Linux高级系统编程-3 进程
概念
进程与程序的区别
单道程序和多道程序
并行和并发
进程块控制(PCB)

进程号
概念:
每个进程都由一个进程号来标识,其类型为 pid_t(整型),进程号的范围:0~ 32767。进程号总是唯一的,但进程号可以重用。当一个进程终止后,其进程号就可以 再次使用
获取进程id
获取进程的父进程id
获取进程所在进程组id
创建进程fork()
概述
父子进程,系统允许一个进程可以创建新进程,该进程即为新进程的父进程,新进程即为子进程
函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{printf("啦啦啦\n");
/**
* fork():创建一个进程
* 参数:无
* 返回值:
* 父进程中返回子进程的id
* 子进程中返回0
* -1表示创建失败
* 注意:子进程执行是从fork后开始执行
*/int id = fork();if (id < 0){printf("创建失败id:%d\n",id);}else if(id > 0){printf("父进程id:%d\n,创建的子进程id:%d\n",getpid(),id);}else if (id == 0){printf("父进程id:%d\n,创建的子进程id:%d\n,创建的id:%d\n",getppid(),getpid(),id);}printf("德玛西亚\n");while(1);return 0;
}父子进程关系
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{printf("啦啦啦\n");int id = fork();printf("德玛西亚\n");while(1);return 0;
}结果:
啦啦啦
德玛西亚
德玛西亚
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{printf("啦啦啦");int id = fork();printf("德玛西亚\n");while(1);return 0;
}结果:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{//printf是库函数有缓冲区 hello world先放入缓冲区 被子进程复制了一份printf("hello world1");//write是系统调用 直接将字符串 写入1号文件 没有缓冲区 不被子进程复制//0,输入//1,输出//2,错误输出write(1,"hello world2",12);//创建子进程pid_t pid = fork();return 0;
}结果:hello world1hello world2hello world1
进程状态
ps查看进程状态

