使用 Tranformer 进行概率时间序列预测实战
使用 Transformers 进行概率时间序列预测实战
通常,经典方法针对数据集中的每个时间序列单独拟合。然而,当处理大量时间序列时,在所有可用时间序列上训练一个“全局”模型是有益的,这使模型能够从许多不同的来源学习潜在的表示。
深度学习非常适合训练 全局概率模型,而不是训练局部点预测模型,因为神经网络可以从几个相关的时间序列中学习表示,并对数据的不确定性进行建模。
在概率设定中学习某些选定参数分布的未来参数很常见,例如高斯分布或 Student-T,或者学习条件分位数函数,或使用适应时间序列设置的共型预测框架。通过采用经验均值或中值,人们总是可以将概率模型转变为点预测模型。
时间序列Transformer
这篇博文中,我们将利用传统 vanilla Transformer 进行单变量概率预测任务 (即预测每个时间序列的一维分布)。由于 Encoder-Decoder Transformer 很好地封装了几个归纳偏差,所以它成为了我们预测的自然选择。
首先,使用 Encoder-Decoder 架构在推理时很有帮助。通常对于一些记录的数据,我们希望提前预知未来的一些预测步骤。我们可以在给定某种分布类型的情况下,从中抽样以提供预测,直到我们期望的预测范围。这被称为贪婪采样 (Greedy Sampling)/搜索。
其次,Transformer 帮助我们训练可能包含成千上万个时间点的时间序列数据。由于时间和内存限制,一次性将所有时间序列的完整历史输入模型或许不太可行。因此,在为随机梯度下降构建批次时,可以考虑适当的上下文窗口大小,并从训练数据中对该窗口和后续预测长度大小的窗口进行采样。可以将调整过大小的上下文窗口传递给编码器、预测窗口传递给 ausal-masked 解码器。
Transformers 相对于其他架构的另一个好处是,我们可以将缺失值作为编码器或解码器的额外掩蔽值,并且仍然可以在不诉诸于填充或插补的情况下进行训练。
01
设置环境
首先,让我们安装必要的库: Transformers、Datasets、Evaluate、Accelerate 和 GluonTS。
正如我们将展示的那样,GluonTS 将用于转换数据以创建特征以及创建适当的训练、验证和测试批次。
!pip install -q transformers
!pip install -q datasets
!pip install -q evaluate
!pip install -q accelerate
!pip install -q gluonts ujson
02
加载数据集
在这篇博文中,我们将使用 Hugging Face Hub 上提供的 tourism_monthly 数据集。该数据集包含澳大利亚 366 个地区的每月旅游流量。
此数据集是 Monash Time Series Forecasting 存储库的一部分,该存储库收纳了是来自多个领域的时间序列数据集。它可以看作是时间序列预测的 GLUE 基准。
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("monash_tsf", "tourism_monthly")
可以看出,数据集包含 3 个片段: 训练、验证和测试。
dataset
DatasetDict({train: Dataset({features: ['start', 'target', 'feat_static_cat', 'feat_dynamic_real', 'item_id'],num_rows: 366})test: Dataset({features: ['start', 'target', 'feat_static_cat', 'feat_dynamic_real', 'item_id'],num_rows: 366})validation: Dataset({features: ['start', 'target', 'feat_static_cat', 'feat_dynamic_real', 'item_id'],num_rows: 366})})
每个示例都包含一些键,其中 start 和 target 是最重要的键。让我们看一下数据集中的第一个时间序列:
train_example = dataset['train'][0]
train_example.keys()dict_keys(['start', 'target', 'feat_static_cat', 'feat_dynamic_real', 'item_id'])
start 仅指示时间序列的开始 (类型为 datetime) ,而 target 包含时间序列的实际值。
start 将有助于将时间相关的特征添加到时间序列值中,作为模型的额外输入 (例如“一年中的月份”) 。因为我们已经知道数据的频率是 每月,所以也能推算第二个值的时间戳为 1979-02-01,等等。
print(train_example['start'])
print(train_example['target'])
1979-01-01 00:00:00[1149.8699951171875, 1053.8001708984375, ..., 5772.876953125]
验证集包含与训练集相同的数据,只是数据时间范围延长了 prediction_length 那么多。这使我们能够根据真实情况验证模型的预测。
与验证集相比,测试集还是比验证集多包含 prediction_length 时间的数据 (或者使用比训练集多出数个 prediction_length 时长数据的测试集,实现在多重滚动窗口上的测试任务)。
validation_example = dataset['validation'][0]
validation_example.keys()dict_keys(['start', 'target', 'feat_static_cat', 'feat_dynamic_real', 'item_id'])
验证的初始值与相应的训练示例完全相同:
print(validation_example['start'])
print(validation_example['target'])1979-01-01 00:00:00[1149.8699951171875, 1053.8001708984375, ..., 5985.830078125]
但是,与训练示例相比,此示例具有 prediction_length=24 个额外的数据。让我们验证一下。
freq = "1M"
prediction_length = 24assert len(train_example["target"]) + prediction_length == len(validation_example["target"]
)
让我们可视化一下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfigure, axes = plt.subplots()
axes.plot(train_example["target"], color="blue")
axes.plot(validation_example["target"], color="red", alpha=0.5)plt.show()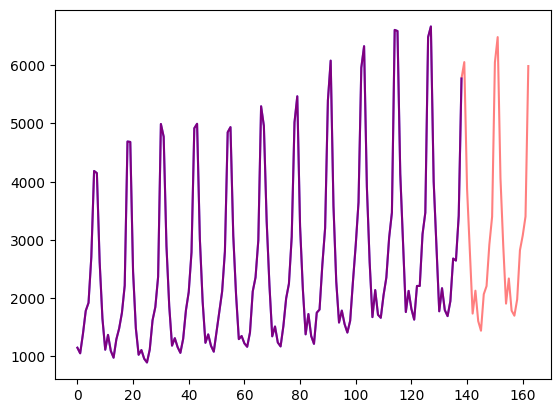
03
将 start 更新为 pd.Period
我们要做的第一件事是根据数据的 freq 值将每个时间序列的 start 特征转换为 pandas 的 Period 索引:
from functools import lru_cacheimport pandas as pd
import numpy as np@lru_cache(10_000)
def convert_to_pandas_period(date, freq):return pd.Period(date, freq)def transform_start_field(batch, freq):batch["start"] = [convert_to_pandas_period(date, freq) for date in batch["start"]]return batch这里我们使用 datasets 的 set_transform 来实现:
from functools import partialtrain_dataset.set_transform(partial(transform_start_field, freq=freq))
test_dataset.set_transform(partial(transform_start_field, freq=freq))定义模型
接下来,让我们实例化一个模型。该模型将从头开始训练,因此我们不使用 from_pretrained 方法,而是从 config 中随机初始化模型。
我们为模型指定了几个附加参数:
-
prediction_length (在我们的例子中是 24 个月) : 这是 Transformer 的解码器将学习预测的范围;
-
context_length: 如果未指定 context_length,模型会将 context_length (编码器的输入) 设置为等于 prediction_length;
-
给定频率的 lags(滞后): 这将决定模型“回头看”的程度,也会作为附加特征。例如对于 Daily 频率,我们可能会考虑回顾 [1, 2, 7, 30, …],也就是回顾 1、2……天的数据,而对于 Minute数据,我们可能会考虑 [1, 30, 60, 60*24, …] 等;
-
时间特征的数量: 在我们的例子中设置为 2,因为我们将添加 MonthOfYear 和 Age 特征;
-
静态类别型特征的数量: 在我们的例子中,这将只是 1,因为我们将添加一个“时间序列 ID”特征;
-
基数: 将每个静态类别型特征的值的数量构成一个列表,对于本例来说将是 [366],因为我们有 366 个不同的时间序列;
-
嵌入维度: 每个静态类别型特征的嵌入维度,也是构成列表。例如 [3] 意味着模型将为每个 366 时间序列 (区域) 学习大小为 3 的嵌入向量。
让我们使用 GluonTS 为给定频率 (“每月”) 提供的默认滞后值:
from gluonts.time_feature import get_lags_for_frequencylags_sequence = get_lags_for_frequency(freq)
print(lags_sequence)>>> [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13, 23, 24, 25, 35, 36, 37]这意味着我们每个时间步将回顾长达 37 个月的数据,作为附加特征。我们还检查 GluonTS 为我们提供的默认时间特征:
from gluonts.time_feature import time_features_from_frequency_strtime_features = time_features_from_frequency_str(freq)
print(time_features)>>> [<function month_of_year at 0x7fa496d0ca70>]在这种情况下,只有一个特征,即“一年中的月份”。这意味着对于每个时间步长,我们将添加月份作为标量值 (例如,如果时间戳为 “january”,则为 1;如果时间戳为 “february”,则为 2,等等) 。
我们现在准备好定义模型需要的所有内容了:
from transformers import TimeSeriesTransformerConfig, TimeSeriesTransformerForPredictionconfig = TimeSeriesTransformerConfig(prediction_length=prediction_length,# context length:context_length=prediction_length * 2,# lags coming from helper given the freq:lags_sequence=lags_sequence,# we'll add 2 time features ("month of year" and "age", see further):num_time_features=len(time_features) + 1,# we have a single static categorical feature, namely time series ID:num_static_categorical_features=1,# it has 366 possible values:cardinality=[len(train_dataset)],# the model will learn an embedding of size 2 for each of the 366 possible values:embedding_dimension=[2],# transformer params:encoder_layers=4,decoder_layers=4,d_model=32,
