C实现的双向链表队列
如下代码所示,一个头文件实现的双向链表,用c代码实现:
#ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H
#define _LINUX_LIST_H#include "stddef.h"
#include "poison.h"#ifndef ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH
#define ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH
static inline void prefetch(const void *x) {;}
#endif/** Simple doubly linked list implementation.** Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can* generate better code by using them directly rather than* using the generic single-entry routines.*/struct list_head {struct list_head *next, *prev;
};#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }#define LIST_HEAD(name) \struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{list->next = list;list->prev = list;
}/** Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.** This is only for internal list manipulation where we know* the prev/next entries already!*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,struct list_head *prev,struct list_head *next)
{next->prev = new;new->next = next;new->prev = prev;prev->next = new;
}/*** list_add - add a new entry* @new: new entry to be added* @head: list head to add it after** Insert a new entry after the specified head.* This is good for implementing stacks.*/
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}/*** list_add_tail - add a new entry* @new: new entry to be added* @head: list head to add it before** Insert a new entry before the specified head.* This is useful for implementing queues.*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}/** Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries* point to each other.** This is only for internal list manipulation where we know* the prev/next entries already!*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{next->prev = prev;prev->next = next;
}/*** list_del - deletes entry from list.* @entry: the element to delete from the list.* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is* in an undefined state.*/
static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);entry->next = LIST_POISON1;entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}/*** list_replace - replace old entry by new one* @old : the element to be replaced* @new : the new element to insert** If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,struct list_head *new)
{new->next = old->next;new->next->prev = new;new->prev = old->prev;new->prev->next = new;
}static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,struct list_head *new)
{list_replace(old, new);INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}/*** list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it.* @entry: the element to delete from the list.*/
static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}/*** list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head* @list: the entry to move* @head: the head that will precede our entry*/
static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{__list_del(list->prev, list->next);list_add(list, head);
}/*** list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail* @list: the entry to move* @head: the head that will follow our entry*/
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{__list_del(list->prev, list->next);list_add_tail(list, head);
}/*** list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head* @list: the entry to test* @head: the head of the list*/
static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,const struct list_head *head)
{return list->next == head;
}/*** list_empty - tests whether a list is empty* @head: the list to test.*/
static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
{return head->next == head;
}/*** list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified* @head: the list to test** Description:* tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be* in the process of modifying either member (next or prev)** NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization* can only be safe if the only activity that can happen* to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used* if another CPU could re-list_add() it.*/
static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head)
{struct list_head *next = head->next;return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
}/*** list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry.* @head: the list to test.*/
static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head)
{return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{struct list_head *new_first = entry->next;list->next = head->next;list->next->prev = list;list->prev = entry;entry->next = list;head->next = new_first;new_first->prev = head;
}/*** list_cut_position - cut a list into two* @list: a new list to add all removed entries* @head: a list with entries* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself* and if so we won't cut the list** This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about* losing its data.**/
static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry)
{if (list_empty(head))return;if (list_is_singular(head) &&(head->next != entry && head != entry))return;if (entry == head)INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);else__list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
}static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,struct list_head *prev,struct list_head *next)
{struct list_head *first = list->next;struct list_head *last = list->prev;first->prev = prev;prev->next = first;last->next = next;next->prev = last;
}/*** list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks* @list: the new list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list))__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
}/*** list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue* @list: the new list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.*/
static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list))__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
}/*** list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.* @list: the new list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.** The list at @list is reinitialised*/
static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list)) {__list_splice(list, head, head->next);INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);}
