算法-3-基本的数据结构
单双链表
1.单链表双链表如何反转
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class Code01_ReverseList {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {value = data;}}public static class DoubleNode {public int value;public DoubleNode last;public DoubleNode next;public DoubleNode(int data) {value = data;}}// head// a -> b -> c -> null// c -> b -> a -> nullpublic static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) {Node pre = null;Node next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {DoubleNode pre = null;DoubleNode next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;head.last = next;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static Node testReverseLinkedList(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {list.add(head);head = head.next;}list.get(0).next = null;int N = list.size();for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {list.get(i).next = list.get(i - 1);}return list.get(N - 1);}public static DoubleNode testReverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ArrayList<DoubleNode> list = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {list.add(head);head = head.next;}list.get(0).next = null;DoubleNode pre = list.get(0);int N = list.size();for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {DoubleNode cur = list.get(i);cur.last = null;cur.next = pre;pre.last = cur;pre = cur;}return list.get(N - 1);}// for testpublic static Node generateRandomLinkedList(int len, int value) {int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));if (size == 0) {return null;}size--;Node head = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));Node pre = head;while (size != 0) {Node cur = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));pre.next = cur;pre = cur;size--;}return head;}// for testpublic static DoubleNode generateRandomDoubleList(int len, int value) {int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));if (size == 0) {return null;}size--;DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));DoubleNode pre = head;while (size != 0) {DoubleNode cur = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));pre.next = cur;cur.last = pre;pre = cur;size--;}return head;}// for testpublic static List<Integer> getLinkedListOriginOrder(Node head) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {ans.add(head.value);head = head.next;}return ans;}// for testpublic static boolean checkLinkedListReverse(List<Integer> origin, Node head) {for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) {return false;}head = head.next;}return true;}// for testpublic static List<Integer> getDoubleListOriginOrder(DoubleNode head) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {ans.add(head.value);head = head.next;}return ans;}// for testpublic static boolean checkDoubleListReverse(List<Integer> origin, DoubleNode head) {DoubleNode end = null;for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) {return false;}end = head;head = head.next;}for (int i = 0; i < origin.size(); i++) {if (!origin.get(i).equals(end.value)) {return false;}end = end.last;}return true;}// for testpublic static void main(String[] args) {int len = 50;int value = 100;int testTime = 100000;System.out.println("test begin!");for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {Node node1 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value);List<Integer> list1 = getLinkedListOriginOrder(node1);node1 = reverseLinkedList(node1);if (!checkLinkedListReverse(list1, node1)) {System.out.println("Oops1!");}Node node2 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value);List<Integer> list2 = getLinkedListOriginOrder(node2);node2 = testReverseLinkedList(node2);if (!checkLinkedListReverse(list2, node2)) {System.out.println("Oops2!");}DoubleNode node3 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value);List<Integer> list3 = getDoubleListOriginOrder(node3);node3 = reverseDoubleList(node3);if (!checkDoubleListReverse(list3, node3)) {System.out.println("Oops3!");}DoubleNode node4 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value);List<Integer> list4 = getDoubleListOriginOrder(node4);node4 = reverseDoubleList(node4);if (!checkDoubleListReverse(list4, node4)) {System.out.println("Oops4!");}}System.out.println("test finish!");}}2.把定值都删除掉
是n就跳过,不是n next指向
public class Code02_DeleteGivenValue {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}// head = removeValue(head, 2);public static Node removeValue(Node head, int num) {// head来到第一个不需要删的位置while (head != null) {if (head.value != num) {break;}head = head.next;}// 1 ) head == null// 2 ) head != nullNode pre = head;Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.value == num) {pre.next = cur.next;} else {pre = cur;}cur = cur.next;}return head;}}
队列跟栈
