【EventBus】EventBus源码浅析
二、EventBus源码解析
目录
- 1、EventBus的构造方法
- 2、订阅者注册
- 2.1 订阅者方法的查找过程
- 2.2 订阅者的注册过程
- 1. subscriptionsByEventType 映射:
- 2. typesBySubscriber 映射:
- 2.3 总结订阅者的注册过程
- 3、事件的发送
- 3.1 使用Post提交事件
- 3.2 使用postSingleEventForEventType处理事件的分发
- 3.2 总结事件的发送过程
- 4、订阅者的取消
1、EventBus的构造方法
我们在使用Eventbus时首先会调用Eventbus.getDefault(),用于获取Eventbus实例,我们可以看见Eventbus.getDefault()使用了DCL模式,下面简单解释一个这个模式。
public static EventBus getDefault() {EventBus instance = defaultInstance;if (instance == null) {synchronized (EventBus.class) {instance = EventBus.defaultInstance;if (instance == null) {instance = EventBus.defaultInstance = new EventBus();}}}return instance;
}
在这里对instance进行了两次判空处理:
- 第一次判空的作用是为了减少不必要的同步开销
假设没有第一次检查,每次调用
getDefault方法时都会进入同步块,即使实例已经被创建。这会导致在多线程环境中,多个线程频繁地竞争同步块,造成性能开销。
- 第二次判空的作用是为了防止多次创建实例
假设没有第二次检查,那么在进入同步块之前,如果有多个线程同时通过了第一次检查,它们都会进入同步块,然后按顺序创建实例。这样就违反了单例模式的初衷,因为会创建多个实例。
注意这句话:instance = EventBus.defaultInstance;
这个双重检查的模式是为了保证在高并发环境下仍能正确实现懒加载的单例模式。虽然在某些情况下可能看起来多余,但是在并发编程中,确保正确性是至关重要的。
接下来看Eventbus构造方法做了什么事情:
public EventBus() {this(DEFAULT_BUILDER);
}
它使用了一个默认的构造器来构造Eventbus
private static final EventBusBuilder DEFAULT_BUILDER = new EventBusBuilder();
这里的this通过调用另一个Eventbus的构造方法使用了建造者模式来创建
EventBus(EventBusBuilder builder) {logger = builder.getLogger();subscriptionsByEventType = new HashMap<>();typesBySubscriber = new HashMap<>();stickyEvents = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();mainThreadSupport = builder.getMainThreadSupport();mainThreadPoster = mainThreadSupport != null ? mainThreadSupport.createPoster(this) : null;backgroundPoster = new BackgroundPoster(this);asyncPoster = new AsyncPoster(this);indexCount = builder.subscriberInfoIndexes != null ? builder.subscriberInfoIndexes.size() : 0;subscriberMethodFinder = new SubscriberMethodFinder(builder.subscriberInfoIndexes,builder.strictMethodVerification, builder.ignoreGeneratedIndex);logSubscriberExceptions = builder.logSubscriberExceptions;logNoSubscriberMessages = builder.logNoSubscriberMessages;sendSubscriberExceptionEvent = builder.sendSubscriberExceptionEvent;sendNoSubscriberEvent = builder.sendNoSubscriberEvent;throwSubscriberException = builder.throwSubscriberException;eventInheritance = builder.eventInheritance;executorService = builder.executorService;}
2、订阅者注册
首先我们明确四个名词的关系:

2.1 订阅者方法的查找过程
当获取Eventbus以后就可以将订阅者注册到Eventbus中了,接下来看一下register方法:
public void register(Object subscriber) {if (AndroidDependenciesDetector.isAndroidSDKAvailable() && !AndroidDependenciesDetector.areAndroidComponentsAvailable()) {// Crash if the user (developer) has not imported the Android compatibility library.throw new RuntimeException("It looks like you are using EventBus on Android, " +"make sure to add the \"eventbus\" Android library to your dependencies.");}Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();//1、List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);//2、synchronized (this) {for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);}}
}
我们可以看出register做了两件事,一件是查找订阅者的订阅方法,另一件事是订阅者的注册。
在第一件事中,SubscribeMethod类中,主要用来保存Method对象,线程模式、事件类型、优先级、是否为黏性事件等等,接下来我们看一下findSubscribeMethod方法。
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass) {//1、List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);if (subscriberMethods != null) {return subscriberMethods;}//2、if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {//使用反射的方法subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);} else {//使用索引的方法查找subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);}//3、if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");} else {//将获取的订阅方法集合放入缓存中METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);return subscriberMethods;}
}
第一步首先在缓存中查找是否存在订阅方法的集合,如果找到了直接返回即可。
第二步是根据ignoreGeneratedIndex的属性选择用何种方法查找订阅集合,
ignoreGeneratedIndex的默认值是false,使用索引的方式用于更高效地查找订阅者方法。
第三步是将找的的订阅集合放入缓存(METHOD_CACHE)中,以免下次继续查找。
顺便说一下这个缓存是什么,这个缓存是一个Map:
private static final Map<Class<?>, List<SubscriberMethod>> METHOD_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ConcurrentHashMap** 是 Java 中的一个特殊的 Map 实现,它提供了一种线程安全的方式来存储键值对。**它主要采用了分段锁(Segment)的机制。其核心思想是将整个数据结构分成多个独立的段,每个段上都有一个独立的锁。这样,不同的线程可以同时访问不同的段,从而提高并发性能。
📌我们在项目中经常使用EventBus单例模式获取默认的EventBus对象,也就是
ignoreGeneratedIndex为fasle的情况,这种情况就是调用了索引的方法查找
此时我们分析索引查找的这个findUsingInfo()方法:
private List<SubscriberMethod> findUsingInfo(Class<?> subscriberClass) {FindState findState = prepareFindState();findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);while (findState.clazz != null) {//1、获取订阅者信息findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {//2、得到订阅方法的相关信息SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);}}} else {//3、使用反射的方法查找,将信息放入findState中findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);}findState.moveToSuperclass();}//对findState做回收处理并返回订阅方法的List集合return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
}
我们对源码分析可以看出来findUsingInfo主要做了三件事。
- 第一件事是获取了获取了订阅者的信息,
FindState是这个SubscriberMethodFinder的内部类,包含了订阅者的信息。 - 第二件事是获取了订阅方法的相关信息,获取了包含订阅方法信息的数组,然后遍历数组存入
findState中。 - 第三件事是如果订阅者信息没有正常获取那么则通过反射的方法查找,这个具体实现在后面会介绍
当完成这三件事情以后就可以返回订阅方法的list集合,在返回之前先注销了订阅者。
现在我们看一下findUsingReflectionInSingleClass方法做了什么事情。
private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(FindState findState) {Method[] methods;try {// This is faster than getMethods, especially when subscribers are fat classes like Activities//1、通过反射的方法获取订阅者中的所有方法methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods();} catch (Throwable th) {// Workaround for java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError, see https://github.com/greenrobot/EventBus/issues/149try {methods = findState.clazz.getMethods();} catch (LinkageError error) { // super class of NoClassDefFoundError to be a bit more broad...String msg = "Could not inspect methods of " + findState.clazz.getName();if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {msg += ". Please consider using EventBus annotation processor to avoid reflection.";} else {msg += ". Please make this class visible to EventBus annotation processor to avoid reflection.";}throw new EventBusException(msg, error);}findState.skipSuperClasses = true;}for (Method method : methods) {int modifiers = method.getModifiers();if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0) {Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);if (subscribeAnnotation != null) {Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0];//2、保存订阅方法if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) {ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode();findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, eventType, threadMode,subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky()));}}} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();throw new EventBusException("@Subscribe method " + methodName +"must have exactly 1 parameter but has " + parameterTypes.length);}} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();throw new EventBusException(methodName +" is a illegal @Subscribe method: must be public, non-static, and non-abstract");}}
