AES - 在tiny-AES-c基础上封装了2个应用函数(加密/解密)
文章目录
- AES - 在tiny-AES-c基础上封装了2个应用函数(加密/解密)
- 概述
- 增加2个封装函数的AES库
- aes.h
- aes.c
- 在官方测试程序上改的测试程序(用来测试这2个封装函数)
- END
AES - 在tiny-AES-c基础上封装了2个应用函数(加密/解密)
概述
在github山有个星数很高的AES的C库 tiny-AES-c (https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-c.git)
这个库用起来挺好的, 但是需要自己考虑key, iv, data的对齐问题.
我对 AES256 + CBC 封装了2个函数, 调用方只需要给出key, iv, in_data, out_data, 只要有数据就行, 不需要考虑对齐(key, iv, data), 其他调用库之前的预操作, 都在封装函数内做了.
初步测试一下, 好使. 有啥bug能用的时候再改.
封装函数的调用例子
void my_test_encrypt_cbc_ex()
{const char* pKey = "my_key";const char* pIv = "my_iv";const char* pIn = "hello world";uint8_t* pszOut = new uint8_t[strlen(pIn) + 32];size_t len_Out = strlen(pIn) + 32;bool b_rc = false;b_rc = AES256_CBC_encrypt_buffer_ex((uint8_t*)pKey, (int)strlen(pKey), (uint8_t*)pIv, (int)strlen(pIv), (uint8_t*)pIn, (size_t)strlen(pIn), (uint8_t*)pszOut, &len_Out);assert(true == b_rc);showBufHex("out buf", pszOut, len_Out);uint8_t* pszDecrypt = new uint8_t[len_Out];size_t lenDecrypt = len_Out;b_rc = AES256_CBC_decrypt_buffer_ex((uint8_t*)pKey, (int)strlen(pKey), (uint8_t*)pIv, (int)strlen(pIv), (uint8_t*)pszOut, len_Out, (uint8_t*)pszDecrypt, &lenDecrypt);assert(true == b_rc);pszDecrypt[lenDecrypt] = 0x00;printf("descrypt data = [%s]\n", pszDecrypt);if (NULL != pszOut){delete []pszOut;pszOut = NULL;}if (NULL != pszDecrypt){delete[]pszDecrypt;pszDecrypt = NULL;}
}增加2个封装函数的AES库
aes.h
#ifndef _AES_H_
#define _AES_H_#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdbool.h> // for bool// Enable ECB, CTR and CBC mode. Note this can be done before including aes.h or at compile-time.
// E.g. with GCC by using the -D flag: gcc -c aes.c -DCBC=0 -DCTR=1 -DECB=1
#define CBC 1 // cbc好一些
#define CTR 1
#define ECB 1// #define the macros below to 1/0 to enable/disable the mode of operation.
//
// CBC enables AES encryption in CBC-mode of operation.
// CTR enables encryption in counter-mode.
// ECB enables the basic ECB 16-byte block algorithm. All can be enabled simultaneously.// The #ifndef-guard allows it to be configured before #include'ing or at compile time.
#ifndef CBC
#define CBC 1
#endif#ifndef ECB
#define ECB 1
#endif#ifndef CTR
#define CTR 1
#endif// #define AES128 1
// #define AES192 1
#define AES256 1#define AES_BLOCKLEN 16 // Block length in bytes - AES is 128b block only#if defined(AES256) && (AES256 == 1)
#define AES_KEYLEN 32
#define AES_keyExpSize 240
#elif defined(AES192) && (AES192 == 1)
#define AES_KEYLEN 24
#define AES_keyExpSize 208
#else
#define AES_KEYLEN 16 // Key length in bytes
#define AES_keyExpSize 176
#endifstruct AES_ctx
{uint8_t RoundKey[AES_keyExpSize];
#if (defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)) || (defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1))uint8_t Iv[AES_BLOCKLEN];
#endif
};void AES_init_ctx(struct AES_ctx* ctx, const uint8_t* key);
#if (defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)) || (defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1))
void AES_init_ctx_iv(struct AES_ctx* ctx, const uint8_t* key, const uint8_t* iv);
void AES_ctx_set_iv(struct AES_ctx* ctx, const uint8_t* iv);
#endif#if defined(ECB) && (ECB == 1)
// buffer size is exactly AES_BLOCKLEN bytes;
// you need only AES_init_ctx as IV is not used in ECB
// NB: ECB is considered insecure for most uses
void AES_ECB_encrypt(const struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf);
void AES_ECB_decrypt(const struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf);#endif // #if defined(ECB) && (ECB == !)#if defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)
// buffer size MUST be mutile of AES_BLOCKLEN;
// Suggest https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Padding_(cryptography)#PKCS7 for padding scheme
// NOTES: you need to set IV in ctx via AES_init_ctx_iv() or AES_ctx_set_iv()
// no IV should ever be reused with the same key
void AES_CBC_encrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf, size_t length);
void AES_CBC_decrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf, size_t length);// 封装的AES_CBC加解密, 只要送入数据(key/iv/bu)和长度(len_key/len_iv/len_buf), 函数里面自己处理(key/iv的对齐(截断或填充)加解密初始化/块尾部填充)
bool AES256_CBC_encrypt_buffer_ex(uint8_t* key, int len_key, uint8_t* iv, int len_iv, uint8_t* buf_in, size_t len_buf_in, uint8_t* buf_out, size_t* len_buf_out);
bool AES256_CBC_decrypt_buffer_ex(uint8_t* key, int len_key, uint8_t* iv, int len_iv, uint8_t* buf_in, size_t len_buf_in, uint8_t* buf_out, size_t* len_buf_out);#endif // #if defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)#if defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1)// Same function for encrypting as for decrypting.
// IV is incremented for every block, and used after encryption as XOR-compliment for output
// Suggesting https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Padding_(cryptography)#PKCS7 for padding scheme
// NOTES: you need to set IV in ctx with AES_init_ctx_iv() or AES_ctx_set_iv()
// no IV should ever be reused with the same key
void AES_CTR_xcrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf, size_t length);#endif // #if defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1)#endif // _AES_H_aes.c
/*This is an implementation of the AES algorithm, specifically ECB, CTR and CBC mode.
Block size can be chosen in aes.h - available choices are AES128, AES192, AES256.The implementation is verified against the test vectors in:National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-38A 2001 EDECB-AES128
----------plain-text:6bc1bee22e409f96e93d7e117393172aae2d8a571e03ac9c9eb76fac45af8e5130c81c46a35ce411e5fbc1191a0a52eff69f2445df4f9b17ad2b417be66c3710key:2b7e151628aed2a6abf7158809cf4f3cresulting cipher3ad77bb40d7a3660a89ecaf32466ef97f5d3d58503b9699de785895a96fdbaaf43b1cd7f598ece23881b00e3ed0306887b0c785e27e8ad3f8223207104725dd4NOTE: String length must be evenly divisible by 16byte (str_len % 16 == 0)You should pad the end of the string with zeros if this is not the case.For AES192/256 the key size is proportionally larger.*//*****************************************************************************/
/* Includes: */
/*****************************************************************************/
#include <string.h> // CBC mode, for memset
#include "aes.h"/*****************************************************************************/
/* Defines: */
/*****************************************************************************/
// The number of columns comprising a state in AES. This is a constant in AES. Value=4
#define Nb 4#if defined(AES256) && (AES256 == 1)
#define Nk 8
#define Nr 14
#elif defined(AES192) && (AES192 == 1)
#define Nk 6
#define Nr 12
#else
#define Nk 4 // The number of 32 bit words in a key.
#define Nr 10 // The number of rounds in AES Cipher.
#endif// jcallan@github points out that declaring Multiply as a function
// reduces code size considerably with the Keil ARM compiler.
// See this link for more information: https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-C/pull/3
#ifndef MULTIPLY_AS_A_FUNCTION
#define MULTIPLY_AS_A_FUNCTION 0
#endif/*****************************************************************************/
/* Private variables: */
/*****************************************************************************/
// state - array holding the intermediate results during decryption.
typedef uint8_t state_t[4][4];// The lookup-tables are marked const so they can be placed in read-only storage instead of RAM
// The numbers below can be computed dynamically trading ROM for RAM -
// This can be useful in (embedded) bootloader applications, where ROM is often limited.
