python进行数据分析:数据预处理
六大数据类型 见python基本功
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
数据预处理
缺失值处理
float_data = pd.Series([1.2, -3.5, np.nan, 0])
float_data
0 1.2
1 -3.5
2 NaN
3 0.0
dtype: float64
查看缺失值
float_data.isna()
0 False
1 False
2 True
3 False
dtype: bool
string_data = pd.Series(["aardvark", np.nan, None, "avocado"])
string_data
string_data.isna()
float_data = pd.Series([1, 2, None], dtype='float64')
float_data
float_data.isna()
0 False
1 False
2 True
dtype: bool
删除缺失值
data = pd.Series([1, np.nan, 3.5, np.nan, 7])
data.dropna()
0 1.0
2 3.5
4 7.0
dtype: float64
data[data.notna()]
0 1.0
2 3.5
4 7.0
dtype: float64
data = pd.DataFrame([[1., 6.5, 3.], [1., np.nan, np.nan], [np.nan, np.nan, np.nan], [np.nan, 6.5, 3.]])
print(data)
data.dropna()
0 1 2
0 1.0 6.5 3.0
1 1.0 NaN NaN
2 NaN NaN NaN
3 NaN 6.5 3.0
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 1.0 | 6.5 | 3.0 |
data.dropna(how="all")##删除行全部都是缺失值
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 1.0 | 6.5 | 3.0 |
| 1 | 1.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | NaN | 6.5 | 3.0 |
data[4] = np.nan
data
data.dropna(axis="columns", how="all")##删除列全部都是缺失值
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 1.0 | 6.5 | 3.0 |
| 1 | 1.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 2 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | NaN | 6.5 | 3.0 |
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.standard_normal((7, 3)))
df.iloc[:4, 1] = np.nan
df.iloc[:2, 2] = np.nan
print(df)
df.dropna()#删除含缺失值的行
0 1 2
0 0.476985 NaN NaN
1 -0.577087 NaN NaN
2 0.523772 NaN 1.343810
3 -0.713544 NaN -2.370232
4 -1.860761 -0.860757 0.560145
5 -1.265934 0.119827 -1.063512
6 0.332883 -2.359419 -0.199543
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 4 | -1.860761 | -0.860757 | 0.560145 |
| 5 | -1.265934 | 0.119827 | -1.063512 |
| 6 | 0.332883 | -2.359419 | -0.199543 |
df.dropna(thresh=2)# 删除至少有两个缺失值的行
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 2 | 0.523772 | NaN | 1.343810 |
| 3 | -0.713544 | NaN | -2.370232 |
| 4 | -1.860761 | -0.860757 | 0.560145 |
| 5 | -1.265934 | 0.119827 | -1.063512 |
| 6 | 0.332883 | -2.359419 | -0.199543 |
缺失值填充
df.fillna(0)##缺失值填充为0
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0.476985 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 1 | -0.577087 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 2 | 0.523772 | 0.000000 | 1.343810 |
| 3 | -0.713544 | 0.000000 | -2.370232 |
| 4 | -1.860761 | -0.860757 | 0.560145 |
| 5 | -1.265934 | 0.119827 | -1.063512 |
| 6 | 0.332883 | -2.359419 | -0.199543 |
df.fillna({1: 0.5, 2: 0})#不同列填充不同缺失值
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0.476985 | 0.500000 | 0.000000 |
| 1 | -0.577087 | 0.500000 | 0.000000 |
| 2 | 0.523772 | 0.500000 | 1.343810 |
| 3 | -0.713544 | 0.500000 | -2.370232 |
| 4 | -1.860761 | -0.860757 | 0.560145 |
| 5 | -1.265934 | 0.119827 | -1.063512 |
| 6 | 0.332883 | -2.359419 | -0.199543 |
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.standard_normal((6, 3)))
df.iloc[2:, 1] = np.nan
df.iloc[4:, 2] = np.nan
df
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | -1.541996 | -0.970736 | -1.307030 |
| 1 | 0.286350 | 0.377984 | -0.753887 |
| 2 | 0.331286 | NaN | 0.069877 |
| 3 | 0.246674 | NaN | 1.004812 |
| 4 | 1.327195 | NaN | NaN |
| 5 | 0.022185 | NaN | NaN |
df.fillna(method="ffill")#向下填充
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | -1.541996 | -0.970736 | -1.307030 |
| 1 | 0.286350 | 0.377984 | -0.753887 |
| 2 | 0.331286 | 0.377984 | 0.069877 |
| 3 | 0.246674 | 0.377984 | 1.004812 |
| 4 | 1.327195 | 0.377984 | 1.004812 |
| 5 | 0.022185 | 0.377984 | 1.004812 |
df.fillna(method="ffill", limit=2)#向下填充,限制填充数量=2
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | -1.541996 | -0.970736 | -1.307030 |
| 1 | 0.286350 | 0.377984 | -0.753887 |
| 2 | 0.331286 | 0.377984 | 0.069877 |
| 3 | 0.246674 | 0.377984 | 1.004812 |
| 4 | 1.327195 | NaN | 1.004812 |
| 5 | 0.022185 | NaN | 1.004812 |
data = pd.Series([1., np.nan, 3.5, np.nan, 7])
data.fillna(data.mean())#以平均值填充
0 1.000000
1 3.833333
2 3.500000
3 3.833333
4 7.000000
dtype: float64
重复值处理
data = pd.DataFrame({"k1": ["one", "two"] * 3 + ["two"], "k2": [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4]})
data
|
| k1 | k2 |
| — | — | — |
| 0 | one | 1 |
| 1 | two | 1 |
| 2 | one | 2 |
| 3 | two | 3 |
| 4 | one | 3 |
| 5 | two | 4 |
| 6 | two | 4 |
查看是否存在重复值
data.duplicated()
0 False
1 False
2 False
3 False
4 False
5 False
6 True
dtype: bool
删除重复值
data.drop_duplicates()
|
| k1 | k2 |
| — | — | — |
| 0 | one | 1 |
| 1 | two | 1 |
| 2 | one | 2 |
| 3 | two | 3 |
| 4 | one | 3 |
| 5 | two | 4 |
data["v1"] = range(7)
data
|
| k1 | k2 | v1 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | one | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | two | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | one | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | two | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | one | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | two | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | two | 4 | 6 |
data.drop_duplicates(subset=["k1"])#只要k1列有重复值就去重,保留第一行
