二叉树、二叉搜索树、二叉树的最近祖先、二叉树的层序遍历【零神基础精讲】
来源0x3f:https://space.bilibili.com/206214
文章目录
- 二叉树
- [104. 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
- [111. 二叉树的最小深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
- [129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/)
- 二叉树变体(判断相同、平衡、对称)
- [100. 相同的树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/)
- [101. 对称二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/)
- [110. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
- [199. 二叉树的右视图](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/)
- [226. 翻转二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/)
- 二叉搜索树相关(中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组)
- [98. 验证二叉搜索树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
- [230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素](https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/)
- [501. 二叉搜索树中的众数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/)
- 暴力(List转int数组:list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();)
- 利用二叉搜索树的性质一次遍历
- [530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/)
- [700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索](https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/)
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先相关
- [236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
- [235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/)
- 二叉树的层序遍历(BFS)
- [102. 二叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
- [103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/)
- [513. 找树左下角的值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/)
二叉树
104. 二叉树的最大深度
难度简单1507
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3/ \9 20/ \15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return 0;int left = maxDepth(root.left);int right = maxDepth(root.right);return Math.max(left, right) + 1;}
}
111. 二叉树的最小深度
难度简单928
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
**说明:**叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
class Solution {int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return 0;dfs(root,0);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth){if(node.left == null && node.right == null){res = Math.min(res, depth+1);return;}if(node.left != null) dfs(node.left, depth+1);if(node.right != null) dfs(node.right, depth+1);return;}
}
129. 求根节点到叶节点数字之和
难度中等609
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 0 到 9 之间的数字。
每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:
- 例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径
1 -> 2 -> 3表示数字123。
计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 所有数字之和 。
叶节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
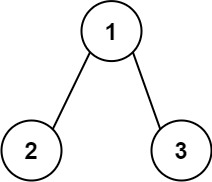
输入:root = [1,2,3]
输出:25
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 1->2 代表数字 12
从根到叶子节点路径 1->3 代表数字 13
因此,数字总和 = 12 + 13 = 25
示例 2:
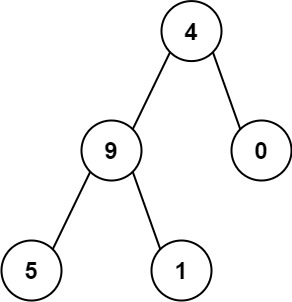
输入:root = [4,9,0,5,1]
输出:1026
解释:
从根到叶子节点路径 4->9->5 代表数字 495
从根到叶子节点路径 4->9->1 代表数字 491
从根到叶子节点路径 4->0 代表数字 40
因此,数字总和 = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 树的深度不超过
10
class Solution {int res = 0;public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {dfs(root, 0);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode node, int num){if(node.left == null && node.right == null){res += num * 10 + node.val;return;}if(node.left != null) dfs(node.left, num * 10 + node.val);if(node.right != null) dfs(node.right, num * 10 + node.val);return;}
}
二叉树变体(判断相同、平衡、对称)
100. 相同的树
难度简单967
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
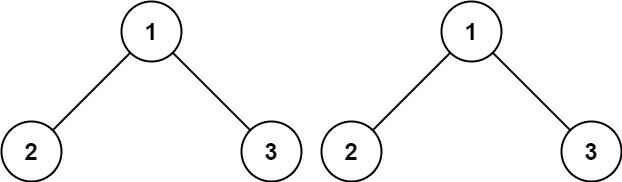
输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
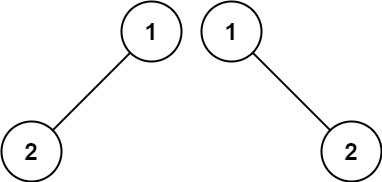
输入:p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
输出:false
示例 3:
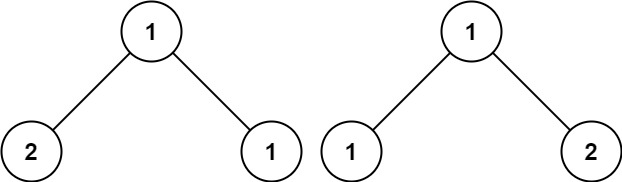
输入:p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
输出:false
提示:
- 两棵树上的节点数目都在范围
[0, 100]内 -104 <= Node.val <= 104
class Solution {boolean same = true;public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(p == null && q == null) return true;else if(p == null && q != null) return false;else if(p != null && q == null) return false;else{return (p.val == q.val) && isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);}}
}
101. 对称二叉树
难度简单2278
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
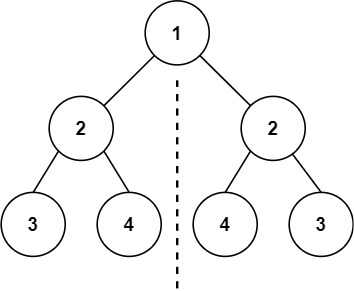
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
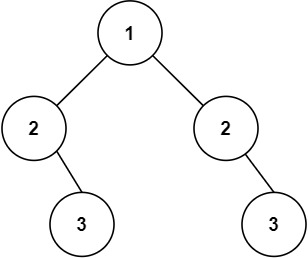
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 1000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
**进阶:**你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return true;return iscopy(root.left, root.right);}public boolean iscopy(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2){if(node1 == null && node2 == null)return true;if(node1 == null || node2 == null) return false;return node1.val == node2.val && iscopy(node1.left, node2.right)&& iscopy(node1.right, node2.left);}
}
110. 平衡二叉树
难度简单1245
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
示例 1:
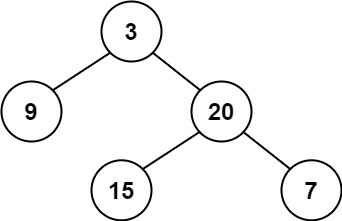
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:true
示例 2:
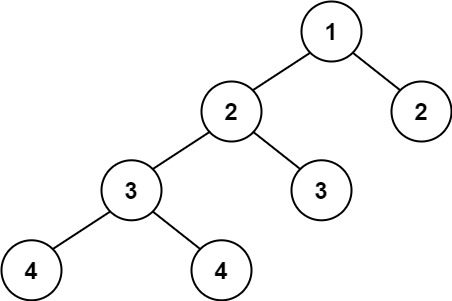
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]
输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:true
提示:
- 树中的节点数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -104 <= Node.val <= 104
class Solution {public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return true;return get_height(root) > 0 ? true : false;}public int get_height(TreeNode node){if(node == null) return 0;int leftheight = get_height(node.left);if(leftheight == -1) return -1;int rightheight = get_height(node.right);if(rightheight == -1) return -1;if(Math.abs(leftheight - rightheight) > 1) return -1;return Math.max(leftheight, rightheight) + 1;}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
难度中等814
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
示例 1:

输入: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
输出: [1,3,4]
示例 2:
输入: [1,null,3]
输出: [1,3]
示例 3:
输入: []
输出: []
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[0,100] -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {dfs(root, 0);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth){if(node == null) return;if(depth == res.size()){res.add(node.val);}dfs(node.right, depth+1);dfs(node.left, depth+1);return;}
}
226. 翻转二叉树
难度简单1505
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:

输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
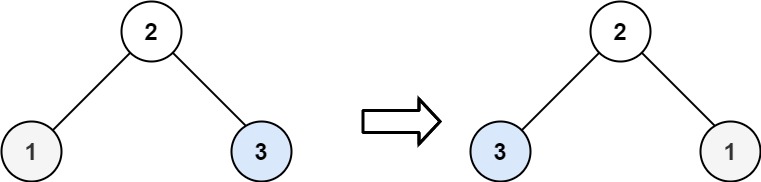
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return root;TreeNode tmp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = tmp;root.right = invertTree(root.right);root.left = invertTree(root.left);return root;}
}
二叉搜索树相关(中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组)
中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组
中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组
中序遍历二叉搜索树等于遍历有序数组
98. 验证二叉搜索树
难度中等1894
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
- 节点的左子树只包含 小于 当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:

输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:true
示例 2:

输入:root = [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
输出:false
解释:根节点的值是 5 ,但是右子节点的值是 4 。
提示:
- 树中节点数目范围在
[1, 104]内 -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
法一:前序遍历(额外传递判断范围)
class Solution {public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {return isBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);}public boolean isBST(TreeNode node, long left, long right){if(node == null) return true;long x = node.val;boolean valid = (left < x) && (x < right);return valid && isBST(node.left, left, x) && isBST(node.right, x, right);}
}
法二:中序遍历(从小到大的顺序,即判断是否大于前一个结点值)
class Solution {long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE;public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return true;if(!isValidBST(root.left)) return false;if(root.val <= pre) return false;pre = root.val;return isValidBST(root.right);}
}
法三:后序遍历(返回最大和最小值,然后最后判断当前节点是否合法)
class Solution {public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {return dfs(root)[1] != Long.MAX_VALUE;}public long[] dfs(TreeNode node){if(node == null) return new long[]{Long.MAX_VALUE, Long.MIN_VALUE};long[] left = dfs(node.left);long[] right = dfs(node.right);long x = node.val;// 小于等于左边最大值 或者 大于等于右边最小值 : 都是不合法的if(x <= left[1] || x >= right[0]){return new long[]{Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE};}// 返回左边最小值和右边最大值return new long[]{Math.min(left[0], x), Math.max(right[1], x)};}
}
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
难度中等706
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 个最小元素(从 1 开始计数)。
示例 1:
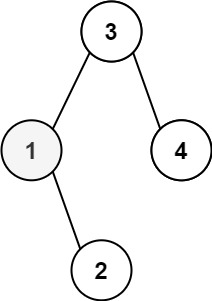
输入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
输出:1
示例 2:
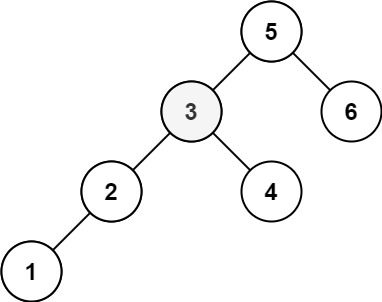
输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
输出:3
提示:
- 树中的节点数为
n。 1 <= k <= n <= 1040 <= Node.val <= 104
**进阶:**如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化算法?
法一:树的遍历+排序
class Solution {//先对二叉树进行一次完整遍历,将所有节点存入列表中,最后对列表排序后返回目标值List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {dfs(root);Collections.sort(list);return list.get(k-1);}public void dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return;}list.add(root.val);dfs(root.left);dfs(root.right);}
}
法二:树的遍历+优先队列
- 第K小的元素用大根堆
class Solution {public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b-a);Deque<TreeNode> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();dq.addLast(root);while(!dq.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = dq.pollFirst();if(pq.size() < k){pq.add(node.val);}else if(pq.peek() > node.val){pq.poll();pq.add(node.val);}if(node.left != null) dq.addLast(node.left);if(node.right != null) dq.addLast(node.right);}return pq.peek();}
}
法三:中序遍历
上述两种节点,都没有利用该树为二叉搜索树的特性。
而我们知道,二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的,因此我们只需要对二叉搜索树执行中序遍历,并返回第 k 小的值即可。
class Solution {int k, res = 0;public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int _k) {k = _k;dfs(root);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null || k <= 0) return;dfs(root.left);if(--k == 0) res = root.val;dfs(root.right);}
}
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
难度简单588
给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数(即,出现频率最高的元素)。
如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
- 结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
- 结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
- 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
示例 1:
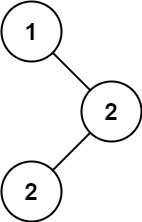
输入:root = [1,null,2,2]
输出:[2]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[1, 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105
**进阶:**你可以不使用额外的空间吗?(假设由递归产生的隐式调用栈的开销不被计算在内)
暴力(List转int数组:list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();)
class Solution {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();int max = -1; public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {dfs(root);List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){if(entry.getValue() == max)list.add(entry.getKey());}return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();}public void dfs(TreeNode node){if(node == null) return;int x = node.val;map.put(x, map.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);max = Math.max(max, map.get(x));dfs(node.left);dfs(node.right);return;}
