「TCG 规范解读」词汇表
可信计算组织(Ttrusted Computing Group,TCG)是一个非盈利的工业标准组织,它的宗旨是加强在相异计算机平台上的计算环境的安全性。TCG于2003年春成立,并采纳了由可信计算平台联盟(the Trusted Computing Platform Alliance,TCPA)所开发的规范。现在的规范都不是最终稿,都还在不断的更新中,比如:TPM的规范就从原来的v1.0更新到v1.2,现在还在不断的修订。

TCG-Glossary-V1.1-Rev-1.0
修订历史

范围
词汇表包含了 TCG 文档中常用到的术语,但是可能不会覆盖 TCG 文档立全部的词汇。比如,词汇表中可能不会包含具体技术或者只有在某一个文档中用到的术语。
本文中的词汇表也不是为了覆盖全部的术语,它只是给读者们一些提示或者说是提醒。
词汇表
| 缩略语 | 术语 | 描述 |
| AIK Credential | 私有 CA 签发的包含 AIK 公开部分内容,由私有 CA 私钥签名。签名及其签名区域的含义以及重要程度由策略决定,通常它会陈述该公钥与一个可用的 TPM 关联。 | |
| Attestation | 保证信息准确性的过程,外部实体可以证实受保护区域、保护能力、信任根,一个平台可以证实其影响自身完整性的平台特性描述,每种证明都要求证明实体提供可靠的证据。 | |
| Attestation by the TPM | TPM 对自己一致数据提供证据的操作,这是通过 AIK 对内部数据进行签名实现的,验证方接收、验证数据完整性以及 AIK 本身有效性, AIK 凭证可以通过私有 CA 或者 DAA 协议获得。 | |
| AIK | Attestation Identity Key | 在 TPMv1.2中,AIK 是 TPM 创建的一个特殊目的的签名,AIK 是非对称密钥,私有部分是不可迁移的并且由 TPM 保护。公开部分是 AIK 凭证的一部分,由私有 CA 或者 DAA 协议签发。AIK 只能由 TPM 拥有者或者拥有者的授权代理创建。AIK 能用于平台认证、平台证明、密钥证明。 AIK 在平台识别的过程中保证了隐私性,AIK 凭证能够保证 AIK 和一个授权的 TPM 绑定,但是除了用户本身和 CA,没有人知道和哪个 TPM 绑定的。 |
| Attestation of the Platform | 对一组平台完整性度量值提供证据的过程,通过 TPM 的 AIK 对 PCRs进行签名实现。 | |
| Attestation to the Platform | An operation that provides proof that a platform can be trusted to report integrity measurements; performed using the set or subset of the credentials associated with the platform; used to create an AIK credential. | |
| Authenticated Boot | A boot after which the platform's Root-of-Trust-for-Reporting (RTR) can report an accurate record of the way that the platform booted. | |
| AC | Authenticated Code | Authenticated code is comprised of an executable module plus a value that attests to the authenticity of the module. The value is signed with a private key corresponding to a public key known to a computing device that is to execute the module. If the module is able to verify the signature, the computing device may execute the module. |
| Authentication | The process of verifying the claimed attributes, such as an identity, of an entity or user | |
| Authentication of the Platform | Provides proof of a claimed platform identity. The claimed identity may or may not be related to the user or any actions performed by the user. Platform Authentication is performed using any non-migratable signing key (e.g., an AIK). Since there are an unlimited number of non-migratable keys associated with the TPM there are an unlimited number of identities that can be authenticated. | |
| Authorization | Granting access to a resource based on an authenticated identity | |
| BLOB | Binary Large OBject | Encrypted or opaque data of fixed or variable size. The meaning and interpretation of the data is outside the scope and context of any entity other than the Subsystem (the TPM in this case) that created the BLOB. |
| BORE | Break Once Run Everywhere | A security design that includes a critical security value that is the same on all instances of the design. If an attacker can access that critical security value on any instance of the design, that information can be used to compromise every instance of the design. For example, a product is designed to use encryption to protect user information and the same encryption key is hardcoded in all instances of the product. If the attacker can acquire the key from one copy of the product, he can use that key to access personal information in all copies of the product. |
| CMK | Certified Migration Key | A key whose migration from a TPM requires an authorization token created with private keys. The corresponding public keys are incorporated in the CMK and referenced when a TPM produces a credential describing the CMK. If a CMK credential is signed by an AIK, an external entity has evidence that a particular key (1) is protected by a valid TPM and (2) requires permission from a specific authority before it can be copied. |
| Challenger (Identity Challenger) | An entity that requests and has the ability to interpret integrity metrics. See also “Integrity Challenge” | |
| CRTM | Code Root of Trust for Measurement | The instructions executed by the platform when it acts as the RTM. [Formerly described as “Core Root of Trust for Measurement”. Code Root of Trust for Measurement is the preferred expansion.] This acronym expansion is preferred. |
| DAA Issuer | A known and recognized entity that interacts with the TPM to install a set of DAA-credentials in the TPM. The DAA issuer provides certification that the holder of such DAA-credentials meets some criteria defined by the Issuer. In many cases the Issuer will be the platform manufacturer, but other entities can become issuers. | |
| Delegation | A process that allows the Owner to delegate a subset of the Owner's privileges (to perform specific TPM operations). | |
| DAA | Direct Anonymous Attestation | A protocol for vouching for an AIK using zero-knowledge-proof technology. |
| DMA Mapping | Controls how hardware devices access Host Platform memory; DMA requests to access memory may be mapped to an alternate memory address. Similar to user mode processes use of virtual memory where page tables control the mapping to physical memory pages. Examples are IOMMU or VT-d. | |
| DMA Protections | Provide a mechanism to allow a Host Platform to prevent hardware devices from accessing certain Host Platform memory. Examples are a DMA exclusion scheme or DMA mapping. | |
| Duplicable Object | In TPM 2.0, a key or data object that is not bound to a specific TPM and with suitable authorization can be used outside a TPM or moved (copied) to another TPM. (See Migratable) | |
| D-HRTM | Dynamic Hardware Root of Trust for Measurement | A D-RTM implemented using an HRTM. |
| DL | Dynamic Launch | This describes the process of starting a software environment at an arbitrary time in the runtime of a system. |
| D-RTM | Dynamic Root of Trust for Measurement | A platform-dependent function that initializes the state of the platform and provides a new instance of a root of trust for measurement without rebooting the platform. The initial state establishes a minimal Trusted Computing Base.This is a function that is built into the Host Platform and is started by the Dynamic Launch Event (DL Event). This function is a Trusted Process. Even though the D-RTM executes after the S-RTM, the D-RTM’s transitive trust chain will not necessarily have a trust dependency on the S-RTM’s transitive trust chain. |
| DCE | Dynamic Root of Trust for Measurement Configuration Environment | The software/firmware that executes between the instantiation of the D-RTM CPU instruction and the transfer of control to the Dynamically Launched Measured Environment (DLME). The DCE is responsible for ensuring the platform is in a trustworthy state. Normally this is defined by the CPU manufacturer, chipset manufacturer, and the platform manufacturer. |
| DLME | Dynamically Launched Measured Environment | The software executed after the DCE- instantiated TCB is established. The DLME would nominally be supplied by an OS vendor. |
| EK | Endorsement Key | An asymmetric Key pair composed of a public key (PubEK) and private (PrivEK). The EK is used to prove the TPM is genuine. |
| Endorsement Key Credential | A credential associated with an PubEK. The credential asserts that the associated PrivEK is unique to a security device conforming to TCG specifications. | |
| H-CRTM | A synonym for the S-HRTM. The preferred term is S-HRTM. | |
| HRTM | Hardware Root of Trust for Measurement | An RTM where hardware performs the initial measurement. |
| Immutable | Unchangeable | |
| ILP | Initiating Logical Processor | The processor that initiates the D-RTM |
| Integrity Challenge | A process used to send accurate integrity measurements and PCR values to a challenger. | |
| Integrity Logging | The storage of integrity metrics in a log for later use. | |
| Integrity Measurement (Metrics) | A value representing a platform characteristic that affects the integrity of a platform | |
| Integrity Reporting | The process of attesting to the contents of integrity storage. | |
| Locality | A mechanism for supporting a privilege hierarchy in the platform | |
| Migratable (key) | A key which is not bound to a specific TPM and with suitable authorization can be used outside a TPM or moved to another TPM. | |
| Non-duplicable Object | In TPM 2.0, a statistically unique object (usually a key) that may only be used on the TPM that created the object. | |
