深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数——paddle.to_tensor
分类目录:《深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数》总目录
相关文章:
· 深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数——paddle.Tensor
· 深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数——paddle.to_tensor
通过已知的data来创建一个Tensor,Tensor类型为paddle.Tensor。data可以是scalar、tuple、list、numpy.ndarray、paddle.Tensor。如果data已经是一个Tensor,且dtype 、 place没有发生变化,将不会发生Tensor的拷贝并返回原来的Tensor。 否则会创建一个新的 Tensor,且不保留原来计算图。
语法
paddle.to_tensor(data, dtype=None, place=None, stop_gradient=True)
参数
data:[scalar/tuple/list/ndarray/Tensor] 初始化Tensor的数据,可以是scalar、tuple、list、numpy.ndarray、paddle.Tensor类型。dtype:[可选,str] 创建Tensor的数据类型,可以是bool、float16、float32、float64、int8、int16、int32、int64、uint8、complex64、complex128。 默认值为None,如果data为 python 浮点类型,则从get_default_dtype获取类型,如果data为其他类型,则会自动推导类型。place:[可选,CPUPlace/CUDAPinnedPlace/CUDAPlace] 创建Tensor的设备位置,可以是CPUPlace、CUDAPinnedPlace、CUDAPlace。默认值为None,使用全局的place。stop_gradient: [可选,bool] 是否阻断Autograd的梯度传导。默认值为True,此时不进行梯度传传导。
返回值
通过data创建的 Tensor。
实例
import paddletype(paddle.to_tensor(1))
# <class 'paddle.Tensor'>paddle.to_tensor(1)
# Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=True,
# [1])x = paddle.to_tensor(1, stop_gradient=False)
print(x)
# Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=False,
# [1])paddle.to_tensor(x) # A new tensor will be created with default stop_gradient=True
# Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=True,
# [1])paddle.to_tensor([[0.1, 0.2], [0.3, 0.4]], place=paddle.CPUPlace(), stop_gradient=False)
# Tensor(shape=[2, 2], dtype=float32, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=False,
# [[0.10000000, 0.20000000],
# [0.30000001, 0.40000001]])type(paddle.to_tensor([[1+1j, 2], [3+2j, 4]], dtype='complex64'))
# <class 'paddle.Tensor'>paddle.to_tensor([[1+1j, 2], [3+2j, 4]], dtype='complex64')
# Tensor(shape=[2, 2], dtype=complex64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=True,
# [[(1+1j), (2+0j)],
# [(3+2j), (4+0j)]])
函数实现
def to_tensor(data, dtype=None, place=None, stop_gradient=True):r"""Constructs a ``paddle.Tensor`` from ``data`` ,which can be scalar, tuple, list, numpy\.ndarray, paddle\.Tensor.If the ``data`` is already a Tensor, copy will be performed and return a new tensor.If you only want to change stop_gradient property, please call ``Tensor.stop_gradient = stop_gradient`` directly.Args:data(scalar|tuple|list|ndarray|Tensor): Initial data for the tensor.Can be a scalar, list, tuple, numpy\.ndarray, paddle\.Tensor.dtype(str|np.dtype, optional): The desired data type of returned tensor. Can be 'bool' , 'float16' ,'float32' , 'float64' , 'int8' , 'int16' , 'int32' , 'int64' , 'uint8','complex64' , 'complex128'. Default: None, infers dtype from ``data``except for python float number which gets dtype from ``get_default_type`` .place(CPUPlace|CUDAPinnedPlace|CUDAPlace|str, optional): The place to allocate Tensor. Can beCPUPlace, CUDAPinnedPlace, CUDAPlace. Default: None, means global place. If ``place`` isstring, It can be ``cpu``, ``gpu:x`` and ``gpu_pinned``, where ``x`` is the index of the GPUs.stop_gradient(bool, optional): Whether to block the gradient propagation of Autograd. Default: True.Returns:Tensor: A Tensor constructed from ``data`` .Examples:.. code-block:: pythonimport paddletype(paddle.to_tensor(1))# <class 'paddle.Tensor'>paddle.to_tensor(1)# Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=True,# [1])x = paddle.to_tensor(1, stop_gradient=False)print(x)# Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=False,# [1])paddle.to_tensor(x) # A new tensor will be created with default stop_gradient=True# Tensor(shape=[1], dtype=int64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=True,# [1])paddle.to_tensor([[0.1, 0.2], [0.3, 0.4]], place=paddle.CPUPlace(), stop_gradient=False)# Tensor(shape=[2, 2], dtype=float32, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=False,# [[0.10000000, 0.20000000],# [0.30000001, 0.40000001]])type(paddle.to_tensor([[1+1j, 2], [3+2j, 4]], dtype='complex64'))# <class 'paddle.Tensor'>paddle.to_tensor([[1+1j, 2], [3+2j, 4]], dtype='complex64')# Tensor(shape=[2, 2], dtype=complex64, place=CPUPlace, stop_gradient=True,# [[(1+1j), (2+0j)],# [(3+2j), (4+0j)]])"""place = _get_paddle_place(place)if place is None:place = _current_expected_place()if _non_static_mode():return _to_tensor_non_static(data, dtype, place, stop_gradient)# call assign for static graphelse:re_exp = re.compile(r'[(](.+?)[)]', re.S)place_str = re.findall(re_exp, str(place))[0]with paddle.static.device_guard(place_str):return _to_tensor_static(data, dtype, stop_gradient)def full_like(x, fill_value, dtype=None, name=None):"""This function creates a tensor filled with ``fill_value`` which has identical shape of ``x`` and ``dtype``.If the ``dtype`` is None, the data type of Tensor is same with ``x``.Args:x(Tensor): The input tensor which specifies shape and data type. The data type can be bool, float16, float32, float64, int32, int64.fill_value(bool|float|int): The value to fill the tensor with. Note: this value shouldn't exceed the range of the output data type.dtype(np.dtype|str, optional): The data type of output. The data type can be oneof bool, float16, float32, float64, int32, int64. The default value is None, which means the outputdata type is the same as input.name(str, optional): For details, please refer to :ref:`api_guide_Name`. Generally, no setting is required. Default: None.Returns:Tensor: Tensor which is created according to ``x``, ``fill_value`` and ``dtype``.Examples:.. code-block:: pythonimport paddleinput = paddle.full(shape=[2, 3], fill_value=0.0, dtype='float32', name='input')output = paddle.full_like(input, 2.0)# [[2. 2. 2.]# [2. 2. 2.]]"""if dtype is None:dtype = x.dtypeelse:if not isinstance(dtype, core.VarDesc.VarType):dtype = convert_np_dtype_to_dtype_(dtype)if in_dygraph_mode():return _C_ops.full_like(x, fill_value, dtype, x.place)if _in_legacy_dygraph():return _legacy_C_ops.fill_any_like(x, 'value', fill_value, 'dtype', dtype)helper = LayerHelper("full_like", **locals())check_variable_and_dtype(x,'x',['bool', 'float16', 'float32', 'float64', 'int16', 'int32', 'int64'],'full_like',)check_dtype(dtype,'dtype',['bool', 'float16', 'float32', 'float64', 'int16', 'int32', 'int64'],'full_like/zeros_like/ones_like',)out = helper.create_variable_for_type_inference(dtype=dtype)helper.append_op(type='fill_any_like',inputs={'X': [x]},attrs={'value': fill_value, "dtype": dtype},outputs={'Out': [out]},)out.stop_gradient = Truereturn out
相关文章:

深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数——paddle.to_tensor
分类目录:《深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数》总目录 相关文章: 深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数——paddle.Tensor 深入浅出PaddlePaddle函数——paddle.to_tensor 通过已知的data来创建一个Tensor,Tensor类型为paddle.Tensor。data可以是scalar、tupl…...

