PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(一百三十八)|深入理解PostgreSQL数据库之Protocol message构造和解析逻辑
目录结构
注:提前言明 本文借鉴了以下博主、书籍或网站的内容,其列表如下:
1、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》
2、参考书籍:《数据库事务处理的艺术:事务管理与并发控制》
3、PostgreSQL数据库仓库链接,点击前往
4、日本著名PostgreSQL数据库专家 铃木启修 网站主页,点击前往
5、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL中文手册》
6、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL指南:内幕探索》,点击前往
7、深度解析 PostgreSQL Protocol v3.0(一),点击前往
8、技术贴 | 深度解析 PostgreSQL Protocol v3.0(二)— 扩展查询,点击前往
1、本文内容全部来源于开源社区 GitHub和以上博主的贡献,本文也免费开源(可能会存在问题,评论区等待大佬们的指正)
2、本文目的:开源共享 抛砖引玉 一起学习
3、本文不提供任何资源 不存在任何交易 与任何组织和机构无关
4、大家可以根据需要自行 复制粘贴以及作为其他个人用途,但是不允许转载 不允许商用 (写作不易,还请见谅 💖)
5、本文内容基于PostgreSQL master源码开发而成
深入理解PostgreSQL数据库之Protocol message构造和解析逻辑
- 文章快速说明索引
- 功能使用背景说明
- 功能实现源码解析
- 辅助调试信息
- 前端信息构造
- 后端消息解析

