【OpenAI】基于 Gym-CarRacing 的自动驾驶练习项目 | 路径训练功能的实现 | GYM-Box2D CarRacing
 限时开放,猛戳订阅! 👉 《一起玩蛇》🐍
限时开放,猛戳订阅! 👉 《一起玩蛇》🐍
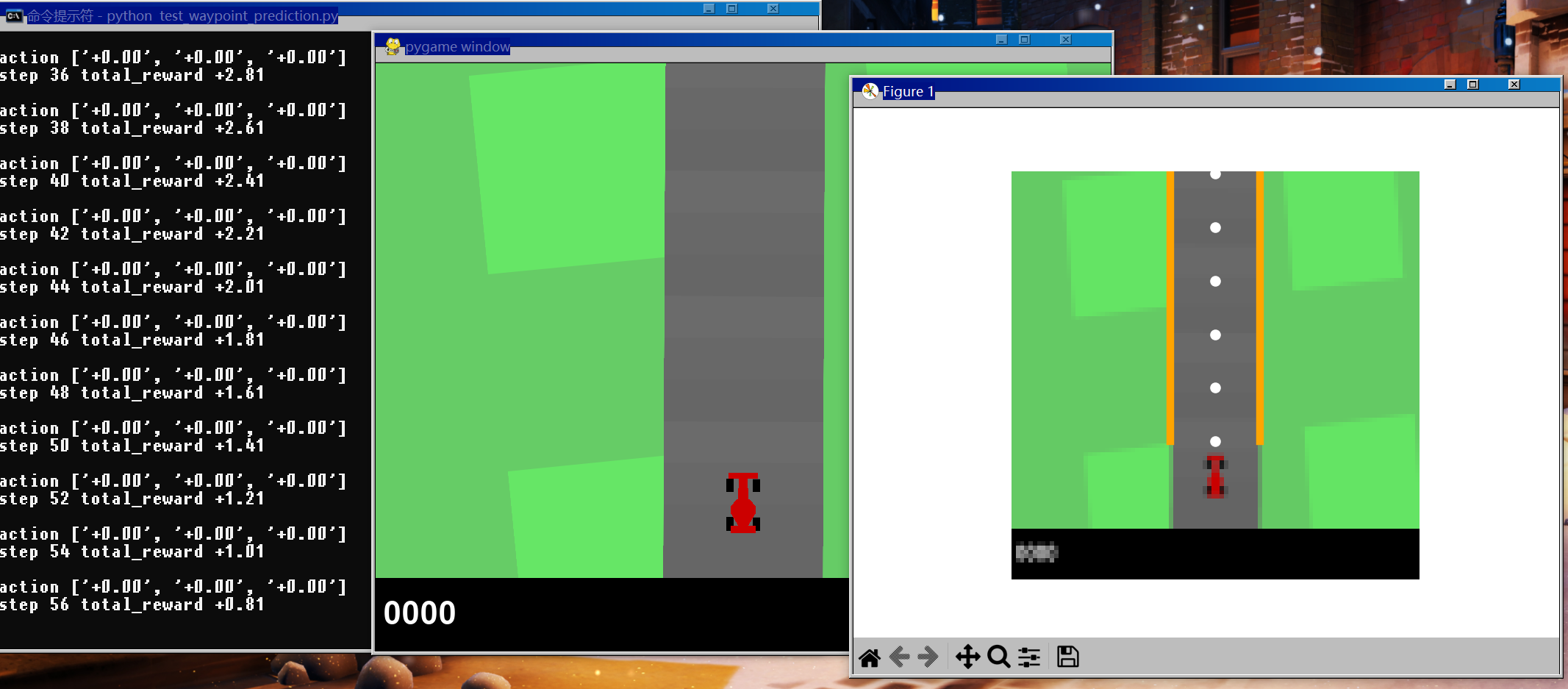
💭 写在前面: 本篇是关于多伦多大学自动驾驶专业项目的博客。GYM-Box2D CarRacing 是一种在 OpenAI Gym 平台上开发和比较强化学习算法的模拟环境。它是流行的 Box2D 物理引擎的一个版本,经过修改以支持模拟汽车在赛道上行驶的物理过程。模块化组件 (Modular Pipeline) 分为 低层次感知与场景解析、路径训练 和车辆控制,本章我们要讲解的内容是 路径训练 (Path training) 部分。
🔗 多伦多大学自动驾驶专项课程:Motion Planning for Self-Driving Cars | Coursera
🔗 Gym Car Racing 文档:Car Racing - Gym Documentation
Ⅰ. 前置知识(Antecedent)
0x00 规划与决策
问题
- ➢ 目标:寻找并遵循一条从这里到目的地的路径(需要考虑静态基础设施和动态物体)
- ➢ 输入:车辆和感知的周围环境状态
- ➢ 输出:将路径或轨迹解析给车辆控制器
难点
- ➢ 驾驶情况和行为是非常复杂的
- ➢ 因此很难将其作为一个单一的优化问题来建模
然而要考虑的东西可远不止这些……
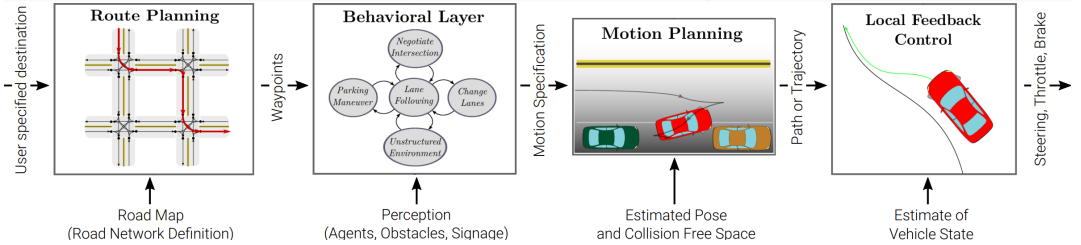
💡 思路:
- 将规划问题分解成更简单的问题的层次结构。
- 每个问题都根据其范围和抽象程度进行调整。
- 在这个层次结构中,越前意味着抽象程度越高。
- 每个优化问题都会有约束条件和目标函数。
路线规划:通过道路网络的路线。
行为层面:响应环境的运动规范。
运动规划:解决一个完成规范的可行路径。
反馈控制:调整执行变量以纠正执行路径中的错误。
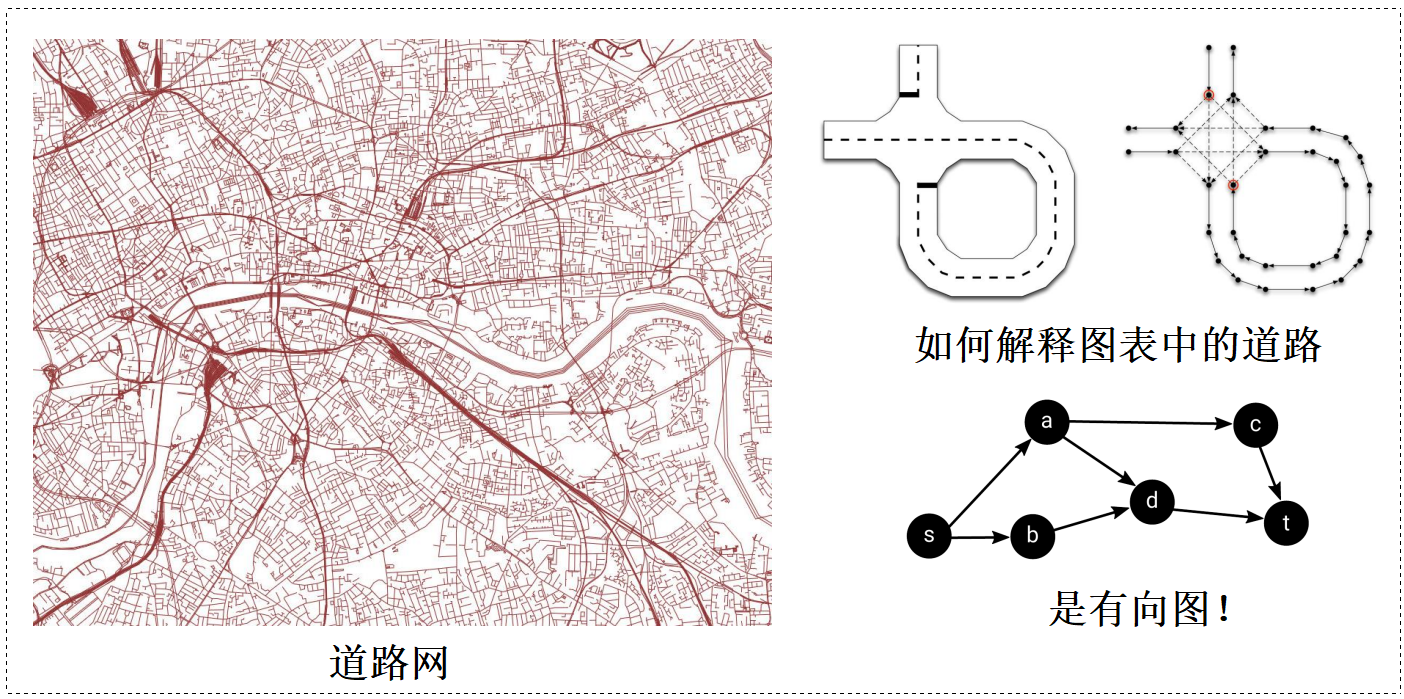
0x01 路径规划(Route Planning)