进程资源的回收
wait函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int pid = fork();if(pid < 0){printf("创建进程失败");}else if(pid == 0){for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("子进程%u正在执行第%d次\n",getpid(),i);/*sleep:休眠参数休眠时间liunx下参数单位秒,windows下单位毫秒*/sleep(1);}}else if(pid > 0){printf("父进程正在等待子进程执行完毕\n");wait(NULL);printf("父进程已经回收了子进程%u\n",pid);}return 0;
}exit函数与_exit函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int pid = fork();if(pid < 0){printf("创建进程失败");}else if(pid == 0){for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){printf("子进程%u正在执行第%d次\n",getpid(),i);/*sleep:休眠参数休眠时间liunx下参数单位秒,windows下单位毫秒*/sleep(1);}//进程退出//参数0正常退出,非0异常退出,参数就是子进程退出状态值//exit(-1);//库函数,底层封装_exit,效率低_exit(-1);//系统调用函数,效率高printf("Hello");//因为子进程已经退出,所以此代码不会执行}else if(pid > 0){printf("父进程正在等待子进程执行完毕\n");wait(NULL);printf("父进程已经回收了子进程%u\n",pid);}return 0;
}WIFEXITED(status)与WEXITSTATUS(status)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int pid = fork();if(pid < 0){printf("创建进程失败");}else if(pid == 0){for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){printf("子进程%u正在执行第%d次\n",getpid(),i);/*sleep:休眠参数休眠时间liunx下参数单位秒,windows下单位毫秒*/sleep(1);}//进程退出//参数就是子进程退出状态值//exit(100);//库函数,底层封装_exit,效率低_exit(100);//系统调用函数,效率高printf("Hello");//因为子进程已经退出,所以此代码不会执行}else if(pid > 0){printf("父进程正在等待子进程执行完毕\n");int status = 0;pid_t ret = wait(&status);printf("子进程%u,是否正常退出(WIFEXITED):%d\t,退出状态值(WEXITSTATUS)为:%d\n",ret,WIFEXITED(status),WEXITSTATUS(status));printf("父进程已经回收了子进程%u\n",pid);}return 0;
}waitpid函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//exit
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{//创建子进程pid_t pid = fork();if(pid < 0){perror("fork\n");}else if(pid == 0)//子进程{int i=0;for(i=10;i>0;i--){printf("子进程%u剩余的生命%d\n", getpid(), i);sleep(1);}//进程退出//exit(-1);//库函数 底层调用的系统调用_exit_exit(10);//系统调用函数 10就是子进程退出的状态值}else if(pid > 0)//父进程{int status = 0;printf("父进程%u 等待子进程%u的结束\n",getpid(),pid );pid_t ret = waitpid(-1, &status, 0);//不关心状态 直接实参为NULLif(WIFEXITED(status))//子进程正常退出{//取出状态值printf("子进程%u已经结束 状态值为:%d\n", ret,WEXITSTATUS(status));}}return 0;
}atexit 函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void fun()
{printf("进程退出\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//atexit()int p_id = fork();if(p_id == 0){atexit(fun);//子进程printf("子进程已开启\n");sleep(1);printf("子进程退出\n");exit(10);}else if(p_id > 0){//主进程wait(NULL);sleep(5);printf("父进程结束\n");}return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void fun01()
{printf("函数1\n");
}
void fun02()
{printf("函数2\n");
}
void fun03()
{printf("函数3\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{atexit(fun01);atexit(fun02);atexit(fun03);atexit(fun01);sleep(3);return 0;
}特殊进程
僵尸进程
孤儿进程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//exit
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{//创建子进程pid_t pid = fork();if(pid < 0){perror("fork\n");}else if(pid == 0)//子进程{printf("子进程%u\n", getpid());while(1);_exit(-1);}else if(pid > 0)//父进程{}return 0;
}守护进程
创建守护进程步骤
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{// 1,忽略挂断信号SIGHUP,防止被终端误杀//SIG_IGN:忽略指定的信号signal(SIGHUP, SIG_IGN);pid_t pid = fork();//父进程结束if (pid > 0)_exit(-1);//子进程设置会话setsid();//改变工作目录(非必须)chdir("/");//设置权限掩码umask(0002);//关闭文件描述符0 1 2close(0);close(1);close(2);//守护进程的核心任务while (1){//核心任务}return 0;
}多进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//错误演示:创建两个子进程//实际创建了3个,主线程2个,子线程一个// for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)// {// int pid = fork();// }//正确演示:创建两个子进程//主线程创建2个,子线程不创建for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++){int pid = fork();if(pid == 0){break;}}return 0;
}退出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//exit
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{//创建3个子进程int i=0;for(i=0;i<3;i++){pid_t pid = fork();if(pid == 0)//子进程break;}if(i==0)//子进程1{//任务1的代码printf("子进程1:%u\n", getpid());sleep(5);_exit(-1);}else if(i==1)//子进程2{//任务2的代码printf("子进程2:%u\n", getpid());sleep(3);_exit(-1);}else if(i==2)//子进程3{//任务3的代码printf("子进程3:%u\n", getpid());sleep(4);_exit(-1);}else if(i == 3)//父进程{//回收子进程的资源while(1){//-1:等待任一子进程//WNOHANG:不阻塞pid_t ret = waitpid(-1, NULL, WNOHANG);if(ret > 0){printf("子进程:%u已经退出\n", ret);}else if(ret == 0){continue;//还有子进程在运行 需要继续等待}else if(ret < 0){break;//所有子进程都已经结束}}}return 0;
}进程补充
终端

#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//exit
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{pid_t pid = fork();if(pid == 0)//子进程{sleep(3);int num = 0;scanf("%d", &num);printf("子进程%u中的num=%d,所属终端名:%s\n", getpid(), num,ttyname(0));}else if(pid > 0)//父进程{int num = 0;scanf("%d", &num);printf("父进程%u中的num=%d,所属终端名:%s\n", getpid(), num,ttyname(0));}return 0;
}进程组
获取所属进程组id
设置进程组
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//exit
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{pid_t pid = fork();setpgid(pid,pid);if(pid == 0)//子进程{printf("子进程%d,所属组id:%d\n", getpid(), getpgrp());}else if(pid > 0)//父进程{printf("父进程%d,所属组id:%d\n", getpid(), getpgrp());}while(1);return 0;
}会话
函数getsid
函数setid
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//exit
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{pid_t pid = fork();if(pid == 0)//子进程{printf("子进程1id:%d\t,所属组id:%d\t,会话id:%d\n",getpid(),getpgrp(),getsid(getpid()));sleep(2);setsid();printf("子进程2id:%d\t,所属组id:%d\t,会话id:%d\n",getpid(),getpgrp(),getsid(getpid()));while(1);}else if(pid > 0)//父进程{printf("主进程id:%d\t,所属组id:%d\t,会话id:%d\n",getpid(),getpgrp(),getsid(getpid()));while(1);}return 0;
}vfork函数
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int num = 10;// pid_t pid = fork();pid_t pid = vfork();if(pid == 0)//子进程{num=100;printf("子进程num=%d\n",num);// sleep(3);_exit(-1);}else if(pid > 0)//父进程{// wait(NULL);printf("主进程num=%d\n",num);}return 0;
}exec函数族
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{//which 命令,查看命令存储路径/*execl("命令存储路径","命令名","参数1","参数2",...,NULL);*/// execl("/usr/games/sl","sl",NULL);// execl("/bin/ls","ls","-a","-l","-h",NULL);// execl("/bin/ls","ls","-alh",NULL);/*execlp:从path环境变量下查找指定名,如果没有无法运行execlp("命令名","命令名","参数1","参数2",...,NULL)env命令查看环境变量*/// execlp("ls","ls","-alh",NULL);// char *tem[] = {"/ls","-alh",NULL};// execv("/bin/ls",tem);char *tem[] = {"/ls","-alh",NULL};//execvp("ls",tem);execvpe("ls",tem);return 0;
}exec函数和当前进程的关系
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{printf("exec执行前\n");//exec后的程序将不在执行execl("/bin/ls","ls","-alh",NULL);printf("exec执行后\n");return 0;
}exec函数vfork的关系
#45_test.c文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>q
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){printf("test:%d\n",i);sleep(1);}return 0;}
#使用gcc 45_test.c -o 45_test,将源文件编译为可执行文件
#45_code.c文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{int pid = vfork();if (pid < 0){printf("创建进程失败");return 0;}else if(pid == 0){//子进程中代码// for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)// {// sleep(1);// printf("子进程:%d\n",i);// }execl("./45_test","45_test",NULL);_exit(-1);}else if(pid > 0){// 父进程中代码for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){printf("code:%d\n",i);sleep(1);}return 0;
}system函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{printf("system前\n");system("ls -alh");printf("system后\n");return 0;
}相关文章:

Linux高级系统编程-3 进程
概念 进程与程序的区别 程序:一个可执行文件, 占磁盘空间,是静态的 进程:一个程序运行的过程, 占内存,动态的。 单道程序和多道程序 单道程序设计: 所有进程一个一个排队执行。若 A 阻塞, B 只能等待࿰…...
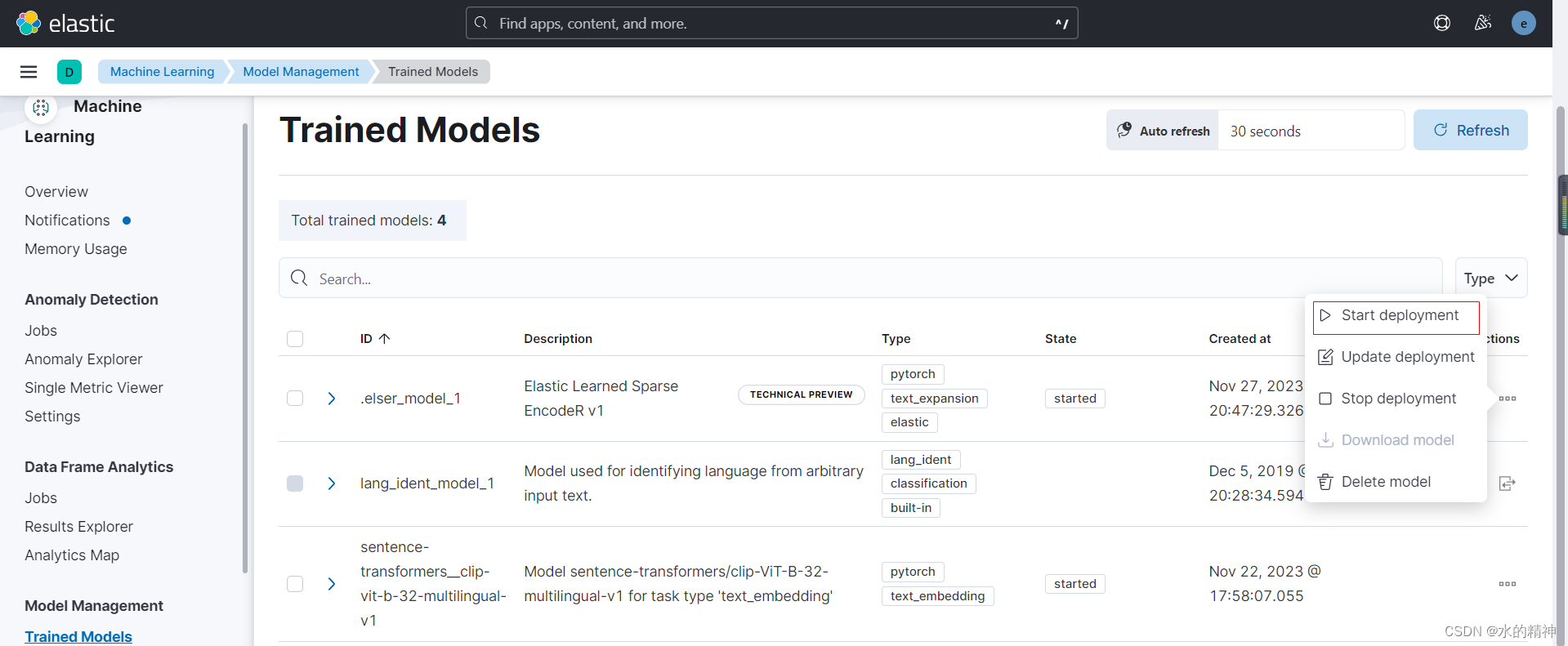
ES-ELSER 如何在内网中离线导入ES官方的稀疏向量模型(国内网络环境下操作方法)
ES官方训练了稀疏向量模型,用来支持语义检索。(目前该模型只支持英文) 最好是以离线的方式安装。在线的方式,在国内下载也麻烦,下载速度也慢。还不如用离线的方式。对于一般的生产环境,基本上也是网络隔离的…...

