USB总线-Linux内核USB3.0主机控制器驱动框架分析(十二)
1.概述
如下图所示,Linux内核中USB主机体系结构由五部分组成,分别为Application Software、USB Class Driver、USB Core(USB Driver)、USB Host Controller Driver、USB Host Controller。应用程序处于用户空间,通过系统调用访问Class Driver,从而间接的访问USB设备,如主机端的应用程序aplay、arecord可以访问USB音频设备。Class Driver是某一类设备驱动,不同类设备会匹配不同的Class Driver,如USB音频设备会匹配Audio驱动,USB存储设备会匹配Mass Storage驱动,鼠标和键盘会匹配HID驱动。USB Core(USB Driver)是内核设计的一个抽象层,目的是将Class Driver和USB Host Controller Driver分隔开,使两者都依赖一个稳定的中间层;USB Core(USB Driver)向上提供通信接口,向下统一管理USB设备,同时完成USB设备和USB Class Driver的匹配工作。USB Host Controller目前有4种不同的硬件级接口标准,分别为OHCI、UHCI、EHCI、xHCI,OHCI和UHCI实现了USB1.1,EHCI实现了USB2.0,xHCI实现了USB3.2,不同的接口标准都有对应的USB Host Controller Driver,如xHCI对应于xhci-hcd驱动,向下兼容OHCI和EHCI。最底层是USB Host Controller硬件。下面将分别介绍Linux内核中USB主机体系结构USB Class Driver、USB Core(USB Driver)、USB Host Controller Driver四个部分。


