4.2 C++ Boost 内存池管理库
Boost 库是一个由C/C++语言的开发者创建并更新维护的开源类库,其提供了许多功能强大的程序库和工具,用于开发高质量、可移植、高效的C应用程序。Boost库可以作为标准C库的后备,通常被称为准标准库,是C标准化进程的重要开发引擎之一。使用Boost库可以加速C应用程序的开发过程,提高代码质量和性能,并且可以适用于多种不同的系统平台和编译器。Boost库已被广泛应用于许多不同领域的C++应用程序开发中,如网络应用程序、图像处理、数值计算、多线程应用程序和文件系统处理等。
C++的指针操作可以说是继承了C语言的优点,但同时也带来了一些问题,例如内存泄漏、悬挂指针、访问越界等。这些问题不仅会导致程序运行错误,还会对系统稳定性造成影响。为了避免这些问题,Boost库提供了一套高效的自动内存管理指针操作函数,这些函数使用引用计数技术来管理内存。
2.1 使用Pool内存池
boost::pool是Boost库中一个内存池管理器,用于高效地管理和分配内存。在程序中,动态分配和释放内存是很常见的操作,但频繁的内存分配和释放会导致开销很大,影响程序性能。boost::pool针对这个问题提供了一个解决方案,它可以预分配并缓存一定数量的内存块,通过重复利用这些内存块来减小内存分配释放的开销,提高程序性能。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/pool/pool.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{boost::pool<> pool(sizeof(int)); // 定义整数内存池(int/float/double)int *ptr[10] = { 0 }; // 定义指针列表for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++){ptr[x] = static_cast<int *>(pool.malloc()); // 开辟空间并转为指针if (ptr[x] == nullptr)cout << "分配空间失败" << endl;}// 分别对内存空间赋值for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++)*ptr[x] = x;// 输出数据for (int x = 0; x < 10; x++){cout << "内存地址: " << &ptr[x] << " 数值: " << *ptr[x] << endl;}getchar();return 0;
}
Pool内存池同样提供了对容器的存储方法,我们在使用时只需要包含头文件pool_alloc.hpp,当包含此头文件后读者可使用pool_allocator模板类对容器内的特殊成员进行初始化。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/pool/pool.hpp>
#include <boost/pool/pool_alloc.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;typedef struct
{int uuid;string uname;
}MyStruct;int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{// 应用标准容器: 定义存储string类型的容器std::vector<std::string, pool_allocator<std::string> > vect;// 设置容器vect.push_back("admin");vect.push_back("lyshark");for (int x = 0; x < vect.size(); x++){std::cout << "输出: " << vect[x] << std::endl;}// 应用自定义数据类型std::vector<MyStruct, pool_allocator<MyStruct>> pool_ptr;MyStruct ptr;ptr.uuid = 10001;ptr.uname = "lyshark";pool_ptr.push_back(ptr);ptr.uuid = 1002;ptr.uname = "admin";pool_ptr.push_back(ptr);for (int x = 0; x < pool_ptr.size(); x++){std::cout << "UUID: " << pool_ptr[x].uuid << " Name: " << pool_ptr[x].uname << std::endl;}std::system("pause");return 0;
}
2.2 使用ObjectPool内存池
boost::object_pool是Boost库中的一个内存池管理器,可以用来高效地分配和释放内存,并能够管理多个大小相等的对象。
在使用boost::object_pool时,我们可以先创建一个大小固定的内存池,然后使用malloc()函数从内存池中分配内存,并在内存上构造一个对象。当我们需要释放内存时,可以调用destroy()函数显式地销毁对象,并使用free()函数释放内存。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <boost/pool/object_pool.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;struct MyStruct
{
public:int uuid;string uname;int uage;MyStruct(int uuid_, string uname_, int uage_){uuid = uuid_; uname = uname_; uage = uage_;}
};int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{boost::object_pool<MyStruct> object;auto ptr = object.malloc();// 默认最多只能传递3个参数ptr = object.construct(1001,"lyshark",25); // 为构造函数传递参数cout << "姓名: " << ptr->uname << endl;std::system("pause");return 0;
}
一般在默认情况下object_pool内存池只能接收三个以内的参数传递,当读者需要使用多于三个参数时则需要使用自定义可变参数模板来实现功能,我们以接受四个参数为例,定义construct模板并在该模板内部实现分配资源。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <boost/pool/object_pool.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;struct MyStruct
{
public:int uuid;string uname;int uage;string usex;MyStruct(int uuid_, string uname_, int uage_, string usex_){uuid = uuid_; uname = uname_; uage = uage_; usex = usex_;}
};// 定义可变参数模板,用来实现接受三个以上的参数
template<typename P, typename ... Args> inline typename P::element_type* construct(P& p, Args&& ... args)
{typename P::element_type* mem = p.malloc();new(mem) typename P::element_type(std::forward<Args>(args)...);return mem;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{boost::object_pool<MyStruct> object;auto ptr = object.malloc();// 接收四个参数写法auto ref = construct(object, 1001, "lyshark", 24, "男");cout << "姓名: " << ref->uname << endl;object.free(ref);object.free(ptr);std::system("pause");return 0;
}
2.3 使用SharedPtr智能指针
boost::shared_ptr是Boost库中的一个智能指针,用于自动管理动态分配的内存。它跟踪有多少个shared_ptr实例共享同一个对象,当最后一个实例离开作用域时,它会自动释放分配的内存。
该函数是boost.smart_ptr库中最重要的智能指针,shared_ptr包装了new操作符在堆上分配的动态对象,实现了引用计数型的智能指针,可被自由的拷贝和赋值,并在任意地方共享。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{// 基本的定义与赋值boost::shared_ptr<int> int_ptr(new int);*int_ptr = 1024;cout << "指针: " << &int_ptr << " 数值: " << *int_ptr << endl;boost::shared_ptr<string> string_ptr(new string);*string_ptr = "hello lyshark";cout << "指针: " << &string_ptr << " 长度: " << string_ptr->size() << endl;// 拷贝构造的使用boost::shared_ptr<int> shared_ptr(new int(10)); // 定义指向整数的sharedcout << "持有者: " << shared_ptr.unique() << endl;boost::shared_ptr<int>shared_copy = shared_ptr; // 实现拷贝cout << "引用数: " << shared_ptr.use_count() << endl;shared_ptr.reset(); // 关闭shared的使用getchar();return 0;
}
在有时候我们需要使用多个指针,并将多个指针分别指向不同的数据集合,此时我们可以先封装一个MyShared类,并使用循环的方式初始化创建内存空间,每次创建空间后将该空间存储至vect容器内,最后再以此循环输出该容器内存所有自定义类元素即可;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;// 定义Shared类