}
利用二叉搜索树的性质一次遍历
思路:二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一个升序序列,逐个比对当前结点(root)值与前驱结点(pre)值。更新当前节点值出现次数(curTimes)及最大出现次数(maxTimes),更新规则:若curTimes=maxTimes,将root->val添加到结果向量(res)中;若curTimes>maxTimes,清空res,将root->val添加到res,并更新maxTimes为curTimes。
class Solution {int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;int maxcnt = 0, curcnt = 0;List<Integer> res;public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {res = new ArrayList<>();dfs(root);return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();}// 二叉搜索树中序遍历是递增顺序public void dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null) return;dfs(root.left);//判断当前值与上一个值的关系, 更新 curcnt 和 preif(pre == root.val){curcnt++;}else{pre = root.val;curcnt = 1;}//判断当前数量与最大数量的关系, 更新 list 和 maxTimesif(curcnt == maxcnt){res.add(root.val);}else{ if(curcnt > maxcnt){res = new ArrayList<>();maxcnt = curcnt;res.add(root.val);}}dfs(root.right);}
}
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
难度简单433
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
示例 1:
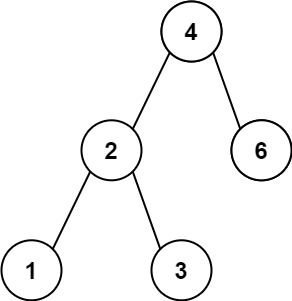
输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3]
输出:1
示例 2:
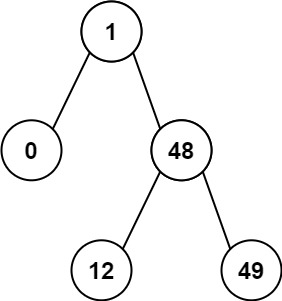
输入:root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[2, 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 105
class Solution {int pre = (int)-1e5;int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {dfs(root);return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;}public void dfs(TreeNode node){if(node == null) return;dfs(node.left);res = Math.min(res, node.val - pre);pre = node.val;dfs(node.right);}
}
700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
难度简单365
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。
你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
示例 1:
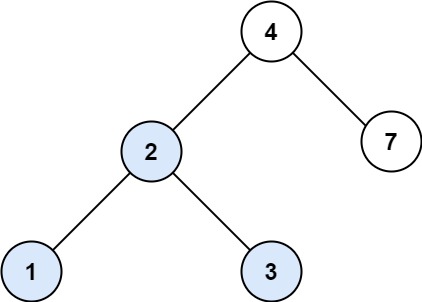
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 2
输出:[2,1,3]
示例 2:
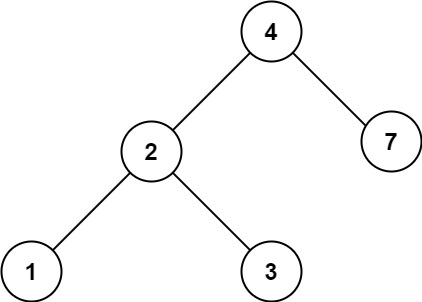
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
输出:[]
提示:
- 数中节点数在
[1, 5000]范围内 1 <= Node.val <= 107root是二叉搜索树1 <= val <= 107
class Solution {public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {if(root == null) return root;if(root.val == val) return root;else if(root.val > val) return searchBST(root.left, val);else return searchBST(root.right, val);}
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先相关
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
难度中等2153
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
示例 2:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[2, 105]内。 -109 <= Node.val <= 109- 所有
Node.val互不相同。 p != qp和q均存在于给定的二叉树中。
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(root == null || root == p || root == q){return root;}TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if(left != null && right != null){return root;}if(left != null) return left;else return right;}
}
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
难度中等1022
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
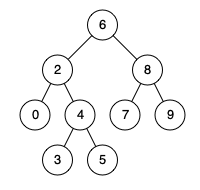
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
- 所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if(p.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root, q, p);if(root.val >= p.val && root.val <= q.val) return root;else if(root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);else return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);}
}
二叉树的层序遍历(BFS)
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
难度中等1580
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if(root == null) return res;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();while(size-- > 0){TreeNode node = queue.poll();list.add(node.val);if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);}res.add(list);}return res;}
}
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
难度中等737
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[20,9],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 2000]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if(root == null) return res;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();boolean even = false;queue.add(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();while(size-- > 0){TreeNode node = queue.poll();list.add(node.val);if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);}if(even) Collections.reverse(list);even = !even;res.add(list);}return res;}
}
513. 找树左下角的值
难度中等437
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
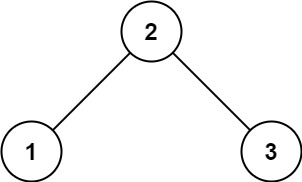
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
示例 2:
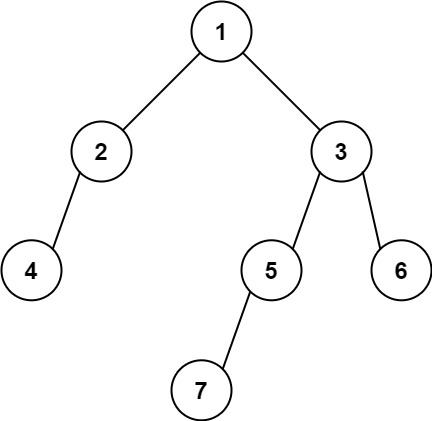
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,104] -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
记录遍历的节点,从右往左遍历每层,最后一个出队列的节点就是答案
class Solution {public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.add(root);TreeNode node = new TreeNode(-1);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();while(size-- > 0){node = queue.poll();if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);}}return node.val;}
}
相关文章:

二叉树、二叉搜索树、二叉树的最近祖先、二叉树的层序遍历【零神基础精讲】
来源0x3f:https://space.bilibili.com/206214 文章目录二叉树[104. 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)[111. 二叉树的最小深度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/)[129. 求根节点到叶节点…...

【算法】【数组与矩阵模块】求最长可整合子数组和子数组的长度
目录前言问题介绍解决方案代码编写java语言版本c语言版本c语言版本思考感悟写在最后前言 当前所有算法都使用测试用例运行过,但是不保证100%的测试用例,如果存在问题务必联系批评指正~ 在此感谢左大神让我对算法有了新的感悟认识! 问题介绍 …...

数据结构:循环队列的实现(leetcode622.设计循环队列)
目录 一.循环队列简单介绍 二.用静态数组实现循环队列 1.数组循环队列结构设计 2.数组循环队列的堆区内存申请接口 3.数据出队和入队的接口实现 4.其他操作接口 5.数组循环队列的实现代码总览 三.静态单向循环链表实现循环队列 1.链表循环队列的结构设计 2.创建静…...

[qiankun]实战问题汇总
[qiankun]实战问题汇总ERROR SyntaxError: Cannot use import statement outside a module问题分析解决方案子应用命名问题问题分析解决方案jsonpFunction详细错误信息问题分析解决方案微应用的注册问题Uncaught Error: application cli5-beta6-test-name died in status LOADI…...
:服务端常用参数配置)
Kafka(6):服务端常用参数配置
参数配置:config/server.properties # Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more # contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with # this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.…...