2.USB Class Driver
Linux内核使用struct usb_driver数据结构描述USB Class Driver,使用usb_register和usb_deregister注册、注销struct usb_driver。USB Class Driver可以使用module_usb_driver宏定义注册驱动。需要注意的是,USB Class Driver是针对USB接口的,如果一个设备是复合设备,每个接口都有不同的功能,则每个接口都有对应的USB Class Driver。主机枚举设备的时候,会识别每个接口的功能同时匹配对应的struct usb_driver,匹配成功后struct usb_driver的probe函数被调用。
[include/linux/usb.h]
struct usb_driver {const char *name; /* USB Class Driver名称,必须唯一且和模块名称一样 *//* 当USB设备的接口和驱动匹配成功后,该函数被调用 */int (*probe) (struct usb_interface *intf,const struct usb_device_id *id);/* 断开USB设备或者卸载驱动模块时调用 */void (*disconnect) (struct usb_interface *intf);/* usbf接口,用户空间可以通过该函数和驱动通信 */int (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct usb_interface *intf,unsigned int code, void *buf);/* 功耗管理相关函数 */int (*suspend) (struct usb_interface *intf, pm_message_t message);int (*resume) (struct usb_interface *intf);int (*reset_resume)(struct usb_interface *intf);/* Called by usb_reset_device() when the device is about to be* reset. This routine must not return until the driver has no active* URBs for the device, and no more URBs may be submitted until the* post_reset method is called. */int (*pre_reset)(struct usb_interface *intf);/* Called by usb_reset_device() after the device has been reset */int (*post_reset)(struct usb_interface *intf);/* 用于匹配USB Class Driver */const struct usb_device_id *id_table;const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;struct usb_dynids dynids;struct usbdrv_wrap drvwrap;unsigned int no_dynamic_id:1;/* if set to 0, the USB core will not allow autosuspend for* interfaces bound to this driver */unsigned int supports_autosuspend:1;/* if set to 1, the USB core will not allow hubs* to initiate lower power link state transitions when an idle timeout* occurs. Device-initiated USB 3.0 link PM will still be allowed.*/unsigned int disable_hub_initiated_lpm:1;/* if set to 1, the USB core will not kill URBs and disable* endpoints before calling the driver's disconnect method.*/unsigned int soft_unbind:1;......
};
/** use these in module_init()/module_exit()* and don't forget MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(usb, ...)*/
extern int usb_register_driver(struct usb_driver *, struct module *,const char *);/* use a define to avoid include chaining to get THIS_MODULE & friends */
#define usb_register(driver) \usb_register_driver(driver, THIS_MODULE, KBUILD_MODNAME)extern void usb_deregister(struct usb_driver *);
/*** module_usb_driver() - Helper macro for registering a USB driver* @__usb_driver: usb_driver struct** Helper macro for USB drivers which do not do anything special in module* init/exit. This eliminates a lot of boilerplate. Each module may only* use this macro once, and calling it replaces module_init() and module_exit()*/
#define module_usb_driver(__usb_driver) \module_driver(__usb_driver, usb_register, usb_deregister)
下面是USB Mass Storage的USB Class Driver定义,使用module_usb_stor_driver宏进行注册。U盘、USB硬盘都使用下面的驱动。
[drivers/usb/storage/usb.c]
#define DRV_NAME "usb-storage"
static struct usb_driver usb_storage_driver = {.name = DRV_NAME,.probe = storage_probe,.disconnect = usb_stor_disconnect,.suspend = usb_stor_suspend,.resume = usb_stor_resume,.reset_resume = usb_stor_reset_resume,.pre_reset = usb_stor_pre_reset,.post_reset = usb_stor_post_reset,.id_table = usb_storage_usb_ids,.supports_autosuspend = 1,.soft_unbind = 1,
};
module_usb_stor_driver(usb_storage_driver, usb_stor_host_template, DRV_NAME);[drivers/usb/storage/usb.h]
#define module_usb_stor_driver(__driver, __sht, __name) \
static int __init __driver##_init(void) \
{ \usb_stor_host_template_init(&(__sht), __name, THIS_MODULE); \return usb_register(&(__driver)); \
} \
module_init(__driver##_init); \
static void __exit __driver##_exit(void) \
{ \usb_deregister(&(__driver)); \
} \
module_exit(__driver##_exit)
3.USB Core(USB Driver)
USB Core(USB Driver)有三个功能,第一是向USB Class Driver提供通信接口,第二是匹配驱动,第三是管理USB Device。
3.1.通信接口
USB Core(USB Driver)层封装了USB Request Block数据结构,即struct urb。USB Class Driver只需要分配并填充struct urb,然后调用通信接口将struct urb提交到USB Core(USB Driver)层即可完成和USB设备的通信。
[include/linux/usb.h]
struct urb {/* private: usb core and host controller only fields in the urb */struct kref kref; /* reference count of the URB */int unlinked; /* unlink error code */void *hcpriv; /* private data for host controller */atomic_t use_count; /* concurrent submissions counter */atomic_t reject; /* submissions will fail *//* public: documented fields in the urb that can be used by drivers */struct list_head urb_list; /* list head for use by the urb's current owner */struct list_head anchor_list; /* the URB may be anchored */struct usb_anchor *anchor;struct usb_device *dev; /* (in) pointer to associated device */struct usb_host_endpoint *ep; /* (internal) pointer to endpoint */unsigned int pipe; /* (in) pipe information */unsigned int stream_id; /* (in) stream ID */int status; /* (return) non-ISO status */unsigned int transfer_flags; /* (in) URB_SHORT_NOT_OK | ...*/void *transfer_buffer; /* (in) associated data buffer */dma_addr_t transfer_dma; /* (in) dma addr for transfer_buffer */struct scatterlist *sg; /* (in) scatter gather buffer list */int num_mapped_sgs; /* (internal) mapped sg entries */int num_sgs; /* (in) number of entries in the sg list */u32 transfer_buffer_length; /* (in) data buffer length */u32 actual_length; /* (return) actual transfer length */unsigned char *setup_packet; /* (in) setup packet (control only) */dma_addr_t setup_dma; /* (in) dma addr for setup_packet */int start_frame; /* (modify) start frame (ISO) */int number_of_packets; /* (in) number of ISO packets */int interval; /* (modify) transfer interval (INT/ISO) */int error_count; /* (return) number of ISO errors */void *context; /* (in) context for completion */usb_complete_t complete; /* (in) completion routine */......
};
主要的通信接口定义如下,包含分配、释放、填充、提交和取消URB。提交URB的接口包含了同步接口和异步接口,异步接口经过封装得到同步接口。内核没有封装ISOC传输类型的同步接口,因此ISOC传输只能使用异步接口。
/* initializes a control urb */
static inline void usb_fill_control_urb(struct urb *urb,struct usb_device *dev, unsigned int pipe,unsigned char *setup_packet, void *transfer_buffer,int buffer_length, usb_complete_t complete_fn, void *context)
{......
}
/* macro to help initialize a bulk urb */
static inline void usb_fill_bulk_urb(struct urb *urb,struct usb_device *dev, unsigned int pipe,void *transfer_buffer, int buffer_length,usb_complete_t complete_fn, void *context)
{......
}
/* macro to help initialize a interrupt urb */
static inline void usb_fill_int_urb(struct urb *urb,struct usb_device *dev, unsigned int pipe,void *transfer_buffer, int buffer_length,usb_complete_t complete_fn, void *context, int interval)
{......
}
extern void usb_init_urb(struct urb *urb);
extern struct urb *usb_alloc_urb(int iso_packets, gfp_t mem_flags);
extern void usb_free_urb(struct urb *urb);/* issue an asynchronous transfer request for an endpoint */
extern int usb_submit_urb(struct urb *urb, gfp_t mem_flags);
/* abort/cancel a transfer request for an endpoint */
extern int usb_unlink_urb(struct urb *urb);/* Builds a control urb, sends it off and waits for completion */
extern int usb_control_msg(struct usb_device *dev, unsigned int pipe,__u8 request, __u8 requesttype, __u16 value, __u16 index,void *data, __u16 size, int timeout);
/* Builds an interrupt urb, sends it off and waits for completion */
extern int usb_interrupt_msg(struct usb_device *usb_dev, unsigned int pipe,void *data, int len, int *actual_length, int timeout);
/* Builds a bulk urb, sends it off and waits for completion */
extern int usb_bulk_msg(struct usb_device *usb_dev, unsigned int pipe,void *data, int len, int *actual_length, int timeout);
通信的目的由pipe表示,pipe的位定义如下所示,其包含了USB设备地址、传输类型、传输方向、端点编号信息。内核提供了一系列定义pipe和解析pipe的宏定义,驱动可以直接使用。
/** For various legacy reasons, Linux has a small cookie that's paired with* a struct usb_device to identify an endpoint queue. Queue characteristics* are defined by the endpoint's descriptor. This cookie is called a "pipe",* an unsigned int encoded as:** - direction: bit 7 (0 = Host-to-Device [Out],* 1 = Device-to-Host [In] ...* like endpoint bEndpointAddress)* - device address: bits 8-14 ... bit positions known to uhci-hcd* - endpoint: bits 15-18 ... bit positions known to uhci-hcd* - pipe type: bits 30-31 (00 = isochronous, 01 = interrupt,* 10 = control, 11 = bulk)** Given the device address and endpoint descriptor, pipes are redundant.*//* NOTE: these are not the standard USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_* values!! */
/* (yet ... they're the values used by usbfs) */
#define PIPE_ISOCHRONOUS 0
#define PIPE_INTERRUPT 1
#define PIPE_CONTROL 2
#define PIPE_BULK 3#define usb_pipein(pipe) ((pipe) & USB_DIR_IN)
#define usb_pipeout(pipe) (!usb_pipein(pipe))#define usb_pipedevice(pipe) (((pipe) >> 8) & 0x7f)
#define usb_pipeendpoint(pipe) (((pipe) >> 15) & 0xf)#define usb_pipetype(pipe) (((pipe) >> 30) & 3)
#define usb_pipeisoc(pipe) (usb_pipetype((pipe)) == PIPE_ISOCHRONOUS)
#define usb_pipeint(pipe) (usb_pipetype((pipe)) == PIPE_INTERRUPT)
#define usb_pipecontrol(pipe) (usb_pipetype((pipe)) == PIPE_CONTROL)