| Non-migratable (key) | A key which is bound to a single TPM; a key that is (statistically) unique to a single TPM. In TPM 1.2, the key may be moved between TPMs using the maintenance process | |
| NV (storage) | Non-volatile (shielded location) | A shielded storage location whose contents are guaranteed to persist between uses by Protected Capabilities. |
| Operator | Anyone who has physical access to a platform | |
| Owner | The entity that has administrative rights over the TPM | |
| Platform | A platform is a collection of resources that provides a service | |
| PCR | Platform Configuration Register | A shielded location containing a digest of integrity measurements |
| Platform Credential | A credential, typically a digital certificate, attesting that a specific platform contains a unique TPM and TBB.A credential that states that a specific platform contains a genuine TCG Subsystem. | |
| PCA | Privacy CA | An entity that issues an Identity Credential for a TPM based on trust in the entities that vouch for the TPM via the Endorsement Credential, the Conformance Credential, and the Platform Credential. |
| PrivEK | Private Endorsement Key | The private portion of the EK. |
| Protected Capabilities | The set of commands with exclusive permission to access shielded locations | |
| PubEK | Public Endorsement Key | The public portion of the EK. |
| RoT | Root of Trust | A component that performs one or more security-specific functions, such as measurement, storage, reporting, verification, and/or update. It is trusted always to behave in the expected manner, because its misbehavior cannot be detected (such as by measurement) under normal operation. |
| RTC | Root of Trust for Confidentiality | An RoT providing confidentiality for data stored in TPM Shielded Locations. |
| RTI | Root of Trust for Integrity | An RoT providing integrity for data stored in TPM Shielded Locations |
| RTM | Root of Trust for Measurement | An RoT that makes the initial integrity measurement, and adds it to a tamper- resistant log. Note: A PCR in a TPM is normally used to provide tamper evidence because the log is not in a shielded location. |
| RTR | Root of Trust for Reporting | An RoT that reliably provides authenticity and non-repudiation services for the purposes of attesting to the origin and integrity of platform characteristics. |
| RTS | Root of Trust for Storage | The combination of an RTC and an RTI |
| RTU | Root of Trust for Update | An RTV that verifies the integrity and authenticity of an update payload before initiating the update process. |
| RTV | Root of Trust for Verification | An RoT that verifies an integrity measurement against a policy. |
| Shielded Location | A place (memory, register, etc.) where it is safe to operate on sensitive data; data locations that can be accessed only by Protected Capabilities. | |
| S-CRTM | Static Code Root of Trust for Measurement | An S-RTM implemented using a CRTM. |
| S-HRTM | Static Hardware Root of Trust for Measurement | An S-RTM implemented using an HRTM. [NOTE: The TPM 2 Library Specification uses the term H-CRTM introduced in Revision 116.] |
| S-RTM | Static Root of Trust for Measurement | An RTM where the initial integrity measurement occurs at platform reset. The S-RTM is static because the PCRs associated with it cannot be re-initialized without a platform reset. |
| SRK | Storage Root Key | A key with no parent that is the root key of a hierarchy of keys associated with a TPM's Protected Storage function. |
| TSS | TCG Software Stack | Untrusted software services that facilitate the use of the TPM and do not require the protections afforded to the TPM. |
| TPM Shielded Location | A location within a TPM that contains data that is shielded from access by any entity other than the TPM and which may only be operated on by a Protected Capability | |
| TSS | TPM Software Stack | An unofficial alias of the term TCG Software Stack. TCG specifications should not use the term TPM Software Stack when referring to the TSS |
| TPM-Protected Capability | An operation performed by a TPM on data in a Shielded Location, usually in response to a command sent to the TPM | |
| Transitive Trust | Also known as "Inductive Trust", in this process a Root of Trust gives a trustworthy description of a second group of functions. Based on this description, an interested entity can determine the trust it is to place in this second group of functions. If the interested entity determines that the trust level of the second group of functions is acceptable, the trust boundary is extended from the Root of Trust to include the second group of functions. In this case, the process can be iterated. The second group of functions can give a trustworthy description of the third group of functions, etc. Transitive trust is used to provide a trustworthy description of platform characteristics, and also to prove that non-migratable keys are non-migratable | |
| Trust | Trust is the expectation that a device will behave in a particular manner for a specific purpose. | |
| TBB | Trusted Building Block | The parts of the Root of Trust that do not have shielded locations or protected capabilities. Typically platform-specific. An example of a TBB is the combination of the CRTM, connection of the CRTM storage to a motherboard, the connection of the TPM to a motherboard, and a mechanisms for determining Physical Presence. |
| Trusted Component | A Trusted Device within a Trusted Platform or another Trusted Device. | |
| Trusted Computing Platform | A Trusted Computing Platform is a computing platform that can be trusted to report its properties | |
| Trusted Device | A Trusted Platform that is not intended to reprogrammed except through a maintenance process. | |
| Trusted Platform | A platform that uses Roots of Trust to provide reliable reporting of the characteristics that determine its trustworthiness. | |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module | A composite of the RTR and the RTS |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module | An implementation of the functions defined in the TCG Trusted Platform Module Specification; the set of Roots of Trust with Shielded Locations and Protected Capabilities. Normally includes just the RTS and the RTR. The set of functions and data that are common to all types of platform, which must be trustworthy if the Subsystem is to be trustworthy; a logical definition in terms of protected capabilities and shielded locations. |
| TPS | Trusted-Platform Support Services | The set of functions and data that are common to all types of platform, which are not required to be trustworthy (and therefore do not need to be part of the TPM). |
| User | An entity that is making use of the TPM capabilities. An entity that uses the platform in which a TPM is installed. The only rights that a User has over a TPM are the rights given to the User by the Owner. These rights are expressed in the form of authentication data, given by the Owner to the User, which permits access to entities protected by the TPM. The User of the platform is not necessarily the “owner” of the platform (e.g., in a corporation, the owner of the platform might be the IT department while the User is an employee). There can be multiple Users. | |
| Validation Credential | A credential that states values of measurements that should be obtained when measuring a particular part of the platform when the part is functioning as expected. | |
| Validation Data | Data inside a Validation Credential; the values that the integrity measurements should produce when the part of a platform described by the Validation Credential is working correctly. | |
| Validation Entity | An entity that issues a Validation Certificate for a component; the manufacturer of that component; an agent of the manufacturer of that component | |
| Verifier | An entity that evaluates credentials to produce a credential. Example 1: the entity that interacts with the TPM using the DAA protocol to verify that the TPM has a valid set of DAA-credentials. The verifier may then produce an AIK credential, without reference to the platform EK. Example 2: the entity that requests, receives, and evaluates attestation information based on the EK. A trusted third party (such as a Privacy CA) may then produce an AIK credential, after verifying the platform EK. |
皮格马利翁效应心理学指出,赞美、赞同能够产生奇迹,越具体,效果越好~
“收藏夹吃灰”是学“器”练“术”非常聪明的方法,帮助我们避免日常低效的勤奋~
相关文章:

