从零开始学习 Java:简单易懂的入门指南之JDK8时间相关类(十八)
JDK8时间相关类
- JDK8时间相关类
- 1.1 ZoneId 时区
- 1.2 Instant 时间戳
- 1.3 ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间
- 1.4DateTimeFormatter 用于时间的格式化和解析
- 1.5LocalDate 年、月、日
- 1.6 LocalTime 时、分、秒
- 1.7 LocalDateTime 年、月、日、时、分、秒
- 1.8 Duration 时间间隔(秒,纳,秒)
- 1.9 Period 时间间隔(年,月,日)
- 1.10 ChronoUnit 时间间隔(所有单位)
JDK8时间相关类
| JDK8时间类类名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ZoneId | 时区 |
| Instant | 时间戳 |
| ZoneDateTime | 带时区的时间 |
| DateTimeFormatter | 用于时间的格式化和解析 |
| LocalDate | 年、月、日 |
| LocalTime | 时、分、秒 |
| LocalDateTime | 年、月、日、时、分、秒 |
| Duration | 时间间隔(秒,纳,秒) |
| Period | 时间间隔(年,月,日) |
| ChronoUnit | 时间间隔(所有单位) |
1.1 ZoneId 时区
/*static Set<string> getAvailableZoneIds() 获取Java中支持的所有时区static ZoneId systemDefault() 获取系统默认时区static Zoneld of(string zoneld) 获取一个指定时区*///1.获取所有的时区名称
Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
System.out.println(zoneIds.size());//600
System.out.println(zoneIds);// Asia/Shanghai//2.获取当前系统的默认时区
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId);//Asia/Shanghai//3.获取指定的时区
ZoneId zoneId1 = ZoneId.of("Asia/Pontianak");
System.out.println(zoneId1);//Asia/Pontianak
1.2 Instant 时间戳
/*static Instant now() 获取当前时间的Instant对象(标准时间)static Instant ofXxxx(long epochMilli) 根据(秒/毫秒/纳秒)获取Instant对象ZonedDateTime atZone(ZoneIdzone) 指定时区boolean isxxx(Instant otherInstant) 判断系列的方法Instant minusXxx(long millisToSubtract) 减少时间系列的方法Instant plusXxx(long millisToSubtract) 增加时间系列的方法*/
//1.获取当前时间的Instant对象(标准时间)
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now);//2.根据(秒/毫秒/纳秒)获取Instant对象
Instant instant1 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
System.out.println(instant1);//1970-01-01T00:00:00zInstant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L);
System.out.println(instant2);//1970-01-01T00:00:01ZInstant instant3 = Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L, 1000000000L);
System.out.println(instant3);//1970-01-01T00:00:027//3. 指定时区
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println(time);//4.isXxx 判断
Instant instant4=Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
Instant instant5 =Instant.ofEpochMilli(1000L);//5.用于时间的判断
//isBefore:判断调用者代表的时间是否在参数表示时间的前面
boolean result1=instant4.isBefore(instant5);
System.out.println(result1);//true//isAfter:判断调用者代表的时间是否在参数表示时间的后面
boolean result2 = instant4.isAfter(instant5);
System.out.println(result2);//false//6.Instant minusXxx(long millisToSubtract) 减少时间系列的方法
Instant instant6 =Instant.ofEpochMilli(3000L);
System.out.println(instant6);//1970-01-01T00:00:03ZInstant instant7 =instant6.minusSeconds(1);
System.out.println(instant7);//1970-01-01T00:00:02Z1.3 ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间
/*static ZonedDateTime now() 获取当前时间的ZonedDateTime对象static ZonedDateTime ofXxxx(。。。) 获取指定时间的ZonedDateTime对象ZonedDateTime withXxx(时间) 修改时间系列的方法ZonedDateTime minusXxx(时间) 减少时间系列的方法ZonedDateTime plusXxx(时间) 增加时间系列的方法*/
//1.获取当前时间对象(带时区)
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);//2.获取指定的时间对象(带时区)1/年月日时分秒纳秒方式指定
ZonedDateTime time1 = ZonedDateTime.of(2023, 10, 1,11, 12, 12, 0, ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println(time1);//通过Instant + 时区的方式指定获取时间对象
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L);
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");
ZonedDateTime time2 = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(instant, zoneId);
System.out.println(time2);//3.withXxx 修改时间系列的方法
ZonedDateTime time3 = time2.withYear(2000);
System.out.println(time3);//4. 减少时间
ZonedDateTime time4 = time3.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(time4);//5.增加时间
ZonedDateTime time5 = time4.plusYears(1);
System.out.println(time5);
1.4DateTimeFormatter 用于时间的格式化和解析