双链表实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;public class Code03_DoubleEndsQueueToStackAndQueue {public static class Node<T> {public T value;public Node<T> last;public Node<T> next;public Node(T data) {value = data;}}public static class DoubleEndsQueue<T> {public Node<T> head;public Node<T> tail;public void addFromHead(T value) {Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);if (head == null) {head = cur;tail = cur;} else {cur.next = head;head.last = cur;head = cur;}}public void addFromBottom(T value) {Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);if (head == null) {head = cur;tail = cur;} else {cur.last = tail;tail.next = cur;tail = cur;}}public T popFromHead() {if (head == null) {return null;}Node<T> cur = head;if (head == tail) {head = null;tail = null;} else {head = head.next;cur.next = null;head.last = null;}return cur.value;}public T popFromBottom() {if (head == null) {return null;}Node<T> cur = tail;if (head == tail) {head = null;tail = null;} else {tail = tail.last;tail.next = null;cur.last = null;}return cur.value;}public boolean isEmpty() {return head == null;}}public static class MyStack<T> {private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;public MyStack() {queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();}public void push(T value) {queue.addFromHead(value);}public T pop() {return queue.popFromHead();}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static class MyQueue<T> {private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;public MyQueue() {queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();}public void push(T value) {queue.addFromHead(value);}public T poll() {return queue.popFromBottom();}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static boolean isEqual(Integer o1, Integer o2) {if (o1 == null && o2 != null) {return false;}if (o1 != null && o2 == null) {return false;}if (o1 == null && o2 == null) {return true;}return o1.equals(o2);}public static void main(String[] args) {int oneTestDataNum = 100;int value = 10000;int testTimes = 100000;for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>();MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>();Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();for (int j = 0; j < oneTestDataNum; j++) {int nums = (int) (Math.random() * value);if (stack.isEmpty()) {myStack.push(nums);stack.push(nums);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.5) {myStack.push(nums);stack.push(nums);} else {if (!isEqual(myStack.pop(), stack.pop())) {System.out.println("oops!");}}}int numq = (int) (Math.random() * value);if (stack.isEmpty()) {myQueue.push(numq);queue.offer(numq);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.5) {myQueue.push(numq);queue.offer(numq);} else {if (!isEqual(myQueue.poll(), queue.poll())) {System.out.println("oops!");}}}}}System.out.println("finish!");}}
数组实现
public class Code04_RingArray {public static class MyQueue {private int[] arr;private int pushi;// endprivate int polli;// beginprivate int size;private final int limit;public MyQueue(int limit) {arr = new int[limit];pushi = 0;polli = 0;size = 0;this.limit = limit;}public void push(int value) {if (size == limit) {throw new RuntimeException("队列满了,不能再加了");}size++;arr[pushi] = value;pushi = nextIndex(pushi);}public int pop() {if (size == 0) {throw new RuntimeException("队列空了,不能再拿了");}size--;int ans = arr[polli];polli = nextIndex(polli);return ans;}public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}// 如果现在的下标是i,返回下一个位置private int nextIndex(int i) {return i < limit - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;}}}
实现一个特殊的栈,在基本功能基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的功能
1.pop,push,getMin,操作的时间复杂度都是O(1)
2.设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构
同步压入,同步弹出
import java.util.Stack;public class Code05_GetMinStack {public static class MyStack1 {private Stack<Integer> stackData;private Stack<Integer> stackMin;public MyStack1() {this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();}public void push(int newNum) {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else if (newNum <= this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);}this.stackData.push(newNum);}public int pop() {if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}int value = this.stackData.pop();if (value == this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.pop();}return value;}public int getmin() {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}return this.stackMin.peek();}}public static class MyStack2 {private Stack<Integer> stackData;private Stack<Integer> stackMin;public MyStack2() {this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();}public void push(int newNum) {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else if (newNum < this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else {int newMin = this.stackMin.peek();this.stackMin.push(newMin);}this.stackData.push(newNum);}public int pop() {if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}this.stackMin.pop();return this.stackData.pop();}public int getmin() {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}return this.stackMin.peek();}}public static void main(String[] args) {MyStack1 stack1 = new MyStack1();stack1.push(3);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());stack1.push(4);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());stack1.push(1);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());System.out.println(stack1.pop());System.out.println(stack1.getmin());System.out.println("=============");MyStack1 stack2 = new MyStack1();stack2.push(3);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());stack2.push(4);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());stack2.push(1);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());System.out.println(stack2.pop());System.out.println(stack2.getmin());}}
如何使用栈结构实现队列结构