「TCG 规范解读」词汇表
可信计算组织(Ttrusted Computing Group,TCG)是一个非盈利的工业标准组织,它的宗旨是加强在相异计算机平台上的计算环境的安全性。TCG于2003年春成立,并采纳了由可信计算平台联盟(the Trusted Computing Platform Alli…...
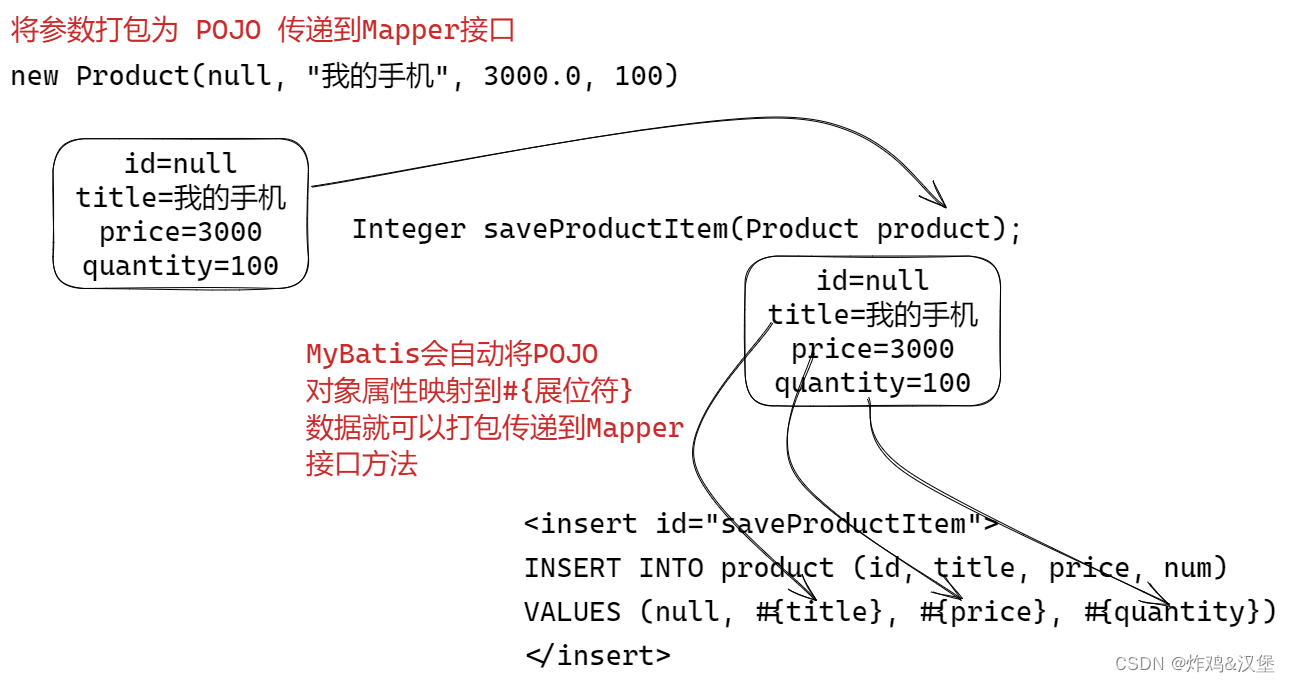
第三阶段-03MyBatis 中使用XML映射文件详解
MyBatis 中使用XML映射文件 什么是XML映射 使用注解的映射SQL的问题: 长SQL需要折行,不方便维护动态SQL查询拼接复杂源代码中的SQL,不方便与DBA协作 MyBatis建议使用XML文件映射SQL才能最大化发挥MySQL的功能 统一管理SQL, 方…...