|
| k1 | k2 | v1 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | one | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | two | 1 | 1 |
data.drop_duplicates(["k1", "k2"], keep="last")#只要k1&k2有重复值就去重,保留最后一行
|
| k1 | k2 | v1 |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | one | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | two | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | one | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | two | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | one | 3 | 4 |
| 6 | two | 4 | 6 |
函数映射
data = pd.DataFrame({"food": ["bacon", "pulled pork", "bacon", "pastrami", "corned beef", "bacon", "pastrami", "honey ham", "nova lox"], "ounces": [4, 3, 12, 6, 7.5, 8, 3, 5, 6]})
data
|
| food | ounces |
| — | — | — |
| 0 | bacon | 4.0 |
| 1 | pulled pork | 3.0 |
| 2 | bacon | 12.0 |
| 3 | pastrami | 6.0 |
| 4 | corned beef | 7.5 |
| 5 | bacon | 8.0 |
| 6 | pastrami | 3.0 |
| 7 | honey ham | 5.0 |
| 8 | nova lox | 6.0 |
map()将字典中的key映射为value
meat_to_animal = { "bacon": "pig", "pulled pork": "pig", "pastrami": "cow", "corned beef": "cow", "honey ham": "pig", "nova lox": "salmon"
}
data["animal"] = data["food"].map(meat_to_animal)
data
|
| food | ounces | animal |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | bacon | 4.0 | pig |
| 1 | pulled pork | 3.0 | pig |
| 2 | bacon | 12.0 | pig |
| 3 | pastrami | 6.0 | cow |
| 4 | corned beef | 7.5 | cow |
| 5 | bacon | 8.0 | pig |
| 6 | pastrami | 3.0 | cow |
| 7 | honey ham | 5.0 | pig |
| 8 | nova lox | 6.0 | salmon |
def get_animal(x): return meat_to_animal[x]
data["food"].map(get_animal)
0 pig
1 pig
2 pig
3 cow
4 cow
5 pig
6 cow
7 pig
8 salmon
Name: food, dtype: object
替换
data = pd.Series([1., -999., 2., -999., -1000., 3.])
data
0 1.0
1 -999.0
2 2.0
3 -999.0
4 -1000.0
5 3.0
dtype: float64
单值替换
data.replace(-999, np.nan)#将-999替换为缺失值
0 1.0
1 NaN
2 2.0
3 NaN
4 -1000.0
5 3.0
dtype: float64
多值替换
data.replace([-999, -1000], np.nan)#将-999&-1000替换为缺失值
0 1.0
1 NaN
2 2.0
3 NaN
4 NaN
5 3.0
dtype: float64
data.replace([-999, -1000], [np.nan, 0])#将-999替换为缺失值,-1000替换为0
0 1.0
1 NaN
2 2.0
3 NaN
4 0.0
5 3.0
dtype: float64
data.replace({-999: np.nan, -1000: 0})#将-999替换为缺失值,-1000替换为0
0 1.0
1 NaN
2 2.0
3 NaN
4 0.0
5 3.0
dtype: float64
data = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3, 4)), index=["Ohio", "Colorado", "New York"], columns=["one", "two", "three", "four"])
def transform(x): return x[:4].upper() data.index.map(transform)
Index(['OHIO', 'COLO', 'NEW '], dtype='object')
data.index = data.index.map(transform)
data
|
| one | two | three | four |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| OHIO | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| COLO | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| NEW | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
重命名rename
data.rename(index=str.title, columns=str.upper)
|
| ONE | TWO | THREE | FOUR |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| Ohio | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Colo | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| New | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
data.rename(index={"OHIO": "INDIANA"}, columns={"three": "peekaboo"})
|
| one | two | peekaboo | four |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| INDIANA | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| COLO | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| NEW | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
数据分箱pd.cut&pd.qcut
-
• pd.cut() 将指定序列 x,按指定数量等间距的划分(根据值本身而不是这些值的频率选择均匀分布的bins),或按照指定间距划分
-
• pd.qcut() 将指定序列 x,划分为 q 个区间,使落在每个区间的记录数一致
ages = [20, 22, 25, 27, 21, 23, 37, 31, 61, 45, 41, 32]
bins = [18, 25, 35, 60, 100]
age_categories = pd.cut(ages, bins)
age_categories
[(18, 25], (18, 25], (18, 25], (25, 35], (18, 25], ..., (25, 35], (60, 100], (35, 60], (35, 60], (25, 35]]
Length: 12
Categories (4, interval[int64, right]): [(18, 25] < (25, 35] < (35, 60] < (60, 100]]
age_categories.codes
age_categories.categories
age_categories.categories[0]
pd.value_counts(age_categories)
(18, 25] 5
(25, 35] 3
(35, 60] 3
(60, 100] 1
dtype: int64
pd.cut(ages, bins, right=False)
[[18, 25), [18, 25), [25, 35), [25, 35), [18, 25), ..., [25, 35), [60, 100), [35, 60), [35, 60), [25, 35)]
Length: 12
Categories (4, interval[int64, left]): [[18, 25) < [25, 35) < [35, 60) < [60, 100)]
group_names = ["Youth", "YoungAdult", "MiddleAged", "Senior"]
pd.cut(ages, bins, labels=group_names)
['Youth', 'Youth', 'Youth', 'YoungAdult', 'Youth', ..., 'YoungAdult', 'Senior', 'MiddleAged', 'MiddleAged', 'YoungAdult']
Length: 12
Categories (4, object): ['Youth' < 'YoungAdult' < 'MiddleAged' < 'Senior']
data = np.random.uniform(size=20)
pd.cut(data, 4, precision=2)
[(0.32, 0.53], (0.74, 0.95], (0.74, 0.95], (0.53, 0.74], (0.11, 0.32], ..., (0.74, 0.95], (0.11, 0.32], (0.74, 0.95], (0.32, 0.53], (0.74, 0.95]]
Length: 20
Categories (4, interval[float64, right]): [(0.11, 0.32] < (0.32, 0.53] < (0.53, 0.74] < (0.74, 0.95]]
data = np.random.standard_normal(1000)
quartiles = pd.qcut(data, 4, precision=2)
quartiles
pd.value_counts(quartiles)
(-2.96, -0.69] 250
(-0.69, -0.032] 250