JavaScript高级程序设计读书分享之10章——函数
JavaScript高级程序设计(第4版)读书分享笔记记录 适用于刚入门前端的同志 定义函数 定义函数有两种方式:函数声明和函数表达式大致看这两种方式没有什么区别,事实上,JavaScript 引擎在加载数据时对它们是区别对待的。JavaScript 引擎在任何代…...

第八章 使用 ^%ZSTART 和 ^%ZSTOP 例程自定义启动和停止行为 - 设计注意事项
文章目录第八章 使用 ^%ZSTART 和 ^%ZSTOP 例程自定义启动和停止行为 - 设计注意事项设计注意事项第八章 使用 ^%ZSTART 和 ^%ZSTOP 例程自定义启动和停止行为 - 设计注意事项 IRIS 可以在特定事件发生时执行自定义代码。需要两个步骤: 定义 ^%ZSTART 例程、^%ZSTO…...
工作实战之拦截器模式
目录 前言 一、结构中包含的角色 二、拦截器使用 1.拦截器角色 a.自定义拦截器UserValidateInterceptor,UserUpdateInterceptor,UserEditNameInterceptor b.拦截器配置者UserInterceptorChainConfigure,任意组装拦截器顺序 c.拦截器管理者…...
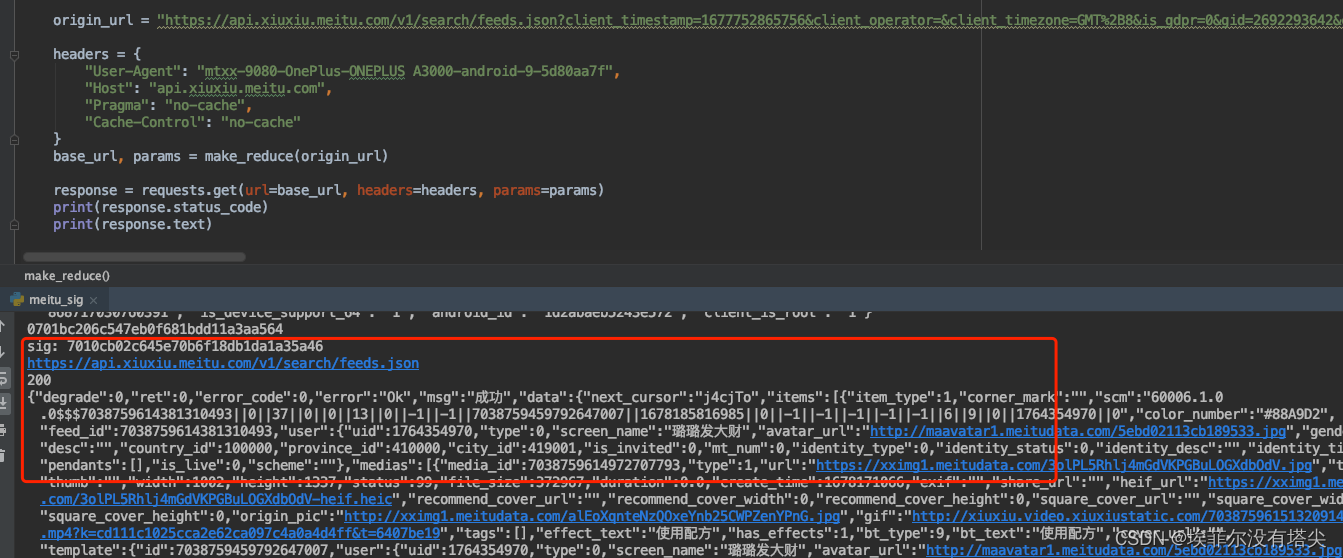
某美颜app sig参数分析
之前转载过该app的文章,今天翻版重新整理下,版本号:576O5Zu56eA56eAYXBwIHY5MDgw (base64 解码)。 上来先抓个包: jadx搜索关键词 "sigTime",然后定位到这里 看这行代码 cVar.addForm(INoCaptchaComponent.sig, genera…...

Linux - Linux系统优化思路
文章目录影响Linux性能的因素CPU内存磁盘I/O性能网络宽带操作系统相关资源系统安装优化内核参数优化文件系统优化应用程序软件资源系统性能分析工具vmstat命令iostat命令sar命令系统性能分析标准小结影响Linux性能的因素 CPU CPU是操作系统稳定运行的根本,CPU的速…...
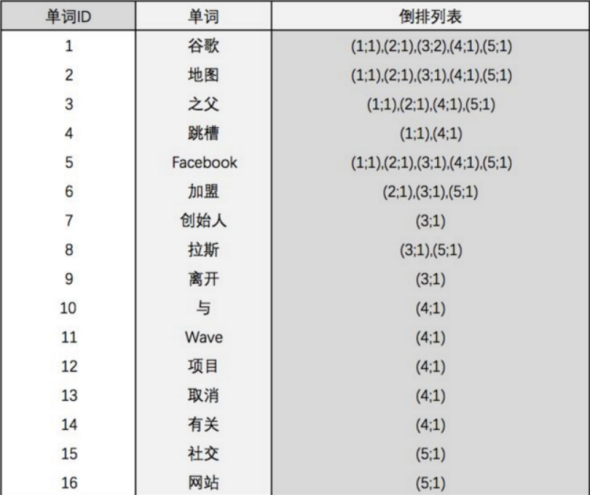
2.Elasticsearch入门
2.Elasticsearch入门[toc]1.Elasticsearch简介Elasticsearch是用Java开发并且是当前最流行的开源的企业级搜索引擎。 能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便。客户端支持Java、.NET(C#)、PHP、Pyth…...