static const uint8_t sbox[256] = {//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F0x63, 0x7c, 0x77, 0x7b, 0xf2, 0x6b, 0x6f, 0xc5, 0x30, 0x01, 0x67, 0x2b, 0xfe, 0xd7, 0xab, 0x76,0xca, 0x82, 0xc9, 0x7d, 0xfa, 0x59, 0x47, 0xf0, 0xad, 0xd4, 0xa2, 0xaf, 0x9c, 0xa4, 0x72, 0xc0,0xb7, 0xfd, 0x93, 0x26, 0x36, 0x3f, 0xf7, 0xcc, 0x34, 0xa5, 0xe5, 0xf1, 0x71, 0xd8, 0x31, 0x15,0x04, 0xc7, 0x23, 0xc3, 0x18, 0x96, 0x05, 0x9a, 0x07, 0x12, 0x80, 0xe2, 0xeb, 0x27, 0xb2, 0x75,0x09, 0x83, 0x2c, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x6e, 0x5a, 0xa0, 0x52, 0x3b, 0xd6, 0xb3, 0x29, 0xe3, 0x2f, 0x84,0x53, 0xd1, 0x00, 0xed, 0x20, 0xfc, 0xb1, 0x5b, 0x6a, 0xcb, 0xbe, 0x39, 0x4a, 0x4c, 0x58, 0xcf,0xd0, 0xef, 0xaa, 0xfb, 0x43, 0x4d, 0x33, 0x85, 0x45, 0xf9, 0x02, 0x7f, 0x50, 0x3c, 0x9f, 0xa8,0x51, 0xa3, 0x40, 0x8f, 0x92, 0x9d, 0x38, 0xf5, 0xbc, 0xb6, 0xda, 0x21, 0x10, 0xff, 0xf3, 0xd2,0xcd, 0x0c, 0x13, 0xec, 0x5f, 0x97, 0x44, 0x17, 0xc4, 0xa7, 0x7e, 0x3d, 0x64, 0x5d, 0x19, 0x73,0x60, 0x81, 0x4f, 0xdc, 0x22, 0x2a, 0x90, 0x88, 0x46, 0xee, 0xb8, 0x14, 0xde, 0x5e, 0x0b, 0xdb,0xe0, 0x32, 0x3a, 0x0a, 0x49, 0x06, 0x24, 0x5c, 0xc2, 0xd3, 0xac, 0x62, 0x91, 0x95, 0xe4, 0x79,0xe7, 0xc8, 0x37, 0x6d, 0x8d, 0xd5, 0x4e, 0xa9, 0x6c, 0x56, 0xf4, 0xea, 0x65, 0x7a, 0xae, 0x08,0xba, 0x78, 0x25, 0x2e, 0x1c, 0xa6, 0xb4, 0xc6, 0xe8, 0xdd, 0x74, 0x1f, 0x4b, 0xbd, 0x8b, 0x8a,0x70, 0x3e, 0xb5, 0x66, 0x48, 0x03, 0xf6, 0x0e, 0x61, 0x35, 0x57, 0xb9, 0x86, 0xc1, 0x1d, 0x9e,0xe1, 0xf8, 0x98, 0x11, 0x69, 0xd9, 0x8e, 0x94, 0x9b, 0x1e, 0x87, 0xe9, 0xce, 0x55, 0x28, 0xdf,0x8c, 0xa1, 0x89, 0x0d, 0xbf, 0xe6, 0x42, 0x68, 0x41, 0x99, 0x2d, 0x0f, 0xb0, 0x54, 0xbb, 0x16 };#if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
static const uint8_t rsbox[256] = {0x52, 0x09, 0x6a, 0xd5, 0x30, 0x36, 0xa5, 0x38, 0xbf, 0x40, 0xa3, 0x9e, 0x81, 0xf3, 0xd7, 0xfb,0x7c, 0xe3, 0x39, 0x82, 0x9b, 0x2f, 0xff, 0x87, 0x34, 0x8e, 0x43, 0x44, 0xc4, 0xde, 0xe9, 0xcb,0x54, 0x7b, 0x94, 0x32, 0xa6, 0xc2, 0x23, 0x3d, 0xee, 0x4c, 0x95, 0x0b, 0x42, 0xfa, 0xc3, 0x4e,0x08, 0x2e, 0xa1, 0x66, 0x28, 0xd9, 0x24, 0xb2, 0x76, 0x5b, 0xa2, 0x49, 0x6d, 0x8b, 0xd1, 0x25,0x72, 0xf8, 0xf6, 0x64, 0x86, 0x68, 0x98, 0x16, 0xd4, 0xa4, 0x5c, 0xcc, 0x5d, 0x65, 0xb6, 0x92,0x6c, 0x70, 0x48, 0x50, 0xfd, 0xed, 0xb9, 0xda, 0x5e, 0x15, 0x46, 0x57, 0xa7, 0x8d, 0x9d, 0x84,0x90, 0xd8, 0xab, 0x00, 0x8c, 0xbc, 0xd3, 0x0a, 0xf7, 0xe4, 0x58, 0x05, 0xb8, 0xb3, 0x45, 0x06,0xd0, 0x2c, 0x1e, 0x8f, 0xca, 0x3f, 0x0f, 0x02, 0xc1, 0xaf, 0xbd, 0x03, 0x01, 0x13, 0x8a, 0x6b,0x3a, 0x91, 0x11, 0x41, 0x4f, 0x67, 0xdc, 0xea, 0x97, 0xf2, 0xcf, 0xce, 0xf0, 0xb4, 0xe6, 0x73,0x96, 0xac, 0x74, 0x22, 0xe7, 0xad, 0x35, 0x85, 0xe2, 0xf9, 0x37, 0xe8, 0x1c, 0x75, 0xdf, 0x6e,0x47, 0xf1, 0x1a, 0x71, 0x1d, 0x29, 0xc5, 0x89, 0x6f, 0xb7, 0x62, 0x0e, 0xaa, 0x18, 0xbe, 0x1b,0xfc, 0x56, 0x3e, 0x4b, 0xc6, 0xd2, 0x79, 0x20, 0x9a, 0xdb, 0xc0, 0xfe, 0x78, 0xcd, 0x5a, 0xf4,0x1f, 0xdd, 0xa8, 0x33, 0x88, 0x07, 0xc7, 0x31, 0xb1, 0x12, 0x10, 0x59, 0x27, 0x80, 0xec, 0x5f,0x60, 0x51, 0x7f, 0xa9, 0x19, 0xb5, 0x4a, 0x0d, 0x2d, 0xe5, 0x7a, 0x9f, 0x93, 0xc9, 0x9c, 0xef,0xa0, 0xe0, 0x3b, 0x4d, 0xae, 0x2a, 0xf5, 0xb0, 0xc8, 0xeb, 0xbb, 0x3c, 0x83, 0x53, 0x99, 0x61,0x17, 0x2b, 0x04, 0x7e, 0xba, 0x77, 0xd6, 0x26, 0xe1, 0x69, 0x14, 0x63, 0x55, 0x21, 0x0c, 0x7d };
#endif// The round constant word array, Rcon[i], contains the values given by
// x to the power (i-1) being powers of x (x is denoted as {02}) in the field GF(2^8)
static const uint8_t Rcon[11] = {0x8d, 0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1b, 0x36 };/** Jordan Goulder points out in PR #12 (https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-C/pull/12),* that you can remove most of the elements in the Rcon array, because they are unused.** From Wikipedia's article on the Rijndael key schedule @ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rijndael_key_schedule#Rcon** "Only the first some of these constants are actually used – up to rcon[10] for AES-128 (as 11 round keys are needed),* up to rcon[8] for AES-192, up to rcon[7] for AES-256. rcon[0] is not used in AES algorithm."*//*****************************************************************************//* Private functions: *//*****************************************************************************//*static uint8_t getSBoxValue(uint8_t num){return sbox[num];}*/
#define getSBoxValue(num) (sbox[(num)])// This function produces Nb(Nr+1) round keys. The round keys are used in each round to decrypt the states.
static void KeyExpansion(uint8_t* RoundKey, const uint8_t* Key)
{unsigned i, j, k;uint8_t tempa[4]; // Used for the column/row operations// The first round key is the key itself.for (i = 0; i < Nk; ++i){RoundKey[(i * 4) + 0] = Key[(i * 4) + 0];RoundKey[(i * 4) + 1] = Key[(i * 4) + 1];RoundKey[(i * 4) + 2] = Key[(i * 4) + 2];RoundKey[(i * 4) + 3] = Key[(i * 4) + 3];}// All other round keys are found from the previous round keys.for (i = Nk; i < Nb * (Nr + 1); ++i){{k = (i - 1) * 4;tempa[0] = RoundKey[k + 0];tempa[1] = RoundKey[k + 1];tempa[2] = RoundKey[k + 2];tempa[3] = RoundKey[k + 3];}if (i % Nk == 0){// This function shifts the 4 bytes in a word to the left once.// [a0,a1,a2,a3] becomes [a1,a2,a3,a0]// Function RotWord(){const uint8_t u8tmp = tempa[0];tempa[0] = tempa[1];tempa[1] = tempa[2];tempa[2] = tempa[3];tempa[3] = u8tmp;}// SubWord() is a function that takes a four-byte input word and // applies the S-box to each of the four bytes to produce an output word.// Function Subword(){tempa[0] = getSBoxValue(tempa[0]);tempa[1] = getSBoxValue(tempa[1]);tempa[2] = getSBoxValue(tempa[2]);tempa[3] = getSBoxValue(tempa[3]);}tempa[0] = tempa[0] ^ Rcon[i / Nk];}
#if defined(AES256) && (AES256 == 1)if (i % Nk == 4){// Function Subword(){tempa[0] = getSBoxValue(tempa[0]);tempa[1] = getSBoxValue(tempa[1]);tempa[2] = getSBoxValue(tempa[2]);tempa[3] = getSBoxValue(tempa[3]);}}
#endifj = i * 4; k = (i - Nk) * 4;RoundKey[j + 0] = RoundKey[k + 0] ^ tempa[0];RoundKey[j + 1] = RoundKey[k + 1] ^ tempa[1];RoundKey[j + 2] = RoundKey[k + 2] ^ tempa[2];RoundKey[j + 3] = RoundKey[k + 3] ^ tempa[3];}
}void AES_init_ctx(struct AES_ctx* ctx, const uint8_t* key)
{KeyExpansion(ctx->RoundKey, key);
}
#if (defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)) || (defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1))
void AES_init_ctx_iv(struct AES_ctx* ctx, const uint8_t* key, const uint8_t* iv)
{KeyExpansion(ctx->RoundKey, key);memcpy(ctx->Iv, iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
}
void AES_ctx_set_iv(struct AES_ctx* ctx, const uint8_t* iv)
{memcpy(ctx->Iv, iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
}
#endif// This function adds the round key to state.
// The round key is added to the state by an XOR function.
static void AddRoundKey(uint8_t round, state_t* state, const uint8_t* RoundKey)
{uint8_t i, j;for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i){for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j){(*state)[i][j] ^= RoundKey[(round * Nb * 4) + (i * Nb) + j];}}
}// The SubBytes Function Substitutes the values in the
// state matrix with values in an S-box.
static void SubBytes(state_t* state)
{uint8_t i, j;for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i){for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j){(*state)[j][i] = getSBoxValue((*state)[j][i]);}}
}// The ShiftRows() function shifts the rows in the state to the left.
// Each row is shifted with different offset.
// Offset = Row number. So the first row is not shifted.
static void ShiftRows(state_t* state)
{uint8_t temp;// Rotate first row 1 columns to left temp = (*state)[0][1];(*state)[0][1] = (*state)[1][1];(*state)[1][1] = (*state)[2][1];(*state)[2][1] = (*state)[3][1];(*state)[3][1] = temp;// Rotate second row 2 columns to left temp = (*state)[0][2];(*state)[0][2] = (*state)[2][2];(*state)[2][2] = temp;temp = (*state)[1][2];(*state)[1][2] = (*state)[3][2];(*state)[3][2] = temp;// Rotate third row 3 columns to lefttemp = (*state)[0][3];(*state)[0][3] = (*state)[3][3];(*state)[3][3] = (*state)[2][3];(*state)[2][3] = (*state)[1][3];(*state)[1][3] = temp;
}static uint8_t xtime(uint8_t x)
{return ((x << 1) ^ (((x >> 7) & 1) * 0x1b));
}// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix
static void MixColumns(state_t* state)
{uint8_t i;uint8_t Tmp, Tm, t;for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i){t = (*state)[i][0];Tmp = (*state)[i][0] ^ (*state)[i][1] ^ (*state)[i][2] ^ (*state)[i][3];Tm = (*state)[i][0] ^ (*state)[i][1]; Tm = xtime(Tm); (*state)[i][0] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;Tm = (*state)[i][1] ^ (*state)[i][2]; Tm = xtime(Tm); (*state)[i][1] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;Tm = (*state)[i][2] ^ (*state)[i][3]; Tm = xtime(Tm); (*state)[i][2] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;Tm = (*state)[i][3] ^ t; Tm = xtime(Tm); (*state)[i][3] ^= Tm ^ Tmp;}
}// Multiply is used to multiply numbers in the field GF(2^8)
// Note: The last call to xtime() is unneeded, but often ends up generating a smaller binary
// The compiler seems to be able to vectorize the operation better this way.
// See https://github.com/kokke/tiny-AES-c/pull/34
