CentOS 8 安装指定版本ansible
背景:想要练习ansible使用,用于面试,结果使用centos 8 的yum安装失败,提示版本不兼容(指的是python版本),故而使用python来安装指定版本的ansible,特此记录
环境:win11虚拟机、centos 8.2、ansible 4.9.0、python 3.6.8
1、使用pip方式直接安装(建议使用国内源)
pip3 install ansible==4.9.0
2、测试安装是否成功
ansible --version显示以下内容,说明成功了
ansible [core 2.11.12] config file = Noneconfigured module search path = ['/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']ansible python module location = /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansibleansible collection location = /root/.ansible/collections:/usr/share/ansible/collectionsexecutable location = /usr/local/bin/ansiblepython version = 3.6.8 (default, Apr 16 2020, 01:36:27) [GCC 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5)]jinja version = 3.0.3libyaml = True
其中:config file = None 说明配置文件未生成,需要自己配置(/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg)
下面是默认配置文件内容
# config file for ansible -- https://ansible.com/ # ===============================================# nearly all parameters can be overridden in ansible-playbook # or with command line flags. ansible will read ANSIBLE_CONFIG, # ansible.cfg in the current working directory, .ansible.cfg in # the home directory or /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg, whichever it # finds first[defaults]# some basic default values...inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts #library = /usr/share/my_modules/ #module_utils = /usr/share/my_module_utils/ #remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #plugin_filters_cfg = /etc/ansible/plugin_filters.yml forks = 10 #poll_interval = 15 #sudo_user = root #ask_sudo_pass = True #ask_pass = True #transport = smart #remote_port = 22 #module_lang = C #module_set_locale = False# plays will gather facts by default, which contain information about # the remote system. # # smart - gather by default, but don't regather if already gathered # implicit - gather by default, turn off with gather_facts: False # explicit - do not gather by default, must say gather_facts: True #gathering = implicit# This only affects the gathering done by a play's gather_facts directive, # by default gathering retrieves all facts subsets # all - gather all subsets # network - gather min and network facts # hardware - gather hardware facts (longest facts to retrieve) # virtual - gather min and virtual facts # facter - import facts from facter # ohai - import facts from ohai # You can combine them using comma (ex: network,virtual) # You can negate them using ! (ex: !hardware,!facter,!ohai) # A minimal set of facts is always gathered. #gather_subset = all# some hardware related facts are collected # with a maximum timeout of 10 seconds. This # option lets you increase or decrease that # timeout to something more suitable for the # environment. # gather_timeout = 10# Ansible facts are available inside the ansible_facts.* dictionary # namespace. This setting maintains the behaviour which was the default prior # to 2.5, duplicating these variables into the main namespace, each with a # prefix of 'ansible_'. # This variable is set to True by default for backwards compatibility. It # will be changed to a default of 'False' in a future release. # ansible_facts. # inject_facts_as_vars = True# additional paths to search for roles in, colon separated #roles_path = /etc/ansible/roles# uncomment this to disable SSH key host checking host_key_checking = False# change the default callback, you can only have one 'stdout' type enabled at a time. #stdout_callback = skippy## Ansible ships with some plugins that require whitelisting, ## this is done to avoid running all of a type by default. ## These setting lists those that you want enabled for your system. ## Custom plugins should not need this unless plugin author specifies it.# enable callback plugins, they can output to stdout but cannot be 'stdout' type. #callback_whitelist = timer, mail# Determine whether includes in tasks and handlers are "static" by # default. As of 2.0, includes are dynamic by default. Setting these # values to True will make includes behave more like they did in the # 1.x versions. #task_includes_static = False #handler_includes_static = False# Controls if a missing handler for a notification event is an error or a warning #error_on_missing_handler = True# change this for alternative sudo implementations #sudo_exe = sudo# What flags to pass to sudo # WARNING: leaving out the defaults might create unexpected behaviours #sudo_flags = -H -S -n# SSH timeout #timeout = 10# default user to use for playbooks if user is not specified # (/usr/bin/ansible will use current user as default) #remote_user = root# logging is off by default unless this path is defined # if so defined, consider logrotate #log_path = /var/log/ansible.log# default module name for /usr/bin/ansible #module_name = command# use this shell for commands executed under sudo # you may need to change this to bin/bash in rare instances # if sudo is constrained #executable = /bin/sh# if inventory variables overlap, does the higher precedence one win # or are hash values merged together? The default is 'replace' but # this can also be set to 'merge'. #hash_behaviour = replace# by default, variables from roles will be visible in the global variable # scope. To prevent this, the following option can be enabled, and only # tasks and handlers within the role will see the variables there #private_role_vars = yes# list any Jinja2 extensions to enable here: #jinja2_extensions = jinja2.ext.do,jinja2.ext.i18n# if set, always use this private key file for authentication, same as # if passing --private-key to ansible or ansible-playbook #private_key_file = /path/to/file# If set, configures the path to the Vault password file as an alternative to # specifying --vault-password-file on the command line. #vault_password_file = /path/to/vault_password_file# format of string {{ ansible_managed }} available within Jinja2 # templates indicates to users editing templates files will be replaced. # replacing {file}, {host} and {uid} and strftime codes with proper values. #ansible_managed = Ansible managed: {file} modified on %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S by {uid} on {host} # {file}, {host}, {uid}, and the timestamp can all interfere with idempotence # in some situations so the default is a static string: #ansible_managed = Ansible managed# by default, ansible-playbook will display "Skipping [host]" if it determines a task # should not be run on a host. Set this to "False" if you don't want to see these "Skipping" # messages. NOTE: the task header will still be shown regardless of whether or not the # task is skipped. #display_skipped_hosts = True# by default, if a task in a playbook does not include a name: field then # ansible-playbook will construct a header that includes the task's action but # not the task's args. This is a security feature because ansible cannot know # if the *module* considers an argument to be no_log at the time that the # header is printed. If your environment doesn't have a problem securing # stdout from ansible-playbook (or you have manually specified no_log in your # playbook on all of the tasks where you have secret information) then you can # safely set this to True to get more informative messages. #display_args_to_stdout = False# by default (as of 1.3), Ansible will raise errors when attempting to dereference # Jinja2 variables that are not set in templates or action lines. Uncomment this line # to revert the behavior to pre-1.3. #error_on_undefined_vars = False# by default (as of 1.6), Ansible may display warnings based on the configuration of the # system running ansible itself. This may include warnings about 3rd party packages or # other conditions that should be resolved if possible. # to disable these warnings, set the following value to False: #system_warnings = True# by default (as of 1.4), Ansible may display deprecation warnings for language # features that should no longer be used and will be removed in future versions. # to disable these warnings, set the following value to False: #deprecation_warnings = True# (as of 1.8), Ansible can optionally warn when usage of the shell and # command module appear to be simplified by using a default Ansible module # instead. These warnings can be silenced by adjusting the following # setting or adding warn=yes or warn=no to the end of the command line # parameter string. This will for example suggest using the git module # instead of shelling out to the git command. # command_warnings = False# set plugin path directories here, separate with colons #action_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/action #become_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/become #cache_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/cache #callback_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/callback #connection_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/connection #lookup_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/lookup #inventory_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/inventory #vars_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/vars #filter_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/filter #test_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/test #terminal_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/terminal #strategy_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/strategy# by default, ansible will use the 'linear' strategy but you may want to try # another one #strategy = free# by default callbacks are not loaded for /bin/ansible, enable this if you # want, for example, a notification or logging callback to also apply to # /bin/ansible runs #bin_ansible_callbacks = False# don't like cows? that's unfortunate. # set to 1 if you don't want cowsay support or export ANSIBLE_NOCOWS=1 #nocows = 1# set which cowsay stencil you'd like to use by default. When set to 'random', # a random stencil will be selected for each task. The selection will be filtered # against the `cow_whitelist` option below. #cow_selection = default #cow_selection = random# when using the 'random' option for cowsay, stencils will be restricted to this list. # it should be formatted as a comma-separated list with no spaces between names. # NOTE: line continuations here are for formatting purposes only, as the INI parser # in python does not support them. #cow_whitelist=bud-frogs,bunny,cheese,daemon,default,dragon,elephant-in-snake,elephant,eyes,\ # hellokitty,kitty,luke-koala,meow,milk,moofasa,moose,ren,sheep,small,stegosaurus,\ # stimpy,supermilker,three-eyes,turkey,turtle,tux,udder,vader-koala,vader,www# don't like colors either? # set to 1 if you don't want colors, or export ANSIBLE_NOCOLOR=1 #nocolor = 1# if set to a persistent type (not 'memory', for example 'redis') fact values # from previous runs in Ansible will be stored. This may be useful when # wanting to use, for example, IP information from one group of servers # without having to talk to them in the same playbook run to get their # current IP information. #fact_caching = memory#This option tells Ansible where to cache facts. The value is plugin dependent. #For the jsonfile plugin, it should be a path to a local directory. #For