(-0.032, 0.61] 250
(0.61, 3.93] 250
dtype: int64
pd.qcut(data, [0, 0.1, 0.5, 0.9, 1.]).value_counts()
(-2.9499999999999997, -1.187] 100
(-1.187, -0.0321] 400
(-0.0321, 1.287] 400
(1.287, 3.928] 100
dtype: int64
data = pd.DataFrame(np.random.standard_normal((1000, 4)))
data.describe()
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| count | 1000.000000 | 1000.000000 | 1000.000000 | 1000.000000 |
| mean | -0.047439 | 0.046069 | 0.024366 | -0.006350 |
| std | 0.997187 | 0.998359 | 1.008925 | 0.993665 |
| min | -3.428254 | -3.645860 | -3.184377 | -3.745356 |
| 25% | -0.743886 | -0.599807 | -0.612162 | -0.697084 |
| 50% | -0.086309 | 0.043663 | -0.013609 | -0.026381 |
| 75% | 0.624413 | 0.746527 | 0.690847 | 0.694459 |
| max | 3.366626 | 2.653656 | 3.525865 | 2.735527 |
col = data[2]
col[col.abs() > 3]
55 3.260383
230 -3.056990
317 -3.184377
777 3.525865
Name: 2, dtype: float64
data[(data.abs() > 3).any(axis="columns")]
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| 36 | -2.315555 | 0.457246 | -0.025907 | -3.399312 |
| 55 | 0.050188 | 1.951312 | 3.260383 | 0.963301 |
| 131 | 0.146326 | 0.508391 | -0.196713 | -3.745356 |
| 230 | -0.293333 | -0.242459 | -3.056990 | 1.918403 |
| 254 | -3.428254 | -0.296336 | -0.439938 | -0.867165 |
| 317 | 0.275144 | 1.179227 | -3.184377 | 1.369891 |
| 539 | -0.362528 | -3.548824 | 1.553205 | -2.186301 |
| 631 | 3.366626 | -2.372214 | 0.851010 | 1.332846 |
| 777 | -0.658090 | -0.207434 | 3.525865 | 0.283070 |
| 798 | 0.599947 | -3.645860 | 0.255475 | -0.549574 |
data[data.abs() > 3] = np.sign(data) * 3
data.describe()
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| count | 1000.000000 | 1000.000000 | 1000.000000 | 1000.000000 |
| mean | -0.047378 | 0.047263 | 0.023821 | -0.005206 |
| std | 0.994634 | 0.994342 | 1.005685 | 0.989845 |
| min | -3.000000 | -3.000000 | -3.000000 | -3.000000 |
| 25% | -0.743886 | -0.599807 | -0.612162 | -0.697084 |
| 50% | -0.086309 | 0.043663 | -0.013609 | -0.026381 |
| 75% | 0.624413 | 0.746527 | 0.690847 | 0.694459 |
| max | 3.000000 | 2.653656 | 3.000000 | 2.735527 |
np.sign(data).head()
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | -1.0 | 1.0 | -1.0 | 1.0 |
| 1 | -1.0 | 1.0 | -1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 |
| 3 | -1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | -1.0 |
| 4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | -1.0 |
随机重排列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(5 * 7).reshape((5, 7)))
df
sampler = np.random.permutation(5)#permutation:产生0到n-1的所有整数的随机排列
sampler
array([2, 4, 3, 0, 1])
df.take(sampler)#行随机排列
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 4 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
| 3 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
df.iloc[sampler]
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 4 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
| 3 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
column_sampler = np.random.permutation(7)
column_sampler
df.take(column_sampler, axis="columns")#列随机排列
|
| 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| 1 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 7 | 12 |
| 2 | 20 | 16 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 14 | 19 |
| 3 | 27 | 23 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 21 | 26 |
| 4 | 34 | 30 | 29 | 31 | 32 | 28 | 33 |
随机采样
df.sample(n=3)# n指定采样的个数
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 4 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 |
| 1 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
choices = pd.Series([5, 7, -1, 6, 4])
choices.sample(n=10, replace=True)
0 5
1 7
0 5
0 5
2 -1
4 4
2 -1
2 -1
0 5
4 4
dtype: int64
哑变量编码
df = pd.DataFrame({"key": ["b", "b", "a", "c", "a", "b"], "data1": range(6)})
df
|
| key | data1 |
| — | — | — |
| 0 | b | 0 |
| 1 | b | 1 |
| 2 | a | 2 |
| 3 | c | 3 |
| 4 | a | 4 |
| 5 | b | 5 |
pd.get_dummies(df["key"])
|
| a | b | c |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
dummies = pd.get_dummies(df["key"], prefix="key")##前缀为key
df_with_dummy = df[["data1"]].join(dummies)#合并数据集
df_with_dummy
|
| data1 | key_a | key_b | key_c |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
mnames = ["movie_id", "title", "genres"]
movies = pd.read_table("datasets/movielens/movies.dat", sep="::", header=None, names=mnames, engine="python")
movies[:10]
|
| movie_id | title | genres |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 1 | Toy Story (1995) | Animation|Children’s|Comedy |
| 1 | 2 | Jumanji (1995) | Adventure|Children’s|Fantasy |
| 2 | 3 | Grumpier Old Men (1995) | Comedy|Romance |
| 3 | 4 | Waiting to Exhale (1995) | Comedy|Drama |
| 4 | 5 | Father of the Bride Part II (1995) | Comedy |
| 5 | 6 | Heat (1995) | Action|Crime|Thriller |
| 6 | 7 | Sabrina (1995) | Comedy|Romance |
| 7 | 8 | Tom and Huck (1995) | Adventure|Children’s |
| 8 | 9 | Sudden Death (1995) | Action |
| 9 | 10 | GoldenEye (1995) | Action|Adventure|Thriller |
dummies = movies["genres"].str.get_dummies("|")##将一列中以|分割的字段变成哑变量
dummies.iloc[:10, :6]
|
| Action | Adventure | Animation | Children’s | Comedy | Crime |
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