}/*** list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list* @list: the new list to add.* @head: the place to add it in the first list.** Each of the lists is a queue.* The list at @list is reinitialised*/
static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
{if (!list_empty(list)) {__list_splice(list, head->prev, head);INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);}
}/*** list_entry - get the struct for this entry* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \container_of(ptr, type, member)/*** list_first_entry - get the first element from a list* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Note, that list is expected to be not empty.*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)/*** list_for_each - iterate over a list* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->next; prefetch(pos->next), pos != (head); \pos = pos->next)/*** __list_for_each - iterate over a list* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.** This variant differs from list_for_each() in that it's the* simplest possible list iteration code, no prefetching is done.* Use this for code that knows the list to be very short (empty* or 1 entry) most of the time.*/
#define __list_for_each(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)/*** list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->prev; prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head); \pos = pos->prev)/*** list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \pos = n, n = pos->next)/*** list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.*/
#define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) \for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; \prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head); \pos = n, n = pos->prev)/*** list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member); \prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue()* @pos: the type * to use as a start point* @head: the head of the list* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue().*/
#define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \((pos) ? : list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after* the current position.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after* the current position.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \for (; prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe_continue* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point,* safe against removal of list entry.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member), \n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe_from* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against* removal of list entry.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/*** list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.** Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal* of list entry.*/
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member), \n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \&pos->member != (head); \pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member))/** Double linked lists with a single pointer list head.* Mostly useful for hash tables where the two pointer list head is* too wasteful.* You lose the ability to access the tail in O(1).*/struct hlist_head {struct hlist_node *first;
};struct hlist_node {struct hlist_node *next, **pprev;
};#define HLIST_HEAD_INIT { .first = NULL }
#define HLIST_HEAD(name) struct hlist_head name = { .first = NULL }
#define INIT_HLIST_HEAD(ptr) ((ptr)->first = NULL)
static inline void INIT_HLIST_NODE(struct hlist_node *h)
{h->next = NULL;h->pprev = NULL;
}static inline int hlist_unhashed(const struct hlist_node *h)
{return !h->pprev;
}static inline int hlist_empty(const struct hlist_head *h)
{return !h->first;
}static inline void __hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{struct hlist_node *next = n->next;struct hlist_node **pprev = n->pprev;*pprev = next;if (next)next->pprev = pprev;
}static inline void hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n)
{__hlist_del(n);n->next = LIST_POISON1;n->pprev = LIST_POISON2;
}static inline void hlist_del_init(struct hlist_node *n)
{if (!hlist_unhashed(n)) {__hlist_del(n);INIT_HLIST_NODE(n);}
}static inline void hlist_add_head(struct hlist_node *n, struct hlist_head *h)
{struct hlist_node *first = h->first;n->next = first;if (first)first->pprev = &n->next;h->first = n;n->pprev = &h->first;
}/* next must be != NULL */
static inline void hlist_add_before(struct hlist_node *n,struct hlist_node *next)
{n->pprev = next->pprev;n->next = next;next->pprev = &n->next;*(n->pprev) = n;
}static inline void hlist_add_after(struct hlist_node *n,struct hlist_node *next)
{next->next = n->next;n->next = next;next->pprev = &n->next;if(next->next)next->next->pprev = &next->next;
}#define hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr,type,member)#define hlist_for_each(pos, head) \for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1; }); \pos = pos->next)#define hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }); \pos = n)/*** hlist_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry(tpos, pos, head, member) \for (pos = (head)->first; \pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \pos = pos->next)/*** hlist_for_each_entry_continue - iterate over a hlist continuing after current point* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_continue(tpos, pos, member) \for (pos = (pos)->next; \pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \pos = pos->next)/*** hlist_for_each_entry_from - iterate over a hlist continuing from current point* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_from(tpos, pos, member) \for (; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \pos = pos->next)/*** hlist_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry* @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.* @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor.* @n: another &struct hlist_node to use as temporary storage* @head: the head for your list.* @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct.*/
#define hlist_for_each_entry_safe(tpos, pos, n, head, member) \for (pos = (head)->first; \pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }) && \({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \pos = n)#endif相关文章:

C实现的双向链表队列
如下代码所示,一个头文件实现的双向链表,用c代码实现: #ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H #define _LINUX_LIST_H#include "stddef.h" #include "poison.h"#ifndef ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH #define ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH static inline voi…...
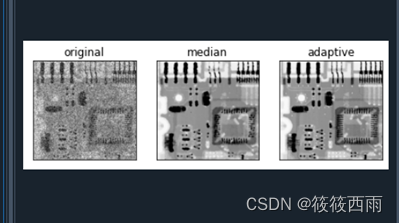
自适应中值滤波器的python代码实现-----冈萨雷斯数字图像处理
基本原理: 自适应中值滤波器是一种图像处理技术,用于去除图像中的噪声。其原理是根据像素周围邻域内像素值的特性,动态地选择滤波器的大小和中值滤波的程度。 **邻域选择:**对于每个像素点,选取一个窗口或者邻域&…...

Python作业答疑_6.22~6.25
一、Python 一班 1. 基数分割列表 1.1 问题描述 给定一无序数列,把数列的第一个数字当成基数,让数列中基数小的数字排在数列前面,比基数大的数字排在数列的后面。 1.2 问题示例 如数列:num[4,1,8,3,9,2,10,7]。基数为 4&…...

Uber Go 语言编码规范
uber-go/guide 的中文翻译 English 文档链接 Uber Go 语言编码规范 Uber 是一家美国硅谷的科技公司,也是 Go 语言的早期 adopter。其开源了很多 golang 项目,诸如被 Gopher 圈熟知的 zap、jaeger 等。2018 年年末 Uber 将内部的 Go 风格规范 开源到 G…...

UniRepLKNet:用于音频、视频、点云、时间序列和图像识别的通用感知大内核ConvNet