the redis plugin, the value is a host:port:database triplet: fact_caching_connection = localhost:6379:0#fact_caching_connection=/tmp# retry files # When a playbook fails a .retry file can be created that will be placed in ~/ # You can enable this feature by setting retry_files_enabled to True # and you can change the location of the files by setting retry_files_save_path#retry_files_enabled = False #retry_files_save_path = ~/.ansible-retry# squash actions # Ansible can optimise actions that call modules with list parameters # when looping. Instead of calling the module once per with_ item, the # module is called once with all items at once. Currently this only works # under limited circumstances, and only with parameters named 'name'. #squash_actions = apk,apt,dnf,homebrew,pacman,pkgng,yum,zypper# prevents logging of task data, off by default #no_log = False# prevents logging of tasks, but only on the targets, data is still logged on the master/controller #no_target_syslog = False# controls whether Ansible will raise an error or warning if a task has no # choice but to create world readable temporary files to execute a module on # the remote machine. This option is False by default for security. Users may # turn this on to have behaviour more like Ansible prior to 2.1.x. See # https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/become.html#becoming-an-unprivileged-user # for more secure ways to fix this than enabling this option. #allow_world_readable_tmpfiles = False# controls the compression level of variables sent to # worker processes. At the default of 0, no compression # is used. This value must be an integer from 0 to 9. #var_compression_level = 9# controls what compression method is used for new-style ansible modules when # they are sent to the remote system. The compression types depend on having # support compiled into both the controller's python and the client's python. # The names should match with the python Zipfile compression types: # * ZIP_STORED (no compression. available everywhere) # * ZIP_DEFLATED (uses zlib, the default) # These values may be set per host via the ansible_module_compression inventory # variable #module_compression = 'ZIP_DEFLATED'# This controls the cutoff point (in bytes) on --diff for files # set to 0 for unlimited (RAM may suffer!). #max_diff_size = 1048576# This controls how ansible handles multiple --tags and --skip-tags arguments # on the CLI. If this is True then multiple arguments are merged together. If # it is False, then the last specified argument is used and the others are ignored. # This option will be removed in 2.8. #merge_multiple_cli_flags = True# Controls showing custom stats at the end, off by default #show_custom_stats = True# Controls which files to ignore when using a directory as inventory with # possibly multiple sources (both static and dynamic) #inventory_ignore_extensions = ~, .orig, .bak, .ini, .cfg, .retry, .pyc, .pyo# This family of modules use an alternative execution path optimized for network appliances # only update this setting if you know how this works, otherwise it can break module execution #network_group_modules=eos, nxos, ios, iosxr, junos, vyos# When enabled, this option allows lookups (via variables like {{lookup('foo')}} or when used as # a loop with `with_foo`) to return data that is not marked "unsafe". This means the data may contain # jinja2 templating language which will be run through the templating engine. # ENABLING THIS COULD BE A SECURITY RISK #allow_unsafe_lookups = False# set default errors for all plays #any_errors_fatal = False[inventory] # enable inventory plugins, default: 'host_list', 'script', 'auto', 'yaml', 'ini', 'toml' #enable_plugins = host_list, virtualbox, yaml, constructed# ignore these extensions when parsing a directory as inventory source #ignore_extensions = .pyc, .pyo, .swp, .bak, ~, .rpm, .md, .txt, ~, .orig, .ini, .cfg, .retry# ignore files matching these patterns when parsing a directory as inventory source #ignore_patterns=# If 'true' unparsed inventory sources become fatal errors, they are warnings otherwise. #unparsed_is_failed=False[privilege_escalation] #become=True #become_method=sudo #become_user=root #become_ask_pass=False[paramiko_connection]# uncomment this line to cause the paramiko connection plugin to not record new host # keys encountered. Increases performance on new host additions. Setting works independently of the # host key checking setting above. #record_host_keys=False# by default, Ansible requests a pseudo-terminal for commands executed under sudo. Uncomment this # line to disable this behaviour. #pty=False# paramiko will default to looking for SSH keys initially when trying to # authenticate to remote devices. This is a problem for some network devices # that close the connection after a key failure. Uncomment this line to # disable the Paramiko look for keys function #look_for_keys = False# When using persistent connections with Paramiko, the connection runs in a # background process. If the host doesn't already have a valid SSH key, by # default Ansible will prompt to add the host key. This will cause connections # running in background processes to fail. Uncomment this line to have # Paramiko automatically add host keys. #host_key_auto_add = True[ssh_connection]# ssh arguments to use # Leaving off ControlPersist will result in poor performance, so use # paramiko on older platforms rather than removing it, -C controls compression use #ssh_args = -C -o ControlMaster=auto -o ControlPersist=60s# The base directory for the ControlPath sockets. # This is the "%(directory)s" in the control_path option # # Example: # control_path_dir = /tmp/.ansible/cp #control_path_dir = ~/.ansible/cp# The path to use for the ControlPath sockets. This defaults to a hashed string of the hostname, # port and username (empty string in the config). The hash mitigates a common problem users # found with long hostnames and the conventional %(directory)s/ansible-ssh-%%h-%%p-%%r format. # In those cases, a "too long for Unix domain socket" ssh error would occur. # # Example: # control_path = %(directory)s/%%h-%%r #control_path =# Enabling pipelining reduces the number of SSH operations required to # execute a module on the remote server. This can result in a significant # performance improvement when enabled, however when using "sudo:" you must # first disable 'requiretty' in /etc/sudoers # # By default, this option is disabled to preserve compatibility with # sudoers configurations that have requiretty (the default on many distros). # #pipelining = False# Control the mechanism for transferring files (old) # * smart = try sftp and then try scp [default] # * True = use scp only # * False = use sftp only #scp_if_ssh = smart# Control the mechanism for transferring files (new) # If set, this will override the scp_if_ssh option # * sftp = use sftp to transfer files # * scp = use scp to transfer files # * piped = use 'dd' over SSH to transfer files # * smart = try sftp, scp, and piped, in that order [default] #transfer_method = smart# if False, sftp will not use batch mode to transfer files. This may cause some # types of file transfer failures impossible to catch however, and should # only be disabled if your sftp version has problems with batch mode #sftp_batch_mode = False# The -tt argument is passed to ssh when pipelining is not enabled because sudo # requires a tty by default. #usetty = True# Number of times to retry an SSH connection to a host, in case of UNREACHABLE. # For each retry attempt, there is an exponential backoff, # so after the first attempt there is 1s wait, then 2s, 4s etc. up to 30s (max). #retries = 3[persistent_connection]# Configures the persistent connection timeout value in seconds. This value is # how long the persistent connection will remain idle before it is destroyed. # If the connection doesn't receive a request before the timeout value # expires, the connection is shutdown. The default value is 30 seconds. #connect_timeout = 30# The command timeout value defines the amount of time to wait for a command # or RPC call before timing out. The value for the command timeout must # be less than the value of the persistent connection idle timeout (connect_timeout) # The default value is 30 second. #command_timeout = 30[accelerate] #accelerate_port = 5099 #accelerate_timeout = 30 #accelerate_connect_timeout = 5.0# The daemon timeout is measured in minutes. This time is measured # from the last activity to the accelerate daemon. #accelerate_daemon_timeout = 30# If set to yes, accelerate_multi_key will allow multiple # private keys to be uploaded to it, though each user must # have access to the system via SSH to add a new key. The default # is "no". #accelerate_multi_key = yes[selinux] # file systems that require special treatment when dealing with security context # the default behaviour that copies the existing context or uses the user default # needs to be changed to use the file system dependent context. #special_context_filesystems=nfs,vboxsf,fuse,ramfs,9p,vfat# Set this to yes to allow libvirt_lxc connections to work without SELinux. #libvirt_lxc_noseclabel = yes[colors] #highlight = white #verbose = blue #warn = bright purple #error = red #debug = dark gray #deprecate = purple #skip = cyan #unreachable = red #ok = green #changed = yellow #diff_add = green #diff_remove = red #diff_lines = cyan[diff] # Always print diff when running ( same as always running with -D/--diff ) # always = no# Set how many context lines to show in diff # context = 3 scp_if_ssh=True
再次执行ansible --version 则显示配置文件路径了,如下:
ansible [core 2.11.12] config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfgconfigured module search path = ['/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']ansible python module location = /usr/local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ansibleansible collection location = /root/.ansible/collections:/usr/share/ansible/collectionsexecutable location = /usr/local/bin/ansiblepython version = 3.6.8 (default, Apr 16 2020, 01:36:27) [GCC 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5)]jinja version = 3.0.3libyaml = True
3、测试
开启一台服务器,作为测试,IP为:192.168.37.5
配置主机清单文件(/etc/ansible/hosts),内容如下:
[webtest]
192.168.37.[4:6] ansible_ssh_user=jack ansible_ssh_pass=root
下载sshpass并安装(https://nchc.dl.sourceforge.net/project/sshpass/sshpass/1.10/sshpass-1.10.tar.gz)
下载后,解压,使用源码安装:
安装gcc等
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make解压并切换目录到sshpass根目录下,执行:
./configure
make && make install参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42405670/article/details/127191983
执行命令:ansible webtest -m ping,如下:
192.168.37.5 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/libexec/platform-python"},"changed": false,"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.37.6 | UNREACHABLE! => {"changed": false,"msg": "Failed to connect to the host via ssh: ssh: connect to host 192.168.37.6 port 22: No route to host","unreachable": true
}
192.168.37.4 | UNREACHABLE! => {"changed": false,"msg": "Invalid/incorrect password: Permission denied, please try again.","unreachable": true
}
只有5是通的,其他均不存在,告一段落
学习参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/keerya/p/7987886.html
相关文章:

CentOS 8 安装指定版本ansible
背景:想要练习ansible使用,用于面试,结果使用centos 8 的yum安装失败,提示版本不兼容(指的是python版本),故而使用python来安装指定版本的ansible,特此记录 环境:win11虚…...
)
策略模式(及案例)
策略模式 1.策略接口 定义一组算法或操作的通用接口,通常是一个抽象类或接口。该接口声明了策略类所必须实现的方法。 示例: class Strategy {doOperation() {} }2.具体策略 实现策略接口,提供具体的算法实现。每个具体策略类负责处理一…...
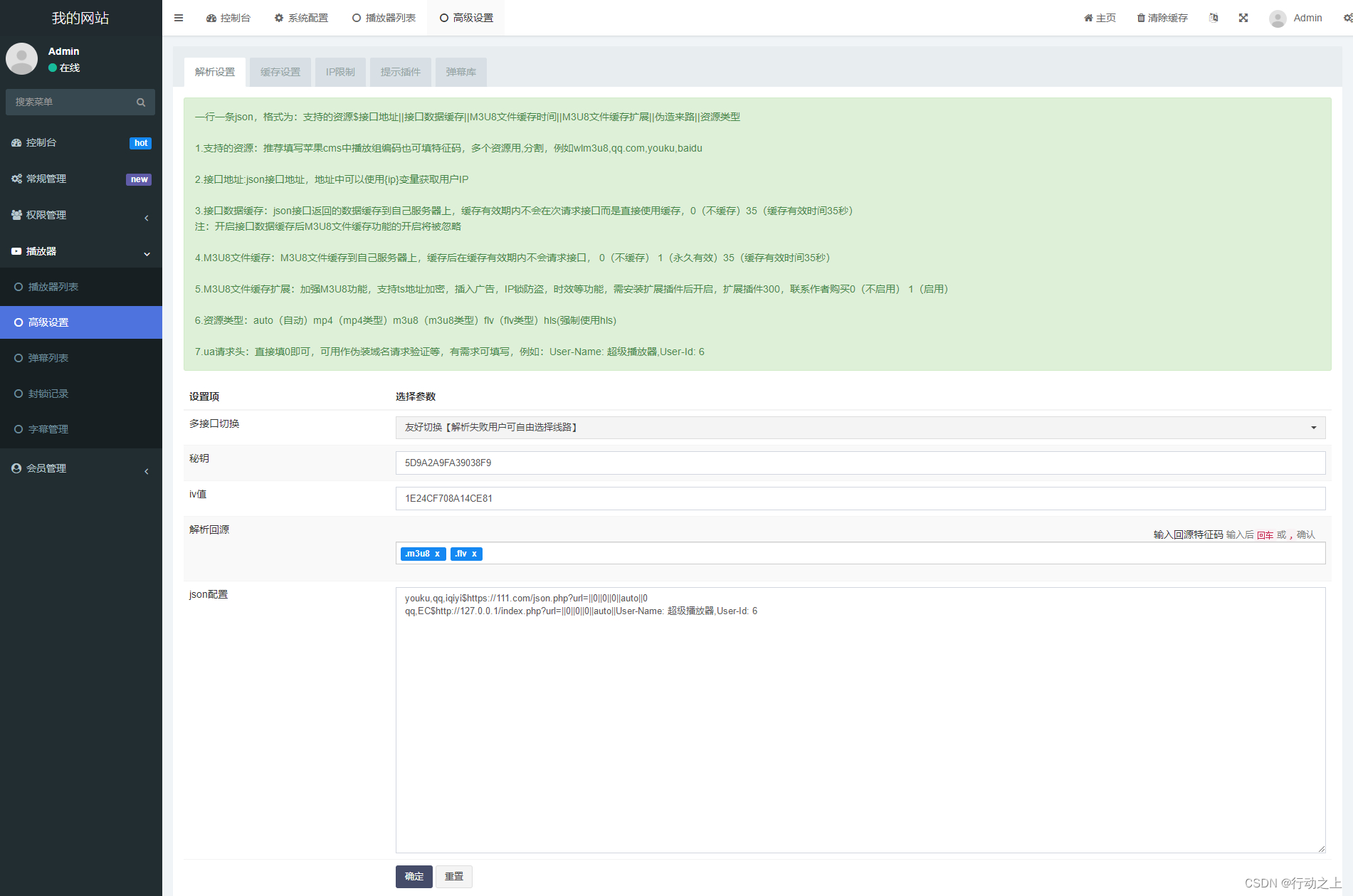
苹果CMS超级播放器专业版无授权全开源,附带安装教程
源码介绍 超级播放器专业版v1.0.8,内置六大主流播放器,支持各种格式的视频播放,支持主要功能在每一个播放器内核中都相同效果。 搭建教程 1.不兼容IE浏览器 2.php版本推荐7.4 支持7.1~7.4 3.框架引入不支持同时引入多个播放器 json对接教…...

