linux cat命令增加-f显示文件名功能
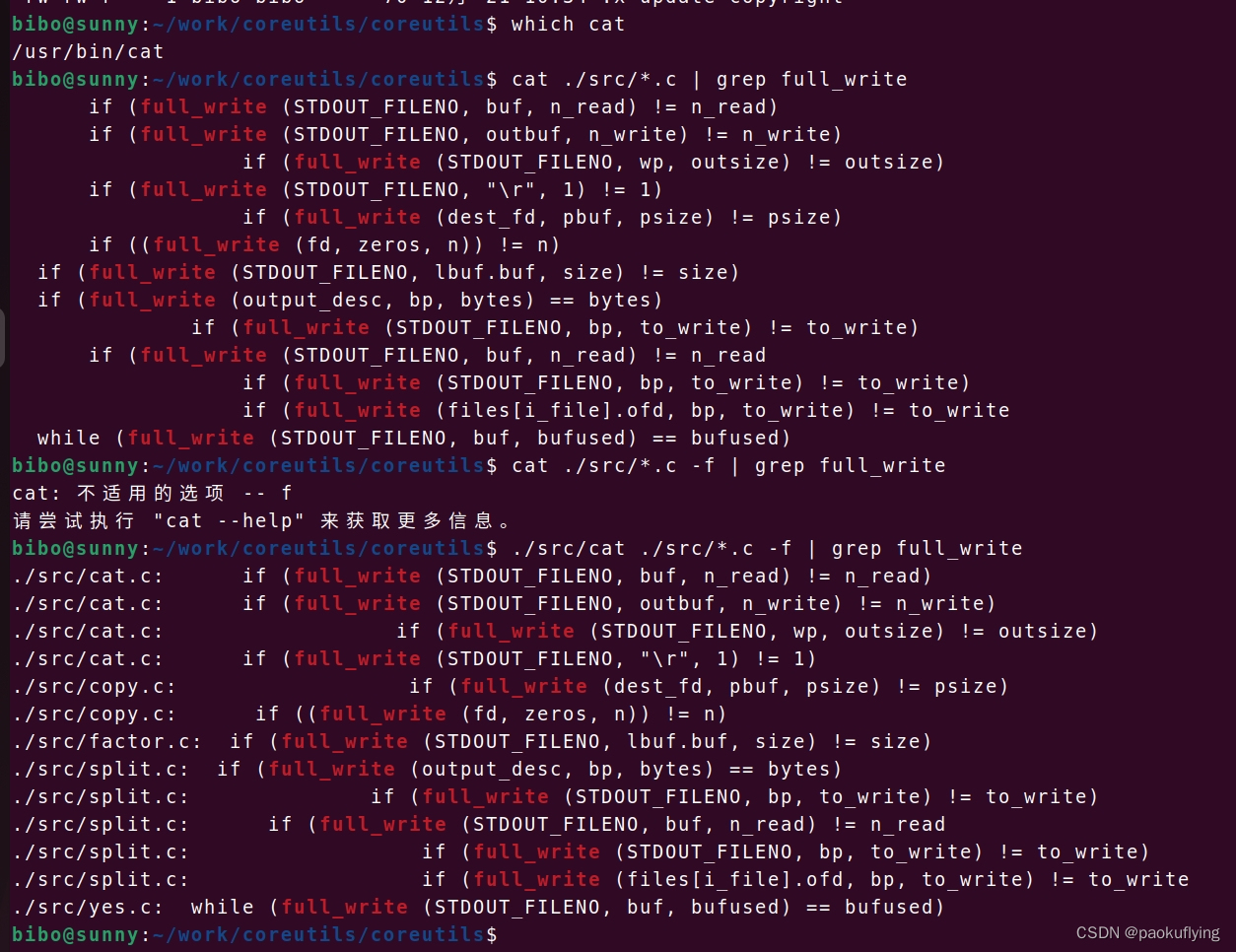
在使用cat命令配合grep批量搜索文件内容时,我仅仅能知道是否搜索到,不知道是在哪个文件里找到的。比如cat ./src/*.c | grep full_write,在src目录下的所有.c文件里找full_write,能匹配到所有的full_write,但是不知道它们分别在哪些文件里。于是我给cat命令增加了一个-f功能,这样能在每一行前面加上文件名,并且加一个冒号':'。这样就能直观的知道它们分别是在哪个文件里找到的,命令为cat ./src/*.c -f | grep full_write。找到之后再配合-n,就能显示出它是在哪个文件的哪一行,cat ./src/x.c -n | grep full_write。
对比效果
拉取项目
git clone https://git.savannah.gnu.org/git/coreutils.git
做出改动的源文件
./src/cat.c
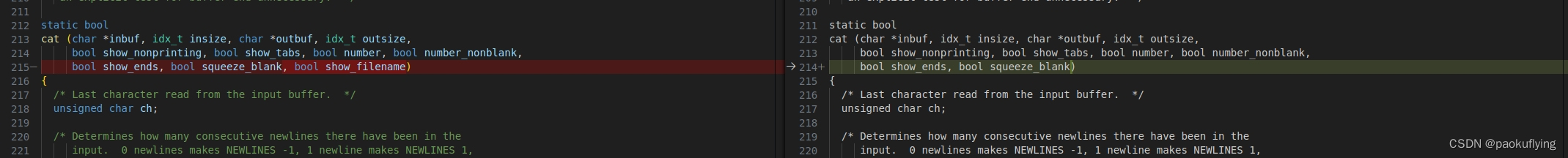
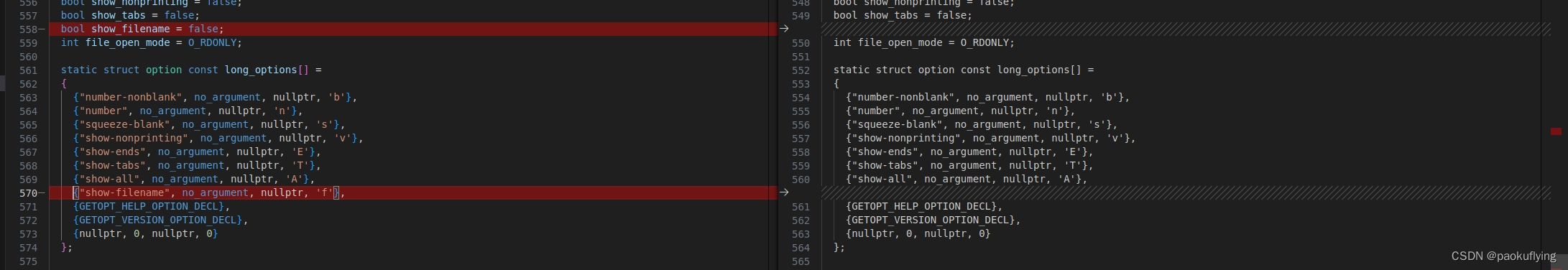
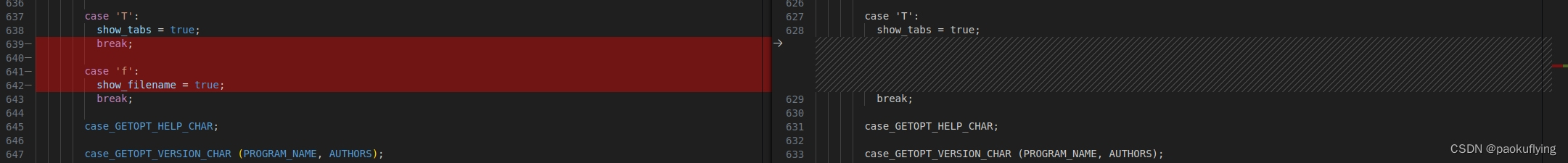
对比改动





修改后的cat.c文件
/* cat -- concatenate files and print on the standard output.Copyright (C) 1988-2023 Free Software Foundation, Inc.This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modifyit under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published bythe Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or(at your option) any later version.This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty ofMERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See theGNU General Public License for more details.You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public Licensealong with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. *//* Differences from the Unix cat:* Always unbuffered, -u is ignored.* Usually much faster than other versions of cat, the differenceis especially apparent when using the -v option.By tege@sics.se, Torbjörn Granlund, advised by rms, Richard Stallman. */#include <config.h>#include <stdio.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <sys/types.h>#if HAVE_STROPTS_H
# include <stropts.h>
#endif
#include <sys/ioctl.h>#include "system.h"
#include "alignalloc.h"
#include "ioblksize.h"
#include "fadvise.h"
#include "full-write.h"
#include "safe-read.h"
#include "xbinary-io.h"/* The official name of this program (e.g., no 'g' prefix). */
#define PROGRAM_NAME "cat"#define AUTHORS \proper_name_lite ("Torbjorn Granlund", "Torbj\303\266rn Granlund"), \proper_name ("Richard M. Stallman")/* Name of input file. May be "-". */
static char const *infile;/* Descriptor on which input file is open. */
static int input_desc;/* Buffer for line numbers.An 11 digit counter may overflow within an hour on a P2/466,an 18 digit counter needs about 1000y */
#define LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN 20
static char line_buf[LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN] ={' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ',' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', '0','\t', '\0'};/* Position in 'line_buf' where printing starts. This will not changeunless the number of lines is larger than 999999. */
static char *line_num_print = line_buf + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 8;/* Position of the first digit in 'line_buf'. */
static char *line_num_start = line_buf + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 3;/* Position of the last digit in 'line_buf'. */
static char *line_num_end = line_buf + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 3;/* Preserves the 'cat' function's local 'newlines' between invocations. */
static int newlines2 = 0;/* Whether there is a pending CR to process. */
static bool pending_cr = false;void
usage (int status)
{if (status != EXIT_SUCCESS)emit_try_help ();else{printf (_("\
Usage: %s [OPTION]... [FILE]...\n\
"),program_name);fputs (_("\
Concatenate FILE(s) to standard output.\n\
"), stdout);emit_stdin_note ();fputs (_("\
\n\-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET\n\-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n\n\-e equivalent to -vE\n\-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line\n\-n, --number number all output lines\n\-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines\n\
"), stdout);fputs (_("\-t equivalent to -vT\n\-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I\n\-u (ignored)\n\-f, --show-filename display filename at begin of each line\n\-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB\n\
"), stdout);fputs (HELP_OPTION_DESCRIPTION, stdout);fputs (VERSION_OPTION_DESCRIPTION, stdout);printf (_("\
\n\
Examples:\n\%s f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.\n\%s Copy standard input to standard output.\n\
"),program_name, program_name);emit_ancillary_info (PROGRAM_NAME);}exit (status);
}/* Compute the next line number. */static void
next_line_num (void)
{char *endp = line_num_end;do{if ((*endp)++ < '9')return;*endp-- = '0';}while (endp >= line_num_start);if (line_num_start > line_buf)*--line_num_start = '1';else*line_buf = '>';if (line_num_start < line_num_print)line_num_print--;
}/* Plain cat. Copy the file behind 'input_desc' to STDOUT_FILENO.BUF (of size BUFSIZE) is the I/O buffer, used by reads and writes.Return true if successful. */static bool