Excel 使用技巧
Excel 使用技巧 注意: excel 中设计计算的字符尽量使用英文。 拼接两段文字(字符串拼接) 方法一 在需要计算的单元格上,键入 点击 A1(点击需要拼接的单元格) & C1(点击需要拼接的单元格) 举例: 姓名栏想要拼接 姓 和 名 两列点击姓名这一…...
-Part.03 资源规划)
Hadoop学习笔记(HDP)-Part.03 资源规划
目录 Part.01 关于HDP Part.02 核心组件原理 Part.03 资源规划 Part.04 基础环境配置 Part.05 Yum源配置 Part.06 安装OracleJDK Part.07 安装MySQL Part.08 部署Ambari集群 Part.09 安装OpenLDAP Part.10 创建集群 Part.11 安装Kerberos Part.12 安装HDFS Part.13 安装Ranger …...

一个最新国内可用的免费GPT4,Midjourney绘画网站+使用教程
一、前言 ChatGPT GPT4.0,Midjourney绘画,相信对大家应该不感到陌生吧?简单来说,GPT-4技术比之前的GPT-3.5相对来说更加智能,会根据用户的要求生成多种内容甚至也可以和用户进行创作交流。 然而,GPT-4对普…...

深入了解Java8新特性-日期时间API之ZonedDateTime类
阅读建议 嗨,伙计!刷到这篇文章咱们就是有缘人,在阅读这篇文章前我有一些建议: 本篇文章大概19000多字,预计阅读时间长需要10分钟以上。本篇文章的实战性、理论性较强,是一篇质量分数较高的技术干货文章&…...

使用Vue写一个日期选择器
在 Vue 中实现日期选择器的方法有很多,下面提供一个简单的实现方法。 首先,在需要使用日期选择器的组件中引用 Vue 和 date-fns 库,date-fns 库是一个轻量级的 JavaScript 时间日期工具库,可以方便地处理日期的格式化和计算。 &…...

19、pytest通过mark标记测试函数
官方实例 [pytest] markers slow:marks tests as slow(deselect with -m "not slow")serial# content of test_mark.py import pytestpytest.mark.slow def test_mark_function():print("test_mark_function was invoked")assert 0解读与实操 通过使用p…...
Linux环境变量与命令行参数
Linux环境变量与命令行参数 一.命令行参数1.语法2.应用1:简易计算器 二.环境变量1.环境变量的概念2.环境变量的作用3.进一步理解环境变量的作用4.常见环境变量5.导出环境变量(添加环境变量)6.环境变量的特性7.另一种获取环境变量的方式8.小功能:用于身份验证的代码9.补充:第三种…...

jQuery实现3D轮播图
通过CSS3的3D变换和jQuery Transit插件实现了一个3D旋转的图片轮播效果 HTML部分: div id“banner”:定义了一个id为"banner"的div标签,作为图片轮播的容器。 ul: 在"banner"中定义了一个无序列表,每个列表项…...
-------连载(43))
Java面试题(每天10题)-------连载(43)
目录 Spring篇 1、请举例说明Qualifier注解 2、构造方法注入和设值注入有什么区别? 3、Spring框架中有哪些不同类型的事件? 4、FileSystemResource和ClassPathResource有什么区别? 5、Spring框架中都用到了哪些设计模式? 6…...
)
Python高级数据结构——并查集(Disjoint Set)
Python中的并查集(Disjoint Set):高级数据结构解析 并查集是一种用于处理集合的数据结构,它主要支持两种操作:合并两个集合和查找一个元素所属的集合。在本文中,我们将深入讲解Python中的并查集࿰…...

pytorch学习9-优化器学习
系列文章目录 pytorch学习1-数据加载以及Tensorboard可视化工具pytorch学习2-Transforms主要方法使用pytorch学习3-torchvisin和Dataloader的使用pytorch学习4-简易卷积实现pytorch学习5-最大池化层的使用pytorch学习6-非线性变换(ReLU和sigmoid)pytorc…...

