[linux]-总线,设备,驱动,dts
1. 总线BUS
在物理层面上,代表不同的工作时序和电平特性:
总线代表着同类设备需要共同遵守的工作时序,不同的总线对于物理电平的要求是不一样的,对于每个比特的电平维持宽度也是不一样,而总线上传递的命令也会有自己的格式约束。如I2C总线、USB总线、PCI总线等等。以I2C总线为例,在同一组I2C总线上连接着不同的I2C设备。
在软件层面上:
总线的主要作用是管理设备与驱动。
Linux内核中使用struct bus_type描述一个总线,其中包含了该总线的所有信息。
/**所在文件:kernel/msm-5.4/include/linux/device.hkernel/drivers/base/base.h
*/
/*** struct bus_type - The bus type of the device** @name: The name of the bus.* @dev_name: Used for subsystems to enumerate devices like ("foo%u", dev->id).* @dev_root: Default device to use as the parent.* @bus_groups: Default attributes of the bus.* @dev_groups: Default attributes of the devices on the bus.* @drv_groups: Default attributes of the device drivers on the bus.* @match: Called, perhaps multiple times, whenever a new device or driver* is added for this bus. It should return a positive value if the* given device can be handled by the given driver and zero* otherwise. It may also return error code if determining that* the driver supports the device is not possible. In case of* -EPROBE_DEFER it will queue the device for deferred probing.* @uevent: Called when a device is added, removed, or a few other things* that generate uevents to add the environment variables.* @probe: Called when a new device or driver add to this bus, and callback* the specific driver's probe to initial the matched device.* @sync_state: Called to sync device state to software state after all the* state tracking consumers linked to this device (present at* the time of late_initcall) have successfully bound to a* driver. If the device has no consumers, this function will* be called at late_initcall_sync level. If the device has* consumers that are never bound to a driver, this function* will never get called until they do.* @remove: Called when a device removed from this bus.* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.** @online: Called to put the device back online (after offlining it).* @offline: Called to put the device offline for hot-removal. May fail.** @suspend: Called when a device on this bus wants to go to sleep mode.* @resume: Called to bring a device on this bus out of sleep mode.* @num_vf: Called to find out how many virtual functions a device on this* bus supports.* @dma_configure: Called to setup DMA configuration on a device on* this bus.* @pm: Power management operations of this bus, callback the specific* device driver's pm-ops.* @iommu_ops: IOMMU specific operations for this bus, used to attach IOMMU* driver implementations to a bus and allow the driver to do* bus-specific setup* @p: The private data of the driver core, only the driver core can* touch this.* @lock_key: Lock class key for use by the lock validator* @need_parent_lock: When probing or removing a device on this bus, the* device core should lock the device's parent.** A bus is a channel between the processor and one or more devices. For the* purposes of the device model, all devices are connected via a bus, even if* it is an internal, virtual, "platform" bus. Buses can plug into each other.* A USB controller is usually a PCI device, for example. The device model* represents the actual connections between buses and the devices they control.* A bus is represented by the bus_type structure. It contains the name, the* default attributes, the bus' methods, PM operations, and the driver core's* private data.*/
struct bus_type {const char *name;const char *dev_name;struct device *dev_root;const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);int (*probe)(struct device *dev);void (*sync_state)(struct device *dev);int (*remove)(struct device *dev);void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);int (*online)(struct device *dev);int (*offline)(struct device *dev);int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);int (*resume)(struct device *dev);int (*num_vf)(struct device *dev);int (*dma_configure)(struct device *dev);const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;struct subsys_private *p;struct lock_class_key lock_key;bool need_parent_lock;ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);
};/*** struct subsys_private - structure to hold the private to the driver core portions of the bus_type/class structure.** @subsys - the struct kset that defines this subsystem* @devices_kset - the subsystem's 'devices' directory* @interfaces - list of subsystem interfaces associated* @mutex - protect the devices, and interfaces lists.** @drivers_kset - the list of drivers associated* @klist_devices - the klist to iterate over the @devices_kset* @klist_drivers - the klist to iterate over the @drivers_kset* @bus_notifier - the bus notifier list for anything that cares about things* on this bus.* @bus - pointer back to the struct bus_type that this structure is associated* with.** @glue_dirs - "glue" directory to put in-between the parent device to* avoid namespace conflicts* @class - pointer back to the struct class that this structure is associated* with.** This structure is the one that is the actual kobject allowing struct* bus_type/class to be statically allocated safely. Nothing outside of the* driver core should ever touch these fields.*/
struct subsys_private {struct kset subsys;struct kset *devices_kset;struct list_head interfaces;struct mutex mutex;struct kset *drivers_kset;struct klist klist_devices;struct klist klist_drivers;struct blocking_notifier_head bus_notifier;unsigned int drivers_autoprobe:1;struct bus_type *bus;struct kset glue_dirs;struct class *class;