项目记录:利用Redis实现缓存以提升查询效率
一、概述 当我们查询所有数据时,如果缓存中没有,则去数据库查询,如果有,直接查缓存的数据就行。注意定期更新缓存数据。 二、主体代码 private static final String ROOM_SCHEDULES_HASH "RoomSchedules";Overridepu…...
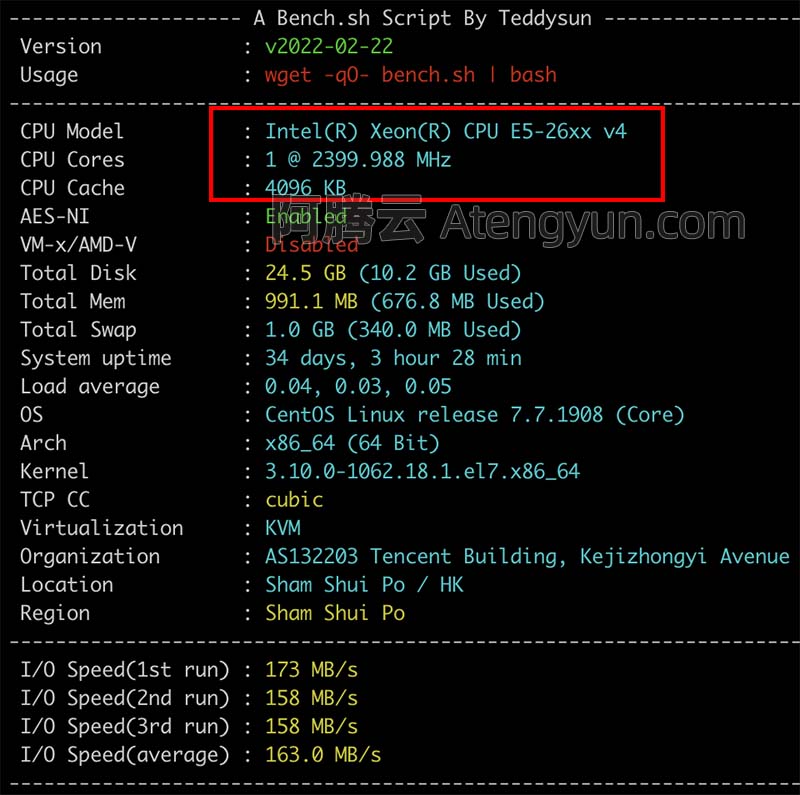
腾讯云16核32G28M轻量服务器CPU流量性能测评
腾讯云轻量16核32G28M服务器28M公网带宽下载速度峰值可达3584KB/s,折合3.5M/秒,系统盘为380GB SSD盘,6000GB月流量,折合每天200GB流量。腾讯云百科txybk.com来详细说下腾讯云轻量应用服务器16核32G28M配置性能、CPU主频型号、公网…...
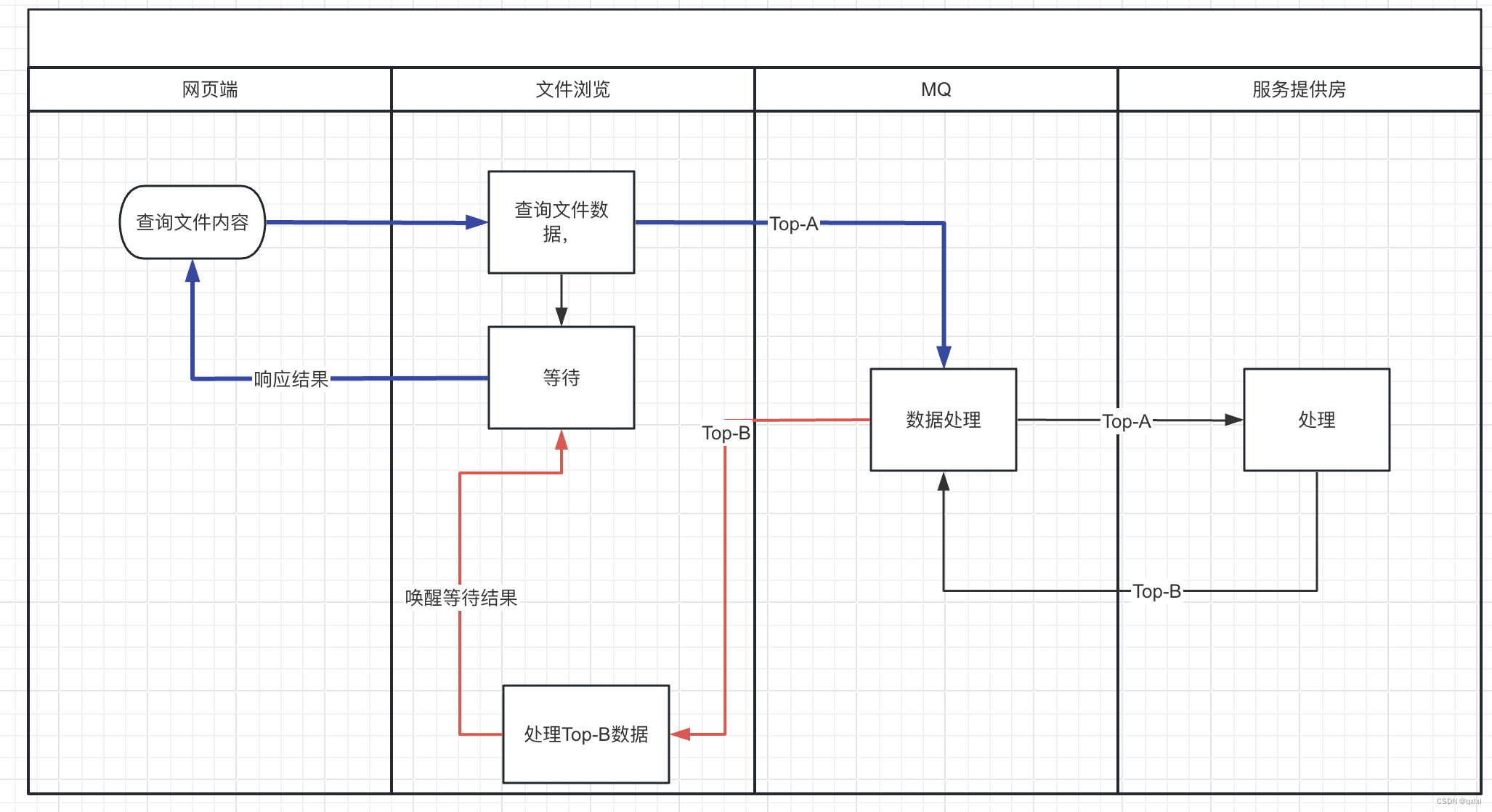
【并发设计模式】聊聊等待唤醒机制的规范实现
在多线程编程中,其实就是分工、协作、互斥。在很多场景中,比如A执行的过程中需要同步等待另外一个线程处理的结果,这种方式下,就是一种等待唤醒的机制。本篇我们来讲述等待唤醒机制的三种实现,以及对应的应用场景。 G…...