MySQL之锁
MySQL之锁 锁是计算机在执行多线程或线程时用于并发访问同一共享资源时的同步机制,MySQL中的锁是在服务器层或者存储引擎层实现的,保证了数据访问的一致性与有效性 MySQL锁可以按模式分类为:乐观锁与悲观锁。 按粒度分可以分为全局锁、表级锁…...

今日现货黄金最新建议
近期现货黄金价格再度逼近历史高位,很多本来在场外观望的投资者,都纷纷希望进场一试身手。然而大涨大跌的行情并不是很适合新手投资者参与,如果大家还没做好技术上的准备,可以多听听正规交易平台的专业人士的意见。 在正式入市之前…...

基于混沌算法的图像加密解密系统
1.研究背景与意义 项目参考AAAI Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence 研究背景与意义: 随着信息技术的迅猛发展,图像的传输和存储已经成为现代社会中不可或缺的一部分。然而,随着互联网的普及和信息的快速传播&am…...
vscode插件离线下载
离线下载插件地址:https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/VSCode...
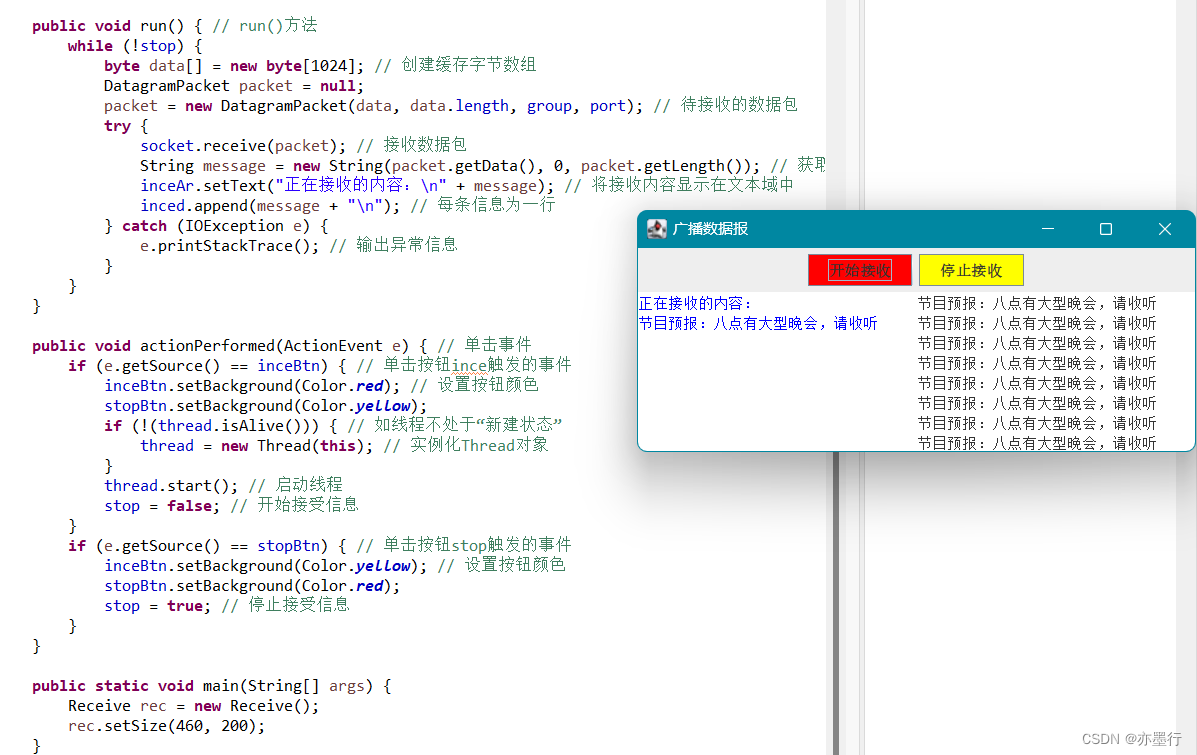
第二十一章总结
一、网络通信: 1.网络程序设计基础:网络程序设计编写的是与其他计算机进行通信的程序。 1.1局域网与互联网:为了实现两台计算机的通信,必须用一个网络线路连接两台计算机 2.网络协议:网络协议规定了计算机之间连接的…...
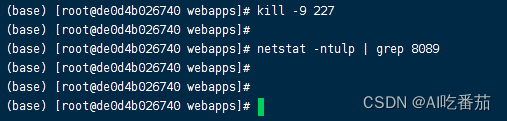
查看端口占用并杀死进程
1.安装查看工具 sudo yum install net-tools 2.查看占用情况 netstat -tunlp | grep 8089 3.杀死进程 kill -9 227...