};2. 设备device
设备代表真实的、具体的物理器件。
在软件层面上,用器件的独特的参数属性来代表该器件。如I2C总线上连接的I2C从设备都有一个标识自己的设备地址,由这个设备地址来确定主设备发过来的命令是否该由它来响应。
struct device是一个基类,被设备相关的数据结构包含,其中包含了该设备的信息。
/*** struct device - The basic device structure* @parent: The device's "parent" device, the device to which it is attached.* In most cases, a parent device is some sort of bus or host* controller. If parent is NULL, the device, is a top-level device,* which is not usually what you want.* @p: Holds the private data of the driver core portions of the device.* See the comment of the struct device_private for detail.* @kobj: A top-level, abstract class from which other classes are derived.* @init_name: Initial name of the device.* @type: The type of device.* This identifies the device type and carries type-specific* information.* @mutex: Mutex to synchronize calls to its driver.* @lockdep_mutex: An optional debug lock that a subsystem can use as a* peer lock to gain localized lockdep coverage of the device_lock.* @bus: Type of bus device is on.* @driver: Which driver has allocated this* @platform_data: Platform data specific to the device.* Example: For devices on custom boards, as typical of embedded* and SOC based hardware, Linux often uses platform_data to point* to board-specific structures describing devices and how they* are wired. That can include what ports are available, chip* variants, which GPIO pins act in what additional roles, and so* on. This shrinks the "Board Support Packages" (BSPs) and* minimizes board-specific #ifdefs in drivers.* @driver_data: Private pointer for driver specific info.* @links: Links to suppliers and consumers of this device.* @power: For device power management.* See Documentation/driver-api/pm/devices.rst for details.* @pm_domain: Provide callbacks that are executed during system suspend,* hibernation, system resume and during runtime PM transitions* along with subsystem-level and driver-level callbacks.* @pins: For device pin management.* See Documentation/driver-api/pinctl.rst for details.* @msi_list: Hosts MSI descriptors* @msi_domain: The generic MSI domain this device is using.* @numa_node: NUMA node this device is close to.* @dma_ops: DMA mapping operations for this device.* @dma_mask: Dma mask (if dma'ble device).* @coherent_dma_mask: Like dma_mask, but for alloc_coherent mapping as not all* hardware supports 64-bit addresses for consistent allocations* such descriptors.* @bus_dma_mask: Mask of an upstream bridge or bus which imposes a smaller DMA* limit than the device itself supports.* @dma_pfn_offset: offset of DMA memory range relatively of RAM* @dma_parms: A low level driver may set these to teach IOMMU code about* segment limitations.* @dma_pools: Dma pools (if dma'ble device).* @dma_mem: Internal for coherent mem override.* @cma_area: Contiguous memory area for dma allocations* @archdata: For arch-specific additions.* @of_node: Associated device tree node.* @fwnode: Associated device node supplied by platform firmware.* @devt: For creating the sysfs "dev".* @id: device instance* @devres_lock: Spinlock to protect the resource of the device.* @devres_head: The resources list of the device.* @knode_class: The node used to add the device to the class list.* @class: The class of the device.* @groups: Optional attribute groups.* @release: Callback to free the device after all references have* gone away. This should be set by the allocator of the* device (i.e. the bus driver that discovered the device).* @iommu_group: IOMMU group the device belongs to.* @iommu_fwspec: IOMMU-specific properties supplied by firmware.* @iommu_param: Per device generic IOMMU runtime data** @offline_disabled: If set, the device is permanently online.* @offline: Set after successful invocation of bus type's .offline().* @of_node_reused: Set if the device-tree node is shared with an ancestor* device.* @state_synced: The hardware state of this device has been synced to match* the software state of this device by calling the driver/bus* sync_state() callback.* @dma_coherent: this particular device is dma coherent, even if the* architecture supports non-coherent devices.* @dma_coherent_hint_cached: Tell the framework to try and treat the device* as DMA coherent when working with CPU cached* buffers.* At the lowest level, every device in a Linux system is represented by an* instance of struct device. The device structure contains the information* that the device model core needs to model the system. Most subsystems,* however, track additional information about the devices they host. As a* result, it is rare for devices to be represented by bare device structures;* instead, that structure, like kobject structures, is usually embedded within* a higher-level representation of the device.*/
struct device {struct kobject kobj;struct device *parent;struct device_private *p;const char *init_name; /* initial name of the device */const struct device_type *type;struct bus_type *bus; /* type of bus device is on */struct device_driver *driver; /* which driver has allocated thisdevice */void *platform_data; /* Platform specific data, devicecore doesn't touch it */void *driver_data; /* Driver data, set and get withdev_set_drvdata/dev_get_drvdata */
#ifdef CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKINGstruct mutex lockdep_mutex;
