Notes for the missing semester. Useful and basic knowledge about Linux.
The Shell
Contents
The first course is to introduce some simple commands.
I’ll list some commands that I’m not familiar with:
# --silent means don't give log info,
# --head means we only want the http head.
curl --head --silent bing.com.cn# cut --delimiter=' ' means we'll use ' ' as delimiter for every line,
# -f2 means we only want the second item for each line (print the second column)
# -i means ignore the case
curl --head --silent bing.com.cn | grep -i content-length | cut --delimiter=' ' -f2# the -L means if we find a symbolic link during search,
# we'll get the real path of this symbolic link
sudo find -L /sys/class/backlight -maxdepth 2 -name '*brightness*'
Extensions
There are two things I’ve learned about the quotations in Linux:
- single quotations show what it looks like, and you cannot add single quotations in single quotations, but you cannot add double quotations in single quotations.
- double quotations show what it exactly is, for example, if you use
$HOME, it will be your home directory which looks like/home/kaiser, and you can add double quotations in double quotations by add back slash before the double quotations, and you can add single quotations in double quotations directly.
Shell Tools and Scripting
Contents
This course introduces some tools and teaches some simple shell scripting.
There is some important knowledge about shell scripting:
# this shows how to define functions in shell scripts
# $1 means the first parameter of this function
mcd () {mkdir -p "$1"cd "$1"
}# $_ represents the last arg of the last command.
# If you are in an interactive shell,
# you can also quickly get this value by typing <Esc> followed by . or <Alt+.>
$_# $? represents the return value of last command
$?# the number of all args
$## pid
$$# the entire last command
!!# all args
$@
You can execute more than one commands separated by a semicolon:
true ; echo "This will always run"
false ; echo "This will always run"
You can get the output of a command by $():
foo=$(pwd)
echo "We are in $(pwd)"
We can get a command’s output by <():
# the output is similar with ls
cat <(ls)
We can use {} to specify multiple strings (note that there must be no blank at commas, and those below are supported by bash, fish does not supported those below):
foo{,1,2}->foo foo1 foo2foo{1,2}{3,4}->foo13 foo14 foo23 foo24foo{a..z}->fooa foob fooc ... fooz
We can use shellcheck (you may need use sudo apt-get install shellcheck to install the tool first) to check our scripts’ semantics.
Some usages of find:
# find src whose type is directory
find . -name src -type d# find some test directory's python files
find . -path '**/test/*.py' -type f# Find all files modified in the last day
find . -mtime -1# Delete all files with .tmp extension
find . -name "*.tmp" -exec rm {} \;# Find all PNG files and convert them to JPG
find . -name '*.png' -exec convert {} {}.jpg \;# Find all zip files with size in range 500k to 10M
find . -size +500k -size -10M -name '*.tar.gz'
Use grep -R foobar . will open files of current directory and of its sub-directories and output all the lines containing the foobar.
Some examples using ripgrep:
# -t means only find the files whose type is py
rg "import sys" -t py .
# -C means to show the context about 10 lines before and after
rg "import sys" -t py -C 10 .
# -u means igore hidden files,
# --stats means some statistic information such the the total number
# --files-without-match means to find those files which don't match the regexpr
rg -u --files-without-match "^#\!" -t sh --stats .
Exercises
You can use --sort=time to let ls sorted by update time:
ls -ahl --sort=time --color=auto
You can use while loop like this in shell scripting:
runTime=0
while true; dorunTime=$((runTime+1))if ! bash "$fileName"; thenbreakfi
done
You can use the command below to zip all html files:
# -print0 means to print the whole file name and add a null character after each file name.
# -0 after xargs means input will be terminated by a null character rather than a white space.
find . -name "*.html" -print0 | xargs -0 zip -r all_html.zip
You can use the command below to get the file whose update time is the latest:
# %p means the file's name
# %T@ means the modification time of the file in seconds since the epoch
find . -type f -printf '%T@ %p\n' | sort -n | tail -1 | cut -f2 -d" "
There are something about args of command. Some commands can get input from standard input and files, and we can use - to get input from standard input. And there are some commands which can only get input from args, such as rm. If you want to let rm get input from standard input you need use xargs which will convert the standard input into the args of the command you want to execute:
# BE CAREFUL, this will try removing all the files of current directory.
ls | xargs rm
Tasks-List
There are some useful commands to learn:
-
ripgrep. - Understand all the
findcommands above. - Learn more about
find.
Editors
I’ve learn vim and configure it by my self.
In visual mode u and U have different meanings with normal mode. u is used to undo in normal mode, and to make the selected letters be lower case in visual mode. U is used to undo the whole line in normal mode, and to make the selected letters be upper case in visual mode.
zt in normal mode can let the line where you cursor is at the top, zb the bottom, and zz the middle.
There are some basic usages of vim’s :s:

When using the c flag, you need to confirm for each match what to do. Vim will output something like: replace with foobar (y/n/a/q/l/^E/^Y)?(where foobar is the replacement part of the :%s/.../.../gc command). You can type y which means to substitute this match, n to skip this match, a to substitute this and all remaining matches (“all” remaining matches), q to quit the command, l to substitute this match and quit (think of “last”), ^E to scroll the screen up by holding the control key and pressing E and ^Y to scroll the screen down by holding the control key and pressing Y.
There are some search and replace examples:

There are some special signatures while searching and replacing:


You can find more information about search and replace in vim through vim wiki search and replace.
Data Wrangling
Contents
sed is a powerful tool which can edit stream input, there are some examples:
sed 's/.*Disconnected from //'
sed 's/[ab]//'
sed 's/[ab]//g'
# -E means extended regexpr
sed -E 's/(ab)*//g'
sed -E 's/(ab|bc)*//g'
There are other useful commands:
# wc -l for counting lines
wc -l# sort lexicographically
sort
# -n: numeric
# k1,1: define sorting key started at first column and ended at first column
sort -nk1,1
# -c will give you the number of occurrence
uniq -c# -s: serial, see all files as entire file instead of pasting each file separately.
# -d,: use , as the delimiter
# paste will connect the input lines with the delimiter you specified
paste -sd,# $0 means the whole line, $1 - $n means the n-th field of the line separated by white space
# you can use -F to assign delimiter (File separator)
awk '{print $2}'
# get $1 == 1 and $2 matches the regexp, print the whole lines
awk '$1 == 1 && $2 ~ /^c.*e$/ {print $0}'
# at the fist line, we define rows and set it as 0,
# for each match, we let rows added by one,
# at the end line, we print the rows to get how many lines match.
awk 'BEGIN { rows = 0 } $1 == 1 && $2 ~ /^c.*e$/ { rows += 1 } END { print rows }'
# we paste all the number by + and use bc to calculate the result of addition
# bc is a programming language, use -l means use math lib in bc
awk '$1 != 1 { print $1 }' | paste -sd+ | bc -l# use -v for invert-match, this will output those which don't match
grep -v# use /dev/video0 to take a picture, and convert it to gray,
# and zip it, then use the gzip on tsp (a server) to unzip the one,
# then use feh to show the result.
ffmpeg -loglevel panic -i /dev/video0 -frames 1 -f image2 - \
| convert --colorspace gray - | gzip | ssh tsp 'gzip -d | tee copy.png' | feh -
Exercises
Find the number of words (in /usr/share/dict/words) that contain at least three as and don’t have a 's ending. What are the three most common last two letters of those words? sed’s y command, or the tr program, may help you with case insensitivity. How many of those two-letter combinations are there? And for a challenge: which combinations do not occur?
# get number
grep -E 'a.*a.*a' /usr/share/dict/words | grep -Ev "'s\$" | wc -l# get the most common last two letters
grep -E 'a.*a.*a' /usr/share/dict/words | grep -Ev "'s\$" \
| awk '{print substr($0, length($0)-1, 2)}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -nk1,1 | tail -n1# the number of combinations
grep -E 'a.*a.*a' /usr/share/dict/words | grep -Ev "'s\$" \
| awk '{print substr($0, length($0)-1, 2)}' | sort | uniq | wc -l# the combinations which do not occur
# comm -23 means don't output the second columns (lines unique to FILE2)
# and the third columns (lines that appear in both files)
comm -23 \
<(echo {a..z}{a..z} | awk 'BEGIN { RS = " " } { print $0 }' \| grep -E '[a-z][a-z]' | sort) \
<(grep -E 'a.*a.*a' /usr/share/dict/words | grep -Ev "'s\$" \| awk '{print substr($0, length($0)-1, 2)}' | sort)
Command-line Environment
Contents
There are some signals that can be triggered by pressing keys:
^\ SIGQUIT
^C SIGINT
^Z SIGSTOP
Note that the SIGKILL and SIGSTOP can not be captured or ignored.
If you start a process, and you press ^Z the process will not be killed. It will just stop, and you can use jobs to show the processes of the session. If you close the terminal, the process will be killed unless you use nohup to start the process or use disown for the processes have been started up. For the processes in jobs list, you can use fg or bg to let it run foreground or background. For example, fg %1 means that let the first job of jobs list run foreground. Use kill -STOP can send SIGSTOP, and the kill -9 is kill -KILL exactly.
The next part is about tmux. I’ve learned and been using it for a while.
The next part is about aliases, and I’ve configured many in my .bashrc and config.fish.
The next part is about dot files, and I’ve created my own repository on github to store my own dot files.
You can execute commands on server through ssh and this can be connected with pipe, for example you can use the command below to append your public ssh-key to the authorized_keys on server:
cat .ssh/id_ed25519.pub | ssh foobar@remote 'cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys'
# the command below can reach the same effect with the last command
ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_ed25519 foobar@remote
ssh+tee, scp, and rsync can copy file from or over ssh:
cat localfile | ssh remote_server 'tee serverfile'
scp path/to/local_fiel remote_server:path/to/remote_file
The next part is about port forwarding which I’ve learned.
Exercises
You can use pgrep to find a process:
# find all processes whose commands is sleep
# -a means all users
# -f means full name, this means that the commands must be sleep
pgrep sleep -af
You can use pkill to kill a process:
# kill all processes whose commands are sleep
# -f means the full name, this means the commands must be sleep
pkill sleep -f
You can use kill -0 to check if a process exists. If the return value of kill -0 is zero, the process exists, otherwise the process doesn’t exists.
In bash, $PS1 is the variable controls the shell prompt:
# You can use the command below to show your prompt format.
echo $PS1