从0开始学python -41
Python3 命名空间和作用域 命名空间 先看看官方文档的一段话: A namespace is a mapping from names to objects.Most namespaces are currently implemented as Python dictionaries。 命名空间(Namespace)是从名称到对象的映射,大部分的命名空间都是…...
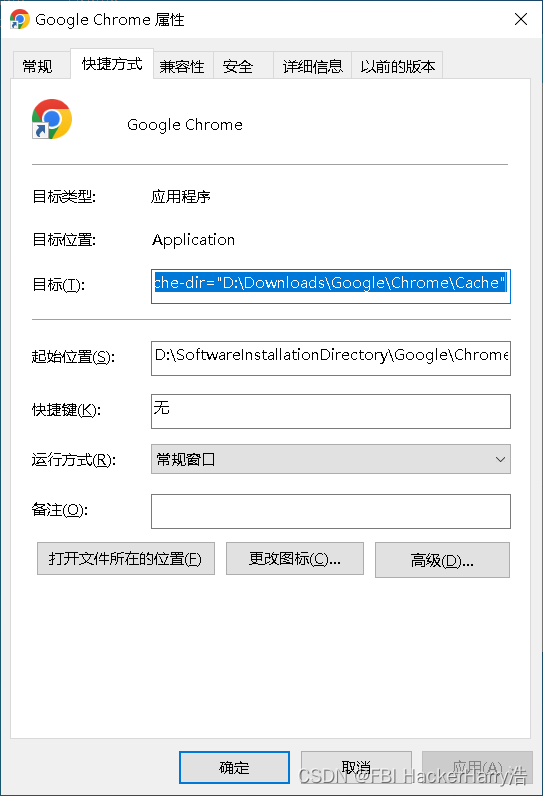
如何将Google浏览器安装到D盘(内含教学视频)
如何将Google浏览器安装到D盘(内含教学视频) 教学视频下载链接地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_46411355/87503968 目录如何将Google浏览器安装到D盘(内含教学视频)教学视频下载链接地址:…...