)model = TimeSeriesTransformerForPrediction(config)请注意,与 Transformers 库中的其他模型类似,TimeSeriesTransformerModel 对应于没有任何顶部前置头的编码器-解码器 Transformer,而 TimeSeriesTransformerForPrediction 对应于顶部有一个分布前置头 (distribution head) 的 TimeSeriesTransformerForPrediction。默认情况下,该模型使用 Student-t 分布 (也可以自行配置):
model.config.distribution_output>>> student_t这是具体实现层面与用于 NLP 的 Transformers 的一个重要区别,其中头部通常由一个固定的分类分布组成,实现为 nn.Linear 层。
定义转换
接下来,我们定义数据的转换,尤其是需要基于样本数据集或通用数据集来创建其中的时间特征。
同样,我们用到了 GluonTS 库。这里定义了一个 Chain (有点类似于图像训练的 torchvision.transforms.Compose) 。它允许我们将多个转换组合到一个流水线中。
from gluonts.time_feature import (time_features_from_frequency_str,TimeFeature,get_lags_for_frequency,
)
from gluonts.dataset.field_names import FieldName
from gluonts.transform import (AddAgeFeature,AddObservedValuesIndicator,AddTimeFeatures,AsNumpyArray,Chain,ExpectedNumInstanceSampler,InstanceSplitter,RemoveFields,SelectFields,SetField,TestSplitSampler,Transformation,ValidationSplitSampler,VstackFeatures,RenameFields,
)下面的转换代码带有注释供大家查看具体的操作步骤。从全局来说,我们将迭代数据集的各个时间序列并添加、删除某些字段或特征:
from transformers import PretrainedConfigdef create_transformation(freq: str, config: PretrainedConfig) -> Transformation:remove_field_names = []if config.num_static_real_features == 0:remove_field_names.append(FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_REAL)if config.num_dynamic_real_features == 0:remove_field_names.append(FieldName.FEAT_DYNAMIC_REAL)if config.num_static_categorical_features == 0:remove_field_names.append(FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_CAT)# a bit like torchvision.transforms.Composereturn Chain(# step 1: remove static/dynamic fields if not specified[RemoveFields(field_names=remove_field_names)]# step 2: convert the data to NumPy (potentially not needed)+ ([AsNumpyArray(field=FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_CAT,expected_ndim=1,dtype=int,)]if config.num_static_categorical_features > 0else [])+ ([AsNumpyArray(field=FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_REAL,expected_ndim=1,)]if config.num_static_real_features > 0else [])+ [AsNumpyArray(field=FieldName.TARGET,# we expect an extra dim for the multivariate case:expected_ndim=1 if config.input_size == 1 else 2,),# step 3: handle the NaN's by filling in the target with zero# and return the mask (which is in the observed values)# true for observed values, false for nan's# the decoder uses this mask (no loss is incurred for unobserved values)# see loss_weights inside the xxxForPrediction modelAddObservedValuesIndicator(target_field=FieldName.TARGET,output_field=FieldName.OBSERVED_VALUES,),# step 4: add temporal features based on freq of the dataset# month of year in the case when freq="M"# these serve as positional encodingsAddTimeFeatures(start_field=FieldName.START,target_field=FieldName.TARGET,output_field=FieldName.FEAT_TIME,time_features=time_features_from_frequency_str(freq),pred_length=config.prediction_length,),# step 5: add another temporal feature (just a single number)# tells the model where in its life the value of the time series is,# sort of a running counterAddAgeFeature(target_field=FieldName.TARGET,output_field=FieldName.FEAT_AGE,pred_length=config.prediction_length,log_scale=True,),# step 6: vertically stack all the temporal features into the key FEAT_TIMEVstackFeatures(output_field=FieldName.FEAT_TIME,input_fields=[FieldName.FEAT_TIME, FieldName.FEAT_AGE]+ ([FieldName.FEAT_DYNAMIC_REAL]if config.num_dynamic_real_features > 0else []),),# step 7: rename to match HuggingFace namesRenameFields(mapping={FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_CAT: "static_categorical_features",FieldName.FEAT_STATIC_REAL: "static_real_features",FieldName.FEAT_TIME: "time_features",FieldName.TARGET: "values",FieldName.OBSERVED_VALUES: "observed_mask",}),])InstanceSplitter
对于训练、验证、测试步骤,接下来我们创建一个 InstanceSplitter,用于从数据集中对窗口进行采样 (因为由于时间和内存限制,我们无法将整个历史值传递给 Transformer)。
实例拆分器从数据中随机采样大小为 context_length 和后续大小为 prediction_length 的窗口,并将 past_ 或 future_ 键附加到各个窗口的任何临时键。这确保了 values 被拆分为 past_values 和后续的 future_values 键,它们将分别用作编码器和解码器的输入。同样我们还需要修改 time_series_fields 参数中的所有键:
from gluonts.transform.sampler import InstanceSampler
from typing import Optionaldef create_instance_splitter(config: PretrainedConfig,mode: str,train_sampler: Optional[InstanceSampler] = None,validation_sampler: Optional[InstanceSampler] = None,
) -> Transformation:assert mode in ["train", "validation", "test"]instance_sampler = {"train": train_sampleror ExpectedNumInstanceSampler(num_instances=1.0, min_future=config.prediction_length),"validation": validation_sampleror ValidationSplitSampler(min_future=config.prediction_length),"test": TestSplitSampler(),}[mode]return InstanceSplitter(target_field="values",is_pad_field=FieldName.IS_PAD,start_field=FieldName.START,forecast_start_field=FieldName.FORECAST_START,instance_sampler=instance_sampler,past_length=config.context_length + max(config.lags_sequence),future_length=config.prediction_length,time_series_fields=["time_features", "observed_mask"],)创建 DataLoader
有了数据,下一步需要创建 PyTorch DataLoaders。它允许我们批量处理成对的 (输入, 输出) 数据,即 (past_values, future_values)。