class MyShared
{
private:int shared_uuid;std::string shared_name;public:MyShared(int x, std::string y){shared_uuid = x;shared_name = y;}std::string GetName(){return shared_name;}int GetUUID(){return shared_uuid;}
};int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{std::vector<boost::shared_ptr<MyShared>> vect;// 循环开辟空间,并放入vector列表for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++){boost::shared_ptr<MyShared> ptr(new MyShared(x,"hello lyshark"));vect.push_back(ptr);}// 输出列表中的元素for (int x = 0; x < vect.size(); x++){std::cout << "UUID: " << vect[x]->GetUUID() << " Name: " << vect[x]->GetName() << std::endl;}std::system("pause");return 0;
}
智能指针同样支持使用引用计数器功能,在指针内部读者可通过使用ptr.use_count()来输出当前的计数器,当此处代码没有被使用是则引用计数器会为0,而当代码或多个进程使用时则引用计数器相应的会增加,查询引用计数器可以如下所示;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <boost/shared_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;class MyShared
{
private:boost::shared_ptr<int> ptr;
public:MyShared(boost::shared_ptr<int> p_) :ptr(p_){}void print(){cout << "内部 计数: " << ptr.use_count() << " 数值: " << *ptr << endl;}
};// 自动拷贝一个对象,所以引用计数会+1
void print_func(boost::shared_ptr<int> ptr)
{cout << "外部 计数: " << ptr.use_count() << " 数值: " << *ptr << endl;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{boost::shared_ptr<int> ptr(new int(100)); // 定义整数指针MyShared s1(ptr), s2(ptr); // 定义两个对象,并初始化s1.print();s2.print();*ptr = 200;print_func(ptr);s1.print();s2.print();std::system("pause");return 0;
}
如上,在声明了shared_ptr和两个MyShared类后,指针被共享,因此引用计数为3,调用print_func()函数,该函数内部拷贝了一个shared_ptr对象,因此引用计数再次增加1,但退出函数时,拷贝自动析构,引用计数又会恢复为3。
2.4 使用MakeShared工厂函数
boost::make_shared是一个工厂函数,用于动态分配一个对象并返回一个智能指针,它是Boost库中的一个组件。使用make_shared我们可以将对象的构造和内存分配合并在一起,避免了常规构造函数和动态内存分配的性能损失和代码冗余。
当读者使用2.3节中所示的shared_ptr智能指针时,虽然能够很好的消除delete释放的调用,但我们还是需要使用new方法来构造初始化数据集,为了能够不再使用new关键字,在smart_ptr库中提供了一个工厂函数make_shared()函数,用于消除使用new创建数据集,工厂函数常用于初始化特定的指针数据,如下所示;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{// make_shared 工厂函数初始化boost::shared_ptr<string> string_ptr = boost::make_shared<string>("hello lyshark");cout << "初始化字符串: " << *string_ptr << endl;// 应用于标准容器中typedef std::vector<boost::shared_ptr<int>> vector_ptr; // 定义标准容器类型vector_ptr vect(10); // 定义拥有十个元素的容器// 初始化赋值int x = 0;for (auto pos = vect.begin(); pos != vect.end(); ++pos){(*pos) = boost::make_shared<int>(++x); // 工厂函数初始化cout << "输出值: " << *(*pos) << endl; // 输出数据(两次解引用)}// 修改数据boost::shared_ptr<int> int_ptr = vect[9]; // 获取最后一个数值*int_ptr = 100; // 修改最后一个数值cout << "修改后: " << *vect[9] << endl;// 第二种输出方式(一次解引用完成)x = 0;for (auto& ptr : vect){cout << "输出值: " << *ptr << endl;}std::system("pause");return 0;
}
2.5 使用SharedPtr桥接模式
在C++中,shared_ptr有一种常用的设计模式是桥接模式(Bridge Design Pattern)又称为PIMPL模式。桥接模式的主要作用是将实现细节从类的接口中分离出来,从而使得接口和实现可以独立变化,提高了类的可扩展性和可维护性。
使用shared_ptr实现桥接模式时,我们可以使用一个基类和多个派生类的继承关系,并使用shared_ptr来管理对象的生命周期。通过使用shared_ptr的引用计数技术,可以动态地改变派生类的具体实现,而不会影响到基类接口的实现。其仅对外部暴漏最小的细节,内部类实现用一个shared_ptr来保存指针。
如下代码所示,首先我们定义MyShared作为基类,其内部存在一个print输出函数,而该函数通过boost::shared_ptr<impl> ptr;指向impl基址,当输出内容时,自动桥接到impl派生类上的print函数上。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;// 定义基类
class MyShared
{
private:class impl;boost::shared_ptr<impl> ptr;public:MyShared();void print();
};// 定义桥接类
class MyShared::impl
{
public:void print(){cout << "输出桥接类" << endl;}
};MyShared::MyShared() :ptr(new impl){}void MyShared::print()
{ptr->print();
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{MyShared lsp;lsp.print();std::system("pause");return 0;
}
2.6 使用SharedPtr工厂模式
在C++中,shared_ptr还可以与工厂模式(Factory Design Pattern)结合使用,工厂模式是一种创建型设计模式,该模式包装了new操作符的使用,使对象的创建工作集中在工厂类或工厂函数上,通过创建和返回智能指针,从而实现动态创建对象并自动管理其生命周期的功能。
通常开发中,自己编写的工厂类都会在堆上使用new动态分配对象,然后返回对象指针,当忘记释放delete时,内存泄漏就会产生。当使用shared_ptr实现工厂模式时,我们可以将工厂类中的创建对象的方法返回一个shared_ptr对象,从而避免手动管理动态分配的内存。
如下代码所示,我们使用shared_ptr封装接口,让impl类不再返回原始指针,而是返回shared_ptr包装的智能指针,这样就可以很好的保护资源。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;// 定义基类 全部为虚函数
class abstract
{
public:virtual void MyPrint() = 0;
protected:virtual ~abstract() = default;
};// 派生类实现虚函数
class impl :public abstract
{
public:impl() = default;virtual ~impl() = default;public:virtual void MyPrint(){cout << "调用方法完成." << endl;}
};// 工厂函数返回基类的 基址指针 返回类型为 shared_ptr
boost::shared_ptr<abstract> create()
{return boost::make_shared<impl>();
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{// 第一种调用方式auto ptr = create();ptr->MyPrint();// 第二种方式abstract *abstract_ptr = ptr.get();abstract_ptr->MyPrint();// 强制转换,后输出impl *impl_ptr = (impl*)(ptr.get());impl_ptr->MyPrint();std::system("pause");return 0;
}
2.7 使用SharedPtr资源共享
使用shared_ptr实现资源共享时,我们可以创建多个shared_ptr对象,让它们共同管理同一个动态分配的对象,从而避免了内存泄漏和错误释放内存的情况。
如下案例中我们定义了shared_vector类,当MyShared中的内容发生变化时,由于ptr指向了MyShared类,则ptr中的值也会随着MyShared中的内容的变化而变化。