#endifstruct mutex mutex; /* mutex to synchronize calls to* its driver.*/struct dev_links_info links;struct dev_pm_info power;struct dev_pm_domain *pm_domain;#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ_DOMAINstruct irq_domain *msi_domain;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PINCTRLstruct dev_pin_info *pins;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQstruct list_head msi_list;
#endifconst struct dma_map_ops *dma_ops;u64 *dma_mask; /* dma mask (if dma'able device) */u64 coherent_dma_mask;/* Like dma_mask, but foralloc_coherent mappings asnot all hardware supports64 bit addresses for consistentallocations such descriptors. */u64 bus_dma_mask; /* upstream dma_mask constraint */unsigned long dma_pfn_offset;struct device_dma_parameters *dma_parms;struct list_head dma_pools; /* dma pools (if dma'ble) */#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_DECLARE_COHERENTstruct dma_coherent_mem *dma_mem; /* internal for coherent memoverride */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DMA_CMAstruct cma *cma_area; /* contiguous memory area for dmaallocations */
#endif/* arch specific additions */struct dev_archdata archdata;struct device_node *of_node; /* associated device tree node */struct fwnode_handle *fwnode; /* firmware device node */#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAint numa_node; /* NUMA node this device is close to */
#endifdev_t devt; /* dev_t, creates the sysfs "dev" */u32 id; /* device instance */spinlock_t devres_lock;struct list_head devres_head;struct class *class;const struct attribute_group **groups; /* optional groups */void (*release)(struct device *dev);struct iommu_group *iommu_group;struct iommu_fwspec *iommu_fwspec;struct iommu_param *iommu_param;bool offline_disabled:1;bool offline:1;bool of_node_reused:1;bool state_synced:1;
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_DEVICE) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU) || \defined(CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SYNC_DMA_FOR_CPU_ALL)bool dma_coherent:1;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_DMA_COHERENT_HINT_CACHED)bool dma_coherent_hint_cached:1;
#endifANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(5);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(6);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(7);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(8);
};/** The type of device, "struct device" is embedded in. A class* or bus can contain devices of different types* like "partitions" and "disks", "mouse" and "event".* This identifies the device type and carries type-specific* information, equivalent to the kobj_type of a kobject.* If "name" is specified, the uevent will contain it in* the DEVTYPE variable.*/
struct device_type {const char *name;const struct attribute_group **groups;int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);char *(*devnode)(struct device *dev, umode_t *mode,kuid_t *uid, kgid_t *gid);void (*release)(struct device *dev);const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
};
/*** struct device_private - structure to hold the private to the driver core portions of the device structure.** @klist_children - klist containing all children of this device* @knode_parent - node in sibling list* @knode_driver - node in driver list* @knode_bus - node in bus list* @knode_class - node in class list* @deferred_probe - entry in deferred_probe_list which is used to retry the* binding of drivers which were unable to get all the resources needed by* the device; typically because it depends on another driver getting* probed first.* @async_driver - pointer to device driver awaiting probe via async_probe* @device - pointer back to the struct device that this structure is* associated with.* @dead - This device is currently either in the process of or has been* removed from the system. Any asynchronous events scheduled for this* device should exit without taking any action.** Nothing outside of the driver core should ever touch these fields.*/
struct device_private {struct klist klist_children;struct klist_node knode_parent;struct klist_node knode_driver;struct klist_node knode_bus;struct klist_node knode_class;struct list_head deferred_probe;struct device_driver *async_driver;struct device *device;u8 dead:1;
};
#define to_device_private_parent(obj) \container_of(obj, struct device_private, knode_parent)
#define to_device_private_driver(obj) \container_of(obj, struct device_private, knode_driver)
#define to_device_private_bus(obj) \container_of(obj, struct device_private, knode_bus)
#define to_device_private_class(obj) \container_of(obj, struct device_private, knode_class)3. 驱动driver
驱动代表着操作设备的方式和流程。
驱动主要包括两部分:
第一是通过对外设的控制寄存器进行编程,按总线要求输出时序和命令,成功地与外围设备进行交互;
第二是对第一步中得到的数据进行处理,并向应用层提供特定格式的数据。
struct driver是一个基类,被驱动相关的数据结构包含,其中包含了该驱动的信息。