from typing import Iterableimport torch
from gluonts.itertools import Cached, Cyclic
from gluonts.dataset.loader import as_stacked_batchesdef create_train_dataloader(config: PretrainedConfig,freq,data,batch_size: int,num_batches_per_epoch: int,shuffle_buffer_length: Optional[int] = None,cache_data: bool = True,**kwargs,
) -> Iterable:PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES = ["past_time_features","past_values","past_observed_mask","future_time_features",]if config.num_static_categorical_features > 0:PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES.append("static_categorical_features")if config.num_static_real_features > 0:PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES.append("static_real_features")TRAINING_INPUT_NAMES = PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES + ["future_values","future_observed_mask",]transformation = create_transformation(freq, config)transformed_data = transformation.apply(data, is_train=True)if cache_data:transformed_data = Cached(transformed_data)# we initialize a Training instanceinstance_splitter = create_instance_splitter(config, "train")# the instance splitter will sample a window of# context length + lags + prediction length (from the 366 possible transformed time series)# randomly from within the target time series and return an iterator.stream = Cyclic(transformed_data).stream()training_instances = instance_splitter.apply(stream, is_train=True)return as_stacked_batches(training_instances,batch_size=batch_size,shuffle_buffer_length=shuffle_buffer_length,field_names=TRAINING_INPUT_NAMES,output_type=torch.tensor,num_batches_per_epoch=num_batches_per_epoch,)def create_test_dataloader(config: PretrainedConfig,freq,data,batch_size: int,**kwargs,
):PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES = ["past_time_features","past_values","past_observed_mask","future_time_features",]if config.num_static_categorical_features > 0:PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES.append("static_categorical_features")if config.num_static_real_features > 0:PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES.append("static_real_features")transformation = create_transformation(freq, config)transformed_data = transformation.apply(data, is_train=False)# we create a Test Instance splitter which will sample the very last# context window seen during training only for the encoder.instance_sampler = create_instance_splitter(config, "test")# we apply the transformations in test modetesting_instances = instance_sampler.apply(transformed_data, is_train=False)return as_stacked_batches(testing_instances,batch_size=batch_size,output_type=torch.tensor,field_names=PREDICTION_INPUT_NAMES,)train_dataloader = create_train_dataloader(config=config,freq=freq,data=train_dataset,batch_size=256,num_batches_per_epoch=100,
)test_dataloader = create_test_dataloader(config=config,freq=freq,data=test_dataset,batch_size=64,
)让我们检查第一批:
batch = next(iter(train_dataloader))
for k, v in batch.items():print(k, v.shape, v.type())>>> past_time_features torch.Size([256, 85, 2]) torch.FloatTensorpast_values torch.Size([256, 85]) torch.FloatTensorpast_observed_mask torch.Size([256, 85]) torch.FloatTensorfuture_time_features torch.Size([256, 24, 2]) torch.FloatTensorstatic_categorical_features torch.Size([256, 1]) torch.LongTensorfuture_values torch.Size([256, 24]) torch.FloatTensorfuture_observed_mask torch.Size([256, 24]) torch.FloatTensor可以看出,我们没有将 input_ids 和 attention_mask 提供给编码器 (训练 NLP 模型时也是这种情况),而是提供 past_values,以及 past_observed_mask、past_time_features、static_categorical_features 和 static_real_features 几项数据。
解码器的输入包括 future_values、future_observed_mask 和 future_time_features。future_values 可以看作等同于 NLP 训练中的 decoder_input_ids。
前向传播
让我们对刚刚创建的批次执行一次前向传播:
# perform forward pass
outputs = model(past_values=batch["past_values"],past_time_features=batch["past_time_features"],past_observed_mask=batch["past_observed_mask"],static_categorical_features=batch["static_categorical_features"]if config.num_static_categorical_features > 0else None,static_real_features=batch["static_real_features"]if config.num_static_real_features > 0else None,future_values=batch["future_values"],future_time_features=batch["future_time_features"],future_observed_mask=batch["future_observed_mask"],output_hidden_states=True,
)print("Loss:", outputs.loss.item())>>> Loss: 9.069628715515137目前,该模型返回了损失值。这是由于解码器会自动将 future_values 向右移动一个位置以获得标签。这允许计算预测结果和标签值之间的误差。
另请注意,解码器使用 Causal Mask 来避免预测未来,因为它需要预测的值在 future_values 张量中。
训练模型
是时候训练模型了!我们将使用标准的 PyTorch 训练循环。
这里我们用到了 Accelerate 库,它会自动将模型、优化器和数据加载器放置在适当的 device 上。
from accelerate import Accelerator
from torch.optim import AdamWaccelerator = Accelerator()
device = accelerator.devicemodel.to(device)
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=6e-4, betas=(0.9, 0.95), weight_decay=1e-1)model, optimizer, train_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(model,optimizer,train_dataloader,
)model.train()
for epoch in range(40):for idx, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):optimizer.zero_grad()outputs = model(static_categorical_features=batch["static_categorical_features"].to(device)if config.num_static_categorical_features > 0else None,static_real_features=batch["static_real_features"].to(device)if config.num_static_real_features > 0else None,past_time_features=batch["past_time_features"].to(device),past_values=batch["past_values"].to(device),future_time_features=batch["future_time_features"].to(device),future_values=batch["future_values"].to(device),past_observed_mask=batch["past_observed_mask"].to(device),future_observed_mask=batch["future_observed_mask"].to(device),)loss = outputs.loss# Backpropagationaccelerator.backward(loss)optimizer.step()if idx % 100 == 0:print(loss.item())模型推理