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <string>using namespace std;class shared_vector
{
public:typedef vector<string>::size_type size_type;shared_vector() : data(make_shared<vector<string>>()){}shared_vector(initializer_list<string> il) : data(make_shared<vector<string>>(il)){}size_type size()const{ return data->size(); }bool empty()const{ return data->empty(); }//尾部插入删除元素 void push_back(const string& s){ data->push_back(s); }void pop_back(){ data->pop_back(); }//访问元素 string& front(){ return data->front(); }string& back(){ return data->back(); }
private:shared_ptr<vector<string>> data;
};int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{shared_vector MyShared{ "admin", "lyshark" };shared_vector ptr(MyShared);ptr.push_back("administrator");cout << "发生变化: " << MyShared.back() << endl;std::system("pause");
}
2.8 使用WeakPtr智能指针
weak_ptr是C++11中的智能指针,它用于解决shared_ptr可能引起的循环引用问题。与shared_ptr不同,weak_ptr并不持有所指对象的所有权,因此它不能直接访问所指向的对象。它只是提供了一种通过shared_ptr访问所指向对象的方式,并且在没有引用时可以自动弱化其引用。
在使用weak_ptr时,通常需要先从一个shared_ptr对象创建一个weak_ptr对象。我们可以通过lock()函数获取指向所指对象的shared_ptr对象,然后通过这个shared_ptr对象来访问所指对象。
如果简单来说,这个指针的出现只是为了配合shared_ptr使用的,其本身并不具备普通指针的行为,其主要的作用在于协助shared_ptr工作,像旁观者一样观察资源的使用情况。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{boost::shared_ptr<int> ptr(new int(10));boost::weak_ptr<int> weak(ptr);// 判断weak_ptr观察的对象是否失效if (!weak.expired()){// 获得一个shared_ptrboost::shared_ptr<int> new_ptr = weak.lock();*new_ptr = 100;}ptr.reset();std::system("pause");return 0;
}
weak_ptr还可以用于对象自我管理,如获得this指针的shared_ptr使对象自己能产生shared_ptr管理自己,使用时需要定义类,并继承于enable_shared_from_this接口。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/enable_shared_from_this.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;class self_my_shared_ptr : public boost::enable_shared_from_this<self_my_shared_ptr>
{
public:self_my_shared_ptr(int n) :x(n){}int x;void print(){std::cout << "自身指针: " << x << std::endl;}
};int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{auto ptr = boost::make_shared<self_my_shared_ptr>(100);ptr->print();auto p = ptr->shared_from_this();p->x = 200;p->print();std::system("pause");return 0;
}
有时候代码中可能会出现循环引用的情况,此时使用shared_ptr指针时计数器就会失效,导致无法正确释放资源,例如如下一个案例,两个节点对象互相持有对方的引用,每个引用计数器都是2,在析构时引用计数没有变为0,因此不会调用删除清理操作,所以会导致内存泄漏的产生。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/enable_shared_from_this.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;class node
{
public:~node(){std::cout << "析构函数,被调用." << std::endl;}typedef boost::shared_ptr<node> ptr_type;ptr_type next;
};int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{auto ptrA = boost::make_shared<node>();auto ptrB = boost::make_shared<node>();ptrA->next = ptrB;ptrB->next = ptrA;std::cout << "ptrA 计数器: "<< ptrA.use_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "ptrB 计数器: " << ptrB.use_count() << std::endl;std::system("pause");return 0;
}
为了解决上述的内存泄露问题,我们需要使用weak_ptr智能指针,将原来的强引用模式改为弱引用模式,即可实现动态释放,循环引用即可消失。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/enable_shared_from_this.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;class node
{
public:~node(){std::cout << "析构函数,被调用." << std::endl;}typedef boost::weak_ptr<node> ptr_type;ptr_type next;
};int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{auto ptrA = boost::make_shared<node>();auto ptrB = boost::make_shared<node>();ptrA->next = ptrB;ptrB->next = ptrA;std::cout << "ptrA 计数器: "<< ptrA.use_count() << std::endl;std::cout << "ptrB 计数器: " << ptrB.use_count() << std::endl;// 检查弱引用是否有效if (!ptrA->next.expired()){// 获取到强引用指针auto ptrC = ptrA->next.lock();}std::system("pause");return 0;
}
2.9 使用IntrusivePtr计数器
intrusive_ptr是一个智能指针,与shared_ptr类似,都具有引用计数的功能。它是一个轻量级的智能指针,相比于标准库中的shared_ptr,intrusive_ptr可以方便地在自定义数据结构中使用,因为它不需要在自定义类型中维护额外的引用计数器。
该指针采用了惯用法,即将引用计数器作为自定义类型的一部分存储在实例中。因此,使用intrusive_ptr时,需要为自定义类型提供一个内部引用计数器的实现。
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/smart_ptr.hpp>
#include <boost/smart_ptr/intrusive_ref_counter.hpp>using namespace std;
using namespace boost;struct data
{int m_count = 0;~data(){cout << "结束." << endl;}
};// 递增
void intrusive_ptr_add_ref(data* p)
{p->m_count = p->m_count + 10;
}// 递减
void intrusive_ptr_release(data* p)
{if (--p->m_count == 0){delete p;}
}int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{// 使用自定义引用计数typedef intrusive_ptr<data> counted_ptr;counted_ptr p(new data);std::cout << "引用数: " << p->m_count << std::endl;counted_ptr weak_p(p.get(), false);std::cout << "引用数: " << p->m_count << std::endl;std::system("pause");return 0;
}
本文作者: 王瑞
本文链接: https://www.lyshark.com/post/bc8ff67e.html
版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
相关文章:

4.2 C++ Boost 内存池管理库
Boost 库是一个由C/C语言的开发者创建并更新维护的开源类库,其提供了许多功能强大的程序库和工具,用于开发高质量、可移植、高效的C应用程序。Boost库可以作为标准C库的后备,通常被称为准标准库,是C标准化进程的重要开发引擎之一。…...