simple_cat (char *buf, idx_t bufsize)
{/* Loop until the end of the file. */while (true){/* Read a block of input. */size_t n_read = safe_read (input_desc, buf, bufsize);if (n_read == SAFE_READ_ERROR){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));return false;}/* End of this file? */if (n_read == 0)return true;/* Write this block out. */if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n_read) != n_read)write_error ();}
}/* Write any pending output to STDOUT_FILENO.Pending is defined to be the *BPOUT - OUTBUF bytes starting at OUTBUF.Then set *BPOUT to OUTPUT if it's not already that value. */static inline void
write_pending (char *outbuf, char **bpout)
{idx_t n_write = *bpout - outbuf;if (0 < n_write){if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, outbuf, n_write) != n_write)write_error ();*bpout = outbuf;}
}/* Copy the file behind 'input_desc' to STDOUT_FILENO.Use INBUF and read INSIZE with each call,and OUTBUF and write OUTSIZE with each call.(The buffers are a bit larger than the I/O sizes.)The remaining boolean args say what 'cat' options to use.Return true if successful.Called if any option more than -u was specified.A newline character is always put at the end of the buffer, to makean explicit test for buffer end unnecessary. */static bool
cat (char *inbuf, idx_t insize, char *outbuf, idx_t outsize,bool show_nonprinting, bool show_tabs, bool number, bool number_nonblank,bool show_ends, bool squeeze_blank, bool show_filename)
{/* Last character read from the input buffer. */unsigned char ch;/* Determines how many consecutive newlines there have been in theinput. 0 newlines makes NEWLINES -1, 1 newline makes NEWLINES 1,etc. Initially 0 to indicate that we are at the beginning of anew line. The "state" of the procedure is determined byNEWLINES. */int newlines = newlines2;#ifdef FIONREAD/* If nonzero, use the FIONREAD ioctl, as an optimization.(On Ultrix, it is not supported on NFS file systems.) */bool use_fionread = true;
#endif/* The inbuf pointers are initialized so that BPIN > EOB, and thereby inputis read immediately. *//* Pointer to the first non-valid byte in the input buffer, i.e., thecurrent end of the buffer. */char *eob = inbuf;/* Pointer to the next character in the input buffer. */char *bpin = eob + 1;/* Pointer to the position where the next character shall be written. */char *bpout = outbuf;while (true){do{/* Write if there are at least OUTSIZE bytes in OUTBUF. */if (outbuf + outsize <= bpout){char *wp = outbuf;idx_t remaining_bytes;do{if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, wp, outsize) != outsize)write_error ();wp += outsize;remaining_bytes = bpout - wp;}while (outsize <= remaining_bytes);/* Move the remaining bytes to the beginning of thebuffer. */memmove (outbuf, wp, remaining_bytes);bpout = outbuf + remaining_bytes;}/* Is INBUF empty? */if (bpin > eob){bool input_pending = false;
#ifdef FIONREADint n_to_read = 0;/* Is there any input to read immediately?If not, we are about to wait,so write all buffered output before waiting. */if (use_fionread&& ioctl (input_desc, FIONREAD, &n_to_read) < 0){/* Ultrix returns EOPNOTSUPP on NFS;HP-UX returns ENOTTY on pipes.SunOS returns EINVAL andMore/BSD returns ENODEV on special fileslike /dev/null.Irix-5 returns ENOSYS on pipes. */if (errno == EOPNOTSUPP || errno == ENOTTY|| errno == EINVAL || errno == ENODEV|| errno == ENOSYS)use_fionread = false;else{error (0, errno, _("cannot do ioctl on %s"),quoteaf (infile));newlines2 = newlines;return false;}}if (n_to_read != 0)input_pending = true;
#endifif (!input_pending)write_pending (outbuf, &bpout);/* Read more input into INBUF. */size_t n_read = safe_read (input_desc, inbuf, insize);if (n_read == SAFE_READ_ERROR){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));write_pending (outbuf, &bpout);newlines2 = newlines;return false;}if (n_read == 0){write_pending (outbuf, &bpout);newlines2 = newlines;return true;}/* Update the pointers and insert a sentinel at the bufferend. */bpin = inbuf;eob = bpin + n_read;*eob = '\n';}else{/* It was a real (not a sentinel) newline. *//* Was the last line empty?