ssh can use -N to disable executing commands through current session, which is useful when port forwarding (this can disable the port sending commands to protect the server and the client).
ssh -f can let the command execute on server background rather than foreground, which is specifically useful for running long-running background tasks or scripts on remote servers without maintaining an interactive shell.
Tasks-List
- Mosh.
- sshfs.
Version Control (Git)
Contents
I’ve been using git for a while. Therefore I just list some commands that I am not familiar with:
# show changes you made relative to the staging area
git diff <filename>
# shows differences in a file between snapshots
git diff <revision> <filename>
# updates HEAD and current branch
git checkout <revision>
# add a remote
git remote add <name> <url>
# set up correspondence between local and remote branch
git branch --set-upstream-to=<remote>/<remote branch>
# you can use -u when pushing to set correspondence between local and remote branch
git push origin -u <local branch>:<remote branch>
# edit a commit's message
git commit --amend
# unstage a file,
# --hard will remove all the contents,
# --soft will leave the contents unstaged
git reset HEAD <file>
# discard changes
git checkout <file>
# temporarily remove modifications to working directory
git stash
# get the stash
git stash pop
# see the contents of a commit
git cat-file -p <commit-id>
# get difference between commits to a specified file
git diff <old-commit-id> <new-commit-id> filename
In git, the ^ means parent, for example HEAD^ means HEAD’s parent. In addition, HEAD~3 means move 3 above HEAD: HEAD’s parent’s parent’s parent.
Note that HEAD^2 means to chose the second path when there are more than one parent of HEAD.
git branch -f branch_name can move the branch to HEAD forcedly.
git revert can cancel modifications. This will create a new commit to cancel modifications rather than change the HEAD to earlier commit compared with git reset. git revert HEAD means revert the last change. Note that this will only cancel the commit you specify, the commits before it or after it will be remained. Or you can use git revert <left>^...<right> to revert the commits between left and right. And this will leave more than one commit (depending on how many commits you revert). If you just want to leave one commit, you can use git revert -n <left>^...<right> to revert but not commit after reversion, you can use git commit to create just one commit.
When using git checkout -b, you can specify the remote branch which is related with you local branch. For example, git checkout -b local_branch origin/remote_branch will let your local branch be related with your remote branch when you create it. If you have already created a branch, you can use git branch -u origin/remote_branch local_branch to let your local branch related with your remote branch.
git push origin <source>:<destination> can push the local branch source to the specified remote branch destination.
git pull origin or git fetch origin is similar with git push origin except the branch position is different. git pull origin or git fetch origin’s first branch is a remote branch rather than a local branch.
For git push origin :foo, it will remove the remote foo branch. For git pull origin :foo will create a local branch called foo.
Sometimes, when you have done a commit, you figure out that there is a little thing you need do, such as removing an empty line, you can use the commands below to do a quick fix (I used to use git rebase -i which is slow and annoying):
git add .
git commit --amend --no-edit
If you have added files to your git, but you want to see what the differences before your commit, you can use git diff --staged to do that.
If you only want to undo specified files you can use git checkout [hash] path/to/files (After this, you usually need re-commit).
Debugging and Profiling
Contents
You can use strace to get all the system calls of a process.
sudo strace -f -e open cmd will trace a command’s all open system calls. -f will show forked process. -e open means that we only want to see the open system call.
Similarly, sudo strace -e write cmd can trace a command’s all write system calls. sudo strace -f -e execve cmd is for execve system calls.
There are the options explanation of strace:
-pcan specify thepidof process you want tostrace.-s 800will show the first800characters of each string.-o filecan store the output ofstarcein the file you specify.
df can display metrics per partitions and du can display disk usage per file for the current directory.
Tasks-List
- Learn more about debuggers (
pdb,ipdb,IPython,gdb,pwndbg, andlldb) - Learn
tcpdump,objdumb, andWireshark. - Learn
pyflakesandmypy. - Learn something about profilers if necessary.
Metaprogramming
Contents
I’ve learned make and used it for many times. So I do not write anything about make in this part.
Semantic Versioning 2.0.0
Given a version number MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, increment the:
- MAJOR version when you make incompatible API changes
- MINOR version when you add functionality in a backward compatible manner
- PATCH version when you make backward compatible bug fixes
Additional labels for pre-release and build metadata are available as extensions to the MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH format.
Some Testing Terminology
Test suite: a collective term for all the testsUnit test: a “micro-test” that tests a specific feature in isolationIntegration test: a “macro-test” that runs a larger part of the system to check that different feature or components work together.Regression test: a test that implements a particular pattern that previously caused a bug to ensure that the bug does not resurface.Mocking: to replace a function, module, or type with a fake implementation to avoid testing unrelated functionality. For example, you might “mock the network” or “mock the disk”.
Security and Cryptography