摘要 https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.15599 大核卷积神经网络(ConvNets)最近受到了广泛的研究关注,但存在两个未解决的关键问题需要进一步研究。(1)现有大核ConvNets的架构在很大程度上遵循传统ConvNets或Transformers的设计原则,而大核ConvNets的架构设计仍未得到充分解决。(2…...
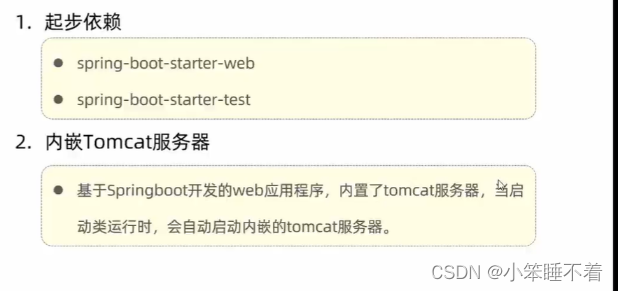
Http协议与Tomcat
HTTP协议 HTTP协议(HyperText Transfer Protocol)即超文本传输协议 ,是TCP/IC网络体系结构应用层的一个客户端-服务端协议,是所有客户端,服务端数据传输的基石(数据传输规则) 特点 ⭐基于TCP协…...
Spring AOP从入门到精通
目录 1. AOP的演化过程 1. 代理模式 2. 动态代理 2.1 JDK动态代理 2.2 Cglib动态代理 3. Spring模式 3.1 ProxyFactory 3.2 ProxyFactoryBean 3.3 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 2. Spring AOP抽象 1. 核心术语 1.1 连接点(JoinPoint) 1.2 切点(Pointcut) 1.3 增强(Ad…...
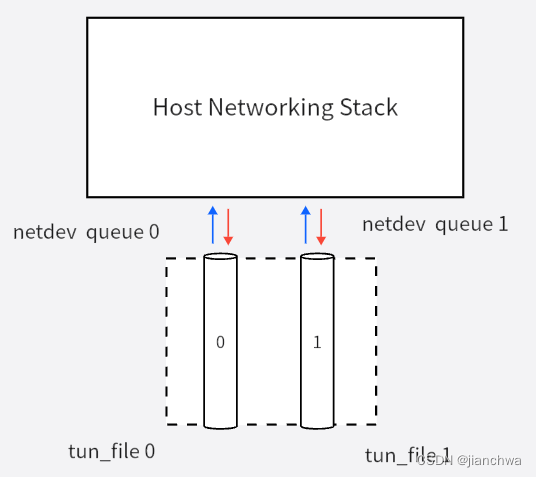
Tap虚拟网卡
1 概述 Tap设备通常用于虚拟化场景下,其驱动代码位于drivers/net/tun.c,tap与tun复用大部分代码, 注:drivers/net/tap.c并不是tap设备的代码,而是macvtap和ipvtap; 下文中,我们统一称tap&#…...
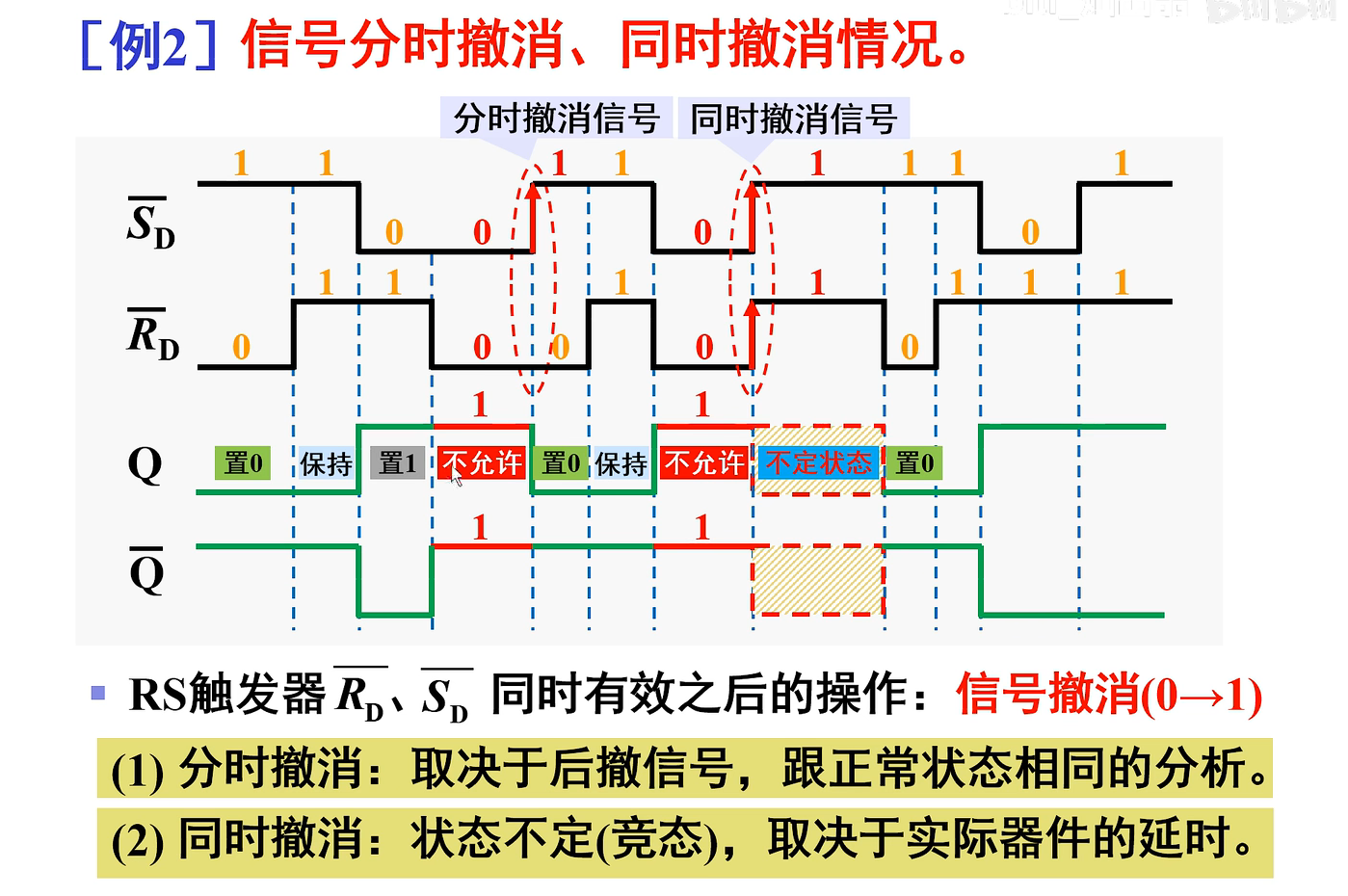
【数电笔记】53-与非门构成的基本RS触发器
目录 说明: 1. 电路组成 2. 逻辑功能 3. 特性表 4. 特性方程 5. 状态转换图 6. 驱动表 7. 例题 例1 例2 说明: 笔记配套视频来源:B站;本系列笔记并未记录所有章节,只对个人认为重要章节做了笔记;…...