(i.e., have two or more consecutive newlines been read?) */if (++newlines > 0){if (newlines >= 2){/* Limit this to 2 here. Otherwise, with lots ofconsecutive newlines, the counter could wraparound at INT_MAX. */newlines = 2;/* Are multiple adjacent empty lines to be substitutedby single ditto (-s), and this was the second emptyline? */if (squeeze_blank){ch = *bpin++;continue;}}/* Are line numbers to be written at empty lines (-n)? */if (number && !number_nonblank){next_line_num ();bpout = stpcpy (bpout, line_num_print);}}/* Output a currency symbol if requested (-e). */if (show_ends){if (pending_cr){*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = 'M';pending_cr = false;}*bpout++ = '$';}/* Output the newline. */*bpout++ = '\n';}ch = *bpin++;}while (ch == '\n');/* Here CH cannot contain a newline character. */if (pending_cr){*bpout++ = '\r';pending_cr = false;}/* Are we at the beginning of a line, and filename are requested? */if (newlines >= 0 && show_filename){bpout = stpcpy (bpout, infile);*bpout++ = ':';}/* Are we at the beginning of a line, and line numbers are requested? */if (newlines >= 0 && number){next_line_num ();bpout = stpcpy (bpout, line_num_print);}/* The loops below continue until a newline character is found,which means that the buffer is empty or that a proper newlinehas been found. *//* If quoting, i.e., at least one of -v, -e, or -t specified,scan for chars that need conversion. */if (show_nonprinting){while (true){if (ch >= 32){if (ch < 127)*bpout++ = ch;else if (ch == 127){*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = '?';}else{*bpout++ = 'M';*bpout++ = '-';if (ch >= 128 + 32){if (ch < 128 + 127)*bpout++ = ch - 128;else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = '?';}}else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = ch - 128 + 64;}}}else if (ch == '\t' && !show_tabs)*bpout++ = '\t';else if (ch == '\n'){newlines = -1;break;}else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = ch + 64;}ch = *bpin++;}}else{/* Not quoting, neither of -v, -e, or -t specified. */while (true){if (ch == '\t' && show_tabs){*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = ch + 64;}else if (ch != '\n'){if (ch == '\r' && *bpin == '\n' && show_ends){if (bpin == eob)pending_cr = true;else{*bpout++ = '^';*bpout++ = 'M';}}else*bpout++ = ch;}else{newlines = -1;break;}ch = *bpin++;}}}
}/* Copy data from input to output using copy_file_range if possible.Return 1 if successful, 0 if ordinary read+write should be tried,-1 if a serious problem has been diagnosed. */static int
copy_cat (void)
{/* Copy at most COPY_MAX bytes at a time; this is min(SSIZE_MAX, SIZE_MAX) truncated to a value that issurely aligned well. */ssize_t copy_max = MIN (SSIZE_MAX, SIZE_MAX) >> 30 << 30;/* copy_file_range does not support some cases, and itincorrectly returns 0 when reading from the proc filesystem on the Linux kernel through at least 5.6.19 (2020),so fall back on read+write if the copy_file_range isunsupported or the input file seems empty. */for (bool some_copied = false; ; some_copied = true)switch (copy_file_range (input_desc, nullptr, STDOUT_FILENO, nullptr,copy_max, 0)){case 0:return some_copied;case -1:if (errno == ENOSYS || is_ENOTSUP (errno) || errno == EINVAL|| errno == EBADF || errno == EXDEV || errno == ETXTBSY|| errno == EPERM)return 0;error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));return -1;}
}int
main (int argc, char **argv)
{/* Nonzero if we have ever read standard input. */bool have_read_stdin = false;struct stat stat_buf;/* Variables that are set according to the specified options. */bool number = false;bool number_nonblank = false;bool squeeze_blank = false;bool show_ends = false;bool show_nonprinting = false;bool show_tabs = false;bool show_filename = false;int file_open_mode = O_RDONLY;static struct option const long_options[] ={{"number-nonblank", no_argument, nullptr, 'b'},{"number", no_argument, nullptr, 'n'},{"squeeze-blank", no_argument, nullptr, 's'},{"show-nonprinting", no_argument, nullptr, 'v'},{"show-ends", no_argument, nullptr, 'E'},{"show-tabs", no_argument, nullptr, 'T'},{"show-all", no_argument, nullptr, 'A'},{"show-filename", no_argument, nullptr, 'f'},{GETOPT_HELP_OPTION_DECL},{GETOPT_VERSION_OPTION_DECL},{nullptr, 0, nullptr, 0}};initialize_main (&argc, &argv);set_program_name (argv[0]);setlocale (LC_ALL, "");bindtextdomain (PACKAGE, LOCALEDIR);textdomain (PACKAGE);/* Arrange to close stdout if we exit via thecase_GETOPT_HELP_CHAR or case_GETOPT_VERSION_CHAR code.Normally STDOUT_FILENO is used rather than stdout, soclose_stdout does nothing. */atexit (close_stdout);/* Parse command line options. */int c;while ((c = getopt_long (argc, argv, "befnstuvAET", long_options, nullptr))!= -1){switch (c){case 'b':number = true;number_nonblank = true;break;case 'e':show_ends = true;show_nonprinting = true;break;case 'n':number = true;break;case 's':squeeze_blank = true;break;case 't':show_tabs = true;show_nonprinting = true;break;case 'u':/* We provide the -u feature unconditionally. */break;case 'v':show_nonprinting = true;break;case 'A':show_nonprinting = true;show_ends = true;show_tabs = true;break;case 'E':show_ends = true;break;case 'T':show_tabs = true;break;case 'f':show_filename = true;break;case_GETOPT_HELP_CHAR;case_GETOPT_VERSION_CHAR (PROGRAM_NAME, AUTHORS);default:usage (EXIT_FAILURE);}}/* Get device, i-node number, and optimal blocksize of output. */if (fstat (STDOUT_FILENO, &stat_buf) < 0)error (EXIT_FAILURE, errno, _("standard output"));/* Optimal size