异步编排CompletableFuture
文章目录
- 一.简介
- 二.并行加载
- 1.为何需要并行加载
- 2.并行加载的实现方式
- 三.CompletableFuture使用与原理
- 1.背景和定义
- 2.常用方法
- 3.CompletableFuture的使用
- 3.CompletableFuture原理
- 4.实践总结
一.简介
CompletableFuture由Java 8提供,是实现异步化的工具类,上手难度较低,且功能强大,支持通过函数式编程的方式对各类操作进行组合编排
随着订单量的持续上升,美团外卖各系统服务面临的压力也越来越大。作为外卖链路的核心环节,商家端提供了商家接单、配送等一系列核心功能,业务对系统吞吐量的要求也越来越高。而商家端API服务是流量入口,所有商家端流量都会由其调度、聚合,对外面向商家提供功能接口,对内调度各个下游服务获取数据进行聚合,具有鲜明的I/O密集型(I/O Bound)特点。在当前日订单规模已达千万级的情况下,使用同步加载方式的弊端逐渐显现,因此我们开始考虑将同步加载改为并行加载的可行性。
二.并行加载
1.为何需要并行加载
外卖商家端API服务是典型的I/O密集型(I/O Bound)服务。除此之外,美团外卖商家端交易业务还有两个比较大的特点:
-
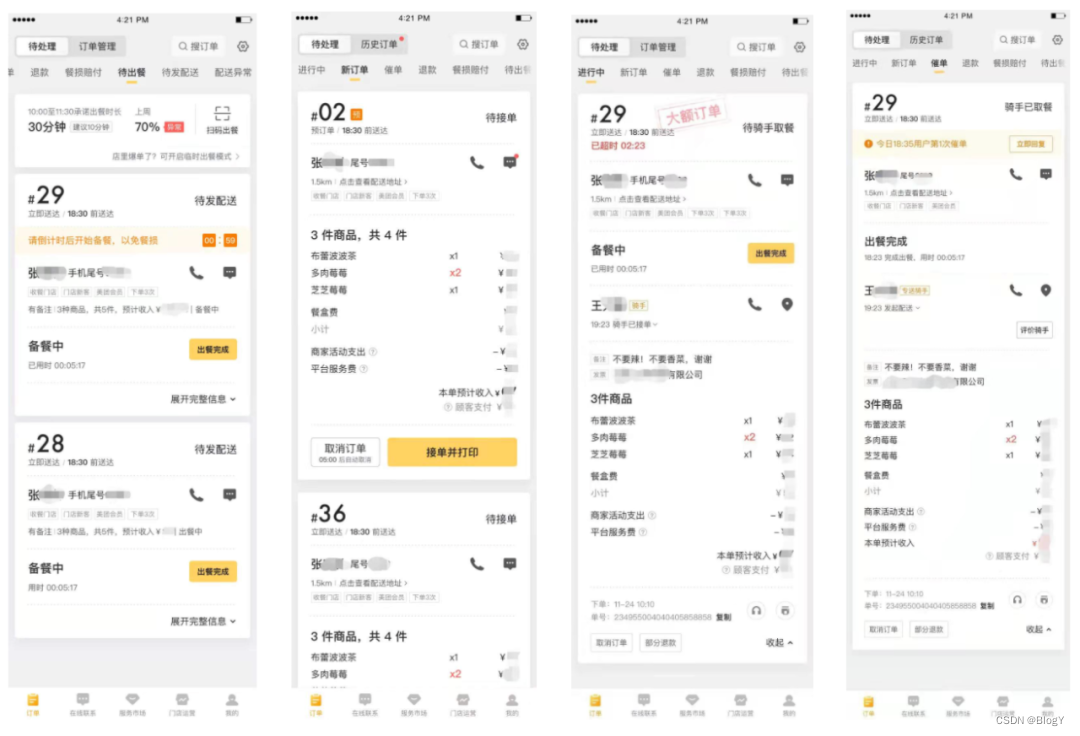
服务端必须一次返回订单卡片所有内容:根据商家端和服务端的“增量同步协议注1”,服务端必须一次性返回订单的所有信息,包含订单主信息、商品、结算、配送、用户信息、骑手信息、餐损、退款、客服赔付(参照下面订单卡片截图)等,需要从下游三十多个服务中获取数据。在特定条件下,如第一次登录和长时间没登录的情况下,客户端会分页拉取多个订单,这样发起的远程调用会更多。
-
商家端和服务端交互频繁:商家对订单状态变化敏感,多种推拉机制保证每次变更能够触达商家,导致App和服务端的交互频繁,每次变更需要拉取订单最新的全部内容。
在外卖交易链路如此大的流量下,为了保证商家的用户体验,保证接口的高性能,并行从下游获取数据就成为必然。
2.并行加载的实现方式
并行从下游获取数据,从IO模型上来讲分为同步模型和异步模型。
同步模型
从各个服务获取数据最常见的是同步调用,如下图所示:
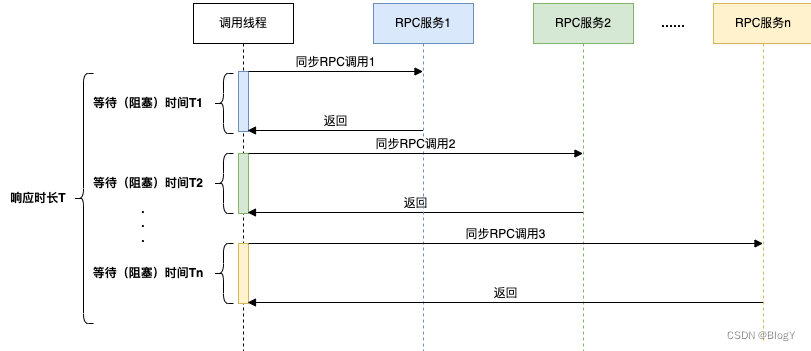
在同步调用的场景下,接口耗时长、性能差,接口响应时长T > T1+T2+T3+……+Tn,这时为了缩短接口的响应时间,一般会使用线程池的方式并行获取数据,商家端订单卡片的组装正是使用了这种方式。
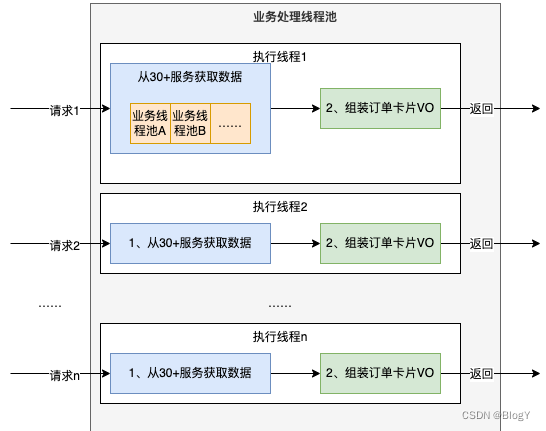
这种方式由于以下两个原因,导致资源利用率比较低:
-
CPU资源大量浪费在阻塞等待上,导致CPU资源利用率低。在Java 8之前,一般会通过回调的方式来减少阻塞,但是大量使用回调,又引发臭名昭著的回调地狱问题,导致代码可读性和可维护性大大降低。
-
为了增加并发度,会引入更多额外的线程池,随着CPU调度线程数的增加,会导致更严重的资源争用,宝贵的CPU资源被损耗在上下文切换上,而且线程本身也会占用系统资源,且不能无限增加。
同步模型下,会导致硬件资源无法充分利用,系统吞吐量容易达到瓶颈。
NIO异步模型
我们主要通过以下两种方式来减少线程池的调度开销和阻塞时间:
- 通过RPC NIO异步调用的方式可以降低线程数,从而降低调度(上下文切换)开销
- 通过引入CompletableFuture(下文简称CF)对业务流程进行编排,降低依赖之间的阻塞。本文主要讲述CompletableFuture的使用和原理。
为什么会选择CompletableFuture?
我们首先对业界广泛流行的解决方案做了横向调研,主要包括Future、CompletableFuture注2、RxJava、Reactor。它们的特性对比如下:
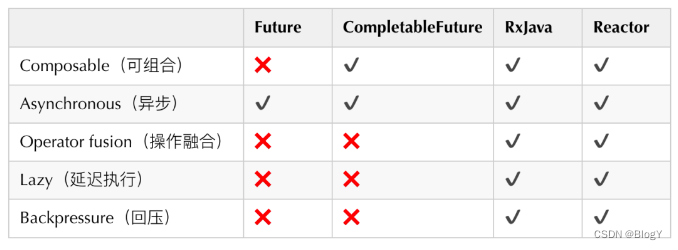
- 可组合:可以将多个依赖操作通过不同的方式进行编排,例如CompletableFuture提供thenCompose、thenCombine等各种then开头的方法,这些方法就是对“可组合”特性的支持。
- 操作融合:将数据流中使用的多个操作符以某种方式结合起来,进而降低开销(时间、内存)。
- 延迟执行:操作不会立即执行,当收到明确指示时操作才会触发。例如Reactor只有当有订阅者订阅时,才会触发操作。
- 回压:某些异步阶段的处理速度跟不上,直接失败会导致大量数据的丢失,对业务来说是不能接受的,这时需要反馈上游生产者降低调用量。
RxJava与Reactor显然更加强大,它们提供了更多的函数调用方式,支持更多特性,但同时也带来了更大的学习成本。而我们本次整合最需要的特性就是“异步”、“可组合”,综合考虑后,我们选择了学习成本相对较低的CompletableFuture。
三.CompletableFuture使用与原理
1.背景和定义
CompletableFuture是由Java 8引入的,在Java8之前我们一般通过Future实现异步。
-
Future用于表示异步计算的结果,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式获取结果,而且不支持设置回调方法,Java 8之前若要设置回调一般会使用guava的ListenableFuture,回调的引入又会导致臭名昭著的回调地狱(下面的例子会通过ListenableFuture的使用来具体进行展示)。
-
CompletableFuture对Future进行了扩展,可以通过设置回调的方式处理计算结果,同时也支持组合操作,支持进一步的编排,同时一定程度解决了回调地狱的问题。
下面将举例来说明,我们通过ListenableFuture、CompletableFuture来实现异步的差异。假设有三个操作step1、step2、step3存在依赖关系,其中step3的执行依赖step1和step2的结果。
Future(ListenableFuture)的实现(回调地狱)如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {//创建线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//转换为支持异步回调的ListeningExecutorServiceListeningExecutorService guavaExecutor = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(executor);//提交两个异步任务ListenableFuture<String> future1 = guavaExecutor.submit(() -> {//step 1System.out.println("执行step 1");return "step1 result";});ListenableFuture<String> future2 = guavaExecutor.submit(() -> {//step 2System.out.println("执行step 2");return "step2 result";});//使用 Futures.allAsList(future1, future2) 方法将 future1 和 future2 这两个异步任务组合起来,形成一个新的 ListenableFuture 对象 future1And2,表示它们都执行完毕后返回一个结果列表。ListenableFuture<List<String>> future1And2 = Futures.allAsList(future1, future2);//使用 Futures.addCallback(future1And2, new FutureCallback<List<String>>()) 方法为 future1And2 注册一个回调函数,当 future1And2 执行成功后自动调用该回调函数,执行 step 3 的操作。Futures.addCallback(future1And2, new FutureCallback<List<String>>() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess(List<String> result) {System.out.println(result);//在回调函数中,使用 guavaExecutor.submit() 方法提交一个新的异步任务 future3,执行 step 3 的操作,并返回其执行结果。ListenableFuture<String> future3 = guavaExecutor.submit(() -> {System.out.println("执行step 3");return "step3 result";});//使用 Futures.addCallback(future3, new FutureCallback<String>()) 方法为 future3 注册一个回调函数,当 future3 执行成功后自动调用该回调函数,在该回调函数中输出 step3 result。Futures.addCallback(future3, new FutureCallback<String>() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess(String result) {System.out.println(result);}@Overridepublic void onFailure(Throwable t) {}}, guavaExecutor);}@Overridepublic void onFailure(Throwable t) {}}, guavaExecutor);}
CompletableFuture的实现如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//CompletableFuture.supplyAsync()方法创建了两个异步任务cf1和cf2//cf1任务使用了线程池executor来执行,它会打印一行输出并返回一个字符串。cf2任务没有指定线程池,所以会使用默认的ForkJoinPool来执行,它也会打印一行输出并返回一个字符串CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行step 1");return "step1 result";}, executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("执行step 2");return "step2 result";});//使用cf1的thenCombine()方法将cf1和cf2合并为一个新的CompletableFuture,并指定一个BiFunction作为合并函数,这个函数会将cf1和cf2的结果合并为一个字符串,并再打印一行输出。在这个合并操作完成后,继续使用CompletableFuture.thenAccept()方法来消费结果,打印出最终结果。cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (result1, result2) -> {System.out.println(result1 + " , " + result2);System.out.println("执行step 3");return "step3 result";}).thenAccept(result3 -> System.out.println(result3));}
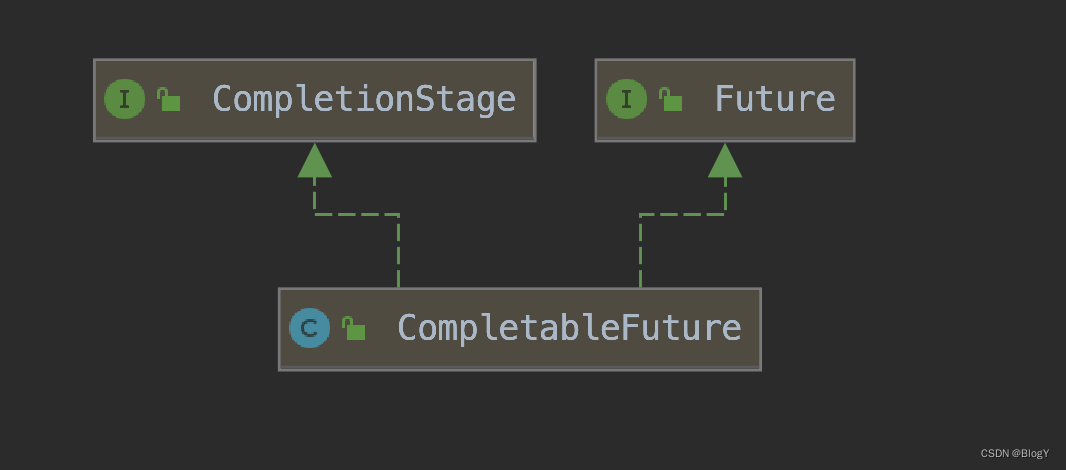
CompletableFuture实现了两个接口(如上图所示):Future、CompletionStage。Future表示异步计算的结果,CompletionStage用于表示异步执行过程中的一个步骤(Stage),这个步骤可能是由另外一个CompletionStage触发的,随着当前步骤的完成,也可能会触发其他一系列CompletionStage的执行。从而我们可以根据实际业务对这些步骤进行多样化的编排组合,CompletionStage接口正是定义了这样的能力,我们可以通过其提供的thenAppy、thenCompose等函数式编程方法来组合编排这些步骤。
2.常用方法