三战阿里测试岗,成功上岸,面试才是测试员涨薪真正的拦路虎...
第一次面试阿里记得是挂在技术面上,当时也是技术不扎实,准备的不充分,面试官出的面试题确实把我问的一头雾水,还没结束我就已经知道我挂了这次面试。 第二次面试,我准备的特别充分,提前刷了半个月的面试题…...
)
Java代码弱点与修复之——ORM persistence error(对象关系映射持久错误)
弱点描述 ORM persistence error, ORM 持久化错误 。表示 ORM 工具在尝试将对象保存到数据库中时出现了问题。可能的原因包括: 数据库连接错误:ORM 工具无法连接到数据库,或者连接到数据库的权限不足。数据库表结构错误:ORM 工具无法正确映射对象和数据库表之间的关系,可…...
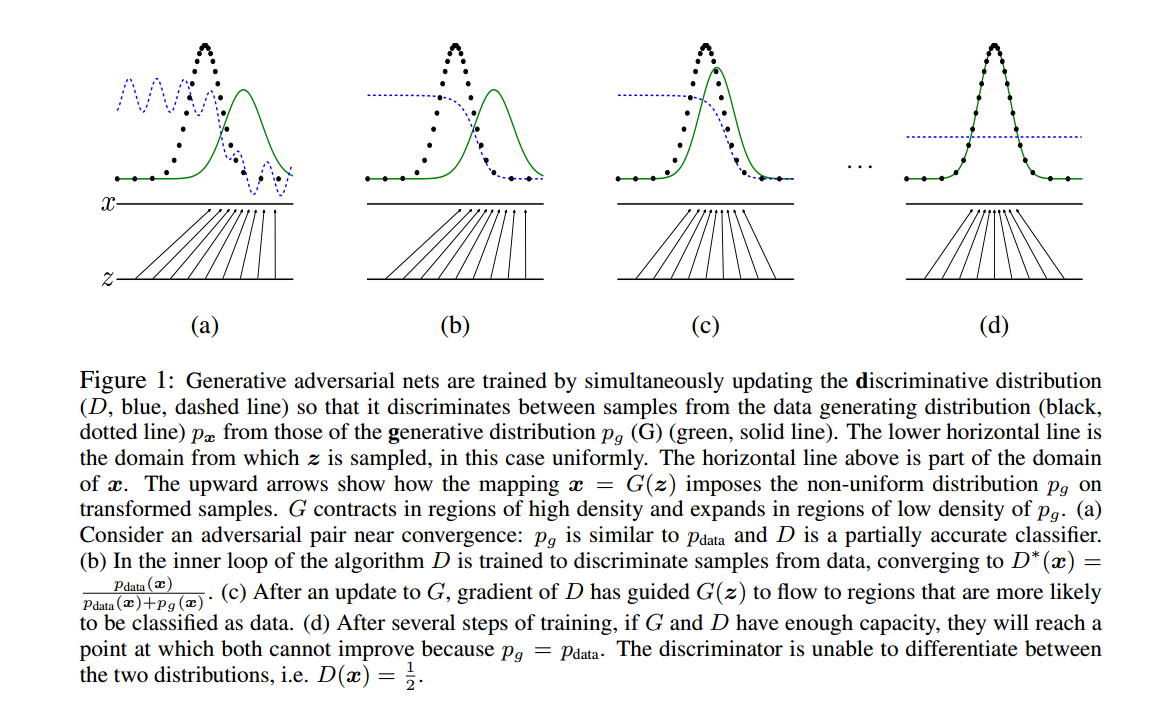
原始GAN-pytorch-生成MNIST数据集(原理)
文章目录1. GAN 《Generative Adversarial Nets》1.1 相关概念1.2 公式理解1.3 图片理解1.4 熵、交叉熵、KL散度、JS散度1.5 其他相关(正在补充!)1. GAN 《Generative Adversarial Nets》 Ian J. Goodfellow, Jean Pouget-Abadie, Yoshua Be…...
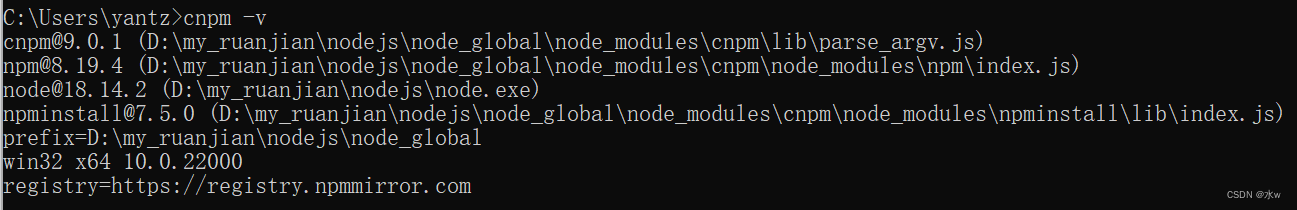
Vue下载安装步骤的详细教程(亲测有效) 1
目录 一、【准备工作】nodejs下载安装(npm环境) 1 下载安装nodejs 2 查看环境变量是否添加成功 3、验证是否安装成功 4、修改模块下载位置 (1)查看npm默认存放位置 (2)在 nodejs 安装目录下,创建 “node_global…...

[Android Studio] Android Studio生成数字证书,为应用签名
🟧🟨🟩🟦🟪 Android Debug🟧🟨🟩🟦🟪 Topic 发布安卓学习过程中遇到问题解决过程,希望我的解决方案可以对小伙伴们有帮助。 📋笔记目…...