of i/o operations of output. */idx_t outsize = io_blksize (&stat_buf);/* Device and I-node number of the output. */dev_t out_dev = stat_buf.st_dev;ino_t out_ino = stat_buf.st_ino;/* True if the output is a regular file. */bool out_isreg = S_ISREG (stat_buf.st_mode) != 0;if (! (number || show_ends || squeeze_blank)){file_open_mode |= O_BINARY;xset_binary_mode (STDOUT_FILENO, O_BINARY);}/* Main loop. */infile = "-";int argind = optind;bool ok = true;idx_t page_size = getpagesize ();do{if (argind < argc)infile = argv[argind];bool reading_stdin = STREQ (infile, "-");if (reading_stdin){have_read_stdin = true;input_desc = STDIN_FILENO;if (file_open_mode & O_BINARY)xset_binary_mode (STDIN_FILENO, O_BINARY);}else{input_desc = open (infile, file_open_mode);if (input_desc < 0){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));ok = false;continue;}}if (fstat (input_desc, &stat_buf) < 0){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));ok = false;goto contin;}/* Optimal size of i/o operations of input. */idx_t insize = io_blksize (&stat_buf);fdadvise (input_desc, 0, 0, FADVISE_SEQUENTIAL);/* Don't copy a nonempty regular file to itself, as that wouldmerely exhaust the output device. It's better to catch thiserror earlier rather than later. */if (out_isreg&& stat_buf.st_dev == out_dev && stat_buf.st_ino == out_ino&& lseek (input_desc, 0, SEEK_CUR) < stat_buf.st_size){error (0, 0, _("%s: input file is output file"), quotef (infile));ok = false;goto contin;}/* Pointer to the input buffer. */char *inbuf;/* Select which version of 'cat' to use. If any format-orientedoptions were given use 'cat'; if not, use 'copy_cat' if itworks, 'simple_cat' otherwise. */if (! (number || show_ends || show_nonprinting|| show_tabs || squeeze_blank || show_filename)){int copy_cat_status =out_isreg && S_ISREG (stat_buf.st_mode) ? copy_cat () : 0;if (copy_cat_status != 0){inbuf = nullptr;ok &= 0 < copy_cat_status;}else{insize = MAX (insize, outsize);inbuf = xalignalloc (page_size, insize);ok &= simple_cat (inbuf, insize);}}else{/* Allocate, with an extra byte for a newline sentinel. */inbuf = xalignalloc (page_size, insize + 1);/* Why are(OUTSIZE - 1 + INSIZE * 4 + LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN)bytes allocated for the output buffer?A test whether output needs to be written is done when the inputbuffer empties or when a newline appears in the input. Afteroutput is written, at most (OUTSIZE - 1) bytes will remain in thebuffer. Now INSIZE bytes of input is read. Each input charactermay grow by a factor of 4 (by the prepending of M-^). If allcharacters do, and no newlines appear in this block of input, wewill have at most (OUTSIZE - 1 + INSIZE * 4) bytes in the buffer.If the last character in the preceding block of input was anewline, a line number may be written (according to the givenoptions) as the first thing in the output buffer. (Done after thenew input is read, but before processing of the input begins.)A line number requires seldom more than LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LENpositions.Align the output buffer to a page size boundary, for efficiencyon some paging implementations. */idx_t bufsize;if (ckd_mul (&bufsize, insize, 4)|| ckd_add (&bufsize, bufsize, outsize)|| ckd_add (&bufsize, bufsize, LINE_COUNTER_BUF_LEN - 1))xalloc_die ();char *outbuf = xalignalloc (page_size, bufsize);ok &= cat (inbuf, insize, outbuf, outsize, show_nonprinting,show_tabs, number, number_nonblank, show_ends,squeeze_blank, show_filename);alignfree (outbuf);}alignfree (inbuf);contin:if (!reading_stdin && close (input_desc) < 0){error (0, errno, "%s", quotef (infile));ok = false;}}while (++argind < argc);if (pending_cr){if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, "\r", 1) != 1)write_error ();}if (have_read_stdin && close (STDIN_FILENO) < 0)error (EXIT_FAILURE, errno, _("closing standard input"));return ok ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE;
}
相关文章:

linux cat命令增加-f显示文件名功能
在使用cat命令配合grep批量搜索文件内容时,我仅仅能知道是否搜索到,不知道是在哪个文件里找到的。比如cat ./src/*.c | grep full_write,在src目录下的所有.c文件里找full_write,能匹配到所有的full_write,但是不知道它们分别在哪些文件里。于…...

linux更改登录shell
从bash修改成python 在/etc/passwd下可以更改用户登录bash 例 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash //更改bin/bash为/bin/python,就可以用root登录python页面了从python修改成bash 方法一 重启页面按e进入内核编辑模式linux16这行后添加:init/bin/…...
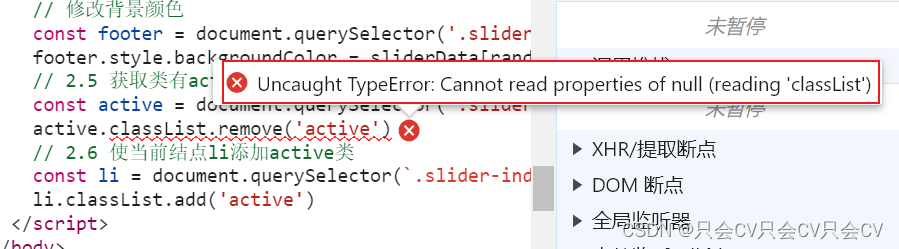
【JS】报错:Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading ‘classList‘)
错误展示 今天写js代码的时候遇到报错: 源代码: <ul class"slider-indicator"><li class"active"></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li></li><li><…...
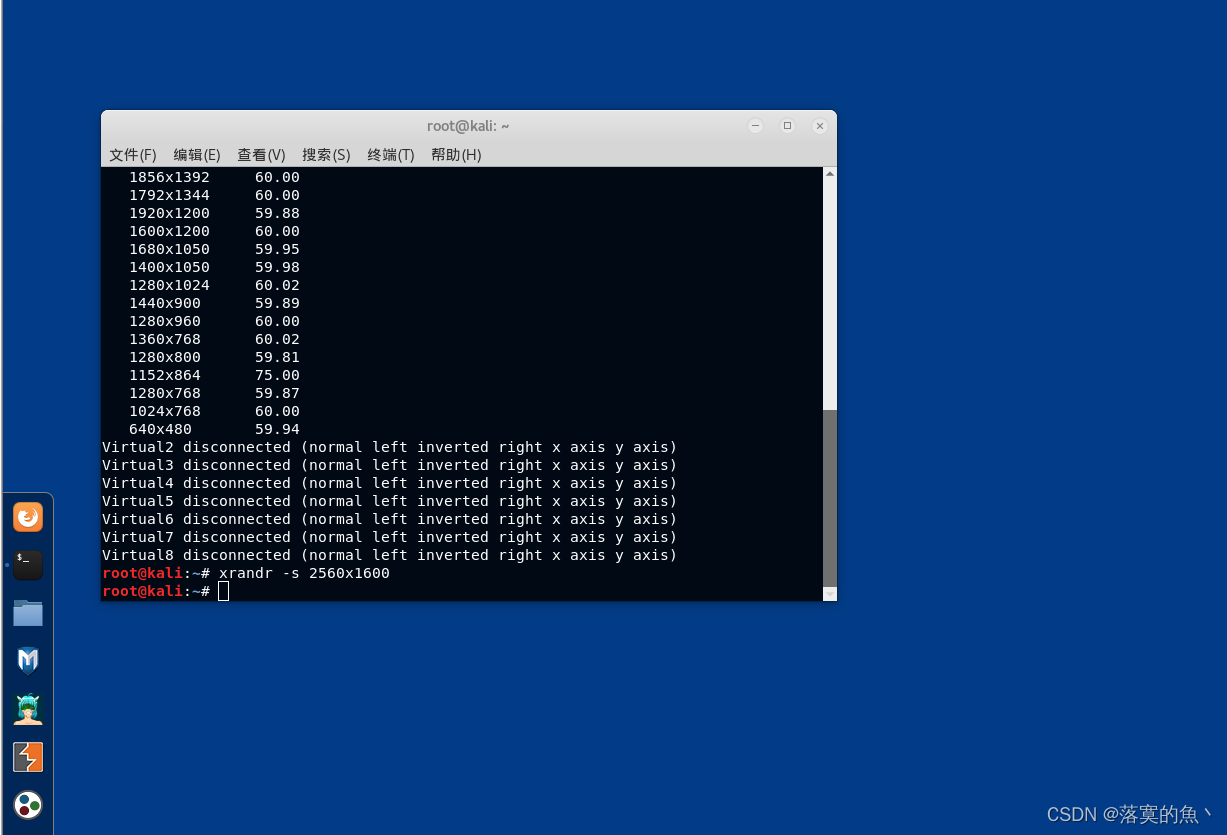
kali2.0安装VMware Tools 和自定义改变分辨率
kali2.0安装VMware Tools 和自定义改变分辨率 VMware Tools 简介:VMware Tools安装:自定义改变分辨率:xrandr命令修改分辨率: 前言: 因为kali2.0比较老 所以需要手动安装 WMware Tools 进行复制粘贴操作! …...