kubernetes(k8s)容器内无法连接同所绑定的Service ClusterIP问题记录
kubernetes(k8s)容器内无法连接同所绑定的Service ClusterIP问题记录 1. k8s环境 k8s使用kubernetes-server-linux-amd64_1.19.10.tar.gz 二进制bin 的方式手动部署 k8s 版本: [rootmaster ~]# kubectl version Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:&…...
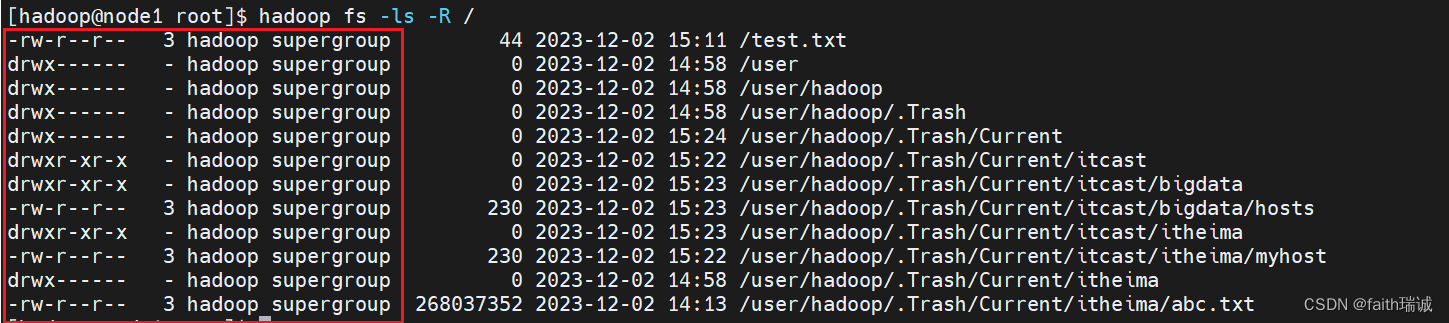
Hadoop入门学习笔记
视频课程地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1WY4y197g7 课程资料链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/15KpnWeKpvExpKmOC8xjmtQ?pwd5ay8 这里写目录标题 一、VMware准备Linux虚拟机1.1. VMware安装Linux虚拟机1.1.1. 修改虚拟机子网IP和网关1.1.2. 安装…...
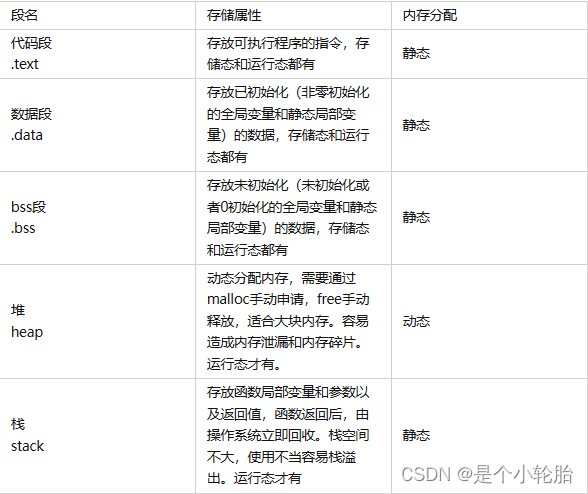
堆栈,BSS,DATA,TEXT
一、目标文件 首先目标文件的构成,Linux下就是.o 文件 编译器编译源码后生成的文件叫目标文件(Object File)。 目标文件和可执行文件一般采用同一种格式,这种存储格式为 ELF。 目前文件的内容至少有编译后的机器指令代码和数据&a…...