在推理时,建议使用 generate() 方法进行自回归生成,类似于 NLP 模型。
预测的过程会从测试实例采样器中获得数据。采样器会将数据集的每个时间序列的最后 context_length 那么长时间的数据采样出来,然后输入模型。请注意,这里需要把提前已知的 future_time_features 传递给解码器。
该模型将从预测分布中自回归采样一定数量的值,并将它们传回解码器最终得到预测输出:
model.eval()forecasts = []for batch in test_dataloader:outputs = model.generate(static_categorical_features=batch["static_categorical_features"].to(device)if config.num_static_categorical_features > 0else None,static_real_features=batch["static_real_features"].to(device)if config.num_static_real_features > 0else None,past_time_features=batch["past_time_features"].to(device),past_values=batch["past_values"].to(device),future_time_features=batch["future_time_features"].to(device),past_observed_mask=batch["past_observed_mask"].to(device),)forecasts.append(outputs.sequences.cpu().numpy())该模型输出一个表示结构的张量 (batch_size, number of samples, prediction length)。
下面的输出说明: 对于大小为 64 的批次中的每个示例,我们将获得接下来 24 个月内的 100 个可能的值:
forecasts[0].shape>>> (64, 100, 24)我们将垂直堆叠它们,以获得测试数据集中所有时间序列的预测:
forecasts = np.vstack(forecasts)
print(forecasts.shape)>>> (366, 100, 24)我们可以根据测试集中存在的样本值,根据真实情况评估生成的预测。这里我们使用数据集中的每个时间序列的 MASE 和 sMAPE 指标 (metrics) 来评估:
from evaluate import load
from gluonts.time_feature import get_seasonalitymase_metric = load("evaluate-metric/mase")
smape_metric = load("evaluate-metric/smape")forecast_median = np.median(forecasts, 1)mase_metrics = []
smape_metrics = []
for item_id, ts in enumerate(test_dataset):training_data = ts["target"][:-prediction_length]ground_truth = ts["target"][-prediction_length:]mase = mase_metric.compute(predictions=forecast_median[item_id], references=np.array(ground_truth), training=np.array(training_data), periodicity=get_seasonality(freq))mase_metrics.append(mase["mase"])smape = smape_metric.compute(predictions=forecast_median[item_id], references=np.array(ground_truth), )smape_metrics.append(smape["smape"])
print(f"MASE: {np.mean(mase_metrics)}")>>> MASE: 1.2564196892177717print(f"sMAPE: {np.mean(smape_metrics)}")>>> sMAPE: 0.1609541520852549我们还可以单独绘制数据集中每个时间序列的结果指标,并观察到其中少数时间序列对最终测试指标的影响很大:
plt.scatter(mase_metrics, smape_metrics, alpha=0.3)
plt.xlabel("MASE")
plt.ylabel("sMAPE")
plt.show()
为了根据基本事实测试数据绘制任何时间序列的预测,我们定义了以下辅助绘图函数:
import matplotlib.dates as mdatesdef plot(ts_index):fig, ax = plt.subplots()index = pd.period_range(start=test_dataset[ts_index][FieldName.START],periods=len(test_dataset[ts_index][FieldName.TARGET]),freq=freq,).to_timestamp()# Major ticks every half year, minor ticks every month,ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.MonthLocator(bymonth=(1, 7)))ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(mdates.MonthLocator())ax.plot(index[-2*prediction_length:], test_dataset[ts_index]["target"][-2*prediction_length:],label="actual",)plt.plot(index[-prediction_length:], np.median(forecasts[ts_index], axis=0),label="median",)plt.fill_between(index[-prediction_length:],forecasts[ts_index].mean(0) - forecasts[ts_index].std(axis=0), forecasts[ts_index].mean(0) + forecasts[ts_index].std(axis=0), alpha=0.3, interpolate=True,label="+/- 1-std",)plt.legend()plt.show()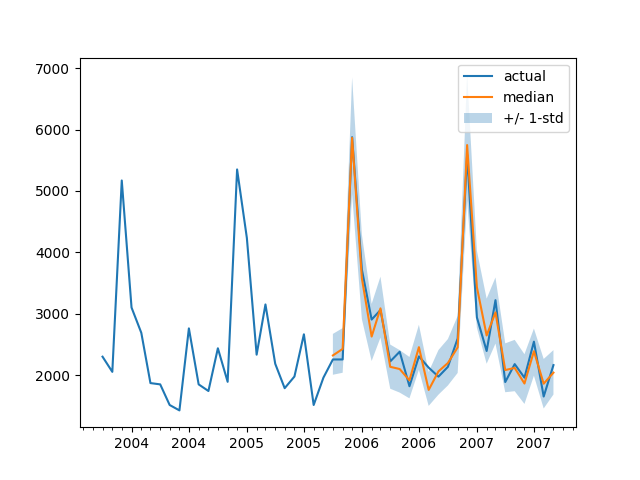
总结
正如时间序列研究人员所知,人们对“将基于 Transformer 的模型应用于时间序列”问题很感兴趣。传统 vanilla Transformer 只是众多基于注意力 (Attention) 的模型之一,因此需要向库中补充更多模型。
目前没有什么能妨碍我们继续探索对多变量时间序列进行建模,但是为此需要使用多变量分布头来实例化模型。目前已经支持了对角独立分布,后续会增加其他多元分布支持。请继续关注未来的博客文章以及其中的教程。
最后,NLP/CV 领域从 大型预训练模型 中获益匪浅,但据我们所知,时间序列领域并非如此。基于 Transformer 的模型似乎是这一研究方向的必然之选,我们迫不及待地想看看研究人员和从业者会发现哪些突破!
相关文章:

使用 Tranformer 进行概率时间序列预测实战
使用 Transformers 进行概率时间序列预测实战 通常,经典方法针对数据集中的每个时间序列单独拟合。然而,当处理大量时间序列时,在所有可用时间序列上训练一个“全局”模型是有益的,这使模型能够从许多不同的来源学习潜在的表示。…...
LLM大语言模型助力DataEase小助手,新增气泡地图,DataEase开源数据可视化分析平台v2.5.0发布
2024年4月8日,DataEase开源数据可视化分析平台正式发布v2.5.0版本。 这一版本的功能升级包括:新增DataEase小助手支持,通过结合智能算法和LLM(即Large Language Model,大语言模型)能力,DataEas…...

维修伊顿触摸屏不显示工业电脑人机界面EATON XVS-430-10MPI-1-10 深圳捷达工控维修
人机界面 (HMI) XP500 工业 PC 系列 以不同的方式思考工业平板电脑 对于严酷、高要求的应用,工业平板电脑设定了可配置性和稳健性的标准。伊顿的 XP500 系列工业平板电脑凭借防刮钢化玻璃屏幕、铸铝外壳和无风扇设计满足了这些需求。这些功能使 XP500 HMI成为一款节…...
趣话最大割问题:花果山之群猴博弈
内容来源:量子前哨(ID:Qforepost) 编辑丨浪味仙 排版丨 沛贤 深度好文:3000字丨15分钟阅读 趋利避害,是所有生物遵循的自然法则,人类也不例外。 举个例子,假如你是某生鲜平台的配…...

上周面试了一个大模型算法岗的女生,有点崩溃。。。
节前,我们星球组织了一场算法岗技术&面试讨论会,邀请了一些互联网大厂朋友、参加社招和校招面试的同学,针对算法岗技术趋势、大模型落地项目经验分享、新手如何入门算法岗、该如何准备、面试常考点分享等热门话题进行了深入的讨论。 汇总…...

AI系列:大语言模型的function calling
目录 大语言模型(LLM) 的function calling实验:OpenAI之function calling序列图:function calling如何工作详情: 对话内容参考代码 后续: 使用LangChain实现function calling参考 大语言模型(LLM) 的function calling 大语言模型(LLM)可以使用自然语言与…...

conda 创建、激活、退出、删除虚拟环境
一、conda 本地环境常用操作 #获取版本号 conda --version 或 conda -V #检查更新当前conda conda update conda #查看当前存在哪些虚拟环境 conda env list 或 conda info -e #查看--安装--更新--删除包 conda list: conda search package_name# 查询包 cond…...

【Entity Framework】聊一聊EF中继承关系
【Entity Framework】聊一聊EF中继承关系 文章目录 【Entity Framework】聊一聊EF中继承关系一、概述二、实体类型层次结构映射三、每个层次结构一张表和鉴别器配置四、共享列五、每个类型一张表配置六、每个具体类型一张表配置七、TPC数据库架构八、总结 一、概述 Entity Fra…...
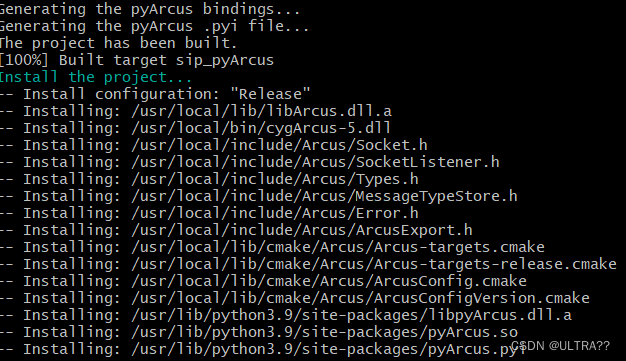
curaengine编译源码之libarcus编译记录
libArcus的编译(成功安装) This library contains C code and Python3 bindings for creating a socket in a thread and using this socket to send and receive messages based on the Protocol Buffers library. It is designed to facilitate the c…...