import java.util.Stack;public class Code06_TwoStacksImplementQueue {public static class TwoStacksQueue {public Stack<Integer> stackPush;public Stack<Integer> stackPop;public TwoStacksQueue() {stackPush = new Stack<Integer>();stackPop = new Stack<Integer>();}// push栈向pop栈倒入数据private void pushToPop() {if (stackPop.empty()) {while (!stackPush.empty()) {stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());}}}public void add(int pushInt) {stackPush.push(pushInt);pushToPop();}public int poll() {if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");}pushToPop();return stackPop.pop();}public int peek() {if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");}pushToPop();return stackPop.peek();}}public static void main(String[] args) {TwoStacksQueue test = new TwoStacksQueue();test.add(1);test.add(2);test.add(3);System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());}}
如何使用队列结构实现栈结构
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;public class Code07_TwoQueueImplementStack {public static class TwoQueueStack<T> {public Queue<T> queue;public Queue<T> help;public TwoQueueStack() {queue = new LinkedList<>();help = new LinkedList<>();}public void push(T value) {queue.offer(value);}public T poll() {while (queue.size() > 1) {help.offer(queue.poll());}T ans = queue.poll();Queue<T> tmp = queue;queue = help;help = tmp;return ans;}public T peek() {while (queue.size() > 1) {help.offer(queue.poll());}T ans = queue.poll();help.offer(ans);Queue<T> tmp = queue;queue = help;help = tmp;return ans;}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("test begin");TwoQueueStack<Integer> myStack = new TwoQueueStack<>();Stack<Integer> test = new Stack<>();int testTime = 1000000;int max = 1000000;for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {if (myStack.isEmpty()) {if (!test.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("Oops");}int num = (int) (Math.random() * max);myStack.push(num);test.push(num);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.25) {int num = (int) (Math.random() * max);myStack.push(num);test.push(num);} else if (Math.random() < 0.5) {if (!myStack.peek().equals(test.peek())) {System.out.println("Oops");}} else if (Math.random() < 0.75) {if (!myStack.poll().equals(test.pop())) {System.out.println("Oops");}} else {if (myStack.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("Oops");}}}}System.out.println("test finish!");}}
Master 公式求递推的时间复杂度
前提,子问题规模一致,(比如,子问题是分两个二分之N区间分别求最大值,可以Master,若分为三分之N那就不行)
公式:T(N)=a*T(N/b)+O(N的d次方)
得到abd之后
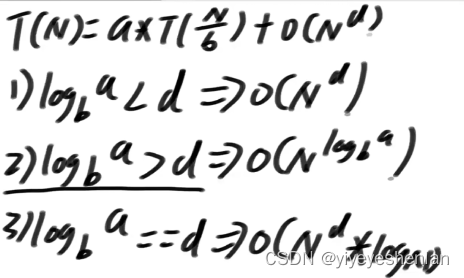
求最大值
public class Code08_GetMax {// 求arr中的最大值public static int getMax(int[] arr) {return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);}// arr[L..R]范围上求最大值 L ... R Npublic static int process(int[] arr, int L, int R) {// arr[L..R]范围上只有一个数,直接返回,base caseif (L == R) { return arr[L];}// L...R 不只一个数// mid = (L + R) / 2int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1); // 中点 1int leftMax = process(arr, L, mid);int rightMax = process(arr, mid + 1, R);return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax);}}
哈希
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.TreeMap;public class HashMapAndSortedMap {public static class Node {public int value;public Node(int v) {value = v;}}public static class Zuo {public int value;public Zuo(int v) {value = v;}}public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap<Integer, String> test = new HashMap<>();Integer a = 19000000;Integer b = 19000000;System.out.println(a == b);test.put(a, "我是3");System.out.println(test.containsKey(b));Zuo z1 = new Zuo(1);Zuo z2 = new Zuo(1);HashMap<Zuo, String> test2 = new HashMap<>();test2.put(z1, "我是z1");System.out.println(test2.containsKey(z2));// UnSortedMapHashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(1000000, "我是1000000");map.put(2, "我是2");map.put(3, "我是3");map.put(4, "我是4");map.put(5, "我是5");map.put(6, "我是6");map.put(1000000, "我是1000001");System.out.println(map.containsKey(1));System.out.println(map.containsKey(10));System.out.println(map.get(4));System.out.println(map.get(10));map.put(4, "他是4");System.out.println(map.get(4));map.remove(4);System.out.println(map.get(4));// keyHashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();set.add("abc");set.contains("abc");set.remove("abc");// 哈希表,增、删、改、查,在使用时,O(1)System.out.println("=====================");Integer c = 100000;Integer d = 100000;System.out.println(c.equals(d));Integer e = 127; // - 128 ~ 127Integer f = 127;System.out.println(e == f);HashMap<Node, String> map2 = new HashMap<>();Node node1 = new Node(1);Node node2 = node1;map2.put(node1, "我是node1");map2.put(node2, "我是node1");System.out.println(map2.size());System.out.println("======================");// TreeMap 有序表:接口名// 红黑树、avl、sb树、跳表// O(logN)System.out.println("有序表测试开始");TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();treeMap.put(3, "我是3");treeMap.put(4, "我是4");treeMap.put(8, "我是8");treeMap.put(5, "我是5");treeMap.put(7, "我是7");treeMap.put(1, "我是1");treeMap.put(2, "我是2");System.out.println(treeMap.containsKey(1));System.out.println(treeMap.containsKey(10));System.out.println(treeMap.get(4));System.out.println(treeMap.get(10));treeMap.put(4, "他是4");System.out.println(treeMap.get(4));// treeMap.remove(4);System.out.println(treeMap.get(4));System.out.println("新鲜:");System.out.println(treeMap.firstKey());System.out.println(treeMap.lastKey());// <= 4System.out.println(treeMap.floorKey(4));// >= 4System.out.println(treeMap.ceilingKey(4));// O(logN)}}
相关文章:
算法-3-基本的数据结构
单双链表 1.单链表双链表如何反转 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;public class Code01_ReverseList {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {value data;}}public static class DoubleNode {public int…...