#define usb_pipebulk(pipe) (usb_pipetype((pipe)) == PIPE_BULK)static inline unsigned int __create_pipe(struct usb_device *dev,unsigned int endpoint)
{return (dev->devnum << 8) | (endpoint << 15);
}/* Create various pipes... */
#define usb_sndctrlpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_CONTROL << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint))
#define usb_rcvctrlpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_CONTROL << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint) | USB_DIR_IN)
#define usb_sndisocpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_ISOCHRONOUS << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint))
#define usb_rcvisocpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_ISOCHRONOUS << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint) | USB_DIR_IN)
#define usb_sndbulkpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_BULK << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint))
#define usb_rcvbulkpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_BULK << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint) | USB_DIR_IN)
#define usb_sndintpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_INTERRUPT << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint))
#define usb_rcvintpipe(dev, endpoint) \((PIPE_INTERRUPT << 30) | __create_pipe(dev, endpoint) | USB_DIR_IN)
创建pipe需要两个参数,一个是struct usb_device和endpoint,endpoint为端点描述符中的bEndpointAddress。当USB Class Driver的probe函数被调用时,内核会传入一个和该驱动匹配成功的接口的数据结构,即struct usb_interface。驱动可以通过interface_to_usbdev函数从struct usb_interface获取struct usb_device,endpoint通过usb_find_xx系列函数中获取(ISOC传输需要驱动自己从struct usb_host_interface数据结构中解析)。
[include/linux/usb.h]
struct usb_interface {/* array of alternate settings for this interface,* stored in no particular order */struct usb_host_interface *altsetting;struct usb_host_interface *cur_altsetting; /* the currently* active alternate setting */unsigned num_altsetting; /* number of alternate settings *//* If there is an interface association descriptor then it will list* the associated interfaces */struct usb_interface_assoc_descriptor *intf_assoc;int minor; /* minor number this interface is bound to */enum usb_interface_condition condition; /* state of binding */unsigned sysfs_files_created:1; /* the sysfs attributes exist */unsigned ep_devs_created:1; /* endpoint "devices" exist */unsigned unregistering:1; /* unregistration is in progress */unsigned needs_remote_wakeup:1; /* driver requires remote wakeup */unsigned needs_altsetting0:1; /* switch to altsetting 0 is pending */unsigned needs_binding:1; /* needs delayed unbind/rebind */unsigned resetting_device:1; /* true: bandwidth alloc after reset */unsigned authorized:1; /* used for interface authorization */struct device dev; /* interface specific device info */struct device *usb_dev;struct work_struct reset_ws; /* for resets in atomic context */......
};
#define to_usb_device(d) container_of(d, struct usb_device, dev)static inline struct usb_device *interface_to_usbdev(struct usb_interface *intf)
{return to_usb_device(intf->dev.parent);
}
int __must_check
usb_find_common_endpoints(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_in,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_out,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_in,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_out);int __must_check
usb_find_common_endpoints_reverse(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_in,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_out,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_in,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_out);static inline int __must_check
usb_find_bulk_in_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_in)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints(alt, bulk_in, NULL, NULL, NULL);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_bulk_out_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_out)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints(alt, NULL, bulk_out, NULL, NULL);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_int_in_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_in)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints(alt, NULL, NULL, int_in, NULL);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_int_out_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_out)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints(alt, NULL, NULL, NULL, int_out);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_last_bulk_in_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_in)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints_reverse(alt, bulk_in, NULL, NULL, NULL);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_last_bulk_out_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **bulk_out)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints_reverse(alt, NULL, bulk_out, NULL, NULL);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_last_int_in_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_in)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints_reverse(alt, NULL, NULL, int_in, NULL);
}static inline int __must_check
usb_find_last_int_out_endpoint(struct usb_host_interface *alt,struct usb_endpoint_descriptor **int_out)
{return usb_find_common_endpoints_reverse(alt, NULL, NULL, NULL, int_out);
}
3.2.匹配驱动和设备及接口
USB Class Driver和USB设备接口、USB设备和USB Core(USB Driver)都是通过struct usb_device_id中的信息进行匹配。struct usb_device_id定义了4中匹配方式,第一种是产品信息匹配,通常情况使用VID和PID;第二种是根据设备类信息进行匹配;第三种根据接口的类信息进行匹配,第四种根据厂家自定义的接口进行匹配。具体使用那种匹配方式,由match_flags决定,内核定义了USB_DEVICE_ID_xx开头的宏,用来设置match_flags。USB Class Driver和USB设备接口、USB设备和USB Core(USB Driver)的匹配工作由usb_bus_type中的usb_device_match函数完成,该函数会进一步调用usb_match_id进行匹配。
[include/linux/mod_devicetable.h]
struct usb_device_id {/* which fields to match against? */__u16 match_flags;/* Used for product specific matches; range is inclusive */__u16 idVendor;__u16 idProduct;__u16 bcdDevice_lo;__u16 bcdDevice_hi;/* Used for device class matches */__u8 bDeviceClass;__u8 bDeviceSubClass;__u8 bDeviceProtocol;/* Used for interface class matches */__u8 bInterfaceClass;__u8 bInterfaceSubClass;__u8 bInterfaceProtocol;/* Used for vendor-specific interface matches */__u8 bInterfaceNumber;/* not matched against */kernel_ulong_t driver_info__attribute__((aligned(sizeof(kernel_ulong_t))));
};
/* Some useful macros to use to create struct usb_device_id */
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR 0x0001
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT 0x0002
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_LO 0x0004
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_HI 0x0008
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_CLASS 0x0010
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_SUBCLASS 0x0020
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_PROTOCOL 0x0040
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_CLASS 0x0080
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_SUBCLASS 0x0100
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_PROTOCOL 0x0200
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_NUMBER 0x0400[include/linux/usb.h]
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEVICE \(USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_VENDOR | USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_PRODUCT)
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_RANGE \(USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_LO | USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_HI)
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEVICE_AND_VERSION \(USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEVICE | USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_RANGE)
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_INFO \(USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_CLASS | \USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_SUBCLASS | \USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEV_PROTOCOL)
#define USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_INFO \(USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_CLASS | \USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_SUBCLASS | \USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_PROTOCOL)/*** USB_DEVICE - macro used to describe a specific usb device* @vend: the 16 bit USB Vendor ID* @prod: the 16 bit USB Product ID** This macro is used to create a struct usb_device_id that matches a* specific device.*/
#define USB_DEVICE(vend, prod) \.match_flags = USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_DEVICE, \.idVendor = (vend), \.idProduct = (prod)/*** USB_INTERFACE_INFO - macro used to describe a class of usb interfaces* @cl: bInterfaceClass value* @sc: bInterfaceSubClass value* @pr: bInterfaceProtocol value** This macro is used to create a struct usb_device_id that matches a* specific class of interfaces.*/
#define USB_INTERFACE_INFO(cl, sc, pr) \.match_flags = USB_DEVICE_ID_MATCH_INT_INFO, \.bInterfaceClass = (cl), \.bInterfaceSubClass = (sc), \.bInterfaceProtocol = (pr)
......const struct usb_device_id *usb_match_id(struct usb_interface *interface,const struct usb_device_id *id);