movies_windic = movies.join(dummies.add_prefix("Genre_"))
movies_windic.iloc[0]
movie_id 1
title Toy Story (1995)
genres Animation|Children's|Comedy
Genre_Action 0
Genre_Adventure 0
Genre_Animation 1
Genre_Children's 1
Genre_Comedy 1
Genre_Crime 0
Genre_Documentary 0
Genre_Drama 0
Genre_Fantasy 0
Genre_Film-Noir 0
Genre_Horror 0
Genre_Musical 0
Genre_Mystery 0
Genre_Romance 0
Genre_Sci-Fi 0
Genre_Thriller 0
Genre_War 0
Genre_Western 0
Name: 0, dtype: object
np.random.seed(12345) # to make the example repeatable
values = np.random.uniform(size=10)
values
bins = [0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1]
pd.get_dummies(pd.cut(values, bins))
|
| (0.0, 0.2] | (0.2, 0.4] | (0.4, 0.6] | (0.6, 0.8] | (0.8, 1.0] |
| — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
正则表达式
s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, None])
s
s.dtype
dtype('float64')
s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, None], dtype=pd.Int64Dtype())
s
s.isna()
s.dtype
Int64Dtype()
s[3]
s[3] is pd.NA
True
s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, None], dtype="Int64")
s = pd.Series(['one', 'two', None, 'three'], dtype=pd.StringDtype())
s
0 one
1 two
2 <NA>
3 three
dtype: string
df = pd.DataFrame({"A": [1, 2, None, 4], "B": ["one", "two", "three", None], "C": [False, None, False, True]})
df
df["A"] = df["A"].astype("Int64")
df["B"] = df["B"].astype("string")
df["C"] = df["C"].astype("boolean")
df
|
| A | B | C |
| — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 1 | one | False |
| 1 | 2 | two | |
| 2 | | three | False |
| 3 | 4 | | True |
val = "a,b, guido"
val.split(",")
['a', 'b', ' guido']
pieces = [x.strip() for x in val.split(",")]
pieces
['a', 'b', 'guido']
first, second, third = pieces
first + "::" + second + "::" + third
'a::b::guido'
"::".join(pieces)
'a::b::guido'
"guido" in val
val.index(",")
val.find(":")
-1
val.index(":")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- ValueError Traceback (most recent call last) ~\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_20552\2601145560.py in <module>
----> 1 val.index(":") ValueError: substring not found
val.count(",")
2
val.replace(",", "::")
val.replace(",", "")
'ab guido'
import re
text = "foo bar\t baz \tqux"
re.split(r"\s+", text)
['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'qux']
regex = re.compile(r"\s+")
regex.split(text)
['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'qux']
regex.findall(text)
[' ', '\t ', ' \t']
text = """Dave dave@google.com
Steve steve@gmail.com
Rob rob@gmail.com
Ryan ryan@yahoo.com"""
pattern = r"[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z]{2,4}" regex = re.compile(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
regex.findall(text)
['dave@google.com', 'steve@gmail.com', 'rob@gmail.com', 'ryan@yahoo.com']
m = regex.search(text)
m
text[m.start():m.end()]
'dave@google.com'
print(regex.match(text))
None
print(regex.sub("REDACTED", text))
Dave REDACTED
Steve REDACTED
Rob REDACTED
Ryan REDACTED
pattern = r"([A-Z0-9._%+-]+)@([A-Z0-9.-]+)\.([A-Z]{2,4})"
regex = re.compile(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
m = regex.match("wesm@bright.net")
m.groups()
('wesm', 'bright', 'net')
regex.findall(text)
[('dave', 'google', 'com'), ('steve', 'gmail', 'com'), ('rob', 'gmail', 'com'), ('ryan', 'yahoo', 'com')]
print(regex.sub(r"Username: \1, Domain: \2, Suffix: \3", text))
Dave Username: dave, Domain: google, Suffix: com
Steve Username: steve, Domain: gmail, Suffix: com
Rob Username: rob, Domain: gmail, Suffix: com
Ryan Username: ryan, Domain: yahoo, Suffix: com
data = {"Dave": "dave@google.com", "Steve": "steve@gmail.com", "Rob": "rob@gmail.com", "Wes": np.nan}
data = pd.Series(data)
data
data.isna()
Dave False
Steve False
Rob False
Wes True
dtype: bool
data.str.contains("gmail")
Dave False
Steve True
Rob True
Wes NaN
dtype: object
data_as_string_ext = data.astype('string')
data_as_string_ext
data_as_string_ext.str.contains("gmail")
Dave False
Steve True
Rob True
Wes <NA>
dtype: boolean
pattern = r"([A-Z0-9._%+-]+)@([A-Z0-9.-]+)\.([A-Z]{2,4})"
data.str.findall(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
Dave [(dave, google, com)]
Steve [(steve, gmail, com)]
Rob [(rob, gmail, com)]
Wes NaN
dtype: object
matches = data.str.findall(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE).str[0]
matches
matches.str.get(1)
Dave google
Steve gmail
Rob gmail
Wes NaN
dtype: object
data.str[:5]
Dave dave@
Steve steve
Rob rob@g
Wes NaN
dtype: object
data.str.extract(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE)
|
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| — | — | — | — |
| Dave | dave | google | com |
| Steve | steve | gmail | com |
| Rob | rob | gmail | com |
| Wes | NaN | NaN | NaN |
values = pd.Series(['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'apple'] * 2)
values
pd.unique(values)
pd.value_counts(values)
apple 6
orange 2
dtype: int64
values = pd.Series([0, 1, 0, 0] * 2)
dim = pd.Series(['apple', 'orange'])
values
dim
0 apple
1 orange
dtype: object
dim.take(values)
0 apple
1 orange
0 apple
0 apple
0 apple
1 orange
0 apple
0 apple
dtype: object