/*static DateTimeFormatter ofPattern(格式) 获取格式对象String format(时间对象) 按照指定方式格式化*/
//获取时间对象
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));// 解析/格式化器
DateTimeFormatter dtf1=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm;ss EE a");
// 格式化
System.out.println(dtf1.format(time));
1.5LocalDate 年、月、日
//1.获取当前时间的日历对象(包含 年月日)
LocalDate nowDate = LocalDate.now();
//System.out.println("今天的日期:" + nowDate);
//2.获取指定的时间的日历对象
LocalDate ldDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 1);
System.out.println("指定日期:" + ldDate);System.out.println("=============================");//3.get系列方法获取日历中的每一个属性值//获取年
int year = ldDate.getYear();
System.out.println("year: " + year);
//获取月//方式一:
Month m = ldDate.getMonth();
System.out.println(m);
System.out.println(m.getValue());//方式二:
int month = ldDate.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("month: " + month);//获取日
int day = ldDate.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("day:" + day);//获取一年的第几天
int dayofYear = ldDate.getDayOfYear();
System.out.println("dayOfYear:" + dayofYear);//获取星期
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = ldDate.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println(dayOfWeek);
System.out.println(dayOfWeek.getValue());//is开头的方法表示判断
System.out.println(ldDate.isBefore(ldDate));
System.out.println(ldDate.isAfter(ldDate));//with开头的方法表示修改,只能修改年月日
LocalDate withLocalDate = ldDate.withYear(2000);
System.out.println(withLocalDate);//minus开头的方法表示减少,只能减少年月日
LocalDate minusLocalDate = ldDate.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(minusLocalDate);//plus开头的方法表示增加,只能增加年月日
LocalDate plusLocalDate = ldDate.plusDays(1);
System.out.println(plusLocalDate);//-------------
// 判断今天是否是你的生日
LocalDate birDate = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
LocalDate nowDate1 = LocalDate.now();MonthDay birMd = MonthDay.of(birDate.getMonthValue(), birDate.getDayOfMonth());
MonthDay nowMd = MonthDay.from(nowDate1);System.out.println("今天是你的生日吗? " + birMd.equals(nowMd));//今天是你的生日吗?
1.6 LocalTime 时、分、秒
// 获取本地时间的日历对象。(包含 时分秒)
LocalTime nowTime = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("今天的时间:" + nowTime);int hour = nowTime.getHour();//时
System.out.println("hour: " + hour);int minute = nowTime.getMinute();//分
System.out.println("minute: " + minute);int second = nowTime.getSecond();//秒
System.out.println("second:" + second);int nano = nowTime.getNano();//纳秒
System.out.println("nano:" + nano);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
System.out.println(LocalTime.of(8, 20));//时分
System.out.println(LocalTime.of(8, 20, 30));//时分秒
System.out.println(LocalTime.of(8, 20, 30, 150));//时分秒纳秒
LocalTime mTime = LocalTime.of(8, 20, 30, 150);//is系列的方法
System.out.println(nowTime.isBefore(mTime));
System.out.println(nowTime.isAfter(mTime));//with系列的方法,只能修改时、分、秒
System.out.println(nowTime.withHour(10));//plus系列的方法,只能修改时、分、秒
System.out.println(nowTime.plusHours(10));
1.7 LocalDateTime 年、月、日、时、分、秒
// 当前时间的的日历对象(包含年月日时分秒)
LocalDateTime nowDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println("今天是:" + nowDateTime);//今天是:
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getYear());//年
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMonthValue());//月
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getDayOfMonth());//日
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getHour());//时
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMinute());//分
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getSecond());//秒
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getNano());//纳秒
// 日:当年的第几天
System.out.println("dayofYear:" + nowDateTime.getDayOfYear());
//星期
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getDayOfWeek());
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getDayOfWeek().getValue());
