技术体系日趋成熟,金仓数据库(KingbaseES)…...

晶振选型实战:从原理到布局,精准匹配有源与无源方案
1. 从需求出发:你的项目到底需要什么样的“心跳”? 做硬件开发,尤其是嵌入式或者物联网设备,选对晶振就像给系统找到了一个稳定可靠的“心跳”。这颗“心脏”跳得准不准、稳不稳,直接决定了你的设备能不能稳定运行、通…...

Z-Image-Turbo_Sugar脸部Lora生成图像超分辨率对比:细节放大后的品质审视
Z-Image-Turbo_Sugar脸部Lora生成图像超分辨率对比:细节放大后的品质审视 最近在玩一个挺有意思的Lora模型,叫Sugar脸部风格。用它生成的人像图,第一眼看上去感觉还不错,风格挺甜美,光影也挺柔和。但有个问题一直让我…...
安装与激活全攻略)
一、从零开始:Keil MDK社区版(免费无限制)安装与激活全攻略
一、从零开始:Keil MDK社区版(免费无限制)安装与激活全攻略 大家好,我是老张,一个在嵌入式行业摸爬滚打多年的工程师。最近有不少刚开始接触ARM单片机(比如STM32)的朋友问我,用什么软…...

GoldHEN_Cheat_Manager:开源PS4全能游戏优化工具完全指南
GoldHEN_Cheat_Manager:开源PS4全能游戏优化工具完全指南 【免费下载链接】GoldHEN_Cheat_Manager GoldHEN Cheats Manager 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/go/GoldHEN_Cheat_Manager 你是否曾因游戏帧率骤降而错失完美操作时机?是否在…...

超详细:解决Tomcat在日志、页面和idea控制台中的中文乱码问题
一、遇到问题 平时在使用tomcat的时候经常遇到各种乱码问题,要么是控制台输出乱码或者输出日志乱码,要么页面接收乱码,非常烦人。 二、乱码原因 产生乱码的根本原因就是编码和解码不一致。 三、解决办法 1、打开tomcat的/conf/server.xml&…...

《创业之路》-896- 以结构化思维、系统化思维、抽象思维、产品思维、用户思维解决跨多领域复杂技术难题
作为一个擅长结构化、系统化、抽象化、产品化和用户化思维的技术专家,解决跨领域复杂难题不仅仅是“修好一个Bug”,而是一场从微观代码到宏观商业价值的全链路认知跃迁。这五种思维不是孤立的,它们构成了一个解决问题的完整闭环:结…...

ubuntu系统下通过 .desktop文件执行qt程序
ubuntu系统下通过 .desktop文件执行qt程序 1.问题描述: 在ubuntu系统下通常可以通过.desktop文件执行qt编译出来的可执行文件,有时候会存在在命令行终端可以执行,但是通过deskton无法顺利执行的情况。 首先我们需要了解desktop文件的书写…...

终极Python 3数据库操作指南:SQLite与MySQL完整连接教程
终极Python 3数据库操作指南:SQLite与MySQL完整连接教程 【免费下载链接】learn-python3 Learn Python 3 Sample Code 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/lea/learn-python3 在Python开发中,数据库操作是核心技能之一。本教程将带你快速掌…...