应用IC 卡继续教育网络管理系统前后影响因素比较
3.1 实现了继续护理教育网络化管理近年来,随着一些医院继续护理教育管理信息系统的建立,有效改进了学分档案管理模式和教学模式,但这些继续护理教育管理信息系统一般为局域网,仅能达到满足自身管理的基本需求,而系统如…...
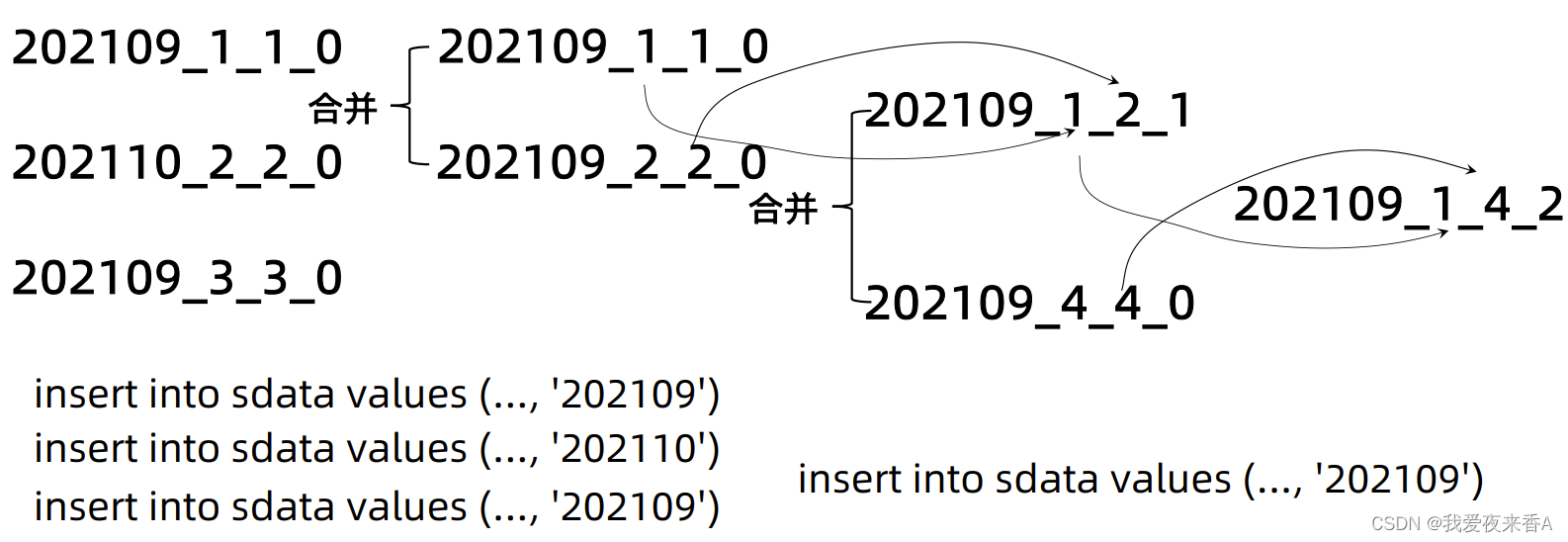
Clickhouse学习(一):MergeTree概述
MergeTree一、Clickhouse表引擎概述二、MergeTree表引擎<一>、ReplacingMergeTree引擎<二>、SummingMergeTree引擎<三>、AggregatingMergeTree引擎三、MergeTree分区一、Clickhouse表引擎概述 MergeTree表引擎:允许根据日期和主键创建索引 1、ReplacingMerge…...

Windows离线安装rust
目前rust安装常用的方式就是通过Rustup安装,此安装方式需要访问互联网。在生产环境中由于网络限制,不能直接访问互联网或者不能访问目标网站,这时候需要用离线安装的方式,本文将详细介绍离线安装步骤,并给出了vscode如…...
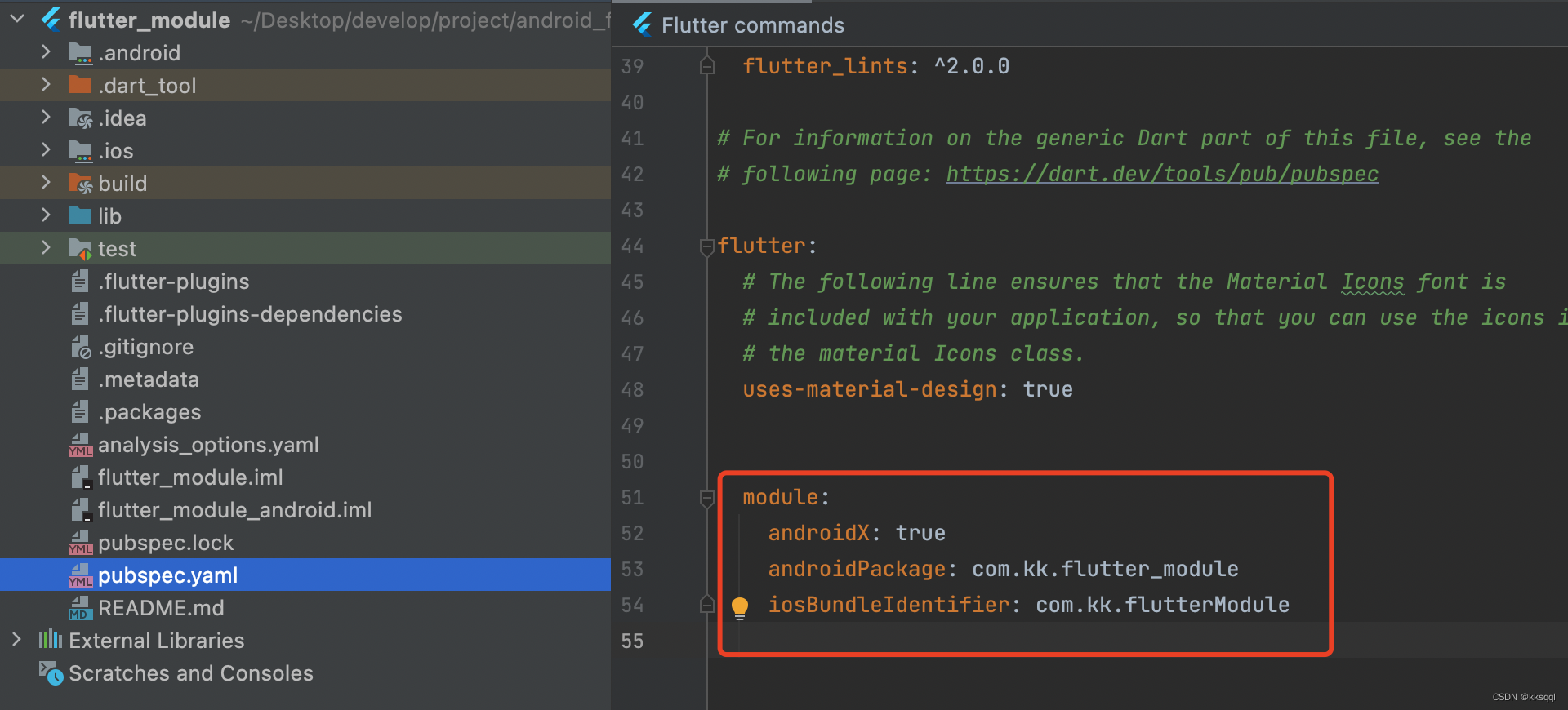
Android与flutter混合开发
这里我使用的android studio版本是2020.3.1;flutter版本2.5.3。此前在网上搜索的很多教教程版本都不一样,新版的IDE和SDK让我遇到了很多坑故这里整理一下。一、创建项目1.在Android项目中点击File->New->New Flutter Project。File->New->Ne…...