extern struct bus_type usb_bus_type;[drivers/usb/core/driver.c]
struct bus_type usb_bus_type = {.name = "usb",.match = usb_device_match,.uevent = usb_uevent,.need_parent_lock = true,
};
struct usb_driver定义的USB Class Driver驱动和USB设备的接口匹配,而struct usb_device_driver定义的驱动和USB设备匹配,使用usb_register_device_driver和usb_deregister_device_driver函数注册和注销struct usb_device_driver。内核提供了通用的struct usb_device_driver,即usb_generic_driver,在USB子系统初始化的时候注册到系统中,通常情况下USB Class Driver无需再提供struct usb_device_driver。
[include/linux/usb.h]
struct usb_device_driver {const char *name;/* If set, used for better device/driver matching. */bool (*match) (struct usb_device *udev);/* Called to see if the driver is willing to manage a particular* device. If it is, probe returns zero and uses dev_set_drvdata()* to associate driver-specific data with the device. If unwilling* to manage the device, return a negative errno value. */int (*probe) (struct usb_device *udev);/* Called when the device is no longer accessible, usually* because it has been (or is being) disconnected or the driver's* module is being unloaded.*/void (*disconnect) (struct usb_device *udev);int (*suspend) (struct usb_device *udev, pm_message_t message);int (*resume) (struct usb_device *udev, pm_message_t message);const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;struct usbdrv_wrap drvwrap;/* used with @match() to select better matching driver at probe() time.*/const struct usb_device_id *id_table;unsigned int supports_autosuspend:1;unsigned int generic_subclass:1;
};extern int usb_register_device_driver(struct usb_device_driver *,struct module *);
extern void usb_deregister_device_driver(struct usb_device_driver *);
extern struct usb_device_driver usb_generic_driver;[drivers/usb/core/generic.c]
struct usb_device_driver usb_generic_driver = {.name = "usb",.match = usb_generic_driver_match,.probe = usb_generic_driver_probe,.disconnect = usb_generic_driver_disconnect,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM.suspend = usb_generic_driver_suspend,.resume = usb_generic_driver_resume,
#endif.supports_autosuspend = 1,
};
3.3.管理设备
USB Core(USB Driver)使用struct usb_device数据结构描述USB设备。该数据结构在系统枚举USB设备的时候,由usb_alloc_dev函数分配和usb_new_device初始化。
[include/linux/usb.h]
struct usb_device {/* device number; address on a USB bus */int devnum;/* device ID string for use in messages (e.g., /port/...) */char devpath[16];/* tree topology hex string for use with xHCI */u32 route;/* device state: configured, not attached, etc. */enum usb_device_state state;/* device speed: high/full/low (or error) */enum usb_device_speed speed;/* number of rx lanes in use, USB 3.2 adds dual-lane support */unsigned int rx_lanes;/* number of tx lanes in use, USB 3.2 adds dual-lane support */unsigned int tx_lanes;/* Transaction Translator info; used with low/full speed dev,* highspeed hub */struct usb_tt *tt;int ttport; /* device port on that tt hub *//* one bit for each endpoint, with ([0] = IN, [1] = OUT) endpoints */unsigned int toggle[2];/* our hub, unless we're the root */struct usb_device *parent;struct usb_bus *bus; /* bus we're part of *//* endpoint 0 data (default control pipe) */struct usb_host_endpoint ep0;struct device dev; /* generic device interface *//* USB device descriptor */struct usb_device_descriptor descriptor;struct usb_host_bos *bos;/* all of the device's configs */struct usb_host_config *config;/* the active configuration */struct usb_host_config *actconfig;struct usb_host_endpoint *ep_in[16]; /* array of IN endpoints */struct usb_host_endpoint *ep_out[16]; /* array of OUT endpoints */char **rawdescriptors; /* raw descriptors for each config *//* Current available from the bus */unsigned short bus_mA;u8 portnum; /* parent port number (origin 1) */u8 level; /* number of USB hub ancestors *//* device address, XHCI: assigned by HW, others: same as devnum */u8 devaddr;....../* ask driver core to reprobe using the generic driver */unsigned use_generic_driver:1;......
};[include/linux/usb/hcd.h]
/* Enumeration is only for the hub driver, or HCD virtual root hubs */
/* usb device constructor (usbcore-internal) */
extern struct usb_device *usb_alloc_dev(struct usb_device *parent,struct usb_bus *, unsigned port);
/* perform initial device setup (usbcore-internal) */
extern int usb_new_device(struct usb_device *dev);
/* disconnect a device (usbcore-internal) */
void usb_disconnect(struct usb_device **pdev);
4. USB Host Controller Driver
Linux内核使用struct usb_hcd数据结构描述USB Host Controller Driver,使用struct hc_driver描述USB Host Controller的操作方法,比如通信接口usb_submit_urb最终会调用到urb_enqueue函数,不同接口协议的USB Host Controller需要提供不同的struct hc_driver。使用usb_create_hcd和__usb_create_hcd函数创建struct usb_hcd,使用usb_add_hcd函数添加struct usb_hcd,使用usb_remove_hcd移除struct usb_hcd。
[include/linux/usb/hcd.h]
struct usb_hcd {struct usb_bus self; /* hcd is-a bus */struct kref kref; /* reference counter */const char *product_desc; /* product/vendor string */int speed; /* Speed for this roothub. */char irq_descr[24]; /* driver + bus # */struct timer_list rh_timer; /* drives root-hub polling */struct urb *status_urb; /* the current status urb */
#ifdef CONFIG_PMstruct work_struct wakeup_work; /* for remote wakeup */
#endifstruct work_struct died_work; /* for when the device dies *//* hardware info/state */const struct hc_driver *driver; /* hw-specific hooks *//* OTG and some Host controllers need software interaction with phys;* other external phys should be software-transparent*/struct usb_phy *usb_phy;struct usb_phy_roothub *phy_roothub;....../* bandwidth_mutex should be taken before adding or removing* any new bus bandwidth constraints:* 1. Before adding a configuration for a new device.* 2. Before removing the configuration to put the device into* the addressed state.* 3. Before selecting a different configuration.* 4. Before selecting an alternate interface setting.** bandwidth_mutex should be dropped after a successful control message* to the device, or resetting the bandwidth after a failed attempt.*/struct mutex *address0_mutex;struct mutex *bandwidth_mutex;struct usb_hcd *shared_hcd;struct usb_hcd *primary_hcd;......
};struct hc_driver {const char *description; /* "ehci-hcd" etc */const char *product_desc; /* product/vendor string */size_t hcd_priv_size; /* size of private data *//* irq handler */irqreturn_t (*irq) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);....../* called to init HCD and root hub */int (*reset) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);int (*start) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);/* NOTE: these suspend/resume calls relate to the HC as* a whole, not just the root hub; they're for PCI bus glue.*//* called after suspending the hub, before entering D3 etc */int (*pci_suspend)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, bool do_wakeup);/* called after entering D0 (etc), before resuming the hub */int (*pci_resume)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, bool hibernated);/* cleanly make HCD stop writing memory and doing I/O */void (*stop) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);/* shutdown HCD */void (*shutdown) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);/* return current frame number */int (*get_frame_number) (struct usb_hcd *hcd);/* manage i/o requests, device state */int (*urb_enqueue)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,struct urb *urb, gfp_t mem_flags);int (*urb_dequeue)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,struct urb *urb, int status);/** (optional) these hooks allow an HCD to override the default DMA* mapping and unmapping routines. In general, they shouldn't be* necessary unless the host controller has special DMA requirements,* such as alignment contraints. If these are not specified, the* general usb_hcd_(un)?map_urb_for_dma functions will be used instead* (and it may be a good idea to call these functions in your HCD* implementation)*/int (*map_urb_for_dma)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct urb *urb,gfp_t mem_flags);void (*unmap_urb_for_dma)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct urb *urb);/* hw synch, freeing endpoint resources that urb_dequeue can't */void (*endpoint_disable)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,struct usb_host_endpoint *ep);/* (optional) reset any endpoint state such as sequence numberand current window */void (*endpoint_reset)(struct usb_hcd *hcd,struct usb_host_endpoint *ep);/* root hub support */int (*hub_status_data) (struct usb_hcd *hcd, char *buf);int (*hub_control) (struct usb_hcd *hcd,u16 typeReq, u16 wValue, u16 wIndex, char *buf, u16 wLength);int (*bus_suspend)(struct usb_hcd *);int (*bus_resume)(struct usb_hcd *);int (*start_port_reset)(struct usb_hcd *, unsigned port_num);unsigned long (*get_resuming_ports)(struct usb_hcd *);/* force handover of high-speed port to full-speed companion */void (*relinquish_port)(struct usb_hcd *, int);/* has a port been handed over to a companion? */int (*port_handed_over)(struct usb_hcd *, int);/* CLEAR_TT_BUFFER completion callback */void (*clear_tt_buffer_complete)(struct usb_hcd *,struct usb_host_endpoint *);/* xHCI specific functions *//* Called by usb_alloc_dev to alloc HC device structures */int (*alloc_dev)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);/* Called by usb_disconnect to free HC device structures */void (*free_dev)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);/* Change a group of bulk endpoints to support multiple stream IDs */int (*alloc_streams)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct usb_device *udev,struct usb_host_endpoint **eps, unsigned int num_eps,unsigned int num_streams, gfp_t mem_flags);/* Reverts a group of bulk endpoints back to not using stream IDs.