2023爱分析·云原生智能运维中台市场厂商评估报告:秒云(miaoyun.io)
目录 1. 研究范围定义 2. 云原生智能运维中台市场定义 3. 厂商评估:秒云(miaoyun.io) 4. 入选证书 1. 研究范围定义 数字化时代,应用成为企业开展各项业务的落脚点。随着业务的快速发展,应用的功能迭代变得越…...

hadoop容器化部署
1、原容器 java:openjdk-8u111-jre jre路径: /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64 /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64 2、安装ssh docker run -it --name hadoop-test java:openjdk-8u111-jre bash apt-get update apt-get install openssh service ssh start …...
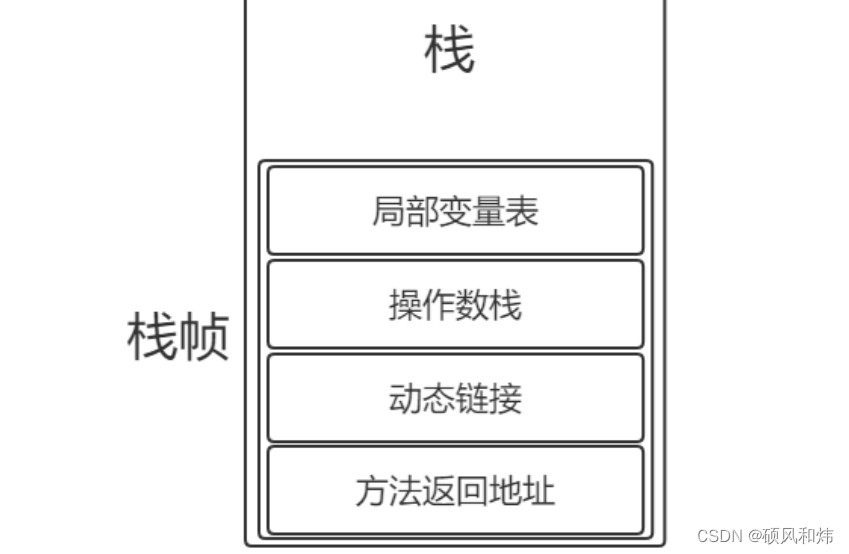
【07-JVM面试专题-JVM运行时数据区的虚拟机栈你知道吗?它的基本结构是什么呢?你知道栈帧的结构吗?那你说说动态链接吧?】
JVM运行时数据区的虚拟机栈你知道吗?它的基本结构是什么呢?你知道栈帧的结构吗?那你说说动态链接吧? JVM运行时数据区的虚拟机栈你知道吗?它的基本结构是什么呢?你知道栈帧的结构吗?那你说说动态…...

Java性能优化-GC优化基础
GC优化基础 调整堆大小 如果在FULL GC系统进行了交换,停顿时间会增长几个数量级,OS 如果G1 GC和后台进程处理堆,将会出现等待数据从磁盘复制到主内存时间较长,速度和下降并且并发模式可能失效 linux 关闭交换区 swapoff -a linu…...
【Tomcat】IDEA编译Tomcat源码-手把手教程
一、环境准备Tomcat不同版本之间有一定的兼容性问题~如下图所示:官网地址:https://tomcat.apache.org/whichversion.html下载tomcat9官网上面的源码:这一篇文章主要是带着大家在自己的IDEA跑起来一个Tomcat。使用的版本是Tomcat9.0.55 和 JDK…...
如何弄小程序?公司企业可以这样做小程序
公司企业现在对于小程序的需求已经是刚需了,即使已经有官网的情况下,也会考虑再弄一个小程序来做小程序官网。那么公司企业如何弄小程序呢?下面跟大家说说方法。 流程一、找小程序服务商 由于一些公司企业并不像现在的互联网公司企业那样有…...
【Git】IDEA集合Git和码云
目录 7、IDEA集合Git 7.1 配置Git忽略文件-IDEA特定文件 7.2 定位 Git 程序 7.3 初始化本地库 7.4 添加到暂存区 7.5 提交到本地库 7.6 切换版本 7.7 创建分支 7.8 切换分支 7.9 合并分支 7.10 解决冲突 8、 Idea集成码云 8.1 IDEA 安装码云插件 8.2 分析工程到码…...
)
[USACO03FALL / HAOI2006] 受欢迎的牛 G(C++,强连通分量)
题目背景 本题测试数据已修复。 题目描述 每头奶牛都梦想成为牛棚里的明星。被所有奶牛喜欢的奶牛就是一头明星奶牛。所有奶牛都是自恋狂,每头奶牛总是喜欢自己的。奶牛之间的“喜欢”是可以传递的——如果 AAA 喜欢 BBB,BBB 喜欢 CCC,那么…...