Contents
Entropy
Entropy is define as l o g 2 ( p o s s i b i l i t i e s ) log_2(possibilities) log2(possibilities). For example, a fair coin flip gives 1 bit of entropy (2 possibilities).
Hash Functions
You can use hash functions to map data of arbitrary size to a fixed size. git uses SHA1 to hash its commits and so others. Moreover, you can use sha1sum to get the value of SHA1 to some contents. echo 'hello' | sha1sum will give you the SHA1 value of hello.
There are some properties that hash functions may obey:
Deterministic: the same input always generates the same output.Non-invertible: it is hard to find an inputmsuch thathash(m) = hfor some desired outputh.Target collision resistant: given an inputm_1, it’s hard to find a different inputm_2such thathash(m_1) = hash(m_2).Collision resistant: it’s hard to find two inputsm_1andm_2such thathash(m_1) = hash(m_2)(note that this is a strictly stronger property than target collision resistance).
Key Derivation Functions
These functions are similar with hash functions except that they are slower than hash functions. These functions are usually used in encrypting passwords, because for a user login, the time can hardly be felt, but for the hackers it is hard to get the passwords by brute force. Besides, the server can generate a random salt for every user, when user login, the server will check KDF(password + salt) to make it harder to be hacked.
Symmetric Cryptography
This is usually used for encrypting files and decrypting files. An example is AES, when you use a key to encrypt a file, you can use the same key to decrypt the file.
Asymmetric Cryptography
This is wildly used in ssh. Its simple conceptions are:
- You can generate a pair of keys, which are called the public key and the private key, to encrypt and decrypt.
- The messages encrypted by the public key only can be decrypted by the paired private key. Vice versa.
The two simple conceptions above make it possible transferring information safely. You just need upload your public key to the server you want to connect with. The process can be simply depicted as below (you have uploaded your public key to the server):
- When you want to connect to the server, the server must check if you are the “right” one. So the server will let you to encrypt some contents (usually related with time) using you own private key.
- You encrypt the contents by your private key, and upload the contents to the server. Then the server will decrypt the encrypted contents by the public key you uploaded before. If the server get the contents decrypted right (same with contents before encrypted), the server will think you are the “right” one. Otherwise, you are rejected.
- Once you are accepted by the server, you can transfer data through private key, and only the server having the public key can get the right contents. And if the server wants to send messages to you, it can encrypt them with your public key too, and only your private key can decrypted the contents.
Potpourri
Contents
sshfs
You can use sudo sshfs user@hostname:directory -p PORT mountpoint to mount on server. Before you mount you should make sure that the local directory is owned by current user. If you want use cp in this mount point, you need add option -o allow_other, which means your command will be sudo sshfs user@hostname:directory -p PORT mountpoint -o allow_other.
You can use sudo umount mountpoint to unmount the directory.
If you want to mount this automatically, you need append the below information to /etc/fstab:
user@address:path mountpoint fuse.sshfs defaults,_netdev,port=ConnectPort,IdentityFile=YourPrivateKeyPos,allow_other 0 0
Backups
The 3-2-1 rule is a general recommended strategy for backing up your data:
- At least 3 copies of your data.
2copies in different mediums.1of the copies being offsite.
Common Flags in Command-Line
Sometimes, you want to input something like options but not options actually. For example, you find there is a file called -r in current directory, and you find that the file is useless. Therefore, you need remove it using rm, but -r is the option for rm command. How to do this? You can use -- to let command not translate the following input as options, so you can use rm -- -r --help to remove two files which are named with -r and --help.
Tasks-List
- Learn something about
DaemonsinLinux. - Learn and use Tarsnap and BorgBase.
- Maybe learn more about
rsynandrclone. - Learn something about WireGuard.
- Learn more about
Docker. This is important.
Q&A
What is the difference between Docker and a Virtual Machine?
Docker is based on a more general concept called containers. The main difference between containers and virtual machines is that virtual machines will execute an entire OS stack, including the kernel, even if the kernel is the same as the host machine. Unlike VMs, containers avoid running another instance of the kernel and instead share the kernel with the host. In Linux, this is achieved through a mechanism called LXC, and it makes use of a series of isolation mechanisms to spin up a program that thinks it’s running on its own hardware but it’s actually sharing the hardware and kernel with the host. Thus, containers have a lower overhead than a full VM. On the flip side, containers have a weaker isolation and only work if the host runs the same kernel. For instance if you run Docker on macOS, Docker needs to spin up a Linux virtual machine to get an initial Linux kernel and thus the overhead is still significant. Lastly, Docker is a specific implementation of containers and it is tailored for software deployment. Because of this, it has some quirks: for example, Docker containers will not persist any form of storage between reboots by default.
END
Note: this note does not contain all the contents the course contain. Some contents are easy for me, so I just skip those; some contents are hard for me, so I just write a single file for each hard part, for example I write config my own vim, learn make, and so on.
相关文章:

Notes for the missing semester. Useful and basic knowledge about Linux.
The Shell Contents The first course is to introduce some simple commands. I’ll list some commands that I’m not familiar with: # --silent means dont give log info, # --head means we only want the http head. curl --head --silent bing.com.cn# cut --deli…...

【信息系统项目管理师知识点速记】资源管理基础
项目团队 执行项目工作,实现项目目标的一组人员。成员具备不同技能,可全职或兼职,随项目进展而变化。参与项目规划和决策,贡献专业技能,增强对项目的责任感。项目管理团队 直接参与项目管理活动的成员,负责项目管理和领导。负责项目各阶段的启动、规划、执行、监督、控制…...

Android性能优化面试题汇总
Android的性能优化涉及多个方面,如启动优化、稳定性优化、内存优化、网络优化、电量优化、安全优化等方面。 一、稳定性优化 1.1 你们做了哪些稳定性方面的优化 随着项目的逐渐成熟,用户基数逐渐增多,DAU持续升高,我们遇到了很多稳定性方面的问题,对于我们技术同学遇到…...
Ansible 自动化运维工具 - 了解和模块应用
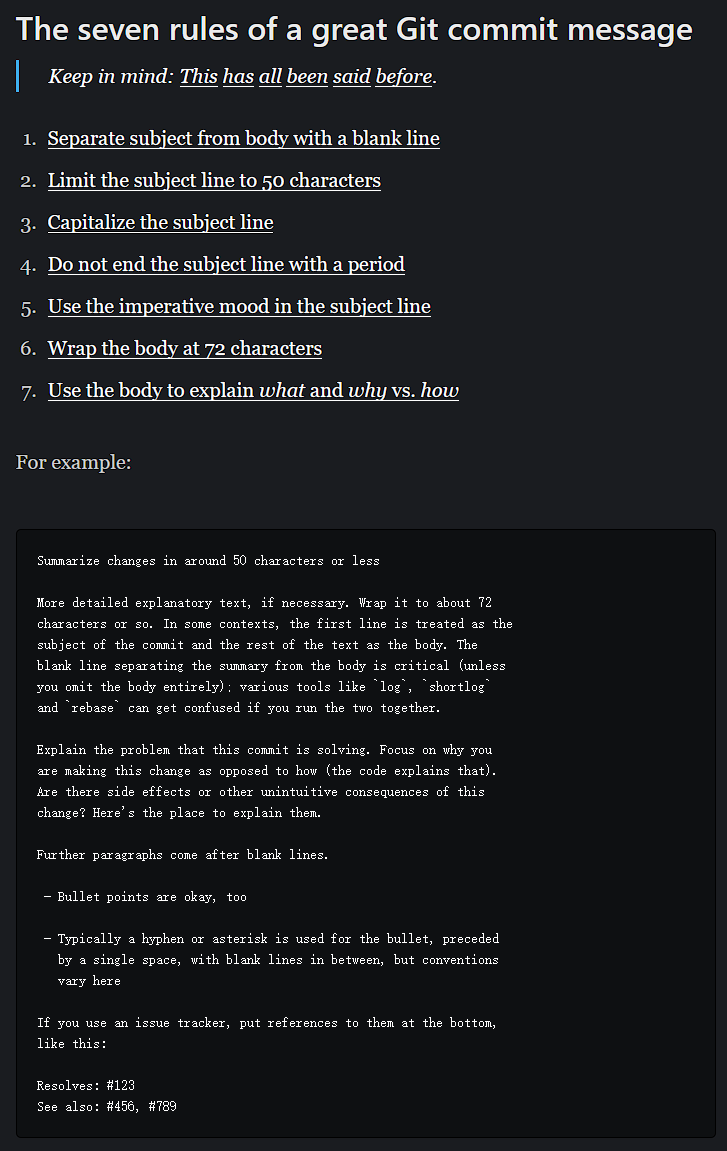
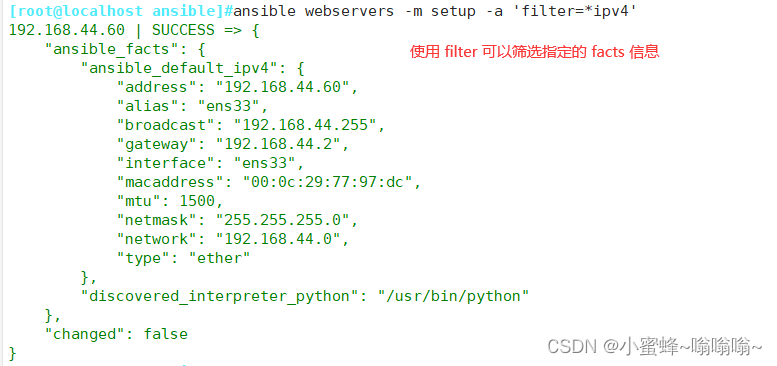
目录 一. Ansible 的相关知识 1.1 Ansible 工具的简介 1.2 Ansible的四大组件 1.3 运维自动化工具 1.4 Ansible 和其它自动化运维工具对比 1.5 Ansible 的优缺点 二. Ansible 环境安装部署 2.1 管理端安装 ansible 2.2 配置主机清单 三. ansible 命令行模块 3.1 comm…...
AI神助攻!小白也能制作自动重命名工具~
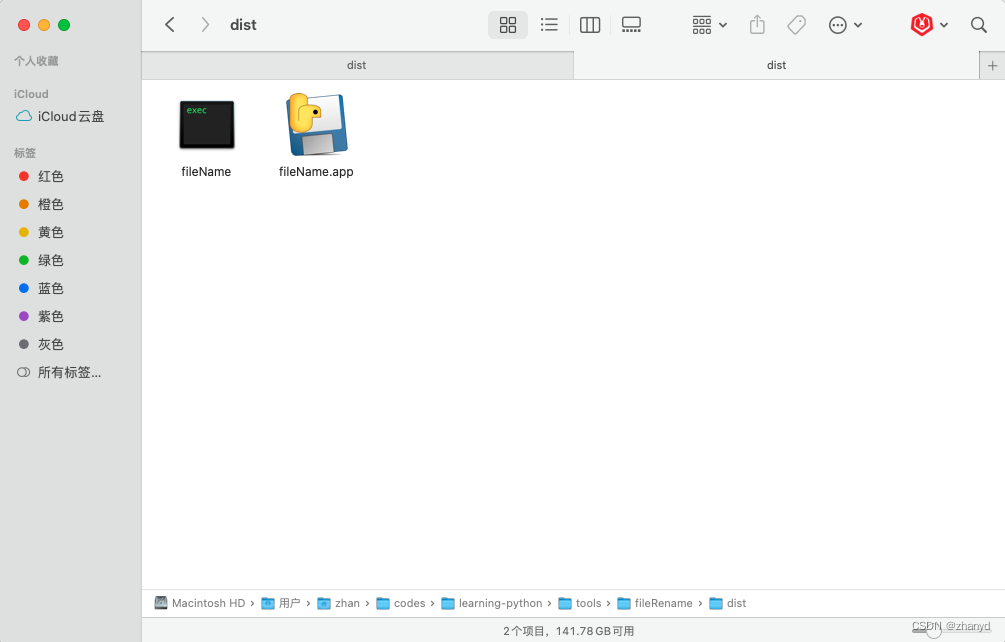
我们平时从网上下载一些文件,文件名很多都是一大串字母和数字,不打开看看,根本不知道里面是什么内容。 我想能不能做个工具,把我们一个文件夹下面的所有word、excel、ppt、pdf文件重命名为文件内容的第一行。 我们有些朋友可能不会…...
(读书笔记-大模型) LLM Powered Autonomous Agents
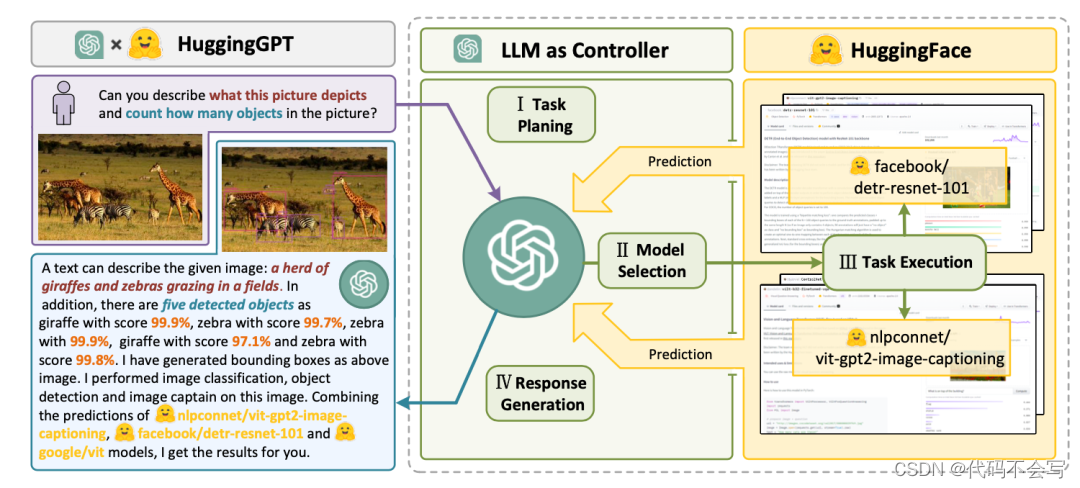
目录 智能体系统的概念 规划组件 记忆组件 工具组件 案例研究 智能体系统的概念 在大语言模型(LLM)赋能的自主智能体系统中,LLM 充当了智能体的大脑,其三个关键组件分别如下: 首先是规划,它又分为以下…...