探秘Java反射:灵活编程的利器
前言 大家好,我是chowley,不知道大家在学习Java的过程中有没有听过反射的概念,今天我来总结一下我心中的Java反射。 在Java编程中,反射是一种强大的工具,它允许程序在运行时检查和操作类、方法、属性等,而…...

记录 | ubuntu pyqt5 pycharm配置
Ubuntu16.04pycharmpyqt5安装与配置_ubuntu pycharm pyqt5-CSDN博客pycharm激活码 6ZUMD7WWWU-eyJsaWNlbnNlSWQiOiI2WlVNRDdXV1dVIiwibGljZW5zZWVOYW1lIjoiSmV0cyBHcm91cCIsImFzc2lnbmVlTmFtZSI6IiIsImFzc2lnbmVlRW1haWwiOiIiLCJsaWNlbnNlUmVzdHJpY3Rpb24iOiIiLCJjaGVja0NvbmN…...
ESP32学习(1)——环境搭建
使用的ESP32板子如下图所示 它可以用Arduino 软件,基于C语言开发。但是,在这里,我是用Thonny软件,基于micro_python对其进行开发。 1.安装Thonny Thonny的软件安装包,可以去它官网上下载。Thonny, Python IDE for begi…...

Attention Is All Your Need论文笔记
论文解决了什么问题? 提出了一个新的简单网络架构——transformer,仅仅是基于注意力机制,完全免去递推和卷积,使得神经网络训练地速度极大地提高。 We propose a new simple network architecture, the Transformer, based sole…...
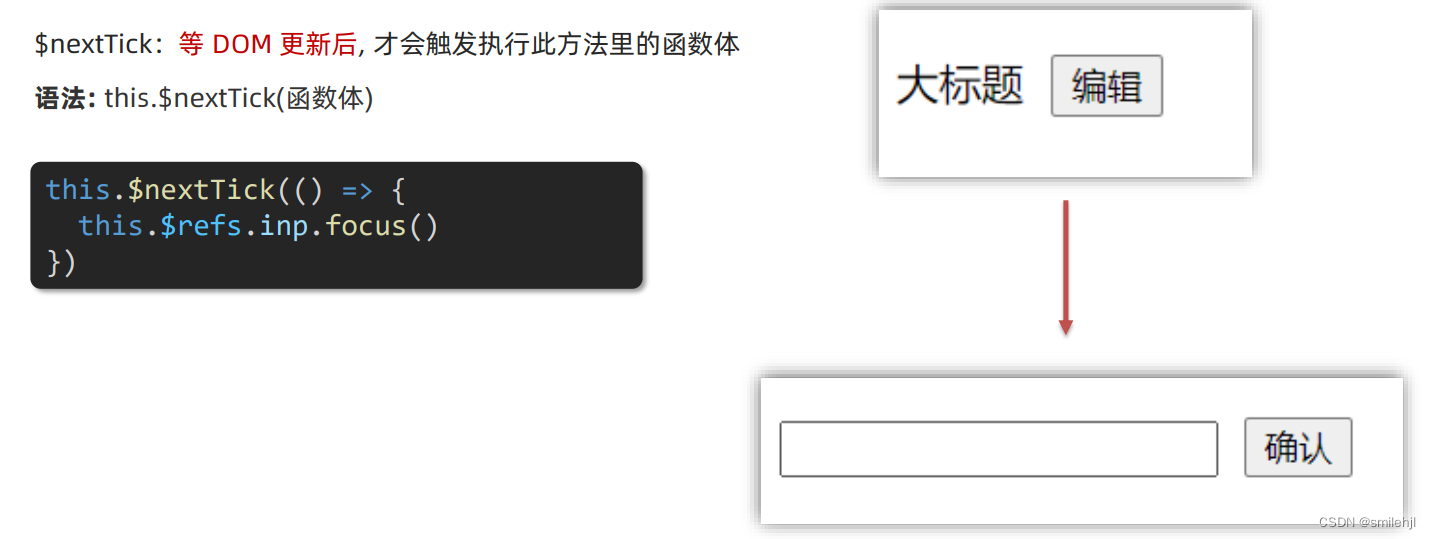
vue-进阶语法(四)
目录 v-model原理 v-model应用于组件 sync修饰符 ref 和 $refs(重点) $nextTick v-model原理 原理:v-model本质上是一个语法糖。例如应用在输入框上,就是 value属性 和 input事件 的合写。 作用:提供数据的双向…...
CGAL::2D Arrangements-7
7 几何Traits 几何Traits封装了几何实体的定义以及处理这些几何实体的几何predicates和构造的实现,供Arrangement_on_surface_2类模板和其他周边模块使用。应用于Arrangement的各种算法所确定的最小要求被组织在精细几何特征概念的层次中。每个概念列出的需求只包括…...