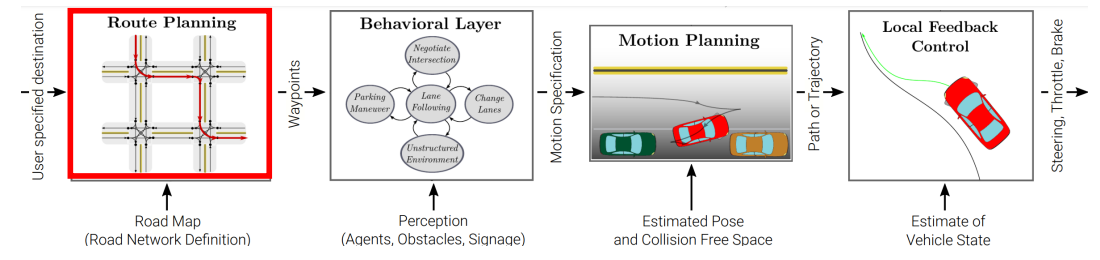
- 以有向图表示道路网络
- 边缘权重对应于路段长度或旅行时间
- 问题转化为一个最小成本的图网络问题
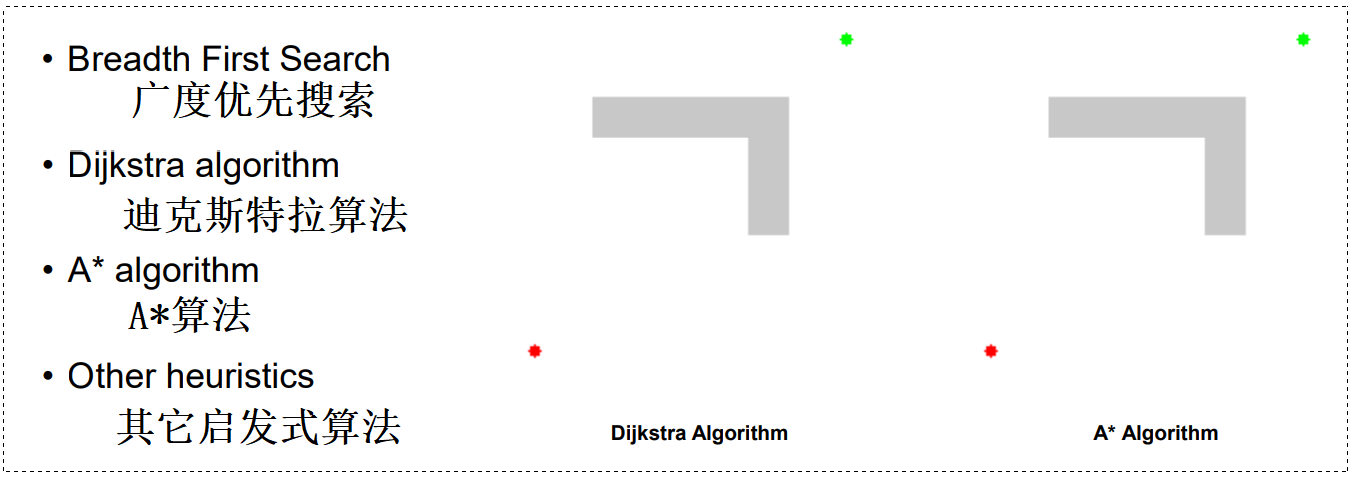
- 推理算法:狄克斯特拉算法,A∗ 算法,……
0x02 行为层(Behavioral Layer)
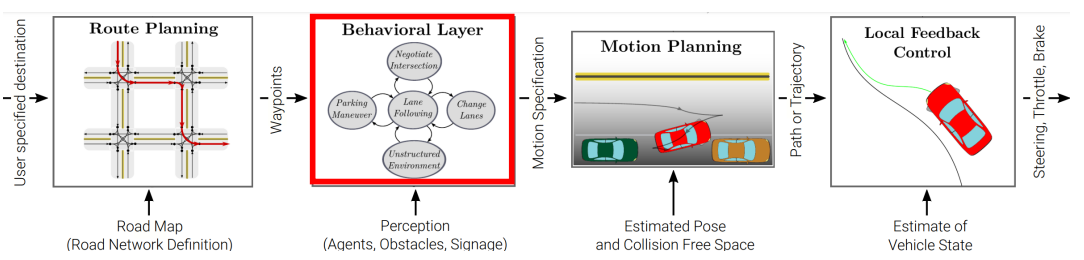
根据当前车辆 / 环境状态选择驾驶行为。
例如,在停车线:停车,观察其他交通参与者,穿行。
通常通过有限状态机进行建模(过渡由感知控制)。
可以通过概率建模,例如使用马尔科夫决策过程(MDPs)。
运动规划:
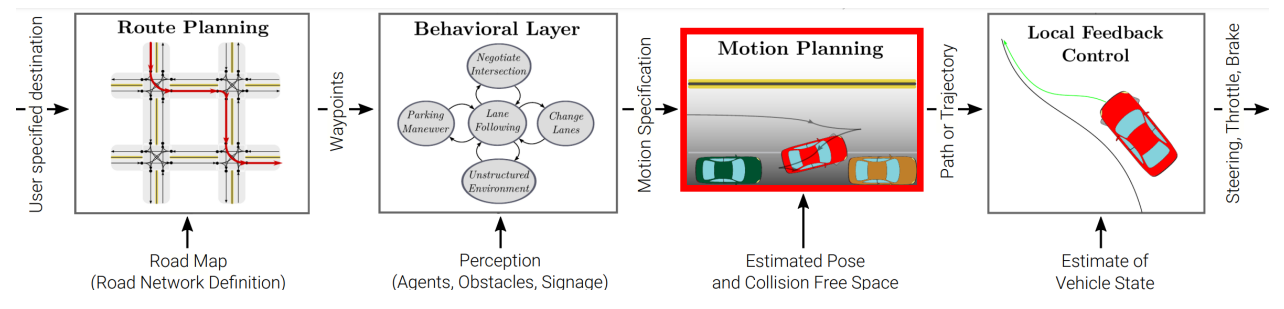
找到可行、舒适、安全和快速的车辆路径 / 轨迹。
在大多数情况下,精确解在计算上难以处理。因此,通常使用数值近似。
方法:变分法、图搜索、基于增量树 。
本地反馈控制:
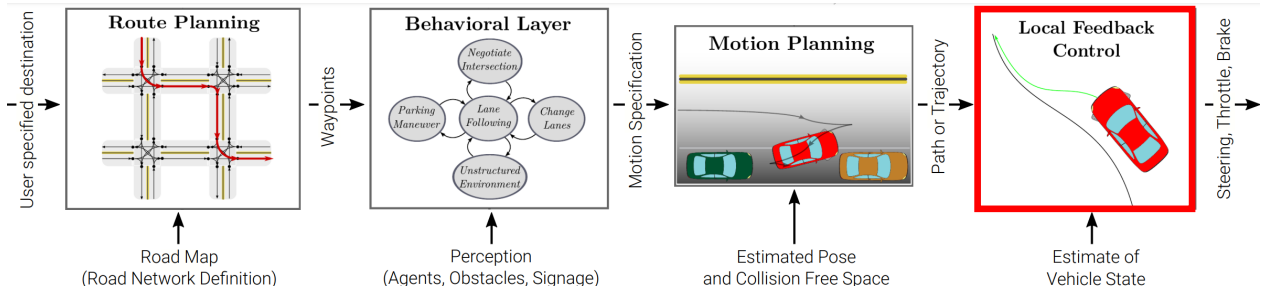
反馈控制器执行来自运动规划器的 路径 / 轨迹
修正了因车辆模型不准确而产生的错误
注重耐用性、稳定性和舒适性
车辆动力学与控制
路径算法:
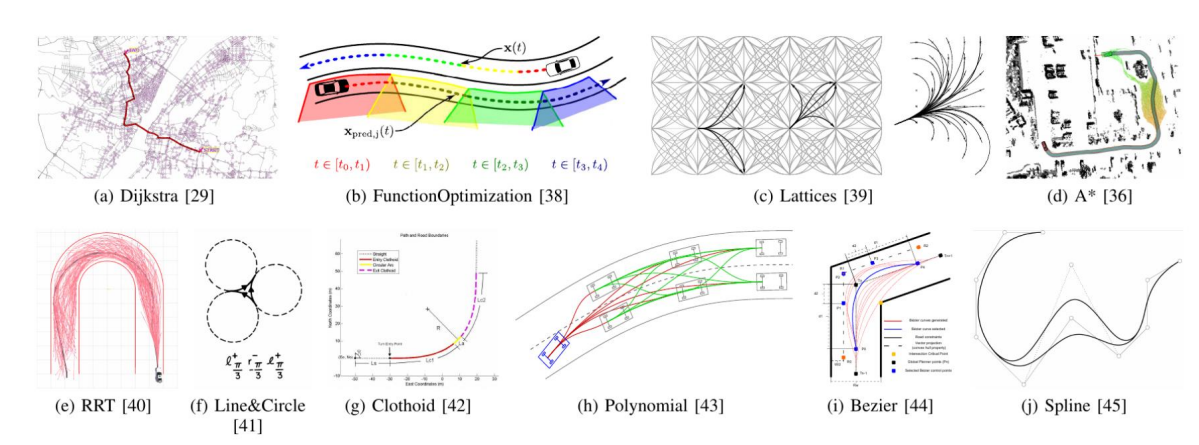
自动驾驶文献中使用的规划算法有很多,本章我们只关注其中的几个即可。
道路网络图:
路径规划算法:
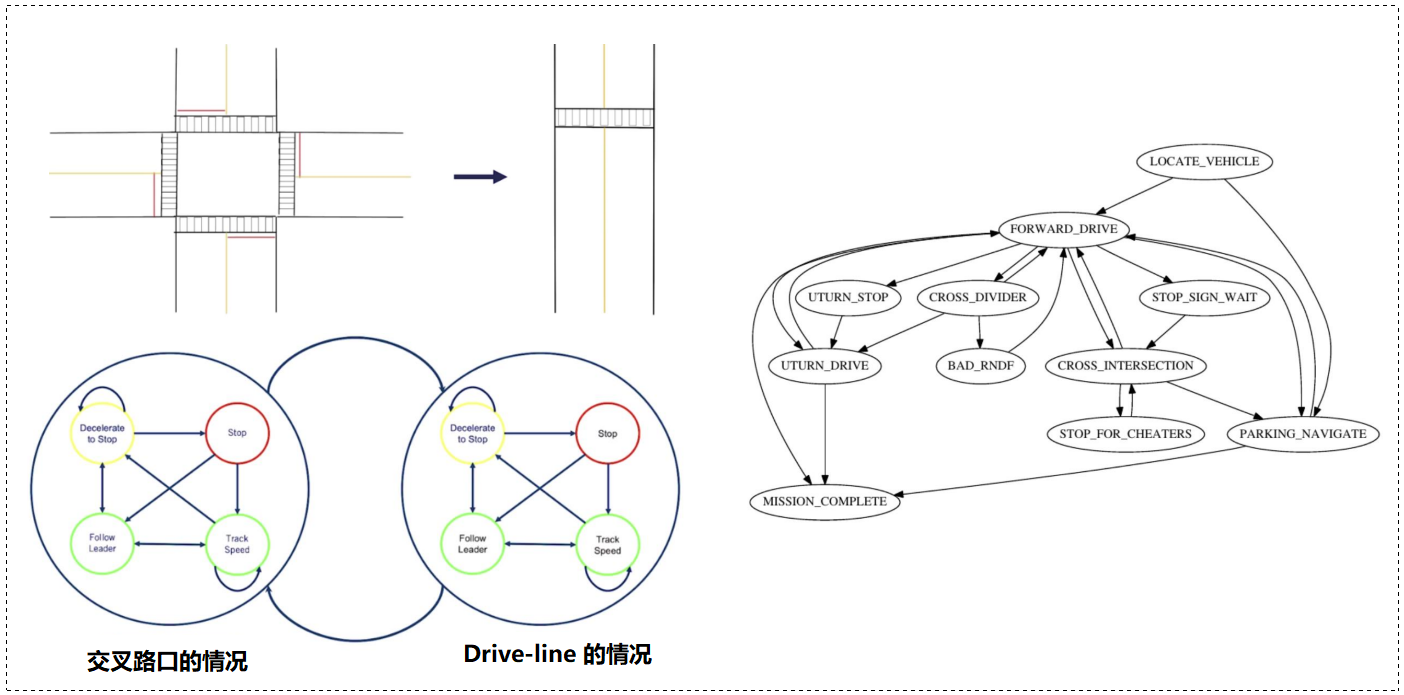
0x03 行为规划(Behavior Planning)
简单车辆行为的有限状态机:在驾驶过程中,汽车需要各种机动动作(减速、停车、沿车道行驶等)。将汽车行为离散化为原子机动,开发人员为每个机动设计一个运动规划器。
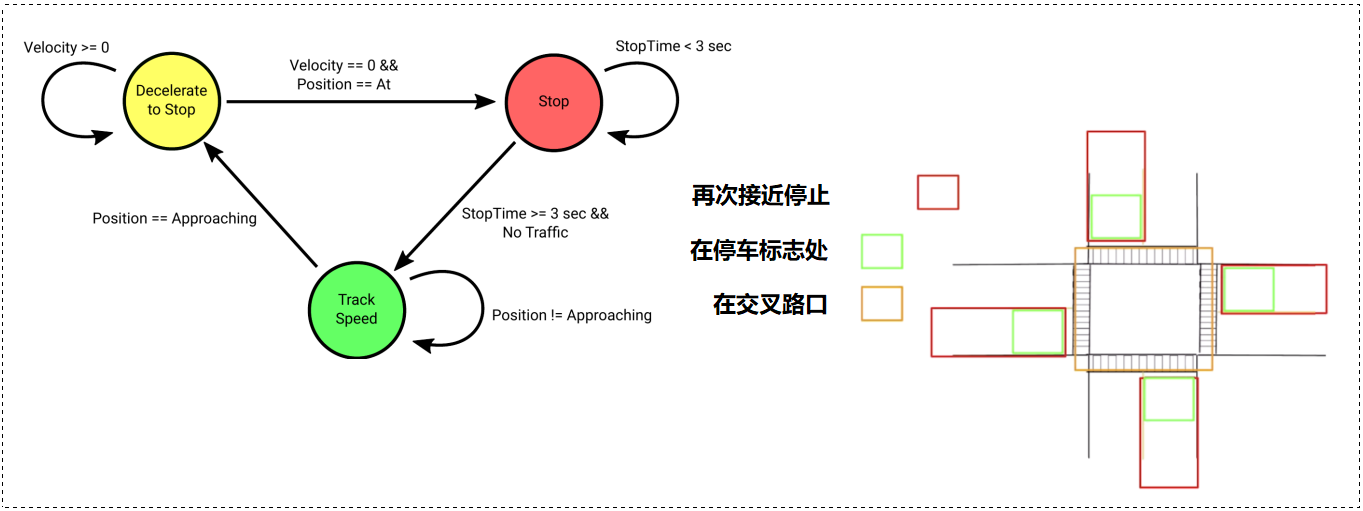
处理多种情况:
0x04 运动规划(Motion Planning)
变分优化分析(Variational Optimization):变分法最小化一个函数(以一个函数作为输入函数):