文章快速说明索引
学习目标:
做数据库内核开发久了就会有一种 少年得志,年少轻狂 的错觉,然鹅细细一品觉得自己其实不算特别优秀 远远没有达到自己想要的。也许光鲜的表面掩盖了空洞的内在,每每想到于此,皆有夜半临渊如履薄冰之感。为了睡上几个踏实觉,即日起 暂缓其他基于PostgreSQL数据库的兼容功能开发,近段时间 将着重于学习分享Postgres的基础知识和实践内幕。
学习内容:(详见目录)
1、深入理解PostgreSQL数据库之Protocol message构造和解析逻辑
学习时间:
2024年04月17日 22:14:16 星期三
学习产出:
1、PostgreSQL数据库基础知识回顾 1个
2、CSDN 技术博客 1篇
3、PostgreSQL数据库内核深入学习
注:下面我们所有的学习环境是Centos8+PostgreSQL master+Oracle19C+MySQL8.0
postgres=# select version();version
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------PostgreSQL 17devel on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (GCC) 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-21), 64-bit
(1 row)postgres=##-----------------------------------------------------------------------------#SQL> select * from v$version; BANNER Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
BANNER_FULL Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 19.17.0.0.0
BANNER_LEGACY Oracle Database 19c EE Extreme Perf Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
CON_ID 0#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------#mysql> select version();
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 8.0.27 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.06 sec)mysql>
功能使用背景说明
在之前的博客 PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(一百三十七)|深入理解PostgreSQL数据库之Add support for Close on portals and statements,点击前往 的结尾的时候,简单介绍了一下close的message构造:
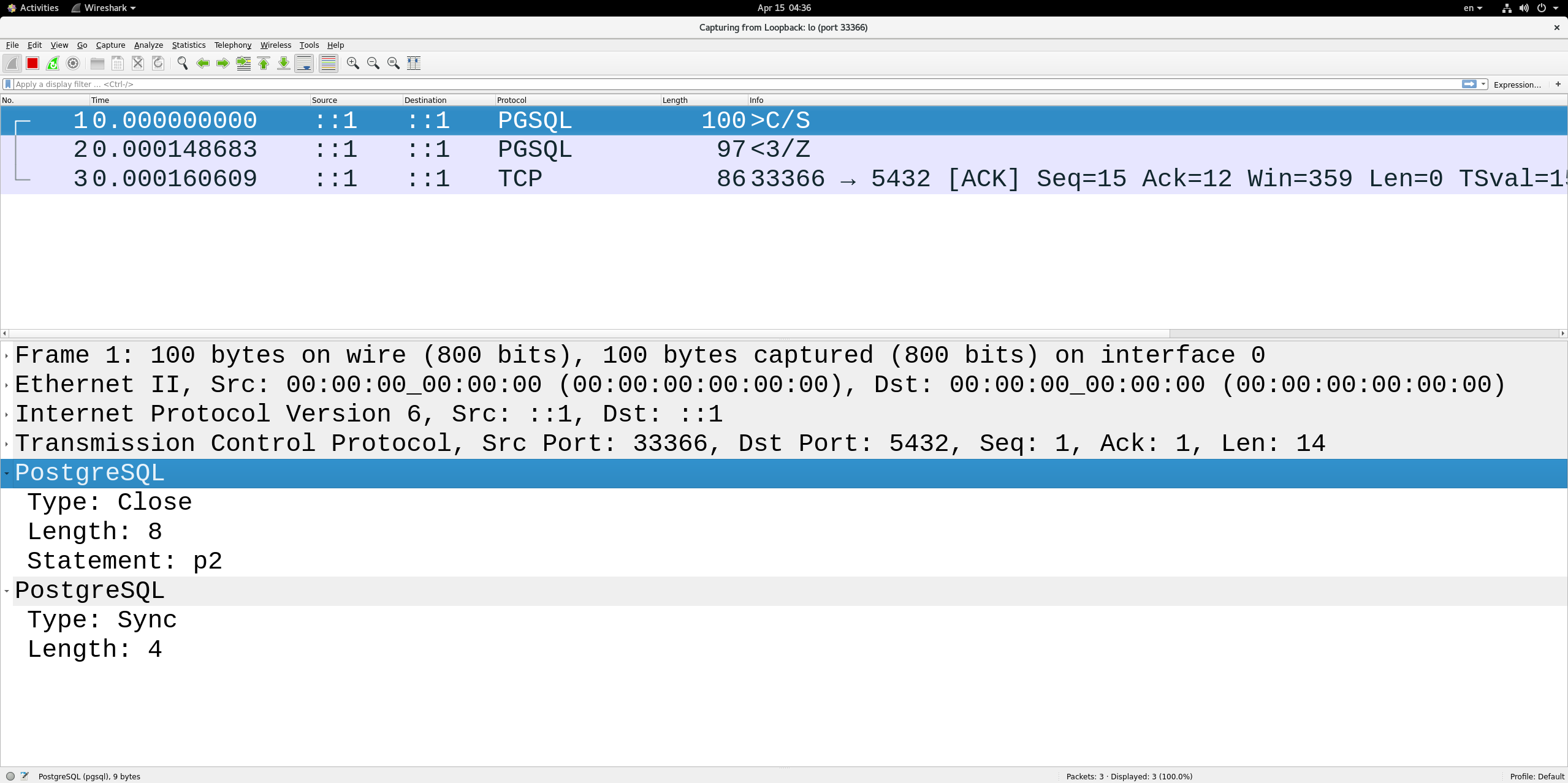
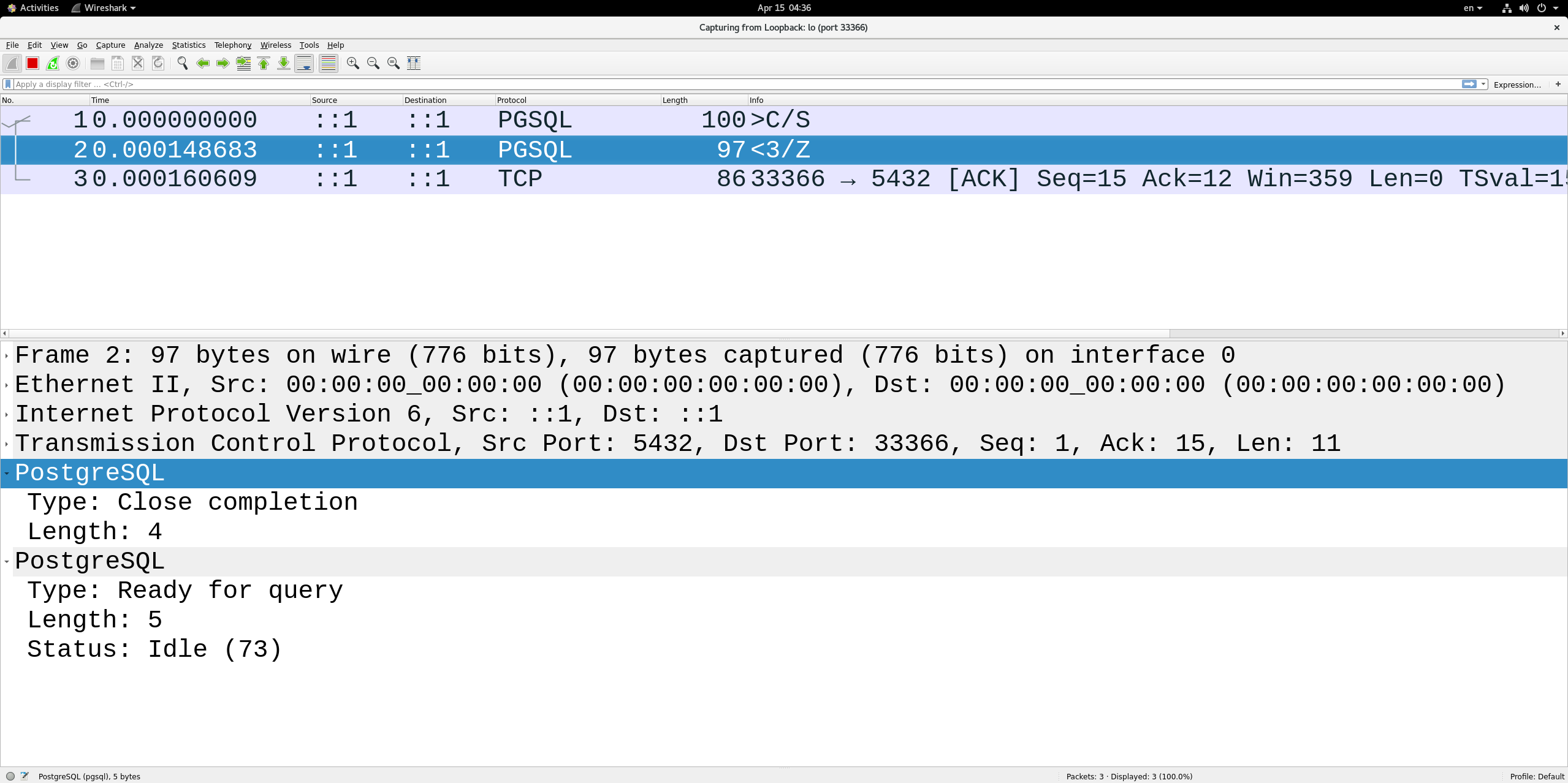
这里解释一下close消息的构造,如下:
/* construct the Close message */if (pqPutMsgStart(command, conn) < 0 ||pqPutc(type, conn) < 0 || // 1字节 SpqPuts(target, conn) < 0 || // strlen("p2") + 1 = 3pqPutMsgEnd(conn) < 0) // (conn->outMsgEnd - conn->outMsgStart)长度 4字节goto sendFailed;
功能实现源码解析
辅助调试信息
上面是通过抓包工具得到的,接下来我们看一下PostgreSQL中提供的debug方式,如下:
#include <iostream>#include "libpq-fe.h"using namespace std;int main()
{const char *conninfo = "host=localhost port=5432 user=postgres dbname=postgres password=1";const char *dropTableCmd = "drop table if exists t1;";const char *createTableCmd = "create table t1(id int, name text);";const char *insertCmd = "insert into t1 values(1, 'Oracle'), (2, 'MySQL'), (3, 'SQL Server');";const char *prepareCmd0 = "table t1;";const char *prepareCmd1 = "select * from t1 where id < $1;";const char *prepareCmd2 = "select * from t1 where id = $1 and name = $2;";PGresult *result = NULL;ExecStatusType result_status;int n_rows = 0, ntups = 0;const char *values2[2] = {"2", "MySQL"};FILE *file = fopen("/home/postgres/test/bin/1.txt", "w+");PGconn *conn = PQconnectdb(conninfo);PQtrace(conn, file);if (PQstatus(conn) == CONNECTION_OK){cout << "连接PostgreSQL数据库 成功!" << endl;if (PQexec(conn, dropTableCmd) != NULL){cout << "删除表成功" << endl;}if (PQexec(conn, createTableCmd) != NULL){cout << "创建表成功" << endl;}if (PQexec(conn, insertCmd) != NULL){cout << "插入表成功" << endl<< endl;}/* ---------------------------------------------------------------- */// prepareif (PQsendPrepare(conn, "p23456789", prepareCmd2, 2, NULL) != NULL) // 异步{cout << "prepare p23456789 send成功" << endl;}while (NULL != (result = PQgetResult(conn))){result_status = PQresultStatus(result);if ((PGRES_EMPTY_QUERY != result_status) && (PGRES_COMMAND_OK != result_status) && (PGRES_TUPLES_OK != result_status) && (PGRES_NONFATAL_ERROR != result_status)){cout << "prepare p23456789 失败" << endl;}else{n_rows = atoi(PQcmdTuples(result));ntups = PQntuples(result);cout << "prepare p23456789 成功"<< " n_rows: " << n_rows << " ntups: " << ntups << endl<< endl;}PQclear(result);}/* ---------------------------------------------------------------- */// exec_preparedif (PQsendQueryPrepared(conn, "p23456789", 2, values2, NULL, NULL, 0) != NULL) // 异步{cout << "exec prepare p23456789 send成功" << endl;}while (NULL != (result = PQgetResult(conn))){result_status = PQresultStatus(result);if ((PGRES_EMPTY_QUERY != result_status) && (PGRES_COMMAND_OK != result_status) && (PGRES_TUPLES_OK != result_status) && (PGRES_NONFATAL_ERROR != result_status)){cout << "exec prepare p23456789 失败" << endl;}else{n_rows = atoi(PQcmdTuples(result));ntups = PQntuples(result);cout << "exec prepare p23456789 send成功"<< " n_rows: " << n_rows << " ntups: " << ntups << endl<< endl;}PQclear(result);}/* ---------------------------------------------------------------- */// deallocateresult = PQexec(conn, "select pg_sleep(60);"); // 同步PQclear(result);if (PQsendClosePrepared(conn, "p23456789") != NULL) // 异步{cout << "close prepare p23456789 send成功" << endl;}while (NULL != (result = PQgetResult(conn))){result_status = PQresultStatus(result);if ((PGRES_EMPTY_QUERY != result_status) && (PGRES_COMMAND_OK != result_status) && (PGRES_TUPLES_OK != result_status) && (PGRES_NONFATAL_ERROR != result_status)){cout << "close prepare p23456789 失败" << endl;}else{n_rows = atoi(PQcmdTuples(result));ntups = PQntuples(result);cout << "close prepare p23456789 成功"<< " n_rows: " << n_rows << " ntups: " << ntups << endl<< endl;}PQclear(result);}/* ---------------------------------------------------------------- */PQfinish(conn);PQuntrace(conn);cout << "与PostgreSQL数据库连接 关闭!" << endl;}else{cout << "连接失败!" << endl;}fclose(file);return 0;
}/** export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$PG_HOME/lib** g++ libpqtest2.cpp -lpq -L/home/postgres/test/lib -I/home/postgres/test/include -o main -w -g -O0*/
执行结果以及打印信息,如下:
[postgres@localhost:~/test/bin]$ ./main
连接PostgreSQL数据库 成功!
删除表成功
创建表成功
插入表成功prepare p23456789 send成功
prepare p23456789 成功 n_rows: 0 ntups: 0exec prepare p23456789 send成功
exec prepare p23456789 send成功 n_rows: 1 ntups: 1close prepare p23456789 send成功
close prepare p23456789 成功 n_rows: 0 ntups: 0与PostgreSQL数据库连接 关闭!
[postgres@localhost:~/test/bin]$ cat 1.txt
2024-04-16 20:22:43.371152 F 29 Query "drop table if exists t1;"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.381514 B 15 CommandComplete "DROP TABLE"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.381531 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:22:43.381561 F 40 Query "create table t1(id int, name text);"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388197 B 17 CommandComplete "CREATE TABLE"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388215 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388239 F 73 Query "insert into t1 values(1, 'Oracle'), (2, 'MySQL'), (3, 'SQL Server');"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388729 B 15 CommandComplete "INSERT 0 3"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388736 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388758 F 62 Parse "p23456789" "select * from t1 where id = $1 and name = $2;" 0
2024-04-16 20:22:43.388762 F 4 Sync
2024-04-16 20:22:43.390728 B 4 ParseComplete
2024-04-16 20:22:43.390767 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:22:43.390772 F 37 Bind "" "p23456789" 0 2 1 '2' 5 'MySQL' 1 0
2024-04-16 20:22:43.390775 F 6 Describe P ""
2024-04-16 20:22:43.390777 F 9 Execute "" 0
2024-04-16 20:22:43.390779 F 4 Sync
2024-04-16 20:22:43.392433 B 4 BindComplete
2024-04-16 20:22:43.392483 B 50 RowDescription 2 "id" 16403 1 23 4 -1 0 "name" 16403 2 25 65535 -1 0
2024-04-16 20:22:43.392494 B 20 DataRow 2 1 '2' 5 'MySQL'
2024-04-16 20:22:43.392500 B 13 CommandComplete "SELECT 1"