#if MULTIPLY_AS_A_FUNCTION
static uint8_t Multiply(uint8_t x, uint8_t y)
{return (((y & 1) * x) ^((y >> 1 & 1) * xtime(x)) ^((y >> 2 & 1) * xtime(xtime(x))) ^((y >> 3 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))) ^((y >> 4 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))))); /* this last call to xtime() can be omitted */
}
#else
#define Multiply(x, y) \( ((y & 1) * x) ^ \((y>>1 & 1) * xtime(x)) ^ \((y>>2 & 1) * xtime(xtime(x))) ^ \((y>>3 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))) ^ \((y>>4 & 1) * xtime(xtime(xtime(xtime(x)))))) \
#endif#if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
/*
static uint8_t getSBoxInvert(uint8_t num)
{return rsbox[num];
}
*/
#define getSBoxInvert(num) (rsbox[(num)])// MixColumns function mixes the columns of the state matrix.
// The method used to multiply may be difficult to understand for the inexperienced.
// Please use the references to gain more information.
static void InvMixColumns(state_t* state)
{int i;uint8_t a, b, c, d;for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i){a = (*state)[i][0];b = (*state)[i][1];c = (*state)[i][2];d = (*state)[i][3];(*state)[i][0] = Multiply(a, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(d, 0x09);(*state)[i][1] = Multiply(a, 0x09) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(d, 0x0d);(*state)[i][2] = Multiply(a, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(b, 0x09) ^ Multiply(c, 0x0e) ^ Multiply(d, 0x0b);(*state)[i][3] = Multiply(a, 0x0b) ^ Multiply(b, 0x0d) ^ Multiply(c, 0x09) ^ Multiply(d, 0x0e);}
}// The SubBytes Function Substitutes the values in the
// state matrix with values in an S-box.
static void InvSubBytes(state_t* state)
{uint8_t i, j;for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i){for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j){(*state)[j][i] = getSBoxInvert((*state)[j][i]);}}
}static void InvShiftRows(state_t* state)
{uint8_t temp;// Rotate first row 1 columns to right temp = (*state)[3][1];(*state)[3][1] = (*state)[2][1];(*state)[2][1] = (*state)[1][1];(*state)[1][1] = (*state)[0][1];(*state)[0][1] = temp;// Rotate second row 2 columns to right temp = (*state)[0][2];(*state)[0][2] = (*state)[2][2];(*state)[2][2] = temp;temp = (*state)[1][2];(*state)[1][2] = (*state)[3][2];(*state)[3][2] = temp;// Rotate third row 3 columns to righttemp = (*state)[0][3];(*state)[0][3] = (*state)[1][3];(*state)[1][3] = (*state)[2][3];(*state)[2][3] = (*state)[3][3];(*state)[3][3] = temp;
}
#endif // #if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)// Cipher is the main function that encrypts the PlainText.
static void Cipher(state_t* state, const uint8_t* RoundKey)
{uint8_t round = 0;// Add the First round key to the state before starting the rounds.AddRoundKey(0, state, RoundKey);// There will be Nr rounds.// The first Nr-1 rounds are identical.// These Nr rounds are executed in the loop below.// Last one without MixColumns()for (round = 1; ; ++round){SubBytes(state);ShiftRows(state);if (round == Nr) {break;}MixColumns(state);AddRoundKey(round, state, RoundKey);}// Add round key to last roundAddRoundKey(Nr, state, RoundKey);
}#if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)
static void InvCipher(state_t* state, const uint8_t* RoundKey)
{uint8_t round = 0;// Add the First round key to the state before starting the rounds.AddRoundKey(Nr, state, RoundKey);// There will be Nr rounds.// The first Nr-1 rounds are identical.// These Nr rounds are executed in the loop below.// Last one without InvMixColumn()for (round = (Nr - 1); ; --round){InvShiftRows(state);InvSubBytes(state);AddRoundKey(round, state, RoundKey);if (round == 0) {break;}InvMixColumns(state);}}
#endif // #if (defined(CBC) && CBC == 1) || (defined(ECB) && ECB == 1)/*****************************************************************************/
/* Public functions: */
/*****************************************************************************/
#if defined(ECB) && (ECB == 1)void AES_ECB_encrypt(const struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf)
{// The next function call encrypts the PlainText with the Key using AES algorithm.Cipher((state_t*)buf, ctx->RoundKey);
}void AES_ECB_decrypt(const struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf)
{// The next function call decrypts the PlainText with the Key using AES algorithm.InvCipher((state_t*)buf, ctx->RoundKey);
}#endif // #if defined(ECB) && (ECB == 1)#if defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)static void XorWithIv(uint8_t* buf, const uint8_t* Iv)
{uint8_t i;for (i = 0; i < AES_BLOCKLEN; ++i) // The block in AES is always 128bit no matter the key size{buf[i] ^= Iv[i];}
}void AES_CBC_encrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf, size_t length)
{size_t i;uint8_t* Iv = ctx->Iv;for (i = 0; i < length; i += AES_BLOCKLEN){XorWithIv(buf, Iv);Cipher((state_t*)buf, ctx->RoundKey);Iv = buf;buf += AES_BLOCKLEN;}/* store Iv in ctx for next call */memcpy(ctx->Iv, Iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);
}void AES_CBC_decrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf, size_t length)
{size_t i;uint8_t storeNextIv[AES_BLOCKLEN];for (i = 0; i < length; i += AES_BLOCKLEN){memcpy(storeNextIv, buf, AES_BLOCKLEN);InvCipher((state_t*)buf, ctx->RoundKey);XorWithIv(buf, ctx->Iv);memcpy(ctx->Iv, storeNextIv, AES_BLOCKLEN);buf += AES_BLOCKLEN;}}static bool safe_fill_buf(uint8_t* pBufDst, size_t len_bufDst, uint8_t* pBufSrc, size_t len_bufSrc)
{bool b_rc = false;uint8_t* pBufDstCur = NULL;size_t len_bufDstCur = 0;size_t len_to_copy = 0;do {if ((NULL == pBufDst) || (len_bufDst <= 0)){break;}if ((NULL == pBufSrc) || (len_bufSrc <= 0)){break;}if (len_bufDst <= len_bufSrc){memcpy(pBufDst, pBufSrc, len_bufDst);}else {// 将pBufSrc依次附加到pBufDst, 直到将pBufDst填满pBufDstCur = pBufDst;len_bufDstCur = len_bufDst;len_to_copy = len_bufSrc;do {if (len_bufDstCur <= len_to_copy){len_to_copy = len_bufDstCur;}memcpy(pBufDstCur, pBufSrc, len_to_copy);len_bufDstCur -= len_to_copy;pBufDstCur += len_to_copy;} while (len_bufDstCur > 0);}b_rc = true;} while (false);return b_rc;
}static bool buf_add_padding(uint8_t* buf, size_t len_buf, size_t len_data, size_t* len_out_with_padding)
{bool b_rc = false;int iMod16 = 0;int iPaddingLen = 0;int i = 0;uint8_t* pBufCur = NULL;do {// 只有 (len_data > 0) 满足时, 才能加paddingif ((NULL == buf) || (len_data <= 0) || ((len_buf - len_data) < 32) || (NULL == len_out_with_padding)){break;}iPaddingLen = 0x10; // 即使原始数据长度是0x10的倍数, 也需要加0x10个padding, 这样才能区分出原始数据iMod16 = len_data % 0x10;if (iMod16 > 0){iPaddingLen += (0x10 - iMod16); // 最多加31个padding}*len_out_with_padding = (len_data + iPaddingLen);pBufCur = buf;for (i = 0; i < iPaddingLen; i++){*(pBufCur + len_data + i) = (uint8_t)iPaddingLen;}b_rc = true;} while (false);return b_rc;
}bool AES256_CBC_encrypt_buffer_ex(uint8_t* key, int len_key, uint8_t* iv, int len_iv, uint8_t* buf_in, size_t len_buf_in, uint8_t* buf_out, size_t* len_buf_out)
{bool b_rc = false;struct AES_ctx ctx;// key = 32bytesuint8_t key_new[32];// iv = 16 bytesuint8_t iv_new[16];// 要求给出的输出buf长度 = (buf_in_len + 32)// in = 16的倍数, 如果原始输入不够16倍数, 填充(16 + N%16)个字节, 填充的字节为0x10 ~ (0x10 + N%16)// 如果输入数据len = 16 x N + 0, 那么填充0x10个0x10// 如果输入数据len = 16 x N + 1, 那么填充0x11个0x11// 解密数据后, 用返回的buf_out内容和len_buf_out长度, 函数内会处理好// 原始数据长度 >0就行, 会处理成加密输入数据// 输入数据的长度必须 >= 32(包括填充的16 + N%16 个字节)do {// 处理key的对齐if ((NULL == key) || (len_key <= 0)){break;}if (!safe_fill_buf(key_new, sizeof(key_new), key, len_key)){break;}// 处理iv的对齐if ((NULL == iv) || (len_iv <= 0)){break;}if (!safe_fill_buf(iv_new, sizeof(iv_new), iv, len_iv)){break;}// 处理buf的对齐if ((NULL == buf_in) || (len_buf_in <= 0)){break;}if ((NULL == buf_out) || (NULL == len_buf_out) || (*len_buf_out <= 0)){break;}if ((*len_buf_out - len_buf_in) < 32){// 为了在buf_out末尾填充buf, 要有16~31个字节空间break;}// 将输入数据拷贝到输出数据memcpy(buf_out, buf_in, len_buf_in);// 填充(add padding)输出数据if (!buf_add_padding(buf_out, *len_buf_out, len_buf_in, len_buf_out)){break;}// 将准备好的输出数据送AES加密AES_init_ctx_iv(&ctx, key_new, iv_new);AES_CBC_encrypt_buffer(&ctx, buf_out, *len_buf_out);b_rc = true;} while (false);return b_rc;
}bool AES256_CBC_decrypt_buffer_ex(uint8_t* key, int len_key, uint8_t* iv, int len_iv, uint8_t* buf_in, size_t len_buf_in, uint8_t* buf_out, size_t* len_buf_out)