}
在最上面的注释1中,通过反射的方法获取了订阅者的所有方法,然后根据方法的类型,参数、注解来找到订阅方法。在注释2中将找到的订阅方法保存在分findState中。
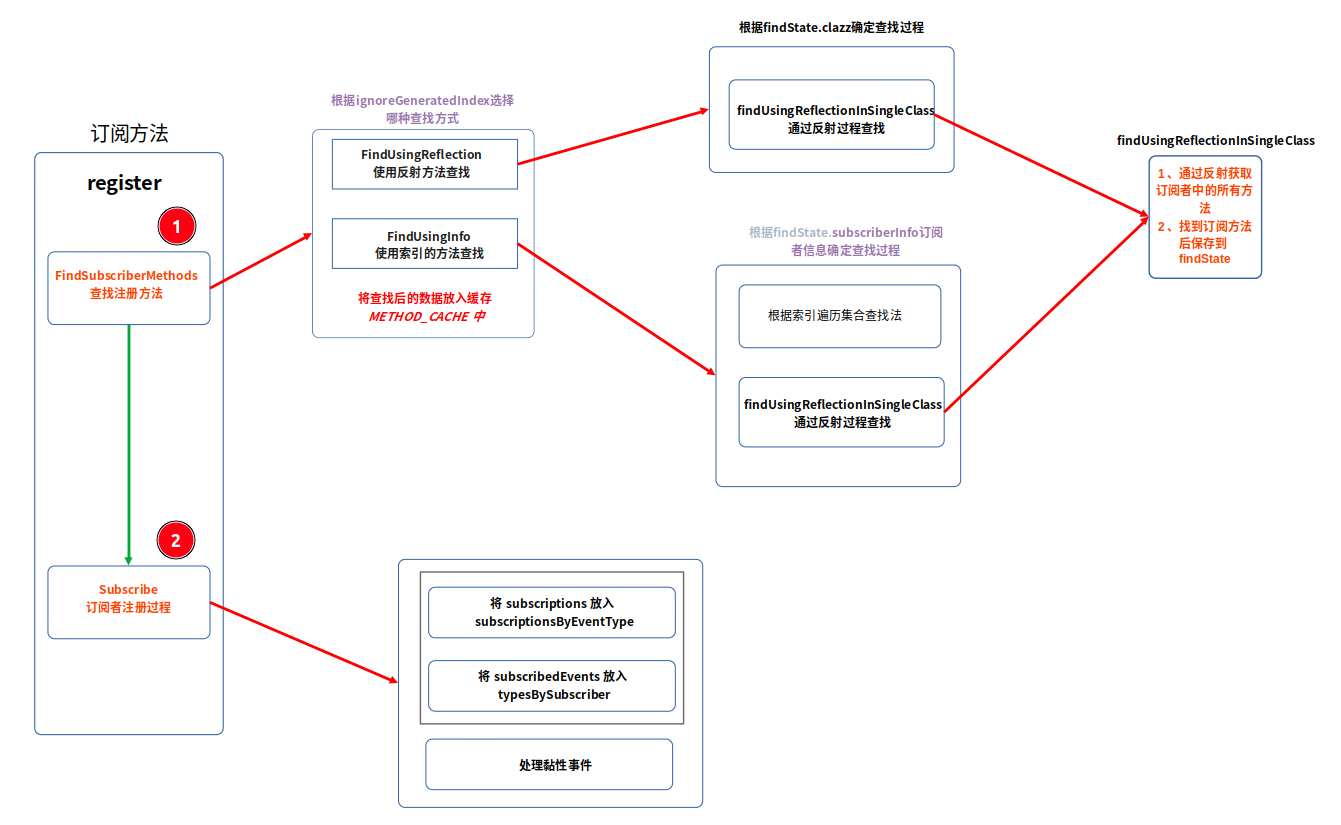
2.2 订阅者的注册过程
在查找完订阅者的订阅方法以后,对所有的订阅方法进行注册。使用流程图理解这个方法的运行过程:
subscribe源码分析如下:
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {//获取方法的事件类型Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;//1、根据订阅者信息和订阅者方法创建一个订阅对象Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);//2、获取订阅对象的集合CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);if (subscriptions == null) { //如果订阅对象集合为null则重新创建并保存subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);} else {if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "+ eventType);}}int size = subscriptions.size();for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {//3、更具订阅方法的优先级插入到订阅对象集合中完成注册subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);break;}}//4、subscribedEvents(事件类型集合)List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);if (subscribedEvents == null) {subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);}subscribedEvents.add(eventType);if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {if (eventInheritance) {// Existing sticky events of all subclasses of eventType have to be considered.// Note: Iterating over all events may be inefficient with lots of sticky events,// thus data structure should be changed to allow a more efficient lookup// (e.g. an additional map storing sub classes of super classes: Class -> List<Class>).//如果是黏性事件的处理方法Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);}}} else {Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);}}
}
我们更具四个注解对这个方法进行分析:
- 在注释1通过subscriber(订阅者信息)和SubscriberMethod(订阅者方法)创建一个订阅对象
- 在注释2中根据eventType(方法事件类型)获取subscriptions(订阅对象集合),如果订阅对象集合为null则重新创建集合并保存到subscriptionsByEventType
- 在注释3中根据订阅方法的优先级插入到订阅对象集合中完成注册
- 在注解4中根据subscriber获取subscribedEvents(事件类型集合),如果为事件类型集合null则重新创建并保存到typesBySubscriber,接下来eventType(方法事件类型)添加到subscribedEvents(事件类型集合)
如果是黏性事件则从stickyEvents事件保存队列中取出该事件类型发送给当前订阅者。
总结来说这个方法做了两件事,第一件事情是将subscriptions根据eventType封装到subscriptionsByEventType中,将subscribedEvents根据subscriber封装到typesBySubscriber中。
📌subscriptionsByEventType与typesBySubscriber的作用?
1. subscriptionsByEventType 映射:
- 类型:
Map<Class<?>, CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>> - 作用:
- 维护事件类型到订阅者列表的映射。
- 允许快速查找对特定事件类型感兴趣的订阅者。
- 详细说明:
- 这个映射的键是事件类型(
Class<?>表示)——eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType。 - 值是
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>,每个Subscription包含了订阅该事件类型的订阅者的相关信息——subscriptions。
- 这个映射的键是事件类型(
- 用途:
- 在事件发布时,通过这个映射可以快速找到对应事件类型的订阅者,以便通知它们处理事件。
2. typesBySubscriber 映射:
- 类型:
Map<Object, List<Class<?>>> - 作用:
- 维护订阅者到其关注的事件类型列表的映射。
- 允许快速检索特定订阅者感兴趣的事件类型。
- 详细说明:
- 这个映射的键是订阅者对象(
Object表示)——subscriber。 - 值是
List<Class<?>>,包含了订阅者关注的事件类型——subscribedEvents。
- 这个映射的键是订阅者对象(
- 用途:
- 在订阅者注册和取消注册时,通过这个映射可以快速查找订阅者关注的事件类型,以便更新订阅者的事件类型列表。
总的来说,typesBySubscriber就是用来管理订阅机制、subscriptionsByEventType用于管理事件发送机制。
2.3 总结订阅者的注册过程
3、事件的发送
3.1 使用Post提交事件
在获取EventBus对象以后,可以通过post方法对事件进行提交。可以先通过流程图了解一下Post具体是做了什么
post源码如下:
public void post(Object event) {//PostingThreadState保存事件队列和线程状态信息PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();//获取事件队列,并将当前事件插入事件队列List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;eventQueue.add(event);if (!postingState.isPosting) {postingState.isMainThread = isMainThread();postingState.isPosting = true;if (postingState.canceled) {throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");}try {//处理队列中的所有事件while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);}} finally {postingState.isPosting = false;postingState.isMainThread = false;}}
}
首先从PostingThreadState对象中取出事件队列,然后将当前事件放入事件队列中。最后将队列中的事件依次交由postSingleEvent方法处理,并移除该事件。
接下来查看postSingleEvent方法做了什么:
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();boolean subscriptionFound = false;//eventInheritance表示是否向上查找事件的父类,默认为trueif (eventInheritance) {//找到父类的所有事件并保存List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);int countTypes = eventTypes.size();for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);//处理所有事件subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);}} else {//处理所有事件subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);}//找不到事件进行异常处理if (!subscriptionFound) {if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {logger.log(Level.FINE, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);}if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));}}
}
eventInheritance表示是否向上查找事件的父类,默认为true,可以通过EventBusBuider进行配置。
当eventInheritance为true时,使用lookupAllEventTypes找到父类的所有事件,将这些事件放入一个List中,然后通过postSingleEventForEventType方法对事件逐一处理。
📌为什么要向上查找事件的父类?
查找事件类型的所有父类是为了支持事件类型的继承关系。在事件总线系统中,有时候我们可能定义了一些事件类型的继承关系。这种情况下,如果某个订阅者订阅了父类的事件,那么它也应该能够接收到子类的事件。
3.2 使用postSingleEventForEventType处理事件的分发
现在我们分析一下postSingleEventForEventType方法是如何处理每一个事件的。
首先通过流程图分析方法思路:
通过postSingleEventForEventType源码分析:
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;synchronized (this) {//1、取出事件对应的subscriptions(订阅对象集合)subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);}if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {//2、遍历subscriptionsfor (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {postingState.event = event;postingState.subscription = subscription;boolean aborted;try {postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);aborted = postingState.canceled;} finally {postingState.event = null;postingState.subscription = null;postingState.canceled = false;}if (aborted) {break;}}return true;}return false;
}
首先在注释1的同步块中取出该事件对应的Subscriptions(订阅对象集合)。然后在注释2位置遍历Subscriptions,将事件Event和Subscription(订阅对象)传递给postingState并调用postToSubscription方法对事件处理
接下来我们查看postToSubscription方法做了什么事情,这个方法做的事情就很简单了一个Switch语句处理不同线程状态,流程图如下:
然后我们现在看一下源码是怎么样做的:
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) {switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {case POSTING:invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);break;case MAIN:if (isMainThread) {invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);} else {mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);}break;case MAIN_ORDERED:if (mainThreadPoster != null) {mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);} else {// temporary: technically not correct as poster not decoupled from subscriberinvokeSubscriber(subscription, event);}break;case BACKGROUND:if (isMainThread) {backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);} else {invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);}break;case ASYNC:asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);break;default:throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);}
}
取出订阅者的threadMode线程以后,根据不同的threadMode分别处理。如果是MAIN线程则直接通过反射运行订阅方法,如果不是主线程则需要mainThreadPoster添加到主线程队列中。
mainThreadPoster是HandlerPoster类型的,继承自Handler,通过Handler调用订阅方法切换到主线程执行。
3.2 总结事件的发送过程
4、订阅者的取消
订阅者的注销需要使用到unregister方法。如下:
public synchronized void unregister(Object subscriber) {//1、通过subscriber找到事件类型集合List<Class<?>> subscribedTypes = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);if (subscribedTypes != null) {//2、遍历subscribedTypes事件类型集合,并且调用unsubscribeByEventTypefor (Class<?> eventType : subscribedTypes) {unsubscribeByEventType(subscriber, eventType);}//3、移除对应的subscriber对应的eventTypetypesBySubscriber.remove(subscriber);} else {logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Subscriber to unregister was not registered before: " + subscriber.getClass());}
}
这里用到了在注册中使用的typesBySubscriber,这是一个Map集合。在注释1找到这个事件类型集合,然后在注释2遍历事件类型集合,调用unsubscribeByEventType。最后在注释3将subscriber对应的eventType。
我们看一下注释2的unsubscribeByEventType方法做了什么事情:
private void unsubscribeByEventType(Object subscriber, Class<?> eventType) {//1、通过eventType获取对应的subscriptions(订阅对象集合)List<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);if (subscriptions != null) {int size = subscriptions.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {Subscription subscription = subscriptions.get(i);if (subscription.subscriber == subscriber) {subscription.active = false;subscriptions.remove(i);i--;size--;}}}
}
通过eventType获取对应的subscriptions(订阅对象集合),通过一个for移除对应的subscriber即可。
相关文章:

【EventBus】EventBus源码浅析
二、EventBus源码解析 目录 1、EventBus的构造方法2、订阅者注册 2.1 订阅者方法的查找过程2.2 订阅者的注册过程1. subscriptionsByEventType 映射:2. typesBySubscriber 映射:2.3 总结订阅者的注册过程 3、事件的发送 3.1 使用Post提交事件3.2 使用p…...
Buck电源设计常见的一些问题(二)MOS管炸机问题
MOS管炸机问题 1.概述2.MOS管的相关参数3.过电压失效4.过电流失效5.静电放电和热失效1.概述 在我们做电源产品或者电机控制器时候,经常会坏MOS管。我相信90%以上的硬件工程师在职场生涯中都会遇到这类问题。然而这类问题也总是让人防不胜防。经常我们都会开玩笑的说,没烧过管…...

Javascript高频面试题
系列文章目录 文章目录 系列文章目录前言1.JavaScript常见数据类型null 和 undefind区别symbol(ES6新增)、bigInt(ES10新增) 2.JavaScript判断数据类型的方式3. 和 区别,分别在什么情况使用?4.变量声明 va…...
锁--07_2---- index merge(索引合并)引起的死锁
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 案例分析生产背景死锁日志表结构执行计划 EXPLAN为什么会用 index_merge(索引合并)为什么用了 index_merge就死锁了解决方案注:M…...
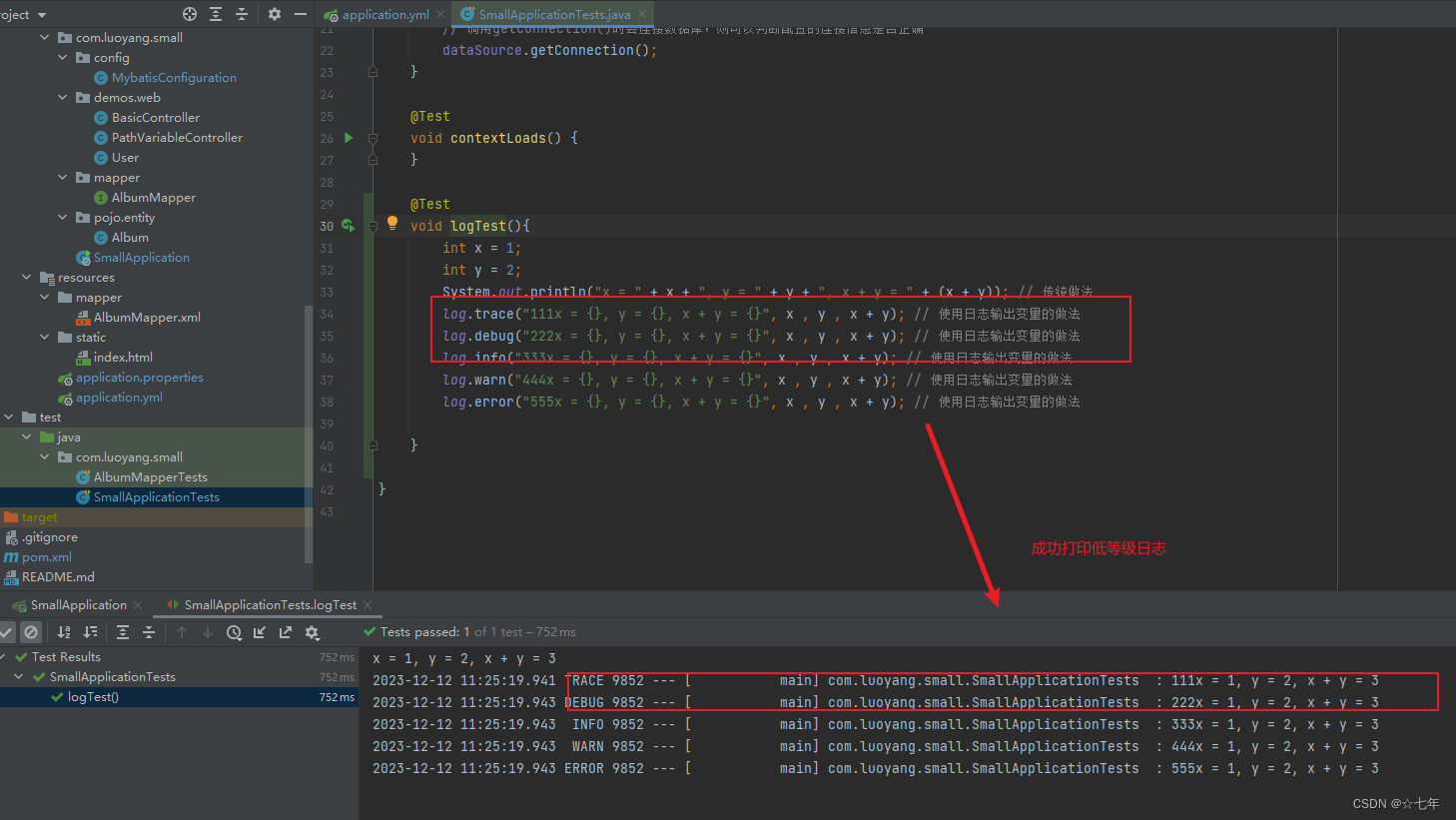
后端打印不了trace等级的日志?-SpringBoot日志打印-Slf4j
在调用log变量的方法来输出日志时,有以上5个级别对应的方法,从不太重要,到非常重要 调用不同的方法,就会输出不同级别的日志。 trace:跟踪信息debug:调试信息info:一般信息warn:警告…...

