Python爬虫 Beautiful Soup库详解#4
爬虫专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/WfCSx
使用 Beautiful Soup
前面介绍了正则表达式的相关用法,但是一旦正则表达式写的有问题,得到的可能就不是我们想要的结果了。而且对于一个网页来说,都有一定的特殊结构和层级关系,而且很多节点都有 id 或 class 来作区分,所以借助它们的结构和属性来提取不也可以吗?
这一节中,我们就来介绍一个强大的解析工具 Beautiful Soup,它借助网页的结构和属性等特性来解析网页。有了它,我们不用再去写一些复杂的正则表达式,只需要简单的几条语句,就可以完成网页中某个元素的提取。
废话不多说,接下来就来感受一下 Beautiful Soup 的强大之处吧。
1. Beautiful Soup 简介
简单来说,BeautifulSoup 就是 Python 的一个 HTML 或 XML 的解析库,我们可以用它来方便地从网页中提取数据,官方的解释如下:
BeautifulSoup 提供一些简单的、Python 式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。 BeautifulSoup 自动将输入文档转换为 Unicode 编码,输出文档转换为 utf-8 编码。你不需要考虑编码方式,除非文档没有指定一个编码方式,这时你仅仅需要说明一下原始编码方式就可以了。 BeautifulSoup 已成为和 lxml、html5lib 一样出色的 Python 解释器,为用户灵活地提供不同的解析策略或强劲的速度。
所以说,利用它可以省去很多烦琐的提取工作,提高了解析效率。
2. 准备工作
在开始之前,请确保已经正确安装好了 Beautiful Soup 和 lxml,如果没有安装,可以参考第 1 章的内容。
3. 解析器
Beautiful Soup 在解析时实际上依赖解析器,它除了支持 Python 标准库中的 HTML 解析器外,还支持一些第三方解析器(比如 lxml)。列出了 Beautiful Soup 支持的解析器。
Beautiful Soup 支持的解析器
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python 标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup, "html.parser") | Python 的内置标准库、执行速度适中 、文档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3 or 3.2.2) 前的版本中文容错能力差 |
| LXML HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, "lxml") | 速度快、文档容错能力强 | 需要安装 C 语言库 |
| LXML XML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, "xml") | 速度快、唯一支持 XML 的解析器 | 需要安装 C 语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup, "html5lib") | 最好的容错性、以浏览器的方式解析文档、生成 HTML5 格式的文档 | 速度慢、不依赖外部扩展 |
通过以上对比可以看出,lxml 解析器有解析 HTML 和 XML 的功能,而且速度快,容错能力强,所以推荐使用它。
如果使用 lxml,那么在初始化 Beautiful Soup 时,可以把第二个参数改为 lxml 即可:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup('<p>Hello</p>', 'lxml')
print(soup.p.string)
在后面,Beautiful Soup 的用法实例也统一用这个解析器来演示。
4. 基本使用
下面首先用实例来看看 Beautiful Soup 的基本用法:
html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.prettify()) print(soup.title.string)
运行结果:
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>and<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p></body> </html> The Dormouse's story
这里首先声明变量 html,它是一个 HTML 字符串。但是需要注意的是,它并不是一个完整的 HTML 字符串,因为 body 和 html 节点都没有闭合。接着,我们将它当作第一个参数传给 BeautifulSoup 对象,该对象的第二个参数为解析器的类型(这里使用 lxml),此时就完成了 BeaufulSoup 对象的初始化。然后,将这个对象赋值给 soup 变量。
接下来,就可以调用 soup 的各个方法和属性解析这串 HTML 代码了。
首先,调用 prettify() 方法。这个方法可以把要解析的字符串以标准的缩进格式输出。这里需要注意的是,输出结果里面包含 body 和 html 节点,也就是说对于不标准的 HTML 字符串 BeautifulSoup,可以自动更正格式。这一步不是由 prettify() 方法做的,而是在初始化 BeautifulSoup 时就完成了。
然后调用 soup.title.string,这实际上是输出 HTML 中 title 节点的文本内容。所以,soup.title 可以选出 HTML 中的 title 节点,再调用 string 属性就可以得到里面的文本了,所以我们可以通过简单调用几个属性完成文本提取,这是不是非常方便?
5. 节点选择器
直接调用节点的名称就可以选择节点元素,再调用 string 属性就可以得到节点内的文本了,这种选择方式速度非常快。如果单个节点结构层次非常清晰,可以选用这种方式来解析。
选择元素
下面再用一个例子详细说明选择元素的方法:
html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.title) print(type(soup.title)) print(soup.title.string) print(soup.head) print(soup.p)
运行结果:
<title>The Dormouse's story</title> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> The Dormouse's story <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
这里依然选用刚才的 HTML 代码,首先打印输出 title 节点的选择结果,输出结果正是 title 节点加里面的文字内容。接下来,输出它的类型,是 bs4.element.Tag 类型,这是 Beautiful Soup 中一个重要的数据结构。经过选择器选择后,选择结果都是这种 Tag 类型。Tag 具有一些属性,比如 string 属性,调用该属性,可以得到节点的文本内容,所以接下来的输出结果正是节点的文本内容。
接下来,我们又尝试选择了 head 节点,结果也是节点加其内部的所有内容。最后,选择了 p 节点。不过这次情况比较特殊,我们发现结果是第一个 p 节点的内容,后面的几个 p 节点并没有选到。也就是说,当有多个节点时,这种选择方式只会选择到第一个匹配的节点,其他的后面节点都会忽略。
提取信息
上面演示了调用 string 属性来获取文本的值,那么如何获取节点属性的值呢?如何获取节点名呢?下面我们来统一梳理一下信息的提取方式。
获取名称
可以利用 name 属性获取节点的名称。这里还是以上面的文本为例,选取 title 节点,然后调用 name 属性就可以得到节点名称:
print(soup.title.name)
运行结果:
title
获取属性
每个节点可能有多个属性,比如 id 和 class 等,选择这个节点元素后,可以调用 attrs 获取所有属性:
print(soup.p.attrs) print(soup.p.attrs['name'])
运行结果:
{'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'}
dromouse
可以看到,attrs 的返回结果是字典形式,它把选择的节点的所有属性和属性值组合成一个字典。接下来,如果要获取 name 属性,就相当于从字典中获取某个键值,只需要用中括号加属性名就可以了。比如,要获取 name 属性,就可以通过 attrs['name'] 来得到。
其实这样有点烦琐,还有一种更简单的获取方式:可以不用写 attrs,直接在节点元素后面加中括号,传入属性名就可以获取属性值了。样例如下:
print(soup.p['name']) print(soup.p['class'])
运行结果如下:
dromouse ['title']
这里需要注意的是,有的返回结果是字符串,有的返回结果是字符串组成的列表。比如,name 属性的值是唯一的,返回的结果就是单个字符串。而对于 class,一个节点元素可能有多个 class,所以返回的是列表。在实际处理过程中,我们要注意判断类型。
获取内容
可以利用 string 属性获取节点元素包含的文本内容,比如要获取第一个 p 节点的文本:
print(soup.p.string)
运行结果如下:
The Dormouse's story
再次注意一下,这里选择到的 p 节点是第一个 p 节点,获取的文本也是第一个 p 节点里面的文本。
嵌套选择
在上面的例子中,我们知道每一个返回结果都是 bs4.element.Tag 类型,它同样可以继续调用节点进行下一步的选择。比如,我们获取了 head 节点元素,我们可以继续调用 head 来选取其内部的 head 节点元素:
html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.head.title) print(type(soup.head.title)) print(soup.head.title.string)
运行结果如下:
<title>The Dormouse's story</title> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> The Dormouse's story
第一行结果是调用 head 之后再次调用 title 而选择的 title 节点元素。然后打印输出了它的类型,可以看到,它仍然是 bs4.element.Tag 类型。也就是说,我们在 Tag 类型的基础上再次选择得到的依然还是 Tag 类型,每次返回的结果都相同,所以这样就可以做嵌套选择了。
最后,输出它的 string 属性,也就是节点里的文本内容。
关联选择
在做选择的时候,有时候不能做到一步就选到想要的节点元素,需要先选中某一个节点元素,然后以它为基准再选择它的子节点、父节点、兄弟节点等,这里就来介绍如何选择这些节点元素。
子节点和子孙节点
选取节点元素之后,如果想要获取它的直接子节点,可以调用 contents 属性,示例如下:
html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p><p class="story">...</p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.p.contents)
运行结果如下:
['\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a>, '\n', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, ' \n and\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ']