/*** struct device_driver - The basic device driver structure* @name: Name of the device driver.* @bus: The bus which the device of this driver belongs to.* @owner: The module owner.* @mod_name: Used for built-in modules.* @suppress_bind_attrs: Disables bind/unbind via sysfs.* @probe_type: Type of the probe (synchronous or asynchronous) to use.* @of_match_table: The open firmware table.* @acpi_match_table: The ACPI match table.* @probe: Called to query the existence of a specific device,* whether this driver can work with it, and bind the driver* to a specific device.* @sync_state: Called to sync device state to software state after all the* state tracking consumers linked to this device (present at* the time of late_initcall) have successfully bound to a* driver. If the device has no consumers, this function will* be called at late_initcall_sync level. If the device has* consumers that are never bound to a driver, this function* will never get called until they do.* @remove: Called when the device is removed from the system to* unbind a device from this driver.* @shutdown: Called at shut-down time to quiesce the device.* @suspend: Called to put the device to sleep mode. Usually to a* low power state.* @resume: Called to bring a device from sleep mode.* @groups: Default attributes that get created by the driver core* automatically.* @dev_groups: Additional attributes attached to device instance once the* it is bound to the driver.* @pm: Power management operations of the device which matched* this driver.* @coredump: Called when sysfs entry is written to. The device driver* is expected to call the dev_coredump API resulting in a* uevent.* @p: Driver core's private data, no one other than the driver* core can touch this.** The device driver-model tracks all of the drivers known to the system.* The main reason for this tracking is to enable the driver core to match* up drivers with new devices. Once drivers are known objects within the* system, however, a number of other things become possible. Device drivers* can export information and configuration variables that are independent* of any specific device.*/
struct device_driver {const char *name;struct bus_type *bus;struct module *owner;const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */enum probe_type probe_type;const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;int (*probe) (struct device *dev);void (*sync_state)(struct device *dev);int (*remove) (struct device *dev);void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);int (*resume) (struct device *dev);const struct attribute_group **groups;const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;void (*coredump) (struct device *dev);struct driver_private *p;ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(3);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(4);
};struct driver_private {struct kobject kobj;struct klist klist_devices;struct klist_node knode_bus;struct module_kobject *mkobj;struct device_driver *driver;
};
#define to_driver(obj) container_of(obj, struct driver_private, kobj)
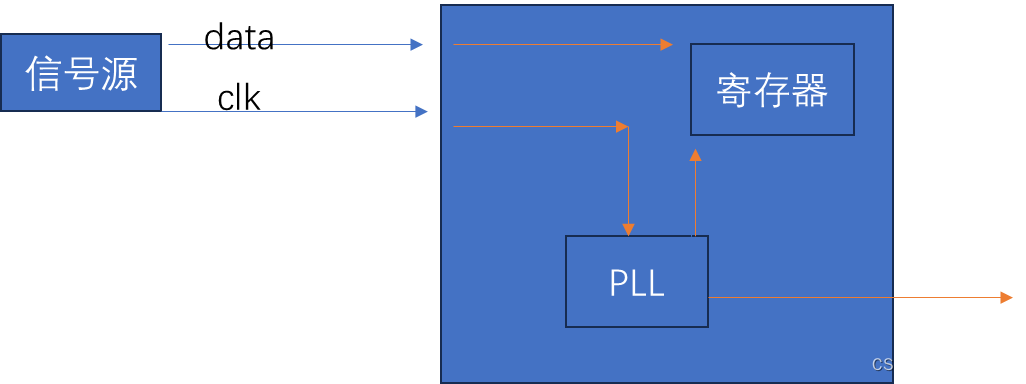
4. bus device driver三者关系
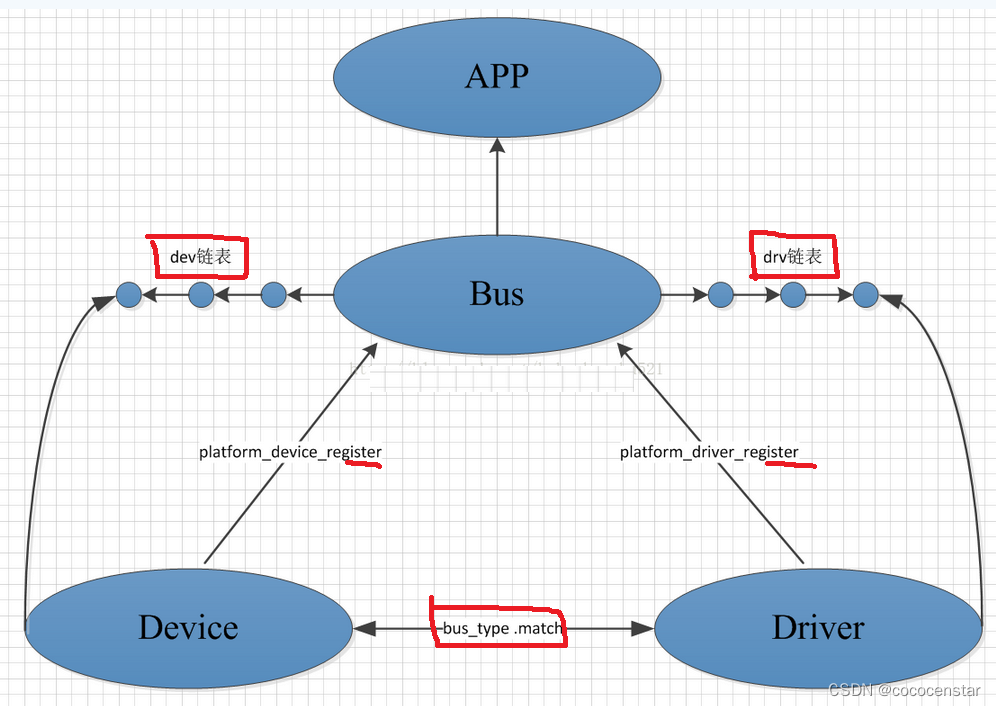
上图为平台总线设备驱动模型的整体框架。
在总线设备驱动模型中,需关心总线、设备和驱动这3个实体,总线将设备和驱动绑定。
1)驱动向总线注册的流程:
当系统向内核注册每一个驱动程序时,都要通过调用驱动注册函数(xxx_driver_register)将驱动程序注册到总线,并将其放入所属总线的drv链表中,注册驱动的时候会调用所属总线的match函数寻找该总线上与之匹配的每一个设备,如果找到与之匹配的设备则会调用相应的probe函数将相应的设备和驱动进行绑定;
2)设备向总线注册的流程:
同样的当系统向内核注册每一个设备时,都要通过调用设备注册函数(xxx_device_register)将设备注册到总线,并将其放入所属总线的dev链表中,注册设备的时候同样也会调用所属总线的match函数寻找该总线上与之匹配的每一个驱动程序,如果找到与之匹配的驱动程序时会调用相应的probe函数将相应的设备和驱动进行绑定;而这一匹配的过程是由总线自动完成的。
3)总线管理
总线在匹配设备和驱动之后驱动要考虑一个这样的问题,设备对应的软件数据结构代表着静态的信息,真实的物理设备此时是否正常还不一定,因此驱动需要探测这个设备是否正常。总线的管理代码中会有这样的逻辑:
if(match(device, driver) == OK)driver->probe();
总线匹配设备和驱动之后,驱动探测到设备正常,开始创建设备文件。调用class_create()、device_create()函数在/dev目录下创建相应的设备文件,其内部原理是通过sysfs文件系统、uevent事件通知机制和后台应用服务mdev程序配合能够成功地在/dev目录创建对应的设备文件。
【创建设备文件的两种方式
(1)手动创建:mknod命令
在驱动程序insmod成功之后,通过mknod命令手动创建设备文件至/dev目录下:mknod /dev/xxx c 主设备号 次设备号。("c"表示字符设备、"b"表示块设备、"p"表示网络设备)
(2)自动创建设备文件:mdev
在设备驱动注册到系统后,调用class_create为该设备在/sys/class目录下创建一个设备类,再调用device_create函数为每个设备创建对应的设备,并通过uevent机制调用mdev(嵌入式linux由busybox提供)来调用mknod创建设备文件至/dev目录下。
详情参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/linfeng-learning/p/9316224.html 】
5. 什么是设备树?
设备树描述开发板上总线所连接的设备的硬件信息,并指定所匹配的驱动。

6. 设备树形态
DTS(devcie tree source):设备树源码文件
DTB(device tree binary):将 .dts 编译后得到二进制文件,下载到 DDR 中的是 .dtb 文件
DTC(device tree compiler):将 .dts 编译为 .dtb 的编译工具,它有个文件夹,经过编译后得到
7. 设备树关键内容解析
设备树由一系列的节点和属性组成,节点可包含子节点。在设备树中,可描述的信息包括:
- CPU数量和类型
- 内存基地址和大小
- 总线和桥
- 外设连接
- 中断控制器和中断使用情况
- GPIO控制器和GPIO使用情况
- 时钟控制器和时钟使用情况
compatible
compatible 属性值为字符串列表,⽤于将设备和驱动绑定起来,字符串列表⽤于选择设备所要使用的驱动程序。
model 属性
model 属性:描述设备模块信息,比如名字什么的,如:model = “XXX”。
#address-cells 和 #size-cells 属性
#address-cells 和 #size-cells 描述⼦节点应如何编写 reg 属性值,
#address-cells表示用于表示reg的地址的长度
#size-cells 从起始地址开始的寄存器值所占用的地址空间长度
中断号和电平触发方式
interrupts = < X Y >; //中断号为X,触发方式为Y
#电平触发方式定义
1 = low-to-high edge triggered
2 = high-to-low edge triggered
4 = active high level-sensitive
8 = active low level-sensitive
8. 设备树和驱动的配合流程:
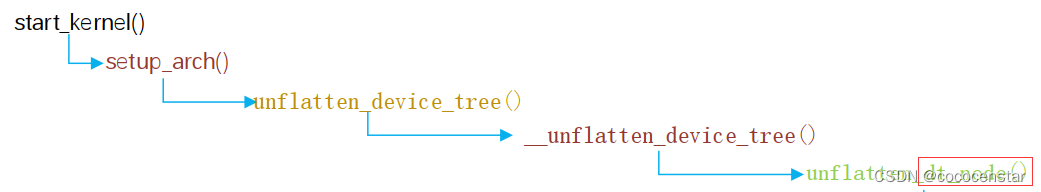
系统启动时会解析dtb,将获得的设备树的所有信息体现在设备文件中,/proc/device-tree目录下根据节点名字创建不同设备节点文件夹,后续驱动初始化时,如果需要获得对应设备的信息,可以通过如下提供的系统函数来获得:
查找节点:of_find_node_by_path 函数,通过指定全路径来查找指定节点。
提取属性值:of_find_property 函数 ,获取到的值保存到了 property 结构体中。
读取属性中字符串值:of_property_read_string 函数。
读取属性中数组数据:of_property_read_u32_array 函数,常用于一次读取 reg 属性的所有数据。
直接内存映射:of_iomap 函数,获取内存地址所对应的虚拟地址(用于将硬件设备的寄存器的物理地址映射到进程空间的虚拟地址空间中,便于访问和操作)
相关文章:

[linux]-总线,设备,驱动,dts
1. 总线BUS 在物理层面上,代表不同的工作时序和电平特性: 总线代表着同类设备需要共同遵守的工作时序,不同的总线对于物理电平的要求是不一样的,对于每个比特的电平维持宽度也是不一样,而总线上传递的命令也会有自己…...

python3实现gitlab备份文件上传腾讯云COS
gitlab备份文件上传腾讯云COS 脚本说明脚本名称:upload.py 假设gitlab备份文件目录:/opt/gitlab/backups gitlab备份文件格式:1706922037_2024_02_06_14.2.1_gitlab_backup.tar1.脚本需和gitlab备份文件同级目录 2.根据备份文件中的日期判断…...

292.Nim游戏
桌子上有一堆石头。 轮流进行自己的回合, 你作为先手 。 每一回合,轮到的人拿掉 1 - 3 块石头。 拿掉最后一块石头的人就是获胜者。 假设你们每一步都是最优解。请编写一个函数,来判断你是否可以在给定石头数量为 n 的情况下赢得游戏。如果可…...
Spring和Spring Boot的区别
Spring 是一个轻量级的 Java 开发框架,它提供了一系列的模块和功能,例如 IoC(控制反转)、AOP(面向方面编程)、数据库访问、Web 开发等。Spring 的目标是使 Java 开发更加简单、高效和可维护。 Spring Boot …...