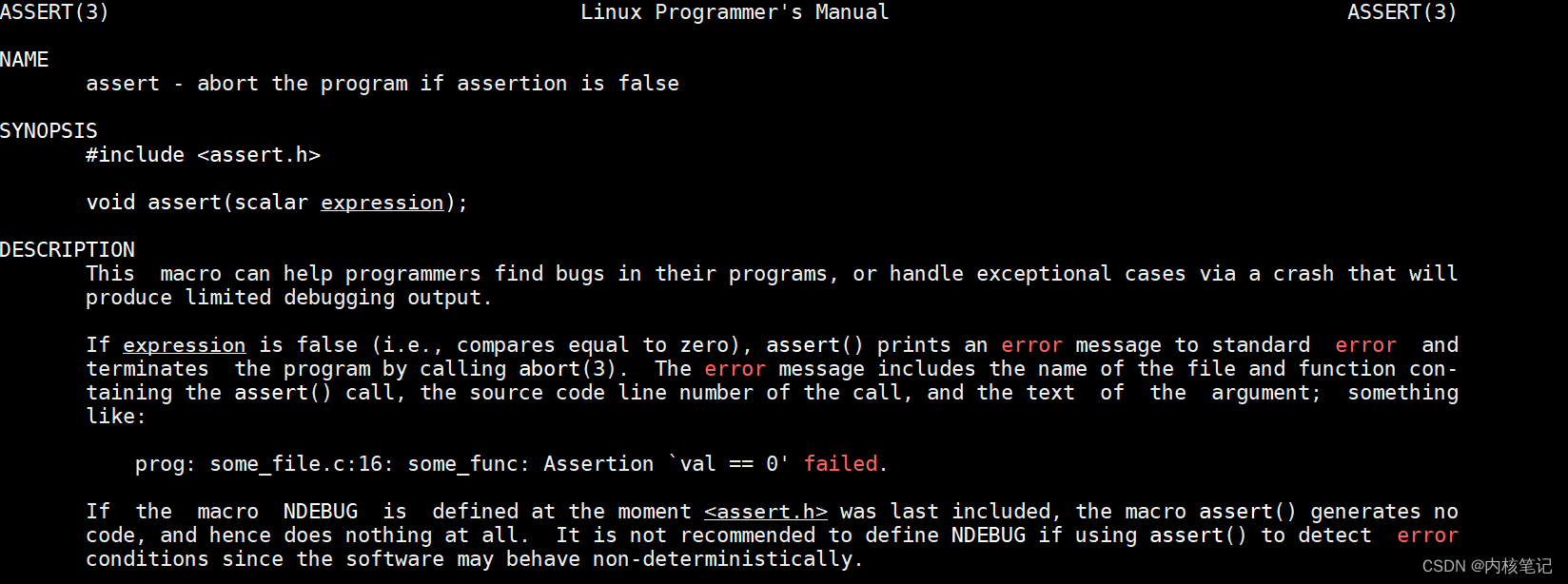
RK3399平台开发系列讲解(应用开发篇)断言的使用
🚀返回专栏总目录 文章目录 一、什么是断言二、静态断言三、运行时断言沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄 📢断言为我们提供了一种可以静态或动态地检查程序在目标平台上整体状态的能力,与它相关的接口由头文件 assert.h 提供。 一、什么是断言 在编程中…...
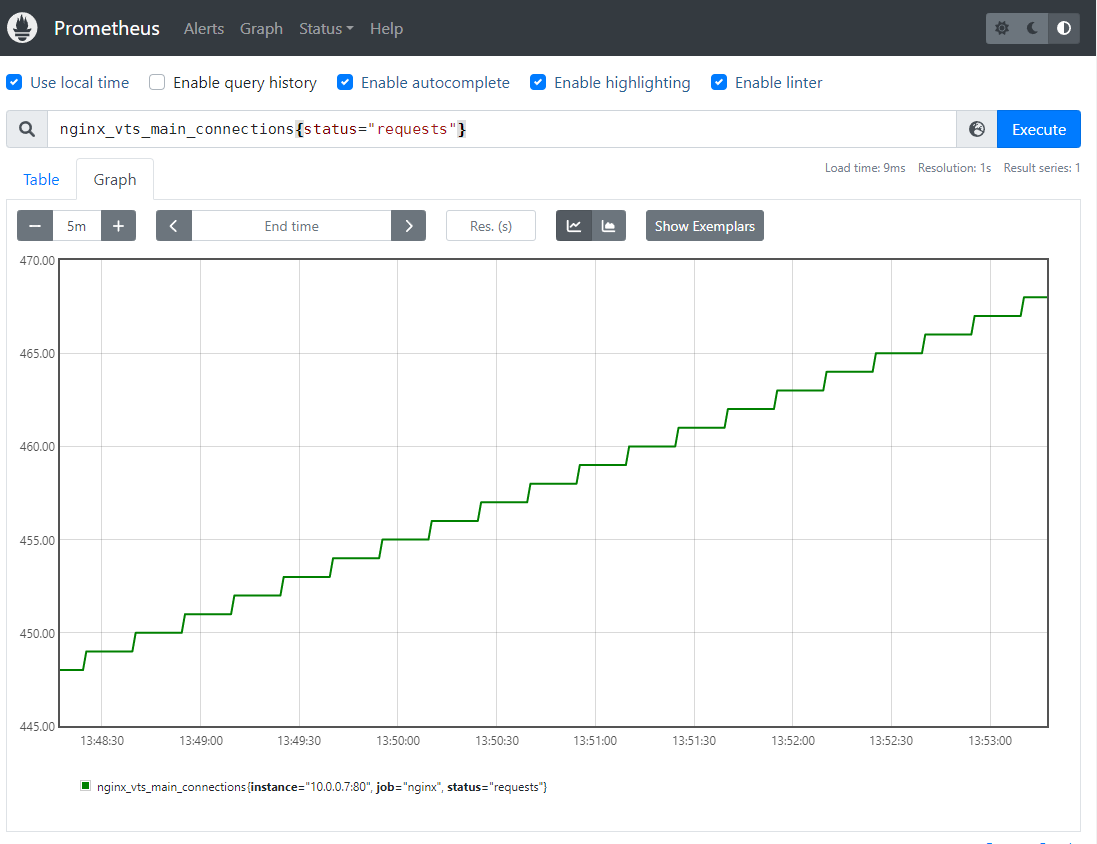
云原生系列之使用prometheus监控nginx
前言 大家好,又见面了,我是沐风晓月,本文主要讲解云原生系列之使用prometheus监控nginx 文章收录到 csdn 我是沐风晓月的博客【prometheus监控系列】专栏,此专栏是沐风晓月对云原生prometheus的的总结,希望能够加深自…...