linux系统下vscode portable版本的rust环境搭建004:rust
目的:希望在获得一个新的系统之后,以最简便快速的方式搭配一个rust的编程环境命令在线安装只执行这句就行了 :curl --proto https --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh,因为是要portable安装所以按照以下的方式执行。 下载…...

从汇编角度解释线程间互斥-mutex互斥锁与lock_guard的使用
多线程并发的竞态问题 我们创建三个线程同时进行购票,代码如下 #include<iostream> #include<thread> #include<list> using namespace std; //总票数 int ticketCount100; //售票线程 void sellTicket(int idx) {while(ticketCount>0){cou…...
)
高程 | 多态性(c++)
文章目录 📚多态📚运算符重载🐇定义🐇规则🐇友元运算符重载函数🐇成员运算符重载函数 📚虚函数📚纯虚函数和抽象类 📚多态 多态:同样的消息被不同类型的对象…...
LV.23 D2 开发环境搭建及平台介绍 学习笔记
一、Keil MDK-ARM简介及安装 Keil MDK,也称MDK-ARM,Realview MDK (Microcontroller Development Kit)等。目前Keil MDK 由三家国内代理商提供技术支持和相关服务。 MDK-ARM软件为基于Cortex-M、Cortex-R4、ARM7、ARM9处理器设备…...