可以看到,返回结果是列表形式。p 节点里既包含文本,又包含节点,最后会将它们以列表形式统一返回。
需要注意的是,列表中的每个元素都是 p 节点的直接子节点。比如第一个 a 节点里面包含一层 span 节点,这相当于孙子节点了,但是返回结果并没有单独把 span 节点选出来。所以说,contents 属性得到的结果是直接子节点的列表。
同样,我们可以调用 children 属性得到相应的结果:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.p.children) for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.children):print(i, child)
运行结果如下:
<list_iterator object at 0x1064f7dd8> 0 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were1 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> 2 3 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> 4 and5 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> 6 and they lived at the bottom of a well.
还是同样的 HTML 文本,这里调用了 children 属性来选择,返回结果是生成器类型。接下来,我们用 for 循环输出相应的内容。
如果要得到所有的子孙节点的话,可以调用 descendants 属性:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.p.descendants) for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):print(i, child)
运行结果如下:
<generator object descendants at 0x10650e678> 0 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were1 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> 2 3 <span>Elsie</span> 4 Elsie 5 6 7 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> 8 Lacie 9 and10 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> 11 Tillie 12 and they lived at the bottom of a well.
此时返回结果还是生成器。遍历输出一下可以看到,这次的输出结果就包含了 span 节点。descendants 会递归查询所有子节点,得到所有的子孙节点。
父节点和祖先节点
如果要获取某个节点元素的父节点,可以调用 parent 属性:
html = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a></p><p class="story">...</p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.a.parent)
运行结果如下:
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> </p>
这里我们选择的是第一个 a 节点的父节点元素。很明显,它的父节点是 p 节点,输出结果便是 p 节点及其内部的内容。
需要注意的是,这里输出的仅仅是 a 节点的直接父节点,而没有再向外寻找父节点的祖先节点。如果想获取所有的祖先节点,可以调用 parents 属性:
html = """ <html><body><p class="story"><a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a></p> """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(type(soup.a.parents)) print(list(enumerate(soup.a.parents)))
运行结果如下:
<class 'generator'> [(0, <p class="story"> <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> </p>), (1, <body> <p class="story"> <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> </p> </body>), (2, <html> <body> <p class="story"> <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> </p> </body></html>), (3, <html> <body> <p class="story"> <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1"> <span>Elsie</span> </a> </p> </body></html>)]
可以发现,返回结果是生成器类型。这里用列表输出了它的索引和内容,而列表中的元素就是 a 节点的祖先节点。
兄弟节点
上面说明了子节点和父节点的获取方式,如果要获取同级的节点(也就是兄弟节点),应该怎么办呢?示例如下:
html = """
<html><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><span>Elsie</span></a>Hello<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print('Next Sibling', soup.a.next_sibling)
print('Prev Sibling', soup.a.previous_sibling)
print('Next Siblings', list(enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings)))
print('Prev Siblings', list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings)))
运行结果如下:
Next Sibling HelloPrev Sibling Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names wereNext Siblings [(0, '\n Hello\n '), (1, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>), (2, ' \n and\n '), (3, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>), (4, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ')] Prev Siblings [(0, '\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ')]
可以看到,这里调用了 4 个属性,其中 next_sibling 和 previous_sibling 分别获取节点的下一个和上一个兄弟元素,next_siblings 和 previous_siblings 则分别返回后面和前面的兄弟节点。
提取信息
前面讲解了关联元素节点的选择方法,如果想要获取它们的一些信息,比如文本、属性等,也用同样的方法,示例如下:
html = """
<html><body><p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Bob</a><a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> </p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print('Next Sibling:')
print(type(soup.a.next_sibling))
print(soup.a.next_sibling)
print(soup.a.next_sibling.string)
print('Parent:')
print(type(soup.a.parents))
print(list(soup.a.parents)[0])
print(list(soup.a.parents)[0].attrs['class'])
运行结果:
Next Sibling: <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> Lacie Parent: <class 'generator'> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Bob</a><a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> </p> ['story']
如果返回结果是单个节点,那么可以直接调用 string、attrs 等属性获得其文本和属性;如果返回结果是多个节点的生成器,则可以转为列表后取出某个元素,然后再调用 string、attrs 等属性获取其对应节点的文本和属性。
6. 方法选择器
前面所讲的选择方法都是通过属性来选择的,这种方法非常快,但是如果进行比较复杂的选择的话,它就比较烦琐,不够灵活了。幸好,Beautiful Soup 还为我们提供了一些查询方法,比如 find_all 和 find 等,调用它们,然后传入相应的参数,就可以灵活查询了。
find_all
find_all,顾名思义,就是查询所有符合条件的元素,可以给它传入一些属性或文本来得到符合条件的元素,功能十分强大。
它的 API 如下:
find_all(name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs)
name
我们可以根据节点名来查询元素,下面我们用一个实例来感受一下:
html=''' <div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div> </div> ''' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.find_all(name='ul')) print(type(soup.find_all(name='ul')[0]))
运行结果:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul>, <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> </ul>] <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
这里我们调用了 find_all 方法,传入 name 参数,其参数值为 ul。也就是说,我们想要查询所有 ul 节点,返回结果是列表类型,长度为 2,每个元素依然都是 bs4.element.Tag 类型。