{bool b_rc = false;struct AES_ctx ctx;// key = 32bytesuint8_t key_new[32];// iv = 16 bytesuint8_t iv_new[16];// 要求给出的输出buf长度 = (buf_in_len + 32)// in = 16的倍数, 如果原始输入不够16倍数, 填充(16 + N%16)个字节, 填充的字节为0x10 ~ (0x10 + N%16)// 如果输入数据len = 16 x N + 0, 那么填充0x10个0x10// 如果输入数据len = 16 x N + 1, 那么填充0x11个0x11// 解密数据后, 用返回的buf_out内容和len_buf_out长度, 函数内会处理好// 原始数据长度 >0就行, 会处理成加密输入数据// 输入数据的长度必须 >= 32(包括填充的16 + N%16 个字节)do {// 处理key的对齐if ((NULL == key) || (len_key <= 0)){break;}if (!safe_fill_buf(key_new, sizeof(key_new), key, len_key)){break;}// 处理iv的对齐if ((NULL == iv) || (len_iv <= 0)){break;}if (!safe_fill_buf(iv_new, sizeof(iv_new), iv, len_iv)){break;}// 处理buf的对齐if ((NULL == buf_in) || (len_buf_in <= 0)){break;}if ((NULL == buf_out) || (NULL == len_buf_out) || (*len_buf_out <= 0)){break;}// 解密的buf长度至少要不比加密的buf长度小if ((*len_buf_out - len_buf_in) < 0){break;}// 将输入数据拷贝到输出数据memcpy(buf_out, buf_in, len_buf_in);// 解密时, 不需要考虑padding填充// 将准备好的输出数据送AES解密AES_init_ctx_iv(&ctx, key_new, iv_new);AES_CBC_decrypt_buffer(&ctx, buf_out, len_buf_in);// 将去掉padding的解密数据长度更新到 *len_buf_out*len_buf_out = len_buf_in;*len_buf_out -= buf_out[len_buf_in - 1];b_rc = true;} while (false);return b_rc;
}#endif // #if defined(CBC) && (CBC == 1)#if defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1)/* Symmetrical operation: same function for encrypting as for decrypting. Note any IV/nonce should never be reused with the same key */
void AES_CTR_xcrypt_buffer(struct AES_ctx* ctx, uint8_t* buf, size_t length)
{uint8_t buffer[AES_BLOCKLEN];size_t i;int bi;for (i = 0, bi = AES_BLOCKLEN; i < length; ++i, ++bi){if (bi == AES_BLOCKLEN) /* we need to regen xor compliment in buffer */{memcpy(buffer, ctx->Iv, AES_BLOCKLEN);Cipher((state_t*)buffer, ctx->RoundKey);/* Increment Iv and handle overflow */for (bi = (AES_BLOCKLEN - 1); bi >= 0; --bi){/* inc will overflow */if (ctx->Iv[bi] == 255){ctx->Iv[bi] = 0;continue;}ctx->Iv[bi] += 1;break;}bi = 0;}buf[i] = (buf[i] ^ buffer[bi]);}
}#endif // #if defined(CTR) && (CTR == 1)在官方测试程序上改的测试程序(用来测试这2个封装函数)
// @file test.cpp
// env = vs2019 vc++ console#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <assert.h> // for assert() #ifdef __cplusplus
#define INCLUDE_C_HEADER_BEGIN extern "C" {
#define INCLUDE_C_HEADER_END }
#else
#define INCLUDE_C_HEADER_BEGIN
#define INCLUDE_C_HEADER_END
#endif Enable ECB, CTR and CBC mode. Note this can be done before including aes.h or at compile-time.
E.g. with GCC by using the -D flag: gcc -c aes.c -DCBC=0 -DCTR=1 -DECB=1
//#define CBC 1
//#define CTR 1
//#define ECB 1INCLUDE_C_HEADER_BEGIN
#include "aes.h"
INCLUDE_C_HEADER_ENDstatic void phex(uint8_t* str);
static int test_encrypt_cbc(void);
static int test_decrypt_cbc(void);
static int test_encrypt_ctr(void);
static int test_decrypt_ctr(void);
static int test_encrypt_ecb(void);
static int test_decrypt_ecb(void);
static void test_encrypt_ecb_verbose(void);void my_test_encrypt_cbc_ex();int main(void)
{int exit = 0;#if defined(AES256)printf("\nTesting AES256\n\n");
#elif defined(AES192)printf("\nTesting AES192\n\n");
#elif defined(AES128)printf("\nTesting AES128\n\n");
#elseprintf("You need to specify a symbol between AES128, AES192 or AES256. Exiting");return 0;
#endifmy_test_encrypt_cbc_ex();// // cbc好一些// test_encrypt_cbc();// test_decrypt_cbc();// exit = test_encrypt_cbc() + test_decrypt_cbc() +//test_encrypt_ctr() + test_decrypt_ctr() +//test_decrypt_ecb() + test_encrypt_ecb();// test_encrypt_ecb_verbose();return exit;
}void showBufHex(const char* pszTip, uint8_t* pBuf, size_t len_Buf)
{size_t i = 0;int i_line_char_cnt = 0;do {if (NULL != pszTip){printf("%s\n", pszTip);}for (i = 0; i < len_Buf; i++){printf("%2.2X ", pBuf[i]);if (16 == ++i_line_char_cnt){i_line_char_cnt = 0;printf("\n");}}} while (false);
}void my_test_encrypt_cbc_ex()
{const char* pKey = "my_key";const char* pIv = "my_iv";const char* pIn = "hello world";uint8_t* pszOut = new uint8_t[strlen(pIn) + 32];size_t len_Out = strlen(pIn) + 32;bool b_rc = false;b_rc = AES256_CBC_encrypt_buffer_ex((uint8_t*)pKey, (int)strlen(pKey), (uint8_t*)pIv, (int)strlen(pIv), (uint8_t*)pIn, (size_t)strlen(pIn), (uint8_t*)pszOut, &len_Out);assert(true == b_rc);showBufHex("out buf", pszOut, len_Out);uint8_t* pszDecrypt = new uint8_t[len_Out];size_t lenDecrypt = len_Out;b_rc = AES256_CBC_decrypt_buffer_ex((uint8_t*)pKey, (int)strlen(pKey), (uint8_t*)pIv, (int)strlen(pIv), (uint8_t*)pszOut, len_Out, (uint8_t*)pszDecrypt, &lenDecrypt);assert(true == b_rc);pszDecrypt[lenDecrypt] = 0x00;printf("descrypt data = [%s]\n", pszDecrypt);if (NULL != pszOut){delete []pszOut;pszOut = NULL;}if (NULL != pszDecrypt){delete[]pszDecrypt;pszDecrypt = NULL;}
}// prints string as hex
static void phex(uint8_t* str)
{#if defined(AES256)uint8_t len = 32;
#elif defined(AES192)uint8_t len = 24;
#elif defined(AES128)uint8_t len = 16;
#endifunsigned char i;for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)printf("%.2x", str[i]);printf("\n");
}static void test_encrypt_ecb_verbose(void)
{// Example of more verbose verificationuint8_t i;// 128bit keyuint8_t key[16] = { (uint8_t)0x2b, (uint8_t)0x7e, (uint8_t)0x15, (uint8_t)0x16, (uint8_t)0x28, (uint8_t)0xae, (uint8_t)0xd2, (uint8_t)0xa6, (uint8_t)0xab, (uint8_t)0xf7, (uint8_t)0x15, (uint8_t)0x88, (uint8_t)0x09, (uint8_t)0xcf, (uint8_t)0x4f, (uint8_t)0x3c };// 512bit textuint8_t plain_text[64] = { (uint8_t)0x6b, (uint8_t)0xc1, (uint8_t)0xbe, (uint8_t)0xe2, (uint8_t)0x2e, (uint8_t)0x40, (uint8_t)0x9f, (uint8_t)0x96, (uint8_t)0xe9, (uint8_t)0x3d, (uint8_t)0x7e, (uint8_t)0x11, (uint8_t)0x73, (uint8_t)0x93, (uint8_t)0x17, (uint8_t)0x2a,(uint8_t)0xae, (uint8_t)0x2d, (uint8_t)0x8a, (uint8_t)0x57, (uint8_t)0x1e, (uint8_t)0x03, (uint8_t)0xac, (uint8_t)0x9c, (uint8_t)0x9e, (uint8_t)0xb7, (uint8_t)0x6f, (uint8_t)0xac, (uint8_t)0x45, (uint8_t)0xaf, (uint8_t)0x8e, (uint8_t)0x51,(uint8_t)0x30, (uint8_t)0xc8, (uint8_t)0x1c, (uint8_t)0x46, (uint8_t)0xa3, (uint8_t)0x5c, (uint8_t)0xe4, (uint8_t)0x11, (uint8_t)0xe5, (uint8_t)0xfb, (uint8_t)0xc1, (uint8_t)0x19, (uint8_t)0x1a, (uint8_t)0x0a, (uint8_t)0x52, (uint8_t)0xef,(uint8_t)0xf6, (uint8_t)0x9f, (uint8_t)0x24, (uint8_t)0x45, (uint8_t)0xdf, (uint8_t)0x4f, (uint8_t)0x9b, (uint8_t)0x17, (uint8_t)0xad, (uint8_t)0x2b, (uint8_t)0x41, (uint8_t)0x7b, (uint8_t)0xe6, (uint8_t)0x6c, (uint8_t)0x37, (uint8_t)0x10 };// print text to encrypt, key and IVprintf("ECB encrypt verbose:\n\n");printf("plain text:\n");for (i = (uint8_t)0; i < (uint8_t)4; ++i){phex(plain_text + i * (uint8_t)16);}printf("\n");printf("key:\n");phex(key);printf("\n");// print the resulting cipher as 4 x 16 byte stringsprintf("ciphertext:\n");struct AES_ctx ctx;AES_init_ctx(&ctx, key);for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i){AES_ECB_encrypt(&ctx, plain_text + (i * 16));phex(plain_text + (i * 16));}printf("\n");
}static int test_encrypt_ecb(void)
{
#if defined(AES256)uint8_t key[] = { 0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4 };uint8_t out[] = { 0xf3, 0xee, 0xd1, 0xbd, 0xb5, 0xd2, 0xa0, 0x3c, 0x06, 0x4b, 0x5a, 0x7e, 0x3d, 0xb1, 0x81, 0xf8 };
#elif defined(AES192)uint8_t key[] = { 0x8e, 0x73, 0xb0, 0xf7, 0xda, 0x0e, 0x64, 0x52, 0xc8, 0x10, 0xf3, 0x2b, 0x80, 0x90, 0x79, 0xe5,0x62, 0xf8, 0xea, 0xd2, 0x52, 0x2c, 0x6b, 0x7b };uint8_t out[] = { 0xbd, 0x33, 0x4f, 0x1d, 0x6e, 0x45, 0xf2, 0x5f, 0xf7, 0x12, 0xa2, 0x14, 0x57, 0x1f, 0xa5, 0xcc };
#elif defined(AES128)uint8_t key[] = { 0x2b, 0x7e, 0x15, 0x16, 0x28, 0xae, 0xd2, 0xa6, 0xab, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x88, 0x09, 0xcf, 0x4f, 0x3c };uint8_t out[] = { 0x3a, 0xd7, 0x7b, 0xb4, 0x0d, 0x7a, 0x36, 0x60, 0xa8, 0x9e, 0xca, 0xf3, 0x24, 0x66, 0xef, 0x97 };
#endifuint8_t in[] = { 0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a };struct AES_ctx ctx;AES_init_ctx(&ctx, key);AES_ECB_encrypt(&ctx, in);printf("ECB encrypt: ");if (0 == memcmp((char*)out, (char*)in, 16)) {printf("SUCCESS!\n");return(0);}else {printf("FAILURE!\n");return(1);}
}static int test_decrypt_cbc(void)
{#if defined(AES256)uint8_t key[] = { 0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4 };uint8_t in[] = { 0xf5, 0x8c, 0x4c, 0x04, 0xd6, 0xe5, 0xf1, 0xba, 0x77, 0x9e, 0xab, 0xfb, 0x5f, 0x7b, 0xfb, 0xd6,0x9c, 0xfc, 0x4e, 0x96, 0x7e, 0xdb, 0x80, 0x8d, 0x67, 0x9f, 0x77, 0x7b, 0xc6, 0x70, 0x2c, 0x7d,0x39, 0xf2, 0x33, 0x69, 0xa9, 0xd9, 0xba, 0xcf, 0xa5, 0x30, 0xe2, 0x63, 0x04, 0x23, 0x14, 0x61,0xb2, 0xeb, 0x05, 0xe2, 0xc3, 0x9b, 0xe9, 0xfc, 0xda, 0x6c, 0x19, 0x07, 0x8c, 0x6a, 0x9d, 0x1b };