fruits = ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'apple'] * 2
N = len(fruits)
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=12345)
df = pd.DataFrame({'fruit': fruits, 'basket_id': np.arange(N), 'count': rng.integers(3, 15, size=N), 'weight': rng.uniform(0, 4, size=N)}, columns=['basket_id', 'fruit', 'count', 'weight'])
df
|
| basket_id | fruit | count | weight |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 0 | apple | 11 | 1.564438 |
| 1 | 1 | orange | 5 | 1.331256 |
| 2 | 2 | apple | 12 | 2.393235 |
| 3 | 3 | apple | 6 | 0.746937 |
| 4 | 4 | apple | 5 | 2.691024 |
| 5 | 5 | orange | 12 | 3.767211 |
| 6 | 6 | apple | 10 | 0.992983 |
| 7 | 7 | apple | 11 | 3.795525 |
fruit_cat = df['fruit'].astype('category')
fruit_cat
0 apple
1 orange
2 apple
3 apple
4 apple
5 orange
6 apple
7 apple
Name: fruit, dtype: category
Categories (2, object): ['apple', 'orange']
c = fruit_cat.array
type(c)
pandas.core.arrays.categorical.Categorical
c.categories
c.codes
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], dtype=int8)
dict(enumerate(c.categories))
{0: 'apple', 1: 'orange'}
df['fruit'] = df['fruit'].astype('category')
df["fruit"]
0 apple
1 orange
2 apple
3 apple
4 apple
5 orange
6 apple
7 apple
Name: fruit, dtype: category
Categories (2, object): ['apple', 'orange']
my_categories = pd.Categorical(['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo', 'bar'])
my_categories
['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo', 'bar']
Categories (3, object): ['bar', 'baz', 'foo']
categories = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']
codes = [0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1]
my_cats_2 = pd.Categorical.from_codes(codes, categories)
my_cats_2
['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar']
Categories (3, object): ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']
ordered_cat = pd.Categorical.from_codes(codes, categories, ordered=True)
ordered_cat
['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar']
Categories (3, object): ['foo' < 'bar' < 'baz']
my_cats_2.as_ordered()
['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar']
Categories (3, object): ['foo' < 'bar' < 'baz']
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=12345)
draws = rng.standard_normal(1000)
draws[:5]
array([-1.4238, 1.2637, -0.8707, -0.2592, -0.0753])
bins = pd.qcut(draws, 4)
bins
[(-3.121, -0.675], (0.687, 3.211], (-3.121, -0.675], (-0.675, 0.0134], (-0.675, 0.0134], ..., (0.0134, 0.687], (0.0134, 0.687], (-0.675, 0.0134], (0.0134, 0.687], (-0.675, 0.0134]]
Length: 1000
Categories (4, interval[float64, right]): [(-3.121, -0.675] < (-0.675, 0.0134] < (0.0134, 0.687] < (0.687, 3.211]]
bins = pd.qcut(draws, 4, labels=['Q1', 'Q2', 'Q3', 'Q4'])
bins
bins.codes[:10]
array([0, 3, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0], dtype=int8)
bins = pd.Series(bins, name='quartile')
results = (pd.Series(draws) .groupby(bins) .agg(['count', 'min', 'max']) .reset_index())
results
|
| quartile | count | min | max |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | Q1 | 250 | -3.119609 | -0.678494 |
| 1 | Q2 | 250 | -0.673305 | 0.008009 |
| 2 | Q3 | 250 | 0.018753 | 0.686183 |
| 3 | Q4 | 250 | 0.688282 | 3.211418 |
results['quartile']
0 Q1
1 Q2
2 Q3
3 Q4
Name: quartile, dtype: category
Categories (4, object): ['Q1' < 'Q2' < 'Q3' < 'Q4']
N = 10_000_000
labels = pd.Series(['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'qux'] * (N // 4))
categories = labels.astype('category')
labels.memory_usage(deep=True)
categories.memory_usage(deep=True)
10000540
%time _ = labels.astype('category')
Wall time: 560 ms
%timeit labels.value_counts()
%timeit categories.value_counts()
366 ms ± 9.3 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
67.6 ms ± 2.89 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)
s = pd.Series(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] * 2)
cat_s = s.astype('category')
cat_s
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 d
4 a
5 b
6 c
7 d
dtype: category
Categories (4, object): ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
cat_s.cat.codes
cat_s.cat.categories
Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], dtype='object')
actual_categories = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
cat_s2 = cat_s.cat.set_categories(actual_categories)
cat_s2
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 d
4 a
5 b
6 c
7 d
dtype: category
Categories (5, object): ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
cat_s.value_counts()
cat_s2.value_counts()
a 2
b 2
c 2
d 2
e 0
dtype: int64
cat_s3 = cat_s[cat_s.isin(['a', 'b'])]
cat_s3
cat_s3.cat.remove_unused_categories()
0 a
1 b
4 a
5 b
dtype: category
Categories (2, object): ['a', 'b']
cat_s = pd.Series(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] * 2, dtype='category')
pd.get_dummies(cat_s)
|
| a | b | c | d |
| — | — | — | — | — |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1
|
题外话

感兴趣的小伙伴,赠送全套Python学习资料,包含面试题、简历资料等具体看下方。
👉CSDN大礼包🎁:全网最全《Python学习资料》免费赠送🆓!(安全链接,放心点击)
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照下面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
二、Python必备开发工具
工具都帮大家整理好了,安装就可直接上手!