//月份
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMonth());
System.out.println(nowDateTime.getMonth().getValue());LocalDate ld = nowDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println(ld);LocalTime lt = nowDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println(lt.getHour());
System.out.println(lt.getMinute());
System.out.println(lt.getSecond());
1.8 Duration 时间间隔(秒,纳,秒)
// 本地日期时间对象。
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(today);// 出生的日期时间对象
LocalDateTime birthDate = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(birthDate);Duration duration = Duration.between(birthDate, today);//第二个参数减第一个参数
System.out.println("相差的时间间隔对象:" + duration);System.out.println("============================================");
System.out.println(duration.toDays());//两个时间差的天数
System.out.println(duration.toHours());//两个时间差的小时数
System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());//两个时间差的分钟数
System.out.println(duration.toMillis());//两个时间差的毫秒数
System.out.println(duration.toNanos());//两个时间差的纳秒数
1.9 Period 时间间隔(年,月,日)
// 当前本地 年月日
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(today);// 生日的 年月日
LocalDate birthDate = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
System.out.println(birthDate);Period period = Period.between(birthDate, today);//第二个参数减第一个参数System.out.println("相差的时间间隔对象:" + period);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());System.out.println(period.toTotalMonths());
1.10 ChronoUnit 时间间隔(所有单位)
// 当前时间
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(today);
// 生日时间
LocalDateTime birthDate = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 1, 1,0, 0, 0);
System.out.println(birthDate);System.out.println("相差的年数:" + ChronoUnit.YEARS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的月数:" + ChronoUnit.MONTHS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的周数:" + ChronoUnit.WEEKS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的天数:" + ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的时数:" + ChronoUnit.HOURS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的分数:" + ChronoUnit.MINUTES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的秒数:" + ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的毫秒数:" + ChronoUnit.MILLIS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的微秒数:" + ChronoUnit.MICROS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的纳秒数:" + ChronoUnit.NANOS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的半天数:" + ChronoUnit.HALF_DAYS.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的十年数:" + ChronoUnit.DECADES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的世纪(百年)数:" + ChronoUnit.CENTURIES.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的千年数:" + ChronoUnit.MILLENNIA.between(birthDate, today));
System.out.println("相差的纪元数:" + ChronoUnit.ERAS.between(birthDate, today));
后记
👉👉💕💕美好的一天,到此结束,下次继续努力!欲知后续,请看下回分解,写作不易,感谢大家的支持!! 🌹🌹🌹
相关文章:
)
从零开始学习 Java:简单易懂的入门指南之JDK8时间相关类(十八)
JDK8时间相关类 JDK8时间相关类1.1 ZoneId 时区1.2 Instant 时间戳1.3 ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间1.4DateTimeFormatter 用于时间的格式化和解析1.5LocalDate 年、月、日1.6 LocalTime 时、分、秒1.7 LocalDateTime 年、月、日、时、分、秒1.8 Duration 时间间隔(秒…...
)
Spring Boot实践八--用户管理系统(下)
step3:多线程task 首先,实现两个UserService和AsyncUserService两个服务接口: 接口: package com.example.demospringboot.service;public interface UserService {void checkUserStatus(); }package com.example.demospringbo…...
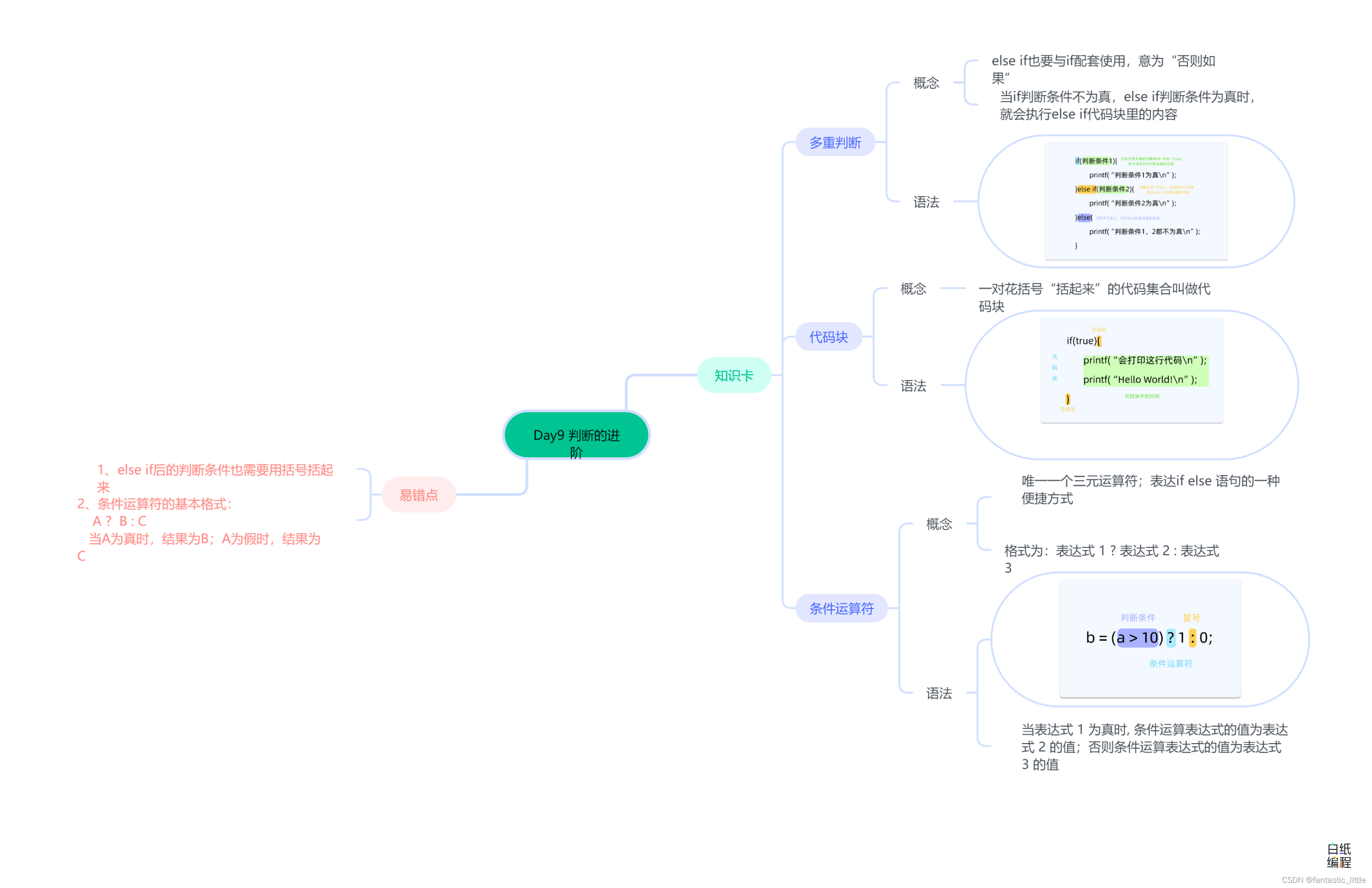
C语言入门 Day_10 判断的进阶
目录 前言 1.多重判断 2.代码块 3.条件运算符 3.易错点 4.思维导图 前言 if和else能够处理两种不同的情况,如果(if)满足条件,我们就执行这几行代码;否则(else)的话,我们就执行…...
)
机器学习基础13-基于集成算法优化模型(基于印第安糖尿病 Pima Indians数据集)
有时提升一个模型的准确度很困难。如果你曾纠结于类似的问题,那 我相信你会同意我的看法。你会尝试所有曾学习过的策略和算法,但模型正确率并没有改善。这时你会觉得无助和困顿,这也是 90%的数据科学家开始放弃的时候。不过,这才是…...