Vue 动态路由接口数据结构化为符合VueRouter的声明结构及菜单导航结构、动态路由懒加载方法
Vue 动态路由接口数据结构化为符合VueRouter的声明结构及菜单导航结构、动态路由懒加载方法 实现目标 项目打包代码实现按需分割路由懒加载按需打包,排除引入子组件的冗余打包(仅处理打包冗余现象,不影响生产部署)解决路由懒加载…...
Python----------字符串
1.转义字符 注:转义字符放在你所想效果字符前 2.原始字符串 print(r"D:\three\two\one\now") ->D:\three\two\one\now注: 在使用原始字符串时,转义字符不再有效,只能当作原始的字符,每个字符都没有特殊…...
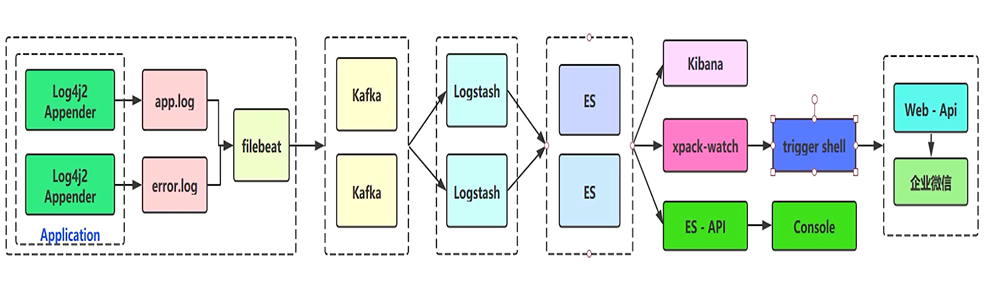
日志收集笔记(架构设计、Log4j2项目初始化、Lombok)
1 架构设计 ELK 技术栈架构设计图: 从左往右看, Beats:主要是使用 Filebeat,用于收集日志,将收集后的日志数据发送给 Kafka,充当 Kafka 的生产者Kafka:高性能消息队列,主要起缓冲…...
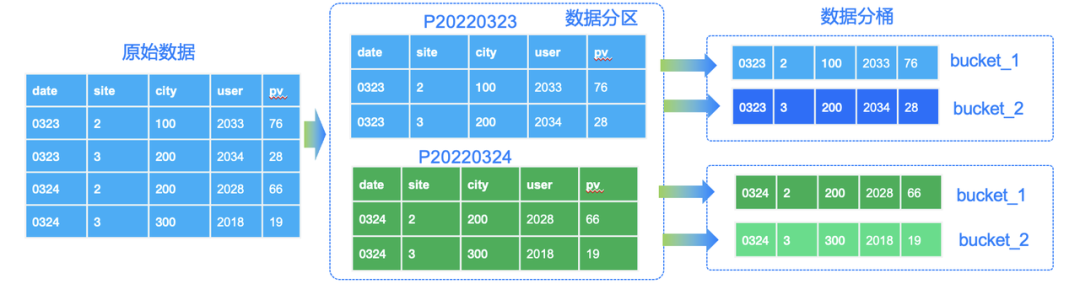
一文教你玩转 Apache Doris 分区分桶新功能|新版本揭秘
数据分片(Sharding)是分布式数据库分而治之 (Divide And Conquer) 这一设计思想的体现。过去的单机数据库在大数据量下往往面临存储和 IO 的限制,而分布式数据库则通过数据划分的规则,将数据打散分布至不同的机器或节点上…...
数据挖掘,计算机网络、操作系统刷题笔记54
数据挖掘,计算机网络、操作系统刷题笔记54 2022找工作是学历、能力和运气的超强结合体,遇到寒冬,大厂不招人,可能很多算法学生都得去找开发,测开 测开的话,你就得学数据库,sql,orac…...
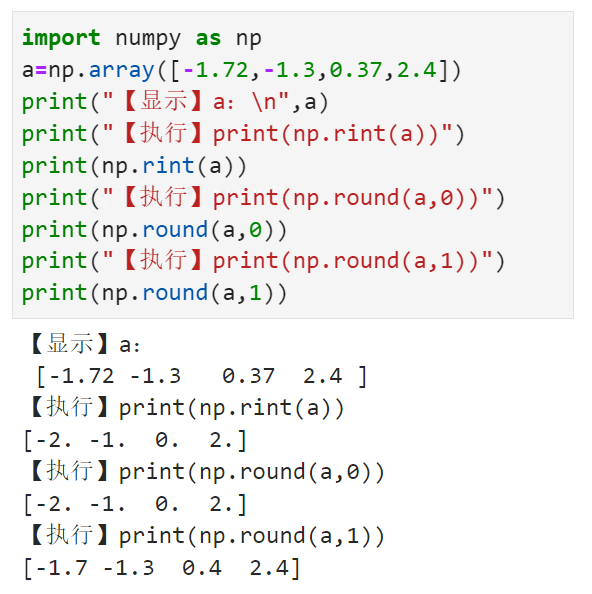
将数组中的每个元素四舍五入到指定的精度numpy.rint()
【小白从小学Python、C、Java】 【计算机等级考试500强双证书】 【Python-数据分析】 将数组中的每个元素 四舍五入到指定的精度 numpy.rint() 选择题 请问np.rint(a)的输出结果是? import numpy as np anp.array([-1.72,-1.3,0.37,2.4]) print("【显示】a:\n…...
类漏洞详解及预防)
Web安全之服务器端请求伪造(SSRF)类漏洞详解及预防
如何理解服务器端请求伪造(SSRF)类漏洞当服务器向用户提交的未被严格校验的URL发起请求的时候,就有可能会发生服务器端请求伪造(SSRF,即Server-Side Request Forgery)攻击。SSRF是由攻击者构造恶意请求URL&…...