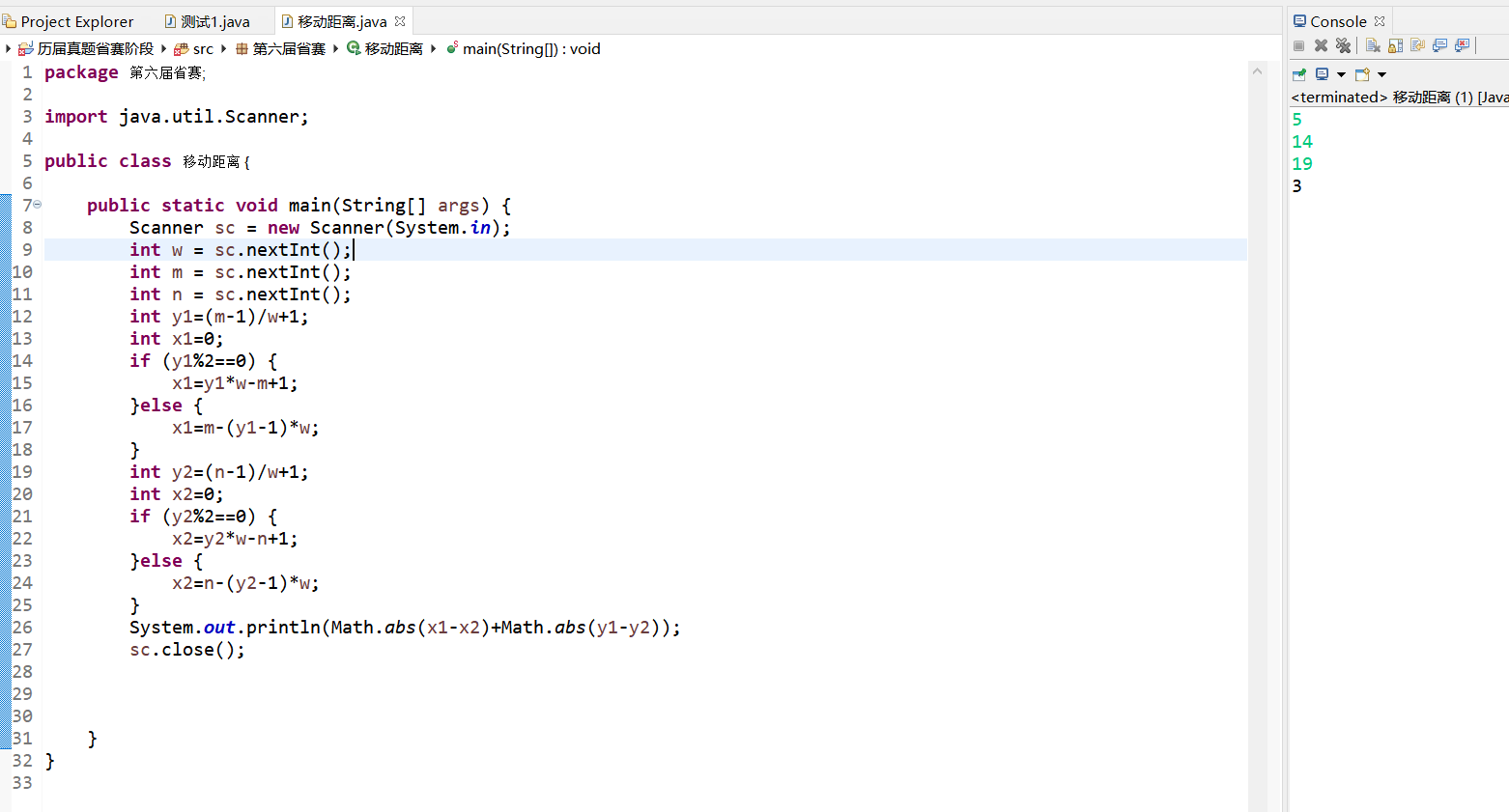
第六届省赛——8移动距离(总结规律)
题目:X星球居民小区的楼房全是一样的,并且按矩阵样式排列。其楼房的编号为1,2,3...当排满一行时,从下一行相邻的楼往反方向排号。比如:当小区排号宽度为6时,开始情形如下:1 2 3 4 5 612 11 10 9 8 713 14 1…...
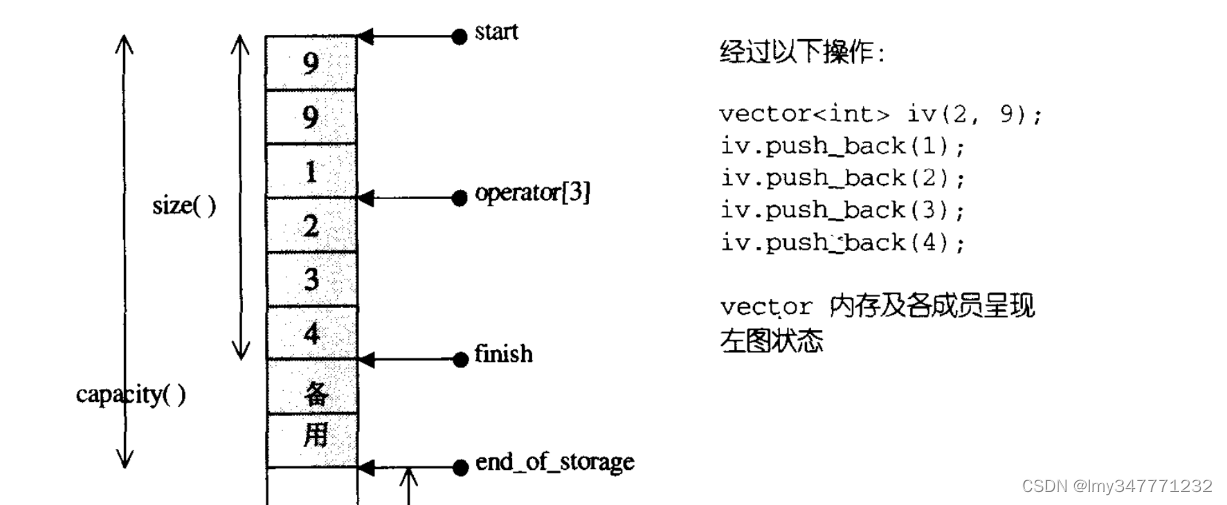
C++vector 简单实现
一。概述 vector是我们经常用的一个容器,其本质是一个线性数组。通过对动态内存的管理,增删改查数据,达到方便使用的目的。 作为一个线性表,控制元素个数,容量,开始位置的指针分别是: start …...