Rancher部署k8s集群
Rancher部署 Rancher是一个开源的企业级容器管理平台。通过Rancher,企业再也不必自己使用一系列的开源软件去从头搭建容器服务平台。Rancher提供了在生产环境中使用的管理Docker和Kubernetes的全栈化容器部署与管理平台。 首先所有节点部署docker 安装docker 安…...

前端油猴脚本开发小技巧笔记
调试模式下,单击选中某dom代码,控制台里可以用$0访问到该dom对象。 $0.__vue___ 可以访问到该dom对应的vue对象。 jquery 对象 a,a[0]是对应的原生dom对象,$(原生对象) 得到对应的 jquery 对象。 jquery 选择器,加空格是匹配下…...

软考高级系统架构设计师系列之:搭建论文写作的万能模版
软考高级系统架构设计师系列之:搭建论文写作的万能模版 一、选择合适的模版二、论文摘要模版1.论文摘要模版一2.论文摘要模版二3.论文摘要模版三4.论文摘要模版四三、项目背景四、正文写作五、论文结尾六、论文万能模版一、选择合适的模版 选择中、大型商业项目,一般金额在2…...
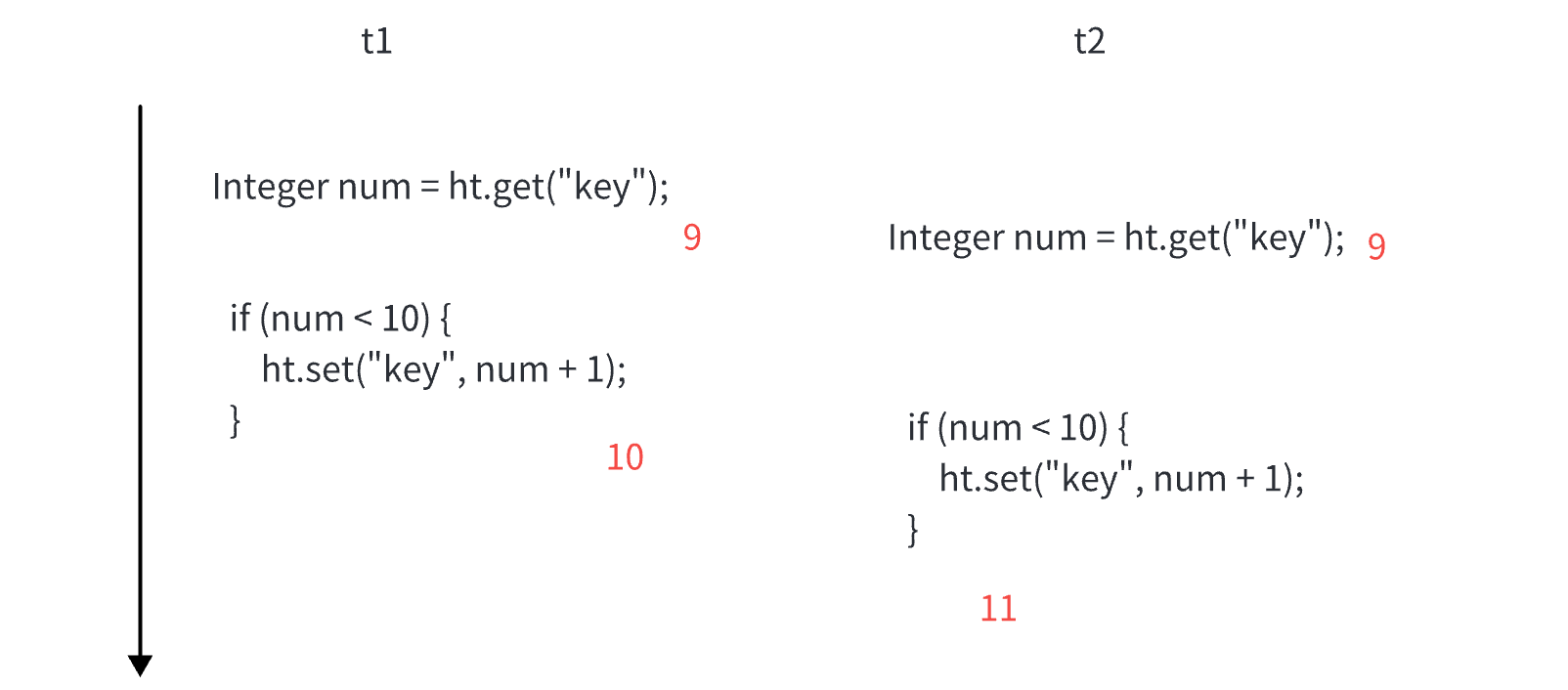
多线程常见面试题
常见的锁策略 这里讨论的锁策略,不仅仅局限于 Java 乐观锁 vs 悲观锁 锁冲突: 两个线程尝试获取一把锁,一个线程能获取成功,另一个线程阻塞等待。 乐观锁: 预该场景中,不太会出现锁冲突的情况。后续做的工作会更少。 悲观锁: 预测该场景,非常容易出现锁冲突。后…...