Django模型基础
文章目录 一、models字段类型概述属性命名限制使用方式逻辑删除和物理删除常用字段类型 二、常用字段参数常用字段选项(通过字段选项,可以实现对字段的约束) 实践创建模型执行迁移命令 并 创建超级用户登录admin后台添加文件和图片字段定义模型字段和约束及在Admin后…...

导读-Linux简介
Linux简介 总所周知,计算机系统包含硬件和软件两部分。硬件部分被称为裸机,主要包括中央处理器(CPU)、内存、外存和各种外部设备。软件部分主要包括系统软件和应用软件两部分。系统软件包括操作系统、汇编语言、编译程序、数据…...
判断平面中两射线是否相交的高效方法
1. 简介 最近在工作中遇到判断平面内两射线是否相交的问题。 对于这个问题的解决,常规的方法是将两条射线拓展为直线,计算直线的交点,而后判断交点是否在射线上。 这种方法,在思路上较为直观,也易于理解。然后,该方法在计算量上相对较大。对于少量射线间的交点计算尚可…...
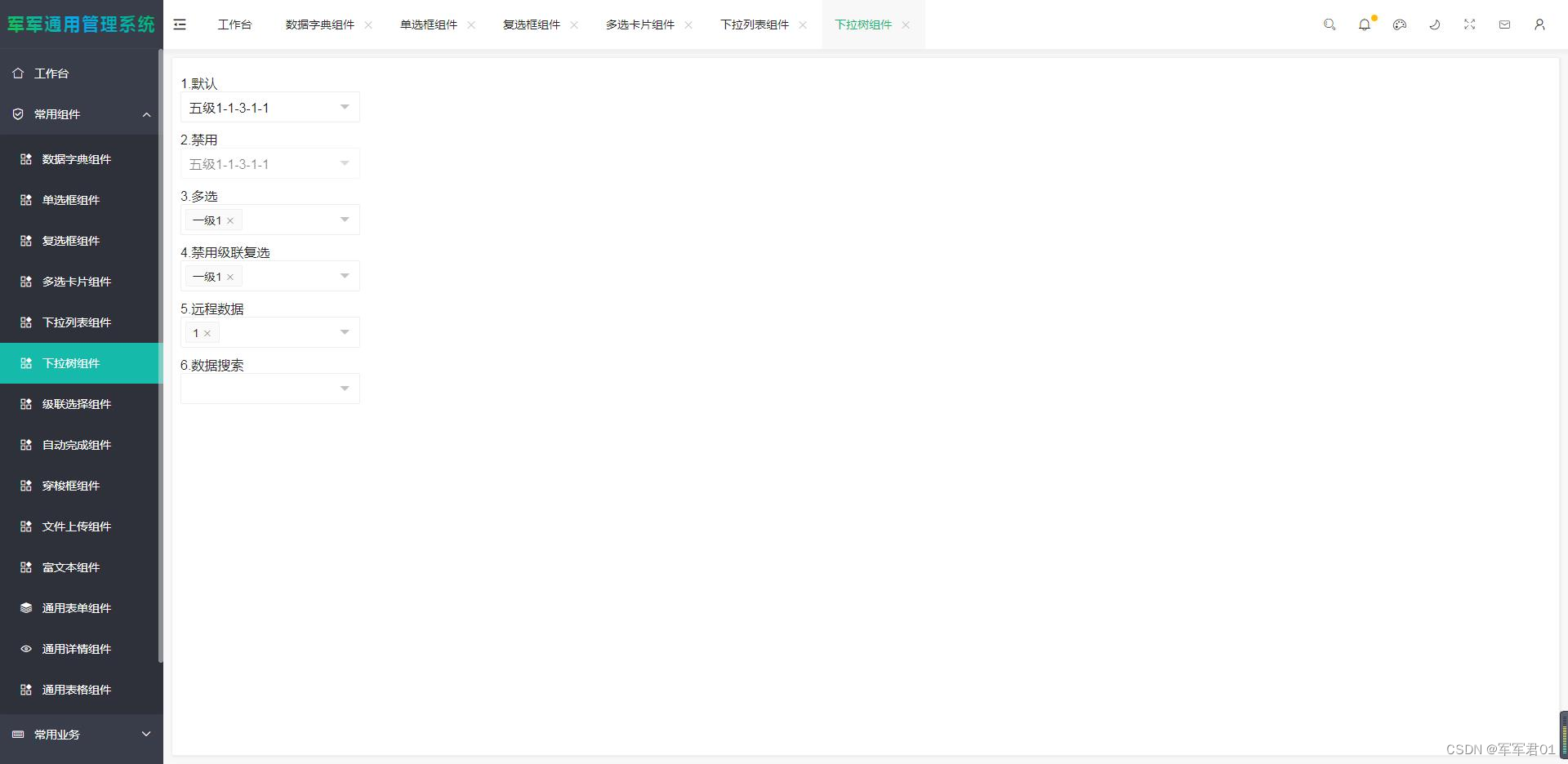
基于VUE3+Layui从头搭建通用后台管理系统(前端篇)八:自定义组件封装上
一、本章内容 本章实现一些自定义组件的封装,包括数据字典组件的封装、下拉列表组件封装、复选框单选框组件封装、单选框组件封装、文件上传组件封装、级联选择组件封装、富文本组件封装等。 1. 详细课程地址: 待发布 2. 源码下载地址: 待发布 二、界面预览 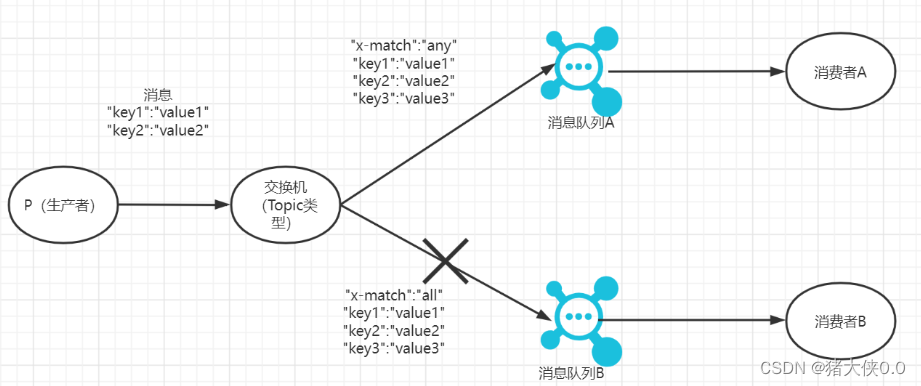
RabbitMq交换机类型介绍
RabbitMq交换机类型介绍 在RabbitMq中,生产者的消息都是通过交换器来接收,然后再从交换器分发到不同的队列,再由消费者从队列获取消息。这种模式也被成为“发布/订阅”。 分发的过程中交换器类型会影响分发的逻辑。 直连交换机:…...