因为都是 Tag 类型,所以依然可以进行嵌套查询。还是同样的文本,这里查询出所有 ul 节点后,再继续查询其内部的 li 节点:
for ul in soup.find_all(name='ul'):print(ul.find_all(name='li'))
运行结果如下:
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>] [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
返回结果是列表类型,列表中的每个元素依然还是 Tag 类型。
接下来我们就可以遍历每个 li 获取它的文本了。
for ul in soup.find_all(name='ul'):print(ul.find_all(name='li'))for li in ul.find_all(name='li'):print(li.string)
运行结果如下:
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>] Foo Bar Jay [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>] Foo Bar
attrs
除了根据节点名查询,我们也可以传入一些属性来进行查询,我们用一个实例感受一下:
html='''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'id': 'list-1'}))
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'name': 'elements'}))
运行结果:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul>] [<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul>]
这里查询的时候传入的是 attrs 参数,参数的类型是字典类型。比如,要查询 id 为 list-1 的节点,可以传入 attrs={'id': 'list-1'} 的查询条件,得到的结果是列表形式,包含的内容就是符合 id 为 list-1 的所有节点。在上面的例子中,符合条件的元素个数是 1,所以结果是长度为 1 的列表。
对于一些常用的属性,比如 id 和 class 等,我们可以不用 attrs 来传递。比如,要查询 id 为 list-1 的节点,可以直接传入 id 这个参数。还是上面的文本,我们换一种方式来查询:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.find_all(id='list-1')) print(soup.find_all(class_='element'))
运行结果如下:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul>] [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>, <li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
这里直接传入 id='list-1',就可以查询 id 为 list-1 的节点元素了。而对于 class 来说,由于 class 在 Python 里是一个关键字,所以后面需要加一个下划线,即 class_='element',返回的结果依然还是 Tag 组成的列表。
text
text 参数可用来匹配节点的文本,传入的形式可以是字符串,可以是正则表达式对象,示例如下:
import re
html='''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-body"><a>Hello, this is a link</a><a>Hello, this is a link, too</a></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile('link')))
运行结果:
['Hello, this is a link', 'Hello, this is a link, too']
这里有两个 a 节点,其内部包含文本信息。这里在 find_all() 方法中传入 text 参数,该参数为正则表达式对象,结果返回所有匹配正则表达式的节点文本组成的列表。
find
除了 find_all 方法,还有 find 方法,只不过 find 方法返回的是单个元素,也就是第一个匹配的元素,而 find_all 返回的是所有匹配的元素组成的列表。示例如下:
html=''' <div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div> </div> ''' from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.find(name='ul')) print(type(soup.find(name='ul'))) print(soup.find(class_='list'))
运行结果:
<ul class="list" id="list-1"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'> <ul class="list" id="list-1"> <li class="element">Foo</li> <li class="element">Bar</li> <li class="element">Jay</li> </ul>
返回结果不再是列表形式,而是第一个匹配的节点元素,类型依然是 Tag 类型。
另外还有许多的查询方法,用法与前面介绍的 find_all、find 方法完全相同,只不过查询范围不同,在此做一下简单的说明。
find_parents 和 find_parent:前者返回所有祖先节点,后者返回直接父节点。
find_next_siblings 和 find_next_sibling:前者返回后面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回后面第一个兄弟节点。
find_previous_siblings 和 find_previous_sibling:前者返回前面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回前面第一个兄弟节点。
find_all_next 和 find_next:前者返回节点后所有符合条件的节点,后者返回第一个符合条件的节点。
find_all_previous 和 find_previous:前者返回节点前所有符合条件的节点,后者返回第一个符合条件的节点。
7. CSS 选择器
Beautiful Soup 还提供了另外一种选择器,那就是 CSS 选择器。如果对 Web 开发熟悉的话,那么对 CSS 选择器肯定也不陌生。如果不熟悉的话,可以参考 CSS 选择器参考手册 了解。
使用 CSS 选择器,只需要调用 select 方法,传入相应的 CSS 选择器即可,我们用一个实例来感受一下:
html='''
<div class="panel"><div class="panel-heading"><h4>Hello</h4></div><div class="panel-body"><ul class="list" id="list-1"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li><li class="element">Jay</li></ul><ul class="list list-small" id="list-2"><li class="element">Foo</li><li class="element">Bar</li></ul></div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.select('.panel .panel-heading'))
print(soup.select('ul li'))
print(soup.select('#list-2 .element'))
print(type(soup.select('ul')[0]))
运行结果如下:
[<div class="panel-heading"> <h4>Hello</h4> </div>] [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>, <li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>] [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>] <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
这里我们用了 3 次 CSS 选择器,返回的结果均是符合 CSS 选择器的节点组成的列表。例如,select('ul li') 则是选择所有 ul 节点下面的所有 li 节点,结果便是所有的 li 节点组成的列表。
最后一句我们打印输出了列表中元素的类型,可以看到类型依然是 Tag 类型。
嵌套选择
select 方法同样支持嵌套选择,例如我们先选择所有 ul 节点,再遍历每个 ul 节点选择其 li 节点,样例如下:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):print(ul.select('li'))
运行结果如下:
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>] [<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
可以看到正常输出了遍历每个 ul 节点之后,其下的所有 li 节点组成的列表。
获取属性
我们知道节点类型是 Tag 类型,所以获取属性还可以用原来的方法。仍然是上面的 HTML 文本,这里尝试获取每个 ul 节点的 id 属性:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):print(ul['id'])print(ul.attrs['id'])
运行结果如下:
list-1 list-1 list-2 list-2
可以看到直接传入中括号和属性名和通过 attrs 属性获取属性值都是可以成功的。
获取文本
要获取文本,当然也可以用前面所讲的 string 属性。此外,还有一个方法,那就是 get_text,示例如下:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for li in soup.select('li'):print('Get Text:', li.get_text())print('String:', li.string)
运行结果:
Get Text: Foo String: Foo Get Text: Bar String: Bar Get Text: Jay String: Jay Get Text: Foo String: Foo Get Text: Bar String: Bar
二者的效果是完全一致的,都可以获取到节点的文本值。
8. 结语
到此 BeautifulSoup 的使用介绍基本就结束了,最后做一下简单的总结:
-
推荐使用 LXML 解析库,必要时使用 html.parser。
-
节点选择筛选功能弱但是速度快。
-
建议使用 find、find_all 方法查询匹配单个结果或者多个结果。
-
如果对 CSS 选择器熟悉的话可以使用 select 选择法。
如果本文对你有帮助不要忘记点赞,收藏+关注!