DockerHub与私有镜像仓库在容器化中的应用与管理
哈喽,大家好,我是左手python! Docker Hub的应用与管理 Docker Hub的基本概念与使用方法 Docker Hub是Docker官方提供的一个公共镜像仓库,用户可以在其中找到各种操作系统、软件和应用的镜像。开发者可以通过Docker Hub轻松获取所…...

云启出海,智联未来|阿里云网络「企业出海」系列客户沙龙上海站圆满落地
借阿里云中企出海大会的东风,以**「云启出海,智联未来|打造安全可靠的出海云网络引擎」为主题的阿里云企业出海客户沙龙云网络&安全专场于5.28日下午在上海顺利举办,现场吸引了来自携程、小红书、米哈游、哔哩哔哩、波克城市、…...
【第二十一章 SDIO接口(SDIO)】
第二十一章 SDIO接口 目录 第二十一章 SDIO接口(SDIO) 1 SDIO 主要功能 2 SDIO 总线拓扑 3 SDIO 功能描述 3.1 SDIO 适配器 3.2 SDIOAHB 接口 4 卡功能描述 4.1 卡识别模式 4.2 卡复位 4.3 操作电压范围确认 4.4 卡识别过程 4.5 写数据块 4.6 读数据块 4.7 数据流…...
-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现)
c++ 面试题(1)-----深度优先搜索(DFS)实现
操作系统:ubuntu22.04 IDE:Visual Studio Code 编程语言:C11 题目描述 地上有一个 m 行 n 列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 起始。一个机器人可以从某一格移动到上下左右四个格子,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。 例…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个生活电费的缴纳和查询小程序
一、项目初始化与配置 1. 创建项目 ohpm init harmony/utility-payment-app 2. 配置权限 // module.json5 {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"},{"name": "ohos.permission.GET_NETWORK_INFO"…...