CentOS:docker同一容器间通信
docker同一容器中不同服务以别名访问 1、创建bridge网络 docker network create testnet 2、查看Docker网络 docker network ls 3、运行容器连接到testnet网络 使用方法:docker run -it --name <容器名> —network --network-alias <网络别名> <…...
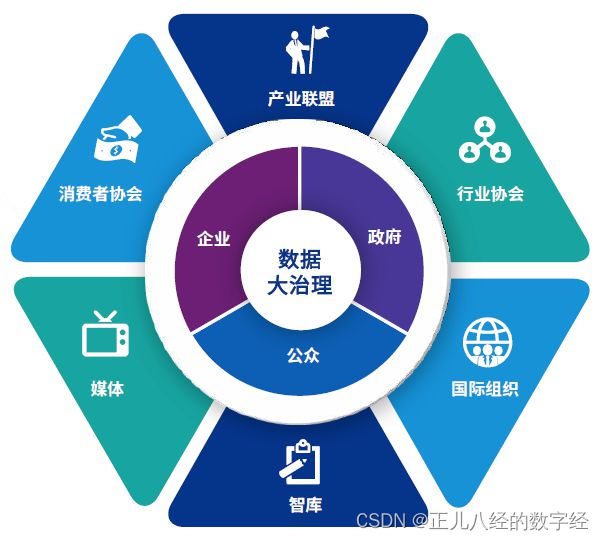
数据治理:释放数据价值的关键
随着数字化时代的到来,数据已成为组织和企业最重要的资产之一。然而,数据的快速增长和复杂性也给数据管理带来了巨大的挑战。为了确保数据的质量、安全性和合规性,数据治理已成为组织和企业必须面对的重要问题。数据治理是数据要素市场建设的…...