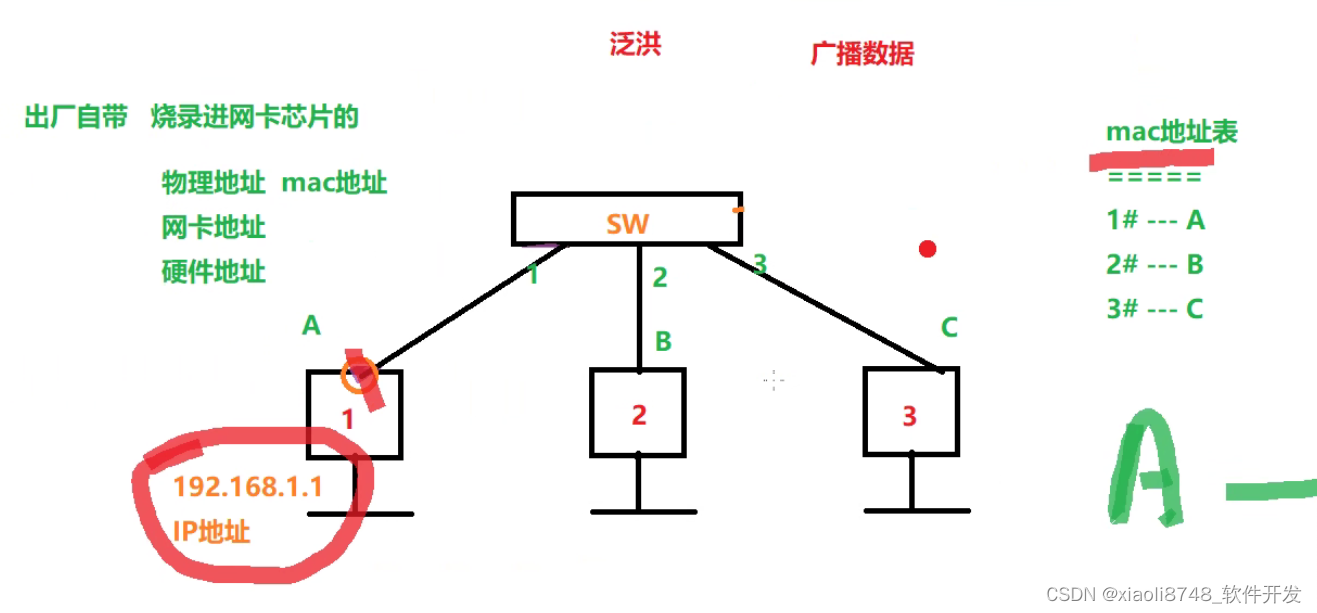
运用OSI模型提升排错能力
1. OSI模型有什么实际的应用价值? 2. 二层和三层网络的区别和应用; 3. 如何通过OSI模型提升组网排错能力? -- OSI - 开放式系统互联 - 一个互联标准 - 从软件和硬件 定义标准 - 不同厂商的设备 研发的技术 - 具备兼容性 -- O…...
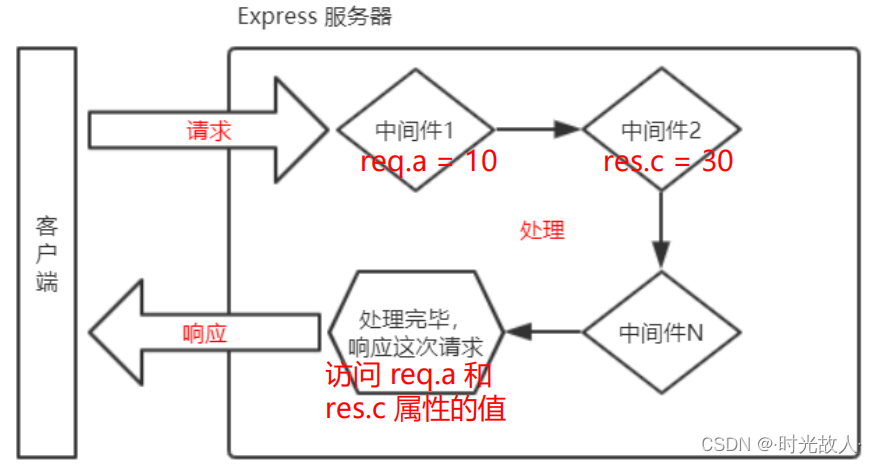
【Node.js】Express学习笔记(黑马)
目录 初识 ExpressExpress 简介Express 的基本使用托管静态资源nodemon Express 路由路由的概念路由的使用 Express 中间件中间件的概念Express 中间件的初体验中间件的分类 初识 Express Express 简介 什么是 Express? 官方给出的概念:Express 是基于…...
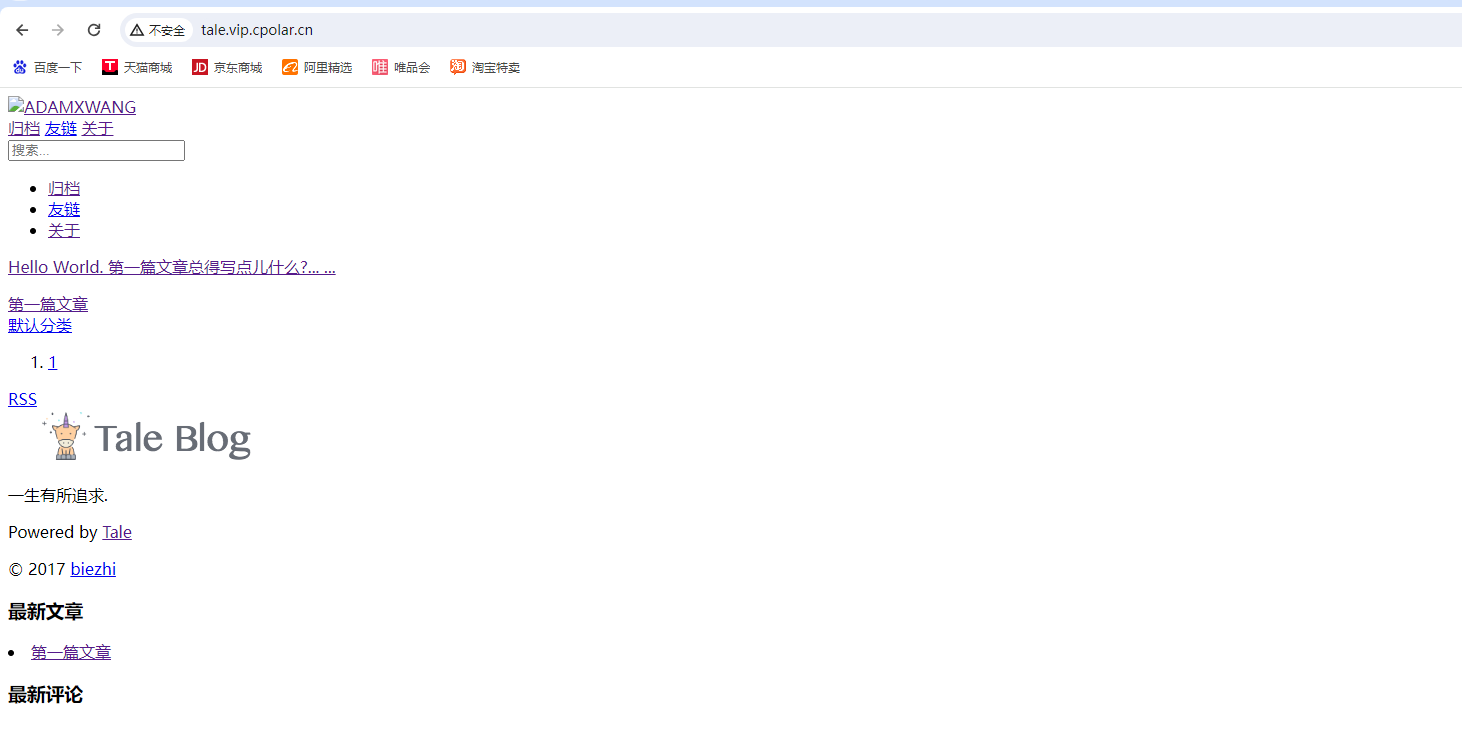
Linux系统部署Tale个人博客并发布到公网访问
目录 ⛳️推荐 前言 1. Tale网站搭建 1.1 检查本地环境 1.2 部署Tale个人博客系统 1.3 启动Tale服务 1.4 访问博客地址 2. Linux安装Cpolar内网穿透 3. 创建Tale博客公网地址 4. 使用公网地址访问Tale ⛳️推荐 前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通…...