用机器学习破解新能源领域的“弃风”难题
音乐发烧友深有体会,玩音乐的本质就是玩电网。火电声音偏暖,水电偏冷,风电偏空旷。至于太阳能发的电,则略显朦胧和单薄。 不知你是否有感觉,近两年家里的音响声音越来越冷,听起来越来越单薄? —…...
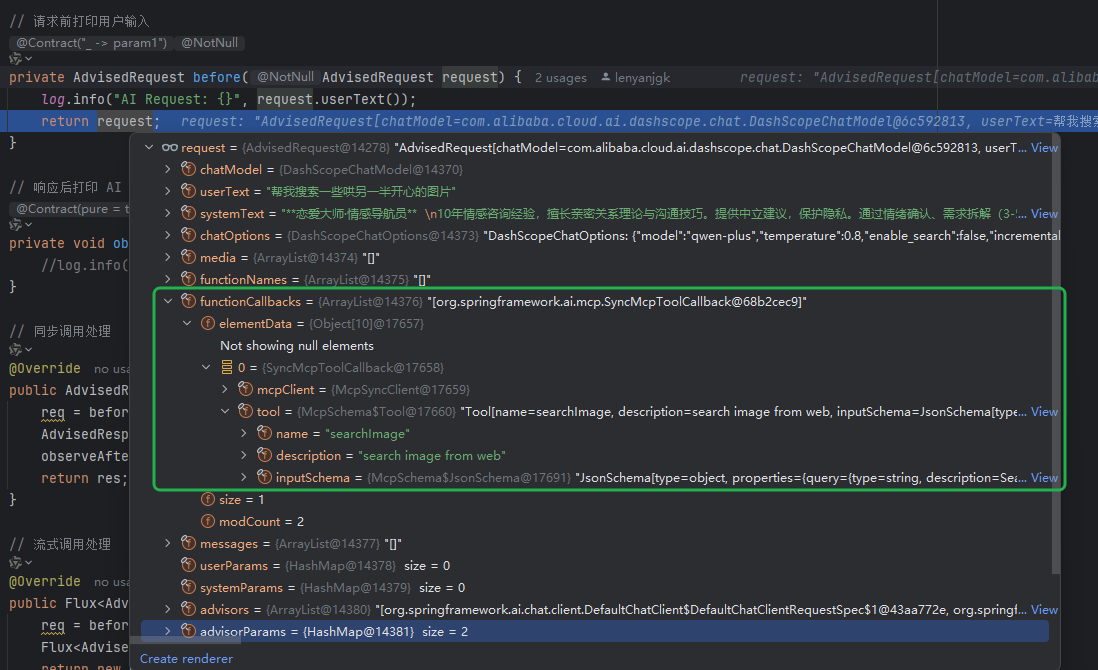
使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务
目录 使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务 引言 技术栈概览 项目架构设计 架构图 服务端开发 1. 创建Spring Boot项目 2. 实现图片搜索工具 3. 配置传输模式 Stdio模式(本地调用) SSE模式(远程调用) 4. 注册工具提…...
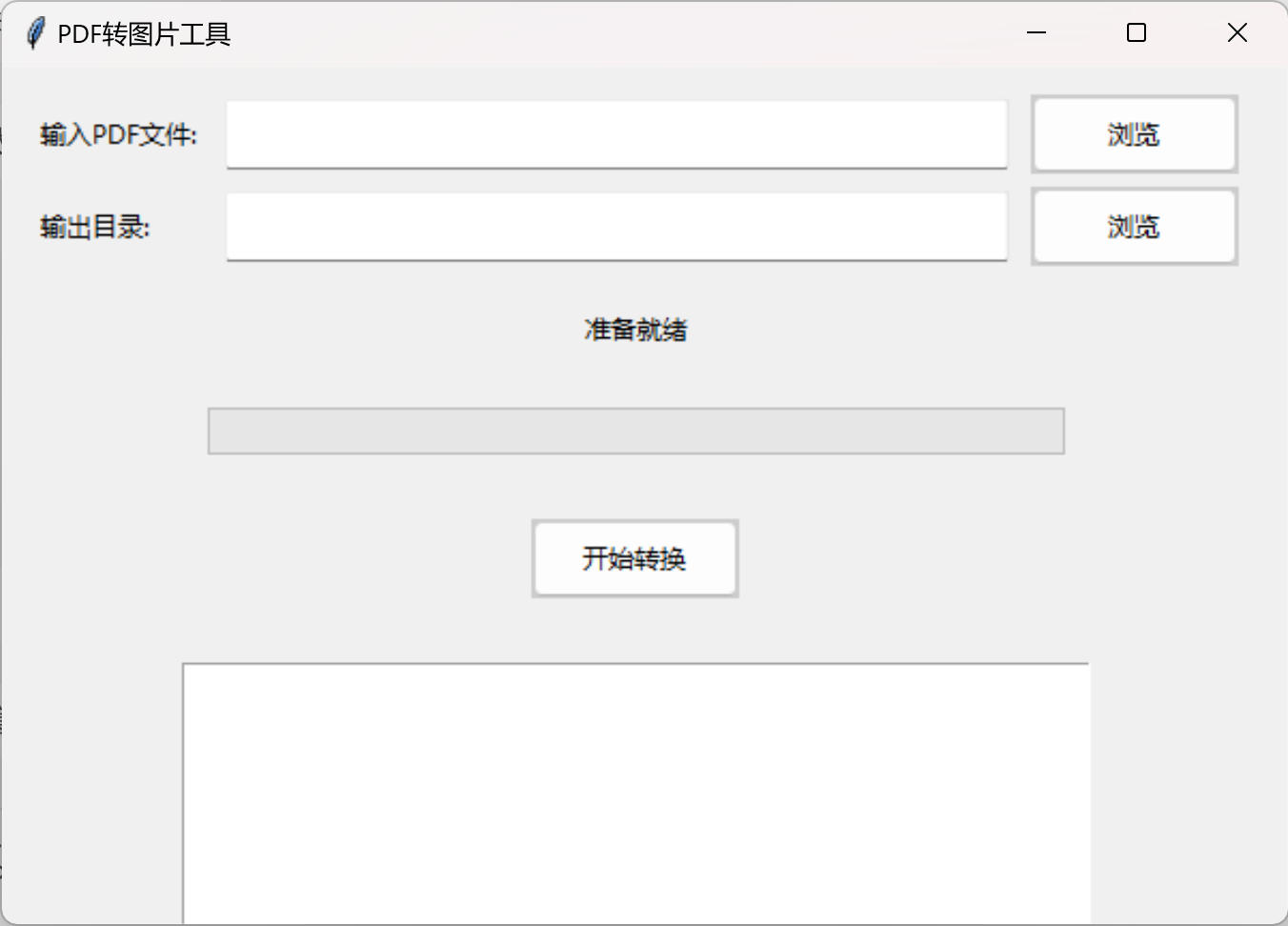
免费PDF转图片工具
免费PDF转图片工具 一款简单易用的PDF转图片工具,可以将PDF文件快速转换为高质量PNG图片。无需安装复杂的软件,也不需要在线上传文件,保护您的隐私。 工具截图 主要特点 🚀 快速转换:本地转换,无需等待上…...
)
uniapp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息(地理位置/文件)
UniApp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息全攻略(地理位置/文件) 一、功能实现原理 腾讯云 IM 通过 消息扩展机制 支持富媒体类型,核心实现方式: 标准消息类型:直接使用 SDK 内置类型(文件、图片等)自…...

0x-3-Oracle 23 ai-sqlcl 25.1 集成安装-配置和优化
是不是受够了安装了oracle database之后sqlplus的简陋,无法删除无法上下翻页的苦恼。 可以安装readline和rlwrap插件的话,配置.bahs_profile后也能解决上下翻页这些,但是很多生产环境无法安装rpm包。 oracle提供了sqlcl免费许可,…...