2024-04-16 20:22:43.392644 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:22:43.392725 F 25 Query "select pg_sleep(60);"
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406609 B 33 RowDescription 1 "pg_sleep" 0 0 2278 4 -1 0
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406637 B 10 DataRow 1 0 ''
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406642 B 13 CommandComplete "SELECT 1"
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406645 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406654 F 15 Close S "p23456789"
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406657 F 4 Sync
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406885 B 4 CloseComplete
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406928 B 5 ReadyForQuery I
2024-04-16 20:23:43.406938 F 4 Terminate
[postgres@localhost:~/test/bin]$
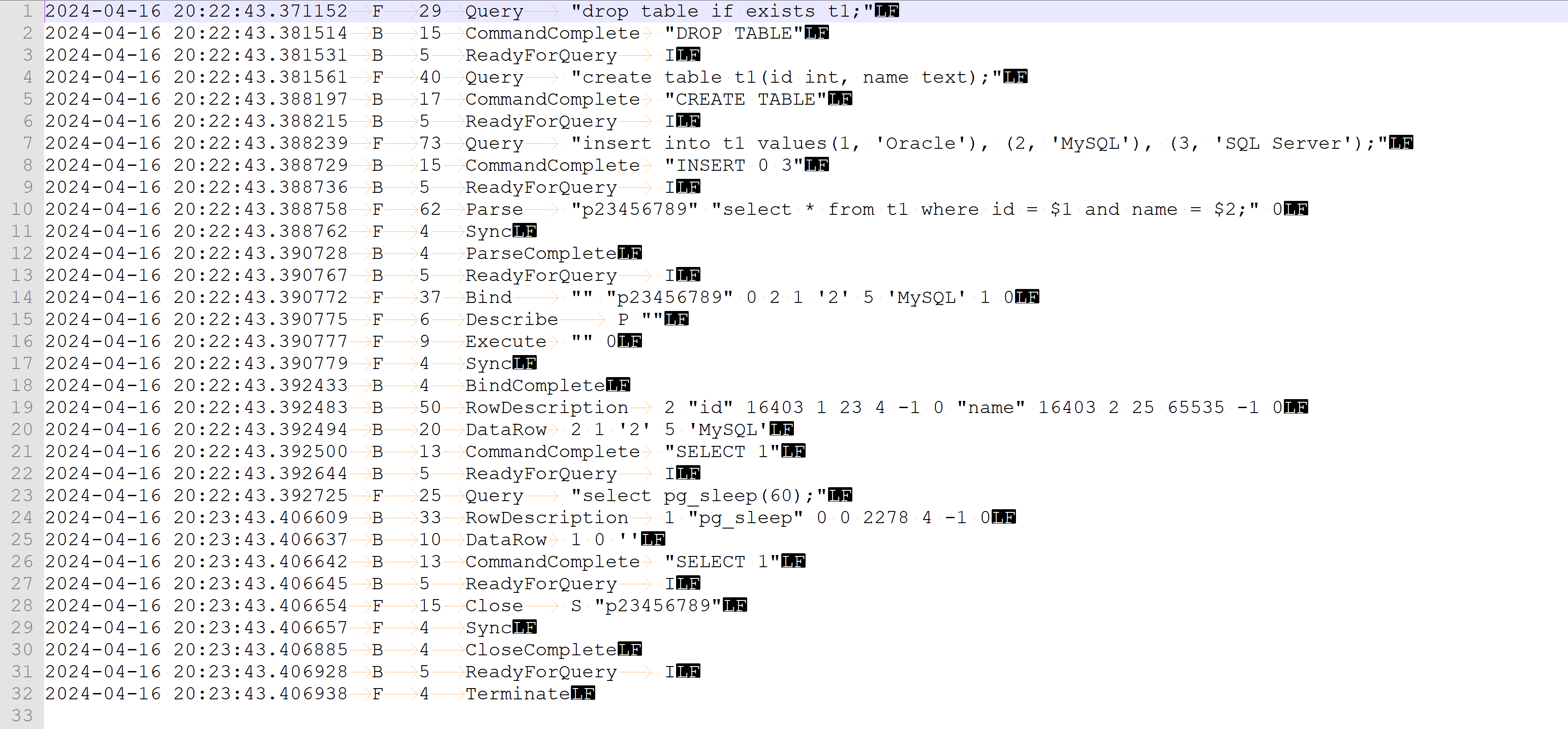
如上是通过直接调用libpq中的函数PQtrace和PQuntrace,如下:
// src/interfaces/libpq/fe-trace.c/* Enable tracing */
void
PQtrace(PGconn *conn, FILE *debug_port)
{if (conn == NULL)return;PQuntrace(conn);if (debug_port == NULL)return;conn->Pfdebug = debug_port;conn->traceFlags = 0;
}/* Disable tracing */
void
PQuntrace(PGconn *conn)
{if (conn == NULL)return;if (conn->Pfdebug){fflush(conn->Pfdebug);conn->Pfdebug = NULL;}conn->traceFlags = 0;
}
当然如上两函数是trace的开关函数,真正实现打印的逻辑 如下:
// src/interfaces/libpq/fe-trace.c/** Print the given message to the trace output stream.* 将给定消息打印到跟踪输出流*/
void
pqTraceOutputMessage(PGconn *conn, const char *message, bool toServer)
{char id;int length;char *prefix = toServer ? "F" : "B"; // 这里指的是 Front / Backendint logCursor = 0;bool regress;if ((conn->traceFlags & PQTRACE_SUPPRESS_TIMESTAMPS) == 0){char timestr[128];pqTraceFormatTimestamp(timestr, sizeof(timestr));fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "%s\t", timestr);}regress = (conn->traceFlags & PQTRACE_REGRESS_MODE) != 0;id = message[logCursor++];memcpy(&length, message + logCursor, 4);length = (int) pg_ntoh32(length);logCursor += 4;/** In regress mode, suppress the length of ErrorResponse and* NoticeResponse. The F (file name), L (line number) and R (routine* name) fields can change as server code is modified, and if their* lengths differ from the originals, that would break tests.* * 在回归模式下,抑制ErrorResponse和NoticeResponse的长度* F(文件名)、L(行号)和 R(例程名称)字段可能会随着服务器代码的修改而更改* 如果它们的长度与原始长度不同,则会破坏测试*/if (regress && !toServer && (id == 'E' || id == 'N'))fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "%s\tNN\t", prefix);elsefprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "%s\t%d\t", prefix, length);switch (id){case PqMsg_ParseComplete:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "ParseComplete");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_BindComplete:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "BindComplete");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_CloseComplete:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "CloseComplete");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_NotificationResponse:pqTraceOutputA(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_Bind:pqTraceOutputB(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_CopyDone:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "CopyDone");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_CommandComplete:/* Close(F) and CommandComplete(B) use the same identifier. */Assert(PqMsg_Close == PqMsg_CommandComplete);pqTraceOutputC(conn->Pfdebug, toServer, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_CopyData:/* Drop COPY data to reduce the overhead of logging. */break;case PqMsg_Describe:/* Describe(F) and DataRow(B) use the same identifier. */Assert(PqMsg_Describe == PqMsg_DataRow);pqTraceOutputD(conn->Pfdebug, toServer, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_Execute:/* Execute(F) and ErrorResponse(B) use the same identifier. */Assert(PqMsg_Execute == PqMsg_ErrorResponse);pqTraceOutputE(conn->Pfdebug, toServer, message, &logCursor,regress);break;case PqMsg_CopyFail:pqTraceOutputf(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_FunctionCall:pqTraceOutputF(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_CopyInResponse:pqTraceOutputG(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_Flush:/* Flush(F) and CopyOutResponse(B) use the same identifier */Assert(PqMsg_CopyOutResponse == PqMsg_Flush);if (!toServer)pqTraceOutputH(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);elsefprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "Flush"); /* no message content */break;case PqMsg_EmptyQueryResponse:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "EmptyQueryResponse");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_BackendKeyData:pqTraceOutputK(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_NoData:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "NoData");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_NoticeResponse:pqTraceOutputNR(conn->Pfdebug, "NoticeResponse", message,&logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_Parse:pqTraceOutputP(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_Query:pqTraceOutputQ(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_AuthenticationRequest:pqTraceOutputR(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_PortalSuspended:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "PortalSuspended");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_Sync:/* Parameter Status(B) and Sync(F) use the same identifier */Assert(PqMsg_ParameterStatus == PqMsg_Sync);if (!toServer)pqTraceOutputS(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);elsefprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "Sync"); /* no message content */break;case PqMsg_ParameterDescription:pqTraceOutputt(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_RowDescription:pqTraceOutputT(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, regress);break;case PqMsg_NegotiateProtocolVersion:pqTraceOutputv(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_FunctionCallResponse:pqTraceOutputV(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;case PqMsg_CopyBothResponse:pqTraceOutputW(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor, length);break;case PqMsg_Terminate:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "Terminate");/* No message content */break;case PqMsg_ReadyForQuery:pqTraceOutputZ(conn->Pfdebug, message, &logCursor);break;default:fprintf(conn->Pfdebug, "Unknown message: %02x", id);break;}fputc('\n', conn->Pfdebug);/** Verify the printing routine did it right. Note that the one-byte* message identifier is not included in the length, but our cursor does* include it.* * 验证打印例程是否正确* 请注意,一字节消息标识符不包括在长度中,但我们的光标确实包括它*/if (logCursor - 1 != length)fprintf(conn->Pfdebug,"mismatched message length: consumed %d, expected %d\n",logCursor - 1, length);
}
接下来我们重点看一下close消息的打印,如下:
pqTraceOutputMessage|pqTraceOutputC/* Close(F) or CommandComplete(B) */
static void
pqTraceOutputC(FILE *f, bool toServer, const char *message, int *cursor)
{if (toServer){fprintf(f, "Close\t");pqTraceOutputByte1(f, message, cursor);pqTraceOutputString(f, message, cursor, false);}else{fprintf(f, "CommandComplete\t");pqTraceOutputString(f, message, cursor, false);}
}
/** pqTraceOutputByte1: output a 1-char message to the log* pqTraceOutputByte1:将 1 个字符的消息输出到日志*/