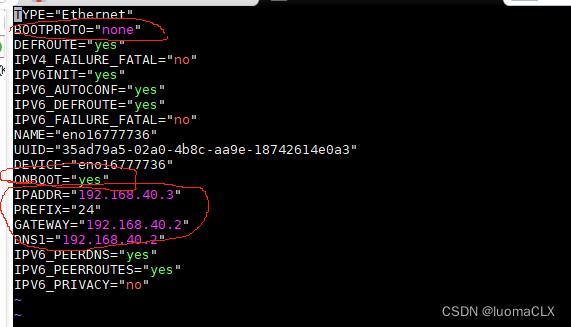
CentOS7里ifcfg-eth0文件不存在解决方案/Centos7修改网络IP解决方案
Centos7网络IP地址手动设置 1、centos7没有ifcfg-eth0,我的centos7也没有其他博客说的什么ifcfg-ens33、ifcfg-ens32,然后我打开了我这里的ifcfg-eno***,结果发现就是centos6里的ifcfg-eth0里的网络配置。2、vim ifcfg-eno***(按t…...

go第三方库go.uber.org介绍
Uber 是一家美国硅谷的科技公司,也是 Go 语言的早期 adopter。其开源了很多 golang 项目,诸如被 Gopher 圈熟知的 zap、jaeger 等。2018 年年末 Uber 将内部的 Go 风格规范 开源到 GitHub,经过一年的积累和更新,该规范已经初具规模…...
Oracle 正则表达式
一、Oracle 正则表达式相关函数 (1) regexp_like :同 like 功能相似(模糊 匹配) (2) regexp_instr :同 instr 功能相似(返回字符所在 下标) (3) regexp_substr : 同 substr 功能相似&…...

MongoDB聚合运算符:$rand
MongoDB聚合运算符:$rand 文章目录 MongoDB聚合运算符:$rand语法举例生成随机数据点从集合中随机选择条目 $rand聚合运算符用于返回一个0~1之间的随机浮点数。 语法 { $rand: {} }$rand运算符不需要任何参数。每次调用$rand都会返回一个小数点后最多17位…...
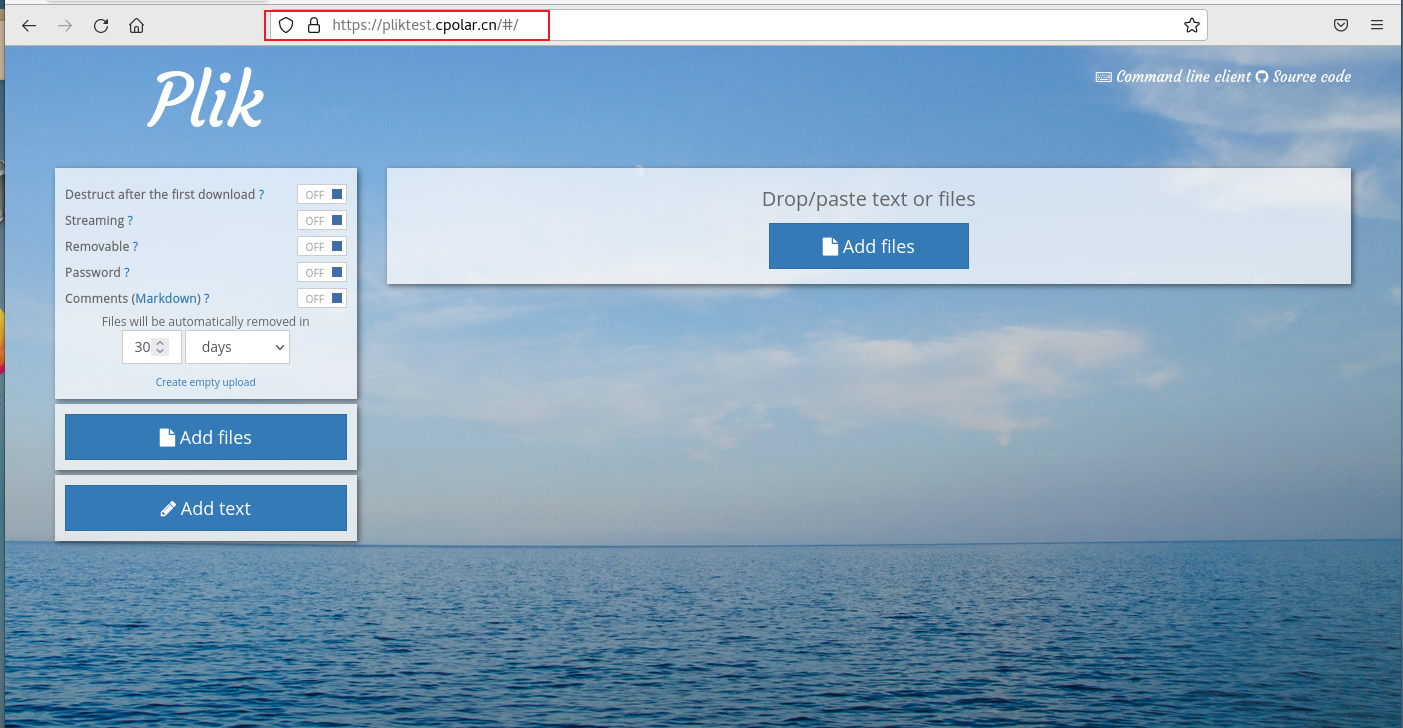
如何在Linux通过docker搭建Plik文件系统并实现无公网IP管理内网文件
文章目录 1. Docker部署Plik2. 本地访问Plik3. Linux安装Cpolar4. 配置Plik公网地址5. 远程访问Plik6. 固定Plik公网地址7. 固定地址访问Plik 本文介绍如何使用Linux docker方式快速安装Plik并且结合Cpolar内网穿透工具实现远程访问,实现随时随地在任意设备上传或者…...
k8s部署efk
环境简介: kubernetes: v1.22.2 helm: v3.12.0 elasticsearch: 8.8.0 chart包:19.10.0 fluentd: 1.16.2 chart包: 5.9.4 kibana: 8.2.2 chart包:10.1.9 整体架构图: 一、Elasticsearch安装…...

AI模型大PK
🤖AI模型大PK!免费测试GPT-4等36款顶级聊天机器人 近年来,大型语言模型(LLM)的发展日新月异,各大科技巨头和研究机构纷纷推出了自己的聊天机器人。那么,如何才能知道哪个模型更强大、更智能呢&…...