备战蓝桥杯---动态规划(理论基础)
目录 动态规划的概念: 解决多阶段决策过程最优化的一种方法 阶段: 状态: 决策: 策略: 状态转移方程: 适用的基本条件 1.具有相同的子问题 2.满足最优子结构 3.满足无后效性 动态规划的实现方式…...
FPGA_ip_pll
常使用插件管理器进行ip核的配置,ip核分为计算,存储,输入输出,视频图像处理,接口,调试等。 一 pll ip核简介 pll 即锁相环,可以对输入到fpga的时钟信号,进行分频,倍频&…...

【实验3】统计某电商网站买家收藏商品数量
文章目录 一、实验目的和要求∶二、实验任务∶三、实验准备方案,包括以下内容:实验内容一、实验环境二、实验内容与步骤(过程及数据记录):三、实验结果分析、思考题解答∶四、感想、体会、建议∶一、实验目的和要求∶ 现有某电商网站用户对商品的收藏数据,记录了用户收藏…...
【Qt】Android上运行keeps stopping, Desktop上正常
文章目录 问题 & 背景背景问题 解决方案One More ThingTake Away 问题 & 背景 背景 在文章【Qt】最详细教程,如何从零配置Qt Android安卓环境中,我们在Qt中配置了安卓开发环境,并且能够正常运行。 但笔者在成功配置并完成上述文章…...
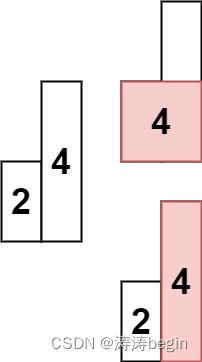
算法学习打卡day47|单调栈系列题目
单调栈题目思路 通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置,此时我们就要想到可以用单调栈了。时间复杂度为O(n)。单调栈的本质是空间换时间,因为在遍历的过程中需要用一个栈来记录右边第一个比当前元…...
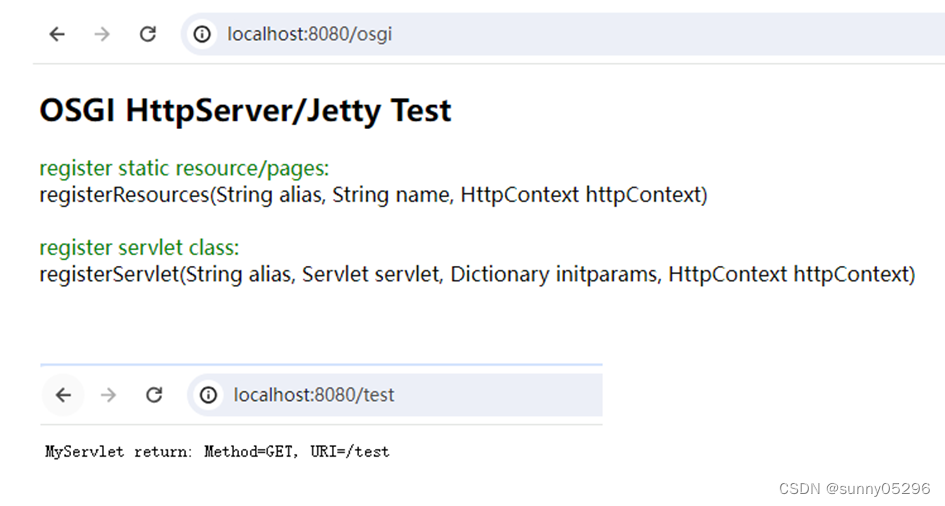
Maven构建OSGI+HttpServer应用
Maven构建OSGIHttpServer应用 官网(https://eclipse.dev/equinox/server/http_in_equinox.php)介绍有两种方式: 一种是基于”org.eclipse.equinox.http”包的轻量级实现,另一种是基于”org.eclipse.equinox.http.jetty”包&#…...

chrome扩展插件常用文件及作用
Chrome扩展通常包含以下常用文件及其作用: manifest.json: 描述了扩展的基本信息,如名称、版本、权限、图标等。定义了扩展的各种组件和功能,包括后台脚本、内容脚本、页面、浏览器动作按钮等。 background.js: 后台脚…...

PdfFactory Pro软件下载以及序列号注册码生成器
PdfFactory Pro注册机是一款针对同名虚拟打印机软件所推出的用户名和序列号生成器。PdfFactory Pro是一款非常专业的PDF虚拟打印软件,通过使用这款注册机,就能帮助用户免费获取注册码,一键激活,永久免费使用。 pdffactory7注册码如…...
jsp康养小镇管理系统Myeclipse开发mysql数据库web结构java编程计算机网页项目
一、源码特点 JSP康养小镇管理系统是一套完善的java web信息管理系统,对理解JSP java编程开发语言有帮助,系统具有完整的源代码和数据库,系统主要采用B/S模式开发。开发环境为TOMCAT7.0,Myeclipse8.5开发,数据库为Mysql5.0&a…...

Android 无操作之后定时退出
android定时器监用户听对页面无操作5分钟退出登录实现 - 简书 private long advertisingTime 600000;///定时结束退出登录10分(分钟)600000毫秒public CountDownTimer countDownTimer;Overrideprotected void onResume() {super.onResume();//启动定时if (isTimedExitApp()) …...
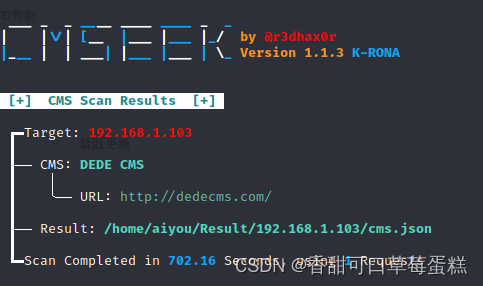
CMS 检测神器:CMSeek 保姆级教程(附链接)
一、介绍 CMSeek(Content Management System Exploitation and Enumeration Toolkit)是一款用于检测和利用网站上可能存在的内容管理系统(CMS)漏洞的开源工具。它旨在帮助安全研究人员和渗透测试人员识别目标网站所使用的CMS&…...