超分辨率重建——BSRN网络训练自己数据集并推理测试(详细图文教程)
目录 一、BSRN网络总结二、源码包准备三、环境准备3.1 报错KeyError: "No object named BSRN found in arch registry!"3.2 安装basicsr源码包3.3 参考环境 四、数据集准备五、训练5.1 配置文件参数修改5.2 启动训练5.2.1 命令方式训练5.2.2 配置Configuration方式训…...
C语言实现贪吃蛇
目录 前言一 . 游戏背景1. 背景介绍2. 项目目标3. 技术要点 二 . 效果演示三 . 游戏的设计与分析1. 核心逻辑2. 设计与分析游戏开始Gamestart()函数游戏运行Gamerun()函数游戏结束Gameend()函数 四 . 参考代码五 . 总结 前言 本文旨在使用C语言和基础数据结构链表来实现贪吃蛇…...

高可用系列四:loadbalancer 负载均衡
负载均衡可以单独使用,也常常与注册中心结合起来使用,其需要解决的问题是流量分发,这是就需要定义分发策略,当然也包括了故障切换的能力。 故障切换 故障切换是负载均衡的基本能力,和注册中心结合时比较简单…...

Ruby递归目录文件的又一种方法
经常派得上用场,记录一下。 递归文件做一些操作 #encoding:utf-8require pathnamedef recursive_enum_files(from_path)from_path Pathname.new(from_path)raise ArgumentError,must start at a directory. unless from_path.directory?from_path.enum_for(:fin…...
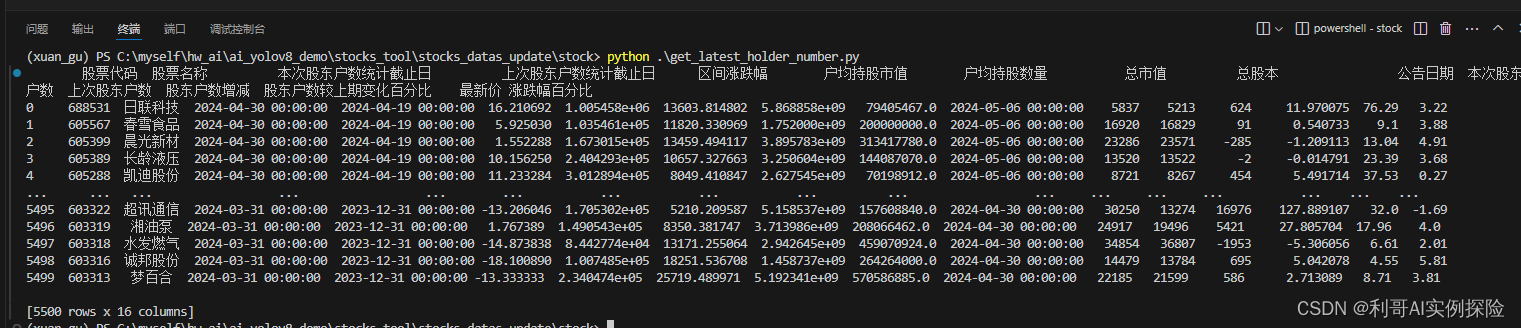
【爬虫】爬取A股数据写入数据库(一)
1. 对东方财富官网的分析 步骤: 通过刷新网页,点击等操作,我们发现https://datacenter-web.eastmoney.com/api/data/v1/get?请求后面带着一些参数即可以获取到相应数据。我们使用python来模拟这个请求即可。 我们以如下选择的页面为切入点…...
1-38 流资源类结构
一 简介 1. Java中所说的流资源--IO流 2.为什么学习留资源? --要操作文件中的数据 将数据写入指定的文件 将数据从指定的文件读取 3.分类 -- 四大基流 , 八大子流 (重点) 按照流向分 : 输入流 和输出流 按照操作数据资源的类型划分 字符流 (重点) Reader -- 字符…...

nginx的前世今生(二)
书接上回: 上回书说到,nginx的前世今生,这回我们继续说 3.缓冲秘籍,洪流控水 Nginx的缓冲区是其处理数据传输和提高性能的关键设计之一,主要用于暂存和管理进出的数据流,以应对不同组件间速度不匹配的问题…...