* Can fail if we run out of memory.*/int (*free_streams)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, struct usb_device *udev,struct usb_host_endpoint **eps, unsigned int num_eps,gfp_t mem_flags);/* Bandwidth computation functions *//* Note that add_endpoint() can only be called once per endpoint before* check_bandwidth() or reset_bandwidth() must be called.* drop_endpoint() can only be called once per endpoint also.* A call to xhci_drop_endpoint() followed by a call to* xhci_add_endpoint() will add the endpoint to the schedule with* possibly new parameters denoted by a different endpoint descriptor* in usb_host_endpoint. A call to xhci_add_endpoint() followed by a* call to xhci_drop_endpoint() is not allowed.*//* Allocate endpoint resources and add them to a new schedule */int (*add_endpoint)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *,struct usb_host_endpoint *);/* Drop an endpoint from a new schedule */int (*drop_endpoint)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *,struct usb_host_endpoint *);/* Check that a new hardware configuration, set using* endpoint_enable and endpoint_disable, does not exceed bus* bandwidth. This must be called before any set configuration* or set interface requests are sent to the device.*/int (*check_bandwidth)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);/* Reset the device schedule to the last known good schedule,* which was set from a previous successful call to* check_bandwidth(). This reverts any add_endpoint() and* drop_endpoint() calls since that last successful call.* Used for when a check_bandwidth() call fails due to resource* or bandwidth constraints.*/void (*reset_bandwidth)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);/* Returns the hardware-chosen device address */int (*address_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *udev);/* prepares the hardware to send commands to the device */int (*enable_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *udev);/* Notifies the HCD after a hub descriptor is fetched.* Will block.*/int (*update_hub_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *hdev,struct usb_tt *tt, gfp_t mem_flags);int (*reset_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);/* Notifies the HCD after a device is connected and its* address is set*/int (*update_device)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *);int (*set_usb2_hw_lpm)(struct usb_hcd *, struct usb_device *, int);/* USB 3.0 Link Power Management *//* Returns the USB3 hub-encoded value for the U1/U2 timeout. */int (*enable_usb3_lpm_timeout)(struct usb_hcd *,struct usb_device *, enum usb3_link_state state);/* The xHCI host controller can still fail the command to* disable the LPM timeouts, so this can return an error code.*/int (*disable_usb3_lpm_timeout)(struct usb_hcd *,struct usb_device *, enum usb3_link_state state);int (*find_raw_port_number)(struct usb_hcd *, int);/* Call for power on/off the port if necessary */int (*port_power)(struct usb_hcd *hcd, int portnum, bool enable);......
};struct usb_hcd *__usb_create_hcd(const struct hc_driver *driver,struct device *sysdev, struct device *dev, const char *bus_name,struct usb_hcd *primary_hcd);
/* create and initialize an HCD structure */
extern struct usb_hcd *usb_create_hcd(const struct hc_driver *driver,struct device *dev, const char *bus_name);
/* finish generic HCD structure initialization and register */
extern int usb_add_hcd(struct usb_hcd *hcd,unsigned int irqnum, unsigned long irqflags);
/* shutdown processing for generic HCDs */
extern void usb_remove_hcd(struct usb_hcd *hcd);
xHCI、EHCI、OHCI三种接口协议标准的USB Host Controller Driver的struct hc_driver定义如下。
[drivers/usb/host/xhci.c]
static const struct hc_driver xhci_hc_driver = {.description = "xhci-hcd",.product_desc = "xHCI Host Controller",.hcd_priv_size = sizeof(struct xhci_hcd),/* generic hardware linkage */.irq = xhci_irq,.flags = HCD_MEMORY | HCD_DMA | HCD_USB3 | HCD_SHARED | HCD_BH,/* basic lifecycle operations */.reset = NULL, /* xhci_plat_setup */.start = xhci_run, /* xhci_plat_start */.stop = xhci_stop,.shutdown = xhci_shutdown,/* managing i/o requests and associated device resources */.map_urb_for_dma = xhci_map_urb_for_dma,.urb_enqueue = xhci_urb_enqueue,.urb_dequeue = xhci_urb_dequeue,.alloc_dev = xhci_alloc_dev,.free_dev = xhci_free_dev,.alloc_streams = xhci_alloc_streams,.free_streams = xhci_free_streams,.add_endpoint = xhci_add_endpoint,.drop_endpoint = xhci_drop_endpoint,.endpoint_disable = xhci_endpoint_disable,.endpoint_reset = xhci_endpoint_reset,.check_bandwidth = xhci_check_bandwidth,.reset_bandwidth = xhci_reset_bandwidth,.address_device = xhci_address_device,.enable_device = xhci_enable_device,.update_hub_device = xhci_update_hub_device,.reset_device = xhci_discover_or_reset_device,/* scheduling support */.get_frame_number = xhci_get_frame,/* root hub support */.hub_control = xhci_hub_control,.hub_status_data = xhci_hub_status_data,.bus_suspend = xhci_bus_suspend,.bus_resume = xhci_bus_resume,.get_resuming_ports = xhci_get_resuming_ports,/* call back when device connected and addressed */.update_device = xhci_update_device,.set_usb2_hw_lpm = xhci_set_usb2_hardware_lpm,.enable_usb3_lpm_timeout = xhci_enable_usb3_lpm_timeout,.disable_usb3_lpm_timeout = xhci_disable_usb3_lpm_timeout,.find_raw_port_number = xhci_find_raw_port_number,.clear_tt_buffer_complete = xhci_clear_tt_buffer_complete,
};[drivers/usb/host/ehci-hcd.c]
static const struct hc_driver ehci_hc_driver = {.description = hcd_name,.product_desc = "EHCI Host Controller",.hcd_priv_size = sizeof(struct ehci_hcd),/* generic hardware linkage */.irq = ehci_irq,.flags = HCD_MEMORY | HCD_DMA | HCD_USB2 | HCD_BH,/* basic lifecycle operations */.reset = ehci_setup,.start = ehci_run,.stop = ehci_stop,.shutdown = ehci_shutdown,/* managing i/o requests and associated device resources */.urb_enqueue = ehci_urb_enqueue,.urb_dequeue = ehci_urb_dequeue,.endpoint_disable = ehci_endpoint_disable,.endpoint_reset = ehci_endpoint_reset,.clear_tt_buffer_complete = ehci_clear_tt_buffer_complete,/* scheduling support */.get_frame_number = ehci_get_frame,/* root hub support */.hub_status_data = ehci_hub_status_data,.hub_control = ehci_hub_control,.bus_suspend = ehci_bus_suspend,.bus_resume = ehci_bus_resume,.relinquish_port = ehci_relinquish_port,.port_handed_over = ehci_port_handed_over,.get_resuming_ports = ehci_get_resuming_ports,/* device support */.free_dev = ehci_remove_device,
};[drivers/usb/host/ohci-hcd.c]
static const struct hc_driver ohci_hc_driver = {.description = hcd_name,.product_desc = "OHCI Host Controller",.hcd_priv_size = sizeof(struct ohci_hcd),/* generic hardware linkage */.irq = ohci_irq,.flags = HCD_MEMORY | HCD_DMA | HCD_USB11,/* basic lifecycle operations */.reset = ohci_setup,.start = ohci_start,.stop = ohci_stop,.shutdown = ohci_shutdown,/* managing i/o requests and associated device resources */.urb_enqueue = ohci_urb_enqueue,.urb_dequeue = ohci_urb_dequeue,.endpoint_disable = ohci_endpoint_disable,/* scheduling support */.get_frame_number = ohci_get_frame,/* root hub support */.hub_status_data = ohci_hub_status_data,.hub_control = ohci_hub_control,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM.bus_suspend = ohci_bus_suspend,.bus_resume = ohci_bus_resume,
#endif.start_port_reset = ohci_start_port_reset,
};
5. USB子系统
Linux内核主机USB子系统的初始化入口如下所示,注册了usb_bus_type、usbfs_driver、usb_generic_driver,初始化了USB设备的设备号、hub等。
[drivers\usb\core\usb.c]
static int __init usb_init(void)
{......retval = bus_register(&usb_bus_type);if (retval)goto bus_register_failed;retval = bus_register_notifier(&usb_bus_type, &usb_bus_nb);if (retval)goto bus_notifier_failed;retval = usb_major_init();if (retval)goto major_init_failed;retval = usb_register(&usbfs_driver);if (retval)goto driver_register_failed;retval = usb_devio_init();if (retval)goto usb_devio_init_failed;retval = usb_hub_init();if (retval)goto hub_init_failed;retval = usb_register_device_driver(&usb_generic_driver, THIS_MODULE);if (!retval)goto out;......
}
static void __exit usb_exit(void)
{......usb_release_quirk_list();usb_deregister_device_driver(&usb_generic_driver);usb_major_cleanup();usb_deregister(&usbfs_driver);usb_devio_cleanup();usb_hub_cleanup();bus_unregister_notifier(&usb_bus_type, &usb_bus_nb);bus_unregister(&usb_bus_type);usb_acpi_unregister();usb_debugfs_cleanup();idr_destroy(&usb_bus_idr);
}
subsys_initcall(usb_init);
module_exit(usb_exit);
参考资料
- eXtensible Host Controller Interface for Universal Serial Bus
- Linux kernel 5.10
- Linux驱动开发实例
- Linux设备驱动开发详解
相关文章:

USB总线-Linux内核USB3.0主机控制器驱动框架分析(十二)
1.概述 如下图所示,Linux内核中USB主机体系结构由五部分组成,分别为Application Software、USB Class Driver、USB Core(USB Driver)、USB Host Controller Driver、USB Host Controller。应用程序处于用户空间,通过系统调用访问Class Drive…...
SQL模板-用户留存率计算
在这段实习中,我遇到了用户留存率计算的需求,这里做个总结。 首先来讲下,什么是用户留存? 在互联网行业中,用户在某段时间内开始使用应用,经过一段时间后,仍然继续使用该应用的用户。用户留存一…...
LeakCanary 源码详解(3)
上一篇:LeakCanary源码详解(2) 如果你是直接刷到这篇的,建议还是从1开始看,然后2,然后是这篇3,如果你只关注这篇的重点hprof 文件定位泄漏位置的感兴趣,可以试试直接读这篇ÿ…...

springboot使用SSE
1、pom文件 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency> 2、前端代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"en"> <head><meta ch…...

搞定ESD(一):静电放电测试标准解析
文章目录 一、基本术语与定义1.1 基本定义1.2 重要基本术语 二、静电放电发生器介绍2.1 静电放电发生器的特性:通用规范【GB/T17626.2-2018 标准】2.2 ESD 放电发生器电极规格要求:通用规范【GB/T17626.2-2018 标准】2.3 放电回路电缆的要求:…...
)
问界M7的诸多优点(自动驾驶走进我们的生活二)
博主一直在问界工厂工作,从未对自己工厂的车如此关注过;但问界系列上市后,经常在茶余饭后看B站视频,发现问界车越来越多不可比拟的优点如下: 一、绿牌 绿牌特权在重庆可以随时过桥,不受限号限制。 二、增…...