新手快速上手掌握基础排序<一>
听说看到日落金山的人,接下来的日子会顺顺利利,万事胜意,生活明朗-----------林辞忧 引言 从基础的两数交换排序,三四个数排序输出,到学习入门级的排序方法,如冒泡法,选择法,再学…...

2023年03月21日_chatgpt宕机事件的简单回顾
你能想象吗 ChatGPT挂了 昨天半夜呢 来自全球各地的用户纷纷发现 ChatGPT的网站弹出了报错警告的信息 然后立即就无法使用了 即使是有特权的plus账户也未能幸免 一时之间呢 chatgptdown的话题在Twitter刷屏 不少重度的用户表示很着急 有的用户说呢没了ChatGPT 这工作…...
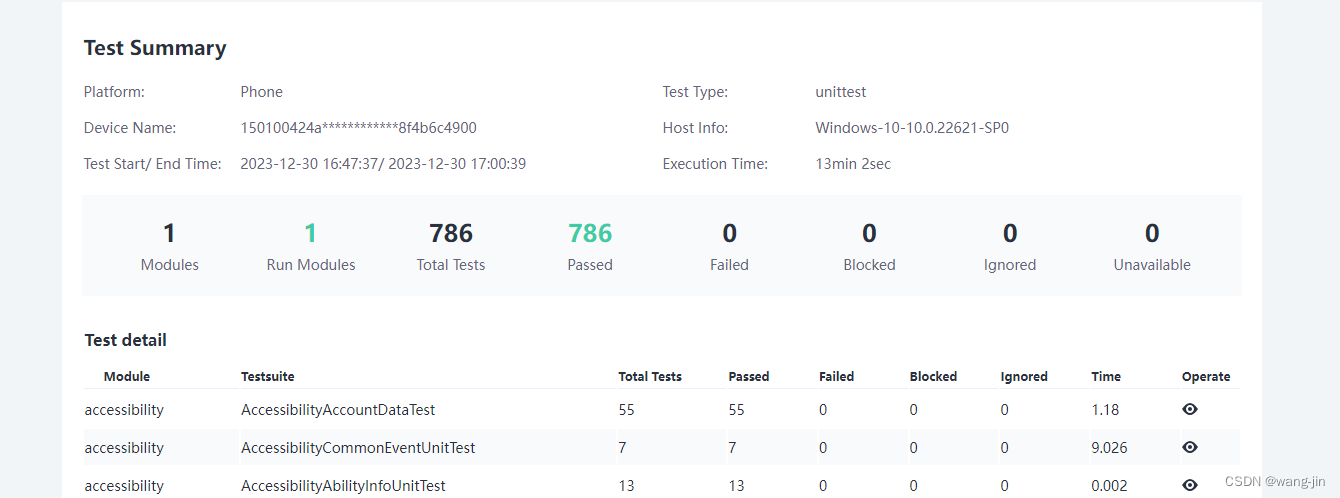
RK3568测试tdd
RK3568测试tdd 一、门禁取包二、烧录三、跑tdd用例四、查看结果参考资料 一、门禁取包 右键复制链接,粘贴下载;解压到文件夹; 二、烧录 双击\windows\RKDevTool.exe打开烧写工具,工具界面击烧写步骤如图所示: 推荐…...
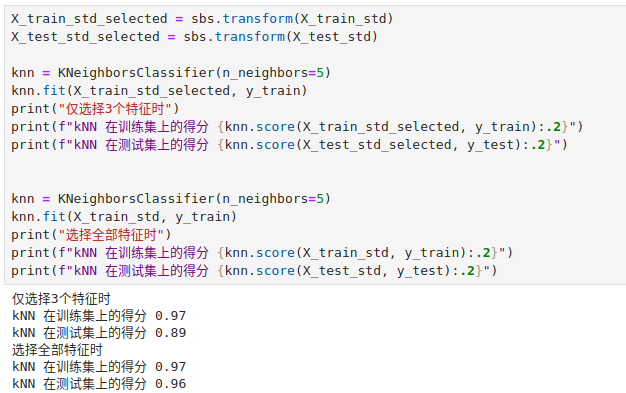
机器学习系列13:通过随机森林获取特征重要性
我们已经知道通过 L1 正则化和 SBS 算法可以用来做特征选择。 我们还可以通过随机森林从数据集中选择相关的特征。随机森林里面包含了多棵决策树,我们可以通过计算特征在每棵决策树决策过程中所产生的的信息增益平均值来衡量该特征的重要性。 你可能需要参考&…...