- supplyAsync
supplyAsync是创建带有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法
//supplyAsync 默认线程池public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("hello test supplyAsync 默认线程池");return "result";});//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("结果-》"+cf.get());}
//supplyAsync 自定义线程池public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("hello test supplyAsync 自定义线程池");return "result";}, executor);//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("结果-》"+cf.get());}
- runAsync
runAsync是创建没有返回值的异步任务。它有如下两个方法,一个是使用默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一个是带有自定义线程池的重载方法
//runAsync 默认线程池public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something.... runAsync 默认线程池");});//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());}
//runAsync 自定义线程池public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();CompletableFuture<Void> cf = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("do something...runAsync 自定义线程池");}, executorService);//等待任务执行完成System.out.println("结果->" + cf.get());}
- 获取任务结果的方法
// 如果完成则返回结果,否则就抛出具体的异常
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException // 最大时间等待返回结果,否则就抛出具体异常
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException// 完成时返回结果值,否则抛出unchecked异常。为了更好地符合通用函数形式的使用,如果完成此 CompletableFuture所涉及的计算引发异常,则此方法将引发unchecked异常并将底层异常作为其原因
// 调用 join() 方法时,它会阻塞当前线程,直到关联的 CompletableFuture 完成并返回结果。如果任务已经完成,join() 方法会立即返回结果;如果任务尚未完成,它会一直等待直到任务完成。与之相反,get() 方法也会等待任务完成并返回结果,但它会抛出 InterruptedException 和 ExecutionException 异常,而 join() 方法则不会抛出任何受检异常。
//这使得 join() 方法更适合在 Lambda 表达式或流式操作中使用,因为它不需要显式处理异常或声明 throws 子句。
public T join()// 如果完成则返回结果值(或抛出任何遇到的异常),否则返回给定的 valueIfAbsent。
//获取异步任务的结果,如果任务已经完成,则返回结果;如果任务尚未完成,则返回一个默认值 valueIfAbsent。这个方法不会等待任务的完成,而是立即返回结果或默认值。
public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)// 如果任务没有完成,返回的值设置为给定值
public boolean complete(T value)// 如果任务没有完成,就抛出给定异常
public boolean completeExceptionally(Throwable ex) get()
//get()方法设置超时时间public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {//自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("hello test get()方法设置超时时间");try {Thread.sleep(20000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "result";}, executor);//等待子任务执行完成System.out.println("结果-》"+cf.get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS));}