Linux和C语言的学习方法你真的知道吗?
★Linux的使用 第一天,就给我们讲了为什么要先学c、学linux:因为嵌入式的根本就是软件驱动硬件,而C语言是最接近硬件的语言、有指针的概念、可以直接操作硬件,另外,功能复杂的硬件是含有操作系统的,这就需…...

代码随想录day42
1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II https://leetcode.cn/problems/last-stone-weight-ii/ 这个自己还是没想出来01背包对应。 本题其实就是尽量让石头分成重量相同的两堆,相撞之后剩下的石头最小,这样就化解成01背包问题了。 stones [2,7,4,1,8,1]也就是sum…...

【笔记】两台1200PLC进行S7 通信(1)
使用两台1200系列PLC进行S7通信(入门) 文章目录 目录 文章目录 前言 一、通信 1.概念 2.PLC通信 1.串口 2.网口 …...

统一网关Gateway
为什么需要网关 网关功能: 身份认证和权限校验服务路由,负载均衡 根据请求判断找到对应的服务路由,然后服务可能有多个实例,这个时候网关就会做一个负载均衡去挑选一个实例调用.请求限流 限制请求的数量,这是微服务的…...
安装)
6、kubernetes(k8s)安装
本文内容以语雀为准 文档 等等,Docker 被 Kubernetes 弃用了?容器运行时端口和协议kubeadm initkubeadm config安装网络策略驱动使用 kubeadm 创建集群 控制平面节点隔离 持久卷为容器设置环境变量在CentOS上安装Docker引擎Pod 网络无法访问排查处理 说明 本文…...
python-批量下载某短视频平台音视频标题、评论、点赞数
python-批量下载某短视频平台音视频标题、评论数、点赞数前言一、获取单个视频信息1、获取视频 url2、发送请求3、数据解析二、批量获取数据1、批量导入地址2、批量导出excel文件3、批量存入mysql数据库三、完整代码前言 1、Cookie中文名称为小型文本文件,指某些网…...

【数据结构与算法】单链表的增删查改(附源码)
这么可爱的猫猫不值得点个赞吗😽😻 目录 一.链表的概念和结构 二.单链表的逻辑结构和物理结构 1.逻辑结构 2.物理结构 三.结构体的定义 四.增加 1.尾插 SListpushback 2.头插 SListpushfront 五.删除 1.尾删 SListpopback 2.头删 SListpo…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...

OkHttp 中实现断点续传 demo
在 OkHttp 中实现断点续传主要通过以下步骤完成,核心是利用 HTTP 协议的 Range 请求头指定下载范围: 实现原理 Range 请求头:向服务器请求文件的特定字节范围(如 Range: bytes1024-) 本地文件记录:保存已…...
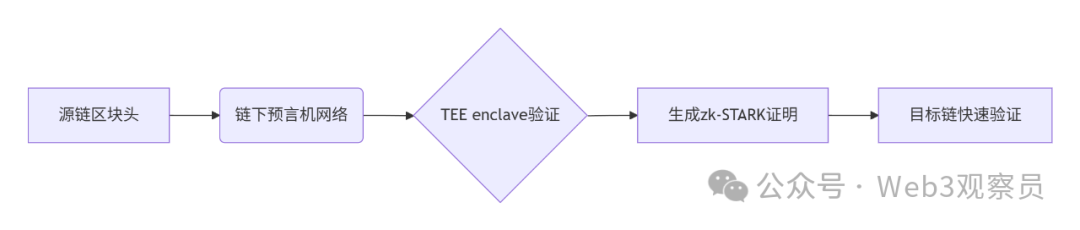
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案
跨链模式:多链互操作架构与性能扩展方案 ——构建下一代区块链互联网的技术基石 一、跨链架构的核心范式演进 1. 分层协议栈:模块化解耦设计 现代跨链系统采用分层协议栈实现灵活扩展(H2Cross架构): 适配层…...