flink中值得监控的几个指标
背景 为了维持flink的正常运行,对flink的日常监控就变得很重要,本文我们就来看一下flink中要监控的几个重要的指标 重要的监控指标 1.算子的处理速度的指标:numRecordsInPerSecond/numRecordsOutPerSecond,这有助于你了解到算子的是否正在…...

最优化方法Python计算:无约束优化应用——逻辑分类模型
逻辑回归模型更多地用于如下例所示判断或分类场景。 例1 某银行的贷款用户数据如下表: 欠款(元)收入(元)是否逾期17000800Yes220002500No350003000Yes440004000No520003800No 显然,客户是否逾期ÿ…...
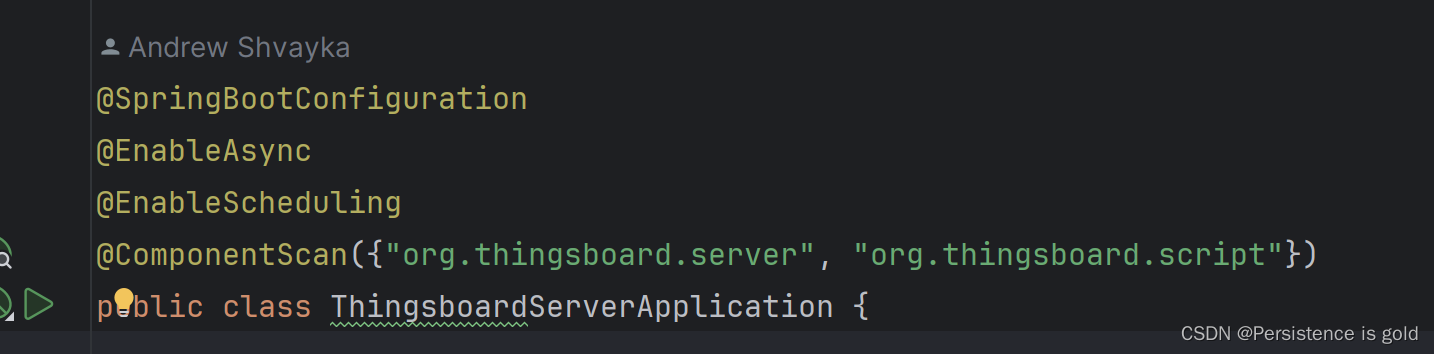
springboot定时执行某个任务
springboot定时执行某个任务 要定时执行的方法加上Schedule注解 括号内跟 cron表达式 “ 30 15 10 * * ?” 代表秒 分 时 日 月 周几 启动类上加上EnableScheduling 注释...
Java EE Servlet之Servlet API详解
文章目录 1. HttpServlet1.1 核心方法 2. HttpServletRequest3. HttpServletResponse 接下来我们来学习 Servlet API 里面的详细情况 1. HttpServlet 写一个 Servlet 代码,都是要继承这个类,重写里面的方法 Servlet 这里的代码,只需要继承…...