Java接收json参数
JSON 并不是唯一能够实现在互联网中传输数据的方式,除此之外还有一种 XML 格式。JSON 和 XML 能够执行许多相同的任务,那么我们为什么要使用 JSON,而不是 XML 呢? 之所以使用 JSON,最主要的原因是 JavaScript。众所周知…...

赤峰100吨每天医院污水处理设备产品特点
赤峰100吨每天医院污水处理设备产品特点 设备调试要求: 1、要清洗水池内所有的赃物、杂物。 2、对水泵及空压机等需要润滑部位进行加油滑。 3、通电源,启动水泵,检查转向是否与箭头所标方向一致。用水动控制启动空压机,检查空压机…...

nodejs+vue+elementui健身房教练预约管理系统nt5mp
运用新技术,构建了以vue.js为基础的私人健身和教练预约管理信息化管理体系。根据需求分析结果进行了系统的设计,并将其划分为管理员,教练和用户三种角色:主要功能包括首页,个人中心,用户管理,教…...
视频分割合并工具说明
使用说明书:视频分割合并工具 欢迎使用视频生成工具!本工具旨在帮助您将视频文件按照指定的规则分割并合并,以生成您所需的视频。 本程序还自带提高分辨率1920:1080,以及增加10db声音的功能 软件下载地址 https://github.com/c…...