static void
pqTraceOutputByte1(FILE *pfdebug, const char *data, int *cursor)
{const char *v = data + *cursor;/** Show non-printable data in hex format, including the terminating \0* that completes ErrorResponse and NoticeResponse messages.* * 以十六进制格式显示不可打印的数据* 包括完成ErrorResponse 和NoticeResponse 消息的终止\0*/if (!isprint((unsigned char) *v))fprintf(pfdebug, " \\x%02x", *v);elsefprintf(pfdebug, " %c", *v);*cursor += 1;
}
/** pqTraceOutputString: output a string message to the log* pqTraceOutputString:输出字符串消息到日志*/
static void
pqTraceOutputString(FILE *pfdebug, const char *data, int *cursor, bool suppress)
{int len;if (suppress){fprintf(pfdebug, " \"SSSS\"");*cursor += strlen(data + *cursor) + 1;}else{len = fprintf(pfdebug, " \"%s\"", data + *cursor);/** This is a null-terminated string. So add 1 after subtracting 3* which is the double quotes and space length from len.* * 这是一个以 null 结尾的字符串* 因此,从 len 中减去双引号和空格长度 3 后加 1*/*cursor += (len - 3 + 1);}
}
接下来我们继续以close消息为例,详细看一下message的构造和解析过程!
## len = 152024-04-16 20:23:43.406654 F 15 Close S "p23456789"
前端信息构造
此时的函数堆栈,如下:
libpq.so.5!PQsendTypedCommand(PGconn * conn, char command, char type, const char * target) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2605)
libpq.so.5!PQsendClosePrepared(PGconn * conn, const char * stmt) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2558)
main() (\home\postgres\test\bin\libpqtest2.cpp:110)
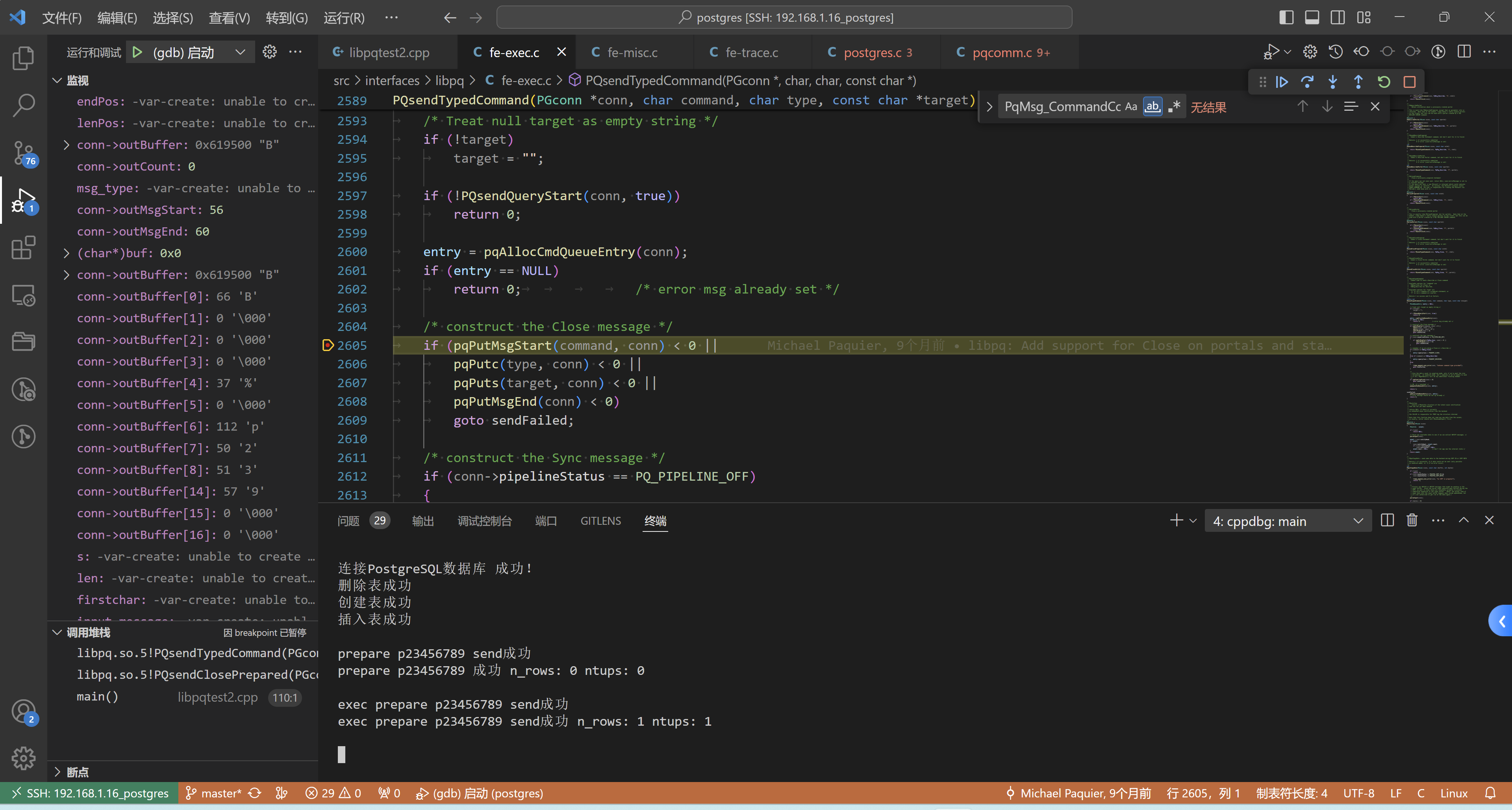
接下来就详细看一下这里的处理逻辑,如下:
第一步:
// src/interfaces/libpq/fe-exec.c/** pqPutMsgStart: begin construction of a message to the server* pqPutMsgStart:开始向服务器构造消息** msg_type is the message type byte, or 0 for a message without type byte* (only startup messages have no type byte)* msg_type 是消息类型字节,如果没有类型字节,则为 0(只有启动消息没有类型字节)** Returns 0 on success, EOF on error* 成功时返回 0,错误时返回 EOF** The idea here is that we construct the message in conn->outBuffer,* beginning just past any data already in outBuffer (ie, at* outBuffer+outCount). We enlarge the buffer as needed to hold the message.* When the message is complete, we fill in the length word (if needed) and* then advance outCount past the message, making it eligible to send.* 这里的想法是,我们在 conn->outBuffer 中构造消息,从 outBuffer 中已有的任何数据开始(即,在 outBuffer+outCount 处)* 我们根据需要扩大缓冲区来保存消息* 消息完成后,我们填写长度字(如果需要),然后将 outCount 提前到消息后面,使其符合发送条件** The state variable conn->outMsgStart points to the incomplete message's* length word: it is either outCount or outCount+1 depending on whether* there is a type byte. The state variable conn->outMsgEnd is the end of* the data collected so far.* 状态变量 conn->outMsgStart 指向不完整消息的长度字:* 它是 outCount 或 outCount+1,具体取决于是否存在类型字节* 状态变量 conn->outMsgEnd 是迄今为止收集的数据的结尾*/
int
pqPutMsgStart(char msg_type, PGconn *conn)
{int lenPos;int endPos;/* allow room for message type byte */if (msg_type)endPos = conn->outCount + 1;elseendPos = conn->outCount;/* do we want a length word? */lenPos = endPos;/* allow room for message length */endPos += 4;/* make sure there is room for message header */if (pqCheckOutBufferSpace(endPos, conn))return EOF;/* okay, save the message type byte if any */if (msg_type)conn->outBuffer[conn->outCount] = msg_type;/* set up the message pointers */conn->outMsgStart = lenPos;conn->outMsgEnd = endPos;/* length word, if needed, will be filled in by pqPutMsgEnd */return 0;
}
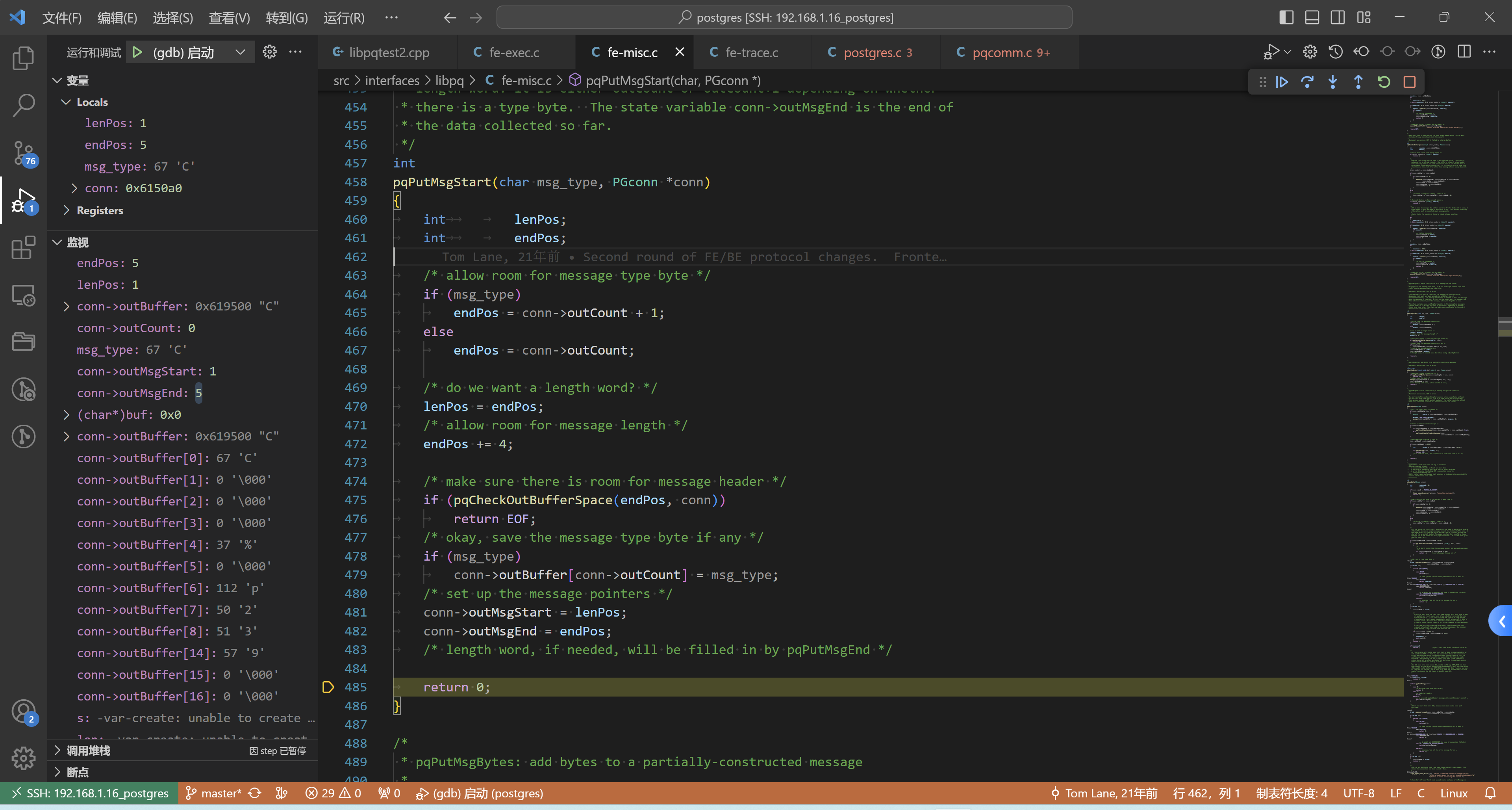
解释一下:
- msg_type此时是
C endPos += 4;就代表了 已经把消息长度的空间分配好了- conn->outCount = 0
- conn->outBuffer[conn->outCount] = msg_type; // 放的就是 C
- conn->outMsgStart = 1
- conn->outMsgEnd = 5
第二步:
libpq.so.5!pqPutMsgBytes(const void * buf, size_t len, PGconn * conn) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-misc.c:497)
libpq.so.5!pqPutc(char c, PGconn * conn) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-misc.c:94)
libpq.so.5!PQsendTypedCommand(PGconn * conn, char command, char type, const char * target) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2606)
libpq.so.5!PQsendClosePrepared(PGconn * conn, const char * stmt) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2558)
main() (\home\postgres\test\bin\libpqtest2.cpp:110)
/** pqPutc: write 1 char to the current message*/
int
pqPutc(char c, PGconn *conn)
{if (pqPutMsgBytes(&c, 1, conn))return EOF;return 0;
}.../** pqPutMsgBytes: add bytes to a partially-constructed message* pqPutMsgBytes:向部分构造的消息添加字节** Returns 0 on success, EOF on error*/
static int
pqPutMsgBytes(const void *buf, size_t len, PGconn *conn)
{/* make sure there is room for it */if (pqCheckOutBufferSpace(conn->outMsgEnd + len, conn))return EOF;/* okay, save the data */memcpy(conn->outBuffer + conn->outMsgEnd, buf, len);conn->outMsgEnd += len;/* no Pfdebug call here, caller should do it */return 0;
}
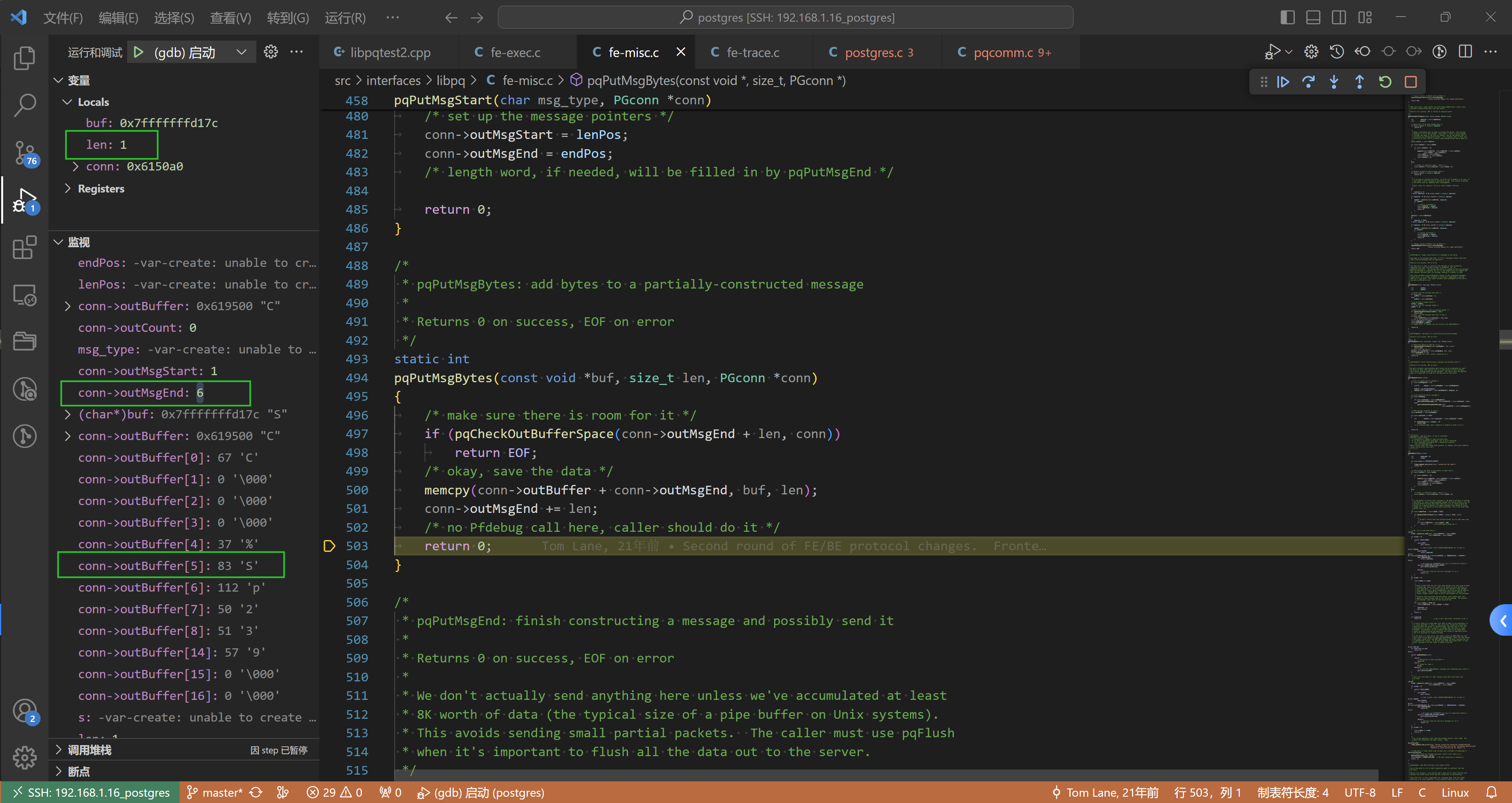
解释一下:
- 因为 type 是’S’,因此这里写的就是它
- 因为内存copy是从
conn->outBuffer + conn->outMsgEnd开始的,也就放到了conn->outBuffer[5] - conn->outMsgEnd += 1
第三步:
libpq.so.5!pqPutMsgBytes(const void * buf, size_t len, PGconn * conn) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-misc.c:500)
libpq.so.5!pqPuts(const char * s, PGconn * conn) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-misc.c:154)
libpq.so.5!PQsendTypedCommand(PGconn * conn, char command, char type, const char * target) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2607)
libpq.so.5!PQsendClosePrepared(PGconn * conn, const char * stmt) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2558)
main() (\home\postgres\test\bin\libpqtest2.cpp:110)
/** pqPuts: write a null-terminated string to the current message* pqPuts:将空终止字符串写入当前消息*/
int
pqPuts(const char *s, PGconn *conn)
{if (pqPutMsgBytes(s, strlen(s) + 1, conn))return EOF;return 0;
}
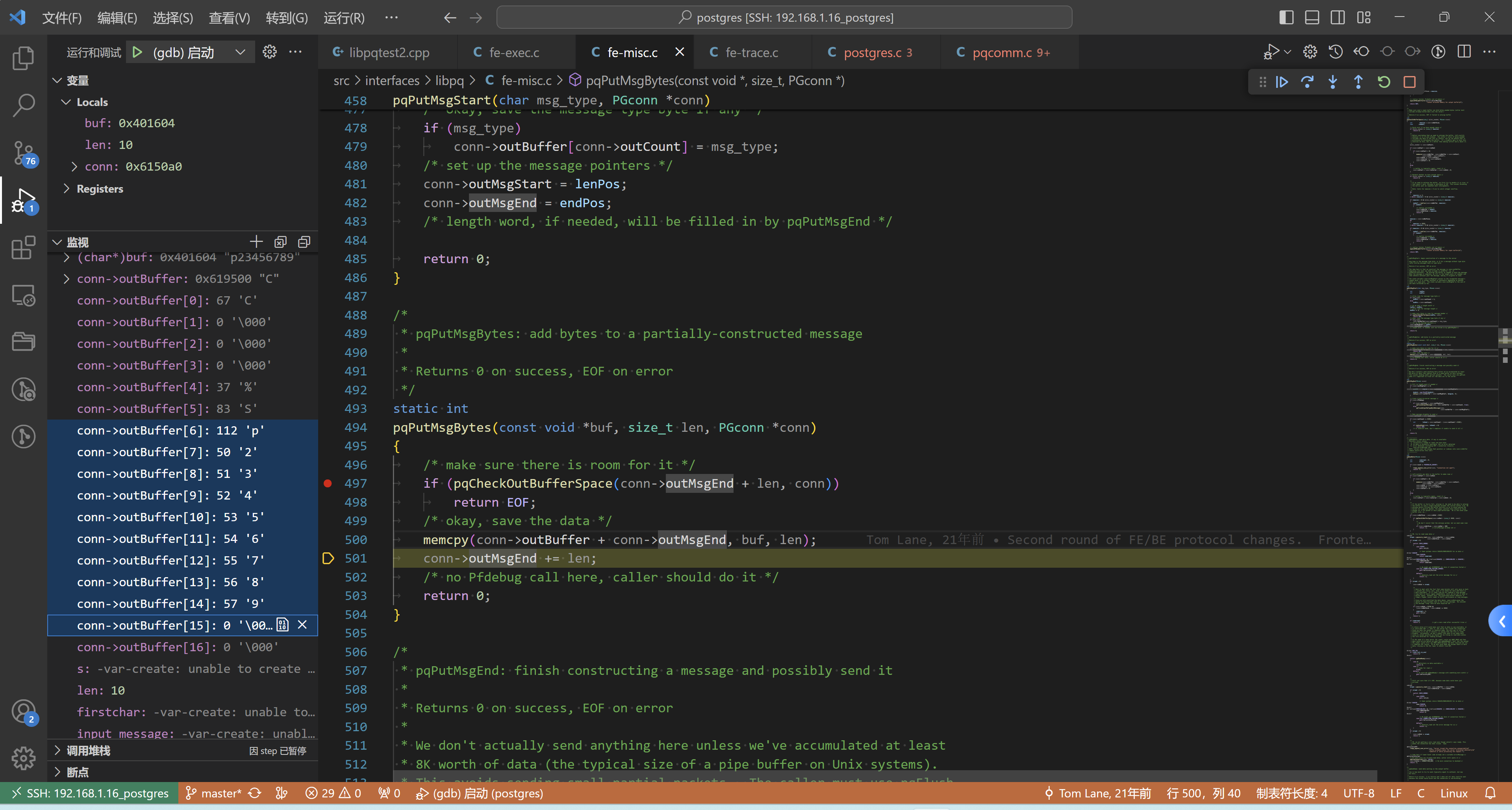
解释一下:
- len = strlen + 1; strlen(“p23456789”) + 1 = 10
- 内存copy是从
conn->outMsgEnd = 6开始的,len = 10。自然结果如上 - conn->outMsgEnd += 10
第四步:
libpq.so.5!pqPutMsgEnd(PGconn * conn) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-misc.c:520)
libpq.so.5!PQsendTypedCommand(PGconn * conn, char command, char type, const char * target) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2608)
libpq.so.5!PQsendClosePrepared(PGconn * conn, const char * stmt) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\interfaces\libpq\fe-exec.c:2558)
main() (\home\postgres\test\bin\libpqtest2.cpp:110)
/** pqPutMsgEnd: finish constructing a message and possibly send it* pqPutMsgEnd:完成构建消息并可能发送它** Returns 0 on success, EOF on error** We don't actually send anything here unless we've accumulated at least* 8K worth of data (the typical size of a pipe buffer on Unix systems).* This avoids sending small partial packets. The caller must use pqFlush* when it's important to flush all the data out to the server.* * 除非我们已经积累了至少 8K 的数据(Unix 系统上管道缓冲区的典型大小),否则我们实际上不会在这里发送任何内容* 这避免了发送小部分数据包* 当需要将所有数据刷新到服务器时,调用者必须使用 pqFlush*/
int
pqPutMsgEnd(PGconn *conn)
{/* Fill in length word if needed */if (conn->outMsgStart >= 0){uint32 msgLen = conn->outMsgEnd - conn->outMsgStart;msgLen = pg_hton32(msgLen);memcpy(conn->outBuffer + conn->outMsgStart, &msgLen, 4);}/* trace client-to-server message */if (conn->Pfdebug){if (conn->outCount < conn->outMsgStart)pqTraceOutputMessage(conn, conn->outBuffer + conn->outCount, true);elsepqTraceOutputNoTypeByteMessage(conn,conn->outBuffer + conn->outMsgStart);}/* Make message eligible to send */conn->outCount = conn->outMsgEnd;if (conn->outCount >= 8192){int toSend = conn->outCount - (conn->outCount % 8192);if (pqSendSome(conn, toSend) < 0)return EOF;/* in nonblock mode, don't complain if unable to send it all */}return 0;