neo4j运维管理
管理数据库 概念 Neo4j 5(从v4.0),可以同时创建和使用多个活动数据库。 DBMS Neo4j是一个数据库管理系统(DBMS),能够管理多个数据库。DBMS可以管理一个独立的服务器,也可以管理集群中的一组服务器。 实例 Neo4j实例是运行Neo4j服务器代…...
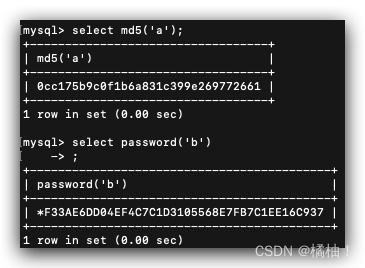
【MYSQL】-函数
💖作者:小树苗渴望变成参天大树🎈 🎉作者宣言:认真写好每一篇博客💤 🎊作者gitee:gitee✨ 💞作者专栏:C语言,数据结构初阶,Linux,C 动态规划算法🎄 如 果 你 …...
传统船检已经过时?AR智慧船检来助力!!
想象一下,在茫茫大海中,一艘巨型货轮正缓缓驶过。船上的工程师戴着一副先进的AR眼镜,他们不再需要反复翻阅厚重的手册,一切所需信息都实时显示在眼前。这不是科幻电影的场景,而是智慧船检技术带来的现实变革。那么问题…...

JAVA进化史: JDK11特性及说明
JDK 11(Java Development Kit 11)是Java平台的一个版本,于2018年9月发布。这个版本引入了一些新特性和改进,以下是其中一些主要特性。 HTTP Client(标准化) JDK 11引入了一个新的HTTP客户端,用…...

Java基础语法全解析:从入门到实践
Java语法是编写Java程序的“规则手册”,具有严谨性、面向对象性和跨平台性的特点。掌握基础语法是实现复杂功能的前提,本文将以“概念语法实例”的形式,全面覆盖Java入门阶段的核心语法知识,帮助初学者快速建立Java编程思维。一、…...

prompttools常见问题解答:从API密钥到实验调试
prompttools常见问题解答:从API密钥到实验调试 【免费下载链接】prompttools Open-source tools for prompt testing and experimentation, with support for both LLMs (e.g. OpenAI, LLaMA) and vector databases (e.g. Chroma, Weaviate, LanceDB). 项目地址: …...

【深度学习】Upsample模块采样方式实战对比:从原理到代码实现
1. 上采样:从“放大镜”到“想象力”的跨越 在深度学习的图像世界里,上采样(Upsample)就像是一个神奇的“放大镜”。想象一下,你有一张模糊的老照片,想把它放大看清楚细节,但又不想让它变得更模…...

Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct-GGUF应用场景:博物馆藏品图智能导览+多语种解说生成
Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct-GGUF应用场景:博物馆藏品图智能导览多语种解说生成 想象一下,你站在一件精美的古代瓷器前,想了解它的故事,但展牌上的文字有限,讲解员又不在身边。或者,一位外国游客面对一件国宝&am…...

从零构建51单片机电子秤:10kg量程HX711传感器与Proteus仿真全解析
1. 项目开篇:为什么选择51单片机做电子秤? 很多刚接触单片机的小伙伴,可能都听说过STM32、ESP32这些更“时髦”的芯片,心里可能会犯嘀咕:现在还用老掉牙的51单片机做项目,是不是有点过时了?作为…...

Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct部署避坑指南:vLLM加载失败、Chainlit连接超时解决方案
Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct部署避坑指南:vLLM加载失败、Chainlit连接超时解决方案 你是不是也遇到过这种情况:兴致勃勃地部署一个最新的AI模型,结果卡在模型加载或者前端连接上,折腾半天也没搞定?今天咱们就来聊聊Phi-…...

新手零基础入门:在快马平台动手实现第一个虚拟机监控界面
对于刚接触开发的新手来说,虚拟机监控听起来是个挺“高大上”的概念,涉及到服务器、后端数据采集、复杂图表库等等,光是想想配置环境就让人头大。但最近我在InsCode(快马)平台上尝试了一下,发现其实可以抛开那些复杂的后端和运维知…...

Minecraft世界数据救援指南:Region Fixer危机处理全解析
Minecraft世界数据救援指南:Region Fixer危机处理全解析 【免费下载链接】Minecraft-Region-Fixer Python script to fix some of the problems of the Minecraft save files (region files, *.mca). 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/mi/Minecraft-Regi…...

鸿蒙生态崛起:深度解析鸿蒙开发人员职责、技能要求与面试指南
前言随着万物互联时代的加速到来,鸿蒙操作系统(HarmonyOS)作为面向未来的全场景分布式操作系统,正展现出强大的生命力和广阔的发展前景。其“一次开发,多端部署”的理念,以及对分布式能力的原生支持&#x…...

安装docker后,一段时间后,ssh连不上
昨天还能正常 SSH 连接,今天失败🛠️ 分步排查与修复1. 先恢复网卡与网络在虚拟机内执行以下命令,重新启用网卡并获取 IP:# 启用 ens33 网卡 sudo ip link set ens33 up# 向 DHCP 服务器申请 IP(恢复昨天的网络配置&am…...