中国电信秋招攻略,考试内容分析
电信秋招简介 每年的毕业生人数都在逐年递增,逐年递增就意味着竞争会越来越大,最好比别人做更充足的准备。要确定好就业方向以及就业的岗位,要了解各种各样的流程,做好一切自己能做到的准备。而对于有想法进入电信公司工作的人来…...

prompt-engineering-note(面向开发者的ChatGPT提问工程学习笔记)
介绍: ChatGPT Prompt Engineering Learning Notesfor Developers (面向开发者的ChatGPT提问工程学习笔记) 课程简单介绍了语言模型的工作原理,提供了最佳的提示工程实践,并展示了如何将语言模型 API 应用于各种任务的应用程序中。 此外&am…...
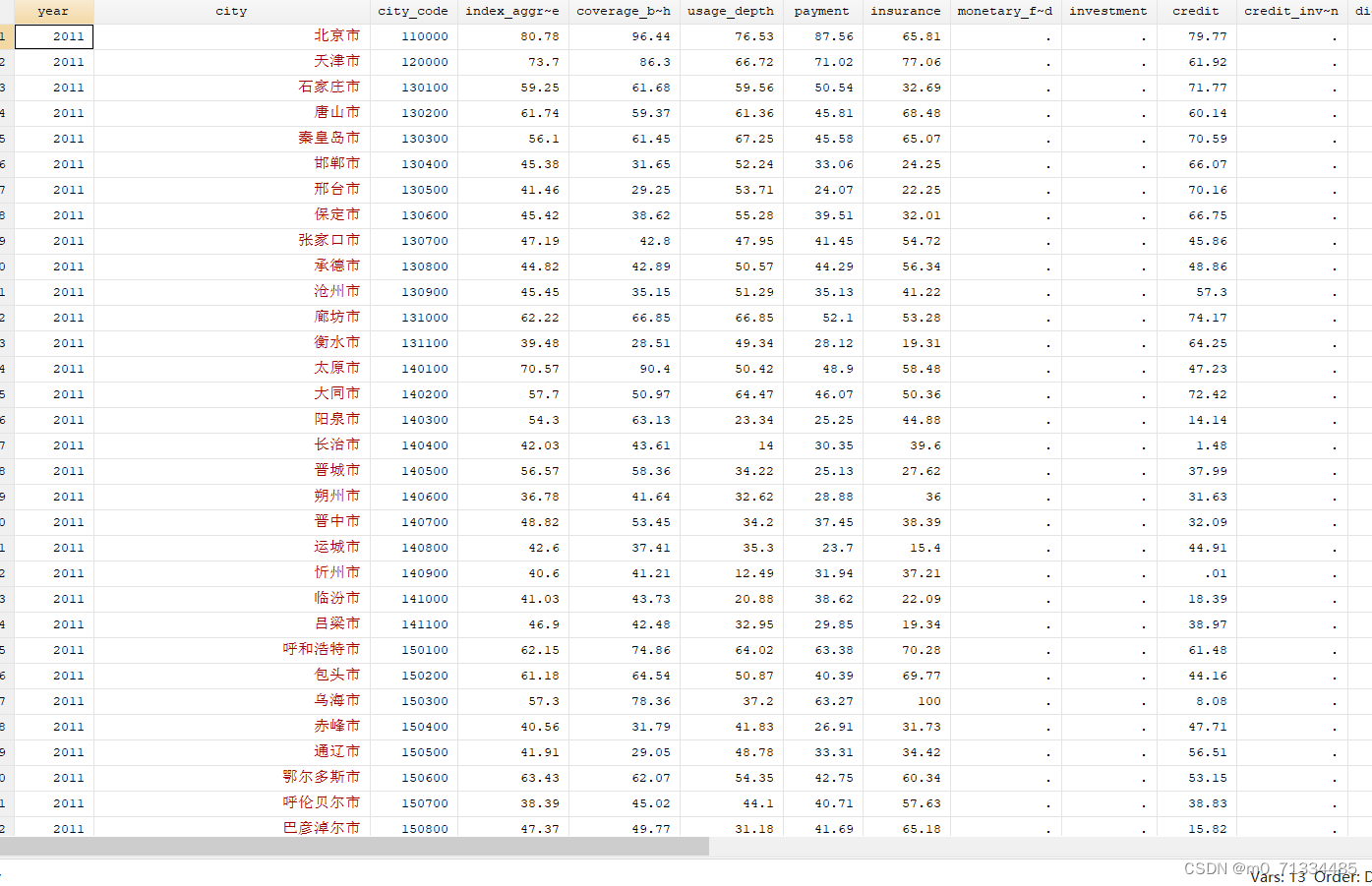
2011-2021年数字普惠金融指数Bartik工具变量法(含原始数据和Bartik工具变量法代码)
2011-2021年数字普惠金融指数Bartik工具变量法(含原始数据和Bartik工具变量法代码) 1、时间:2011-2020(省级、城市),2014-2020(区县) 2、原始数据来源:北大金融研究中心…...

[ MySQL ] — 常见函数的使用
目录 日期函数 current_date — 获取当前日期 current_time — 获取当前时间 current_timestamp — 获取当前时间戳 date — 获取参数的日期部分 编辑 date_add — 在日期或时间的基础上进行增加 date_sub — 在日期或时间的基础上进行减少 datediff — 计算两个日期相差…...
-Demo)
Spring AOP实现切入增强的两种方式(execution+annotation)-Demo
pom文件依赖 <!-- AOP切面编程启动环境依赖组 --> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency> 1、通过execution表达式实现切入增强 package com…...

人工智能在网络安全中的作用:当前的局限性和未来的可能性
人工智能 (AI) 激发了网络安全行业的想象力,有可能彻底改变安全和 IT 团队处理网络危机、漏洞和勒索软件攻击的方式。 然而,对人工智能的能力和局限性的现实理解至关重要,并且存在许多挑战阻碍人工智能对网络安全产生直接的变革性影响。 在…...