[运维|数据库] msql中的 FIND_IN_SET如何转化为pg数据中的ARRAY_POSITION的函数
在 MySQL 中,FIND_IN_SET 函数用于查找一个值是否存在于逗号分隔的字符串列表中。在 PostgreSQL 中,可以使用 string_to_array 函数将逗号分隔的字符串转换为数组,然后使用 ARRAY_POSITION 函数来查找值是否在数组中。 以下是如何将MySQL中的…...

LeetCode 面试题 05.03. 翻转数位
文章目录 一、题目二、Java 题解 一、题目 给定一个32位整数 num,你可以将一个数位从0变为1。请编写一个程序,找出你能够获得的最长的一串1的长度。 示例 1: 输入: num 1775(110111011112) 输出: 8 示例 2: 输入: num 7(01112)…...
Fiddler抓包工具配置+Jmeter基本使用
一、Fiddler抓包工具的配置和使用 在编写网关自动化脚本之前,得先学会如何抓包,这里以Fiddler为例。会抓包的同学可以跳过这一步,当然看看也是没坏处的…… 局域网络配置 将要进行抓包的手机与电脑连入同一局域网,电脑才能够抓到…...

IOTE 2023国际物联网展直击:芯与物发布全新定位芯片,助力多领域智能化发展
IOTE 2023国际物联网展,作为全球物联网领域的盛会,于9月20日在中国深圳拉开帷幕。北斗星通集团应邀参展,旗下专业从事物联网、消费类GNSS芯片研发设计的芯与物公司也随其亮相本届盛会。 展会上,芯与物展示了一系列创新的GNSS定位…...

【软件设计师-从小白到大牛】上午题基础篇:第二章 操作系统
文章目录 前言章节提要一、进程管理1、进程的状态2、前趋图3、进程的同步与互斥4、PV操作6、PV操作与前趋图7、死锁问题进程资源图(补充)真题链接 二、存储管理1、分区存储组织2、页式存储组织3、段式存储组织4、段页式存储组织5、快表6、页面置换算法单…...
【20230921】关于sing-box命令行程序开机自启动运行(Windows、Linux)
1 背景 sing-box是一个命令行程序,官网给出的教程是复制链接到Git Bash(windows)或终端运行(Linux)。每次开机都进行复制运行是一件繁琐的事情。 复制的内容其实就是下次并运行shell脚本,其实系统只需要运…...

LeetCode 75-02:字符串的最大公因子
前置知识:使用欧几里得算法求出最大公约数 func gcdOfStrings(str1 string, str2 string) string {if str1str2 ! str2str1 {return ""}return str1[:gcd(len(str1), len(str2))] }func gcd(a, b int)int{if b 0{return a}return gcd(b, a%b) }...

k8s1.19使用ceph14
一、静态 pv (rbd)方式 1、所有k8s节点安装依赖组件 注意:安装ceph-common软件包推荐使用软件包源与Ceph集群源相同,软件版本一致。 cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/ceph.repo << EOF [ceph] name=ceph baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ceph/rpm-nautilus/el7/x86_…...

Leetcode 50. Pow(x, n)
文章目录 题目代码(9.19 首刷看解析) 题目 Leetcode 50. Pow(x, n) 代码(9.19 首刷看解析) 快速幂 class Solution { public:double myPow(double x, int n) {if(n 0)return 1;if(n 1)return x;if(n INT_MIN) { // 避免-n整…...

hive分区表的元数据信息numRows显示为0
创建分区表 CREATE TABLE `dept_partition`(`deptno` int, `dname` string, `loc` string) PARTITIONED BY (...
Baumer工业相机堡盟工业相机如何通过BGAPI SDK设置相机的图像剪切(ROI)功能(C++)
Baumer工业相机堡盟工业相机如何通过BGAPI SDK设置相机的图像剪切(ROI)功能(C) Baumer工业相机Baumer工业相机的图像剪切(ROI)功能的技术背景CameraExplorer如何使用图像剪切(ROI)功…...
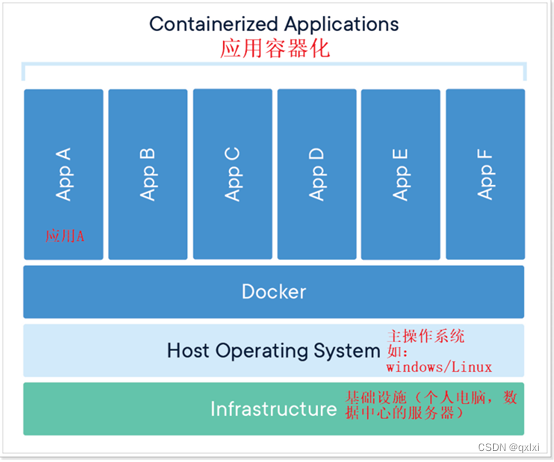
【云原生】聊聊为什么需要docker以及其基础架构
为什么需要docker 在没有docker之前,我们开发、测试、生产其实是根据不同的服务器进行配置的,很可能因为软件配置不同而导致的生产事故,那么如果能较好的解决软件和配置等封装成一个可运行的软件,无需关注配置,那么是…...
“高级前端开发技术探索路由的使用及Node安装使用“
目录 引言1. Vue路由的使用2. VueNode.js的安装使用总结 引言 在当今互联网时代,前端开发技术日新月异,不断涌现出各种新的框架和工具。作为一名前端开发者,我们需要不断学习和探索新的技术,以提升自己的开发能力。本文将深入探讨…...

LeetCode 494.目标和 (动态规划 + 性能优化)二维数组 压缩成 一维数组
494. 目标和 - 力扣(LeetCode) 给你一个非负整数数组 nums 和一个整数 target 。 向数组中的每个整数前添加 或 - ,然后串联起所有整数,可以构造一个 表达式 : 例如,nums [2, 1] ,可以在 2…...

深度学习在微纳光子学中的应用
深度学习在微纳光子学中的主要应用方向 深度学习与微纳光子学的结合主要集中在以下几个方向: 逆向设计 通过神经网络快速预测微纳结构的光学响应,替代传统耗时的数值模拟方法。例如设计超表面、光子晶体等结构。 特征提取与优化 从复杂的光学数据中自…...

模型参数、模型存储精度、参数与显存
模型参数量衡量单位 M:百万(Million) B:十亿(Billion) 1 B 1000 M 1B 1000M 1B1000M 参数存储精度 模型参数是固定的,但是一个参数所表示多少字节不一定,需要看这个参数以什么…...

条件运算符
C中的三目运算符(也称条件运算符,英文:ternary operator)是一种简洁的条件选择语句,语法如下: 条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2• 如果“条件表达式”为true,则整个表达式的结果为“表达式1”…...

智能在线客服平台:数字化时代企业连接用户的 AI 中枢
随着互联网技术的飞速发展,消费者期望能够随时随地与企业进行交流。在线客服平台作为连接企业与客户的重要桥梁,不仅优化了客户体验,还提升了企业的服务效率和市场竞争力。本文将探讨在线客服平台的重要性、技术进展、实际应用,并…...