join()
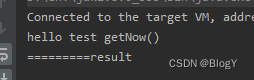
//join()方法public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {//自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("hello test join()");try {Thread.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "result";}, executor);System.out.println("========="+cf.join());}

getNow()
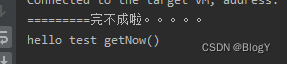
//getNow()方法public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {//自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("hello test getNow()");try {Thread.sleep(20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "result";}, executor);System.out.println("========="+cf.getNow("完不成啦。。。。。"));}
//getNow()方法public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {//自定义线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("hello test getNow()");return "result";}, executor);Thread.sleep(100);System.out.println("========="+cf.getNow("完不成啦。。。。。"));}
complete()
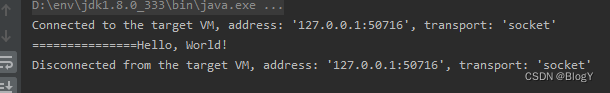
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<String> future = new CompletableFuture<>();// 在另一个线程中手动完成 CompletableFuturenew Thread(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}future.complete("Hello, World!");}).start();// 等待 CompletableFuture 完成并获取结果System.out.println("==============="+future.join());}
- thenApply()和thenApplyAsync()
thenApply 表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,带有返回值。

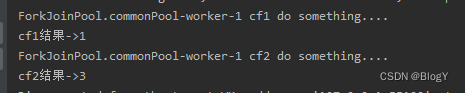
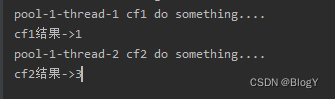
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");result += 2;try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return result;});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}
既然调用thenApplyAsync()不应该是在不同的线程去执行吗
那输出的线程名称为什么都是ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1呢?

使用自定义线程池
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.thenApplyAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");result += 2;try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return result;},executor);//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}
- thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync

thenAccept()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAccept((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" cf1 返回result:"+result+ " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}
thenAcceptAsync()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenAcceptAsync((result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" cf1 返回result:"+result+ " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
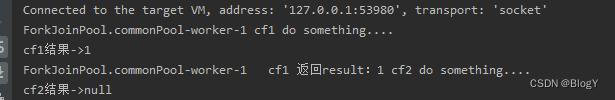
调用thenAcceptAsync()方法了,为什么线程名称都为ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1

- thenRun和thenRunAsync

thenRun()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;});CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRun(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");});//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}
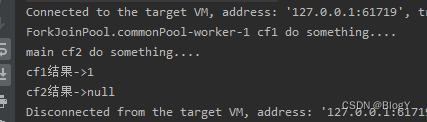
thenRunAsync()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Void> cf2 = cf1.thenRunAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");},executor);//等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}

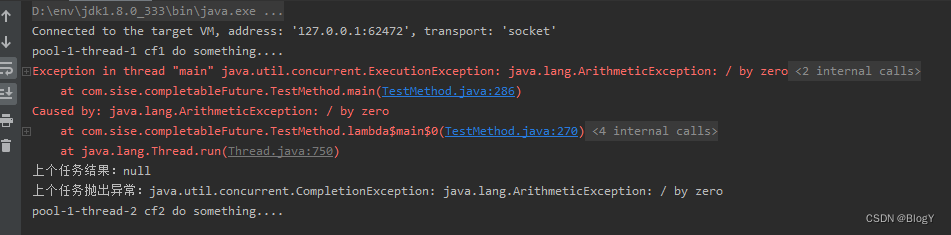
- whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
whenComplete()
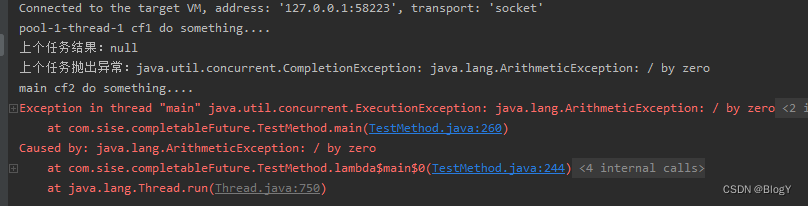
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");int a = 1/0;return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenComplete((result, e) -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException ex) {ex.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");});// //等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
// //等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}
whenCompleteAsync()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");int a = 1/0;return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.whenCompleteAsync((result, e) -> {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException ex) {ex.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");},executor);// //等待任务1执行完成System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());
// //等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());}
- handle和handleAsync
跟whenComplete基本一致,区别在于handle的回调方法有返回值。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");// int a = 1/0;return 1;});CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = cf1.handle((result, e) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");System.out.println("上个任务结果:" + result);System.out.println("上个任务抛出异常:" + e);return result+2;});//等待任务2执行完成System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());
}
- thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
这三个方法都是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,只有两个任务都正常完成时,才进行下阶段任务。
区别:thenCombine会将两个任务的执行结果作为所提供函数的参数,且该方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth同样将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterBoth没有入参,也没有返回值。注意两个任务中只要有一个执行异常,则将该异常信息作为指定任务的执行结果。
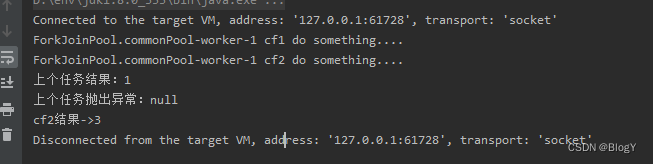
thenCombine
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");try {Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 2;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf3 = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (a, b) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");return a + b;});System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());}
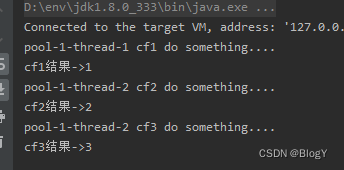
thenAcceptBoth()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");try {Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 2;},executor);CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2, (a, b) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");System.out.println(a + b);});System.out.println("cf1结果->" + cf1.get());System.out.println("cf2结果->" + cf2.get());System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());}
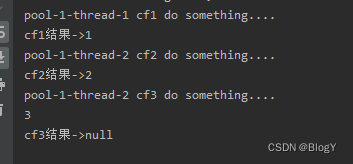
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");//int i = 1/0;return 1;},executor);CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(10000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
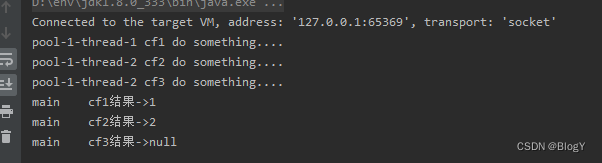
// }return 2;},executor);CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2, () -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" cf1结果->" + cf1.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" cf2结果->" + cf2.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" cf3结果->" + cf3.get());}
- applyToEither、acceptEither和runAfterEither
这三个方法和上面一样也是将两个CompletableFuture组合起来处理,当有一个任务正常完成时,就会进行下阶段任务。
区别:applyToEither会将已经完成任务的执行结果作为所提供函数的参数,且该方法有返回值;acceptEither同样将已经完成任务的执行结果作为方法入参,但是无返回值;runAfterEither没有入参,也没有返回值。
applyToEither()
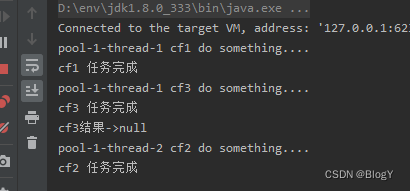
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf1 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(10000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf2 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = cf1.applyToEither(cf2, (result) -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");System.out.println("接收到" + result);return "cf3 任务完成";});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" cf1结果->" + cf1.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" cf2结果->" + cf2.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" cf3结果->" + cf3.get());}