BC99 序列中整数去重
描述 输入n个整数的序列,要求对这个序列进行去重操作。所谓去重,是指对这个序列中每个重复出现的整数,只保留该数第一次出现的位置,删除其余位置。 输入描述 输入包含两行,第一行包含一个正整数n(1 ≤ n…...
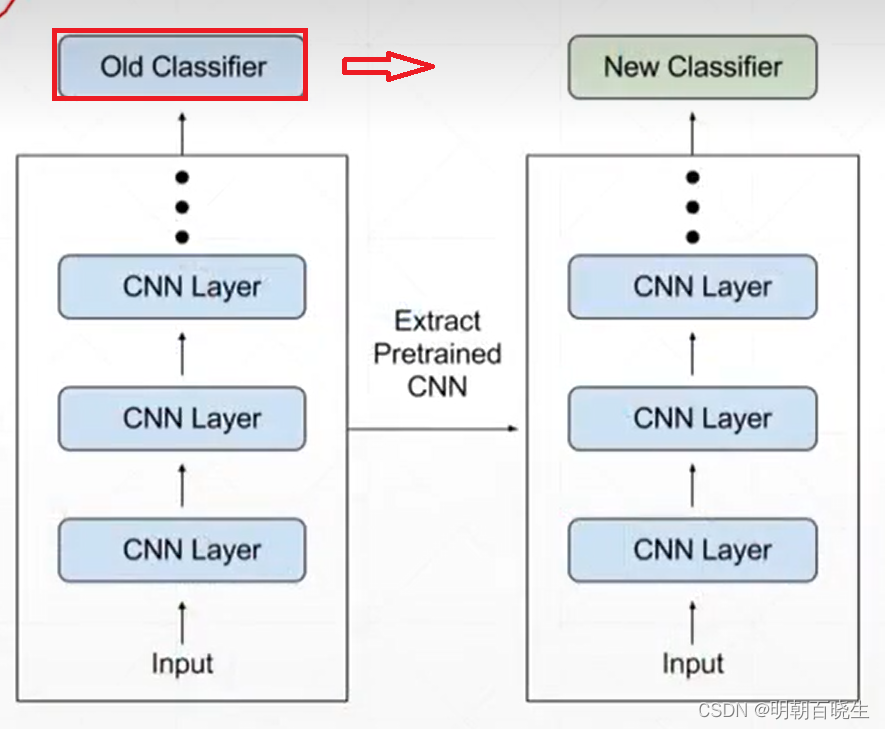
[PyTorch][chapter 52][迁移学习]
前言: 迁移学习(Transfer Learning)是一种机器学习方法,它通过将一个领域中的知识和经验迁移到另一个相关领域中,来加速和改进新领域的学习和解决问题的能力。 这里面主要结合前面ResNet18 例子,详细讲解一…...
Ceph如何操作底层对象数据
1.基本原理介绍 1.1 ceph中的对象(object) 在Ceph存储中,一切数据最终都会以对象(Object)的形式存储在硬盘(OSD)上,每个的Object默认大小为4M。 通过rados命令,可以查看一个存储池中的所有object信息,例如…...

sklearn机器学习库(二)sklearn中的随机森林
sklearn机器学习库(二)sklearn中的随机森林 集成算法会考虑多个评估器的建模结果,汇总之后得到一个综合的结果,以此来获取比单个模型更好的回归或分类表现。 多个模型集成成为的模型叫做集成评估器(ensemble estimator)…...

FlutterBoost 实现Flutter页面内嵌iOS view
在使用Flutter混合开发中会遇到一些原生比Flutter优秀的控件,不想使用Flutter的控件,想在Flutter中使用原生控件。这时就会用到 Flutter页面中内嵌 原生view,这里简单介绍一个 内嵌 iOS 的view。 注:这里使用了 FlutterBoost。网…...

走嵌入式还是纯软件?学长告诉你怎么选
最近有不少理工科的本科生问我,未来是走嵌入式还是纯软件好,究竟什么样的同学适合学习嵌入式呢?在这里我整合一下给他们的回答,根据自己的经验提供一些建议。 嵌入式领域也可以分为单片机方向、Linux方向和安卓方向。如果你的专业…...
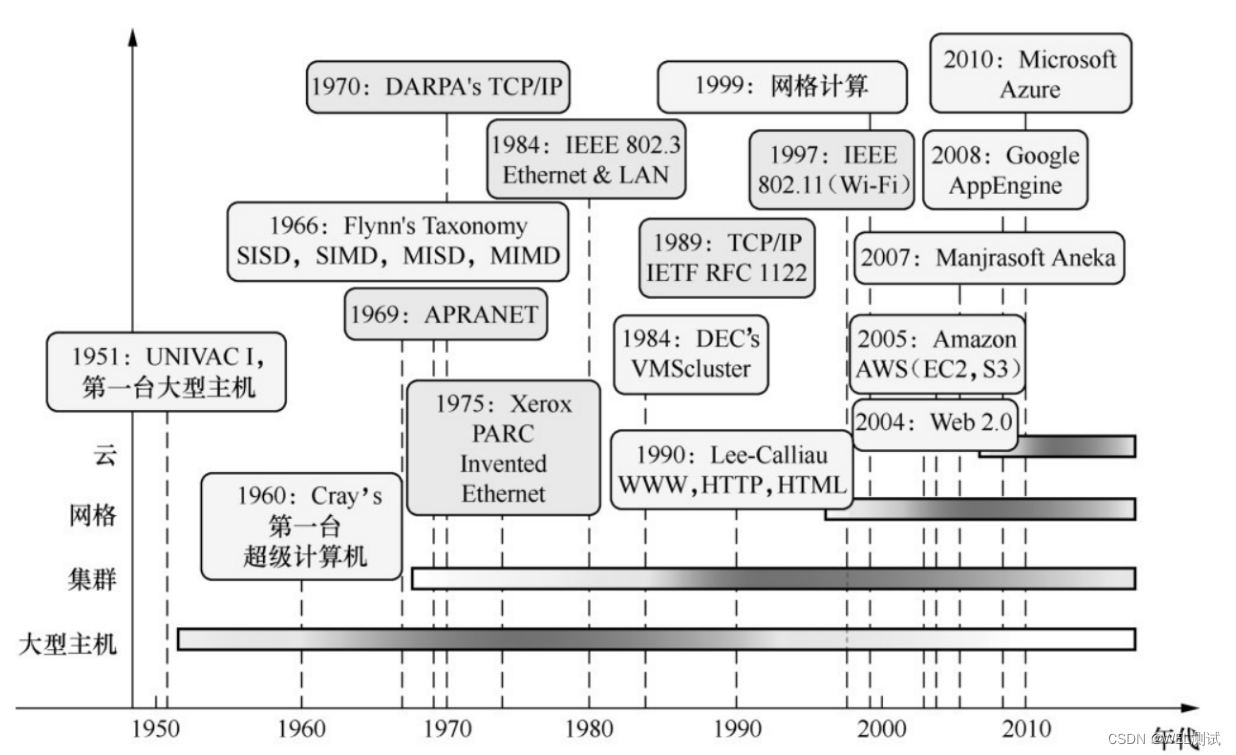
【云计算原理及实战】初识云计算
该学习笔记取自《云计算原理及实战》一书,关于具体描述可以查阅原本书籍。 云计算被视为“革命性的计算模型”,因为它通过互联网自由流通使超级计算能力成为可能。 2006年8月,在圣何塞举办的SES(捜索引擎战略)大会上&a…...