三、最新Python学习笔记
当我学到一定基础,有自己的理解能力的时候,会去阅读一些前辈整理的书籍或者手写的笔记资料,这些笔记详细记载了他们对一些技术点的理解,这些理解是比较独到,可以学到不一样的思路。
四、Python视频合集
观看全面零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
五、实战案例
纸上得来终觉浅,要学会跟着视频一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
六、面试宝典
简历模板
👉CSDN大礼包🎁:全网最全《Python学习资料》免费赠送🆓!(安全链接,放心点击)
相关文章:

python进行数据分析:数据预处理
六大数据类型 见python基本功 import numpy as np import pandas as pd数据预处理 缺失值处理 float_data pd.Series([1.2, -3.5, np.nan, 0]) float_data0 1.2 1 -3.5 2 NaN 3 0.0 dtype: float64查看缺失值 float_data.isna()0 False 1 …...

百度Apollo:引领自动驾驶技术的创新与突破
文章目录 前言一、技术创新二、开放合作三、生态建设四、安全可靠性总结 前言 随着科技的迅猛发展,自动驾驶技术正成为未来交通领域的重要发展方向。在这个领域中,百度Apollo作为中国领先的自动驾驶平台,以其卓越的创新能力和开放合作精神&a…...

Python爬虫 异步、缓存技巧
在进行大规模数据抓取时,Python爬虫的速度和效率是至关重要的。本文将介绍如何通过异步请求、缓存和代理池等技巧来优化Python爬虫的速度和性能。我们提供了实用的方案和代码示例,帮助你加速数据抓取过程,提高爬虫的效率。 使用异步请求、缓…...

YOLOv5屏蔽区域检测(选择区域检测)
YOLOv5屏蔽区域检测以及选择区域检测 前期准备labelme选择mask区域 代码改动 前期准备 思路就是通过一个mask掩膜,对我们想要屏蔽或者选择的区域进行遮挡处理,在推理的时候,将有mask掩膜的图像输入,将最后的结果显示在原始图像上…...
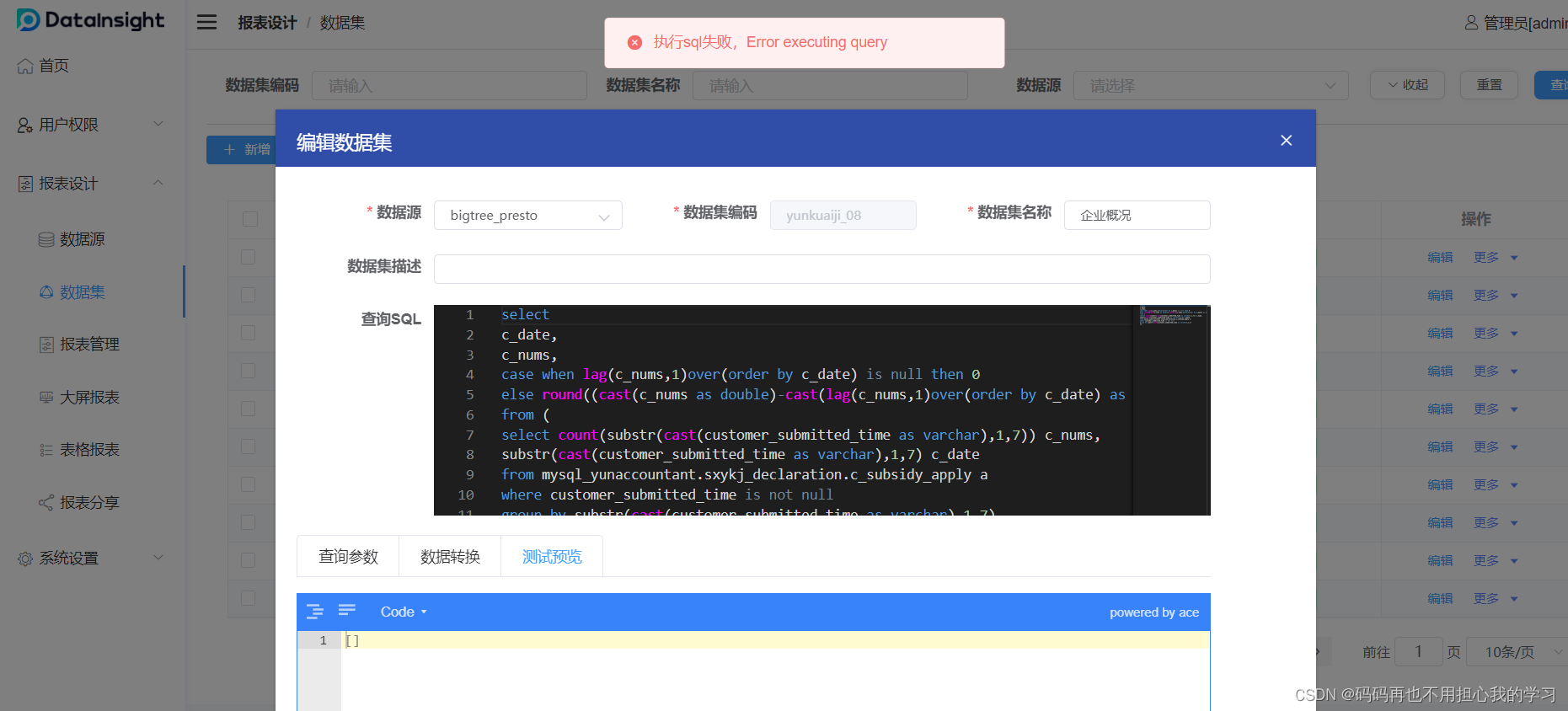
记录一次presto sql执行报错 Error executing query的解决办法
在执行presto sql 时报错截图如下: 查看后台执行报错日志: java.sql.SQLException: Error executing query at com.facebook.presto.jdbc.PrestoStatement.internalExecute(PrestoStatement.java:307) at com.facebook.presto.jdbc.PrestoStatement.exe…...