声明式编程Declarative Programming
接下来要介绍第五种编程范式 -- 声明式编程。分别从它的优缺点、案例分析和适用的编程语言这三个方面来介绍这个歌编程范式。 声明式编程是一种编程范式,其核心思想是通过描述问题的性质和约束,而不是通过描述解决问题的步骤来进行编程。这与命令式编程…...

人工智能与天文:技术前沿与未来展望
人工智能与天文:技术前沿与未来展望 一、引言 随着科技的飞速发展,人工智能(AI)在各个领域的应用越来越广泛。在天文领域,AI也发挥着越来越重要的作用。本文将探讨人工智能与天文学的结合,以及这种结合带…...

JeecgBoot 框架升级至 Spring Boot3 的实战步骤
JeecgBoot 框架升级 Spring Boot 3.1.5 步骤 JEECG官方推出SpringBoot3分支:https://github.com/jeecgboot/jeecg-boot/tree/springboot3 本次更新由于属于破坏式更新,有几个生态内的组件,无法进行找到平替或无法升级,目前尚不完…...
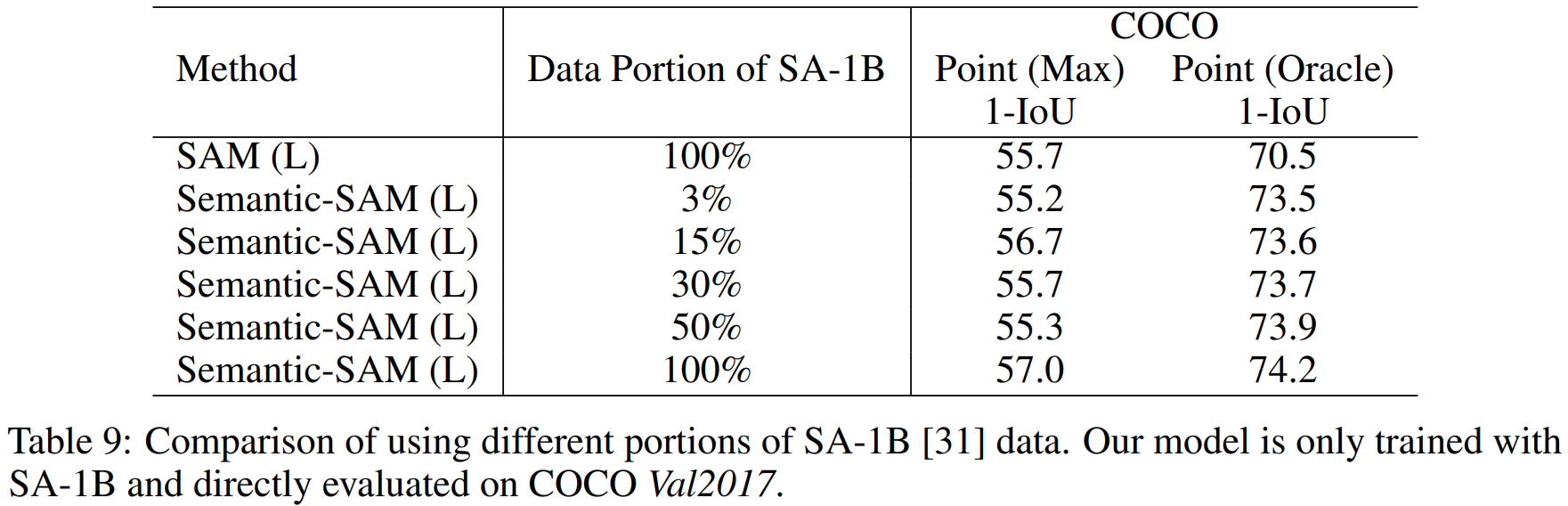
论文阅读——Semantic-SAM
Semantic-SAM可以做什么: 整合了七个数据集: 一般的分割数据集,目标级别分割数据集:MSCOCO, Objects365, ADE20k 部分分割数据集:PASCAL Part, PACO, PartImagenet, and SA-1B The datasets are SA-1B, COCO panopt…...
gitlab下载,离线安装
目录 1.下载 2.安装 3.配置 4.启动 5.登录 参考: 1.下载 根据服务器操作系统版本,下载对应的RPM包。 gitlab官网: The DevSecOps Platform | GitLab rpm包官网下载地址: gitlab/gitlab-ce - Results in gitlab/gitlab-ce 国内镜像地…...

【SpringBoot篇】Interceptor拦截器 | 拦截器和过滤器的区别
文章目录 🌹概念⭐作用 🎄快速入门⭐入门案例代码实现 🛸拦截路径🍔拦截器interceptor和过滤器filter的区别🎆登录校验 🌹概念 拦截器(Interceptor)是一种软件设计模式,…...
:在set_version方法中从pom.xml中读取版本号实现动态版本定义)
conan入门(三十六):在set_version方法中从pom.xml中读取版本号实现动态版本定义
一般情况下,我们通过self.version字段定义conan 包的版本号如下: class PkgConan(ConanFile):name "pkg"version "1.7.3"因为版本号是写死的,所以这种方式有局限性: 比如我的java项目中版本号是在pom.xml中…...

为什么 GAN 不好训练
为什么 GAN 不好训练?先看 GAN 的损失: 当生成器固定时,堆D(x)求导,推理得到(加号右边先对log求导,再对负项求导) 然后在面对最优Discriminator时,Generator的优化目标就变成了&…...

select、poll、epoll 区别有哪些
文章目录 select、poll、epoll 区别有哪些?select:poll:epoll: select、poll、epoll 区别有哪些? select: 它仅仅知道了,有 I/O 事件发生了,却并不知道是哪那几个流(可…...