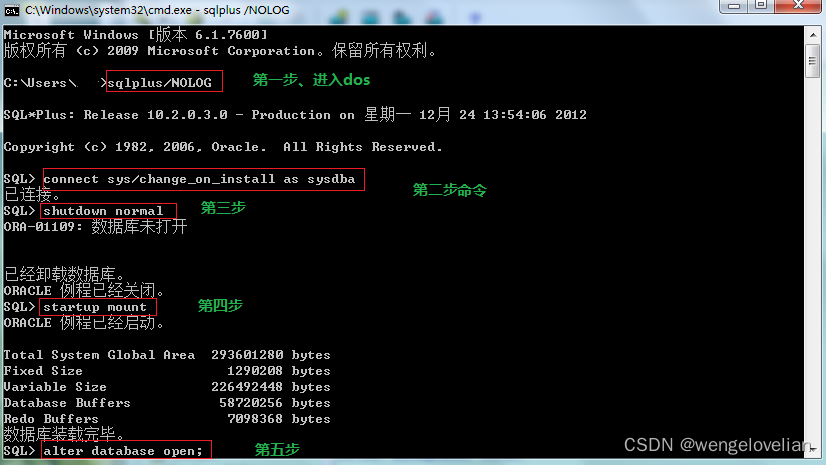
oracle 启动命令以及ORA-01033问题处理、删除归档日志
1 启动数据库:startup 2 关闭数据库:Shutdown immediate 3 查看监听状态:lsnrctl status 4 启动监听:lsnrctl start 5 停止监听:lsnrctl stop 常见问题 1、在服务器重启后会出现,Oracle ORA-01033: ORAC…...
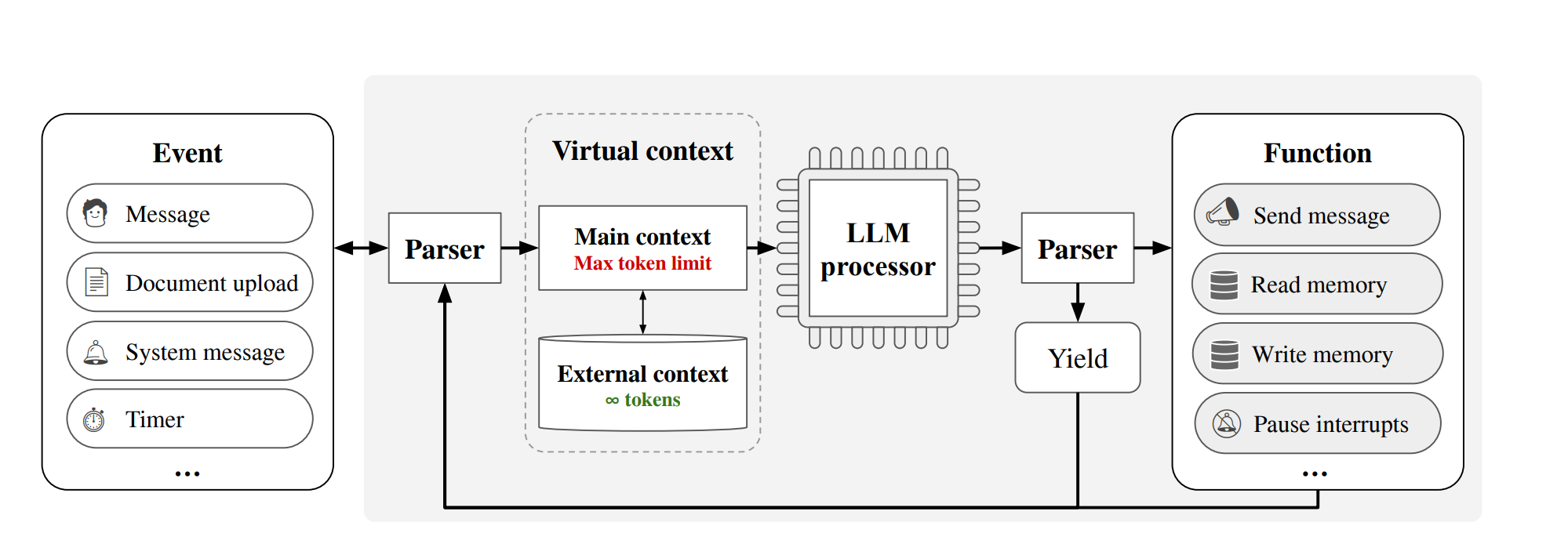
【大模型上下文长度扩展】MedGPT:解决遗忘 + 永久记忆 + 无限上下文
MedGPT:解决遗忘 永久记忆 无限上下文 问题:如何提升语言模型在长对话中的记忆和处理能力?子问题1:有限上下文窗口的限制子问题2:复杂文档处理的挑战子问题3:长期记忆的维护子问题4:即时信息检…...
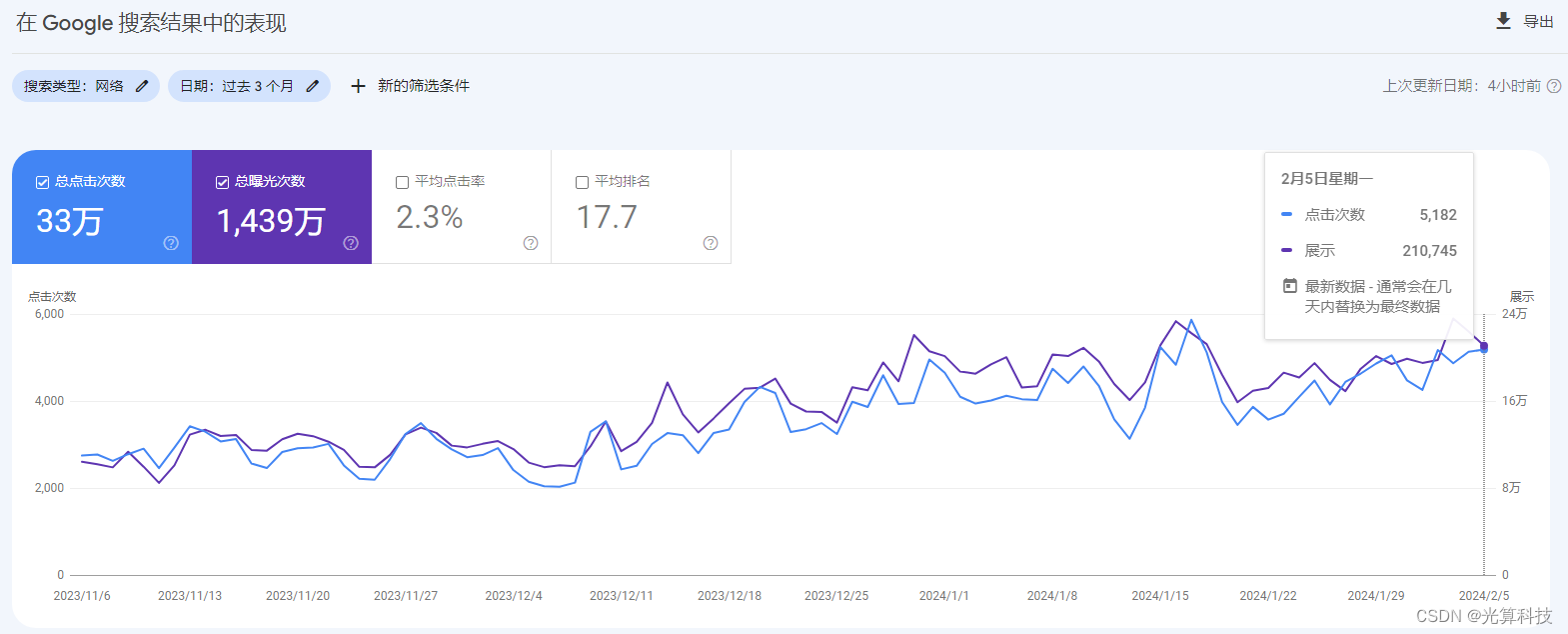
谷歌seo搜索引擎优化有什么思路?