 基于拟合高差的点云地面点提取)
Open3D (C++) 基于拟合高差的点云地面点提取
目录 一、算法原理1、原理概述2、参考文献二、代码实现三、结果展示1、原始点云2、提取结果四、相关链接系列文章(连载中。。。): Open3D (C++) 基于高程的点云地面点提取Open3D (C++) 基于拟合平面的点云地面点提取Open3D (C++) 基于拟合高差的点云地面点提取</...
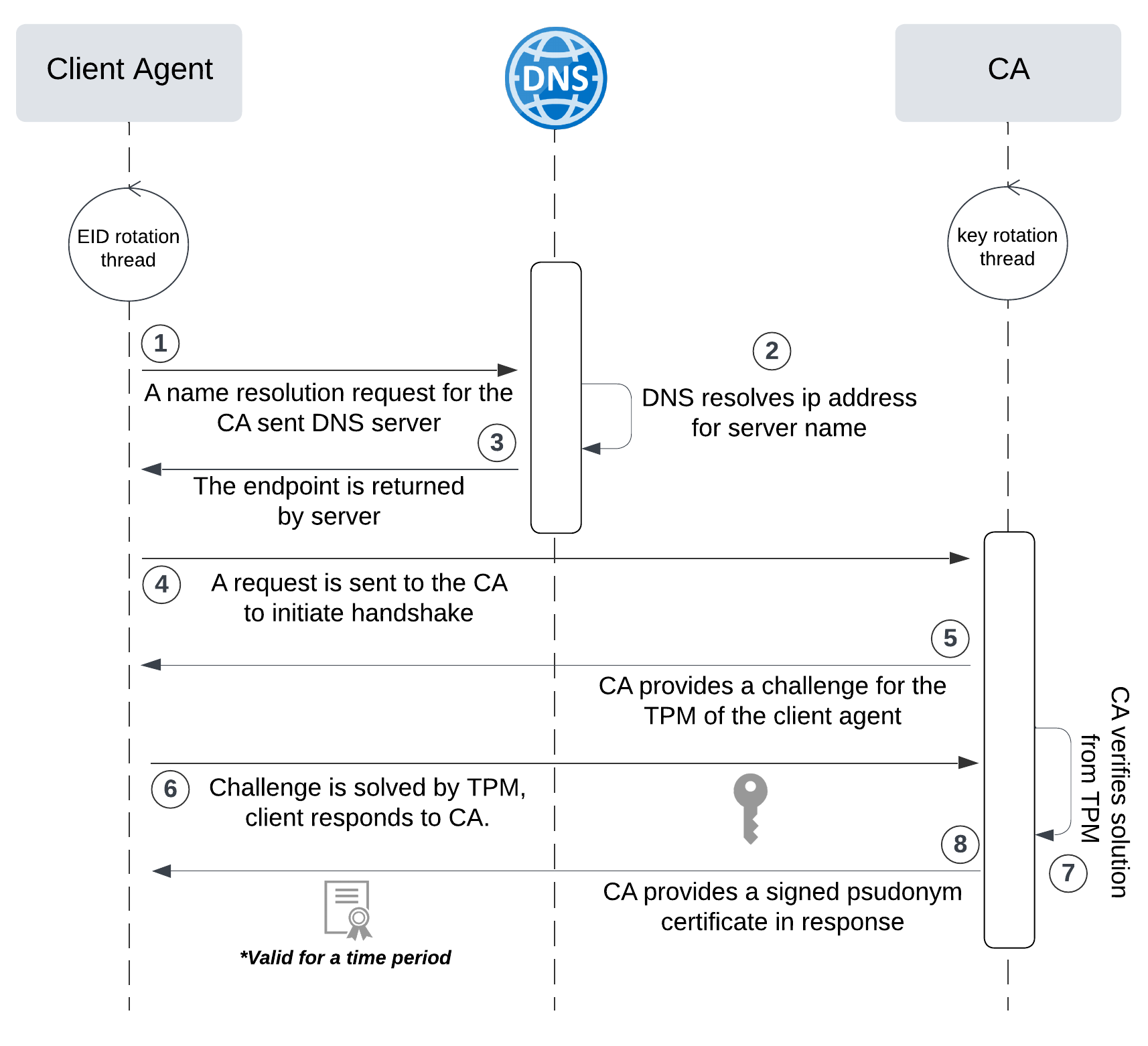
网络六边形受到攻击
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 抽象 现代智能交通系统 (ITS) 的一个关键要求是能够以安全、可靠和匿名的方式从互联车辆和移动设备收集地理参考数据。Nexagon 协议建立在 IETF 定位器/ID 分离协议 (…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...
)
Java 语言特性(面试系列1)
一、面向对象编程 1. 封装(Encapsulation) 定义:将数据(属性)和操作数据的方法绑定在一起,通过访问控制符(private、protected、public)隐藏内部实现细节。示例: public …...
使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频)
树莓派超全系列教程文档--(62)使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频
使用rpicam-app通过网络流式传输视频 使用 rpicam-app 通过网络流式传输视频UDPTCPRTSPlibavGStreamerRTPlibcamerasrc GStreamer 元素 文章来源: http://raspberry.dns8844.cn/documentation 原文网址 使用 rpicam-app 通过网络流式传输视频 本节介绍来自 rpica…...