变分优化的例子:
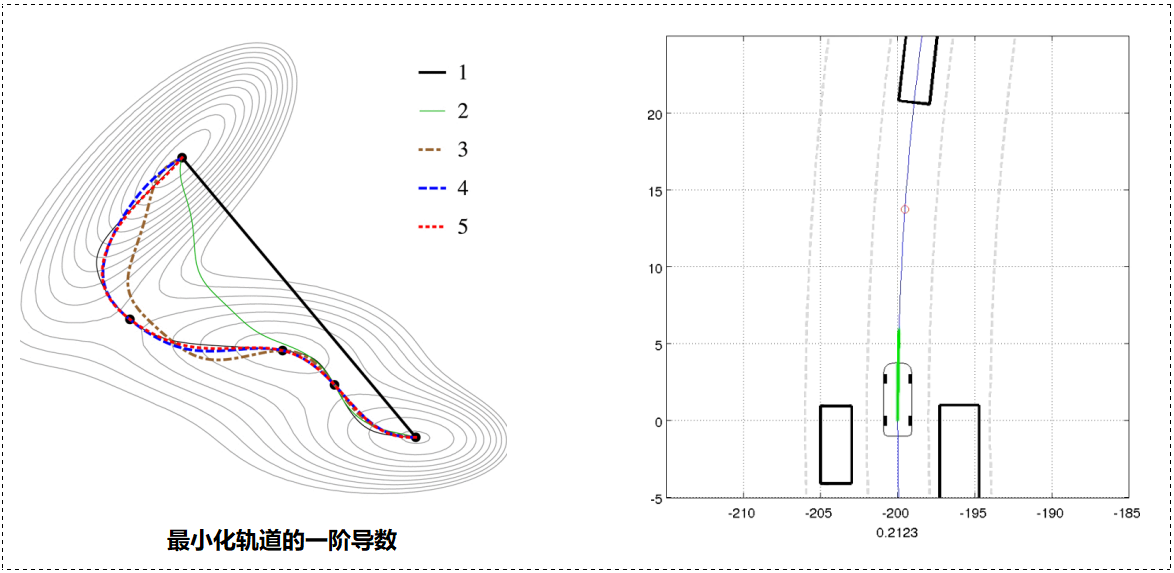
图形搜索方法:将动作空间离散化以绕过变分优化
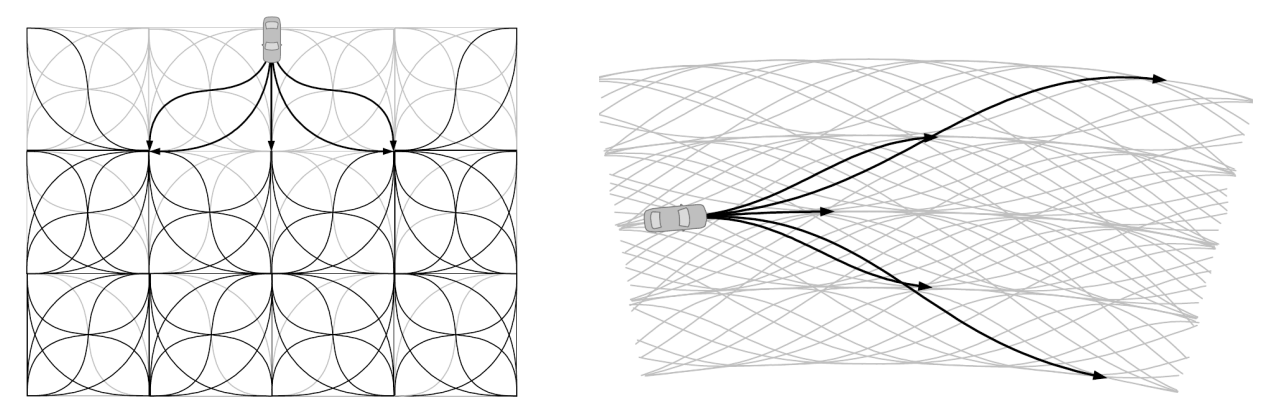
增量搜索技术(Incremental Search Techniques):
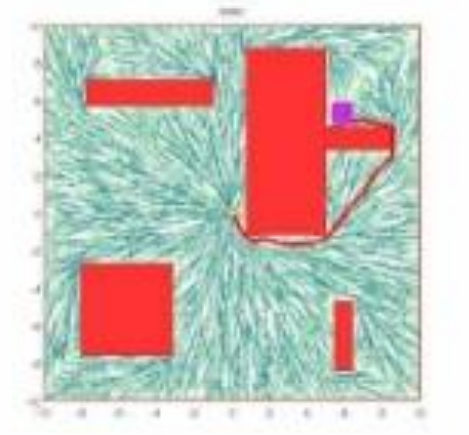 逐步建立配置空间的越来越细的离散化。
逐步建立配置空间的越来越细的离散化。
快速探索随机树(RRT)和 RRT* 算法。
RRT 符合 A* 的算法:
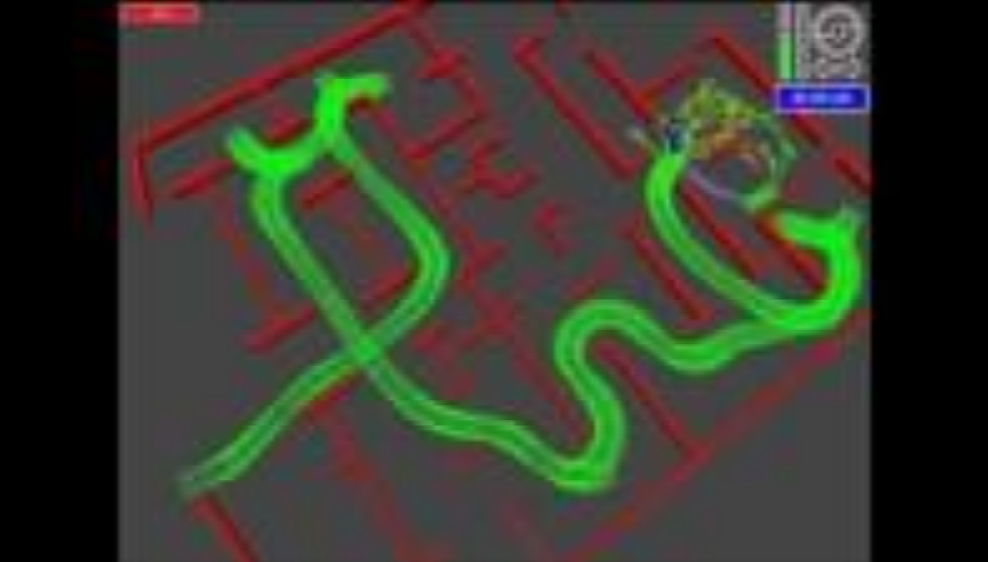
Ⅱ. 实验说明(Experiment)
0x00 模板提供
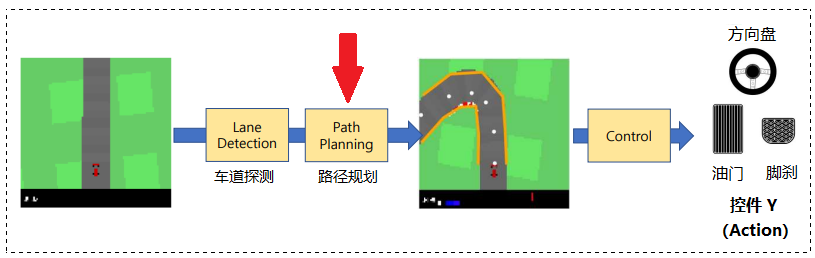
实现模块化管道的简化版本,了解基本概念并获得开发简单自动驾驶应用程序的经验。
📃 提供模板:
1. waypoint_prediction.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
from scipy.interpolate import splprep, splev
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import time
import sysdef normalize(v):norm = np.linalg.norm(v,axis=0) + 0.00001return v / norm.reshape(1, v.shape[1])def curvature(waypoints):'''##### TODO #####Curvature as the sum of the normalized dot product between the way elementsImplement second term of the smoothin objective.args: waypoints [2, num_waypoints] !!!!!''''''Example)norm_diff = normalize(arguments)norm_diff.shape : (2, num_waypoints)curvature example:3.9999937500073246'''return curvaturedef smoothing_objective(waypoints, waypoints_center, weight_curvature=40):'''Objective for path smoothingargs:waypoints [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!waypoints_center [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!weight_curvature (default=40)'''# mean least square error between waypoint and way point centerls_tocenter = np.mean((waypoints_center - waypoints)**2)# derive curvaturecurv = curvature(waypoints.reshape(2,-1))return -1 * weight_curvature * curv + ls_tocenterdef waypoint_prediction(roadside1_spline, roadside2_spline, num_waypoints=6, way_type = "smooth"):'''##### TODO #####Predict waypoint via two different methods:- center- smooth args:roadside1_splineroadside2_splinenum_waypoints (default=6)parameter_bound_waypoints (default=1)waytype (default="smoothed")'''if way_type == "center":##### TODO ###### create spline arguments'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)'''# derive roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# derive center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points = np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )way_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)way_points example :array([[47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''return way_pointselif way_type == "smooth":##### TODO ###### create spline points'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)'''# roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points_center = (np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )).reshape(-1)way_points_center.shape : (num_waypoints*2,)way_points_center example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''# optimization'''scipy.optimize.minimize Doc.)https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.minimize.htmlExample)way_points = minimize(arguments)way_points.shape : (num_way_points*2,)way_points example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''return way_points.reshape(2,-1)def target_speed_prediction(waypoints, num_waypoints_used=5,max_speed=60, exp_constant=4.5, offset_speed=30):'''##### TODO #####Predict target speed given waypointsImplement the function using curvature()args:waypoints [2,num_waypoints] for curv_centernum_waypoints_used (default=5) for curv_centermax_speed (default=60) for target_speedexp_constant (default=4.5) for target_speedoffset_speed (default=30) for target_speedoutput:target_speed (float)''''''Example)curv_center = ~~~target_speed = ~~~'''return target_speed2. Test_waypoint_prediction.py (用于测试)
import gym
from gym.envs.box2d.car_racing import CarRacingfrom lane_detection import LaneDetection
from waypoint_prediction import waypoint_prediction, target_speed_prediction
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pyglet
from pyglet import gl
from pyglet.window import key
import pygame# action variables
action = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
def register_input():for event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:if event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:action[0] = -1.0if event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:action[0] = +1.0if event.key == pygame.K_UP:action[1] = +0.5if event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:action[2] = +0.8 # set 1.0 for wheels to block to zero rotationif event.key == pygame.K_r:global retryretry = Trueif event.key == pygame.K_s:global recordrecord = Trueif event.key == pygame.K_q:global quitquit = Trueif event.type == pygame.KEYUP:if event.key == pygame.K_LEFT and action[0] < 0.0:action[0] = 0if event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT and action[0] > 0.0:action[0] = 0if event.key == pygame.K_UP:action[1] = 0if event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:action[2] = 0# init environement
env = CarRacing()
env.render()
env.reset()# define variables
total_reward = 0.0
steps = 0
restart = False# init modules of the pipeline
LD_module = LaneDetection()# init extra plot
fig = plt.figure()
plt.ion()
plt.show()while True:# perform stepregister_input()s, r, done, speed = env.step(action)# lane detectionlane1, lane2 = LD_module.lane_detection(s)# waypoint and target_speed predictionwaypoints = waypoint_prediction(lane1, lane2)target_speed = target_speed_prediction(waypoints)# rewardtotal_reward += r# outputs during trainingif steps % 2 == 0 or done:print("\naction " + str(["{:+0.2f}".format(x) for x in action]))print("step {} total_reward {:+0.2f}".format(steps, total_reward))LD_module.plot_state_lane(s, steps, fig, waypoints=waypoints)steps += 1env.render()# check if stopif done or restart or steps>=600: print("step {} total_reward {:+0.2f}".format(steps, total_reward))breakenv.close()0x01 道路中心(Road Center)
汽车的一个简单路径是沿着道路中心行驶,使用车道边界样条曲线,导出 6 个等距样条曲线参数值的车道边界点。
→ waypoint_prediction()
使用相同样条曲线参数确定车道边界点之间的中心
→ waypoint_prediction()
0x02 路径平滑(Path Smoothing)