#elif defined(AES192)uint8_t key[] = { 0x8e, 0x73, 0xb0, 0xf7, 0xda, 0x0e, 0x64, 0x52, 0xc8, 0x10, 0xf3, 0x2b, 0x80, 0x90, 0x79, 0xe5, 0x62, 0xf8, 0xea, 0xd2, 0x52, 0x2c, 0x6b, 0x7b };uint8_t in[] = { 0x4f, 0x02, 0x1d, 0xb2, 0x43, 0xbc, 0x63, 0x3d, 0x71, 0x78, 0x18, 0x3a, 0x9f, 0xa0, 0x71, 0xe8,0xb4, 0xd9, 0xad, 0xa9, 0xad, 0x7d, 0xed, 0xf4, 0xe5, 0xe7, 0x38, 0x76, 0x3f, 0x69, 0x14, 0x5a,0x57, 0x1b, 0x24, 0x20, 0x12, 0xfb, 0x7a, 0xe0, 0x7f, 0xa9, 0xba, 0xac, 0x3d, 0xf1, 0x02, 0xe0,0x08, 0xb0, 0xe2, 0x79, 0x88, 0x59, 0x88, 0x81, 0xd9, 0x20, 0xa9, 0xe6, 0x4f, 0x56, 0x15, 0xcd };
#elif defined(AES128)uint8_t key[] = { 0x2b, 0x7e, 0x15, 0x16, 0x28, 0xae, 0xd2, 0xa6, 0xab, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x88, 0x09, 0xcf, 0x4f, 0x3c };uint8_t in[] = { 0x76, 0x49, 0xab, 0xac, 0x81, 0x19, 0xb2, 0x46, 0xce, 0xe9, 0x8e, 0x9b, 0x12, 0xe9, 0x19, 0x7d,0x50, 0x86, 0xcb, 0x9b, 0x50, 0x72, 0x19, 0xee, 0x95, 0xdb, 0x11, 0x3a, 0x91, 0x76, 0x78, 0xb2,0x73, 0xbe, 0xd6, 0xb8, 0xe3, 0xc1, 0x74, 0x3b, 0x71, 0x16, 0xe6, 0x9e, 0x22, 0x22, 0x95, 0x16,0x3f, 0xf1, 0xca, 0xa1, 0x68, 0x1f, 0xac, 0x09, 0x12, 0x0e, 0xca, 0x30, 0x75, 0x86, 0xe1, 0xa7 };
#endifuint8_t iv[] = { 0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f };uint8_t out[] = { 0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a,0xae, 0x2d, 0x8a, 0x57, 0x1e, 0x03, 0xac, 0x9c, 0x9e, 0xb7, 0x6f, 0xac, 0x45, 0xaf, 0x8e, 0x51,0x30, 0xc8, 0x1c, 0x46, 0xa3, 0x5c, 0xe4, 0x11, 0xe5, 0xfb, 0xc1, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x0a, 0x52, 0xef,0xf6, 0x9f, 0x24, 0x45, 0xdf, 0x4f, 0x9b, 0x17, 0xad, 0x2b, 0x41, 0x7b, 0xe6, 0x6c, 0x37, 0x10 };// uint8_t buffer[64];struct AES_ctx ctx;AES_init_ctx_iv(&ctx, key, iv);AES_CBC_decrypt_buffer(&ctx, in, 64);printf("CBC decrypt: ");if (0 == memcmp((char*)out, (char*)in, 64)) {printf("SUCCESS!\n");return(0);}else {printf("FAILURE!\n");return(1);}
}static int test_encrypt_cbc(void)
{
#if defined(AES256)uint8_t key[] = { 0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4 };uint8_t out[] = { 0xf5, 0x8c, 0x4c, 0x04, 0xd6, 0xe5, 0xf1, 0xba, 0x77, 0x9e, 0xab, 0xfb, 0x5f, 0x7b, 0xfb, 0xd6,0x9c, 0xfc, 0x4e, 0x96, 0x7e, 0xdb, 0x80, 0x8d, 0x67, 0x9f, 0x77, 0x7b, 0xc6, 0x70, 0x2c, 0x7d,0x39, 0xf2, 0x33, 0x69, 0xa9, 0xd9, 0xba, 0xcf, 0xa5, 0x30, 0xe2, 0x63, 0x04, 0x23, 0x14, 0x61,0xb2, 0xeb, 0x05, 0xe2, 0xc3, 0x9b, 0xe9, 0xfc, 0xda, 0x6c, 0x19, 0x07, 0x8c, 0x6a, 0x9d, 0x1b };
#elif defined(AES192)uint8_t key[] = { 0x8e, 0x73, 0xb0, 0xf7, 0xda, 0x0e, 0x64, 0x52, 0xc8, 0x10, 0xf3, 0x2b, 0x80, 0x90, 0x79, 0xe5, 0x62, 0xf8, 0xea, 0xd2, 0x52, 0x2c, 0x6b, 0x7b };uint8_t out[] = { 0x4f, 0x02, 0x1d, 0xb2, 0x43, 0xbc, 0x63, 0x3d, 0x71, 0x78, 0x18, 0x3a, 0x9f, 0xa0, 0x71, 0xe8,0xb4, 0xd9, 0xad, 0xa9, 0xad, 0x7d, 0xed, 0xf4, 0xe5, 0xe7, 0x38, 0x76, 0x3f, 0x69, 0x14, 0x5a,0x57, 0x1b, 0x24, 0x20, 0x12, 0xfb, 0x7a, 0xe0, 0x7f, 0xa9, 0xba, 0xac, 0x3d, 0xf1, 0x02, 0xe0,0x08, 0xb0, 0xe2, 0x79, 0x88, 0x59, 0x88, 0x81, 0xd9, 0x20, 0xa9, 0xe6, 0x4f, 0x56, 0x15, 0xcd };
#elif defined(AES128)uint8_t key[] = { 0x2b, 0x7e, 0x15, 0x16, 0x28, 0xae, 0xd2, 0xa6, 0xab, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x88, 0x09, 0xcf, 0x4f, 0x3c };uint8_t out[] = { 0x76, 0x49, 0xab, 0xac, 0x81, 0x19, 0xb2, 0x46, 0xce, 0xe9, 0x8e, 0x9b, 0x12, 0xe9, 0x19, 0x7d,0x50, 0x86, 0xcb, 0x9b, 0x50, 0x72, 0x19, 0xee, 0x95, 0xdb, 0x11, 0x3a, 0x91, 0x76, 0x78, 0xb2,0x73, 0xbe, 0xd6, 0xb8, 0xe3, 0xc1, 0x74, 0x3b, 0x71, 0x16, 0xe6, 0x9e, 0x22, 0x22, 0x95, 0x16,0x3f, 0xf1, 0xca, 0xa1, 0x68, 0x1f, 0xac, 0x09, 0x12, 0x0e, 0xca, 0x30, 0x75, 0x86, 0xe1, 0xa7 };
#endifuint8_t iv[] = { 0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f };uint8_t in[] = { 0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a,0xae, 0x2d, 0x8a, 0x57, 0x1e, 0x03, 0xac, 0x9c, 0x9e, 0xb7, 0x6f, 0xac, 0x45, 0xaf, 0x8e, 0x51,0x30, 0xc8, 0x1c, 0x46, 0xa3, 0x5c, 0xe4, 0x11, 0xe5, 0xfb, 0xc1, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x0a, 0x52, 0xef,0xf6, 0x9f, 0x24, 0x45, 0xdf, 0x4f, 0x9b, 0x17, 0xad, 0x2b, 0x41, 0x7b, 0xe6, 0x6c, 0x37, 0x10 };struct AES_ctx ctx;AES_init_ctx_iv(&ctx, key, iv);AES_CBC_encrypt_buffer(&ctx, in, 64);printf("CBC encrypt: ");if (0 == memcmp((char*)out, (char*)in, 64)) {printf("SUCCESS!\n");return(0);}else {printf("FAILURE!\n");return(1);}
}static int test_xcrypt_ctr(const char* xcrypt);
static int test_encrypt_ctr(void)
{return test_xcrypt_ctr("encrypt");
}static int test_decrypt_ctr(void)
{return test_xcrypt_ctr("decrypt");
}static int test_xcrypt_ctr(const char* xcrypt)
{
#if defined(AES256)uint8_t key[32] = { 0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4 };uint8_t in[64] = { 0x60, 0x1e, 0xc3, 0x13, 0x77, 0x57, 0x89, 0xa5, 0xb7, 0xa7, 0xf5, 0x04, 0xbb, 0xf3, 0xd2, 0x28,0xf4, 0x43, 0xe3, 0xca, 0x4d, 0x62, 0xb5, 0x9a, 0xca, 0x84, 0xe9, 0x90, 0xca, 0xca, 0xf5, 0xc5,0x2b, 0x09, 0x30, 0xda, 0xa2, 0x3d, 0xe9, 0x4c, 0xe8, 0x70, 0x17, 0xba, 0x2d, 0x84, 0x98, 0x8d,0xdf, 0xc9, 0xc5, 0x8d, 0xb6, 0x7a, 0xad, 0xa6, 0x13, 0xc2, 0xdd, 0x08, 0x45, 0x79, 0x41, 0xa6 };
#elif defined(AES192)uint8_t key[24] = { 0x8e, 0x73, 0xb0, 0xf7, 0xda, 0x0e, 0x64, 0x52, 0xc8, 0x10, 0xf3, 0x2b, 0x80, 0x90, 0x79, 0xe5,0x62, 0xf8, 0xea, 0xd2, 0x52, 0x2c, 0x6b, 0x7b };uint8_t in[64] = { 0x1a, 0xbc, 0x93, 0x24, 0x17, 0x52, 0x1c, 0xa2, 0x4f, 0x2b, 0x04, 0x59, 0xfe, 0x7e, 0x6e, 0x0b,0x09, 0x03, 0x39, 0xec, 0x0a, 0xa6, 0xfa, 0xef, 0xd5, 0xcc, 0xc2, 0xc6, 0xf4, 0xce, 0x8e, 0x94,0x1e, 0x36, 0xb2, 0x6b, 0xd1, 0xeb, 0xc6, 0x70, 0xd1, 0xbd, 0x1d, 0x66, 0x56, 0x20, 0xab, 0xf7,0x4f, 0x78, 0xa7, 0xf6, 0xd2, 0x98, 0x09, 0x58, 0x5a, 0x97, 0xda, 0xec, 0x58, 0xc6, 0xb0, 0x50 };
#elif defined(AES128)uint8_t key[16] = { 0x2b, 0x7e, 0x15, 0x16, 0x28, 0xae, 0xd2, 0xa6, 0xab, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x88, 0x09, 0xcf, 0x4f, 0x3c };uint8_t in[64] = { 0x87, 0x4d, 0x61, 0x91, 0xb6, 0x20, 0xe3, 0x26, 0x1b, 0xef, 0x68, 0x64, 0x99, 0x0d, 0xb6, 0xce,0x98, 0x06, 0xf6, 0x6b, 0x79, 0x70, 0xfd, 0xff, 0x86, 0x17, 0x18, 0x7b, 0xb9, 0xff, 0xfd, 0xff,0x5a, 0xe4, 0xdf, 0x3e, 0xdb, 0xd5, 0xd3, 0x5e, 0x5b, 0x4f, 0x09, 0x02, 0x0d, 0xb0, 0x3e, 0xab,0x1e, 0x03, 0x1d, 0xda, 0x2f, 0xbe, 0x03, 0xd1, 0x79, 0x21, 0x70, 0xa0, 0xf3, 0x00, 0x9c, 0xee };
#endifuint8_t iv[16] = { 0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7, 0xf8, 0xf9, 0xfa, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xfd, 0xfe, 0xff };uint8_t out[64] = { 0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a,0xae, 0x2d, 0x8a, 0x57, 0x1e, 0x03, 0xac, 0x9c, 0x9e, 0xb7, 0x6f, 0xac, 0x45, 0xaf, 0x8e, 0x51,0x30, 0xc8, 0x1c, 0x46, 0xa3, 0x5c, 0xe4, 0x11, 0xe5, 0xfb, 0xc1, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x0a, 0x52, 0xef,0xf6, 0x9f, 0x24, 0x45, 0xdf, 0x4f, 0x9b, 0x17, 0xad, 0x2b, 0x41, 0x7b, 0xe6, 0x6c, 0x37, 0x10 };struct AES_ctx ctx;AES_init_ctx_iv(&ctx, key, iv);AES_CTR_xcrypt_buffer(&ctx, in, 64);printf("CTR %s: ", xcrypt);if (0 == memcmp((char*)out, (char*)in, 64)) {printf("SUCCESS!\n");return(0);}else {printf("FAILURE!\n");return(1);}
}static int test_decrypt_ecb(void)
{
#if defined(AES256)uint8_t key[] = { 0x60, 0x3d, 0xeb, 0x10, 0x15, 0xca, 0x71, 0xbe, 0x2b, 0x73, 0xae, 0xf0, 0x85, 0x7d, 0x77, 0x81,0x1f, 0x35, 0x2c, 0x07, 0x3b, 0x61, 0x08, 0xd7, 0x2d, 0x98, 0x10, 0xa3, 0x09, 0x14, 0xdf, 0xf4 };uint8_t in[] = { 0xf3, 0xee, 0xd1, 0xbd, 0xb5, 0xd2, 0xa0, 0x3c, 0x06, 0x4b, 0x5a, 0x7e, 0x3d, 0xb1, 0x81, 0xf8 };
#elif defined(AES192)uint8_t key[] = { 0x8e, 0x73, 0xb0, 0xf7, 0xda, 0x0e, 0x64, 0x52, 0xc8, 0x10, 0xf3, 0x2b, 0x80, 0x90, 0x79, 0xe5,0x62, 0xf8, 0xea, 0xd2, 0x52, 0x2c, 0x6b, 0x7b };uint8_t in[] = { 0xbd, 0x33, 0x4f, 0x1d, 0x6e, 0x45, 0xf2, 0x5f, 0xf7, 0x12, 0xa2, 0x14, 0x57, 0x1f, 0xa5, 0xcc };
#elif defined(AES128)uint8_t key[] = { 0x2b, 0x7e, 0x15, 0x16, 0x28, 0xae, 0xd2, 0xa6, 0xab, 0xf7, 0x15, 0x88, 0x09, 0xcf, 0x4f, 0x3c };uint8_t in[] = { 0x3a, 0xd7, 0x7b, 0xb4, 0x0d, 0x7a, 0x36, 0x60, 0xa8, 0x9e, 0xca, 0xf3, 0x24, 0x66, 0xef, 0x97 };
#endifuint8_t out[] = { 0x6b, 0xc1, 0xbe, 0xe2, 0x2e, 0x40, 0x9f, 0x96, 0xe9, 0x3d, 0x7e, 0x11, 0x73, 0x93, 0x17, 0x2a };struct AES_ctx ctx;AES_init_ctx(&ctx, key);AES_ECB_decrypt(&ctx, in);printf("ECB decrypt: ");if (0 == memcmp((char*)out, (char*)in, 16)) {printf("SUCCESS!\n");return(0);}else {printf("FAILURE!\n");return(1);}
}END
相关文章:
)
AES - 在tiny-AES-c基础上封装了2个应用函数(加密/解密)
文章目录 AES - 在tiny-AES-c基础上封装了2个应用函数(加密/解密)概述增加2个封装函数的AES库aes.haes.c在官方测试程序上改的测试程序(用来测试这2个封装函数)END AES - 在tiny-AES-c基础上封装了2个应用函数(加密/解密) 概述 在github山有个星数很高的AES的C库 tiny-AES-c …...