Java八股文面试全套真题【含答案】-JSON篇
什么是JSON? 答案:JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,基于JavaScript的对象字面量表示法,用于在不同语言和平台之间传输数据。JSON的数据结构是怎样的? 答案…...

数据库管理-第119期 记一次迁移和性能优化(202301130)
数据库管理-第119期 记一次迁移和性能优化(202301130) 1 迁移 之前因为DV组件没有迁移成功的那个PDB,后来想着在目标端安装DV组件迁移,结果目标端装不上,而且开了SR也没看出个所以然来。只能换一个方向,尝…...
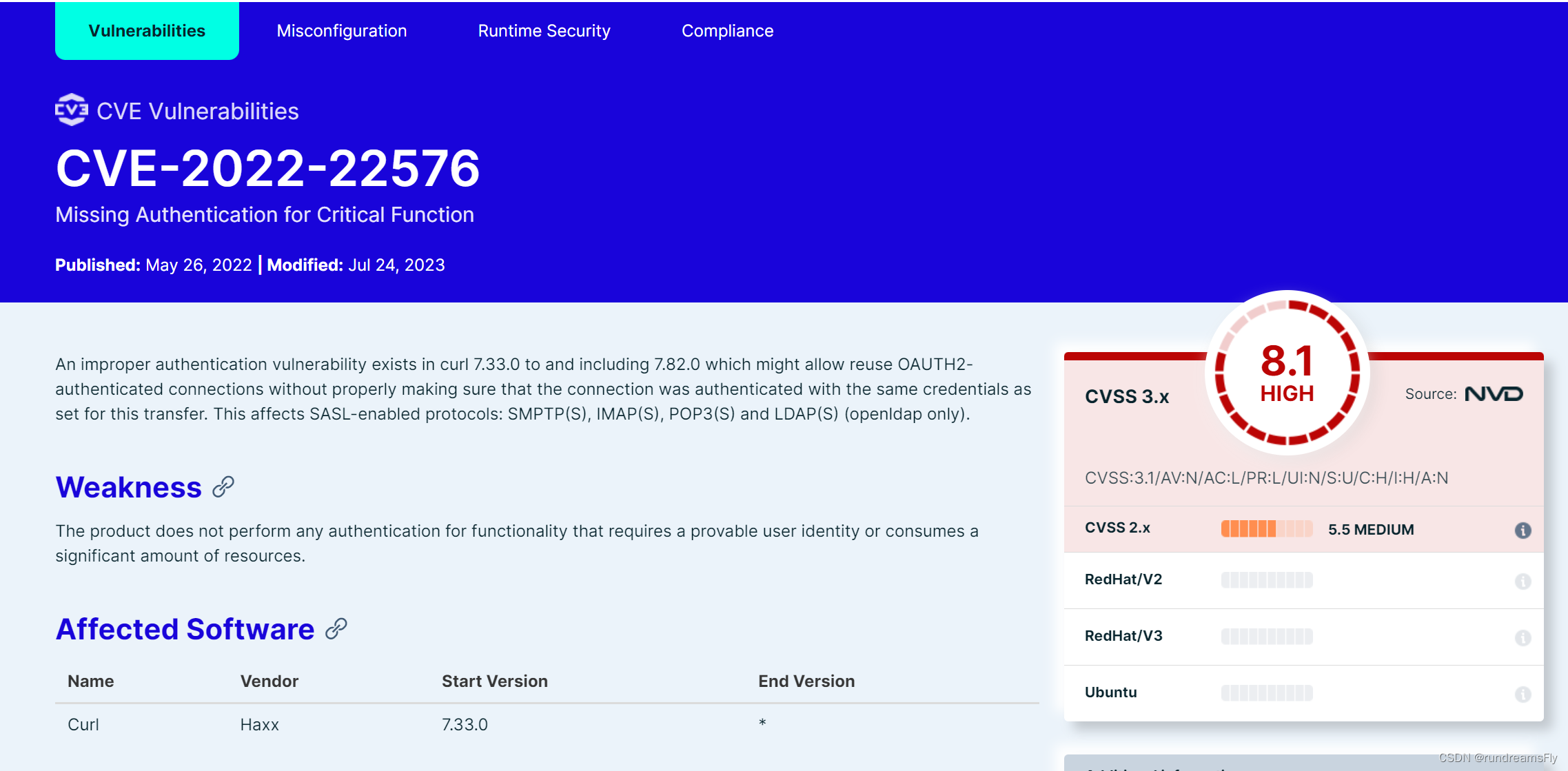
【云原生-K8s】镜像漏洞安全扫描工具Trivy部署及使用
基础介绍基础描述Trivy特点 部署在线下载百度网盘下载安装 使用扫描nginx镜像扫描结果解析json格式输出 总结 基础介绍 基础描述 Trivy是一个开源的容器镜像漏洞扫描器,可以扫描常见的操作系统和应用程序依赖项的漏洞。它可以与Docker和Kubernetes集成,…...
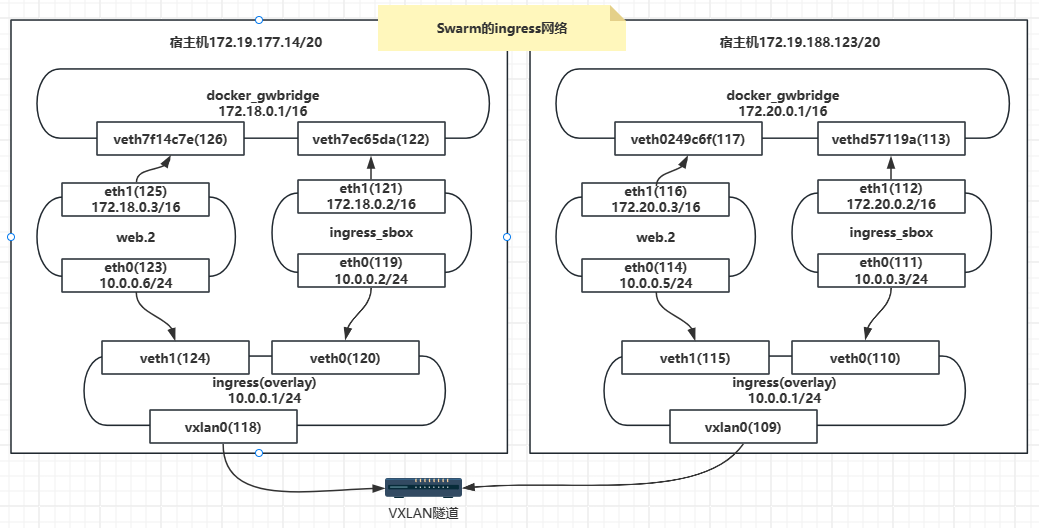
【Docker】Swarm的ingress网络
Docker Swarm Ingress网络是Docker集群中的一种网络模式,它允许在Swarm集群中运行的服务通过一个公共的入口点进行访问。Ingress网络将外部流量路由到Swarm集群中的适当服务,并提供负载均衡和服务发现功能。 在Docker Swarm中,Ingress网络使…...

gcc安全特性之FORTIFY_SOURCE
GCC 4.0引入了FORTIFY_SOURCE特性,旨在加强程序的安全性,特别是对于字符串和内存操作函数的使用。下面是对FORTIFY_SOURCE机制的深入分析: 1. 功能 FORTIFY_SOURCE旨在检测和防止缓冲区溢出,格式化字符串漏洞以及其他与内存操作…...