由于我们正在创建一辆赛车,我们需要根据道路的走向来调整航点,例如打到顶点。我们通过最小化以下方程来做到这一点。在给定中心航路点 的情况下,通过最小化以下关于航路点
的目标来改善路径。
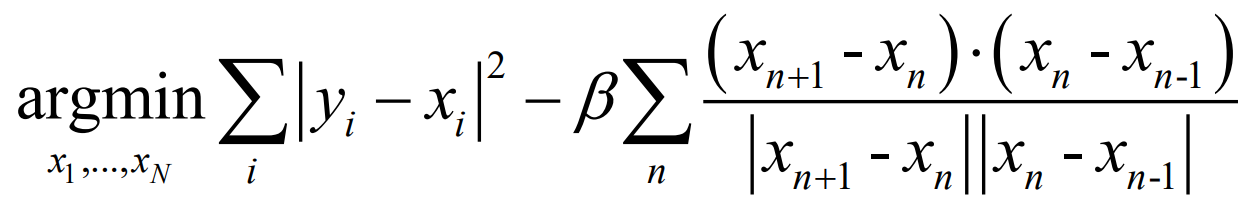
解释第二项的效果,并实施第二项。
其中, 是为了最小化目标而变化的航点,
是任务中估计的中心航点。
→ curvature()
0x03 目标速度预测(Target Speed Prediction)
除了空间路径外,我们还需要知道汽车在路径上应该开多快。从启发式的角度来看,如果路径是平滑的,汽车应该加速到最大速度,并在转弯前减速。实现一个函数,输出状态图像中预测路径的目标速度,参考如下公式:
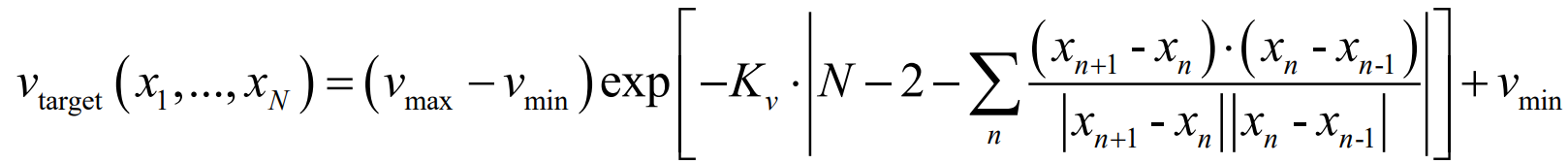
* 初始参数采用:
→ target_speed_prediction()
Ⅲ. 代码实现
0x00 curvature 函数
💬 提供的基础模板如下:
def curvature(waypoints):'''##### TODO #####Curvature as the sum of the normalized dot product between the way elementsImplement second term of the smoothin objective.args: waypoints [2, num_waypoints] !!!!!''''''Example)norm_diff = normalize(arguments)norm_diff.shape : (2, num_waypoints)curvature example:3.9999937500073246'''return curvature根据提示可知,该部分属于计算路径曲率。曲率作为路元素之间的归一化点积之和,实现平滑目标的第二项。根据提示,输入的是一个二维数组,其中每一列代表路径中的一个点。
首先定义出 curv,我们可以从第二个点开始遍历到倒数第二个点,计算每个点的曲率。
curv = 0
for p in range(1, waypoints.shape[1] - 1):...创建数组,分别记录当前点、上一个点和下一个点:
x = np.array(waypoints[:, p])y = np.array(waypoints[:, p + 1])z = np.array(waypoints[:, p - 1])这里可以使用 reshape 函数,reshape() 函数的功能是改变数组或矩阵的形状,并将这些数组改为一个2行的二维新数组。
px, py, pz = x.reshape(N, AUTO_CALC), y.reshape(N, AUTO_CALC), z.reshape(N, AUTO_CALC)
然后可以使用 np.dot() 返回两个数组的点积:
matrixA = normalize(px - pz)matrixB = normalize(py - px)matrixB_T = matrixB.transpose() # .transpose() == .Tdot_product = np.dot(matrixB_T, matrixA)最后再利用 flatten() 将结果降维,最后返回 curv 即可。
curv += dot_product.flatten()return curv0x01 smoothing_objective 函数
def smoothing_objective(waypoints, waypoints_center, weight_curvature=40):'''Objective for path smoothingargs:waypoints [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!waypoints_center [2 * num_waypoints] !!!!!weight_curvature (default=40)'''# mean least square error between waypoint and way point centerls_tocenter = np.mean((waypoints_center - waypoints)**2)# derive curvaturecurv = curvature(waypoints.reshape(2,-1))return -1 * weight_curvature * curv + ls_tocenterls_tocenter = np.mean((waypoints_center - waypoints.reshape(2, -1))**2)
0x02 waypoint_prediction 函数
def waypoint_prediction(roadside1_spline, roadside2_spline, num_waypoints=6, way_type = "smooth"):'''##### TODO #####Predict waypoint via two different methods:- center- smooth args:roadside1_splineroadside2_splinenum_waypoints (default=6)parameter_bound_waypoints (default=1)waytype (default="smoothed")'''if way_type == "center":##### TODO ###### create spline arguments'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)'''num_waypoints_default = 6parameter_bound_waypoints_default = 1# 利用 linsapce() 创建等差数列AP = np.linspace( 0, parameter_bound_waypoints_default, num_waypoints_default)way_points = np.zeros((N, num_waypoints))# derive roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# 中间点可视化: B样条和它的导数插值# display1, display2 = splev(AP, roadside1_spline), splev(AP, roadside2_spline)# p1 = np.array(display1)# p2 = np.array(display2)p1 = np.array(splev(AP, roadside1_spline))p2 = np.array(splev(AP, roadside2_spline))# derive center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points = np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )way_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)way_points example :array([[47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''p1_sp, p2_sp = p1.shape[1], p2.shape[1]for i in range( min(p1_sp, p2_sp) ):way_points[:, i] = np.array( (p1[:, i] + p2[:, i]) / 2) # 求中点return way_pointselif way_type == "smooth":##### TODO ###### create spline points'''Example)t = np.linspace(arguments)t.shape : (num_waypoints,)''' # roadside points from spline'''Example)roadside1_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside2_points = np.array(splev(arguments))roadside1_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside2_points.shape : (2, num_waypoints)roadside1_points example :array([[37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. , 37. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])roadside2_points example :array([[58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. , 58. ],[ 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ]])'''# center between corresponding roadside points'''Example)way_points_center = (np.array( {derive center between corresponding roadside points} )).reshape(-1)way_points_center.shape : (num_waypoints*2,)way_points_center example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''way_points_center = waypoint_prediction(roadside1_spline, roadside2_spline, way_type = "center")# optimization'''scipy.optimize.minimize Doc.)https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.minimize.htmlExample)way_points = minimize(arguments)way_points.shape : (num_way_points*2,)way_points example :array([47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 47.5, 0. , 12.8, 25.6, 38.4, 51.2, 64. ])'''# 利用 minimize 进行非线性优化 # minimize(func, xo, args, **pos) # func:优化目标 # xo:优化参数初始值 # args:优化目标中其他参数的值way_points = minimize (smoothing_objective,(way_points_center),args = way_points_center)["x"]return way_points.reshape(2,-1)0x03 target_speed_prediction 函数
提供的模板如下:
def target_speed_prediction(waypoints, num_waypoints_used=5,max_speed=60, exp_constant=4.5, offset_speed=30):'''##### TODO #####Predict target speed given waypointsImplement the function using curvature()args:waypoints [2,num_waypoints] for curv_centernum_waypoints_used (default=5) for curv_centermax_speed (default=60) for target_speedexp_constant (default=4.5) for target_speedoffset_speed (default=30) for target_speedoutput:target_speed (float)''''''Example)curv_center = ~~~target_speed = ~~~'''return target_speed这里只需要将提供的公式写成代码形式即可,最后将结果返回。
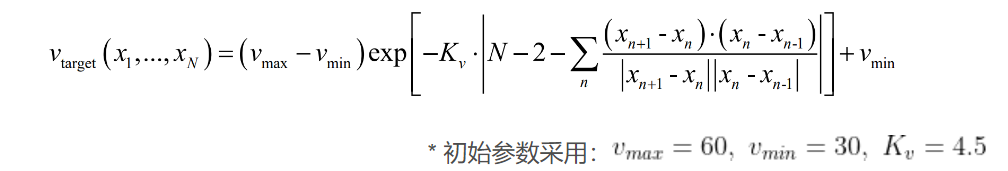
Vmax = max_speedVmin = offset_speedKv = exp_constantN = num_waypoints_usedE = curvature(waypoints)# Path Planning 公式Vtarget = (Vmax - Vmin) * math.exp( -Kv * abs(N - 2 - E) ) + Vmin0x04 运行结果演示
cd 到 skeleton 文件夹的路径下,输入 python test_lane_detection 运行代码:

🚩 运行结果如下:


📌 [ 笔者 ] 王亦优
📃 [ 更新 ] 2023.2.23
❌ [ 勘误 ] /* 暂无 */
📜 [ 声明 ] 由于作者水平有限,本文有错误和不准确之处在所难免,本人也很想知道这些错误,恳望读者批评指正!| 📜 参考资料 [6] Montemerlo M, Becker J, Bhat S, et al. Junior: The Stanford entry in the Urban Challenge Slide Credit: Steven Waslander Course 自动驾驶课程:Motion Planning for Self-Driving Cars | Coursera LaValle: Rapidly-exploring random trees: A new tool for path planning. Techical Report, 1998 Dolgov et al.: Practical Search Techniques in Path Planning for Autonomous Driving. STAIR, 2008. Microsoft. MSDN(Microsoft Developer Network)[EB/OL]. []. . 百度百科[EB/OL]. []. https://baike.baidu.com/. . [EB/OL]. []. https://blog.waymo.com/2021/10/the-waymo-driver-handbook-perception.html. |
相关文章:

【OpenAI】基于 Gym-CarRacing 的自动驾驶练习项目 | 路径训练功能的实现 | GYM-Box2D CarRacing
限时开放,猛戳订阅! 👉 《一起玩蛇》🐍 💭 写在前面: 本篇是关于多伦多大学自动驾驶专业项目的博客。GYM-Box2D CarRacing 是一种在 OpenAI Gym 平台上开发和比较强化学习算法的模拟环境。它是流行的 Box2…...