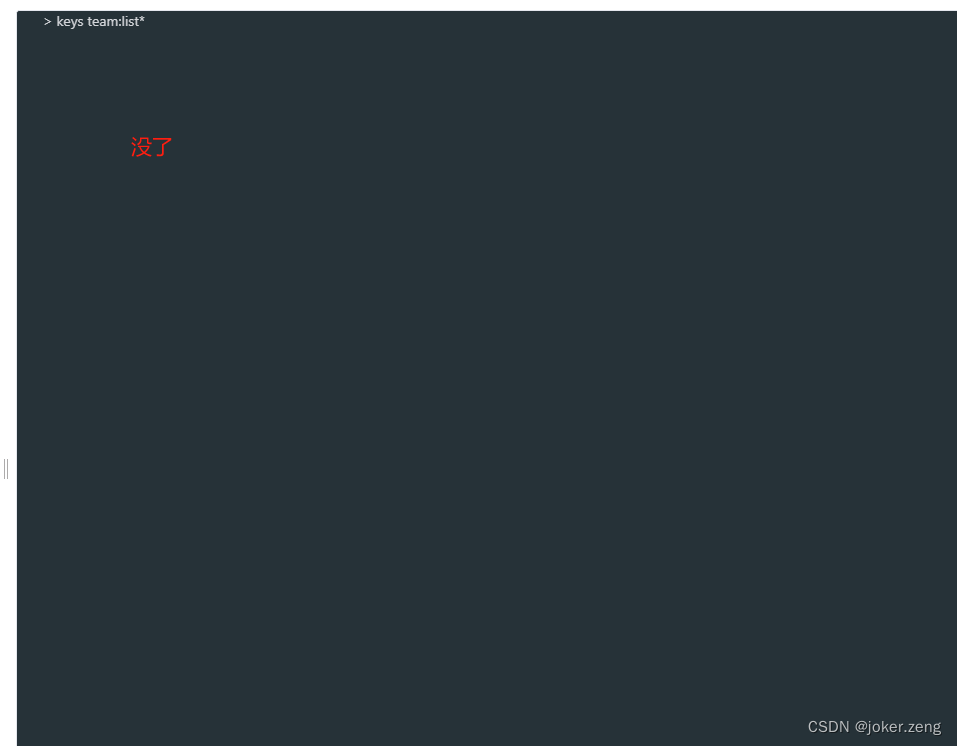
redis中根据通配符删除key
redis中根据通配符删除key 我们是不是在redis中keys user:*可以获取所有key,但是 del user:*却不行这里我提供的命令主要是SCANSCAN 0 MATCH user:* COUNT 100使用lua保证原子性 SCAN参数描述 在示例中,COUNT 被设置为 100。这是一个防止一次性获取大…...
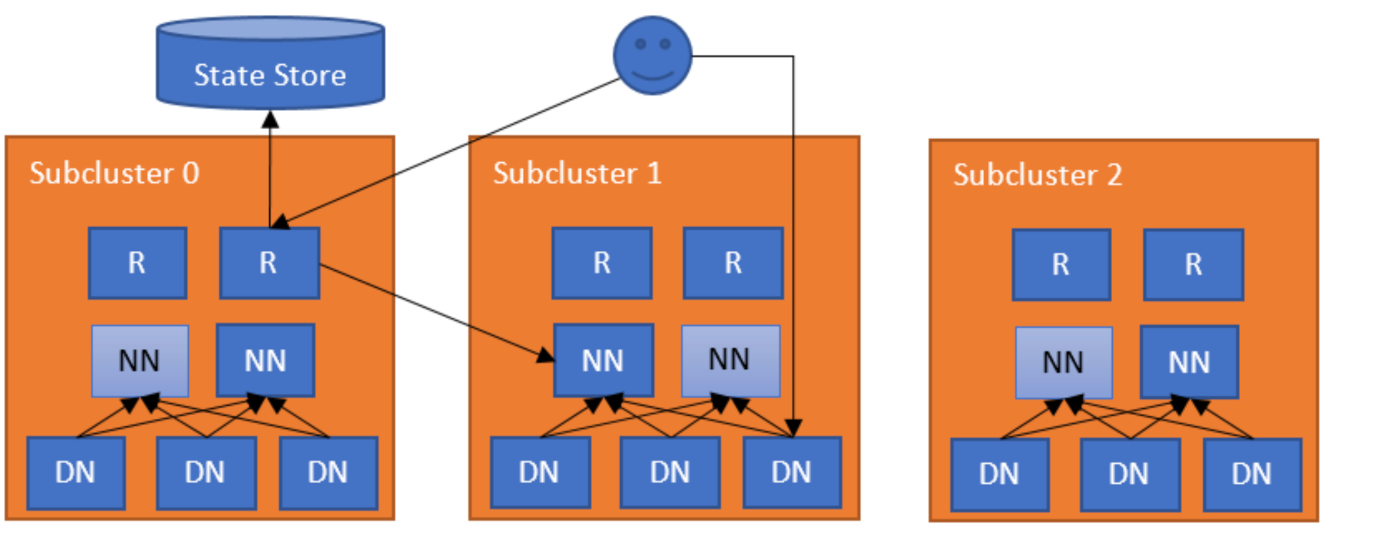
【HDFS联邦(2)】HDFS Router-based Federation官网解读:HDFSRouterFederation的架构、各组件基本原理
文章目录 一. 介绍二、HDFS Router-based Federation 架构1. 示例说明2. Router2.1. Federated interface2.2. Router heartbeat2.3. NameNode heartbeat2.4. Availability and fault toleranceInterfaces 3. Quota management4. State Store 三、部署 ing 本文主要参考官网&am…...