通用缓存存储设计实践
目录介绍 01.整体概述说明 1.1 项目背景介绍1.2 遇到问题记录1.3 基础概念介绍1.4 设计目标1.5 产生收益分析 02.市面存储方案 2.1 缓存存储有哪些2.2 缓存策略有哪些2.3 常见存储方案2.4 市面存储方案说明2.5 存储方案的不足 03.存储方案原理 3.1 Sp存储原理分析3.2 MMKV存储…...
sheng的学习笔记Eureka Ribbon
Eureka-注册中心Eureka简介官方网址:https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-netflixEureka介绍Spring Cloud 封装了 Netflix 公司开发的 Eureka 模块来实现服务注册和发现(请对比Zookeeper)。Zooleeper nacos.Eureka 采用了 C-S 的设计架构。Eureka Server 作为服…...
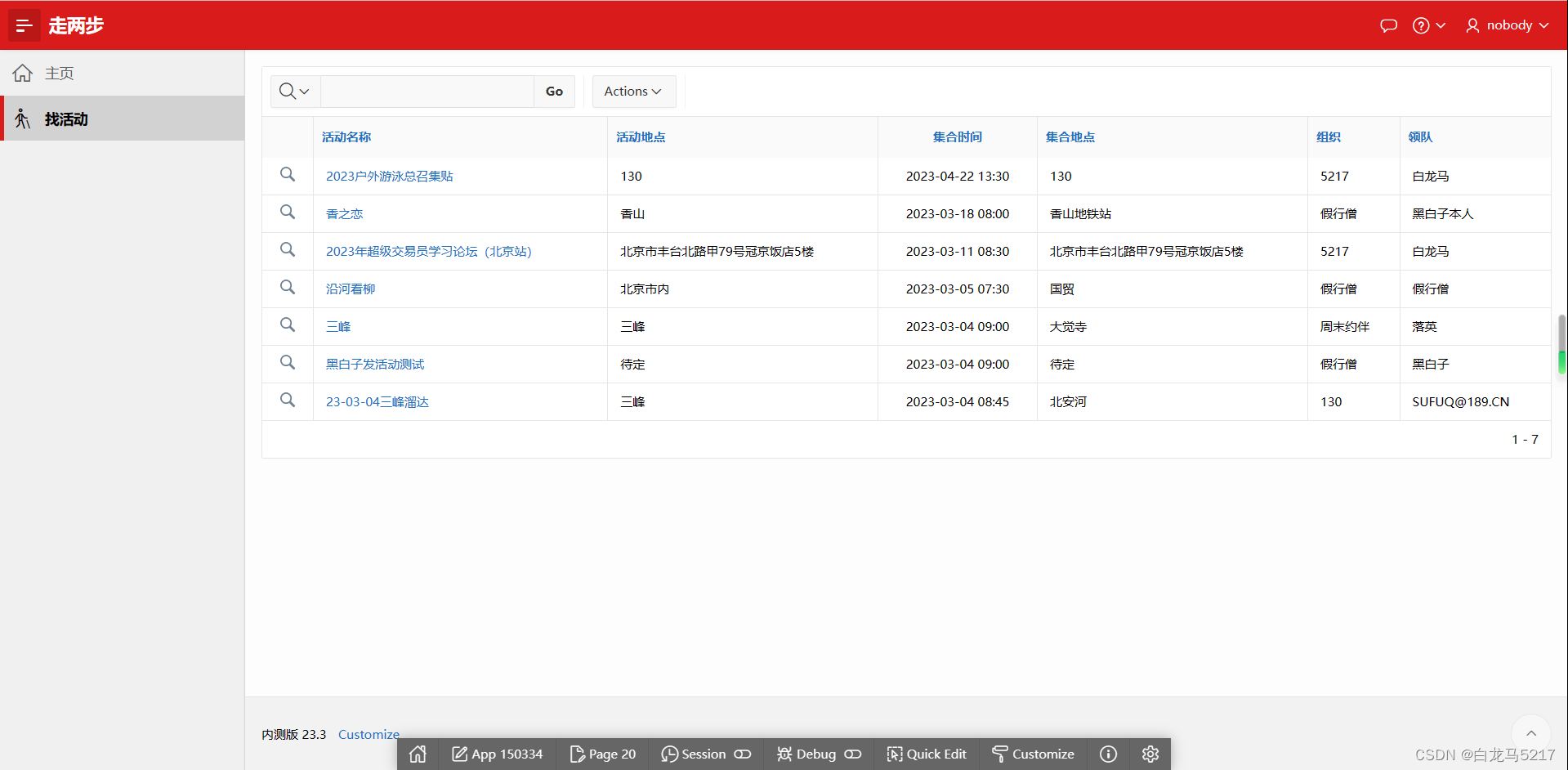
零代码工具我推荐Oracle APEX
云原生时代零代码工具我推荐Oracle APEX 国内的低码开发平台我也看了很多,感觉还是不太适合我这个被WEB抛弃的老炮。自从看了Oracle APEX就不打算看其它的了。太强大了,WEB服务器都省了,直接数据库到WEB页面。功能很强大,震撼到我…...