}
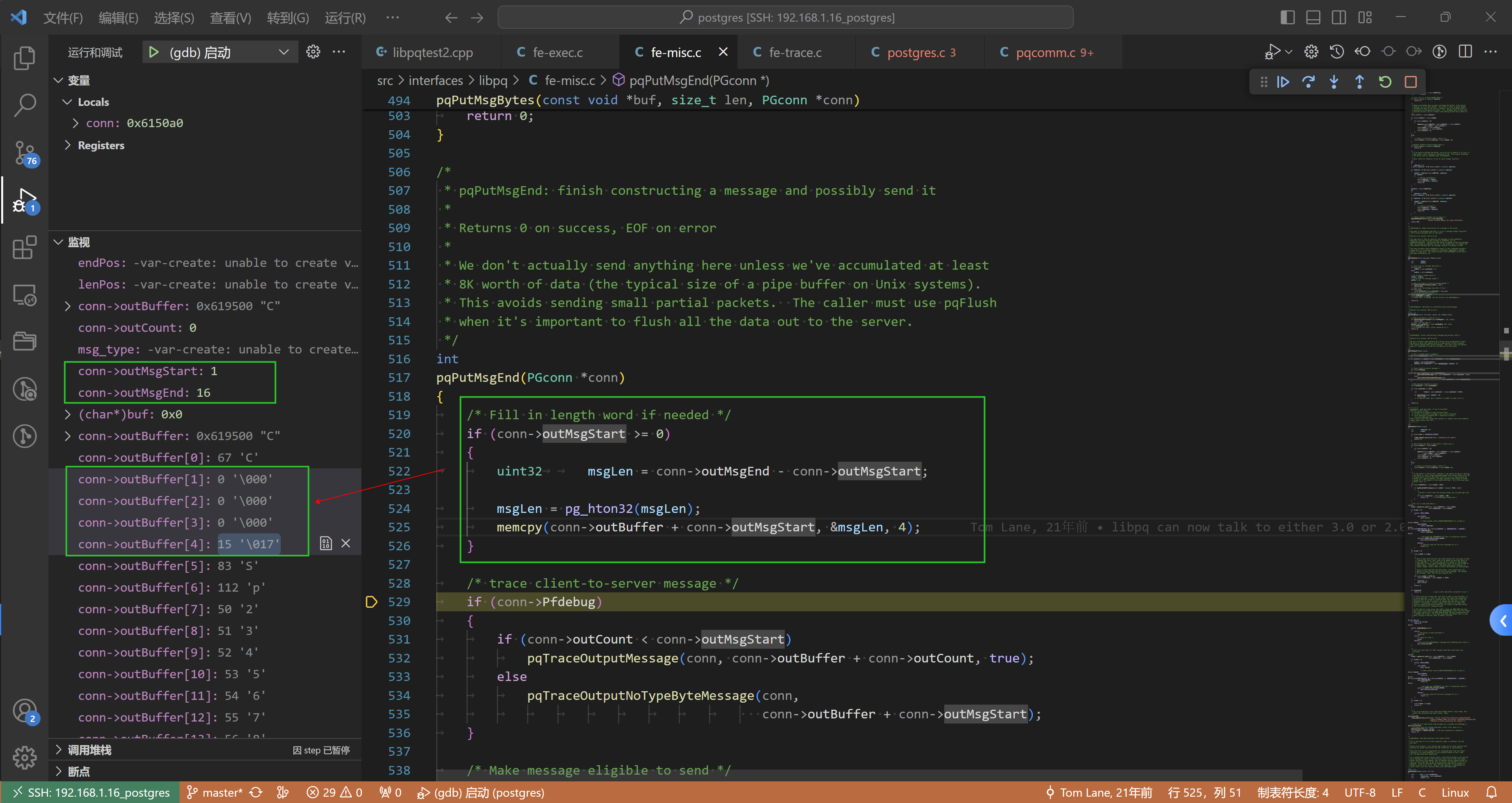
解释一下:
- 如上 message_len = 16 - 1 = 15,然后大端存储
- 内存copy是从
conn->outMsgStart = 1开始,长度是4 自然就是上面的四字节 - conn->outCount = conn->outMsgEnd = 16
至此,该15字节的close消息构建完毕!
后端消息解析
我们这里调试服务进程,如下:
第一步:消息读取,如下:
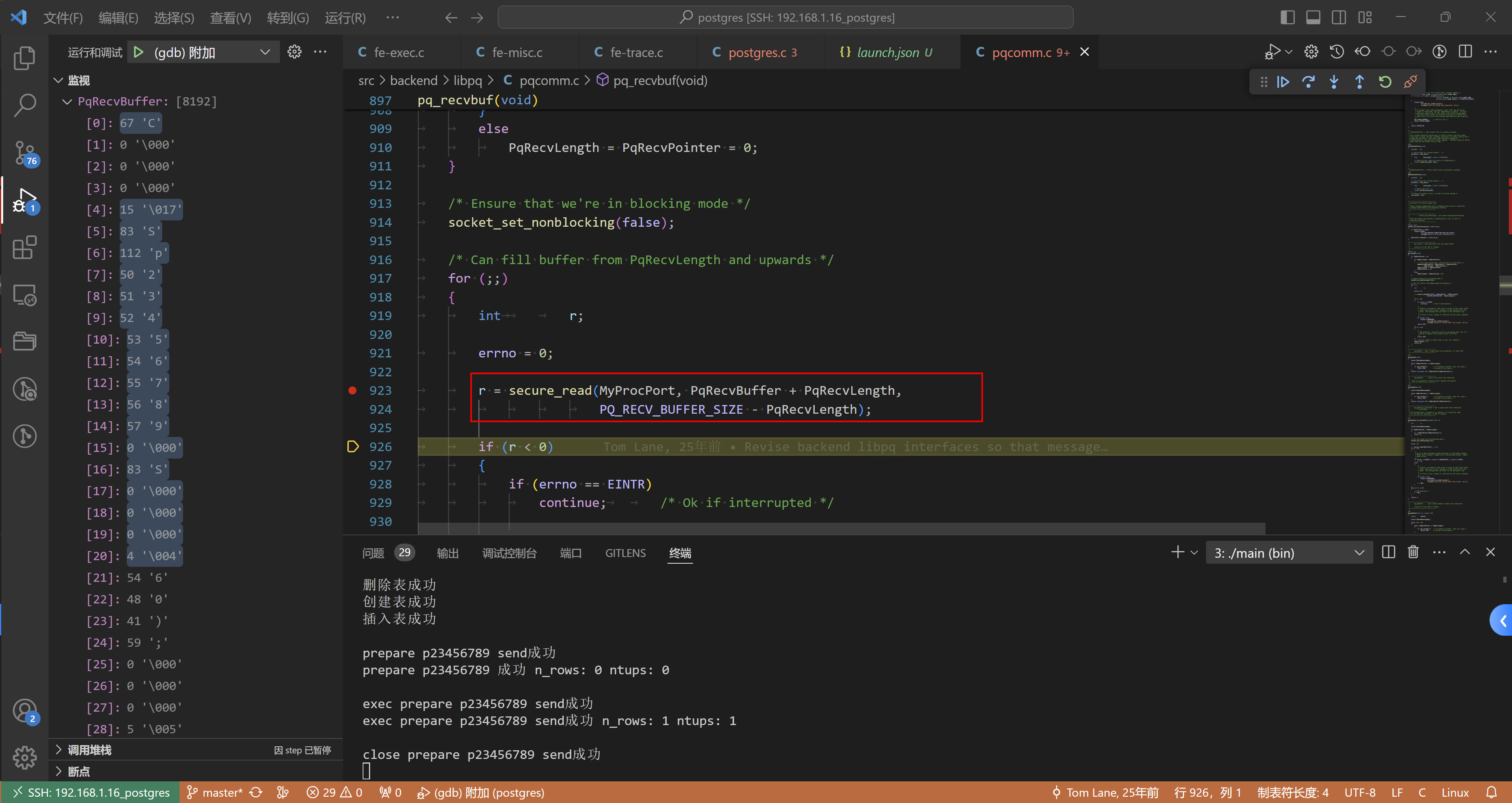
pq_recvbuf() (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\libpq\pqcomm.c:926)
pq_getbyte() (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\libpq\pqcomm.c:969)
SocketBackend(StringInfo inBuf) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\tcop\postgres.c:370)
ReadCommand(StringInfo inBuf) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\tcop\postgres.c:493)
PostgresMain(const char * dbname, const char * username) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\tcop\postgres.c:4612)
BackendMain(char * startup_data, size_t startup_data_len) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\tcop\backend_startup.c:105)
postmaster_child_launch(BackendType child_type, char * startup_data, size_t startup_data_len, ClientSocket * client_sock) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\postmaster\launch_backend.c:265)
BackendStartup(ClientSocket * client_sock) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\postmaster\postmaster.c:3593)
ServerLoop() (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\postmaster\postmaster.c:1674)
PostmasterMain(int argc, char ** argv) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\postmaster\postmaster.c:1372)
main(int argc, char ** argv) (\home\postgres\postgres\src\backend\main\main.c:197)
// src/backend/libpq/pqcomm.c/* --------------------------------* pq_recvbuf - load some bytes into the input buffer* pq_recvbuf - 将一些字节加载到输入缓冲区中** returns 0 if OK, EOF if trouble* --------------------------------*/
static int
pq_recvbuf(void)
{if (PqRecvPointer > 0){if (PqRecvLength > PqRecvPointer){/* still some unread data, left-justify it in the buffer */// 还有一些未读数据,将其在缓冲区中左对齐memmove(PqRecvBuffer, PqRecvBuffer + PqRecvPointer,PqRecvLength - PqRecvPointer);PqRecvLength -= PqRecvPointer;PqRecvPointer = 0;}elsePqRecvLength = PqRecvPointer = 0;}/* Ensure that we're in blocking mode */// 确保我们处于阻塞模式socket_set_nonblocking(false);/* Can fill buffer from PqRecvLength and upwards */// 可以从 PqRecvLength 及以上填充缓冲区for (;;){int r;errno = 0;r = secure_read(MyProcPort, PqRecvBuffer + PqRecvLength,PQ_RECV_BUFFER_SIZE - PqRecvLength);if (r < 0){if (errno == EINTR)continue; /* Ok if interrupted *//** Careful: an ereport() that tries to write to the client would* cause recursion to here, leading to stack overflow and core* dump! This message must go *only* to the postmaster log.* 小心:尝试写入客户端的 ereport() 会导致递归到此处,从而导致堆栈溢出和核心转储* 此消息必须 *仅* 发送到邮件管理员日志** If errno is zero, assume it's EOF and let the caller complain.* 如果 errno 为零,则假设它是 EOF 并让调用者抱怨*/if (errno != 0)ereport(COMMERROR,(errcode_for_socket_access(),errmsg("could not receive data from client: %m")));return EOF;}if (r == 0){/** EOF detected. We used to write a log message here, but it's* better to expect the ultimate caller to do that.* 检测到 EOF* 我们曾经在这里编写日志消息,但最好期望最终调用者这样做*/return EOF;}/* r contains number of bytes read, so just incr length */// r 包含读取的字节数,因此只需增加长度PqRecvLength += r;return 0;}
}
解释一下:
- PqRecvLength = 21 这个其实是两条消息 如下:
/* construct the Close message */ // 0 - 15if (pqPutMsgStart(command, conn) < 0 ||pqPutc(type, conn) < 0 ||pqPuts(target, conn) < 0 ||pqPutMsgEnd(conn) < 0)goto sendFailed;/* construct the Sync message */ // 16 - 20if (conn->pipelineStatus == PQ_PIPELINE_OFF){if (pqPutMsgStart(PqMsg_Sync, conn) < 0 ||pqPutMsgEnd(conn) < 0)goto sendFailed;}
第二步:
/* --------------------------------* pq_getbyte - get a single byte from connection, or return EOF* --------------------------------*/
int
pq_getbyte(void)
{Assert(PqCommReadingMsg);while (PqRecvPointer >= PqRecvLength){if (pq_recvbuf()) /* If nothing in buffer, then recv some */return EOF; /* Failed to recv data */}return (unsigned char) PqRecvBuffer[PqRecvPointer++];
}
解释一下:
- 此时 PqRecvPointer = 0,自然返回的是
'C'
第三步:
.../** In protocol version 3, all frontend messages have a length word next* after the type code; we can read the message contents independently of* the type.* * 在协议版本 3 中,所有前端消息在类型代码之后都有一个长度字* 我们可以独立于类型来读取消息内容*/if (pq_getmessage(inBuf, maxmsglen))return EOF; /* suitable message already logged */RESUME_CANCEL_INTERRUPTS();
...
/* --------------------------------* pq_getmessage - get a message with length word from connection* pq_getmessage - 从连接获取长度字的消息** The return value is placed in an expansible StringInfo, which has* already been initialized by the caller.* Only the message body is placed in the StringInfo; the length word* is removed. Also, s->cursor is initialized to zero for convenience* in scanning the message contents.* 返回值放置在可扩展的 StringInfo 中,该 StringInfo 已由调用者初始化* StringInfo中只放置消息体; 长度词被删除* 另外,为了方便扫描消息内容,s->cursor 被初始化为零** maxlen is the upper limit on the length of the* message we are willing to accept. We abort the connection (by* returning EOF) if client tries to send more than that.* maxlen 是我们愿意接受的消息长度的上限* 如果客户端尝试发送更多内容,我们将中止连接(通过返回 EOF)** returns 0 if OK, EOF if trouble* --------------------------------*/
int
pq_getmessage(StringInfo s, int maxlen)
{int32 len;Assert(PqCommReadingMsg);resetStringInfo(s);/* Read message length word */if (pq_getbytes((char *) &len, 4) == EOF){ereport(COMMERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_PROTOCOL_VIOLATION),errmsg("unexpected EOF within message length word")));return EOF;}len = pg_ntoh32(len);if (len < 4 || len > maxlen){ereport(COMMERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_PROTOCOL_VIOLATION),errmsg("invalid message length")));return EOF;}len -= 4; /* discount length itself */if (len > 0){/** Allocate space for message. If we run out of room (ridiculously* large message), we will elog(ERROR), but we want to discard the* message body so as not to lose communication sync.*/PG_TRY();{enlargeStringInfo(s, len);}PG_CATCH();{if (pq_discardbytes(len) == EOF)ereport(COMMERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_PROTOCOL_VIOLATION),errmsg("incomplete message from client")));/* we discarded the rest of the message so we're back in sync. */PqCommReadingMsg = false;PG_RE_THROW();}PG_END_TRY();/* And grab the message */if (pq_getbytes(s->data, len) == EOF){ereport(COMMERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_PROTOCOL_VIOLATION),errmsg("incomplete message from client")));return EOF;}s->len = len;/* Place a trailing null per StringInfo convention */s->data[len] = '\0';}/* finished reading the message. */PqCommReadingMsg = false;return 0;
}
解释一下:
- 读取长度 4字节:
memcpy(s, PqRecvBuffer + PqRecvPointer, amount);此时 PqRecvPointer = 1 - pg_ntoh32 网络序–>主机序 len = 15
len -= 4; /* discount length itself */- 读取长度 11 字节:
memcpy(s, PqRecvBuffer + PqRecvPointer, amount);此时 PqRecvPointer = 5 - 此时读取的内容:
0x1e54c88 "Sp23456789",也就是input_message
接下来ReadCommand的结果,如下:
firstchar = ReadCommand(&input_message); // C
最后一步,如下:
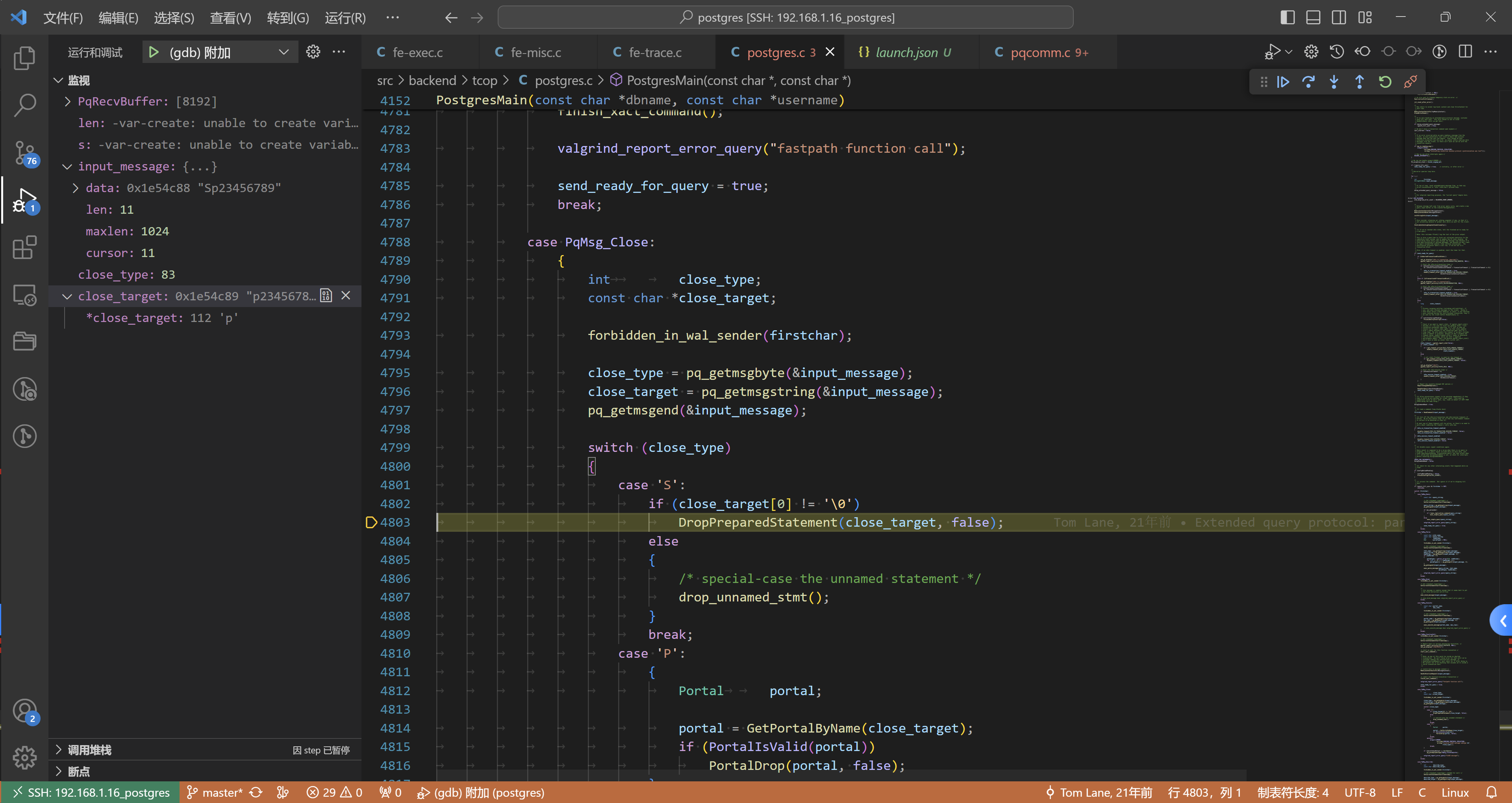
OK,至此 服务端解析完毕!
相关文章:

PostgreSQL的学习心得和知识总结(一百三十八)|深入理解PostgreSQL数据库之Protocol message构造和解析逻辑
目录结构 注:提前言明 本文借鉴了以下博主、书籍或网站的内容,其列表如下: 1、参考书籍:《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》 2、参考书籍:《数据库事务处理的艺术:事务管理与并发控制》 3、PostgreSQL数据库仓库…...

爬虫开发教程
一、爬虫概述 爬虫(也称为网络爬虫或蜘蛛)是一种自动化程序,能够模拟人类在互联网上浏览和抓取数据的行为。它通过发送HTTP请求,获取网页的HTML代码,然后解析这些代码以提取有用的数据。爬虫在数据分析、价格监测、竞…...
【Python】高级进阶(专版提升3)
Python 1 程序结构1.1 模块 Module1.1.1 定义1.1.2 作用1.1.3 导入1.1.3.1 import1.1.3.2 from import 1.1.4 模块变量1.1.5 加载过程1.1.6 分类 1.2 包package1.2.1 定义1.2.2 作用1.2.3 导入1.1.3.1 import1.1.3.2 from import 2 异常处理Error2.1 异常2.2 处理 3 迭代3.1 可…...

LeetCode 1378、1277、2944
1378 二级排序,compare函数必须是static的 class Solution { public:struct node {int val;int priority;};static bool compare(const node &n1, const node &n2) {if (n1.priority n2.priority) {return n1.val < n2.val;}return n1.priority < n…...
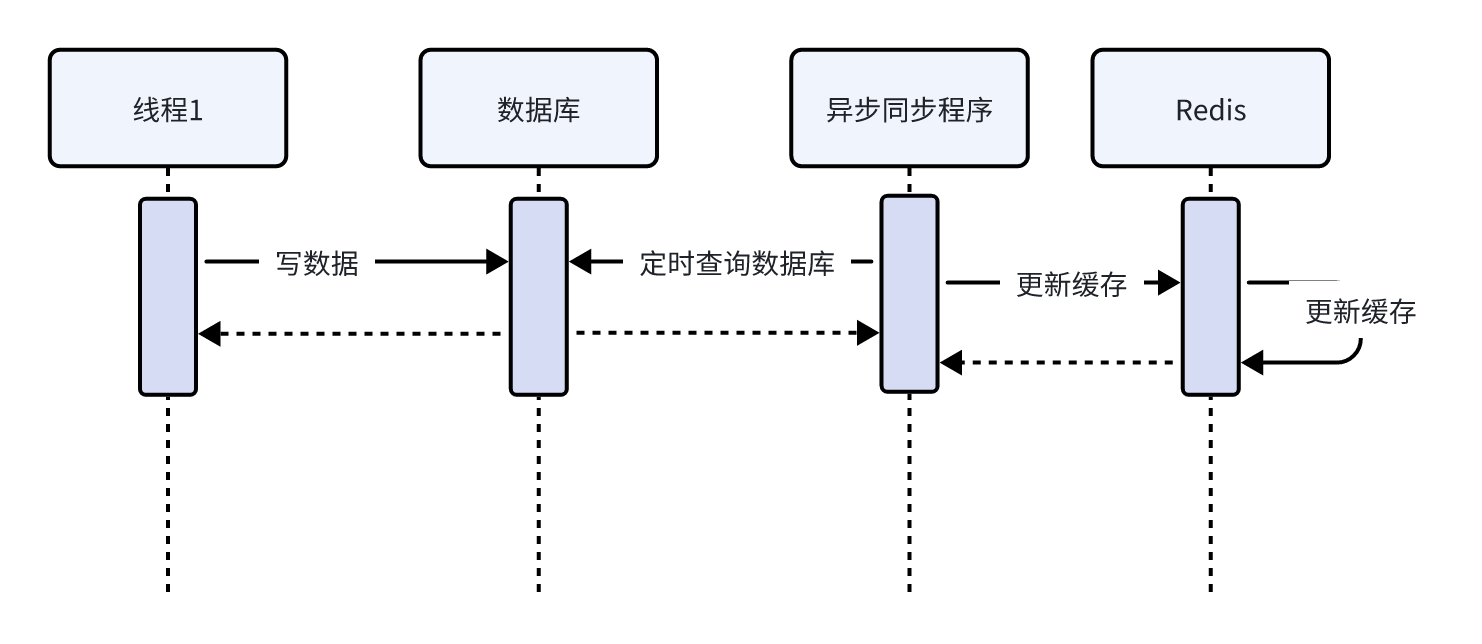
【缓存常见问题】
在使用缓存时特别是在高并发场景下会遇到很多问题,常用的问题有缓存穿透、缓存击穿、缓存雪崩以及缓存一致性问题。 1、缓存穿透 首先,什么是缓存穿透呢? 缓存穿透是指请求一个不存在的数据,缓存层和数据库层都没有这个数据&…...