acceptEither()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf1 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(10000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf2 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.acceptEither(cf2, (result) -> {System.out.println("接收到" + result);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");});System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3结果->" + cf3.get());}
runAfterEither()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");return "cf1 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(10000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");return "cf2 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<Void> cf3 = cf1.runAfterEither(cf2, () -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");});System.out.println("cf3结果->" + cf3.get());}
- allOf / anyOf
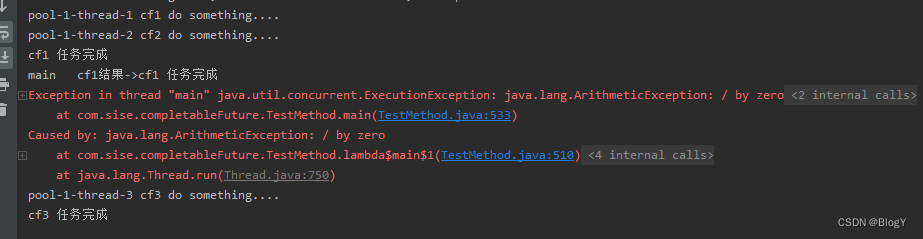
allOf:CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null。
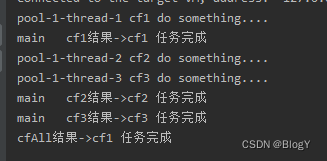
anyOf :CompletableFuture是多个任务只要有一个任务执行完成,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回执行完成任务的结果。
allOf()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");return "cf1 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");int a = 1/0;Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");return "cf2 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(30000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");return "cf3 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<Void> cfAll = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1结果->" + cf1.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2结果->" + cf2.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3结果->" + cf3.get());System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());}
anyOf()
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1 do something....");return "cf1 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2 do something....");Thread.sleep(50000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf2 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3 do something....");Thread.sleep(30000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "cf3 任务完成";},executor);CompletableFuture<Object> cfAll = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf1结果->" + cf1.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf2结果->" + cf2.get());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " cf3结果->" + cf3.get());System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());}
3.CompletableFuture的使用
下面我们通过一个例子来讲解CompletableFuture如何使用,使用CompletableFuture也是构建依赖树的过程。一个CompletableFuture的完成会触发另外一系列依赖它的CompletableFuture的执行:

如上图所示,这里描绘的是一个业务接口的流程,其中包括CF1\CF2\CF3\CF4\CF5共5个步骤,并描绘了这些步骤之间的依赖关系,每个步骤可以是一次RPC调用、一次数据库操作或者是一次本地方法调用等,在使用CompletableFuture进行异步化编程时,图中的每个步骤都会产生一个CompletableFuture对象,最终结果也会用一个CompletableFuture来进行表示。
根据CompletableFuture依赖数量,可以分为以下几类:零依赖、一元依赖、二元依赖和多元依赖。
- 零依赖:CompletableFuture的创建
我们先看下如何不依赖其他CompletableFuture来创建新的CompletableFuture: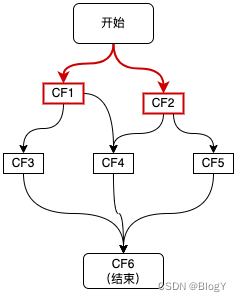
如上图红色链路所示,接口接收到请求后,首先发起两个异步调用CF1、CF2,主要有三种方式:
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
//1、使用runAsync或supplyAsync发起异步调用
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "result1";
}, executor);//2、CompletableFuture.completedFuture()直接创建一个已完成状态的CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("result2");//3、先初始化一个未完成的CompletableFuture,然后通过complete()、completeExceptionally(),完成该CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> cf = new CompletableFuture<>();
cf.complete("success");
第三种方式的一个典型使用场景,就是将回调方法转为CompletableFuture,然后再依赖CompletableFure的能力进行调用编排,示例如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ThriftAsyncCall {void invoke() throws TException;
}/*** 该方法为美团内部rpc注册监听的封装,可以作为其他实现的参照* OctoThriftCallback 为thrift回调方法* ThriftAsyncCall 为自定义函数,用来表示一次thrift调用(定义如上)*/public static <T> CompletableFuture<T> toCompletableFuture(final OctoThriftCallback<?,T> callback , ThriftAsyncCall thriftCall) {//新建一个未完成的CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<T> resultFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();//监听回调的完成,并且与CompletableFuture同步状态callback.addObserver(new OctoObserver<T>() {@Overridepublic void onSuccess(T t) {resultFuture.complete(t);}@Overridepublic void onFailure(Throwable throwable) {resultFuture.completeExceptionally(throwable);}});if (thriftCall != null) {try {thriftCall.invoke();} catch (TException e) {resultFuture.completeExceptionally(e);}}return resultFuture;}
- 一元依赖:依赖一个CF
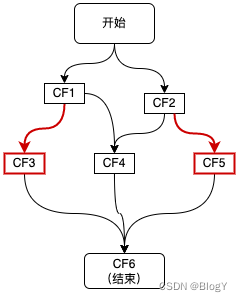
如上图红色链路所示,CF3,CF5分别依赖于CF1和CF2,这种对于单个CompletableFuture的依赖可以通过thenApply、thenAccept、thenCompose等方法来实现,代码如下所示:
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = cf1.thenApply(result1 -> {//result1为CF1的结果//......return "result3";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf5 = cf2.thenApply(result2 -> {//result2为CF2的结果//......return "result5";
});
- 二元依赖:依赖两个CF
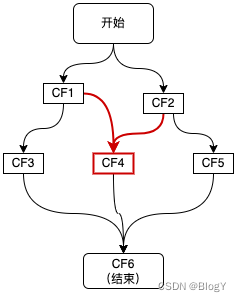
如上图红色链路所示,CF4同时依赖于两个CF1和CF2,这种二元依赖可以通过thenCombine等回调来实现,如下代码所示:
CompletableFuture<String> cf4 = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (result1, result2) -> {//result1和result2分别为cf1和cf2的结果return "result4";
});
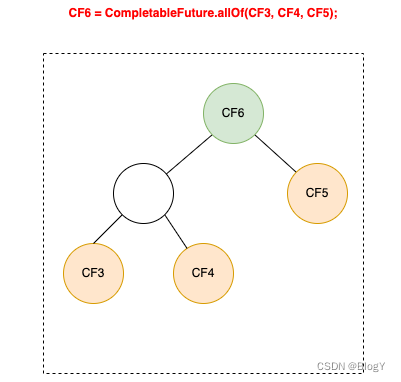
- 多元依赖:依赖多个CF
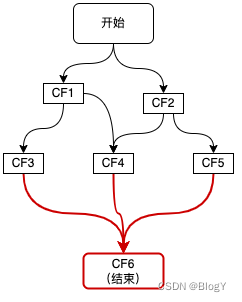
如上图红色链路所示,整个流程的结束依赖于三个步骤CF3、CF4、CF5,这种多元依赖可以通过allOf或anyOf方法来实现,区别是当需要多个依赖全部完成时使用allOf,当多个依赖中的任意一个完成即可时使用anyOf,如下代码所示:
CompletableFuture<Void> cf6 = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf3, cf4, cf5);
CompletableFuture<String> result = cf6.thenApply(v -> {//这里的join并不会阻塞,因为传给thenApply的函数是在CF3、CF4、CF5全部完成时,才会执行 。result3 = cf3.join();result4 = cf4.join();result5 = cf5.join();//根据result3、result4、result5组装最终result;return "result";
});
3.CompletableFuture原理
CompletableFuture中包含两个字段:result和stack。result用于存储当前CF的结果,stack(Completion)表示当前CF完成后需要触发的依赖动作(Dependency Actions),去触发依赖它的CF的计算,依赖动作可以有多个(表示有多个依赖它的CF),以栈(Treiber stack)的形式存储,stack表示栈顶元素。