相关文章:

Python爬虫 Beautiful Soup库详解#4
爬虫专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/WfCSx 使用 Beautiful Soup 前面介绍了正则表达式的相关用法,但是一旦正则表达式写的有问题,得到的可能就不是我们想要的结果了。而且对于一个网页来说,都有一定的特殊结构和层级关系,…...

Tkinter教程21:Listbox列表框+OptionMenu选项菜单+Combobox下拉列表框控件的使用+绑定事件
------------★Tkinter系列教程★------------ Tkinter教程21:Listbox列表框OptionMenu选项菜单Combobox下拉列表框控件的使用绑定事件 Tkinter教程20:treeview树视图组件,表格数据的插入与表头排序 Python教程57:tkinter中如何…...

Django中的SQL注入攻击防御策略
Django中的SQL注入攻击防御策略 SQL注入是一种常见的网络安全威胁,可以导致数据库被非法访问和数据泄露。本文将介绍在Django框架中防止SQL注入攻击的关键方法,包括使用参数化查询、使用ORM、进行输入验证和使用安全的编码实践。 SQL注入是一种利用应用程…...
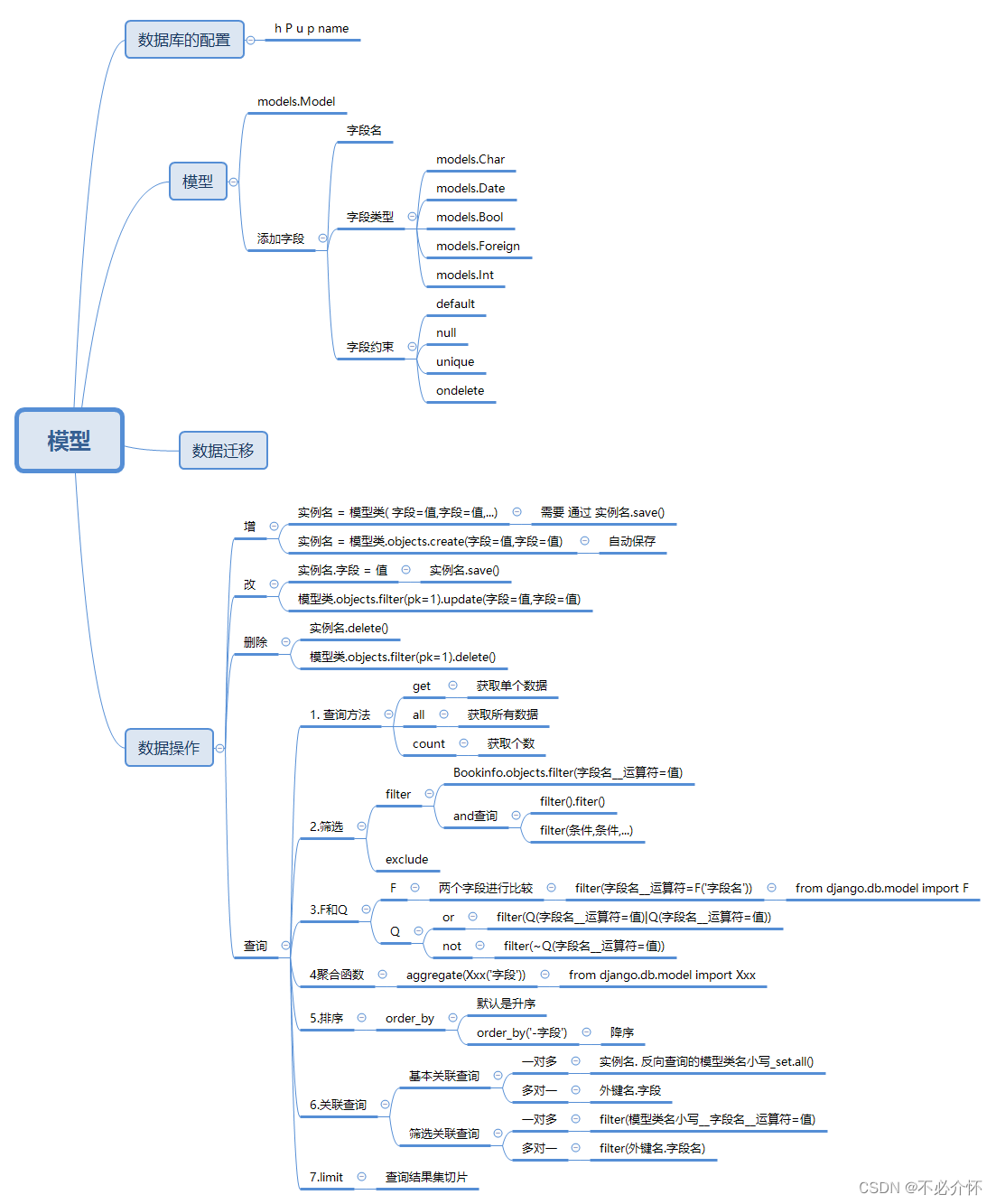
ORM模型类
模型 创建两个表 创建模型类 from django.db import models# Create your models here. class BookInfo(models.Model):name models.CharField(max_length10, uniqueTrue) # 书名pub_date models.DateField(nullTrue) # 发布时间read_count models.IntegerField(default…...
Java强训day14(选择题编程题)
选择题 编程题 题目1 import java.util.Scanner;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {//读入年月日(字符串形式读入)Scanner sc new Scanner(System.in);String s sc.nextLine();String[] ss s.split(" ");i…...
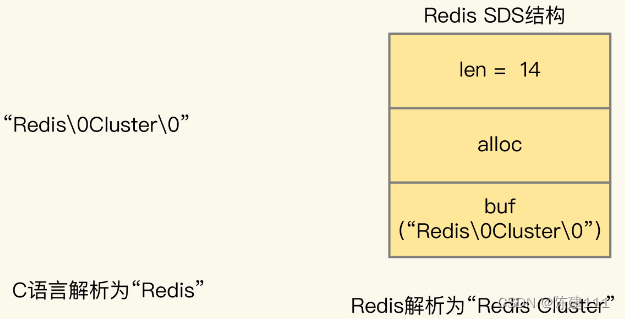
Redis核心技术与实战【学习笔记】 - 31.番外篇:Redis客户端如何与服务器端交换命令和数据
简述 Redis 使用 RESP 协议(Redis Serialzation Protocol)协议定义了客户端和服务器端交互的命令、数据的编码格式。在 Redis 2.0 版本中,RESP 协议正式称为客户端和服务器端的标准通信协议。从 Redis 2.0 到 Redis 5.0 ,RESP 协…...