2023java面试深入探析Nginx的处理流程
推荐阅读 AI文本 OCR识别最佳实践 AI Gamma一键生成PPT工具直达链接 玩转cloud Studio 在线编码神器 玩转 GPU AI绘画、AI讲话、翻译,GPU点亮AI想象空间 资源分享 史上最全文档AI绘画stablediffusion资料分享 「java、python面试题」来自UC网盘app分享,打开手…...
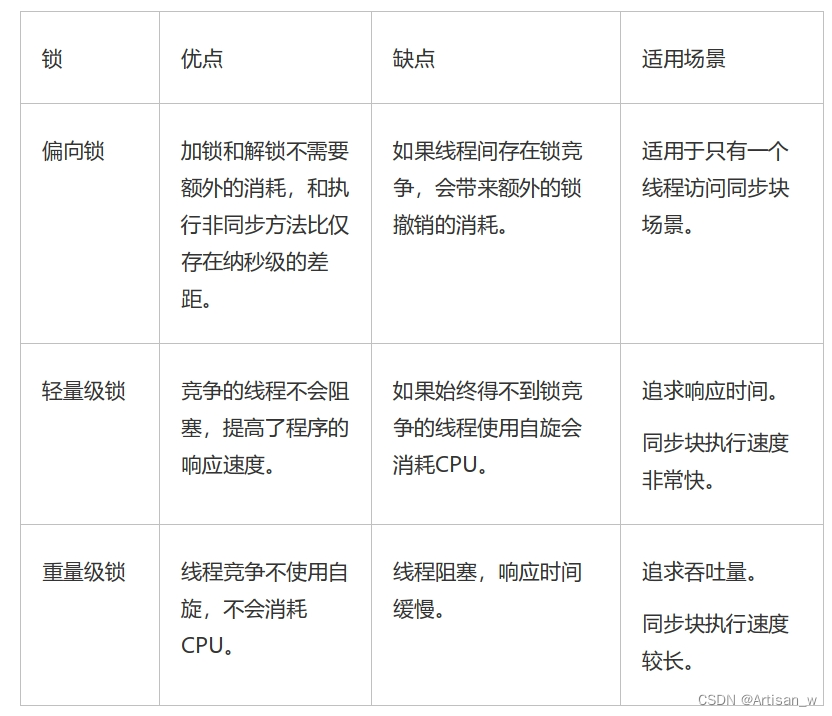
Java的锁大全
Java的锁 各种锁的类型 乐观锁 VS 悲观锁 乐观锁与悲观锁是一种广义上的概念,体现了看待线程同步的不同角度。在Java和数据库中都有此概念对应的实际应用。 先说概念。对于同一个数据的并发操作,悲观锁认为自己在使用数据的时候一定有别的线程来修改数…...

Leetcode80. 删除有序数组中的重复项 II
给你一个有序数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使得出现次数超过两次的元素只出现两次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。 不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。 class Solu…...
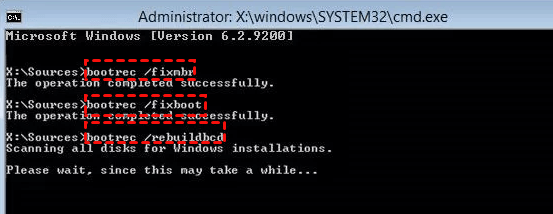
电脑显示“Operating System not found”该怎么办?
“Operating System not found”是一种常见的电脑错误提示,这类错误会导致你无法成功启动Windows。那么电脑显示“Operating System not found”该怎么办呢? 方法1. 检查硬盘 首先,您可以测试硬盘是否存在问题。为此,您可以采取以…...

简析SCTP开发指南
目录 前言一、SCTP基本概念二、SCTP开发步骤1. **环境配置**:2. **建立Socket**:3. **绑定和监听**:4. **接收和发送数据**:5. **关闭连接**: 三、 C语言实现SCTP3.1SCTP客户端代码:3.2 SCTP服务器端代码&a…...
把Android手机变成电脑摄像头
一、使用 DroidCam 使用 DroidCam,你可以将手机作为电脑摄像头和麦克风。一则省钱,二则可以在紧急情况下使用,比如要在电脑端参加一个紧急会议,但电脑却没有摄像头和麦克风。 DroidCam 的安卓端分为免费的 DroidCam 版和收费的 …...