这种方式类似“观察者模式”,依赖动作(Dependency Action)都封装在一个单独Completion子类中。下面是Completion类关系结构图。CompletableFuture中的每个方法都对应了图中的一个Completion的子类,Completion本身是观察者的基类。
- UniCompletion继承了Completion,是一元依赖的基类,例如thenApply的实现类UniApply就继承自UniCompletion。
- BiCompletion继承了UniCompletion,是二元依赖的基类,同时也是多元依赖的基类。例如thenCombine的实现类BiRelay就继承自BiCompletion。

CompletableFuture的设计思想
按照类似“观察者模式”的设计思想,原理分析可以从“观察者”和“被观察者”两个方面着手。由于回调种类多,但结构差异不大,所以这里单以一元依赖中的thenApply为例,不再枚举全部回调类型。如下图所示:
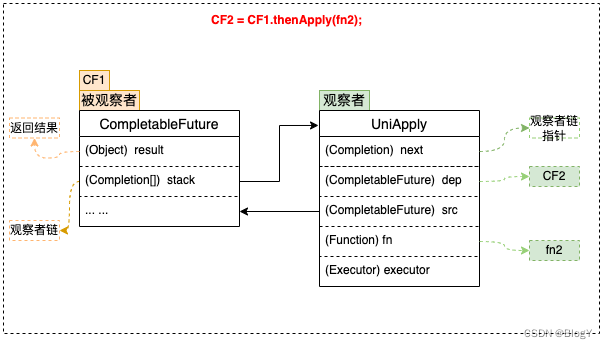
- 被观察者
每个CompletableFuture都可以被看作一个被观察者,其内部有一个Completion类型的链表成员变量stack,用来存储注册到其中的所有观察者。当被观察者执行完成后会弹栈stack属性,依次通知注册到其中的观察者。上面例子中步骤fn2就是作为观察者被封装在UniApply中。
被观察者CF中的result属性,用来存储返回结果数据。这里可能是一次RPC调用的返回值,也可能是任意对象,在上面的例子中对应步骤fn1的执行结果。
- 观察者
CompletableFuture支持很多回调方法,例如thenAccept、thenApply、exceptionally等,这些方法接收一个函数类型的参数f,生成一个Completion类型的对象(即观察者),并将入参函数f赋值给Completion的成员变量fn,然后检查当前CF是否已处于完成状态(即result != null),如果已完成直接触发fn,否则将观察者Completion加入到CF的观察者链stack中,再次尝试触发,如果被观察者未执行完则其执行完毕之后通知触发。
1.观察者中的dep属性:指向其对应的CompletableFuture,在上面的例子中dep指向CF2。
2.观察者中的src属性:指向其依赖的CompletableFuture,在上面的例子中src指向CF1。
3.观察者Completion中的fn属性:用来存储具体的等待被回调的函数。这里需要注意的是不同的回调方法(thenAccept、thenApply、exceptionally等)接收的函数类型也不同,即fn的类型有很多种,在上面的例子中fn指向fn2。
整体流程
一元依赖
这里仍然以thenApply为例来说明一元依赖的流程:
1.将观察者Completion注册到CF1,此时CF1将Completion压栈。
2.当CF1的操作运行完成时,会将结果赋值给CF1中的result属性。
3.依次弹栈,通知观察者尝试运行。
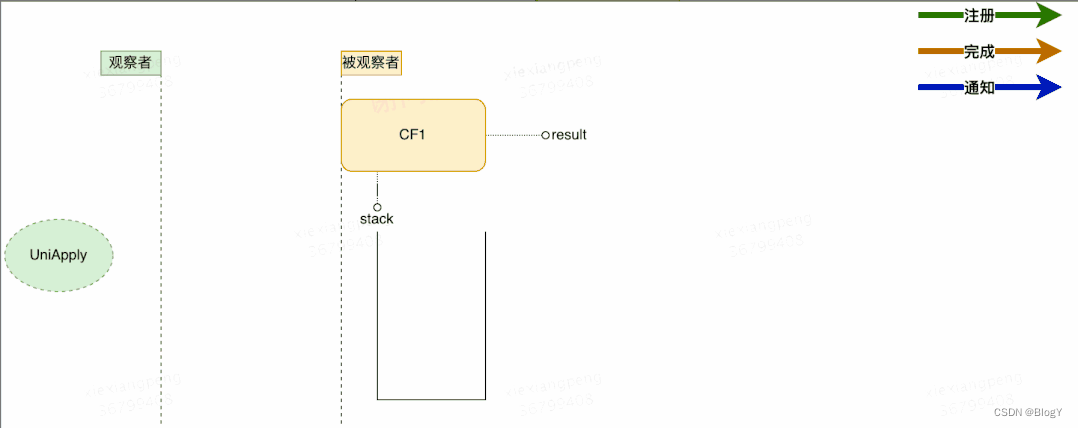
初步流程设计如上图所示,这里有几个关于注册与通知的并发问题,大家可以思考下:
Q1:在观察者注册之前,如果CF已经执行完成,并且已经发出通知,那么这时观察者由于错过了通知是不是将永远不会被触发呢 ?
A1:不会。在注册时检查依赖的CF是否已经完成。如果未完成(即result == null)则将观察者入栈,如果已完成(result != null)则直接触发观察者操作。
Q2:在”入栈“前会有”result == null“的判断,这两个操作为非原子操作,CompletableFufure的实现也没有对两个操作进行加锁,完成时间在这两个操作之间,观察者仍然得不到通知,是不是仍然无法触发?
A3:CompletableFuture的实现是这样解决该问题的:观察者在执行之前会先通过CAS操作设置一个状态位,将status由0改为1。如果观察者已经执行过了,那么CAS操作将会失败,取消执行。
通过对以上3个问题的分析可以看出,CompletableFuture在处理并行问题时,全程无加锁操作,极大地提高了程序的执行效率。我们将并行问题考虑纳入之后,可以得到完善的整体流程图如下所示:
CompletableFuture支持的回调方法十分丰富,但是正如上一章节的整体流程图所述,他们的整体流程是一致的。所有回调复用同一套流程架构,不同的回调监听通过策略模式实现差异化。
二元依赖
我们以thenCombine为例来说明二元依赖:

thenCombine操作表示依赖两个CompletableFuture。其观察者实现类为BiApply,如上图所示,BiApply通过src和snd两个属性关联被依赖的两个CF,fn属性的类型为BiFunction。与单个依赖不同的是,在依赖的CF未完成的情况下,thenCombine会尝试将BiApply压入这两个被依赖的CF的栈中,每个被依赖的CF完成时都会尝试触发观察者BiApply,BiApply会检查两个依赖是否都完成,如果完成则开始执行。这里为了解决重复触发的问题,同样用的是上一章节提到的CAS操作,执行时会先通过CAS设置状态位,避免重复触发。
多元依赖
依赖多个CompletableFuture的回调方法包括allOf、anyOf,区别在于allOf观察者实现类为BiRelay,需要所有被依赖的CF完成后才会执行回调;而anyOf观察者实现类为OrRelay,任意一个被依赖的CF完成后就会触发。二者的实现方式都是将多个被依赖的CF构建成一棵平衡二叉树,执行结果层层通知,直到根节点,触发回调监听。
4.实践总结
本章节为CompletableFuture实现原理的科普,旨在尝试不粘贴源码,而通过结构图、流程图以及搭配文字描述把CompletableFuture的实现原理讲述清楚。把晦涩的源码翻译为“整体流程”章节的流程图,并且将并发处理的逻辑融入,便于大家理解。
在商家端API异步化的过程中,我们遇到了一些问题,这些问题有的会比较隐蔽,下面把这些问题的处理经验整理出来。希望能帮助到更多的同学,大家可以少踩一些坑。
线程阻塞问题
代码执行在哪个线程上?
要合理治理线程资源,最基本的前提条件就是要在写代码时,清楚地知道每一行代码都将执行在哪个线程上。下面我们看一下CompletableFuture的执行线程情况。
CompletableFuture实现了CompletionStage接口,通过丰富的回调方法,支持各种组合操作,每种组合场景都有同步和异步两种方法。
同步方法(即不带Async后缀的方法)有两种情况。
- 如果注册时被依赖的操作已经执行完成,则直接由当前线程执行。
- 如果注册时被依赖的操作还未执行完,则由回调线程执行。
异步方法(即带Async后缀的方法):可以选择是否传递线程池参数Executor运行在指定线程池中;当不传递Executor时,会使用ForkJoinPool中的共用线程池CommonPool(CommonPool的大小是CPU核数-1,如果是IO密集的应用,线程数可能成为瓶颈)。
ExecutorService threadPool1 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100));
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("supplyAsync 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());//业务操作return "";
}, threadPool1);
//此时,如果future1中的业务操作已经执行完毕并返回,则该thenApply直接由当前main线程执行;否则,将会由执行以上业务操作的threadPool1中的线程执行。
future1.thenApply(value -> {System.out.println("thenApply 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());return value + "1";
});
//使用ForkJoinPool中的共用线程池CommonPool
future1.thenApplyAsync(value -> {
//do somethingreturn value + "1";
});
//使用指定线程池
future1.thenApplyAsync(value -> {
//do somethingreturn value + "1";
}, threadPool1);
线程池须知
异步回调要传线程池
前面提到,异步回调方法可以选择是否传递线程池参数Executor,这里我们建议强制传线程池,且根据实际情况做线程池隔离。
当不传递线程池时,会使用ForkJoinPool中的公共线程池CommonPool,这里所有调用将共用该线程池,核心线程数=处理器数量-1(单核核心线程数为1),所有异步回调都会共用该CommonPool,核心与非核心业务都竞争同一个池中的线程,很容易成为系统瓶颈。手动传递线程池参数可以更方便的调节参数,并且可以给不同的业务分配不同的线程池,以求资源隔离,减少不同业务之间的相互干扰。
线程池循环引用会导致死锁
public Object doGet() {ExecutorService threadPool1 = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100));CompletableFuture cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {//do sthreturn CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("child");return "child";}, threadPool1).join();//子任务}, threadPool1);return cf1.join();
}
如上代码块所示,doGet方法第三行通过supplyAsync向threadPool1请求线程,并且内部子任务又向threadPool1请求线程。threadPool1大小为10,当同一时刻有10个请求到达,则threadPool1被打满,子任务请求线程时进入阻塞队列排队,但是父任务的完成又依赖于子任务,这时由于子任务得不到线程,父任务无法完成。主线程执行cf1.join()进入阻塞状态,并且永远无法恢复。
为了修复该问题,需要将父任务与子任务做线程池隔离,两个任务请求不同的线程池,避免循环依赖导致的阻塞。
异步RPC调用注意不要阻塞IO线程池
服务异步化后很多步骤都会依赖于异步RPC调用的结果,这时需要特别注意一点,如果是使用基于NIO(比如Netty)的异步RPC,则返回结果是由IO线程负责设置的,即回调方法由IO线程触发,CompletableFuture同步回调(如thenApply、thenAccept等无Async后缀的方法)如果依赖的异步RPC调用的返回结果,那么这些同步回调将运行在IO线程上,而整个服务只有一个IO线程池,这时需要保证同步回调中不能有阻塞等耗时过长的逻辑,否则在这些逻辑执行完成前,IO线程将一直被占用,影响整个服务的响应。
EG:
public class ServiceExample {private RemoteRpcService rpcService;public void process() {CompletableFuture<String> future = rpcService.getDataAsync();future.thenApply(data -> {// 在这里进行数据处理,可能包含一些耗时操作String processedData = processData(data);return processedData;}).thenAccept(processedData -> {// 在这里进行处理后的数据的后续操作doSomething(processedData);});}private String processData(String data) {// 进行数据处理,可能是一些耗时操作return "Processed " + data;}private void doSomething(String processedData) {// 处理后续操作System.out.println("Processed data: " + processedData);}
}
在上面的代码中,process()方法调用了rpcService.getDataAsync()来获取远程RPC服务的数据,然后使用thenApply()和thenAccept()方法对数据进行处理和后续操作。
然而,如果processData()方法中包含了一个耗时长的操作,例如执行一个复杂的计算或者访问一个慢速的外部资源,那么这个同步回调将会在IO线程上执行,阻塞IO线程的执行。这将导致整个服务的响应性能下降,因为IO线程无法及时处理其他请求。为了解决这个问题,可以将耗时长的操作放到单独的线程池中执行,以释放IO线程。
异常处理
由于异步执行的任务在其他线程上执行,而异常信息存储在线程栈中,因此当前线程除非阻塞等待返回结果,否则无法通过try\catch捕获异常。CompletableFuture提供了异常捕获回调exceptionally,相当于同步调用中的try\catch。使用方法如下所示:
@Autowired
private WmOrderAdditionInfoThriftService wmOrderAdditionInfoThriftService;//内部接口
public CompletableFuture<Integer> getCancelTypeAsync(long orderId) {CompletableFuture<WmOrderOpRemarkResult> remarkResultFuture = wmOrderAdditionInfoThriftService.findOrderCancelledRemarkByOrderIdAsync(orderId);//业务方法,内部会发起异步rpc调用return remarkResultFuture.exceptionally(err -> {//通过exceptionally 捕获异常,打印日志并返回默认值log.error("WmOrderRemarkService.getCancelTypeAsync Exception orderId={}", orderId, err);return 0;});
}
有一点需要注意,CompletableFuture在回调方法中对异常进行了包装。大部分异常会封装成CompletionException后抛出,真正的异常存储在cause属性中,因此如果调用链中经过了回调方法处理那么就需要用Throwable.getCause()方法提取真正的异常。但是,有些情况下会直接返回真正的异常,最好使用工具类提取异常,如下代码所示:
@Autowired
private WmOrderAdditionInfoThriftService wmOrderAdditionInfoThriftService;//内部接口
public CompletableFuture<Integer> getCancelTypeAsync(long orderId) {CompletableFuture<WmOrderOpRemarkResult> remarkResultFuture = wmOrderAdditionInfoThriftService.findOrderCancelledRemarkByOrderIdAsync(orderId);//业务方法,内部会发起异步rpc调用return remarkResultFuture.thenApply(result -> {//这里增加了一个回调方法thenApply,如果发生异常thenApply内部会通过new CompletionException(throwable) 对异常进行包装//这里是一些业务操作}).exceptionally(err -> {//通过exceptionally 捕获异常,这里的err已经被thenApply包装过,因此需要通过Throwable.getCause()提取异常log.error("WmOrderRemarkService.getCancelTypeAsync Exception orderId={}", orderId, ExceptionUtils.extractRealException(err));return 0;});
}
上面代码中用到了一个自定义的工具类ExceptionUtils,用于CompletableFuture的异常提取,在使用CompletableFuture做异步编程时,可以直接使用该工具类处理异常。实现代码如下:
public class ExceptionUtils {public static Throwable extractRealException(Throwable throwable) {//这里判断异常类型是否为CompletionException、ExecutionException,如果是则进行提取,否则直接返回。if (throwable instanceof CompletionException || throwable instanceof ExecutionException) {if (throwable.getCause() != null) {return throwable.getCause();}}return throwable;}
}
参考链接:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/NXaP1xPL7_At9e-MVad4cQ
https://tech.meituan.com/2022/05/12/principles-and-practices-of-completablefuture.html
相关文章:

异步编排CompletableFuture
文章目录 一.简介二.并行加载1.为何需要并行加载2.并行加载的实现方式 三.CompletableFuture使用与原理1.背景和定义2.常用方法3.CompletableFuture的使用3.CompletableFuture原理4.实践总结 一.简介 CompletableFuture由Java 8提供,是实现异步化的工具类ÿ…...
linux_常用命令
一、日常使用命令/常用快捷键命令 开关机命令 1、shutdown –h now:立刻进行关机 2、shutdown –r now:现在重新启动计算机 3、reboot:现在重新启动计算机 4、su -:切换用户;passwd:修改用户密码 5、logou…...

Mac OS键盘常用快捷键
图形按键⌘Command 键⌃Control 键⌥Option 键⇧Shift 键⇪Caps Lockfn功能键 常用快捷键剪切、拷贝和粘贴 您可以在大多数 app 中使用这些快捷键来剪切、拷贝或粘贴选中的项目。其中包括文本、图片、音乐等等。您甚至可以在 Finder 中拷贝和粘贴文件,来将文件拷贝到…...