【头歌实训】Spark 完全分布式的安装和部署
文章目录 第1关: Standalone 分布式集群搭建任务描述相关知识课程视频Spark分布式安装模式示例集群信息配置免密登录准备Spark安装包配置环境变量修改 spark-env.sh 配置文件修改 slaves 文件分发安装包启动spark验证安装 编程要求测试说明答案代码报错问题基本过程…...
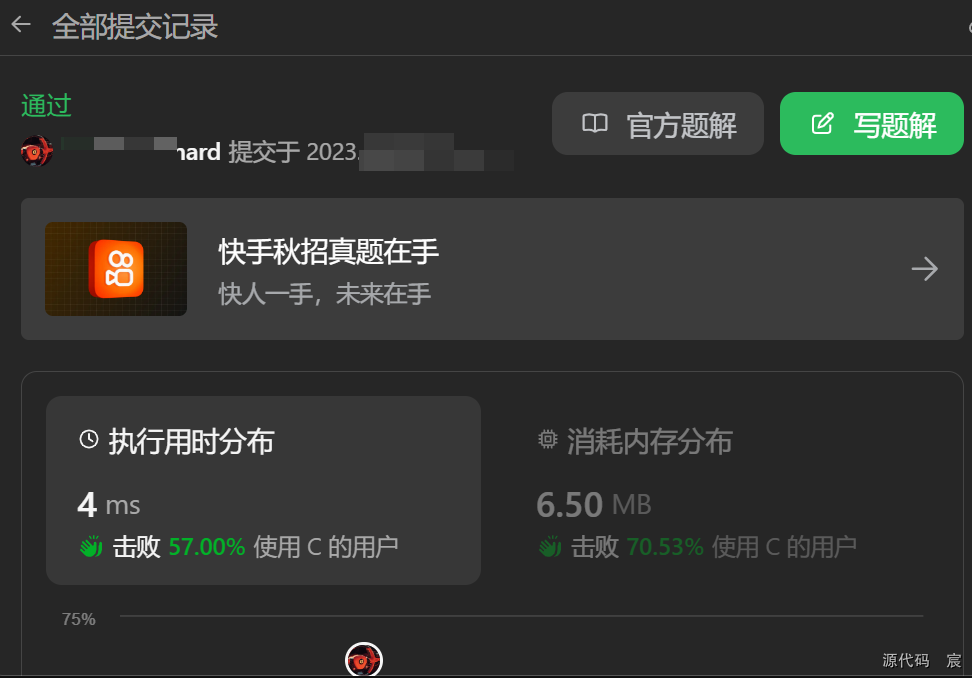
Leetcode—86.分隔链表【中等】
2023每日刷题(六十九) Leetcode—86.分隔链表 实现代码 /*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/ struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x) {struct ListNode…...

淘宝/天猫商品API:实时数据获取与安全隐私保护的指南
一、引言 随着电子商务的快速发展,淘宝/天猫等电商平台已成为商家和消费者的重要交易场所。对于电商企业而言,实时掌握店铺商品的销售情况、库存状态等信息至关重要。然而,手动管理和更新商品信息既费时又费力。因此,淘宝/天猫提…...
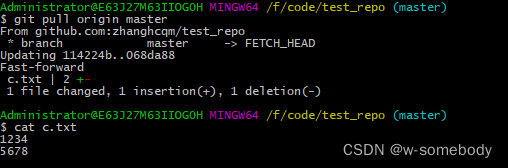
使用 SSH 方式实现 Git 远程连接GitHub
git是目前世界上最先进的分布式版本控制系统,相比于SVN,分布式版本系统的最大好处之一是在本地工作完全不需要考虑远程库的存在,也就是有没有联网都可以正常工作!当有网络的时候,再把本地提交推送一下就完成了同步&…...
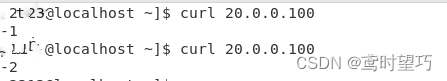
Centos7部署Keepalived+lvs服务
IP规划: 服务器IP地址主服务器20.0.0.22/24从服务器20.0.0.24/24Web-120.0.0.26/24Web-220.0.0.27/24 一、主服务器安装部署keepalivedlvs服务 1、调整/proc响应参数 关闭Linux内核的重定向参数,因为LVS负载服务器和两个页面服务器需要共用一个VIP地…...
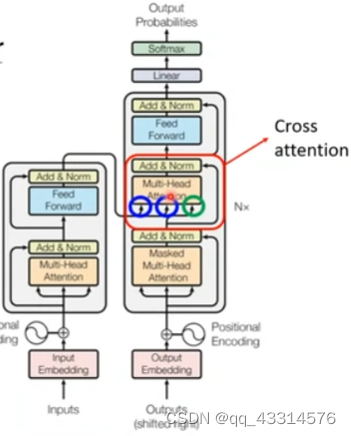
12/31
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 摘要Abstract文献阅读:用于密集预测的多路径视觉Transformer1、研究背景2、方法提出3、相关方法3.1、Vision Transformers for dense predictions3.2、C…...
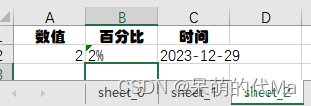
python使用openpyxl为excel模版填充数据,生成多个Sheet页面
目标:希望根据一个给定的excel模版,生成多个Sheet页面,比如模版: 示例程序 import openpyxlexcel_workbook openpyxl.load_workbook("模版.xlsx") for _i in range(3): # 比如填充3个页面# 复制模版sheet页&#x…...
基于ssm的4S店预约保养系统开发+vue论文
目 录 目 录 I 摘 要 III ABSTRACT IV 1 绪论 1 1.1 课题背景 1 1.2 研究现状 1 1.3 研究内容 2 2 系统开发环境 3 2.1 vue技术 3 2.2 JAVA技术 3 2.3 MYSQL数据库 3 2.4 B/S结构 4 2.5 SSM框架技术 4 3 系统分析 5 3.1 可行性分析 5 3.1.1 技术可行性 5 3.1.2 操作可行性 5 3…...
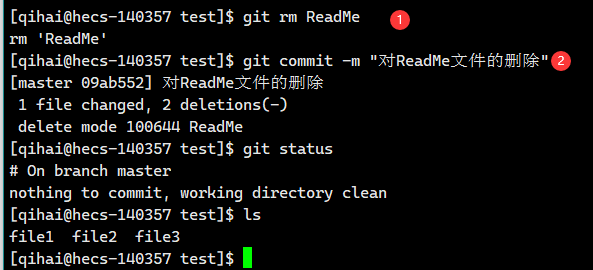
【Git】Git的基本操作
前言 Git是当前最主流的版本管理器,它可以控制电脑上的所有格式的文件。 它对于开发人员,可以管理项目中的源代码文档。(可以记录不同提交的修改细节,并且任意跳转版本) 本篇博客基于最近对Git的学习,简单介…...