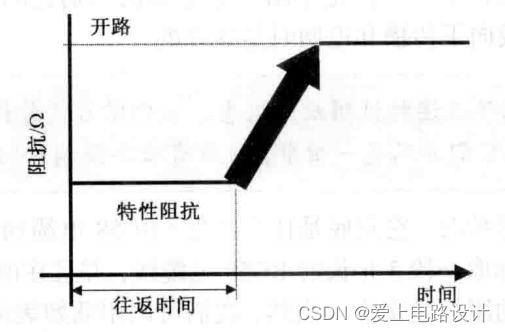
电缆线的阻抗50Ω,真正含义是什么?
当我们提到电缆线的阻抗时,它到底是什么意思?RG58电缆通常指的是50Ω的电缆线。它的真正含义是什么?假如取一段3英尺(0.9144米)长的RG58电缆线,并且在前端测量信号路径与返回路径之间的阻抗。那么测得的阻抗是多少?当然…...

校园团餐SAAS系统源码
## 项目介绍 校园团餐SAAS系统,是全新推出的一款轻量级、高性能、前后端分离的团餐系统,支持微信小程序 。 技术特点 > * 前后端完全分离 (互不依赖 开发效率高) > * 采用PHP8 (强类型严格模式) > * ThinkPHP8.0(轻量级PHP开发框…...

图数据库neo4j入门
neo4j 一、安装二、简单操作<一>、创建<二>、查询<三>、关系<四>、修改<五>、删除 三、常见报错<一>、默认的数据库密码是neo4j,打开浏览器http://localhost:7474登录不上,报错: Neo.ClientError.Security.Unauthorized: The client is un…...
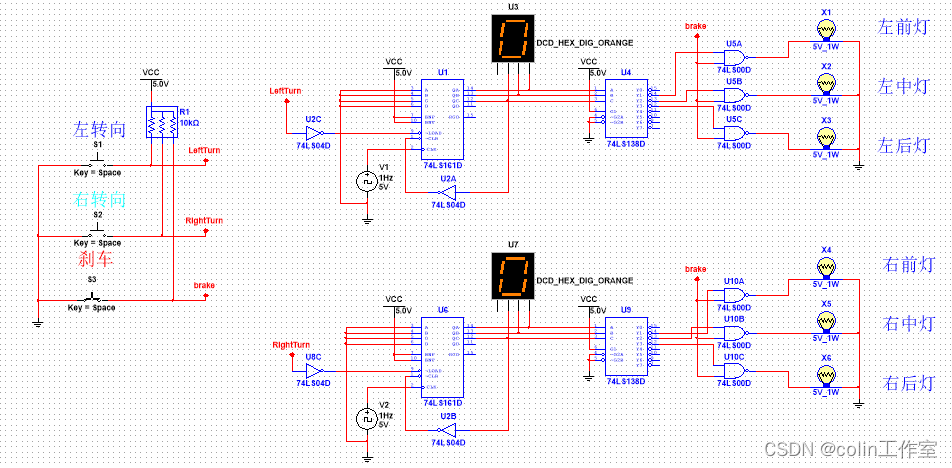
Multisim14.0仿真(五十五)汽车转向灯设计
一、功能描述: 左转向:左侧指示灯循环依次闪亮; 右转向:右侧指示灯循环依次闪亮; 刹车: 所有灯常亮; 正常: 所有灯熄灭。 二、主要芯片: 74LS161D 74LS04D 74…...

2402C++,C++的反向代理
原文 cinatra支持反向代理很简单,5行代码就可以了.先看一个简单的示例: #include "cinatra/coro_http_reverse_proxy.hpp" using namespace cinatra; int main() {reverse_proxy proxy_rr(10, 8091);proxy_rr.add_dest_host("127.0.0.1:9001");proxy_rr.a…...

[职场] 服务行业个人简历 #笔记#笔记
服务行业个人简历 服务员个人简历范文1 姓名: XXX国籍:中国 目前所在地:天河区民族:汉族 户口所在地:阳江身材: 160cm43kg 婚姻状况:未婚年龄: 21岁 培训认证:诚信徽章: 求职意向及工作经历 人才类型:普通求职 应聘职位: 工作年限:职称:初级 求职类型:全职可到职日期:随时 月薪…...

代码随想录算法训练营|day30
第七章 回溯算法 332.重新安排行程51.N皇后37.解数独代码随想录文章详解 332.重新安排行程 (1)参考 创建map存储src,[]dest映射关系,并对[]dest排序 每次取map中第一个dest访问,将其作为新的src,每访问一条src->destÿ…...

PHPExcel导出excel
PHPExcel下载地址 https://gitee.com/mirrors/phpexcelhttps://github.com/PHPOffice/PHPExcel 下载后目录结构 需要的文件如下图所示 将上面的PHPExcel文件夹和PHPExcel.php复制到你需要的地方 这是一个简单的示例代码 <?php$dir dirname(__FILE__); //require_once …...
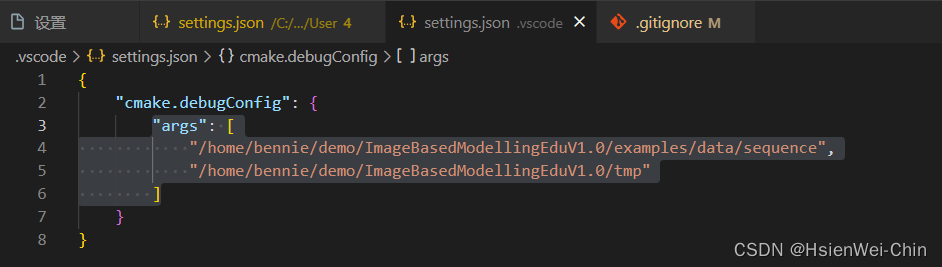
ubuntu系统下c++ cmakelist vscode debug(带传参的debug)的详细示例
c和cmake的debug,网上很多都需要配置launch.json,cpp.json啥的,记不住也太复杂了,我这里使用cmake插件带有的设置,各位可以看一看啊✌(不知不觉,竟然了解了vscode中配置文件的生效逻辑🤣) 克隆…...