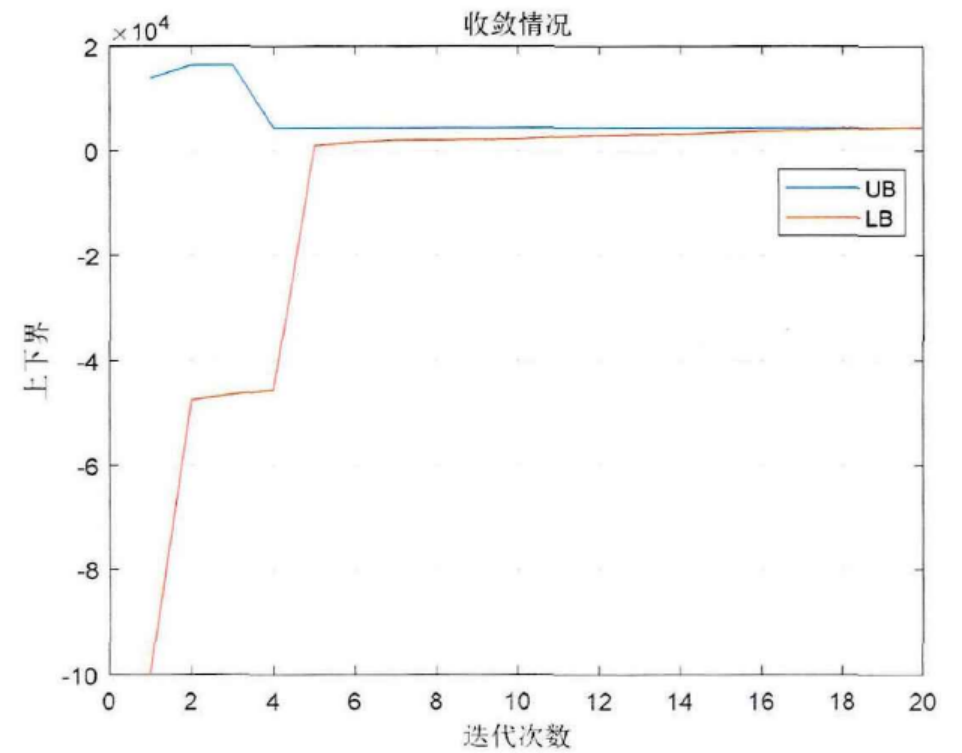
Matlab|基于广义Benders分解法的综合能源系统优化规划
目录 1 主要内容 广义benders分解法流程图: 优化目标: 约束条件: 2 部分代码 3 程序结果 4 下载链接 1 主要内容 该程序复现文章《综合能源系统协同运行策略与规划研究》第四章内容基于广义Benders分解法的综合能源系统优化规划&…...
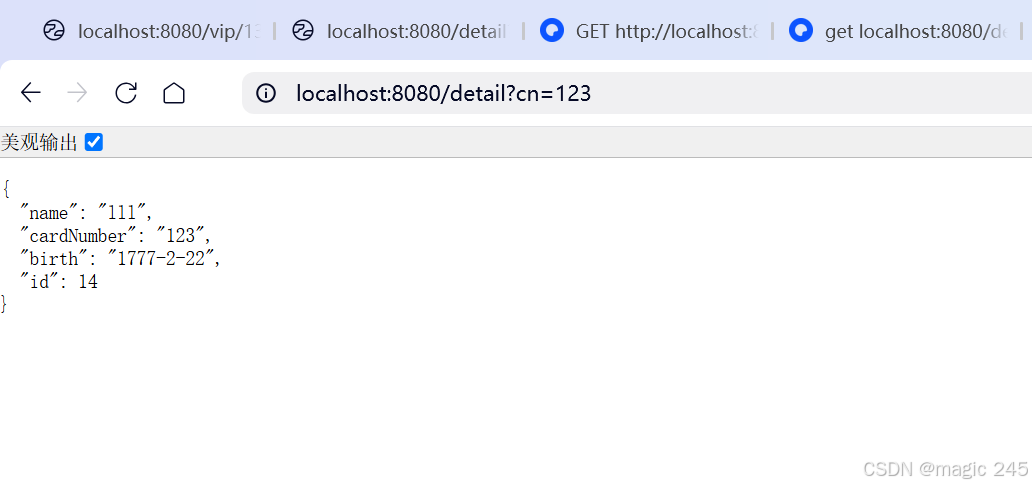
Lombok 的 @Data 注解失效,未生成 getter/setter 方法引发的HTTP 406 错误
HTTP 状态码 406 (Not Acceptable) 和 500 (Internal Server Error) 是两类完全不同的错误,它们的含义、原因和解决方法都有显著区别。以下是详细对比: 1. HTTP 406 (Not Acceptable) 含义: 客户端请求的内容类型与服务器支持的内容类型不匹…...
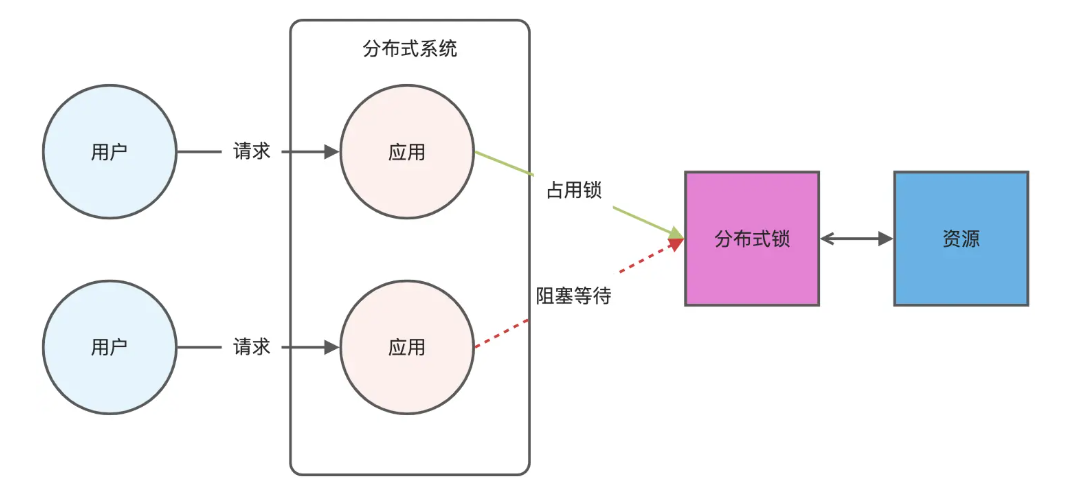
Redis相关知识总结(缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿,Redis实现分布式锁,如何保持数据库和缓存一致)
文章目录 1.什么是Redis?2.为什么要使用redis作为mysql的缓存?3.什么是缓存雪崩、缓存穿透、缓存击穿?3.1缓存雪崩3.1.1 大量缓存同时过期3.1.2 Redis宕机 3.2 缓存击穿3.3 缓存穿透3.4 总结 4. 数据库和缓存如何保持一致性5. Redis实现分布式…...

【Go】3、Go语言进阶与依赖管理
前言 本系列文章参考自稀土掘金上的 【字节内部课】公开课,做自我学习总结整理。 Go语言并发编程 Go语言原生支持并发编程,它的核心机制是 Goroutine 协程、Channel 通道,并基于CSP(Communicating Sequential Processes࿰…...

Robots.txt 文件
什么是robots.txt? robots.txt 是一个位于网站根目录下的文本文件(如:https://example.com/robots.txt),它用于指导网络爬虫(如搜索引擎的蜘蛛程序)如何抓取该网站的内容。这个文件遵循 Robots…...

Python如何给视频添加音频和字幕
在Python中,给视频添加音频和字幕可以使用电影文件处理库MoviePy和字幕处理库Subtitles。下面将详细介绍如何使用这些库来实现视频的音频和字幕添加,包括必要的代码示例和详细解释。 环境准备 在开始之前,需要安装以下Python库:…...

关于 WASM:1. WASM 基础原理
一、WASM 简介 1.1 WebAssembly 是什么? WebAssembly(WASM) 是一种能在现代浏览器中高效运行的二进制指令格式,它不是传统的编程语言,而是一种 低级字节码格式,可由高级语言(如 C、C、Rust&am…...