【腾讯云 Cloud Studio 实战训练营】通过云IDE构建Web3项目
iOS开发上架主页 在强者的眼中,没有最好,只有更好。 移动开发领域优质创作者,阿里云专家博主 文章目录 背景一、 前言二、 Cloud Studio 主要功能和应用场景三、Cloud Studio 实验前期准备3.1. 打开官网3.2. 注册 Cloud Studio:…...
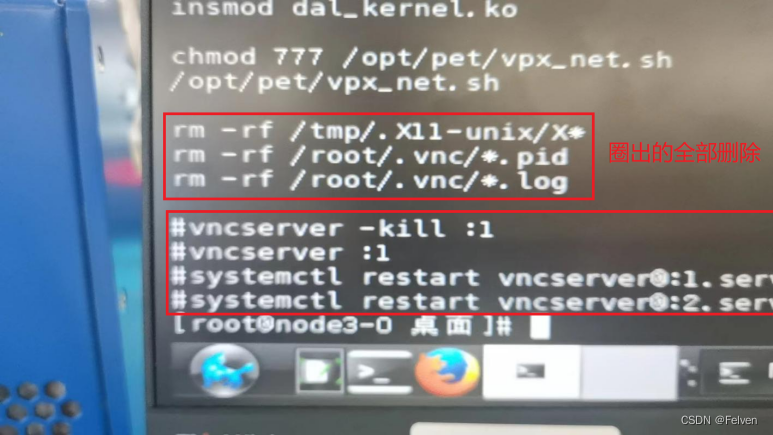
湖南麒麟系统非正常关机导致VNC启动失败原因分析
1、故障描述 掉电后,启动vncserver无法启动,或启动后连接vncserver黑屏 2、影响范围 非正常关机流程的机器 3、故障处理过程 第一次开机后vncserver服务无法正常启动,使用restart手动也无法拉起。按照现场人员提醒使用reboot命令重启机器…...
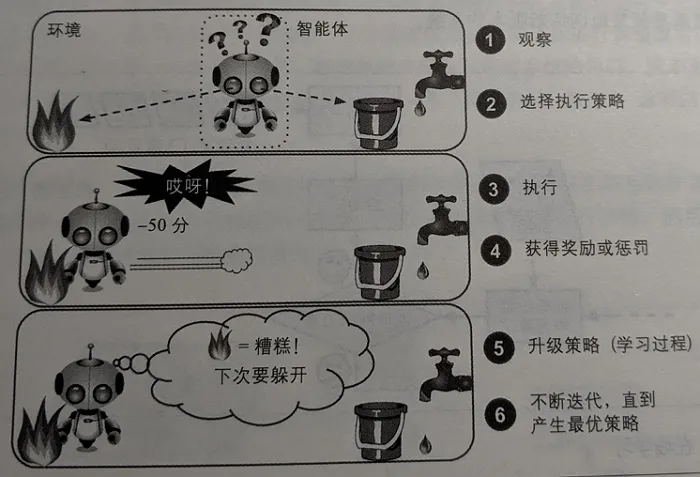
机器学习---监督学习和非监督学习
根据训练期间接受的监督数量和监督类型,可以将机器学习分为以下四种类型:监督学习、非监督学习、半监督学习和强化学习。 监督学习 在监督学习中,提供给算法的包含所需解决方案的训练数据,成为标签或标记。 简单地说,…...

【OS】请问,一个需要运行内存10GB的游戏,可以运行在32位物理内存为64GB的电脑上吗?
答案: 可以 解释 操作系统虽然是32位,限制了电脑的虚拟内存最大值为 4GB。如果,电脑开启了虚拟内存,则该款10GB运存的游戏是不可能开启的。期望开启这款游戏的做法是,在这个物理内存为64GB的电脑上关闭虚拟内存机制&…...

C语言 冒泡排序
目录 一、原理 二、代码演示 三、代码优化 一、原理 假设: int arr[] { 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 }; 将 arr 内的元素进行升序排列,得到一个新的数组 int arr[] { 0,1,2,3,4,5,…...
)
docker相关命令总结(停止、重启、重加载配置文件)
常用命令 # 配置 Docker 守护进程的行为和参数 vi /etc/docker/daemon.json# 停止docker服务 sudo systemctl stop docker# 启动 Docker 服务: sudo systemctl start docker# 重新加载systemd守护程序的配置文件,不会重启服务(配置文件&…...
Linux 命令大全(下)
Linux 命令大全(上) 本文目录 6. 网络通讯 常用命令6.1 ssh 命令 – 安全的远程连接服务器6.1.1 含义6.1.2 语法格式6.1.3 常用参数6.1.4 参考示例 6.2 netstat 命令 – 显示网络状态6.2.1 含义6.2.2 语法格式6.2.3 常用参数6.2.4 参考示例 6.3 dhclient…...
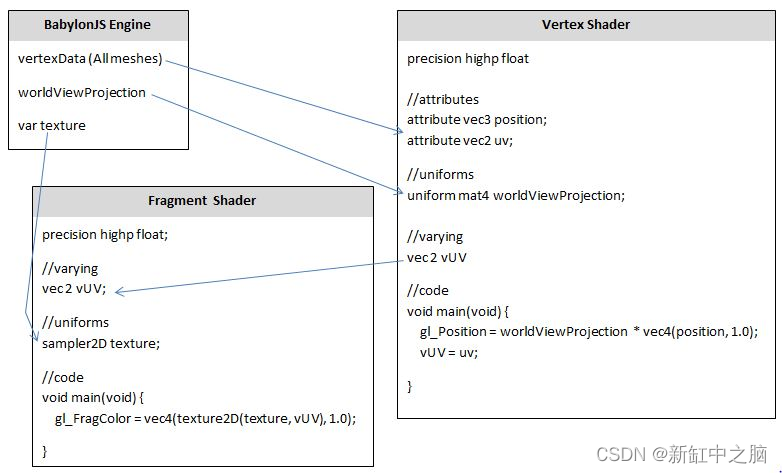
Babylon.js着色器简明简称【Shader】
推荐:用 NSDT设计器 快速搭建可编程3D场景 为了生成 BabylonJS 场景,需要用 Javascript 编写代码,BabylonJS 引擎会处理该代码并将结果显示在屏幕上。 场景可以通过改变网格、灯光或摄像机位置来改变。 为了及时显示可能的变化,屏…...

深入理解Linux内核--信号
信号的作用 信号(signal)是很短的消息,可以被发送到一个进程或一组进程。 使用信号的两个主要目的是: 1.让进程知道已经发生了一个特定的事件。 2.强迫进程执行它自己代码中的信号处理程序。 POSIX标准还引入了一类新的信号,叫做…...