Linux线程篇(中)
有了之前对线程的初步了解我们学习了什么是线程,线程的原理及其控制。这篇文章将继续讲解关于线程的内容以及重要的知识点。 线程的优缺点: 线程的缺点 在这里我们来谈一谈线程健壮性: 首先我们先思考一个问题,如果一个线程出现…...
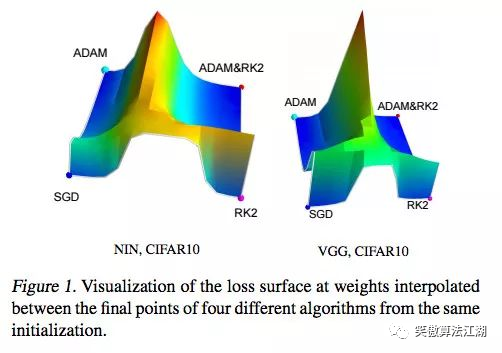
深度学习优化入门:Momentum、RMSProp 和 Adam
目录 深度学习优化入门:Momentum、RMSProp 和 Adam 病态曲率 1牛顿法 2 Momentum:动量 3Adam 深度学习优化入门:Momentum、RMSProp 和 Adam 本文,我们讨论一个困扰神经网络训练的问题,病态曲率。 虽然局部极小值和鞍点会阻碍…...
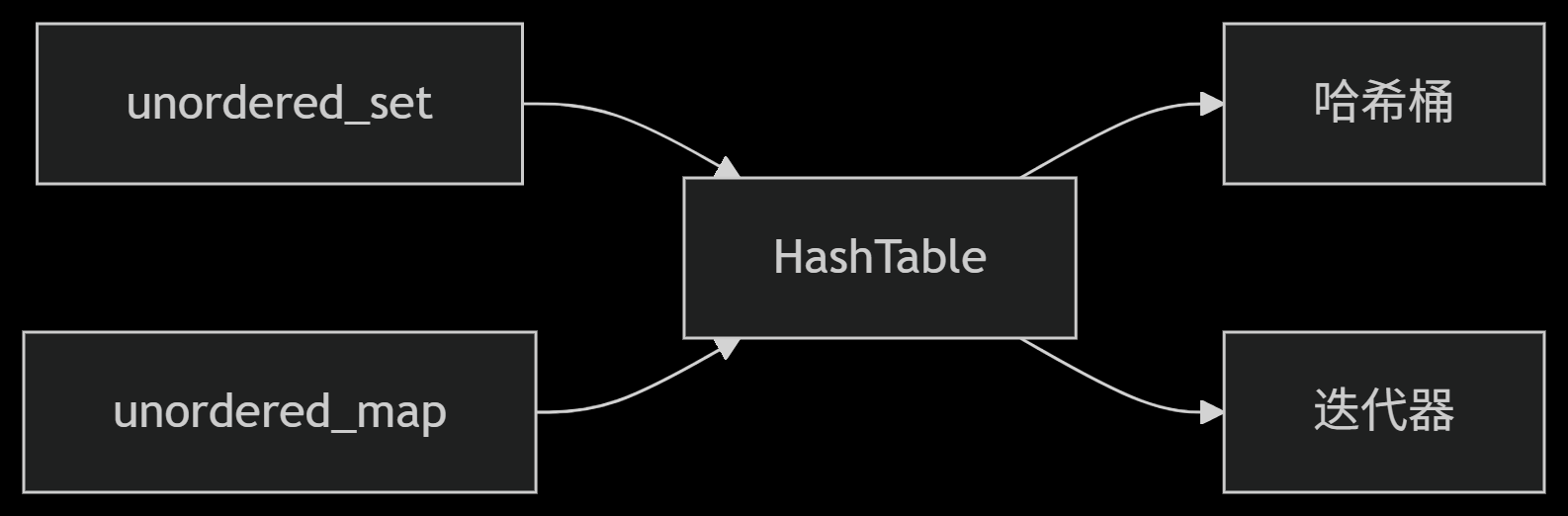
从零实现STL哈希容器:unordered_map/unordered_set封装详解
本篇文章是对C学习的STL哈希容器自主实现部分的学习分享 希望也能为你带来些帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、源码结构分析 1. SGISTL30实现剖析 // hash_set核心结构 template <class Value, class HashFcn, ...> class hash_set {ty…...