前后端数据传输格式(上)
作者简介:大家好,我是smart哥,前中兴通讯、美团架构师,现某互联网公司CTO 联系qq:184480602,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬 作为后端,写…...
)
IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol,内部网关协议)
IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol,内部网关协议) 是一种用于在一个自治系统(AS)内部传递路由信息的路由协议,主要用于在一个组织或机构的内部网络中决定数据包的最佳路径。与用于自治系统之间通信的 EGP&…...

AI,如何重构理解、匹配与决策?
AI 时代,我们如何理解消费? 作者|王彬 封面|Unplash 人们通过信息理解世界。 曾几何时,PC 与移动互联网重塑了人们的购物路径:信息变得唾手可得,商品决策变得高度依赖内容。 但 AI 时代的来…...
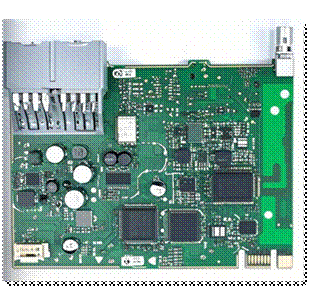
NXP S32K146 T-Box 携手 SD NAND(贴片式TF卡):驱动汽车智能革新的黄金组合
在汽车智能化的汹涌浪潮中,车辆不再仅仅是传统的交通工具,而是逐步演变为高度智能的移动终端。这一转变的核心支撑,来自于车内关键技术的深度融合与协同创新。车载远程信息处理盒(T-Box)方案:NXP S32K146 与…...
springboot整合VUE之在线教育管理系统简介
可以学习到的技能 学会常用技术栈的使用 独立开发项目 学会前端的开发流程 学会后端的开发流程 学会数据库的设计 学会前后端接口调用方式 学会多模块之间的关联 学会数据的处理 适用人群 在校学生,小白用户,想学习知识的 有点基础,想要通过项…...
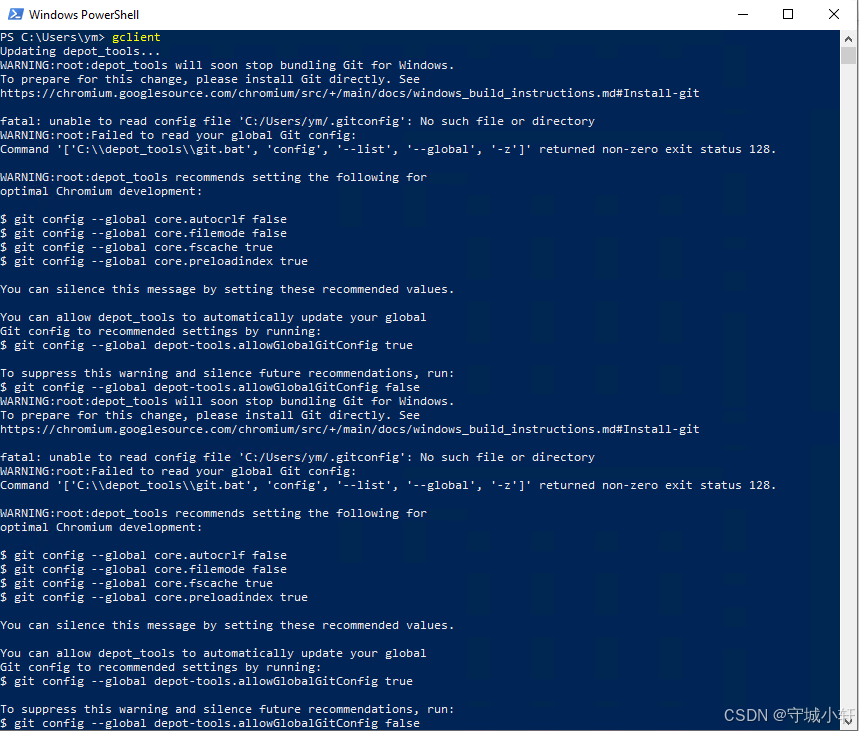
Chromium 136 编译指南 Windows篇:depot_tools 配置与源码获取(二)
引言 工欲善其事,必先利其器。在完成了 Visual Studio 2022 和 Windows SDK 的安装后,我们即将接触到 Chromium 开发生态中最核心的工具——depot_tools。这个由 Google 精心打造的工具集,就像是连接开发者与 Chromium 庞大代码库的智能桥梁…...