转圈打印矩阵
转圈打印矩阵 【题目】 给定一个整型矩阵 matrix,请按照转圈的方式打印它。 例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 打印结果为:1,2,3,4,8,12,16,1…...
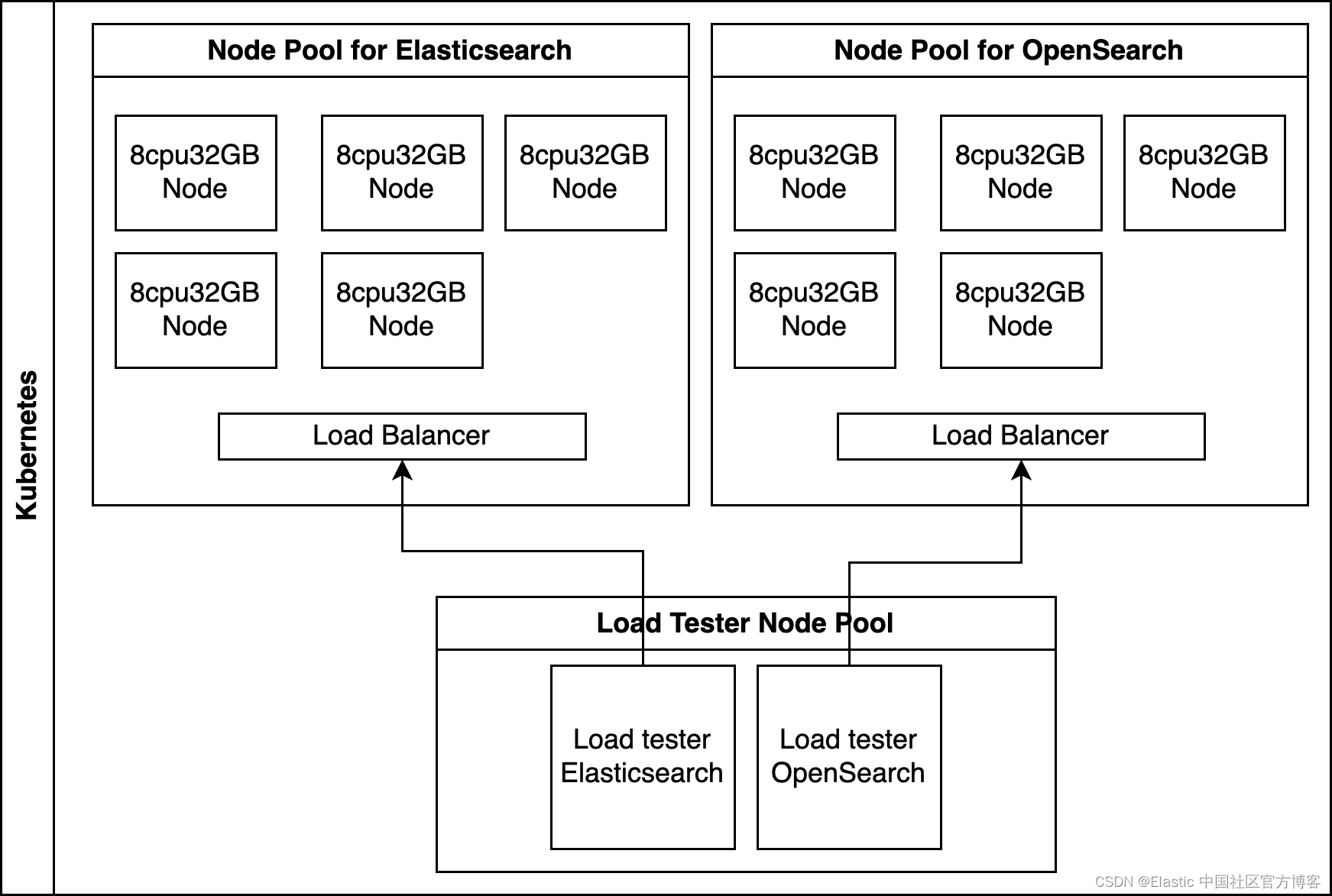
Elasticsearch 与 OpenSearch:揭开性能差距
作者:George Kobar, Ugo Sangiorgi 对于任何依赖快速、准确搜索数据的组织来说,强大、快速且高效的搜索引擎是至关重要的元素。 对于开发人员和架构师来说,选择正确的搜索平台可以极大地影响你的组织提供快速且相关结果的能力。 在我们全面的…...

100个Java工具类之41:系统工具类Apache之SystemUtils
系统工具类Apache之 org.apache.commons.lang3.SystemUtils 根据Apache SystemUtils源码中介绍,SystemUtils是java.lang.System的帮助程序。当因安全限制无法读取系统属性时,则会返回null。下面是为大家整理的几个主要用法。 一、获取主机名 String ho…...
maven Jar包反向install到本地仓库
maven Jar包反向install到本地仓库 需求实现 需求 项目打包时报错,缺少一个jar包。 但是在maven仓库都找不到此jar包,其他人提供了这个jar包。 需要把这个jar包install到本地仓库,使项目能正常打包运行。 实现 使用git bash命令执行以下脚…...
.NET6使用SqlSugar操作数据库
1.//首先引入SqlSugarCore包 2.//新建SqlsugarSetup类 public static class SqlsugarSetup{public static void AddSqlsugarSetup(this IServiceCollection services, IConfiguration configuration,string dbName "ConnectString"){SqlSugarScope sqlSugar new Sq…...

MySQL8是什么-MySQL8知识详解
从今天起,开始更新MySQL8的教程,今天更新MySQL8的第一篇文章,主要讲了MySQL8是什么、MySQL数据库的概念、MySQL的优势和MySQL的发展历史。 1、MySQL8是什么 MySQL 8是一个开源的关系型数据库管理系统。它是MySQL数据库的最新版本,…...
Spring Gateway+Security+OAuth2+RBAC 实现SSO统一认证平台
背景:新项目准备用SSO来整合之前多个项目的登录和权限,同时引入网关来做后续的服务限流之类的操作,所以搭建了下面这个系统雏形。 关键词:Spring Gateway, Spring Security, JWT, OAuth2, Nacos, Redis, Danymic datasource, Jav…...

flutter开发实战-TextPainter计算文本内容的宽度
flutter开发实战-TextPainter计算文本内容的宽度 最近开发过程中根据Text文本的大小判断是否需要进行显示跑马灯效果,获取文本的大小,需要TextPainter来获取Size 一、TextPainter TextPainter主要用于实现文本的绘制。TextPainter类可以将TextSpan渲染…...

RestClient
什么是RestClient RestClient 是 Elasticsearch 官方提供的 Java 低级 REST 客户端,它允许HTTP与Elasticsearch 集群通信,而无需处理 JSON 序列化/反序列化等底层细节。它是 Elasticsearch Java API 客户端的基础。 RestClient 主要特点 轻量级ÿ…...
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...

MySQL 隔离级别:脏读、幻读及不可重复读的原理与示例
一、MySQL 隔离级别 MySQL 提供了四种隔离级别,用于控制事务之间的并发访问以及数据的可见性,不同隔离级别对脏读、幻读、不可重复读这几种并发数据问题有着不同的处理方式,具体如下: 隔离级别脏读不可重复读幻读性能特点及锁机制读未提交(READ UNCOMMITTED)允许出现允许…...
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...

前端倒计时误差!
提示:记录工作中遇到的需求及解决办法 文章目录 前言一、误差从何而来?二、五大解决方案1. 动态校准法(基础版)2. Web Worker 计时3. 服务器时间同步4. Performance API 高精度计时5. 页面可见性API优化三、生产环境最佳实践四、终极解决方案架构前言 前几天听说公司某个项…...
中关于正整数输入的校验规则)
Element Plus 表单(el-form)中关于正整数输入的校验规则
目录 1 单个正整数输入1.1 模板1.2 校验规则 2 两个正整数输入(联动)2.1 模板2.2 校验规则2.3 CSS 1 单个正整数输入 1.1 模板 <el-formref"formRef":model"formData":rules"formRules"label-width"150px"…...

鸿蒙DevEco Studio HarmonyOS 5跑酷小游戏实现指南
1. 项目概述 本跑酷小游戏基于鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5开发,使用DevEco Studio作为开发工具,采用Java语言实现,包含角色控制、障碍物生成和分数计算系统。 2. 项目结构 /src/main/java/com/example/runner/├── MainAbilitySlice.java // 主界…...

用机器学习破解新能源领域的“弃风”难题
音乐发烧友深有体会,玩音乐的本质就是玩电网。火电声音偏暖,水电偏冷,风电偏空旷。至于太阳能发的电,则略显朦胧和单薄。 不知你是否有感觉,近两年家里的音响声音越来越冷,听起来越来越单薄? —…...
嵌入式学习笔记DAY33(网络编程——TCP)
一、网络架构 C/S (client/server 客户端/服务器):由客户端和服务器端两个部分组成。客户端通常是用户使用的应用程序,负责提供用户界面和交互逻辑 ,接收用户输入,向服务器发送请求,并展示服务…...
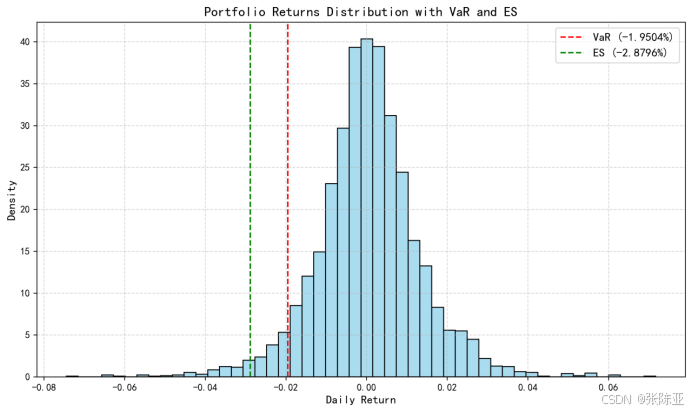
Python基于历史模拟方法实现投资组合风险管理的VaR与ES模型项目实战
说明:这是一个机器学习实战项目(附带数据代码文档),如需数据代码文档可以直接到文章最后关注获取。 1.项目背景 在金融市场日益复杂和波动加剧的背景下,风险管理成为金融机构和个人投资者关注的核心议题之一。VaR&…...