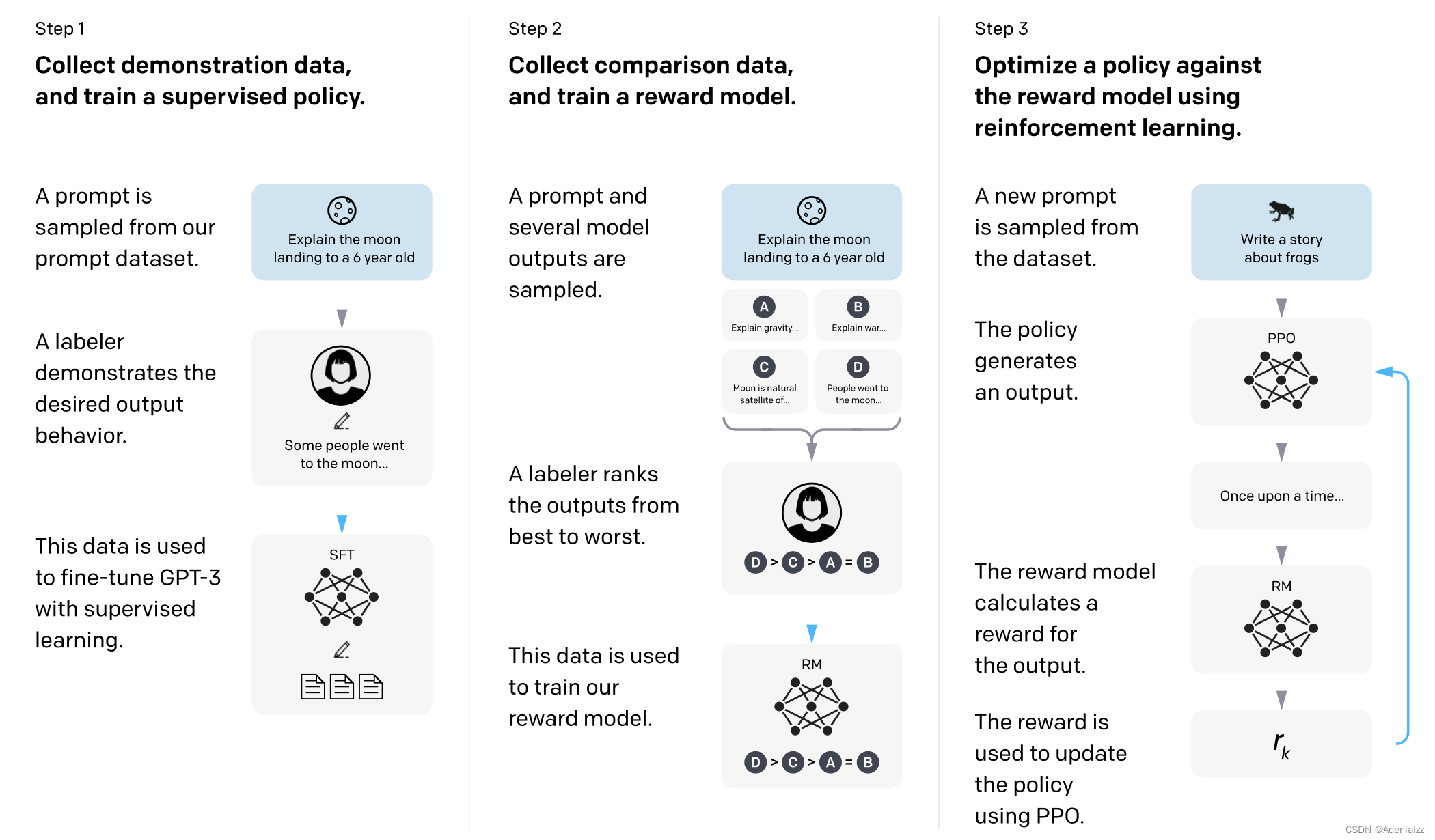
InstructGPT方法简读
InstructGPT方法简读 引言 仅仅通过增大模型规模和数据规模来训练更大的模型并不能使得大模型更好地理解用户意图。由于数据的噪声极大,并且现在的大多数大型语言模型均为基于深度学习的“黑箱模型”,几乎不具有可解释性和可控性,因此&…...

SpringCloud-5_模块集群化
避免一台Server挂掉,影响整个服务,搭建server集群创建e-commerce-eureka-server-9002微服务模块【作为注册中心】创建步骤参考e-commerce-eureka-server-9001修改pom.xml,加入依赖同9001创建resources/application.yml9002的ymlserver: # 修改端口号por…...
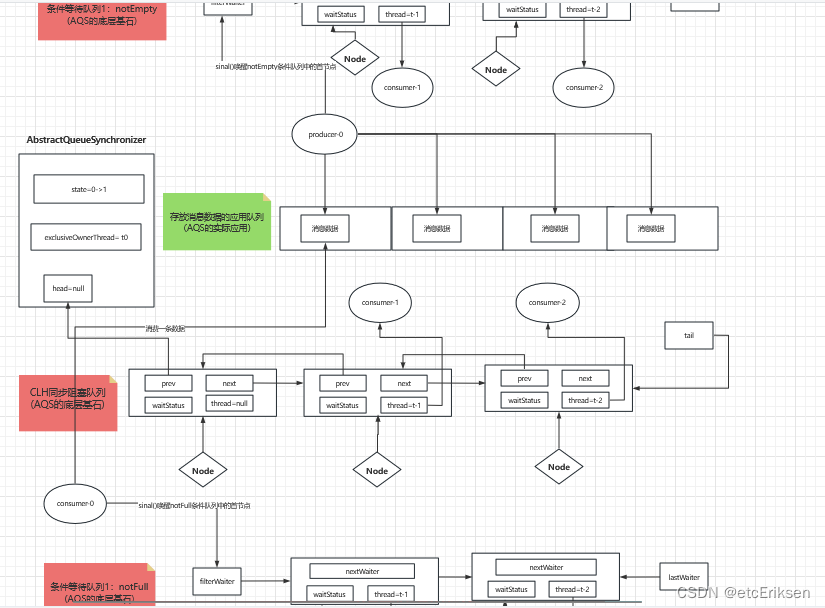
AQS底层源码深度剖析-BlockingQueue
目录 AQS底层源码深度剖析-BlockingQueue BlockingQueue定义 队列类型 队列数据结构 ArrayBlockingQueue LinkedBlockingQueue DelayQueue BlockingQueue API 添加元素 检索(取出)元素 BlockingQueue应用队列总览图 AQS底层源码深度剖析-BlockingQueue【重点中的重…...

Kotlin协程:Flow的异常处理
示例代码如下:launch(Dispatchers.Main) {// 第一部分flow {emit(1)throw NullPointerException("e")}.catch {Log.d("liduo", "onCreate1: $it")}.collect {Log.d("liudo", "onCreate2: $it")}// 第二部分flow …...
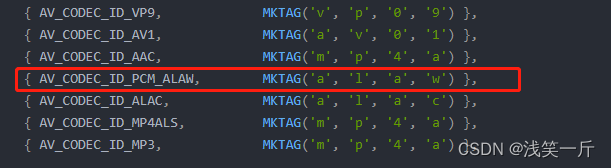
qt下ffmpeg录制mp4经验分享,支持音视频(h264、h265,AAC,G711 aLaw, G711muLaw)
前言 MP4,是最常见的国际通用格式,在常见的播放软件中都可以使用和播放,磁盘空间占地小,画质一般清晰,它本身是支持h264、AAC的编码格式,对于其他编码的话,需要进行额外处理。本文提供了ffmpeg录…...