聊聊JIT优化技术
🎬作者简介:大家好,我是小徐🥇☁️博客首页:CSDN主页小徐的博客🌄每日一句:好学而不勤非真好学者 📜 欢迎大家关注! ❤️ 我们知道,想要把高级语言转变成计算…...
LabVIEW动平衡测试与振动分析系统
LabVIEW动平衡测试与振动分析系统 介绍了利用LabVIEW软件和虚拟仪器技术开发一个动平衡测试与振动分析系统。该系统旨在提高旋转机械设备的测试精度和可靠性,通过精确测量和分析设备的振动数据,以识别和校正不平衡问题,从而保证机械设备的高…...

《低功耗方法学》翻译——附录B:UPF命令语法
附录B:UPF命令语法 本章介绍了文本中引用的所选UPF命令的语法。 节选自“统一电源格式(UPF)标准,1.0版”,经该Accellera许可复制。版权所有:(c)2006-2007。Accellera不声明或代表摘录材料的准确性或内容&…...

Leetcode 3027. Find the Number of Ways to Place People II
Leetcode 3027. Find the Number of Ways to Place People II 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3027. Find the Number of Ways to Place People II 1. 解题思路 这一题的话我也没想到啥特别好的思路,采用的纯粹是遍历剪枝的思路。 遍历的话好理解&…...
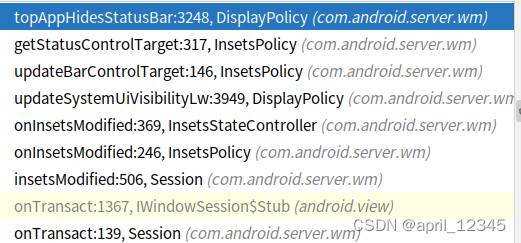
android inset 管理
目录 简介 Insets管理架构 Insets相关类图 app侧的类 WMS侧的类 inset show的流程 接口 流程 WMS侧确定InsetsSourceControl的流程 两个问题 窗口显示时不改变现有的inset状态 全屏窗口上的dialog 不显示statusbar问题 View 和 DecorView 设置insets信息 输入法显…...
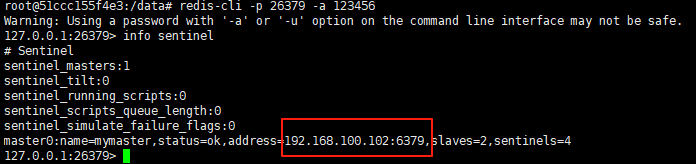
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

React 第五十五节 Router 中 useAsyncError的使用详解
前言 useAsyncError 是 React Router v6.4 引入的一个钩子,用于处理异步操作(如数据加载)中的错误。下面我将详细解释其用途并提供代码示例。 一、useAsyncError 用途 处理异步错误:捕获在 loader 或 action 中发生的异步错误替…...
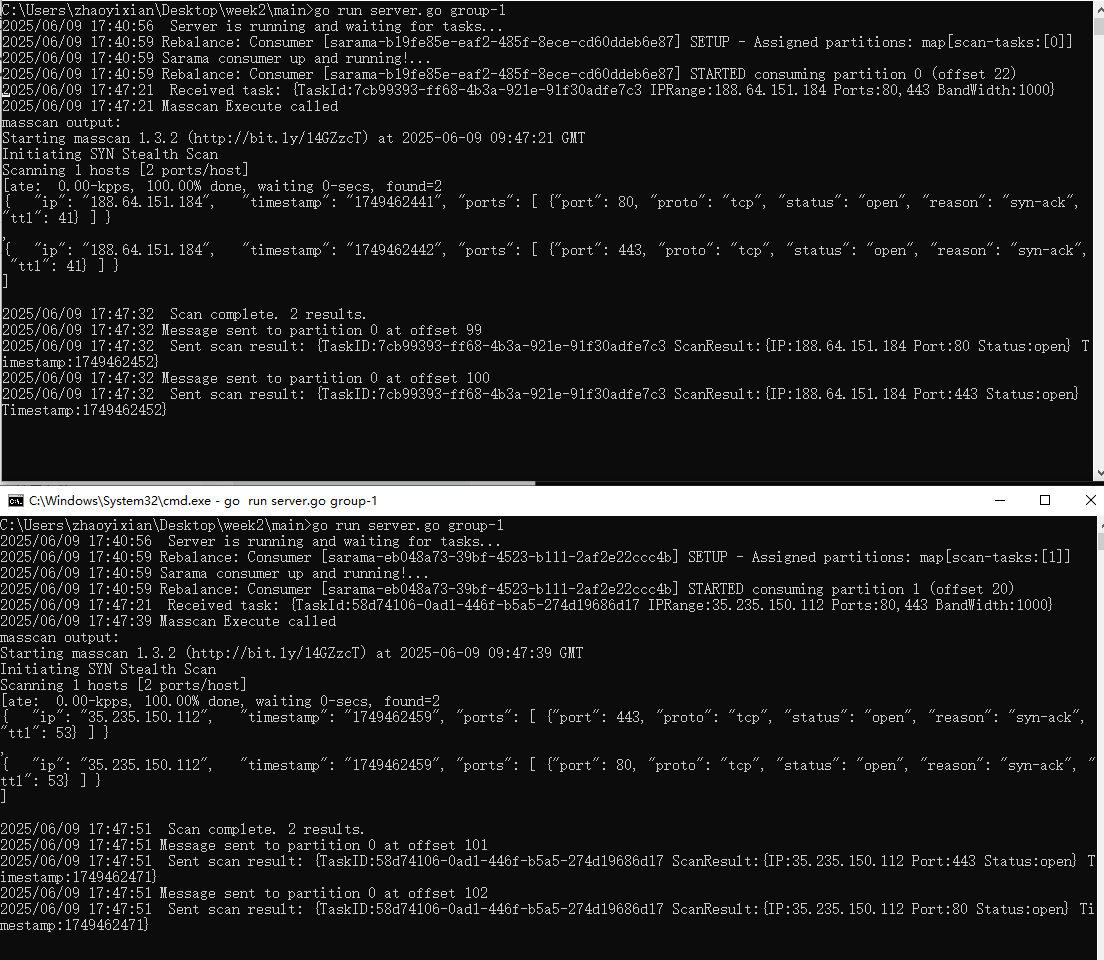
【kafka】Golang实现分布式Masscan任务调度系统
要求: 输出两个程序,一个命令行程序(命令行参数用flag)和一个服务端程序。 命令行程序支持通过命令行参数配置下发IP或IP段、端口、扫描带宽,然后将消息推送到kafka里面。 服务端程序: 从kafka消费者接收…...