51和32单片机读取FSR薄膜压力传感器压力变化
文章目录 简介线性电压转换模块51单片机读取DO接线方式51代码实验效果 32单片机读取AO接线方式32代码实验效果 总结 简介 FSR薄膜压力传感器是可以将压力变化转换为电阻变化的一种传感器,单片机可以读取然后作为粗略测量压力(仅提供压力变化,…...

【maven】pom.xml 文件详解
有关 maven 其他配置讲解参考 maven 配置文件 setting.xml 详解 pom.xml 文件是 Maven 项目的核心配置文件,其中包含了项目的元数据、构建配置、依赖管理等信息。以下是一个 pom.xml 文件的主要部分: <?xml version"1.0" encoding"U…...
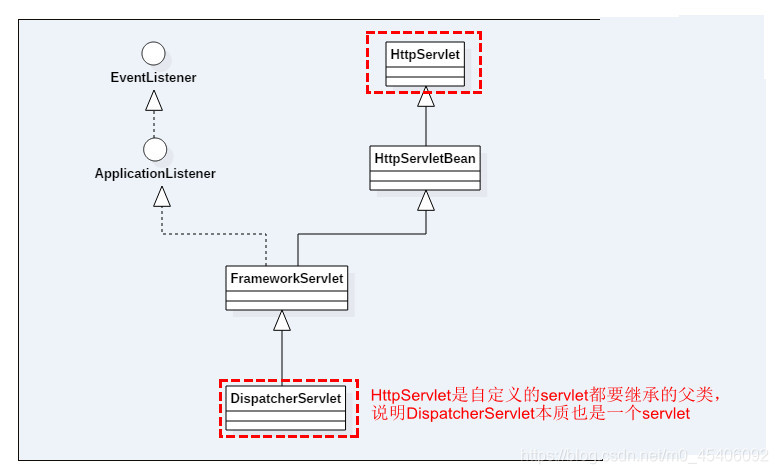
SpringMVC源码解析——DispatcherServlet初始化
在Spring中,ContextLoaderListener只是辅助功能,用于创建WebApplicationContext类型的实例,而真正的逻辑实现其实是在DispatcherServlet中进行的,DispatcherServlet是实现Servlet接口的实现类。Servlet是一个JAVA编写的程序&#…...
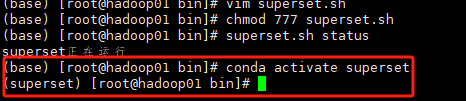
搞定Apache Superset
踩雷了无数次终于解决了Superset的一系列问题 现在是北京时间2023年12月27日,亲测有效。 Superset概述 Apache Superset是一个现代的数据探索和可视化平台。它功能强大且十分易用,可对接各种数据源,包括很多现代的大数据分析引擎ÿ…...