)
OpenLayers 分屏对比(地图联动)
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 地图分屏对比在WebGIS开发中是很常见的功能,和卷帘图层不一样的是,分屏对比是在各个地图中添加相同或者不同的图层进行对比查看。…...
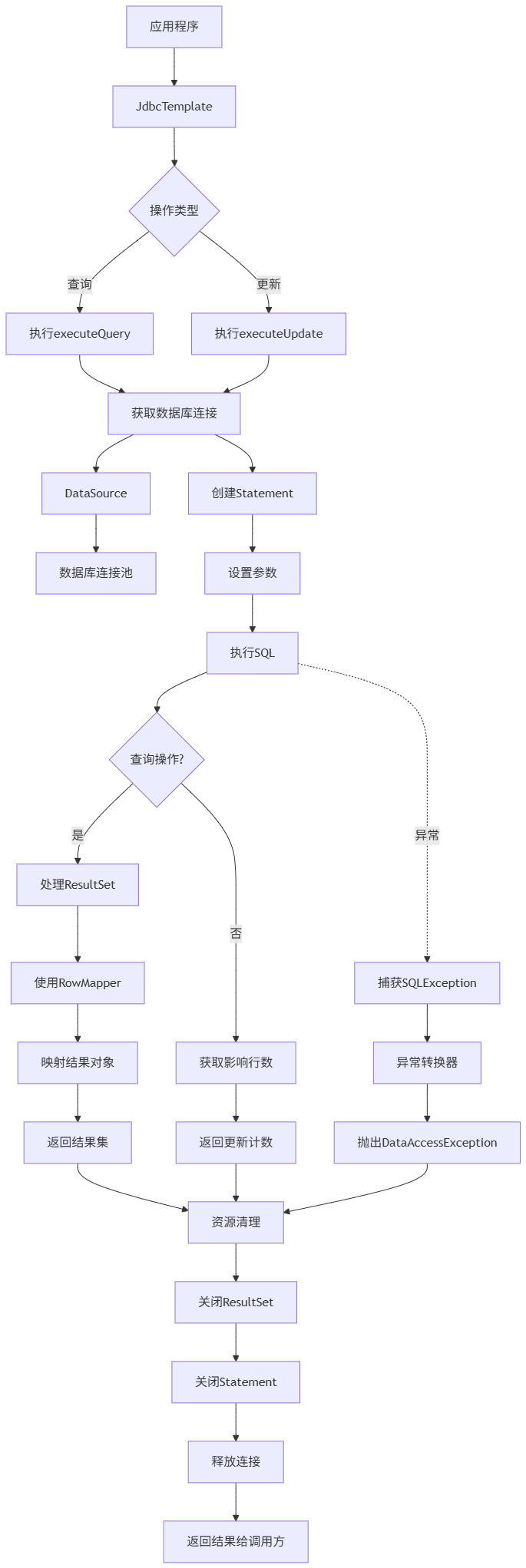
Spring数据访问模块设计
前面我们已经完成了IoC和web模块的设计,聪明的码友立马就知道了,该到数据访问模块了,要不就这俩玩个6啊,查库势在必行,至此,它来了。 一、核心设计理念 1、痛点在哪 应用离不开数据(数据库、No…...
优选算法第十二讲:队列 + 宽搜 优先级队列
优选算法第十二讲:队列 宽搜 && 优先级队列 1.N叉树的层序遍历2.二叉树的锯齿型层序遍历3.二叉树最大宽度4.在每个树行中找最大值5.优先级队列 -- 最后一块石头的重量6.数据流中的第K大元素7.前K个高频单词8.数据流的中位数 1.N叉树的层序遍历 2.二叉树的锯…...
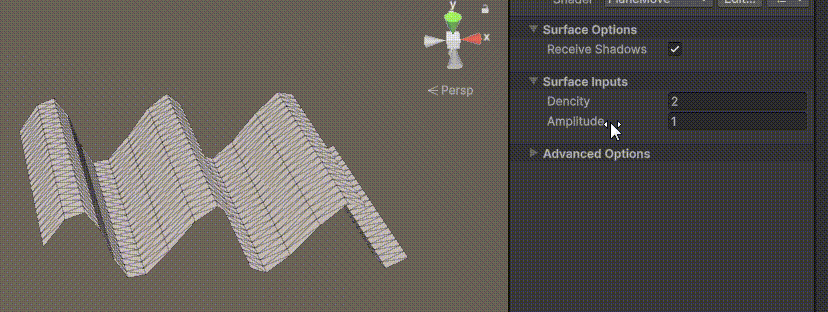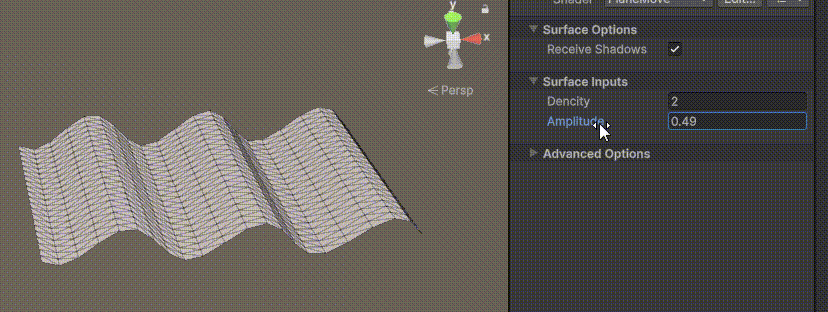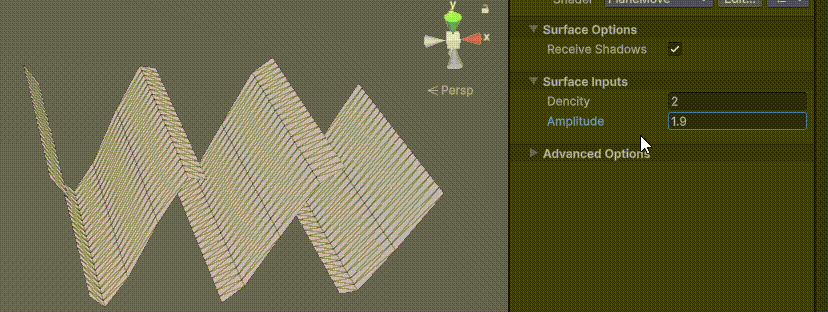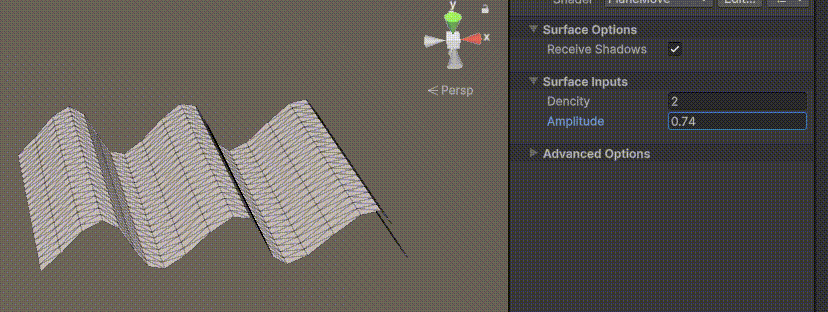
Unity | AmplifyShaderEditor插件基础(第七集:平面波动shader)
目录 一、👋🏻前言 二、😈sinx波动的基本原理 三、😈波动起来 1.sinx节点介绍 2.vertexPosition 3.集成Vector3 a.节点Append b.连起来 4.波动起来 a.波动的原理 b.时间节点 c.sinx的处理 四、🌊波动优化…...