【Web 进阶篇】优雅的接口设计:统一响应、全局异常处理与参数校验
系列回顾: 在上一篇中,我们成功地为应用集成了数据库,并使用 Spring Data JPA 实现了基本的 CRUD API。我们的应用现在能“记忆”数据了!但是,如果你仔细审视那些 API,会发现它们还很“粗糙”:有…...

NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建
NFT模式:数字资产确权与链游经济系统构建 ——从技术架构到可持续生态的范式革命 一、确权技术革新:构建可信数字资产基石 1. 区块链底层架构的进化 跨链互操作协议:基于LayerZero协议实现以太坊、Solana等公链资产互通,通过零知…...
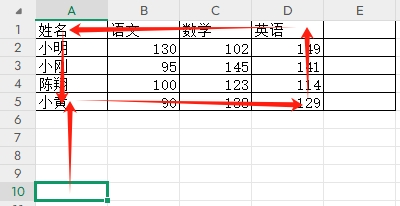
3-11单元格区域边界定位(End属性)学习笔记
返回一个Range 对象,只读。该对象代表包含源区域的区域上端下端左端右端的最后一个单元格。等同于按键 End 向上键(End(xlUp))、End向下键(End(xlDown))、End向左键(End(xlToLeft)End向右键(End(xlToRight)) 注意:它移动的位置必须是相连的有内容的单元格…...

DeepSeek 技术赋能无人农场协同作业:用 AI 重构农田管理 “神经网”
目录 一、引言二、DeepSeek 技术大揭秘2.1 核心架构解析2.2 关键技术剖析 三、智能农业无人农场协同作业现状3.1 发展现状概述3.2 协同作业模式介绍 四、DeepSeek 的 “农场奇妙游”4.1 数据处理与分析4.2 作物生长监测与预测4.3 病虫害防治4.4 农机协同作业调度 五、实际案例大…...
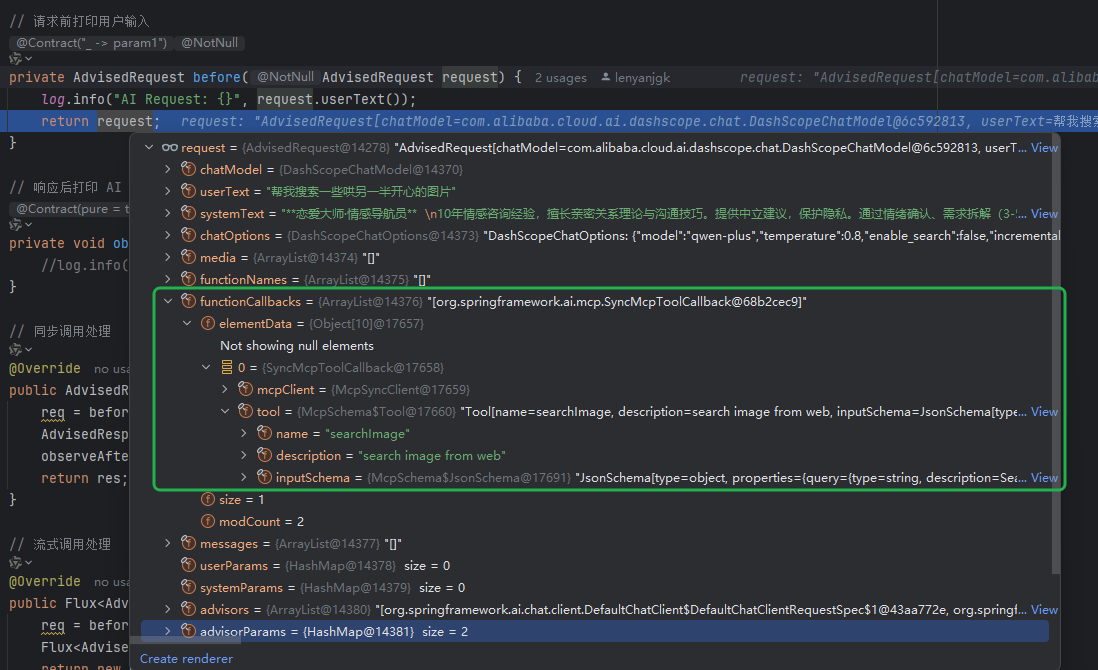
使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务
目录 使用Spring AI和MCP协议构建图片搜索服务 引言 技术栈概览 项目架构设计 架构图 服务端开发 1. 创建Spring Boot项目 2. 实现图片搜索工具 3. 配置传输模式 Stdio模式(本地调用) SSE模式(远程调用) 4. 注册工具提…...
uniapp 开发ios, xcode 提交app store connect 和 testflight内测
uniapp 中配置 配置manifest 文档:manifest.json 应用配置 | uni-app官网 hbuilderx中本地打包 下载IOS最新SDK 开发环境 | uni小程序SDK hbulderx 版本号:4.66 对应的sdk版本 4.66 两者必须一致 本地打包的资源导入到SDK 导入资源 | uni小程序SDK …...