Java数值运算常见陷阱与规避方法
整数除法中的舍入问题 问题现象 当开发者预期进行浮点除法却误用整数除法时,会出现小数部分被截断的情况。典型错误模式如下: void process(int value) {double half = value / 2; // 整数除法导致截断// 使用half变量 }此时...

08. C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险
C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险 嘿,各位编程小白探险家!欢迎来到 C# 的奇幻大陆!今天咱们要深入探索这片大陆上至关重要的 “建筑”—— 类!别害怕,跟着我,保准让你轻松搞…...
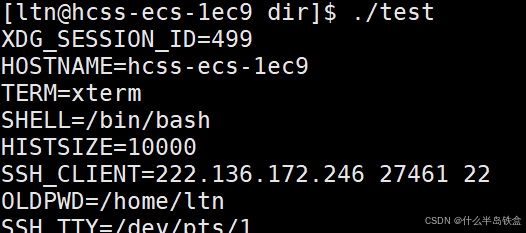
【Linux系统】Linux环境变量:系统配置的隐形指挥官
。# Linux系列 文章目录 前言一、环境变量的概念二、常见的环境变量三、环境变量特点及其相关指令3.1 环境变量的全局性3.2、环境变量的生命周期 四、环境变量的组织方式五、C语言对环境变量的操作5.1 设置环境变量:setenv5.2 删除环境变量:unsetenv5.3 遍历所有环境…...
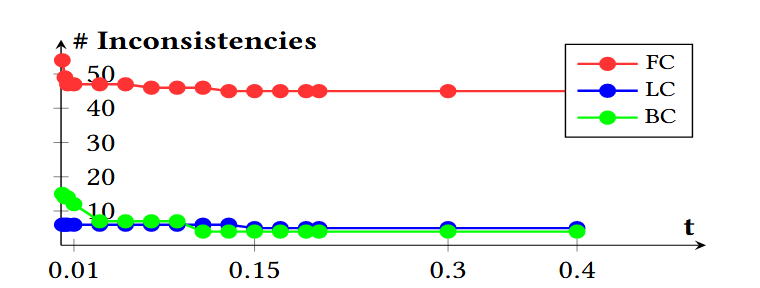
论文阅读笔记——Muffin: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via Neural Architecture Fuzzing
Muffin 论文 现有方法 CRADLE 和 LEMON,依赖模型推理阶段输出进行差分测试,但在训练阶段是不可行的,因为训练阶段直到最后才有固定输出,中间过程是不断变化的。API 库覆盖低,因为各个 API 都是在各种具体场景下使用。…...

用鸿蒙HarmonyOS5实现中国象棋小游戏的过程
下面是一个基于鸿蒙OS (HarmonyOS) 的中国象棋小游戏的实现代码。这个实现使用Java语言和鸿蒙的Ability框架。 1. 项目结构 /src/main/java/com/example/chinesechess/├── MainAbilitySlice.java // 主界面逻辑├── ChessView.java // 游戏视图和逻辑├──…...

SpringAI实战:ChatModel智能对话全解
一、引言:Spring AI 与 Chat Model 的核心价值 🚀 在 Java 生态中集成大模型能力,Spring AI 提供了高效的解决方案 🤖。其中 Chat Model 作为核心交互组件,通过标准化接口简化了与大语言模型(LLM࿰…...

Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法
Python实现简单音频数据压缩与解压算法 引言 在音频数据处理中,压缩算法是降低存储成本和传输效率的关键技术。Python作为一门灵活且功能强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的库和工具来实现音频数据的压缩与解压。本文将通过一个简单的音频数据压缩与解压算法…...

WEB3全栈开发——面试专业技能点P7前端与链上集成
一、Next.js技术栈 ✅ 概念介绍 Next.js 是一个基于 React 的 服务端渲染(SSR)与静态网站生成(SSG) 框架,由 Vercel 开发。它简化了构建生产级 React 应用的过程,并内置了很多特性: ✅ 文件系…...
uni-app学习笔记三十五--扩展组件的安装和使用
由于内置组件不能满足日常开发需要,uniapp官方也提供了众多的扩展组件供我们使用。由于不是内置组件,需要安装才能使用。 一、安装扩展插件 安装方法: 1.访问uniapp官方文档组件部分:组件使用的入门教程 | uni-app官网 点击左侧…...