Python网页自动化Selenium中文文档
1. 安装 1.1. 安装 Selenium Python bindings 提供了一个简单的API,让你使用Selenium WebDriver来编写功能/校验测试。 通过Selenium Python的API,你可以非常直观的使用Selenium WebDriver的所有功能。 Selenium Python bindings 使用非常简洁方便的A…...
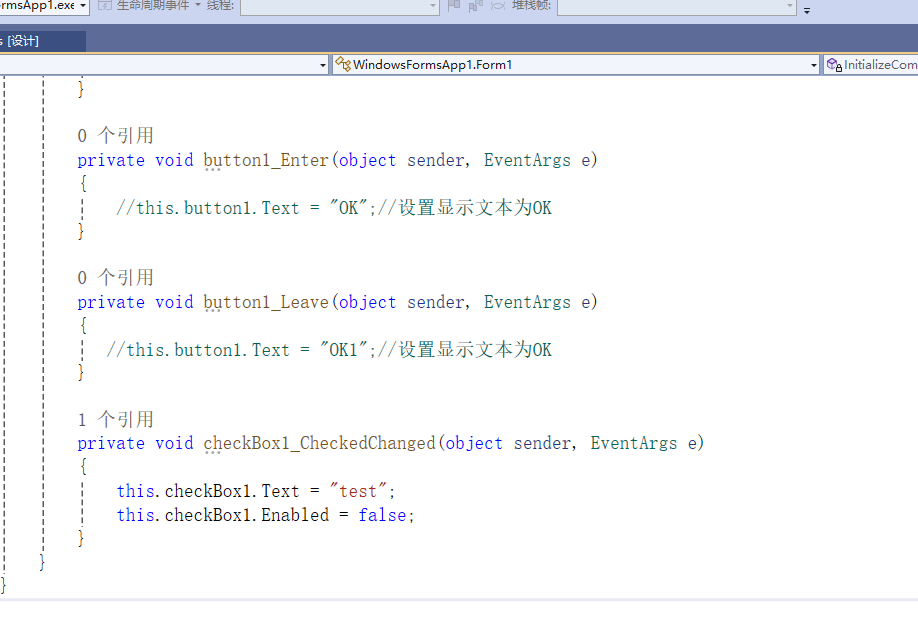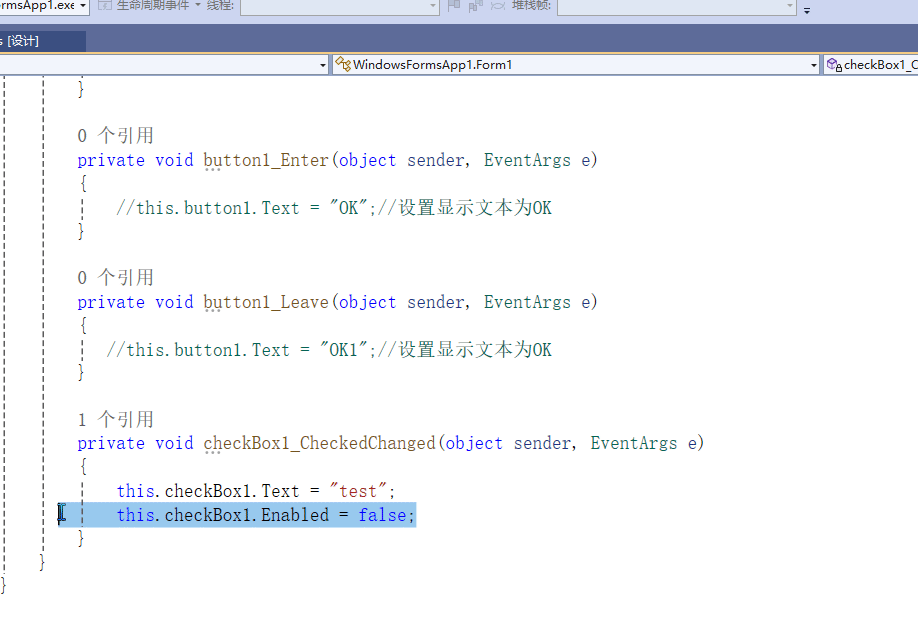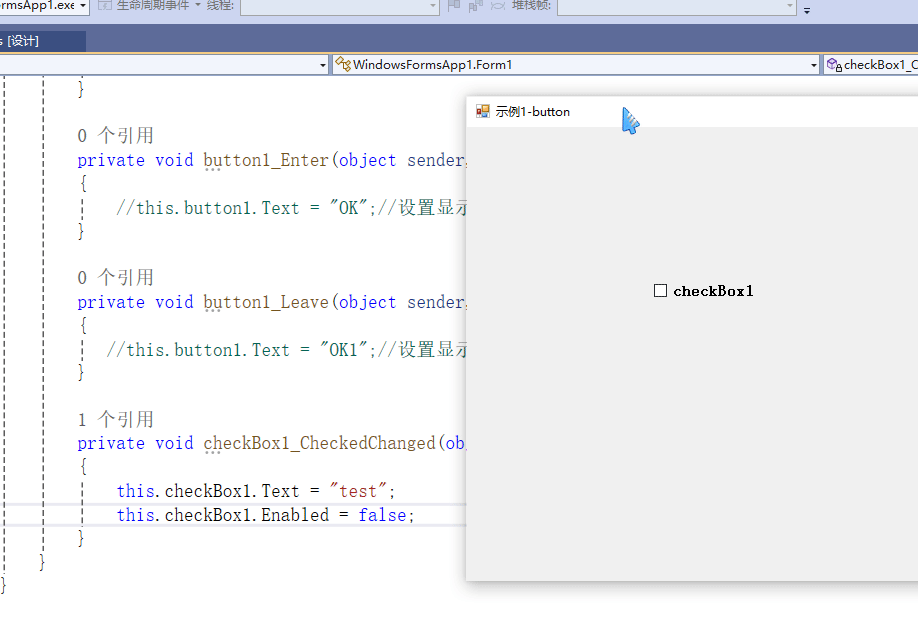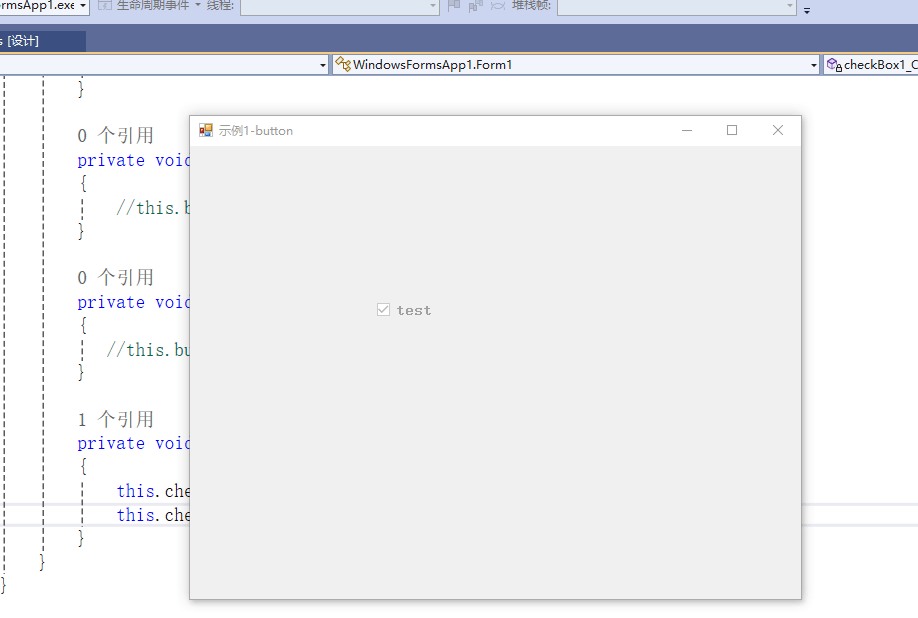
C# winform教程(二)----checkbox
一、作用 提供一个用户选择或者不选的状态,这是一个可以多选的控件。 二、属性 其实功能大差不差,除了特殊的几个外,与button基本相同,所有说几个独有的 checkbox属性 名称内容含义appearance控件外观可以变成按钮形状checkali…...

字符串哈希+KMP
P10468 兔子与兔子 #include<bits/stdc.h> using namespace std; typedef unsigned long long ull; const int N 1000010; ull a[N], pw[N]; int n; ull gethash(int l, int r){return a[r] - a[l - 1] * pw[r - l 1]; } signed main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false), …...

SQL进阶之旅 Day 22:批处理与游标优化
【SQL进阶之旅 Day 22】批处理与游标优化 文章简述(300字左右) 在数据库开发中,面对大量数据的处理任务时,单条SQL语句往往无法满足性能需求。本篇文章聚焦“批处理与游标优化”,深入探讨如何通过批量操作和游标技术提…...

比特币:固若金汤的数字堡垒与它的四道防线
第一道防线:机密信函——无法破解的哈希加密 将每一笔比特币交易比作一封在堡垒内部传递的机密信函。 解释“哈希”(Hashing)就是一种军事级的加密术(SHA-256),能将信函内容(交易细节…...