PL0语法,分析器实现!
简介 PL/0 是一种简单的编程语言,通常用于教学编译原理。它的语法结构清晰,功能包括常量定义、变量声明、过程(子程序)定义以及基本的控制结构(如条件语句和循环语句)。 PL/0 语法规范 PL/0 是一种教学用的小型编程语言,由 Niklaus Wirth 设计,用于展示编译原理的核…...
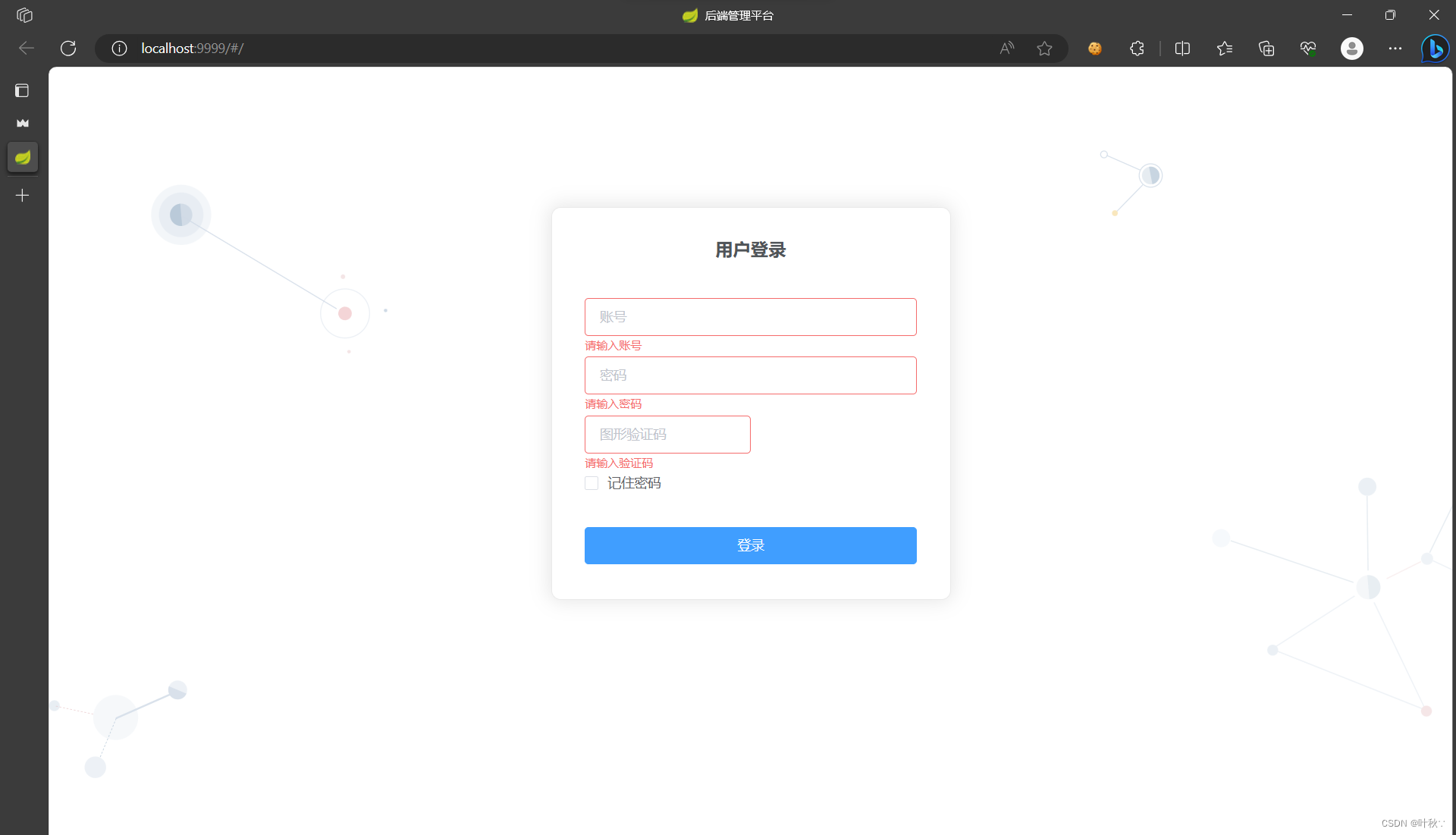
在WSL2的Ubuntu镜像中安装Docker
Docker官网链接: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/ 1、运行以下命令卸载所有冲突的软件包: for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done2、设置Docker…...
:观察者模式)
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式 一、引入 在开发中,我们经常会遇到这样的场景:一个对象的状态变化需要自动通知其他对象,比如: 电商平台中,商品库存变化时需要通知所有订阅该商品的用户;新闻网站中࿰…...
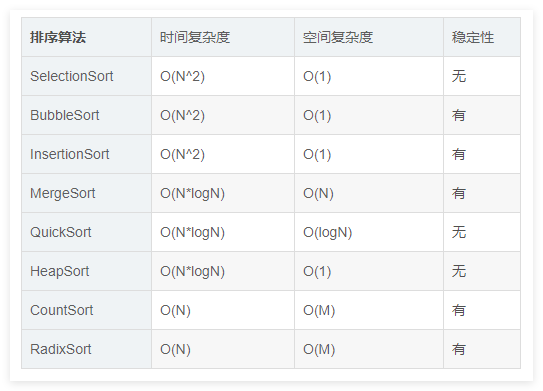
排序算法总结(C++)
目录 一、稳定性二、排序算法选择、冒泡、插入排序归并排序随机快速排序堆排序基数排序计数排序 三、总结 一、稳定性 排序算法的稳定性是指:同样大小的样本 **(同样大小的数据)**在排序之后不会改变原始的相对次序。 稳定性对基础类型对象…...
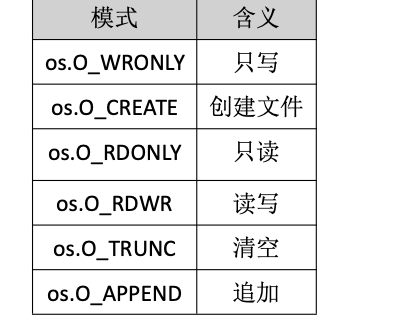
Golang——9、反射和文件操作
反射和文件操作 1、反射1.1、reflect.TypeOf()获取任意值的类型对象1.2、reflect.ValueOf()1.3、结构体反射 2、文件操作2.1、os.Open()打开文件2.2、方式一:使用Read()读取文件2.3、方式二:bufio读取文件2.4、方式三:os.ReadFile读取2.5、写…...

API网关Kong的鉴权与限流:高并发场景下的核心实践
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 引言 在微服务架构中,API网关承担着流量调度、安全防护和协议转换的核心职责。作为云原生时代的代表性网关,Kong凭借其插件化架构…...