正常做seo哪有那么多思路,其实就那么几种方法,无非就关键词,站内优化,外链,可以说万变不离其宗,但如果交给我们,你就可以实现其他的思路,或者说玩法 收录可以说是一个网站的基础&…...

腾讯云与IBM共同打造“高性能计算服务解决方案“
腾讯云与IBM共同打造"高性能计算服务解决方案" 腾讯云与IBM达成战略合作,对优势产品及服务进行深度集成,基于腾讯云产品及服务,共同打造"腾讯-IBM混合云与人工智能解决方案"。双方通过更为紧密的嵌入式解决方案的深度合…...

【SparkML实践7】特征选择器FeatureSelector
本节介绍了用于处理特征的算法,大致可以分为以下几组: 提取(Extraction):从“原始”数据中提取特征。转换(Transformation):缩放、转换或修改特征。选择(Selection&…...
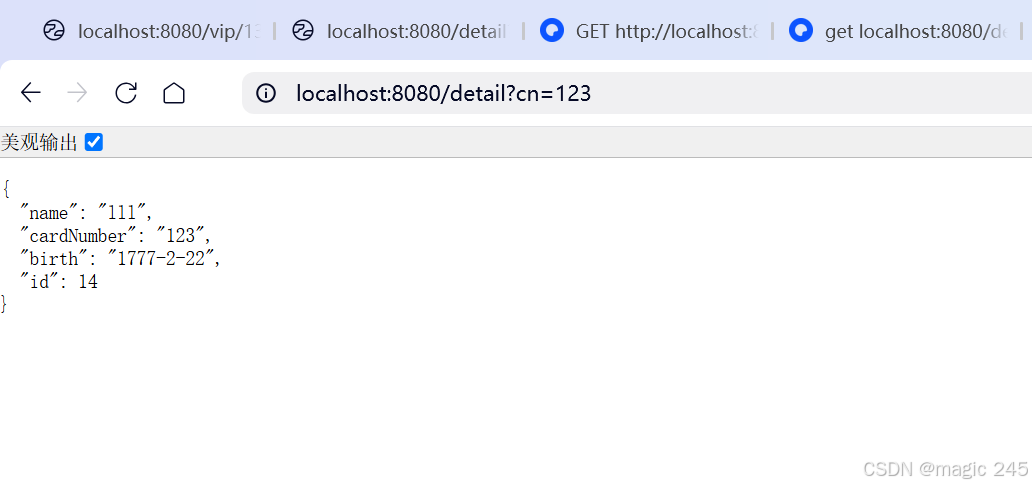
Lombok 的 @Data 注解失效,未生成 getter/setter 方法引发的HTTP 406 错误
HTTP 状态码 406 (Not Acceptable) 和 500 (Internal Server Error) 是两类完全不同的错误,它们的含义、原因和解决方法都有显著区别。以下是详细对比: 1. HTTP 406 (Not Acceptable) 含义: 客户端请求的内容类型与服务器支持的内容类型不匹…...
)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解) 在开始使用 React Native 开发移动应用之前,正确设置开发环境是至关重要的一步。本文将为你提供一份全面的指南,涵盖 macOS 和 Windows 平台的配置步骤,如何在 Android 和 iOS…...

k8s从入门到放弃之Ingress七层负载
k8s从入门到放弃之Ingress七层负载 在Kubernetes(简称K8s)中,Ingress是一个API对象,它允许你定义如何从集群外部访问集群内部的服务。Ingress可以提供负载均衡、SSL终结和基于名称的虚拟主机等功能。通过Ingress,你可…...
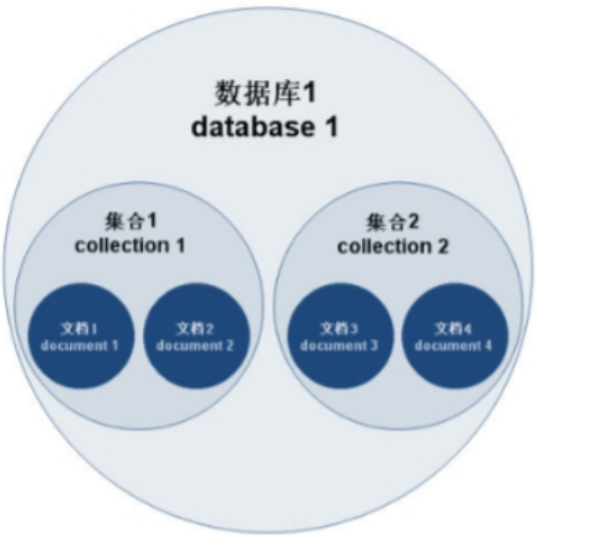
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...