C#读取Excel解析入门-1仅围绕三个主要的为阵地,进行重点解析,就是最理性的应对上法所在
业务中也是同样的功能点实现。只是多扩展了很多代码,构成了项目的其他部分,枝干所在。但是有用的枝干,仅仅不超过三个主要的!所以您仅仅围绕三个主要的为阵地,进行重点解析,就是最理性的应对上法所在了 str…...
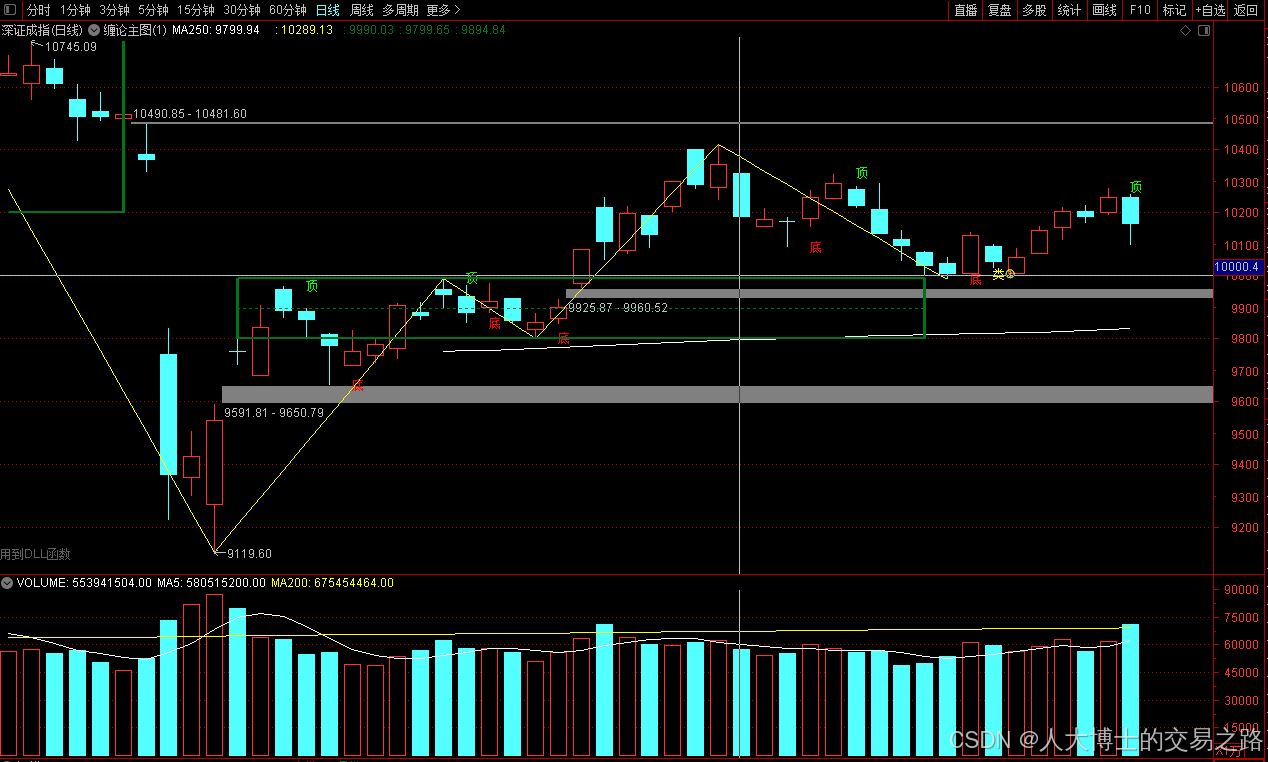
龙虎榜——20250610
上证指数放量收阴线,个股多数下跌,盘中受消息影响大幅波动。 深证指数放量收阴线形成顶分型,指数短线有调整的需求,大概需要一两天。 2025年6月10日龙虎榜行业方向分析 1. 金融科技 代表标的:御银股份、雄帝科技 驱动…...
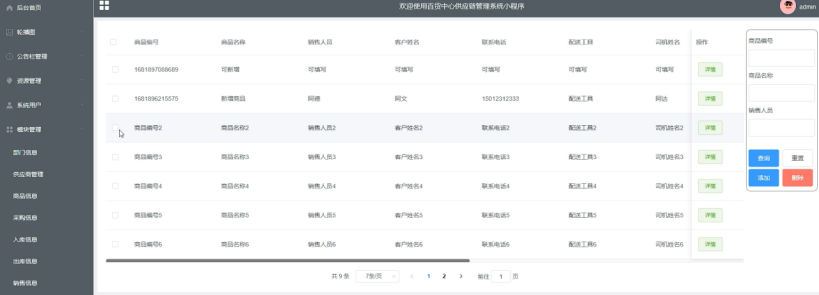
springboot 百货中心供应链管理系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,百货中心供应链管理系统被用户普遍使用,为方…...

PHP和Node.js哪个更爽?
先说结论,rust完胜。 php:laravel,swoole,webman,最开始在苏宁的时候写了几年php,当时觉得php真的是世界上最好的语言,因为当初活在舒适圈里,不愿意跳出来,就好比当初活在…...

基于服务器使用 apt 安装、配置 Nginx
🧾 一、查看可安装的 Nginx 版本 首先,你可以运行以下命令查看可用版本: apt-cache madison nginx-core输出示例: nginx-core | 1.18.0-6ubuntu14.6 | http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 Packages ng…...
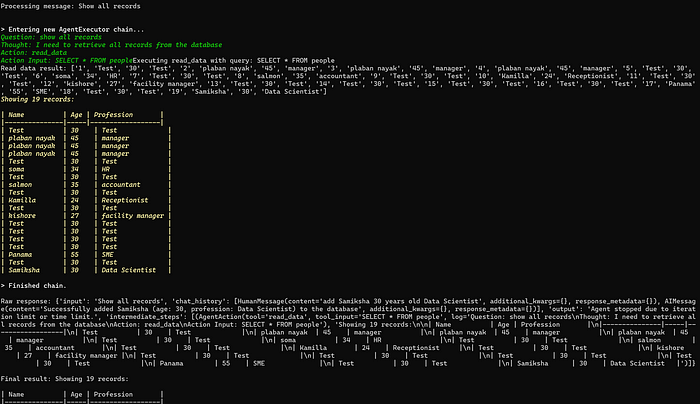
理解 MCP 工作流:使用 Ollama 和 LangChain 构建本地 MCP 客户端
🌟 什么是 MCP? 模型控制协议 (MCP) 是一种创新的协议,旨在无缝连接 AI 模型与应用程序。 MCP 是一个开源协议,它标准化了我们的 LLM 应用程序连接所需工具和数据源并与之协作的方式。 可以把它想象成你的 AI 模型 和想要使用它…...