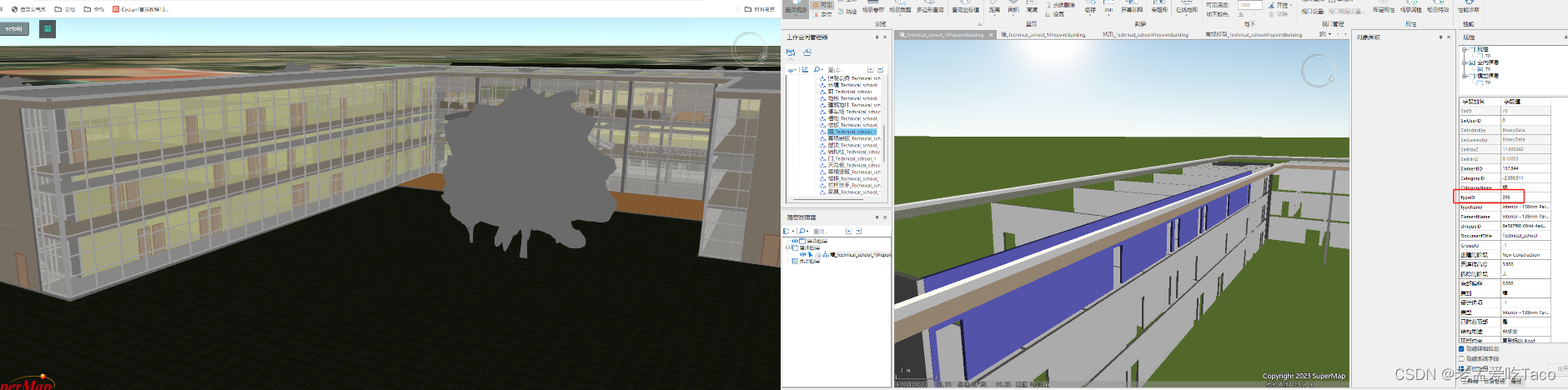
【超图】SuperMap iClient3D for WebGL/WebGPU —— 数据集合并缓存如何控制对象样式
作者:taco 最近在支持的过程中,遇到了一个新问题!之前研究功能的时候竟然没有想到。通常我们控制单个对象的显隐、颜色、偏移的参数都是根据对象所在的图层以及对象单独的id来算的。那么问题来了,合并后的图层。他怎么控制单个对象…...
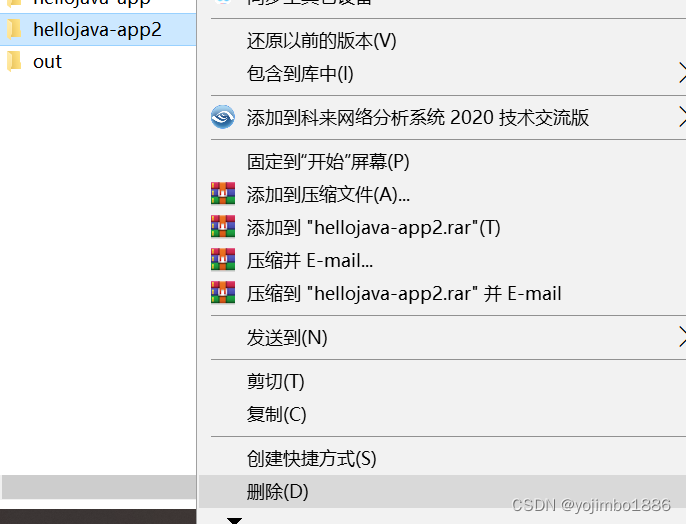
intellij IDEA开发工具的使用(打开/关闭工程;删除类文件;修改类/包/模块/项目名称;导入/删除模块)
1,打开工程 打开IDEA,会看到如下界面 1栏目里是自己曾经打开过的project(工程),直接点击就好。如果需要打开其他工程,则点击open,会出下以下界面。 选择需要加载的project(工程&…...
抖音详情API:开发环境搭建与工具选择
随着短视频的流行,抖音已经成为了一个备受欢迎的社交媒体平台。对于开发人员而言,利用抖音详情API开发定制化的抖音应用具有巨大的潜力。本文将为你详细介绍开发抖音应用的开发环境搭建与工具选择,帮助你顺利地开始开发工作。 一、开发环境搭…...
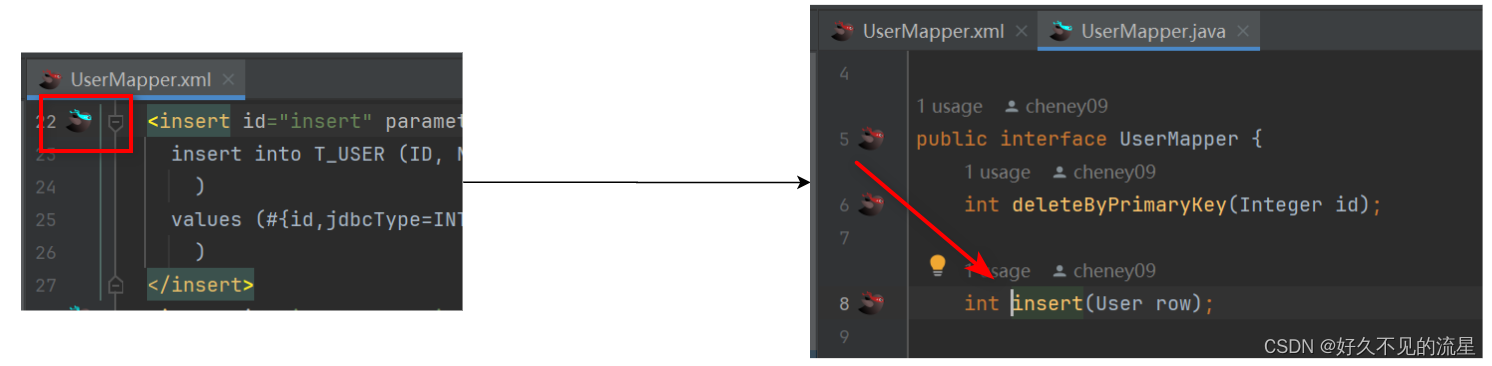
IntelliJ IDEA [插件 MybatisX] mapper和xml间跳转
文章目录 1. 安装插件2. 如何使用3. 主要功能总结 MybatisX 是一款为 IntelliJ IDEA 提供支持的 MyBatis 开发插件 它通过提供丰富的功能集,大大简化了 MyBatis XML 文件的编写、映射关系的可视化查看以及 SQL 语句的调试等操作。本文将介绍如何安装、配置和使用 In…...

Havenask 分布式索引构建服务 --Build Service
Havenask 是阿里巴巴智能引擎事业部自研的开源高性能搜索引擎,深度支持了包括淘宝、天猫、菜鸟、高德、饿了么在内几乎整个阿里的搜索业务。本文针对性介绍了 Havenask 分布式索引构建服务——Build Service,主打稳定、快速、易管理,是在线系…...