Android Studio开发之路 (五)导入OpenCV以及报错解决
一、步骤 官网下载opencv包(我下的是4.7.0)并解压,openvc官网 先创建一个空项目,简单跑一下能正常输出helloworld 点击file->new->Import Module选择解压之后的opencv-android-sdk文件夹中的SDk文件夹, modu…...

vue3.3中ref和reactive原理源代码分析
源码是ts编写的,这里部分简化成js便于阅读 function ref(value) {return createRef(value, false) }function createRef(rawValue, shallow) { //shallow是否是浅层定义数据,用于区别ref和shallowRefif (isRef(rawValue)) {//如果已经是ref直接返回源数据return rawValue}retu…...
10.Oracle中decode函数
【函数格式】: decode ( expression, condition_01, result_01, condition_02, result_02, ......, condition_n, result_n, result_default) 【函数说明】: 若表达式expression值与condition_01值匹配,则返回result_01,…...
)
Podman安装部署kafka和管理界面(快速跑起来)
#1.拉取镜像 podman pull bitnami/zookeeper podman pull bitnami/kafka#2.创建子网 podman network create knet#3.创建zookeeper podman run -itd --name zookeeper-server -p 2181:2181 \ --net knet \ -e ALLOW_ANONYMOUS_LOGINyes \ bitnami/zookeeper:latest#3.1查看z…...
Hbase文档--架构体系
阿丹: 基础概念了解之后了解目标知识的架构体系,就能事半功倍。 架构体系 关键组件介绍: HBase – Hadoop Database,是一个高可靠性、高性能、面向列、可伸缩的分布式存储系统,利用HBase技术可在廉价PC Server上搭建起…...
stm32基于HAL库驱动外部SPI flash制作虚拟U盘
stm32基于HAL库驱动外部SPI flash制作虚拟U盘 📌参考文章:https://xiaozhuanlan.com/topic/6058234791🎞实现效果演示: 🔖上图中的读到的FLASH_ID所指的是针对不同容量,所对应的ID。 //W25X/Q不同容量对应…...

vue3-ts- element-plus新增组件-过滤
新增组件-所有值为空时过滤 <el-form-item label"家庭成员"><divclass"username-box"v-for"(item, index) in form.namelist":key"index"><div>姓名:<el-input v-model"item.name" placeho…...

PostgreSQL SQL优化
Oracle SQL优化 一、在字段里面写的子查询放到from后面,用left join,会大幅提高SQL查询速度。 一、在字段里面写的子查询放到from后面,用left join,会大幅提高SQL查询速度。...

debian12网络静态ip配置-OSSIM 安全漏洞扫描系统平台
本配置适合于服务器上的静态ip配置,该方法简单可靠。 1 临时配置 ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.97 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 ip route add default via 192.168.1.1 2 主要的网络配置文件 /etc/network/interfaces /etc/resolv.conf 3 配置…...
微软 Visual Studio 现已内置 Markdown 编辑器,可直接修改预览 .md 文件
Visual Studio Code V1.66.0 中文版 大小:75.30 MB类别:文字处理 本地下载 Markdown 是一种轻量级标记语言,当开发者想要格式化代码但又不想牺牲易读性时,Markdown 是一个很好的解决方案,比如 GitHub 就使用 Markdo…...

阿里云通义千问开源第二波!大规模视觉语言模型Qwen-VL上线魔搭社区
通义千问开源第二波!8月25日消息,阿里云推出大规模视觉语言模型Qwen-VL,一步到位、直接开源。Qwen-VL以通义千问70亿参数模型Qwen-7B为基座语言模型研发,支持图文输入,具备多模态信息理解能力。在主流的多模态任务评测…...
在腾讯云服务器OpenCLoudOS系统中安装Jenkins(有图详解)
Jenkins介绍 Jenkins是一个开源软件项目,是基于java开发的一种持续集成工具,用于监控持续重复的工作,旨在提供一个开放易用的软件平台,使软件的持续集成变成可能。 将项目代码的svn地址配置在Jenkins,就可以直接在Je…...

《vue3实战》在created生命周期中运用slice()方法结合element plus组件实现电影评价系统的分页
目录 前言 电影评价系统的分页是什么?它具体的作用体现在哪些方面? 一、slice的含义、语法和作用以及created的作用 slice是什么?slice有什么语法?slice的作用体现在哪些方面? created生命周期的作用:…...

NO.04 MyBatis的各种查询功能
目录 1、查询一个实体类对象 2、查询一个List集合 3、查询单个数据 5、查询多条数据并存储在Map集合中 5.1 方法一:将数据存储在map集合中,再将map集合存储在List集合中 5.2 方法二:将数据存储在map集合中 6、MyBatis中为Java中常用的…...