[uniapp生命周期]详细讲解uniapp中那些属于vue生命周期,那些属于uniapp独有的生命周期,以及这中间的区别 相关的内容和api 代码注释
目录 1. Vue.js生命周期函数2.Vue生命周期函数代码beforeCreatecreatedbeforeMountmountedbeforeUpdateupdatedbeforeDestroydestroyed$nextTick$forceUpdate$destroy 3. UniApp独有的生命周期函数onLaunchonShowonHideonError 4.总结 在UniApp中,除了Vue.js的生命周…...

【动态规划】【记忆化搜索】【状态压缩】1681. 最小不兼容性
作者推荐 【数位dp】【动态规划】【状态压缩】【推荐】1012. 至少有 1 位重复的数字 本文涉及知识点 动态规划汇总 状态压缩 记忆化搜索 1681. 最小不兼容性 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k 。你需要将这个数组划分到 k 个相同大小的子集中,使得同一…...
JVM-类加载器 双亲委派机制
申明:文章内容是本人学习极客时间课程所写,文字和图片基本来源于课程资料,在某些地方会插入一点自己的理解,未用于商业用途,侵删。 什么是JVM JVM是Java Virtual Machine(Java虚拟机)的缩写&a…...

vue axios 请求后端无法传参问题
vue请求后端无法传参问题 问题描述处理过程总结 问题描述 在学习vue时,使用axios调用后端,发现无法把参数正确传到后端,现象如下: 使用vue发起请求,浏览器上已经有传参,但是后端没接收到对应的用户名密码&…...

打印最小公倍数
打印最小公倍数 题目描述: 输入2个整数m和n,计算m和n的最小公倍数,并打印出结果 测试1: 输入:18 24 输出:72 测试2: 输入:18 6 输出:18解法思路: 最小公倍数是指两个…...

[AIGC] Java 和 Kotlin 的区别
好的,我还是以“萌萌哒小码农”的身份继续回答您的问题。 Java 和 Kotlin 是两种不同的编程语言,它们有许多共同点,但也有一些重要的区别。以下是一些常见的 Java 和 Kotlin 的区别: 语法 Kotlin 的语法比 Java 简洁得多&#…...
蓝桥杯电子类单片机提升一——超声波测距
前言 单片机资源数据包_2023 一、超声波测距原理 二、超声波测距的应用 1.超声波的发射 2.单片机知识补充:定时器 3.超声波的接收与计时 4.距离的计算 1)定时器1为16位自动重载+1T11.0592MHz 2)定时器1为16位自动重载&am…...

前端架构: 脚手架开发流程中的难点梳理
脚手架的开发流程 1 )开发流程 创建 npm 项目创建脚手架入口文件,最上方添加: #!/usr/bin/env node 配置 package.json, 添加 bin 属性编写脚手架代码将脚手架发布到 npm 2 )使用流程 安装脚手架 npm install -g your-own-cli …...

django中配置使用websocket
Django 默认情况下并不支持 WebSocket,但你可以通过集成第三方库如 channels 来实现 WebSocket 功能。channels 是一个 Django 应用,它提供了对 WebSocket、HTTP2 和其他协议的支持。 下面是如何在 Django 项目中使用 WebSocket 的基本步骤:…...

MySQL 隔离级别:脏读、幻读及不可重复读的原理与示例
一、MySQL 隔离级别 MySQL 提供了四种隔离级别,用于控制事务之间的并发访问以及数据的可见性,不同隔离级别对脏读、幻读、不可重复读这几种并发数据问题有着不同的处理方式,具体如下: 隔离级别脏读不可重复读幻读性能特点及锁机制读未提交(READ UNCOMMITTED)允许出现允许…...