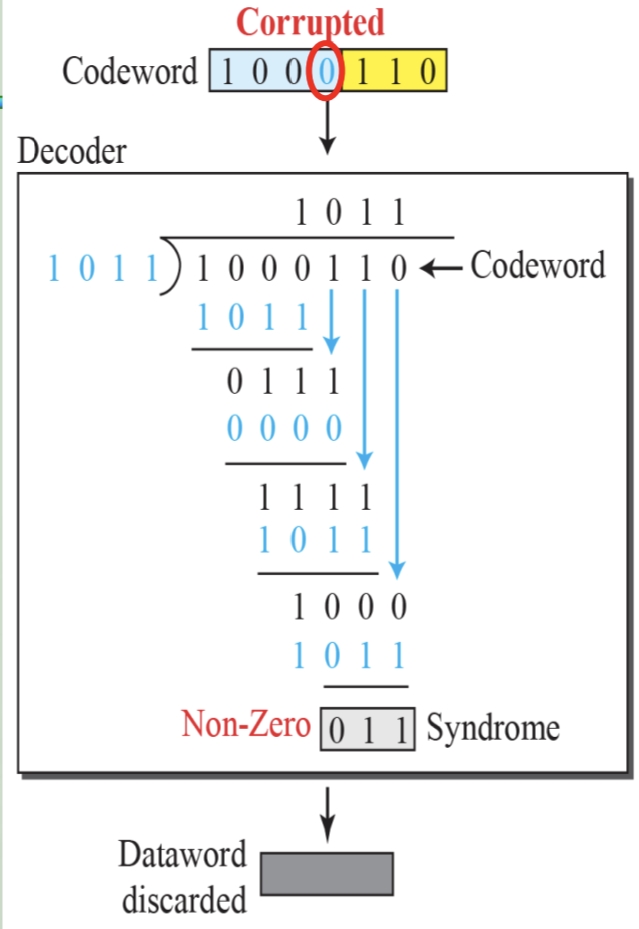
循环冗余码校验CRC码 算法步骤+详细实例计算
通信过程:(白话解释) 我们将原始待发送的消息称为 M M M,依据发送接收消息双方约定的生成多项式 G ( x ) G(x) G(x)(意思就是 G ( x ) G(x) G(x) 是已知的)࿰…...
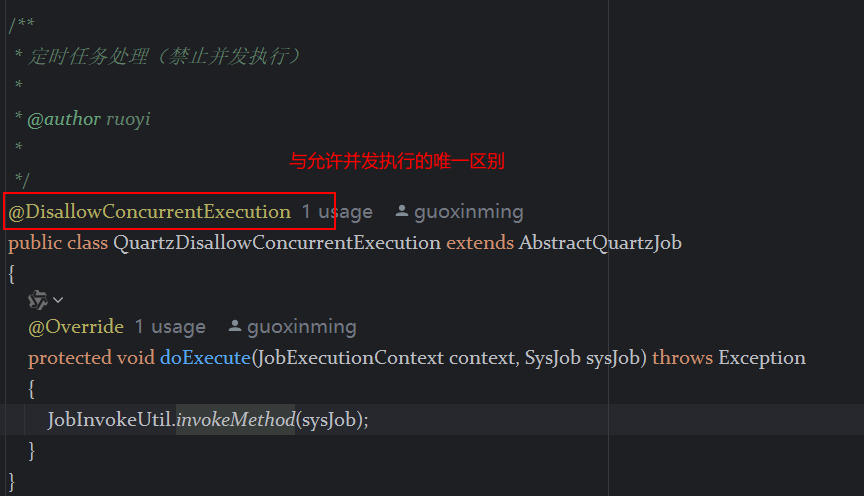
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...

376. Wiggle Subsequence
376. Wiggle Subsequence 代码 class Solution { public:int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int res 1;int prediff 0;int curdiff 0;for(int i 0;i < n-1;i){curdiff nums[i1] - nums[i];if( (prediff > 0 && curdif…...
Mac软件卸载指南,简单易懂!
刚和Adobe分手,它却总在Library里给你写"回忆录"?卸载的Final Cut Pro像电子幽灵般阴魂不散?总是会有残留文件,别慌!这份Mac软件卸载指南,将用最硬核的方式教你"数字分手术"࿰…...