大模型下开源文档解析工具总结及技术思考
1 基于文档解析工具的方法 pdf解析工具 导图一览: PyPDF2提取txt: import PyPDF2 def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):with open(pdf_path, rb) as file:pdf_reader PyPDF2.PdfFileReader(file)num_pages pdf_reader.numPagestext ""f…...
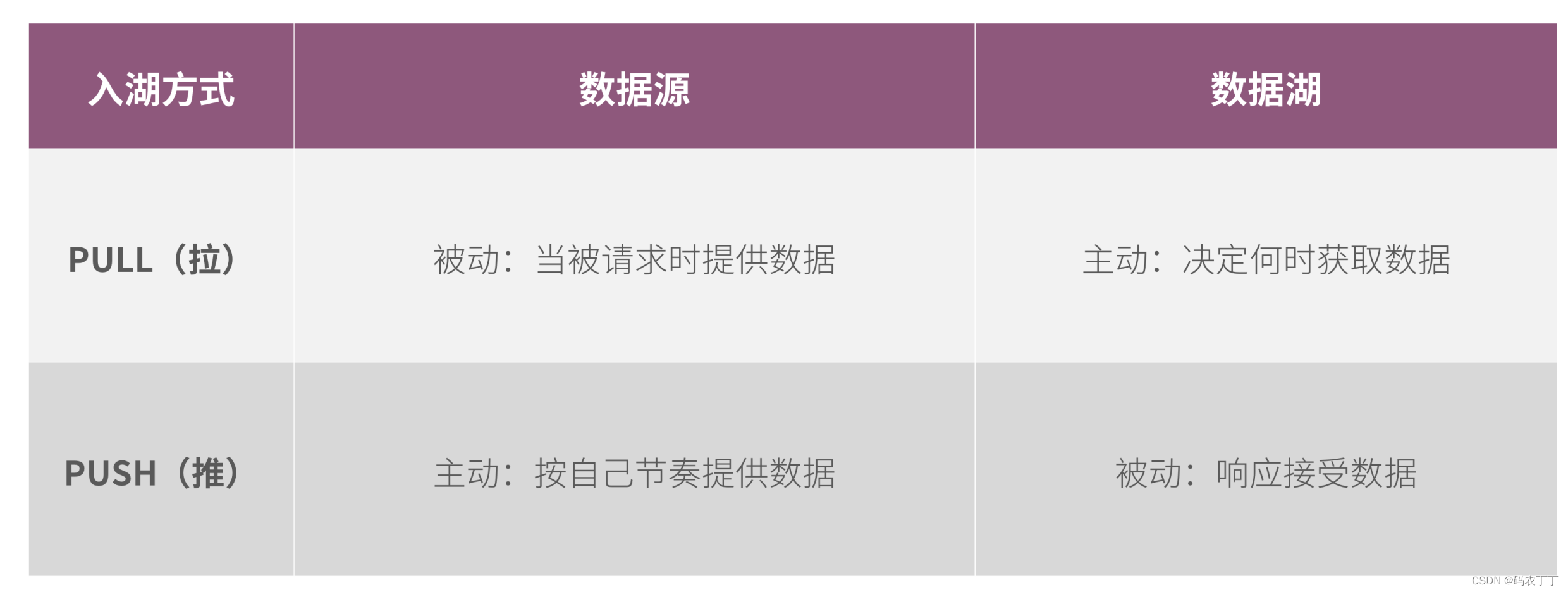
【华为数据之道学习笔记】5-4 数据入湖方式
数据入湖遵循华为信息架构,以逻辑数据实体为粒度入湖,逻辑数据实体在首次入湖时应该考虑信息的完整性。原则上,一个逻辑数据实体的所有属性应该一次性进湖,避免一个逻辑实体多次入湖,增加入湖工作量。 数据入湖的方式…...
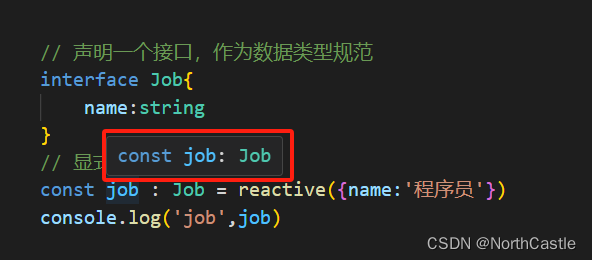
Vue3-03-reactive() 响应式基本使用
reactive() 的简介 reactive() 是vue3 中进行响应式状态声明的另一种方式; 但是,它只能声明 【对象类型】的响应式变量,【不支持声明基本数据类型】。reactive() 与 ref() 一样,都是深度响应式的,即对象嵌套属性发生了…...

OpenAI开源超级对齐方法:用GPT-2,监督、微调GPT-4
12月15日,OpenAI在官网公布了最新研究论文和开源项目——如何用小模型监督大模型,实现更好的新型对齐方法。 目前,大模型的主流对齐方法是RLHF(人类反馈强化学习)。但随着大模型朝着多模态、AGI发展,神经元…...
TeeChart.NET 2023.11.17 Crack
.NET 的 TeeChart 图表控件提供了一个出色的通用组件套件,可满足无数的图表需求,也针对重要的垂直领域,例如金融、科学和统计领域。 数据可视化 数十种完全可定制的交互式图表类型、地图和仪表指示器,以及完整的功能集,…...

计算机网络常见的缩写
计算机网络常见缩写 通讯控制处理机(Communication Control Processor)CCP 前端处理机(Front End Processor)FEP 开放系统互连参考模型 OSI/RM 开放数据库连接(Open Database Connectivity)ODBC 网络操作系…...
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色
visual studio 2022更改主题为深色 点击visual studio 上方的 工具-> 选项 在选项窗口中,选择 环境 -> 常规 ,将其中的颜色主题改成深色 点击确定,更改完成...

STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解
STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解 前言如何确定定时器挂载在哪条时钟线上配置及使用方法参数配置PrescalerCounter ModeCounter Periodauto-reload preloadTrigger Event Selection 中断配置生成的代码及使用方法初始化代码基本定时器触发DCA或者ADC的代码讲解中断代码定时启动…...
)
Angular微前端架构:Module Federation + ngx-build-plus (Webpack)
以下是一个完整的 Angular 微前端示例,其中使用的是 Module Federation 和 npx-build-plus 实现了主应用(Shell)与子应用(Remote)的集成。 🛠️ 项目结构 angular-mf/ ├── shell-app/ # 主应用&…...
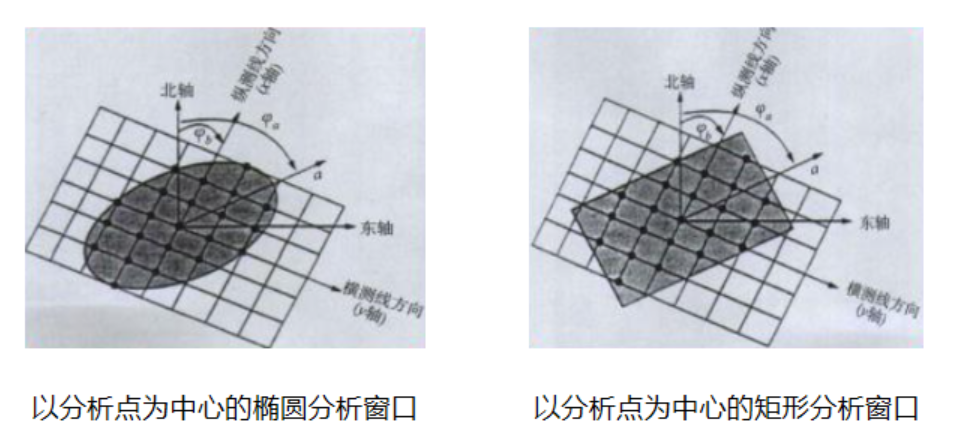
论文笔记——相干体技术在裂缝预测中的应用研究
目录 相关地震知识补充地震数据的认识地震几何属性 相干体算法定义基本原理第一代相干体技术:基于互相关的相干体技术(Correlation)第二代相干体技术:基于相似的相干体技术(Semblance)基于多道相似的相干体…...
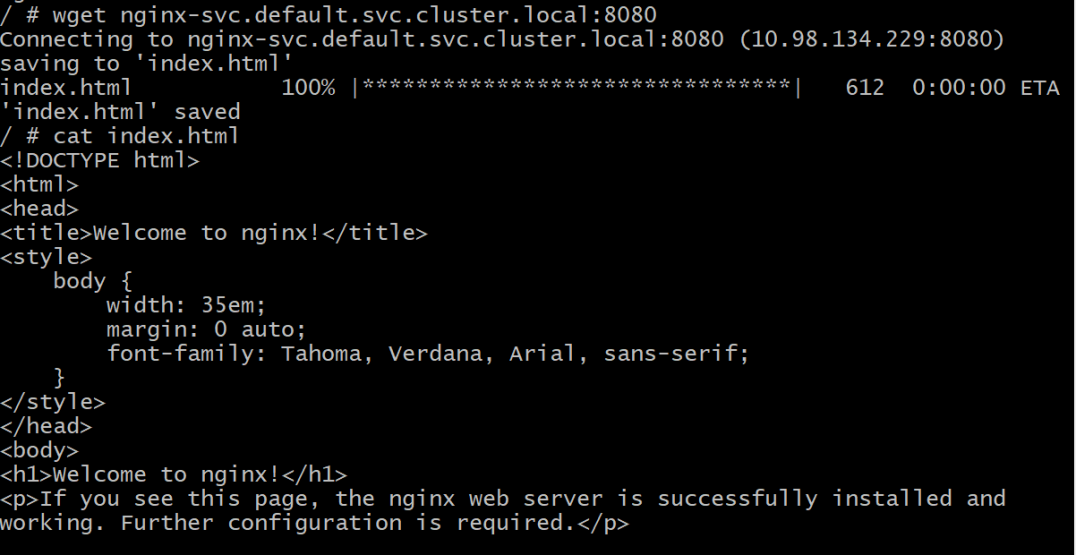
初探Service服务发现机制
1.Service简介 Service是将运行在一组Pod上的应用程序发布为网络服务的抽象方法。 主要功能:服务发现和负载均衡。 Service类型的包括ClusterIP类型、NodePort类型、LoadBalancer类型、ExternalName类型 2.Endpoints简介 Endpoints是一种Kubernetes资源…...

热烈祝贺埃文科技正式加入可信数据空间发展联盟
2025年4月29日,在福州举办的第八届数字中国建设峰会“可信数据空间分论坛”上,可信数据空间发展联盟正式宣告成立。国家数据局党组书记、局长刘烈宏出席并致辞,强调该联盟是推进全国一体化数据市场建设的关键抓手。 郑州埃文科技有限公司&am…...
基于stm32F10x 系列微控制器的智能电子琴(附完整项目源码、详细接线及讲解视频)
注:文章末尾网盘链接中自取成品使用演示视频、项目源码、项目文档 所用硬件:STM32F103C8T6、无源蜂鸣器、44矩阵键盘、flash存储模块、OLED显示屏、RGB三色灯、面包板、杜邦线、usb转ttl串口 stm32f103c8t6 面包板 …...

k8s从入门到放弃之Pod的容器探针检测
k8s从入门到放弃之Pod的容器探针检测 在Kubernetes(简称K8s)中,容器探测是指kubelet对容器执行定期诊断的过程,以确保容器中的应用程序处于预期的状态。这些探测是保障应用健康和高可用性的重要机制。Kubernetes提供了两种种类型…...