基于服务器使用 apt 安装、配置 Nginx
🧾 一、查看可安装的 Nginx 版本 首先,你可以运行以下命令查看可用版本: apt-cache madison nginx-core输出示例: nginx-core | 1.18.0-6ubuntu14.6 | http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 Packages ng…...
2.Vue编写一个app
1.src中重要的组成 1.1main.ts // 引入createApp用于创建应用 import { createApp } from "vue"; // 引用App根组件 import App from ./App.vue;createApp(App).mount(#app)1.2 App.vue 其中要写三种标签 <template> <!--html--> </template>…...

什么是EULA和DPA
文章目录 EULA(End User License Agreement)DPA(Data Protection Agreement)一、定义与背景二、核心内容三、法律效力与责任四、实际应用与意义 EULA(End User License Agreement) 定义: EULA即…...
用docker来安装部署freeswitch记录
今天刚才测试一个callcenter的项目,所以尝试安装freeswitch 1、使用轩辕镜像 - 中国开发者首选的专业 Docker 镜像加速服务平台 编辑下面/etc/docker/daemon.json文件为 {"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.xuanyuan.me"] }同时可以进入轩…...

【C++从零实现Json-Rpc框架】第六弹 —— 服务端模块划分
一、项目背景回顾 前五弹完成了Json-Rpc协议解析、请求处理、客户端调用等基础模块搭建。 本弹重点聚焦于服务端的模块划分与架构设计,提升代码结构的可维护性与扩展性。 二、服务端模块设计目标 高内聚低耦合:各模块职责清晰,便于独立开发…...

【Oracle】分区表
个人主页:Guiat 归属专栏:Oracle 文章目录 1. 分区表基础概述1.1 分区表的概念与优势1.2 分区类型概览1.3 分区表的工作原理 2. 范围分区 (RANGE Partitioning)2.1 基础范围分区2.1.1 按日期范围分区2.1.2 按数值范围分区 2.2 间隔分区 (INTERVAL Partit…...

Linux nano命令的基本使用
参考资料 GNU nanoを使いこなすnano基础 目录 一. 简介二. 文件打开2.1 普通方式打开文件2.2 只读方式打开文件 三. 文件查看3.1 打开文件时,显示行号3.2 翻页查看 四. 文件编辑4.1 Ctrl K 复制 和 Ctrl U 粘贴4.2 Alt/Esc U 撤回 五. 文件保存与退出5.1 Ctrl …...
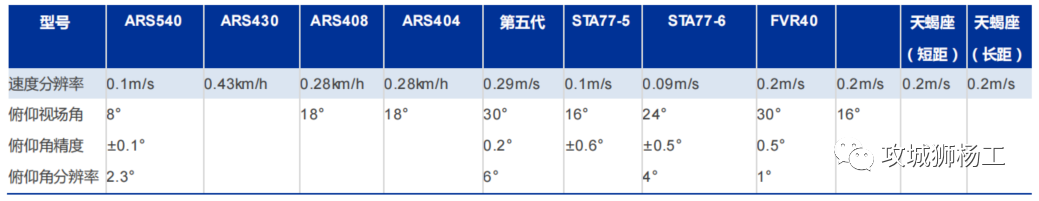
毫米波雷达基础理论(3D+4D)
3D、4D毫米波雷达基础知识及厂商选型 PreView : https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bQkju4r6med7I3TBGJI_bQ 1. FMCW毫米波雷达基础知识 主要参考博文: 一文入门汽车毫米波雷达基本原理 :https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_EN7A5lKcz2Eh8dLnjE19w 毫米波雷达基础…...

【免费数据】2005-2019年我国272个地级市的旅游竞争力多指标数据(33个指标)
旅游业是一个城市的重要产业构成。旅游竞争力是一个城市竞争力的重要构成部分。一个城市的旅游竞争力反映了其在旅游市场竞争中的比较优势。 今日我们分享的是2005-2019年我国272个地级市的旅游竞争力多指标数据!该数据集源自2025年4月发表于《地理学报》的论文成果…...