【每日试题】java面试之ssm框架
以下是20道常见的SSM(SpringSpring MVCMyBatis)面试题目和答案: 什么是SSM框架? SSM是指SpringSpring MVCMyBatis的组合,它是Java Web开发中常用的轻量级框架集合。 介绍一下SSM框架各个组件的作用? Sprin…...

Flutter 疑难杂症集合
一. Flutter集成uni小程序sdk 1. 手机连接电脑测试打开uni小程序没问题,打包成apk后debug编译下的apk也没问题,但就是release编译的apk包打不开小程序。 报错情景:点击后页面会闪现一下黑色的背景,然后又跳转回了点击之前的页面。…...

PHP序列化总结1--序列化和反序列化的基础知识
序列化和反序列化的作用 1.序列化:将对象转化成数组或者字符串的形式 2.反序列化:将数组或字符串的形式转化为对象 为什么要进行序列化 这种数据形式中间会有很多空格,不同人有不同的书写情况,可能还会出现换行的情况 为此为了…...

【Linux】 last 命令使用
last 命令 用于检索和展示系统中用户的登录信息。它从/var/log/wtmp文件中读取记录,并将登录信息按时间顺序列出。 著者 Miquel van Smoorenburg 语法 last [-R] [-num] [ -n num ] [-adiox] [ -f file ] [name...] [tty...]last 命令 -Linux手册页 选项及作用…...

Git 分布式版本控制系统(序章1)
第一章 Git 分布式版本控制系统 为什么学Git? 某些企业面试需要掌握Git,同时,也方便管理自己的Qt项目。 一、Git 客户端下载(Windows) 下载地址 https://gitee.com/all-about-git#git-%E5%A4%A7%E5%85%A8 二、Git 的特点 分支…...

给WordPress网站添加返回顶部按钮
给WordPress网站底部添加一个按钮,点它就可以现实快速返回到顶部。有两种方法可以现实,一种是通过安装相关插件来实现。另外一种方式就是以纯属代码的方式来实现。 给WordPress网站底部添加一个按钮,点它就可以现实快速返回到顶部。有两种方…...

App Inventor 2 接入短信服务,实现短信验证码功能
发送短信验证码功能一般都是基于短信平台提供的sdk进行调用,这里是基于阿里云短信平台进行的开发,阿里云短信平台接入步骤请点此参考。 App Inventor 2拓展提供的函数如下: 主要提供2个函数,生成随机位数的数字随机码 和 发送短信…...
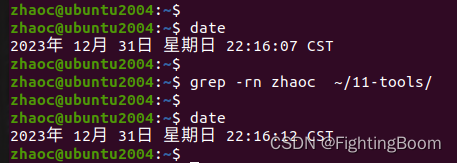
Linux环境grep搜索方法记录
1 grep grep 命令,用来搜索字符串所在位置,可以具体到不同文件,不同行; 在Linux 下,查看命令释义如下 zhaocubuntu2004:~$ grep --help Usage: grep [OPTION]... PATTERNS [FILE]... Search for PATTERNS in each FI…...

C语言-破解密码
题目描述 密码是我们生活中非常重要的东东,我们的那么一点不能说的秘密就全靠它了。哇哈哈. 接下来渊子要在密码之上再加一套密码,虽然简单但也安全。 假设老王原来一个BBS上的密码为zvbo941987,为了方便记忆,他通过一种算法把这个密码变换…...

ffmpeg 解码文件时的时间戳问题
实时流和普通文件 1 实时流 实时流编码时,我们一般不进行b帧编码,但是文件存储时为了减小大小,会增加b帧,实时流只带了I,P帧,那就会好很多 2 普通文件 很多文件带了b帧,所以要使用解码时间去同…...
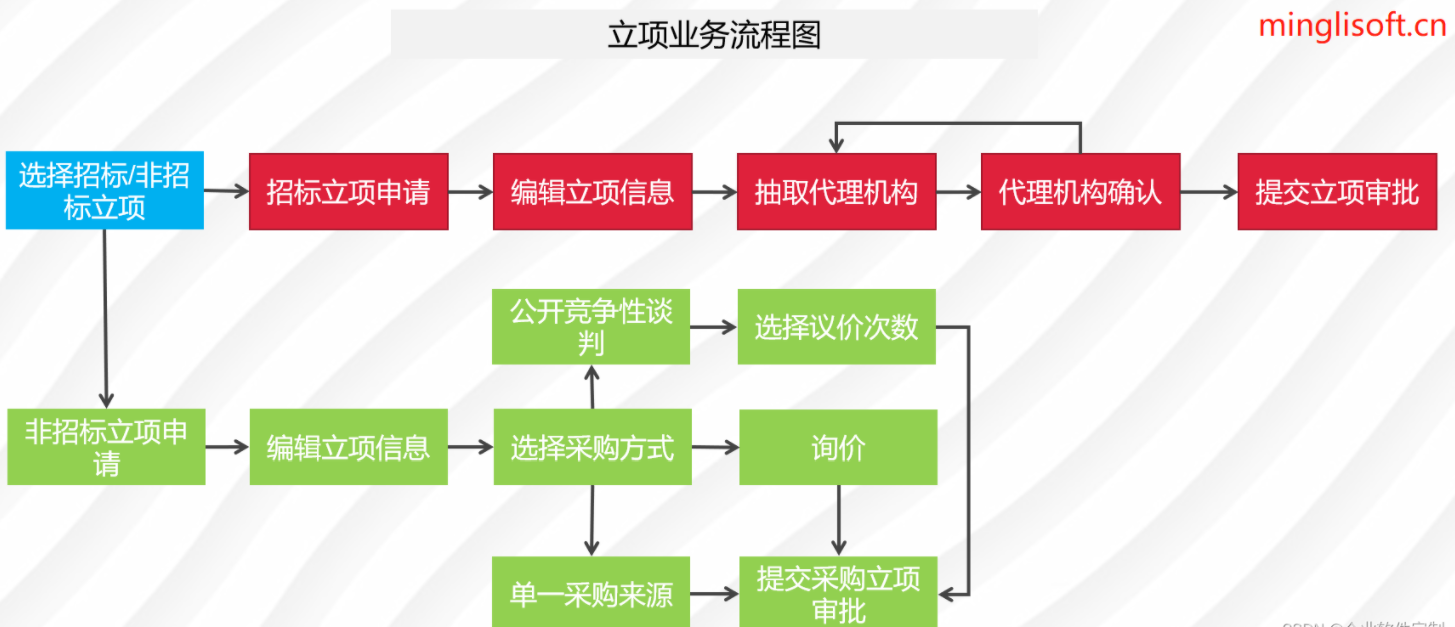
Java企业电子招投标系统源代码,支持二次开发,采用Spring cloud框架
在数字化采购领域,企业需要一个高效、透明和规范的管理系统。通过采用Spring Cloud、Spring Boot2、Mybatis等先进技术,我们打造了全过程数字化采购管理平台。该平台具备内外协同的能力,通过待办消息、招标公告、中标公告和信息发布等功能模块…...
[python]基于faster whisper实时语音识别语音转文本
语音识别转文本相信很多人都用过,不管是手机自带,还是腾讯视频都附带有此功能,今天简单说下: faster whisper地址: https://github.com/SYSTRAN/faster-whisperhttps://link.zhihu.com/?targethttps%3A//github.com…...