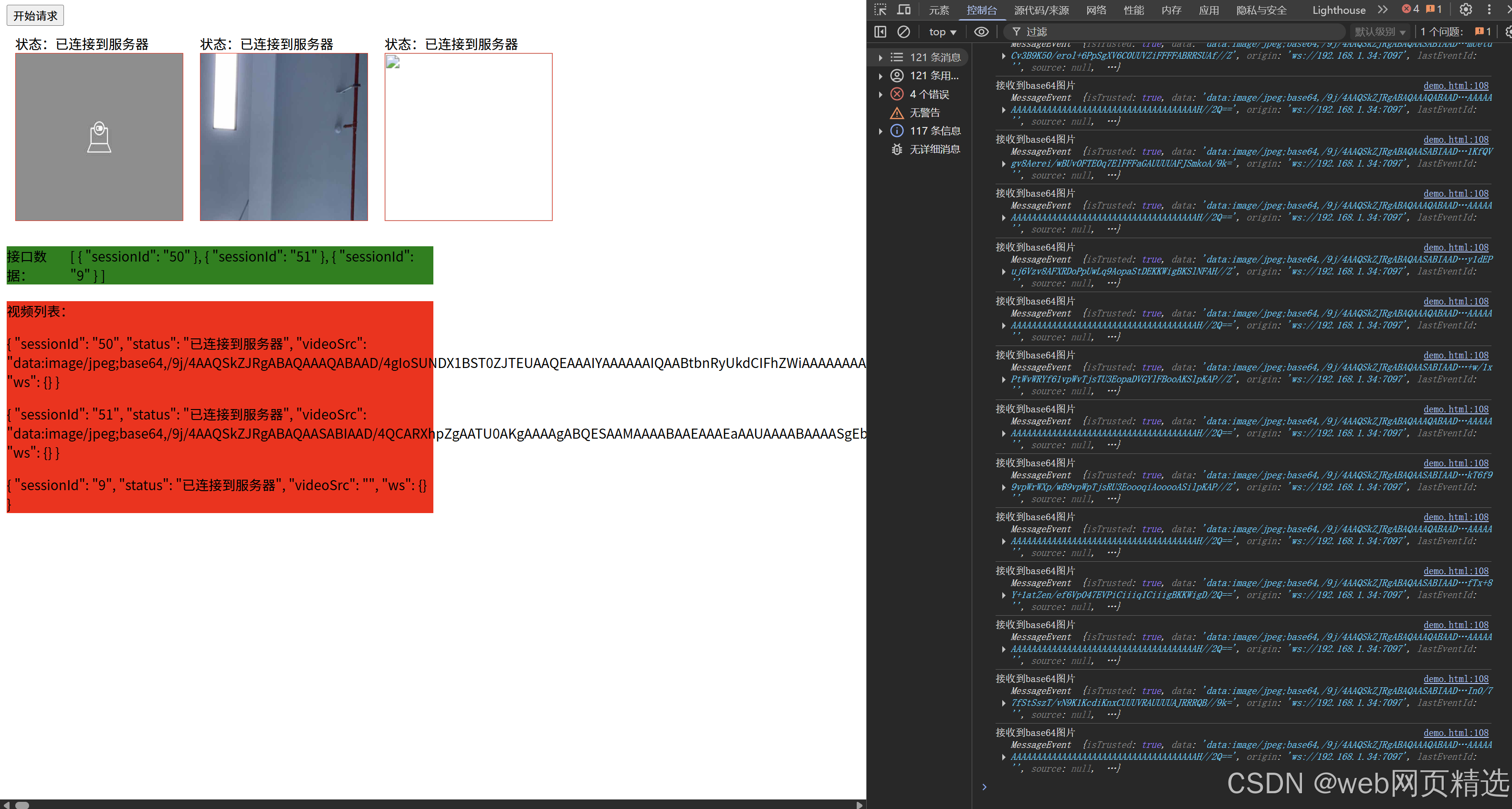
uniapp微信小程序视频实时流+pc端预览方案
方案类型技术实现是否免费优点缺点适用场景延迟范围开发复杂度WebSocket图片帧定时拍照Base64传输✅ 完全免费无需服务器 纯前端实现高延迟高流量 帧率极低个人demo测试 超低频监控500ms-2s⭐⭐RTMP推流TRTC/即构SDK推流❌ 付费方案 (部分有免费额度&#x…...
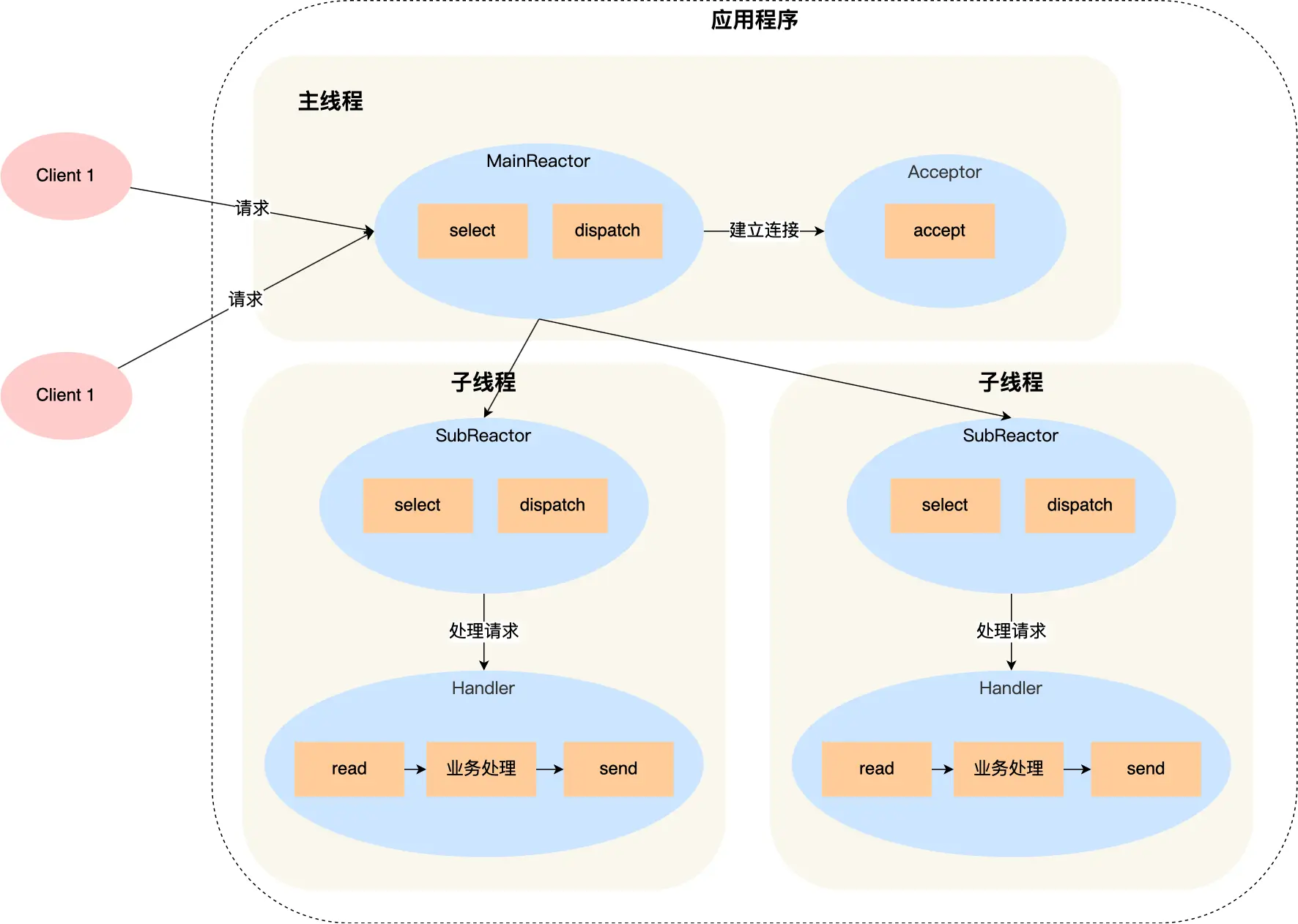
select、poll、epoll 与 Reactor 模式
在高并发网络编程领域,高效处理大量连接和 I/O 事件是系统性能的关键。select、poll、epoll 作为 I/O 多路复用技术的代表,以及基于它们实现的 Reactor 模式,为开发者提供了强大的工具。本文将深入探讨这些技术的底层原理、优缺点。 一、I…...

听写流程自动化实践,轻量级教育辅助
随着智能教育工具的发展,越来越多的传统学习方式正在被数字化、自动化所优化。听写作为语文、英语等学科中重要的基础训练形式,也迎来了更高效的解决方案。 这是一款轻量但功能强大的听写辅助工具。它是基于本地词库与可选在线语音引擎构建,…...