【JUC】二十、volatile变量的特点与使用场景
文章目录 1、volatile可见性案例2、线程工作内存与主内存之间的原子操作3、volatile变量不具有原子性案例4、无原子性的原因分析:i5、volatile变量小总结6、重排序7、volatile变量禁重排的案例8、日常使用场景9、总结 volatile变量的特点: 可见性禁重排无…...
)
软件工程期末复习(2)
学习资料 设计模式与软件体系结构【期末全整理答案】_软件设计模式与体系结构期末考试题_鸽子不二的博客-CSDN博客 软件设计与体系结构(第二版)部分习题_软件设计与体系结构第二版课后答案-CSDN博客 软件体系结构试题库试题和答案 - 豆丁网Docin 软件设计与体系结构复习 - CN…...
[vue3] 使用 vite 创建vue3项目的详细流程
一、vite介绍 Vite(法语意为 “快速的”,发音 /vit/,发音同 “veet”) 是一种新型前端构建工具,能够显著提升前端开发体验(热更新、打包构建速度更快)。 二、使用vite构建项目 【学习指南】学习新技能最…...

MySQL 隔离级别:脏读、幻读及不可重复读的原理与示例
一、MySQL 隔离级别 MySQL 提供了四种隔离级别,用于控制事务之间的并发访问以及数据的可见性,不同隔离级别对脏读、幻读、不可重复读这几种并发数据问题有着不同的处理方式,具体如下: 隔离级别脏读不可重复读幻读性能特点及锁机制读未提交(READ UNCOMMITTED)允许出现允许…...
关于nvm与node.js
1 安装nvm 安装过程中手动修改 nvm的安装路径, 以及修改 通过nvm安装node后正在使用的node的存放目录【这句话可能难以理解,但接着往下看你就了然了】 2 修改nvm中settings.txt文件配置 nvm安装成功后,通常在该文件中会出现以下配置&…...
2.Vue编写一个app
1.src中重要的组成 1.1main.ts // 引入createApp用于创建应用 import { createApp } from "vue"; // 引用App根组件 import App from ./App.vue;createApp(App).mount(#app)1.2 App.vue 其中要写三种标签 <template> <!--html--> </template>…...
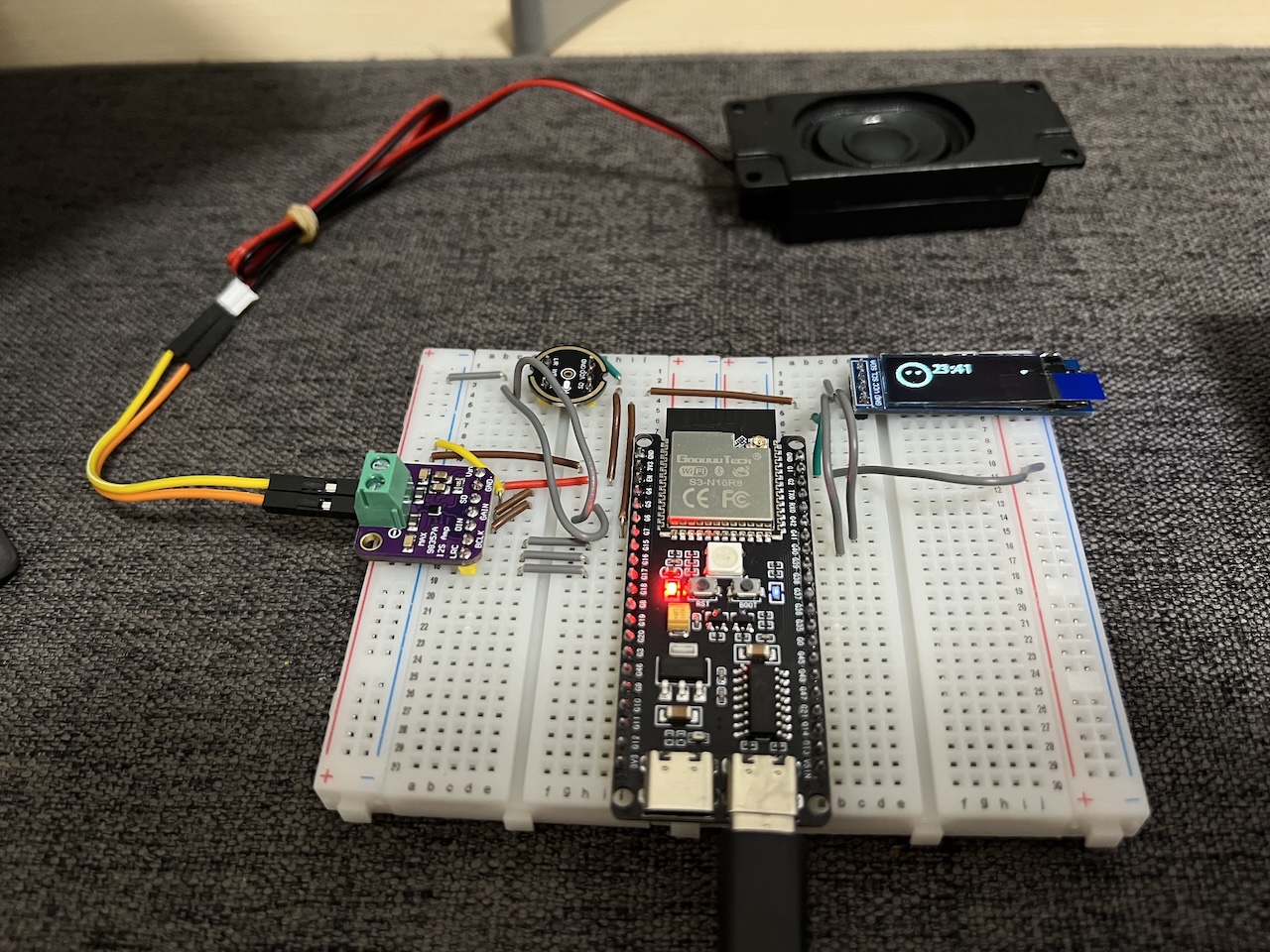
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...