亚马逊、沃尔玛测评自养号测评、退款、撸卡撸货怎么做?
大家好,有很多的测评工作室做亚马逊测评、沃尔玛测评自养号大额退款,撸卡撸货的找到我,问我有什么方式可以解决成本,效率,纯净度,便捷性等问题,测评养号系统从最早的模拟器,虚拟机到…...
Apollo 2.1.0最新版docker 部署多环境 与java spring boot 接入demo (附带一键部署脚本)
最新Apollo 版本发布2.1.0 https://www.apolloconfig.com/#/zh/design/apollo-design 环境说明 ecs 主机一台数据库mysql 8.0docker 环境 apollo 是内网可信应用,最好是部署在内网里面,外网不可使用,避免配置信息泄漏,这里为了方…...
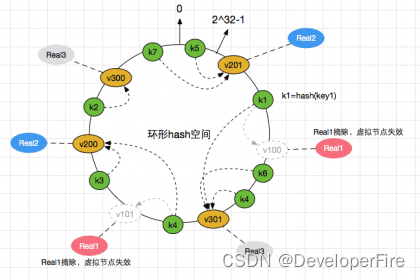
分布式算法 - 一致性Hash算法
一致性Hash算法是个经典算法,Hash环的引入是为解决单调性(Monotonicity) 的问题;虚拟节点的引入是为了解决 平衡性(Balance) 问题。一致性Hash算法引入在分布式集群中,对机器的添加删除,或者机器故障后自动脱离集群这些操作是分布…...
OAuth2.0入门
什么是OAuth2.0 OAuth(Open Authorization)是一个关于授权(authorization)的开放网络标准,允许用户授权第三方应用访问他们存储在另外的服务提供者上的信息,而不需要将用户名和密码提供给第三方移动应用或…...