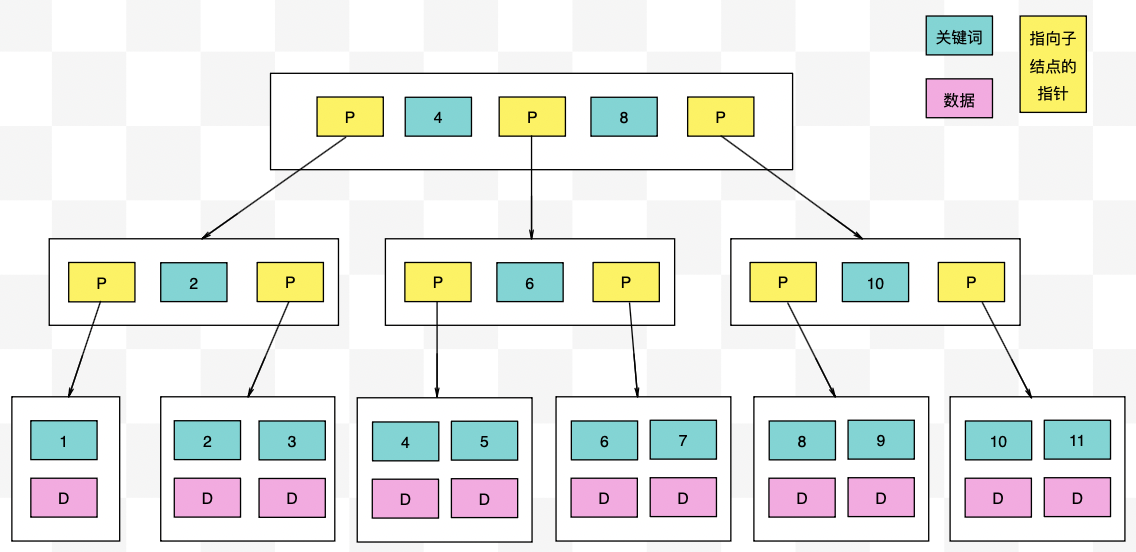
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...

Nginx server_name 配置说明
Nginx 是一个高性能的反向代理和负载均衡服务器,其核心配置之一是 server 块中的 server_name 指令。server_name 决定了 Nginx 如何根据客户端请求的 Host 头匹配对应的虚拟主机(Virtual Host)。 1. 简介 Nginx 使用 server_name 指令来确定…...
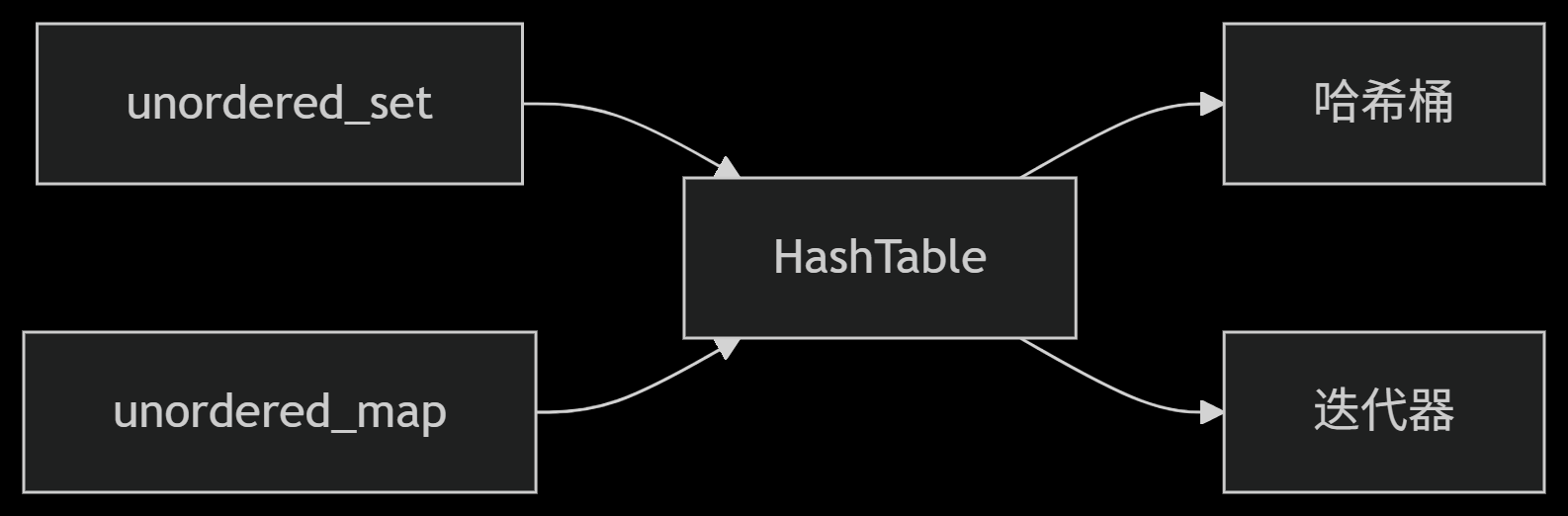
从零实现STL哈希容器:unordered_map/unordered_set封装详解
本篇文章是对C学习的STL哈希容器自主实现部分的学习分享 希望也能为你带来些帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、源码结构分析 1. SGISTL30实现剖析 // hash_set核心结构 template <class Value, class HashFcn, ...> class hash_set {ty…...

实现弹窗随键盘上移居中
实现弹窗随键盘上移的核心思路 在Android中,可以通过监听键盘的显示和隐藏事件,动态调整弹窗的位置。关键点在于获取键盘高度,并计算剩余屏幕空间以重新定位弹窗。 // 在Activity或Fragment中设置键盘监听 val rootView findViewById<V…...

Webpack性能优化:构建速度与体积优化策略
一、构建速度优化 1、升级Webpack和Node.js 优化效果:Webpack 4比Webpack 3构建时间降低60%-98%。原因: V8引擎优化(for of替代forEach、Map/Set替代Object)。默认使用更快的md4哈希算法。AST直接从Loa…...

(一)单例模式
一、前言 单例模式属于六大创建型模式,即在软件设计过程中,主要关注创建对象的结果,并不关心创建对象的过程及细节。创建型设计模式将类对象的实例化过程进行抽象化接口设计,从而隐藏了类对象的实例是如何被创建的,封装了软件系统使用的具体对象类型。 六大创建型模式包括…...
恶补电源:1.电桥
一、元器件的选择 搜索并选择电桥,再multisim中选择FWB,就有各种型号的电桥: 电桥是用来干嘛的呢? 它是一个由四个二极管搭成的“桥梁”形状的电路,用来把交流电(AC)变成直流电(DC)。…...

[USACO23FEB] Bakery S
题目描述 Bessie 开了一家面包店! 在她的面包店里,Bessie 有一个烤箱,可以在 t C t_C tC 的时间内生产一块饼干或在 t M t_M tM 单位时间内生产一块松糕。 ( 1 ≤ t C , t M ≤ 10 9 ) (1 \le t_C,t_M \le 10^9) (1≤tC,tM≤109)。由于空间…...
 ----- Python的类与对象)
Python学习(8) ----- Python的类与对象
Python 中的类(Class)与对象(Object)是面向对象编程(OOP)的核心。我们可以通过“类是模板,对象是实例”来理解它们的关系。 🧱 一句话理解: 类就像“图纸”,对…...

Linux-进程间的通信
1、IPC: Inter Process Communication(进程间通信): 由于每个进程在操作系统中有独立的地址空间,它们不能像线程那样直接访问彼此的内存,所以必须通过某种方式进行通信。 常见的 IPC 方式包括&#…...