JDK 17 新特性
#JDK 17 新特性 /**************** 文本块 *****************/ python/scala中早就支持,不稀奇 String json “”" { “name”: “Java”, “version”: 17 } “”"; /**************** Switch 语句 -> 表达式 *****************/ 挺好的ÿ…...

【HTTP三个基础问题】
面试官您好!HTTP是超文本传输协议,是互联网上客户端和服务器之间传输超文本数据(比如文字、图片、音频、视频等)的核心协议,当前互联网应用最广泛的版本是HTTP1.1,它基于经典的C/S模型,也就是客…...
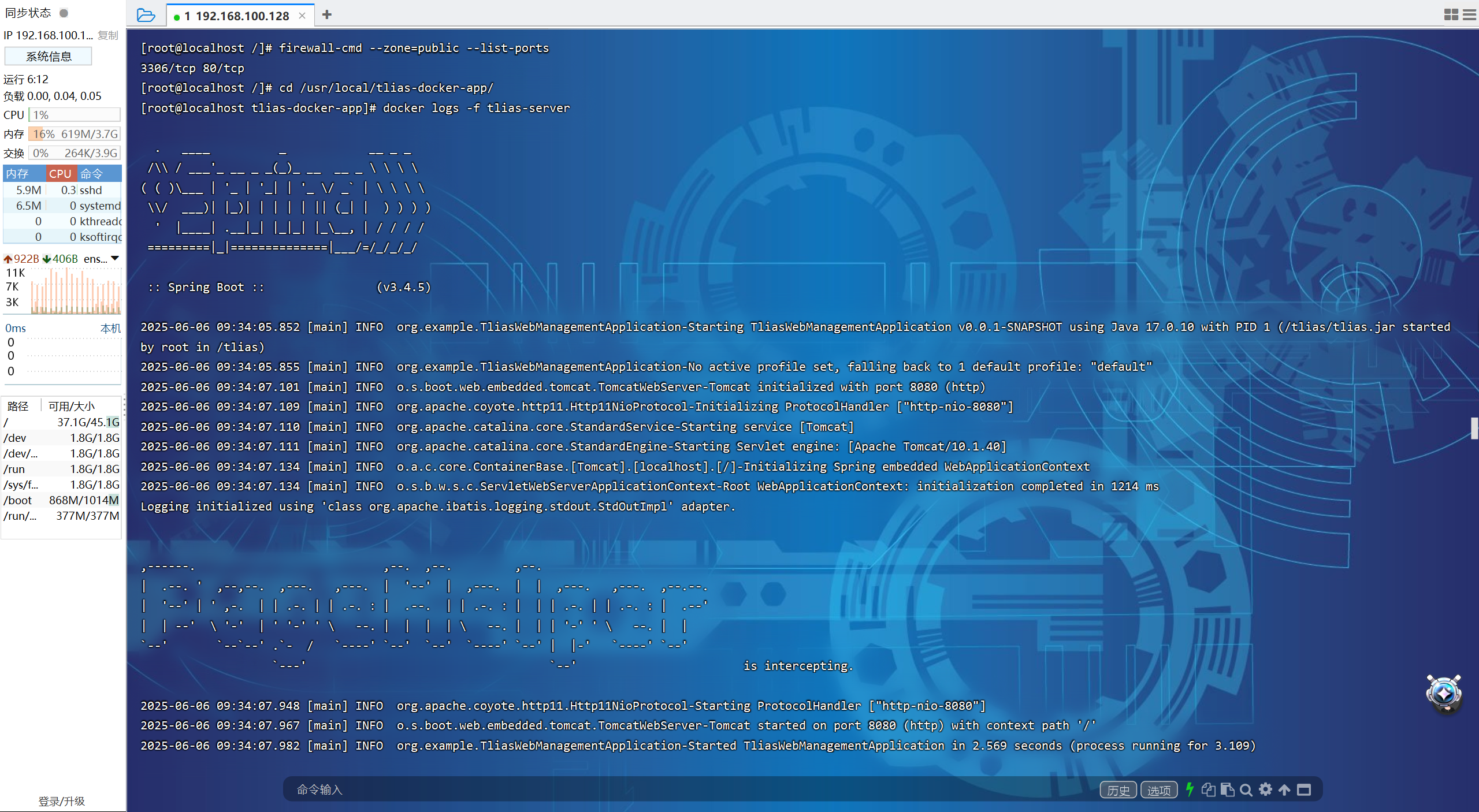
【JavaWeb】Docker项目部署
引言 之前学习了Linux操作系统的常见命令,在Linux上安装软件,以及如何在Linux上部署一个单体项目,大多数同学都会有相同的感受,那就是麻烦。 核心体现在三点: 命令太多了,记不住 软件安装包名字复杂&…...
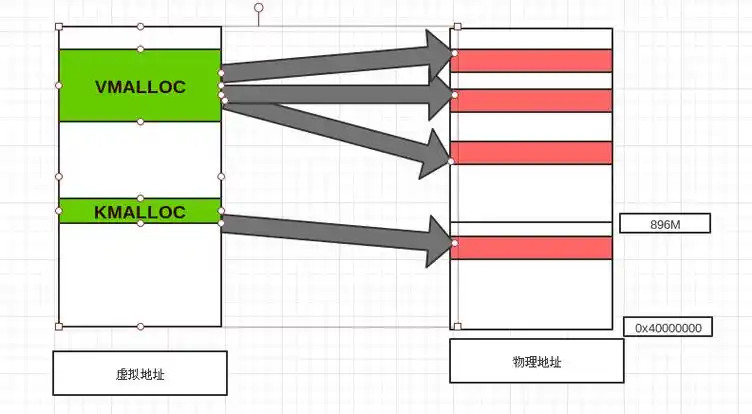
Linux 内存管理实战精讲:核心原理与面试常考点全解析
Linux 内存管理实战精讲:核心原理与面试常考点全解析 Linux 内核内存管理是系统设计中最复杂但也最核心的模块之一。它不仅支撑着虚拟内存机制、物理内存分配、进程隔离与资源复用,还直接决定系统运行的性能与稳定性。无论你是嵌入式开发者、内核调试工…...

提升移动端网页调试效率:WebDebugX 与常见工具组合实践
在日常移动端开发中,网页调试始终是一个高频但又极具挑战的环节。尤其在面对 iOS 与 Android 的混合技术栈、各种设备差异化行为时,开发者迫切需要一套高效、可靠且跨平台的调试方案。过去,我们或多或少使用过 Chrome DevTools、Remote Debug…...