【HTTP——了解HTTP协议及状态码】
一, 什么是通信通信,就是信息的传递和交换。通信三要素:通信的主体,通信的内容,通信的方式现实生活中的通信:我打电话叫小明来我家吃饭【其中通信的主体是,我,小明。通信内容是&…...

骨传导耳机靠谱吗,骨传导耳机的原理是什么
很多人刚开始接触骨传导耳机时都会具有一个疑问,骨传导耳机是不是真的靠谱,是不是真的不伤害听力?骨传导耳机传输声音的原理是什么? 下面就给大家讲解一下骨传导耳机传输声音的原理以及骨传导耳机对听力到底有没有伤害。 骨传导…...
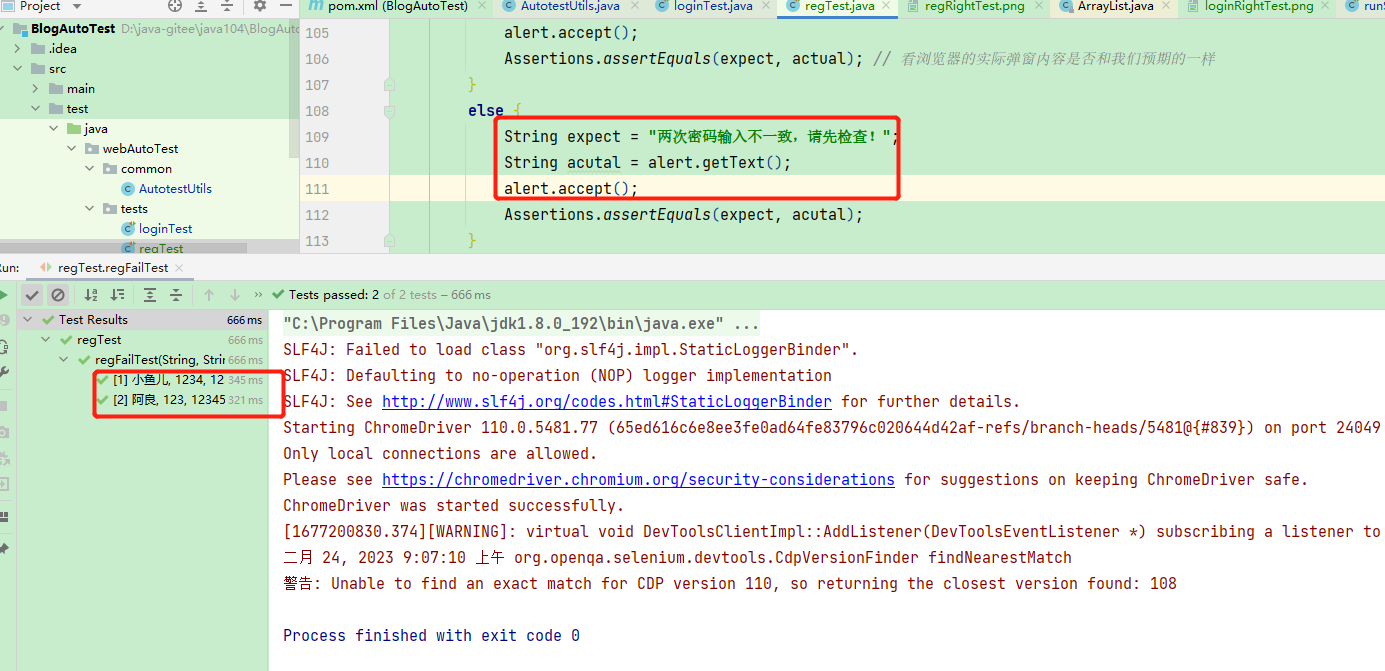
对个人博客系统进行web自动化测试(包含测试代码和测试的详细过程)
目录 一、总述 二、登录页面测试 一些准备工作 验证页面显示是否正确 验证正常登录的情况 该过程中出现的问题 验证登录失败的情况 关于登录界面的总代码 测试视频 三、注册界面的自动化测试 测试代码 过程中出现的bug 测试视频 四、博客列表页测试(…...

[ 2204听力 ] 五
[ 第五次课 对话1 ] Narrator Listen to a conversation between a student and her Ecology professor (woman) Hi, professor, did you want to talk about my paper? I didn’t get a grade. (man) Ah, yes, I think you might have done the wrong assignment. assign…...
嵌入式常问问题和知识
12、并发和并行的区别? 最本质的区别就是:并发是轮流处理多个任务,并行是同时处理多个任务。 你吃饭吃到一半,电话来了,你一直到吃完了以后才去接,这就说明你不支持并发也不支持并行。 你吃饭吃到一半&…...

【数据结构】空间复杂度
🚀write in front🚀 📜所属专栏:初阶数据结构 🛰️博客主页:睿睿的博客主页 🛰️代码仓库:🎉VS2022_C语言仓库 🎡您的点赞、关注、收藏、评论,是对…...

湖南中创教育提醒校外培训留意这几点,避免维权
校外教育培训机构是市场经济发展的必然产物,有需求就有市场,这个无可厚非。而校外教育培训机构的火热,正是反映出人民群众对教育发展的需求在不断增强。 培训机构分类中有面对大学生参加公务员招考、教师考编等考证考试的培训机构࿱…...

docker 配置私有/本地镜像仓库
docker 配置私有/本地镜像仓库docker pull registry mkdir -p /usr/local/docker/registry-data docker tag registry 192.168.28.132:5000/registry docker run -di -p 5000:5000 --namelocal_registry --restartalways --privilegedtrue --log-drivernone -v /usr/local/d…...
每日学术速递2.23
Subjects: Robotics 1.On discrete symmetries of robotics systems: A group-theoretic and data-driven analysis 标题:关于机器人系统的离散对称性:群论和数据驱动分析 作者:Daniel Ordonez-Apraez, Mario Martin, Antonio Agudo, F…...

LeetCode 232. 用栈实现队列
LeetCode 232. 用栈实现队列 难度:easy\color{Green}{easy}easy 题目描述 请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(pushpushpush、poppoppop、peekpeekpeek、emptyemptyempty): 实现 MyQueueM…...

AI算法创新赛-人车目标检测竞赛总结04
队伍:AI000038 小组成员:杨志强,林松 1. 算法介绍 1.1 相关工作 当前流行的目标检测算法主要分为三种,一阶段算法:SSD,FCOS,Scaled,YOLO系列等;二阶段算法:…...

【C语言进阶】动态内存管理详解与常见动态内存错误以及柔性数组使用与介绍
📝个人主页:Sherry的成长之路 🏠学习社区:Sherry的成长之路(个人社区) 📖专栏链接:C语言进阶 🎯长路漫漫浩浩,万事皆有期待 文章目录1.动态内存1.1 概述…...