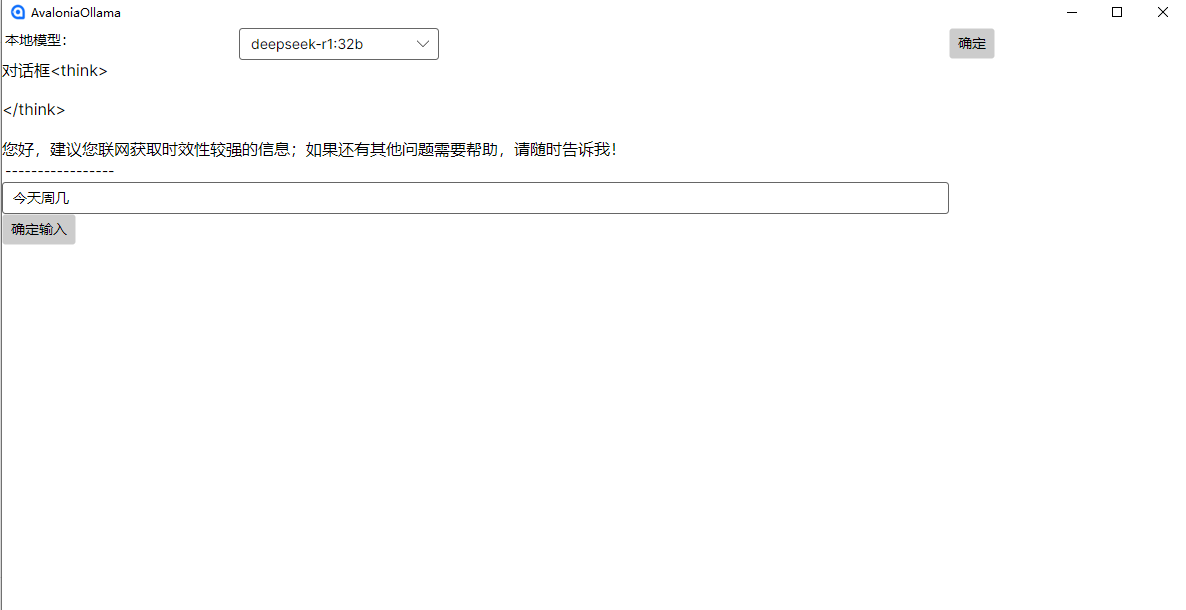
c#开发AI模型对话
AI模型 前面已经介绍了一般AI模型本地部署,直接调用现成的模型数据。这里主要讲述讲接口集成到我们自己的程序中使用方式。 微软提供了ML.NET来开发和使用AI模型,但是目前国内可能使用不多,至少实践例子很少看见。开发训练模型就不介绍了&am…...

代码随想录刷题day30
1、零钱兑换II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。 请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。 假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。 题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带…...

Git 3天2K星标:Datawhale 的 Happy-LLM 项目介绍(附教程)
引言 在人工智能飞速发展的今天,大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)已成为技术领域的焦点。从智能写作到代码生成,LLM 的应用场景不断扩展,深刻改变了我们的工作和生活方式。然而,理解这些模型的内部…...

前端中slice和splic的区别
1. slice slice 用于从数组中提取一部分元素,返回一个新的数组。 特点: 不修改原数组:slice 不会改变原数组,而是返回一个新的数组。提取数组的部分:slice 会根据指定的开始索引和结束索引提取数组的一部分。不包含…...
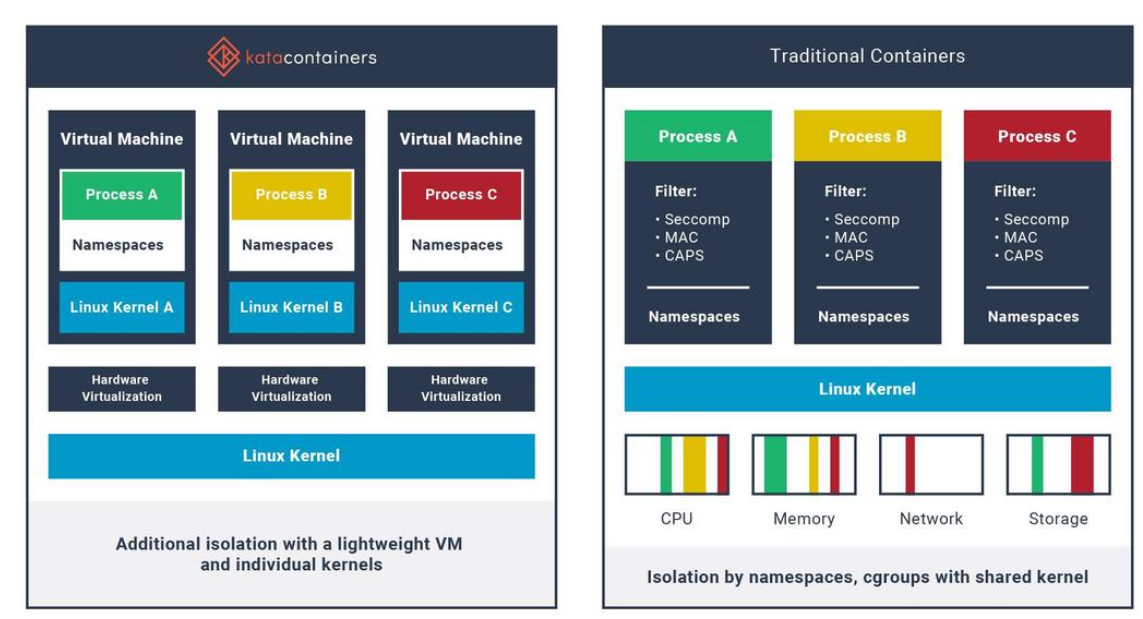
沙箱虚拟化技术虚拟机容器之间的关系详解
问题 沙箱、虚拟化、容器三者分开一一介绍的话我知道他们各自都是什么东西,但是如果把三者放在一起,它们之间到底什么关系?又有什么联系呢?我不是很明白!!! 就比如说: 沙箱&#…...