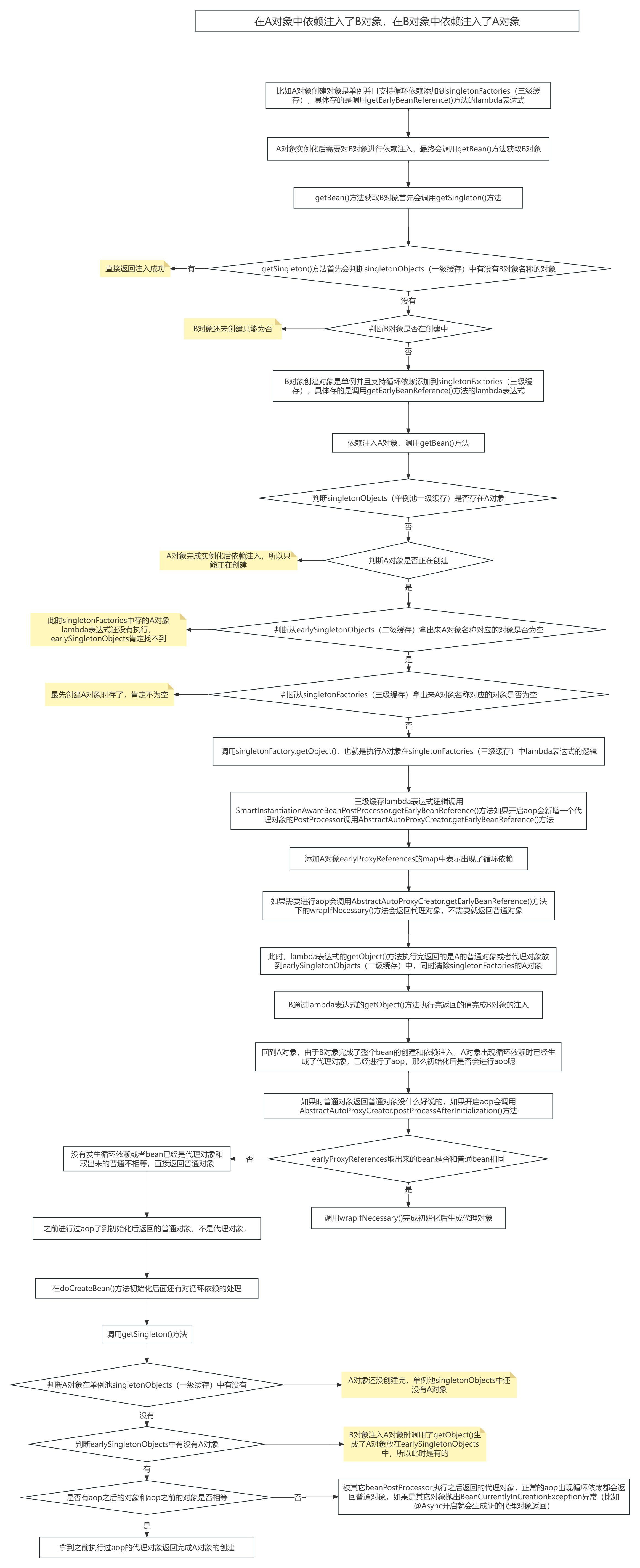
Spring循环依赖
一、Autowired依赖注入的缓存 二、Resource依赖注入过程 三、循环依赖 singletonObjects:缓存经过了完整生命周期的beanearlySingletonObjects:缓存未经过完整生命周期的bean,如果某个bean出现了循环依赖,就会提前把这个暂时未经过…...
)
论文解读:交大港大上海AI Lab开源论文 | 宇树机器人多姿态起立控制强化学习框架(二)
HoST框架核心实现方法详解 - 论文深度解读(第二部分) 《Learning Humanoid Standing-up Control across Diverse Postures》 系列文章: 论文深度解读 + 算法与代码分析(二) 作者机构: 上海AI Lab, 上海交通大学, 香港大学, 浙江大学, 香港中文大学 论文主题: 人形机器人…...
)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解) 在开始使用 React Native 开发移动应用之前,正确设置开发环境是至关重要的一步。本文将为你提供一份全面的指南,涵盖 macOS 和 Windows 平台的配置步骤,如何在 Android 和 iOS…...
Vue3 + Element Plus + TypeScript中el-transfer穿梭框组件使用详解及示例
使用详解 Element Plus 的 el-transfer 组件是一个强大的穿梭框组件,常用于在两个集合之间进行数据转移,如权限分配、数据选择等场景。下面我将详细介绍其用法并提供一个完整示例。 核心特性与用法 基本属性 v-model:绑定右侧列表的值&…...
` 方法)
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 `window.crypto.getRandomValues()` 方法
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 window.crypto.getRandomValues() 方法 在现代 Web 开发中,随机数的生成看似简单,却隐藏着许多玄机。无论是生成密码、加密密钥,还是创建安全令牌,随机数的质量直接关系到系统的安全性。Jav…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...
Cinnamon修改面板小工具图标
Cinnamon开始菜单-CSDN博客 设置模块都是做好的,比GNOME简单得多! 在 applet.js 里增加 const Settings imports.ui.settings;this.settings new Settings.AppletSettings(this, HTYMenusonichy, instance_id); this.settings.bind(menu-icon, menu…...

Java 加密常用的各种算法及其选择
在数字化时代,数据安全至关重要,Java 作为广泛应用的编程语言,提供了丰富的加密算法来保障数据的保密性、完整性和真实性。了解这些常用加密算法及其适用场景,有助于开发者在不同的业务需求中做出正确的选择。 一、对称加密算法…...
微服务商城-商品微服务
数据表 CREATE TABLE product (id bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 商品id,cateid smallint(6) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT 类别Id,name varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT COMMENT 商品名称,subtitle varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT COMMENT 商…...

Android Bitmap治理全解析:从加载优化到泄漏防控的全生命周期管理
引言 Bitmap(位图)是Android应用内存占用的“头号杀手”。一张1080P(1920x1080)的图片以ARGB_8888格式加载时,内存占用高达8MB(192010804字节)。据统计,超过60%的应用OOM崩溃与Bitm…...
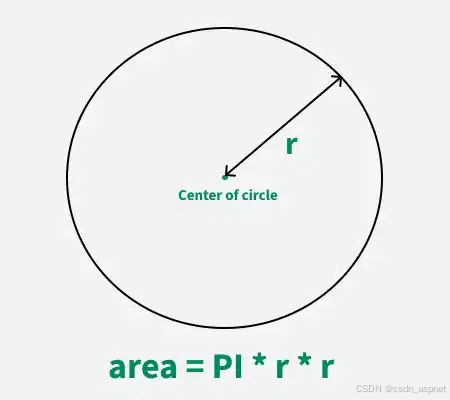
C# 求圆面积的程序(Program to find area of a circle)
给定半径r,求圆的面积。圆的面积应精确到小数点后5位。 例子: 输入:r 5 输出:78.53982 解释:由于面积 PI * r * r 3.14159265358979323846 * 5 * 5 78.53982,因为我们只保留小数点后 5 位数字。 输…...