Python爬取猫眼电影票房 + 数据可视化
目录 主角查看与分析 爬取可视化分析猫眼电影上座率前10分析猫眼电影票房场均人次前10分析猫眼电影票票房占比分析 主角查看与分析 爬取 对猫眼电影票房进行爬取,首先我们打开猫眼 接着我们想要进行数据抓包,就要看网站的具体内容,通过按F12…...

Spring Boot深度解析:是什么、为何使用及其优势所在
在Java企业级应用开发的漫长历史中,Spring框架以其卓越的依赖注入和面向切面编程的能力,赢得了广大开发者的青睐。然而,随着技术的不断进步和项目的日益复杂,传统的Spring应用开发流程逐渐显得繁琐和低效。为了解决这一问题&#…...

面向对象——类与对象
文章目录 类与对象构造函数、析构函数get/set方法函数:类内声明、类外定义static 类与对象 #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; /* 类与对象 */ class Person{public:string name;// 固有属性,成员变量 int age;pu…...

Golang的[]interface{}为什么不能接收[]int?
在 Go 中,[]interface{} 和 []int 是两种不同的类型,虽然它们的底层数据结构都是切片,但是它们的元素类型不同。[]interface{} 是一个空接口切片,可以容纳任意类型的元素,而 []int 是一个整数切片,只能容纳…...
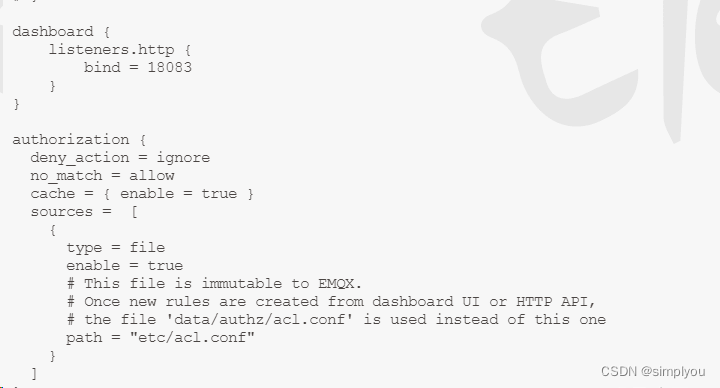
重启服务器或重启docker,导致emqx的Dashboard的密码重置为public
最近在项目中突然发现重启服务器,或者重启docker 修改好的emqx的Dashboard的密码重置为public 技术博客 http://idea.coderyj.com/ 1.解决办法就是固定 emqx的节点 # 拉取镜像 docker pull emqx/emqx# 创建目录,进行目录挂载 mkdir -p /docker/emqx/{etc,lib,data,…...

就业班 第三阶段(ansible) 2401--4.16 day2 ansible2 剧本+角色
六、Ansible playbook 简介 playbook 是 ansible 用于配置,部署,和管理被控节点的剧本。 通过 playbook 的详细描述,执行其中的一系列 tasks ,可以让远端主机达到预期的状态。playbook 就像 Ansible 控制器给被控节点列出的的…...

常用的过滤网站扫描网站攻击的路径是那些,比如:/etc/passwd等
网站攻击中经常被尝试的路径主要包括利用漏洞获取敏感文件、执行系统命令或者注入恶意代码的尝试。以下是一些常见的被攻击者尝试访问的路径和文件,这些通常在网络入侵检测系统(IDS)和网络防火墙的过滤规则中被特别关注: 系统文件…...
考研数学|《1800》《660》《880》如何选择和搭配?(附资料分享)
直接说结论:基础不好先做1800、强化之前660,强化可选880/1000题。 首先,传统习题册存在的一个问题是题量较大,但难度波动较大。《汤家凤1800》和《张宇1000》题量庞大,但有些题目难度不够平衡,有些过于简单…...

论文笔记:Are Human-generated Demonstrations Necessary for In-context Learning?
iclr 2024 reviewer 评分 6668 1 intro 大型语言模型(LLMs)已显示出在上下文中学习的能力 给定几个带注释的示例作为演示,LLMs 能够为新的测试输入生成输出然而,现行的上下文学习(ICL)范式仍存在以下明显…...

C语言 | Leetcode C语言题解之第28题找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
题目: 题解: int strStr(char* haystack, char* needle) {int n strlen(haystack), m strlen(needle);if (m 0) {return 0;}int pi[m];pi[0] 0;for (int i 1, j 0; i < m; i) {while (j > 0 && needle[i] ! needle[j]) {j pi[j - …...

「Python大数据」数据采集-某东产品数据评论获取
前言 本文主要介绍通过python实现数据采集、脚本开发、办公自动化。数据内容范围:星级评分是1-3分、获取数据页面是前50页。 友情提示 法律分析:下列三种情况,爬虫有可能违法,严重的甚至构成犯罪: 爬虫程序规避网站经营者设置的反爬虫措施或者破解服务器防抓取措施,非法…...

ORACLE错误提示概述
OceanBase分布式数据库-海量数据 笔笔算数 保存起来方便自己查看错误代码。 ORA-00001: 违反唯一约束条件 (.) ORA-00017: 请求会话以设置跟踪事件 ORA-00018: 超出最大会话数 ORA-00019: 超出最大会话许可数 ORA-00020: 超出最大进程数 () ORA-00021: 会话附属于其它某些进程…...

2024年4月13日美团春招实习试题【第一题:好子矩阵】-题目+题解+在线评测【模拟】
2024年4月13日美团春招实习试题【第一题:好子矩阵】-题目题解在线评测【模拟】 题目描述:输入描述输出描述样例 解题思路一:模拟解题思路二:思路二解题思路三:直接判断 题目描述: 塔子哥定义一个矩阵是”好矩阵”&…...
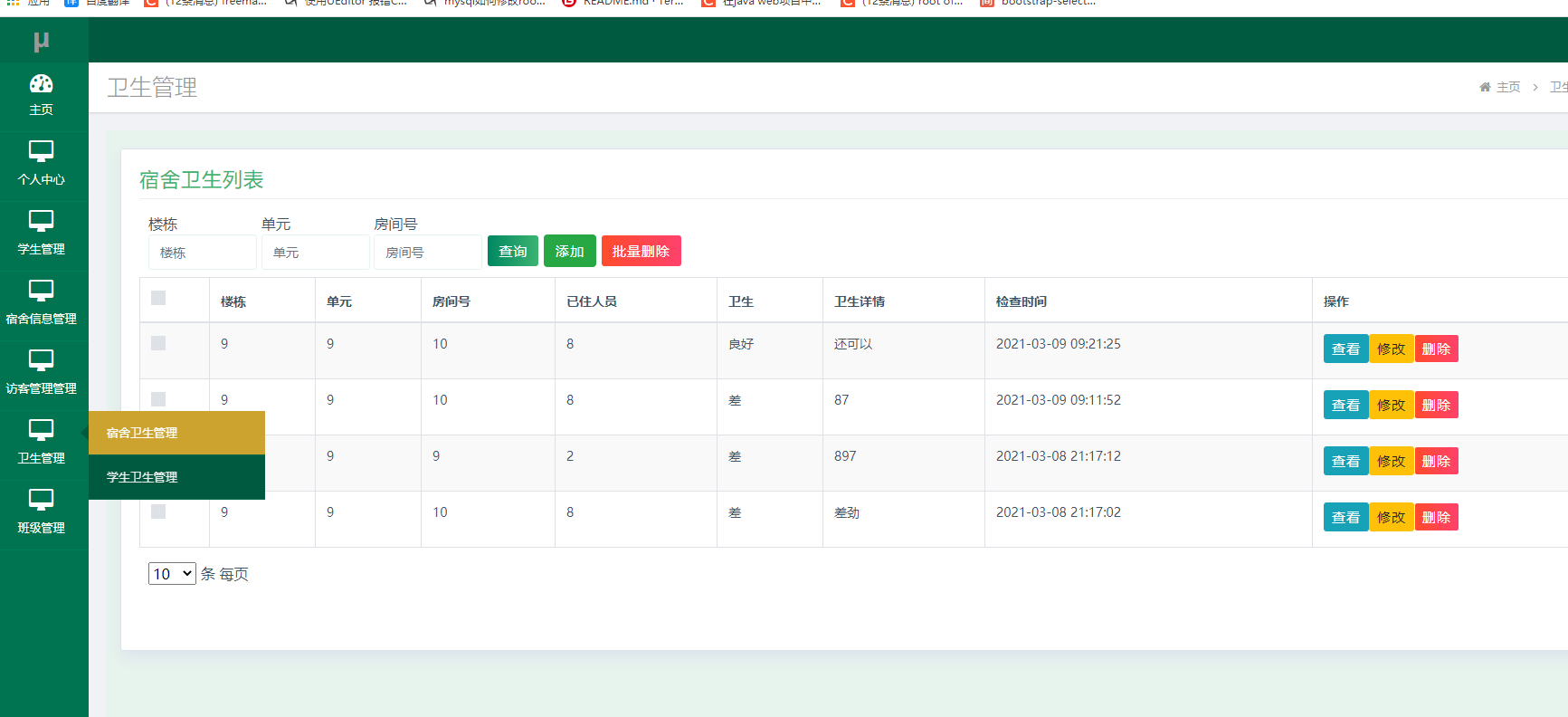
ssm057学生公寓管理中心系统的设计与实现+jsp
学生公寓管理中心系统设计与实现 摘 要 现代经济快节奏发展以及不断完善升级的信息化技术,让传统数据信息的管理升级为软件存储,归纳,集中处理数据信息的管理方式。本学生公寓管理中心系统就是在这样的大环境下诞生,其可以帮助管…...