【Zephyr 系列 10】实战项目:打造一个蓝牙传感器终端 + 网关系统(完整架构与全栈实现)
🧠关键词:Zephyr、BLE、终端、网关、广播、连接、传感器、数据采集、低功耗、系统集成 📌目标读者:希望基于 Zephyr 构建 BLE 系统架构、实现终端与网关协作、具备产品交付能力的开发者 📊篇幅字数:约 5200 字 ✨ 项目总览 在物联网实际项目中,**“终端 + 网关”**是…...

Xen Server服务器释放磁盘空间
disk.sh #!/bin/bashcd /run/sr-mount/e54f0646-ae11-0457-b64f-eba4673b824c # 全部虚拟机物理磁盘文件存储 a$(ls -l | awk {print $NF} | cut -d. -f1) # 使用中的虚拟机物理磁盘文件 b$(xe vm-disk-list --multiple | grep uuid | awk {print $NF})printf "%s\n"…...

elementUI点击浏览table所选行数据查看文档
项目场景: table按照要求特定的数据变成按钮可以点击 解决方案: <el-table-columnprop"mlname"label"名称"align"center"width"180"><template slot-scope"scope"><el-buttonv-if&qu…...

【Java多线程从青铜到王者】单例设计模式(八)
wait和sleep的区别 我们的wait也是提供了一个还有超时时间的版本,sleep也是可以指定时间的,也就是说时间一到就会解除阻塞,继续执行 wait和sleep都能被提前唤醒(虽然时间还没有到也可以提前唤醒),wait能被notify提前唤醒…...

基于谷歌ADK的 智能产品推荐系统(2): 模块功能详解
在我的上一篇博客:基于谷歌ADK的 智能产品推荐系统(1): 功能简介-CSDN博客 中我们介绍了个性化购物 Agent 项目,该项目展示了一个强大的框架,旨在模拟和实现在线购物环境中的智能导购。它不仅仅是一个简单的聊天机器人,更是一个集…...

智能体革命:企业如何构建自主决策的AI代理?
OpenAI智能代理构建实用指南详解 随着大型语言模型(LLM)在推理、多模态理解和工具调用能力上的进步,智能代理(Agents)成为自动化领域的新突破。与传统软件仅帮助用户自动化流程不同,智能代理能够自主执行工…...