【C++】string的模拟实现
文章目录1. string的模拟实现1.构造函数使用new开辟空间优化成全缺省的构造函数2. C_str3. operator[]4.拷贝构造浅拷贝深拷贝5. 赋值三种情况6. 迭代器7.比较(ASCII值)大小8. reserve(扩容)9. push_back(尾插字符)10. append(尾插字符串)11. (字符/字符串)12. insert在pos位置…...
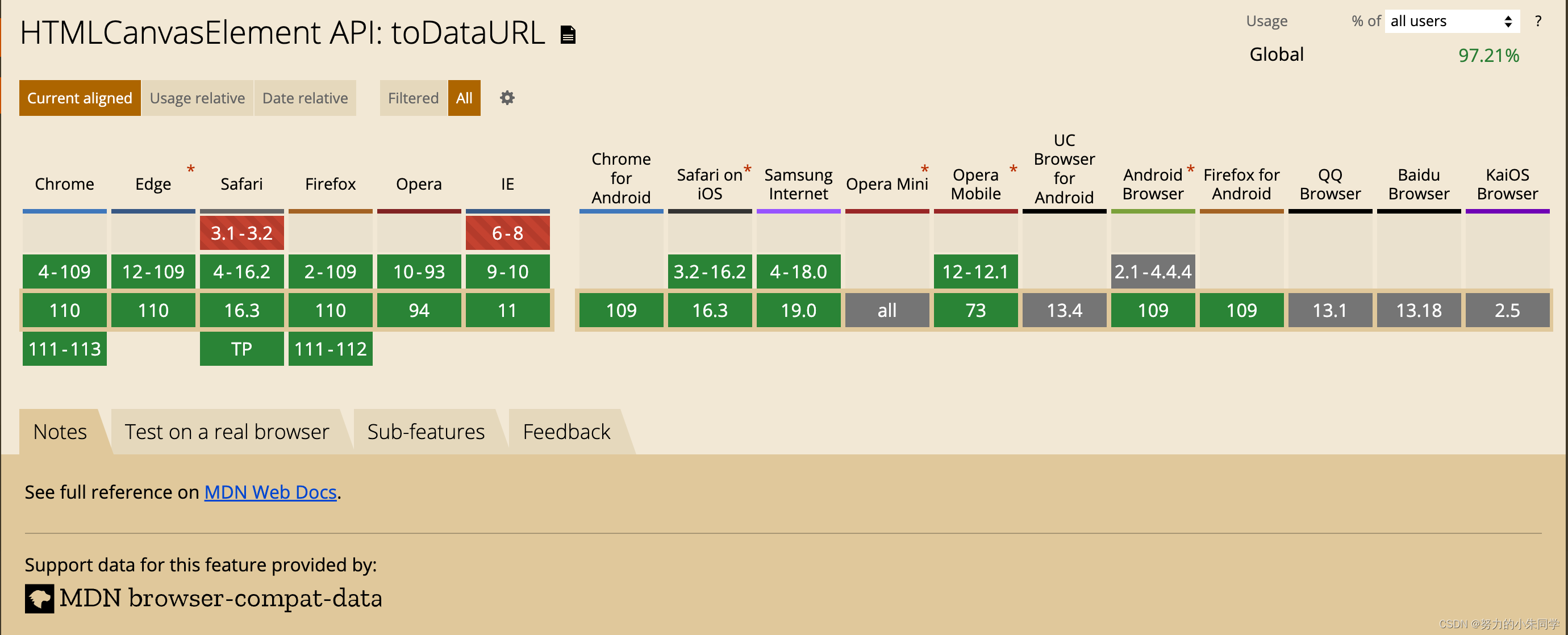
前端借助Canvas实现压缩base64图片两种方法
一、具体代码 1、利用canvas压缩图片方法一 // 第一种压缩图片方法(图片base64,图片类型,压缩比例,回调函数)// 图片类型是指 image/png、image/jpeg、image/webp(仅Chrome支持)// 该方法对以上三种图片类型都适用 压缩结果的图片base64与原类型相同// …...
用ChatGPT生成Excel公式,太方便了
ChatGPT 自去年 11 月 30 日 OpenAI 重磅推出以来,这款 AI 聊天机器人迅速成为 AI 界的「当红炸子鸡」。一经发布,不少网友更是痴迷到通宵熬夜和它对话聊天,就为了探究 ChatGPT 的应用天花板在哪里,经过试探不少人发现,…...
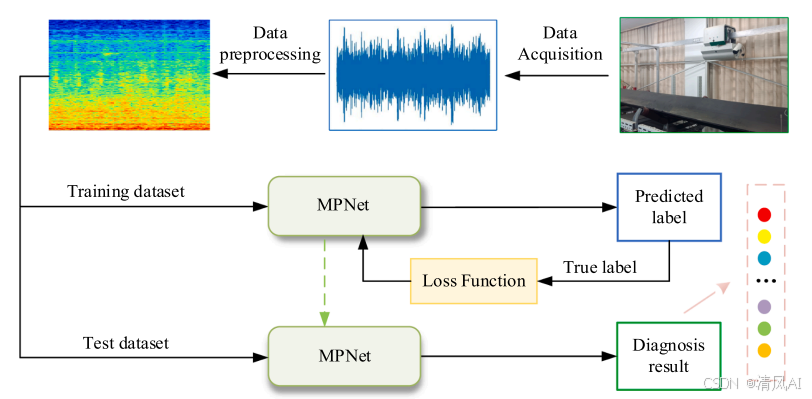
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...
渗透实战PortSwigger靶场-XSS Lab 14:大多数标签和属性被阻止
<script>标签被拦截 我们需要把全部可用的 tag 和 event 进行暴力破解 XSS cheat sheet: https://portswigger.net/web-security/cross-site-scripting/cheat-sheet 通过爆破发现body可以用 再把全部 events 放进去爆破 这些 event 全部可用 <body onres…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...

华为OD机考-机房布局
import java.util.*;public class DemoTest5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseSystem.out.println(solve(in.nextLine()));}}priv…...

如何更改默认 Crontab 编辑器 ?
在 Linux 领域中,crontab 是您可能经常遇到的一个术语。这个实用程序在类 unix 操作系统上可用,用于调度在预定义时间和间隔自动执行的任务。这对管理员和高级用户非常有益,允许他们自动执行各种系统任务。 编辑 Crontab 文件通常使用文本编…...

Ubuntu Cursor升级成v1.0
0. 当前版本低 使用当前 Cursor v0.50时 GitHub Copilot Chat 打不开,快捷键也不好用,当看到 Cursor 升级后,还是蛮高兴的 1. 下载 Cursor 下载地址:https://www.cursor.com/cn/downloads 点击下载 Linux (x64) ,…...
 error)
【前端异常】JavaScript错误处理:分析 Uncaught (in promise) error
在前端开发中,JavaScript 异常是不可避免的。随着现代前端应用越来越多地使用异步操作(如 Promise、async/await 等),开发者常常会遇到 Uncaught (in promise) error 错误。这个错误是由于未正确处理 Promise 的拒绝(r…...

认识CMake并使用CMake构建自己的第一个项目
1.CMake的作用和优势 跨平台支持:CMake支持多种操作系统和编译器,使用同一份构建配置可以在不同的环境中使用 简化配置:通过CMakeLists.txt文件,用户可以定义项目结构、依赖项、编译选项等,无需手动编写复杂的构建脚本…...

云原生周刊:k0s 成为 CNCF 沙箱项目
开源项目推荐 HAMi HAMi(原名 k8s‑vGPU‑scheduler)是一款 CNCF Sandbox 级别的开源 K8s 中间件,通过虚拟化 GPU/NPU 等异构设备并支持内存、计算核心时间片隔离及共享调度,为容器提供统一接口,实现细粒度资源配额…...

消防一体化安全管控平台:构建消防“一张图”和APP统一管理
在城市的某个角落,一场突如其来的火灾打破了平静。熊熊烈火迅速蔓延,滚滚浓烟弥漫开来,周围群众的生命财产安全受到严重威胁。就在这千钧一发之际,消防救援队伍迅速行动,而豪越科技消防一体化安全管控平台构建的消防“…...