循环神经网络(RNN):概念、挑战与应用
循环神经网络(RNN):概念、挑战与应用 1 引言 1.1 简要回顾 RNN 在深度学习中的位置与重要性 在深度学习的壮丽图景中,循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks,RNN)占据着不可或缺的地位。自从…...
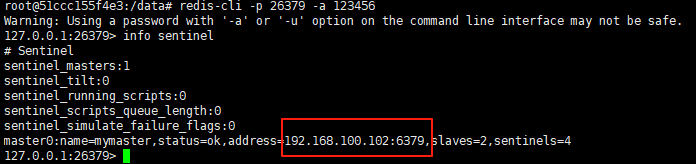
使用docker在3台服务器上搭建基于redis 6.x的一主两从三台均是哨兵模式
一、环境及版本说明 如果服务器已经安装了docker,则忽略此步骤,如果没有安装,则可以按照一下方式安装: 1. 在线安装(有互联网环境): 请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 2. 离线安装(内网环境):请看我这篇文章 传送阵>> 点我查看 说明:假设每台服务器已…...

反向工程与模型迁移:打造未来商品详情API的可持续创新体系
在电商行业蓬勃发展的当下,商品详情API作为连接电商平台与开发者、商家及用户的关键纽带,其重要性日益凸显。传统商品详情API主要聚焦于商品基本信息(如名称、价格、库存等)的获取与展示,已难以满足市场对个性化、智能…...
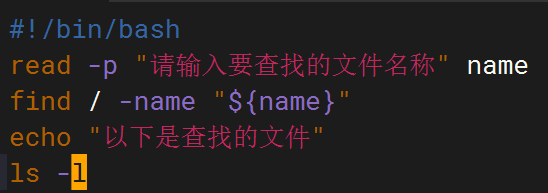
shell脚本--常见案例
1、自动备份文件或目录 2、批量重命名文件 3、查找并删除指定名称的文件: 4、批量删除文件 5、查找并替换文件内容 6、批量创建文件 7、创建文件夹并移动文件 8、在文件夹中查找文件...

蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(2):进阶面试题与实战演练
前文覆盖了 BLE 扫描的基础概念与经典问题蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(1):从基础到实战的深度解析-CSDN博客,但实际面试中,企业更关注候选人对复杂场景的应对能力(如多设备并发扫描、低功耗与高发现率的平衡)和前沿技术的…...

《用户共鸣指数(E)驱动品牌大模型种草:如何抢占大模型搜索结果情感高地》
在注意力分散、内容高度同质化的时代,情感连接已成为品牌破圈的关键通道。我们在服务大量品牌客户的过程中发现,消费者对内容的“有感”程度,正日益成为影响品牌传播效率与转化率的核心变量。在生成式AI驱动的内容生成与推荐环境中࿰…...
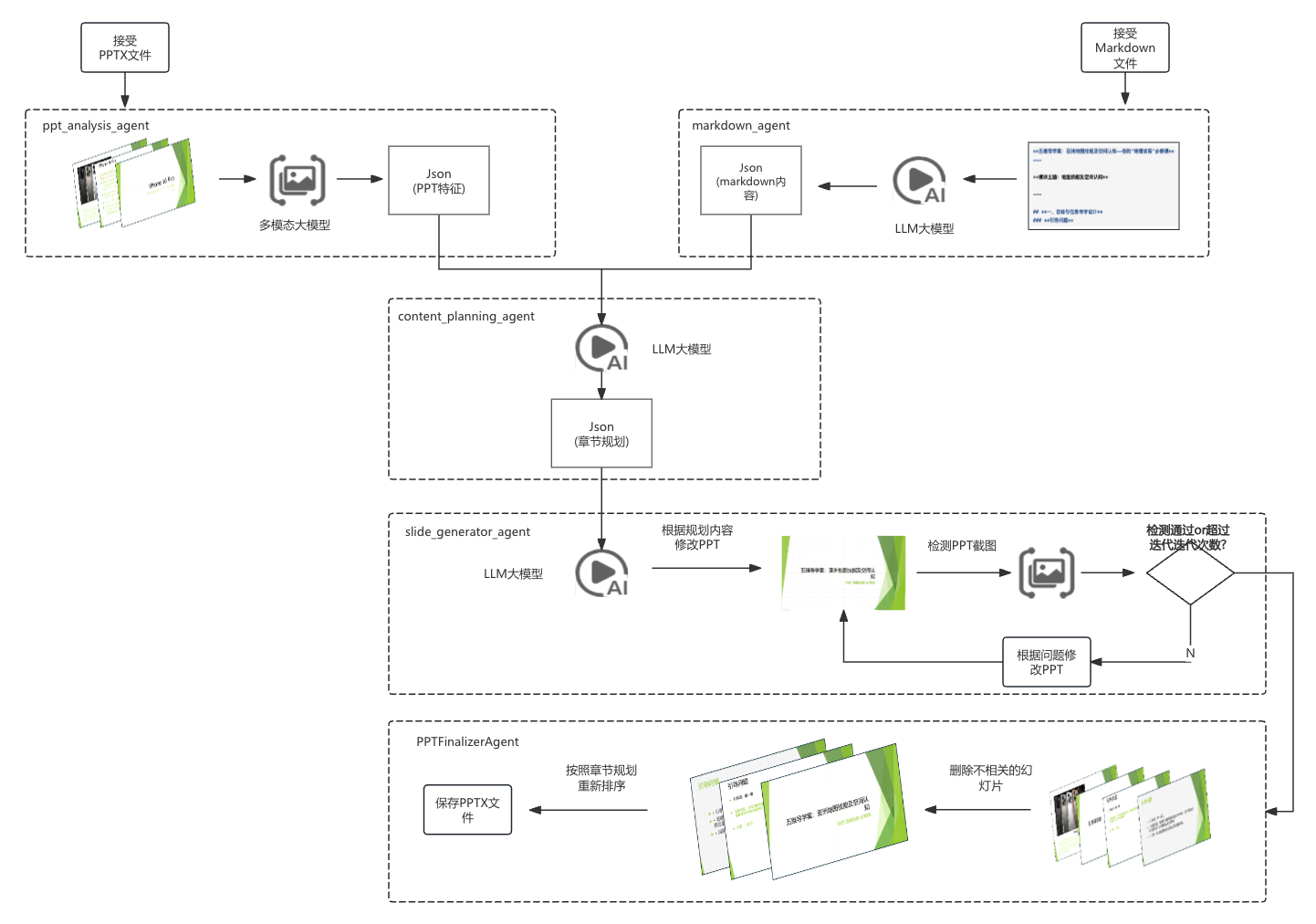
【项目实战】通过多模态+LangGraph实现PPT生成助手
PPT自动生成系统 基于LangGraph的PPT自动生成系统,可以将Markdown文档自动转换为PPT演示文稿。 功能特点 Markdown解析:自动解析Markdown文档结构PPT模板分析:分析PPT模板的布局和风格智能布局决策:匹配内容与合适的PPT布局自动…...
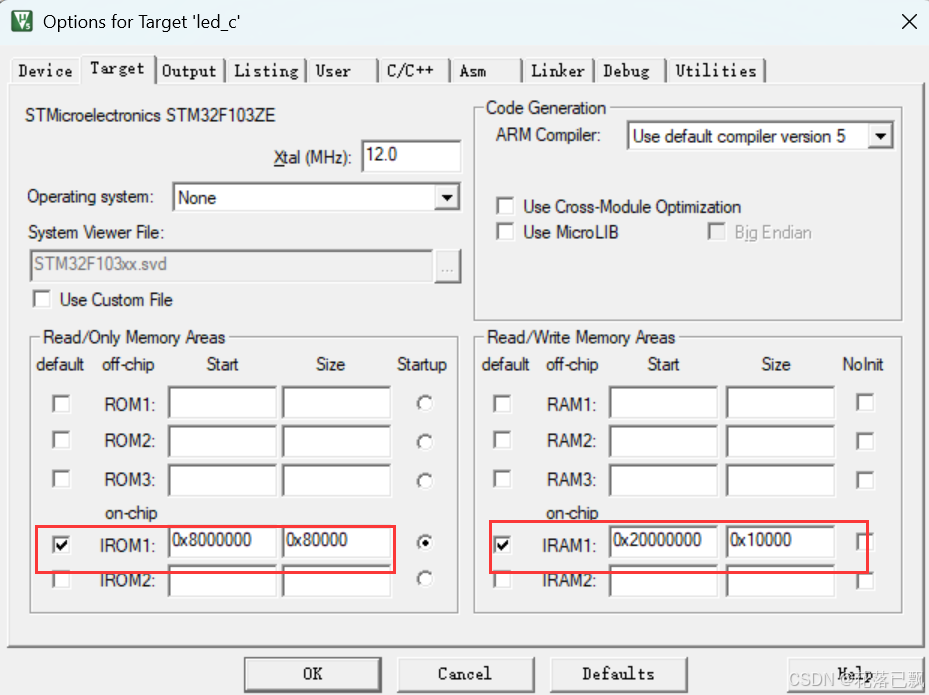
Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解
文章目录 Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解一、Flash 和 RAM 配置界面(Target 选项卡)1. IROM1(用于配置 Flash)2. IRAM1(用于配置 RAM)二、链接器设置界面(Linker 选项卡)1. 勾选“Use Memory Layout from Target Dialog”2. 查看链接器参数(如果没有勾选上面…...
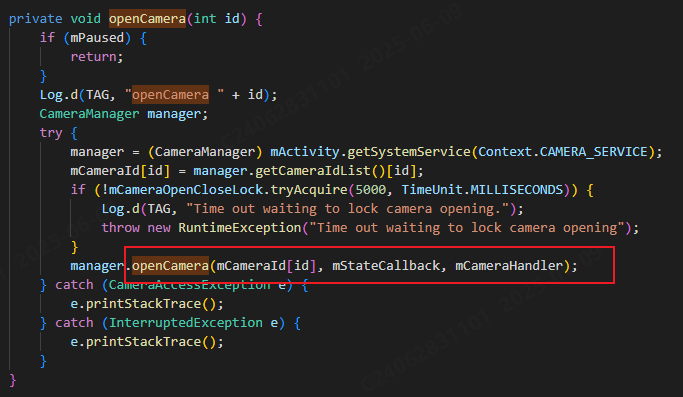
相机从app启动流程
一、流程框架图 二、具体流程分析 1、得到cameralist和对应的静态信息 目录如下: 重点代码分析: 启动相机前,先要通过getCameraIdList获取camera的个数以及id,然后可以通过getCameraCharacteristics获取对应id camera的capabilities(静态信息)进行一些openCamera前的…...
WordPress插件:AI多语言写作与智能配图、免费AI模型、SEO文章生成
厌倦手动写WordPress文章?AI自动生成,效率提升10倍! 支持多语言、自动配图、定时发布,让内容创作更轻松! AI内容生成 → 不想每天写文章?AI一键生成高质量内容!多语言支持 → 跨境电商必备&am…...
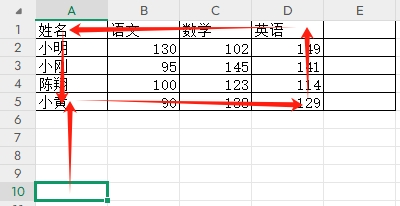
3-11单元格区域边界定位(End属性)学习笔记
返回一个Range 对象,只读。该对象代表包含源区域的区域上端下端左端右端的最后一个单元格。等同于按键 End 向上键(End(xlUp))、End向下键(End(xlDown))、End向左键(End(xlToLeft)End向右键(End(xlToRight)) 注意:它移动的位置必须是相连的有内容的单元格…...