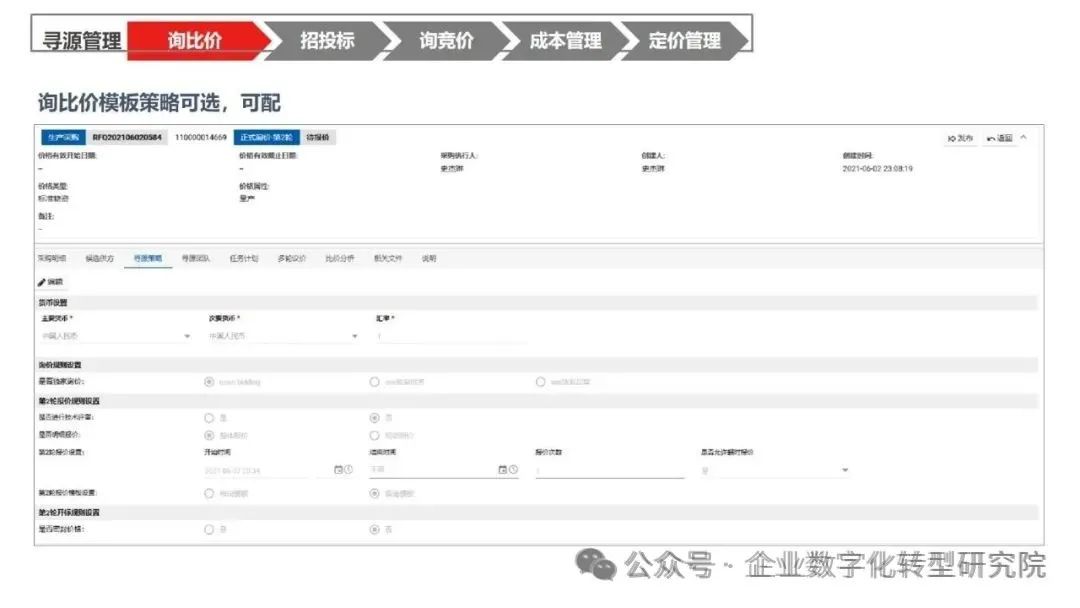
PPT|230页| 制造集团企业供应链端到端的数字化解决方案:从需求到结算的全链路业务闭环构建
制造业采购供应链管理是企业运营的核心环节,供应链协同管理在供应链上下游企业之间建立紧密的合作关系,通过信息共享、资源整合、业务协同等方式,实现供应链的全面管理和优化,提高供应链的效率和透明度,降低供应链的成…...

在 Nginx Stream 层“改写”MQTT ngx_stream_mqtt_filter_module
1、为什么要修改 CONNECT 报文? 多租户隔离:自动为接入设备追加租户前缀,后端按 ClientID 拆分队列。零代码鉴权:将入站用户名替换为 OAuth Access-Token,后端 Broker 统一校验。灰度发布:根据 IP/地理位写…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院查看报告小程序
一、开发环境准备 工具安装: 下载安装DevEco Studio 4.0(支持HarmonyOS 5)配置HarmonyOS SDK 5.0确保Node.js版本≥14 项目初始化: ohpm init harmony/hospital-report-app 二、核心功能模块实现 1. 报告列表…...
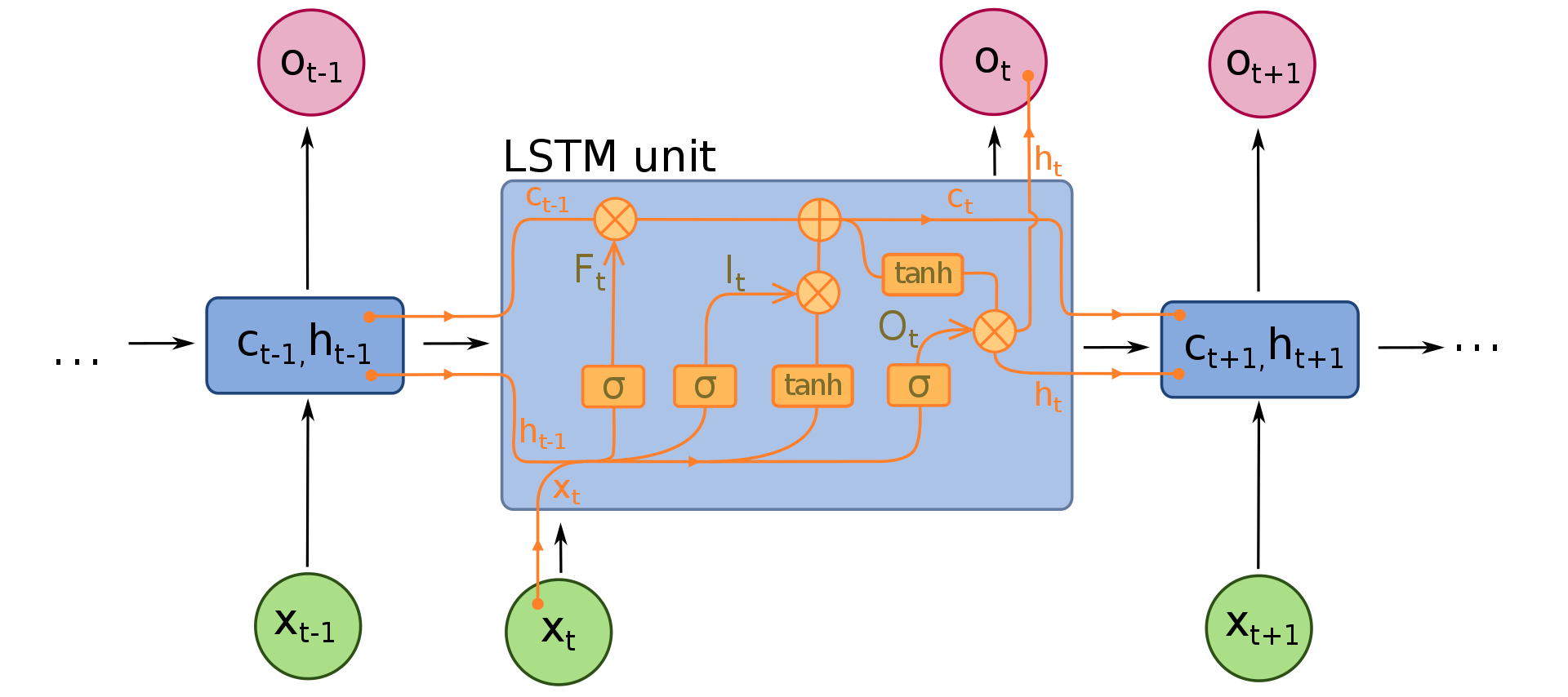
NLP学习路线图(二十三):长短期记忆网络(LSTM)
在自然语言处理(NLP)领域,我们时刻面临着处理序列数据的核心挑战。无论是理解句子的结构、分析文本的情感,还是实现语言的翻译,都需要模型能够捕捉词语之间依时序产生的复杂依赖关系。传统的神经网络结构在处理这种序列依赖时显得力不从心,而循环神经网络(RNN) 曾被视为…...
)
OpenLayers 分屏对比(地图联动)
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 地图分屏对比在WebGIS开发中是很常见的功能,和卷帘图层不一样的是,分屏对比是在各个地图中添加相同或者不同的图层进行对比查看。…...

html-<abbr> 缩写或首字母缩略词
定义与作用 <abbr> 标签用于表示缩写或首字母缩略词,它可以帮助用户更好地理解缩写的含义,尤其是对于那些不熟悉该缩写的用户。 title 属性的内容提供了缩写的详细说明。当用户将鼠标悬停在缩写上时,会显示一个提示框。 示例&#x…...