2023纠结中前行? 2024继续还是放下?
喝下2023年的第一口雪碧,没有想像中的那么期待,甜水,放弃吧;还是吃些水果吧,不行吃块肉、喝两口酒~ 关于生活 挣扎了10几年的一颗牙“终于“掉了,几个月时间都在为新牙努力着;”进了医院就不在…...
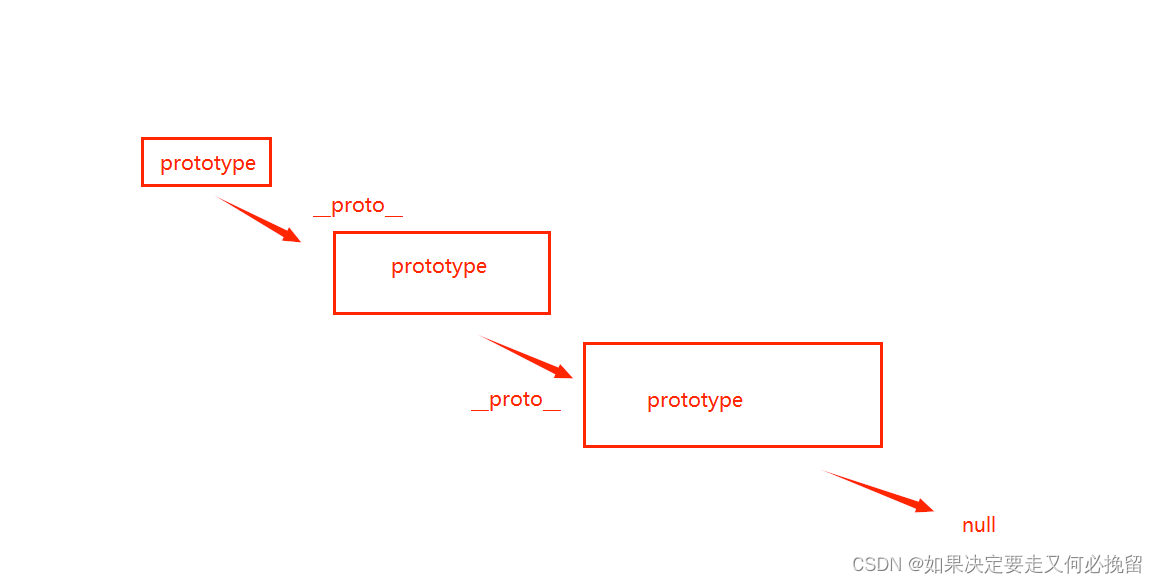
原型链补充
1.什么是原型对象 函数的独有属性,他用prototype来表示,可以在函数的prototype上挂载一些公用的属性和方法,供实例化对象来访问。 2.__proto__属性 这个属性每一个对象都有,实例化对象就是通过这个属性,来访问原型对象上的属性和方法的。 3.三者之间的关系 1.在构造函数的原型…...

《Linux Nano命令详解:小而强大的文本编辑器》
《Linux Nano命令详解:小而强大的文本编辑器》 引言: 在Linux系统中,文本编辑是开发和系统管理中不可或缺的一部分。虽然有许多强大的文本编辑器可供选择,但Nano以其简单易用、小巧灵活而备受喜爱。本文将深入探讨Nano命令&…...

模型参数、模型存储精度、参数与显存
模型参数量衡量单位 M:百万(Million) B:十亿(Billion) 1 B 1000 M 1B 1000M 1B1000M 参数存储精度 模型参数是固定的,但是一个参数所表示多少字节不一定,需要看这个参数以什么…...

day52 ResNet18 CBAM
在深度学习的旅程中,我们不断探索如何提升模型的性能。今天,我将分享我在 ResNet18 模型中插入 CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module)模块,并采用分阶段微调策略的实践过程。通过这个过程,我不仅提升…...

在rocky linux 9.5上在线安装 docker
前面是指南,后面是日志 sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y docker version sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl status docker …...
UE5 学习系列(三)创建和移动物体
这篇博客是该系列的第三篇,是在之前两篇博客的基础上展开,主要介绍如何在操作界面中创建和拖动物体,这篇博客跟随的视频链接如下: B 站视频:s03-创建和移动物体 如果你不打算开之前的博客并且对UE5 比较熟的话按照以…...
现代密码学 | 椭圆曲线密码学—附py代码
Elliptic Curve Cryptography 椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)是一种基于有限域上椭圆曲线数学特性的公钥加密技术。其核心原理涉及椭圆曲线的代数性质、离散对数问题以及有限域上的运算。 椭圆曲线密码学是多种数字签名算法的基础,例如椭圆曲线数字签…...
详解:相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位)
css的定位(position)详解:相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位
在 CSS 中,元素的定位通过 position 属性控制,共有 5 种定位模式:static(静态定位)、relative(相对定位)、absolute(绝对定位)、fixed(固定定位)和…...
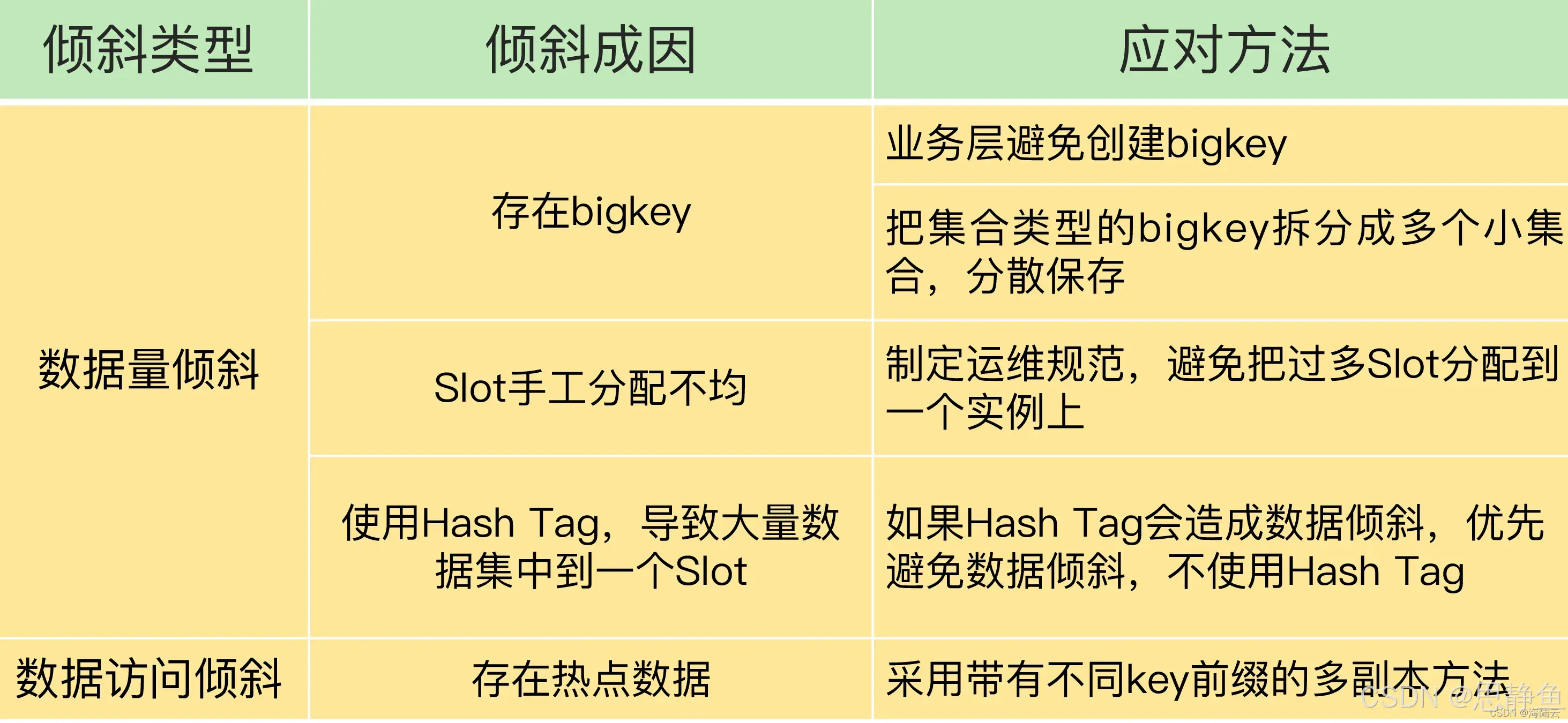
Redis数据倾斜问题解决
Redis 数据倾斜问题解析与解决方案 什么是 Redis 数据倾斜 Redis 数据倾斜指的是在 Redis 集群中,部分节点存储的数据量或访问量远高于其他节点,导致这些节点负载过高,影响整体性能。 数据倾斜的主要表现 部分节点内存使用率远高于其他节…...
Springboot社区养老保险系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,社区养老保险系统小程序被用户普遍使用,为方…...

React---day11
14.4 react-redux第三方库 提供connect、thunk之类的函数 以获取一个banner数据为例子 store: 我们在使用异步的时候理应是要使用中间件的,但是configureStore 已经自动集成了 redux-thunk,注意action里面要返回函数 import { configureS…...

CRMEB 中 PHP 短信扩展开发:涵盖一号通、阿里云、腾讯云、创蓝
目前已有一号通短信、阿里云短信、腾讯云短信扩展 扩展入口文件 文件目录 crmeb\services\sms\Sms.php 默认驱动类型为:一号通 namespace crmeb\services\sms;use crmeb\basic\BaseManager; use crmeb\services\AccessTokenServeService; use crmeb\services\sms\…...