浏览器跨域详解
一、什么是跨域 浏览器跨域是指当一个Web应用程序试图访问另一个协议、主机或端口不同的资源时,所发生的情况。这主要是由于浏览器的同源策略造成的,它是为了网站的安全而设置的安全限制,防止一个网站恶意访问另一个网站的资源。当然这是比较…...
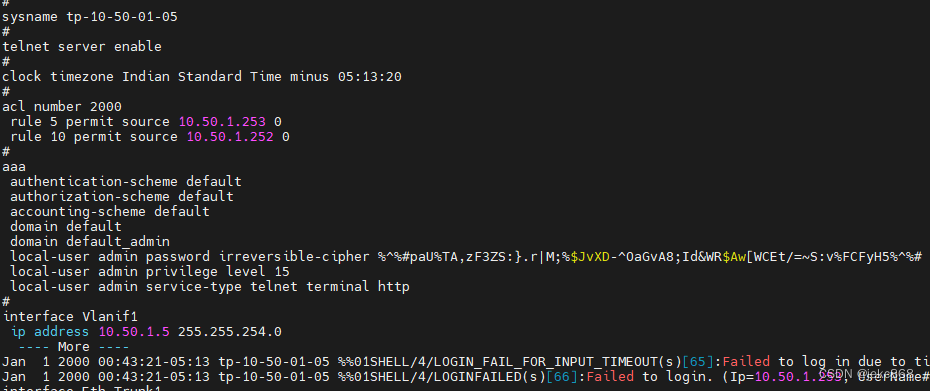
华为5700配置
恢复出厂设置,清空配置 1、更改名字 system-view sysname tp-10-50-01-04 2、配置管理接口 int vlan 1 ip add 10.50.1.4 255.255.254.0 quit 2、链路汇聚 interface eth-trunk 1 mode lacp quit 3、绑定端口 interface eth-trunk 1 trunkport gigabitethernet …...

使用Axios从前端上传文件并且下载后端返回的文件
前端代码: function uploadAndDownload(){showLoading();const fileInput document.querySelector(#uploadFile);const file fileInput.files[0];const formData new FormData()formData.append(file, file)return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {axios({…...
open 函数到底做了什么
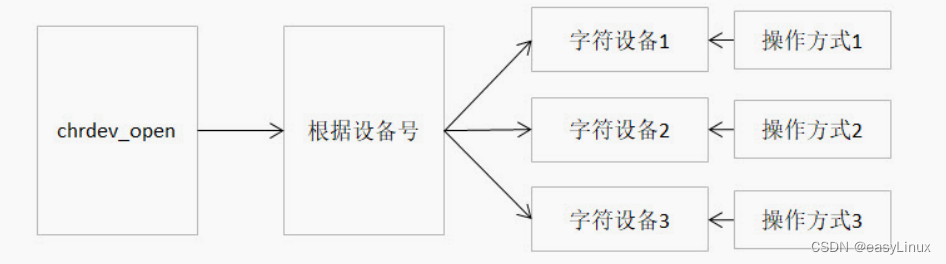
使用设备之前我们通常都需要调用 open 函数,这个函数一般用于设备专有数据的初始化,申请相关资源及进行设备的初始化等工作,对于简单的设备而言,open 函数可以不做具体的工作,你在应用层通过系统调用 open 打开设备…...

ue引擎游戏开发笔记(32)——为游戏添加新武器装备
1.需求分析: 游戏中角色不会只有一种武器,不同武器需要不同模型,甚至可能需要角色持握武器的不同位置,因此需要添加专门的武器类,方便武器后续更新,建立一个武器类。 2.操作实现: 1.在ue5中新建…...
【个人博客搭建】(17)使用FluentValidation 参数校验
FluentValidation 是一个用于 .NET 的开源验证库,它提供了一种流畅的接口和强类型验证规则,使得验证逻辑表达得更加清晰和简洁。(Apache-2.0) FluentValidation 的主要作用包括: 提高代码可读性:通过使用 F…...

数据结构===散列表
文章目录 概要散列思想散列函数散列冲突开放寻址法装载因子 链表法 代码Java小结 概要 散列表是一种很有趣的数据结构。 散列表是一个很有用的数据结构。它是数组演练而来的,又是一个基于数组的扩展的数据结构。接下来看看。 散列思想 散列表用的是数组支持按照下…...

【大模型RAG】拍照搜题技术架构速览:三层管道、两级检索、兜底大模型
摘要 拍照搜题系统采用“三层管道(多模态 OCR → 语义检索 → 答案渲染)、两级检索(倒排 BM25 向量 HNSW)并以大语言模型兜底”的整体框架: 多模态 OCR 层 将题目图片经过超分、去噪、倾斜校正后,分别用…...

PHP和Node.js哪个更爽?
先说结论,rust完胜。 php:laravel,swoole,webman,最开始在苏宁的时候写了几年php,当时觉得php真的是世界上最好的语言,因为当初活在舒适圈里,不愿意跳出来,就好比当初活在…...
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
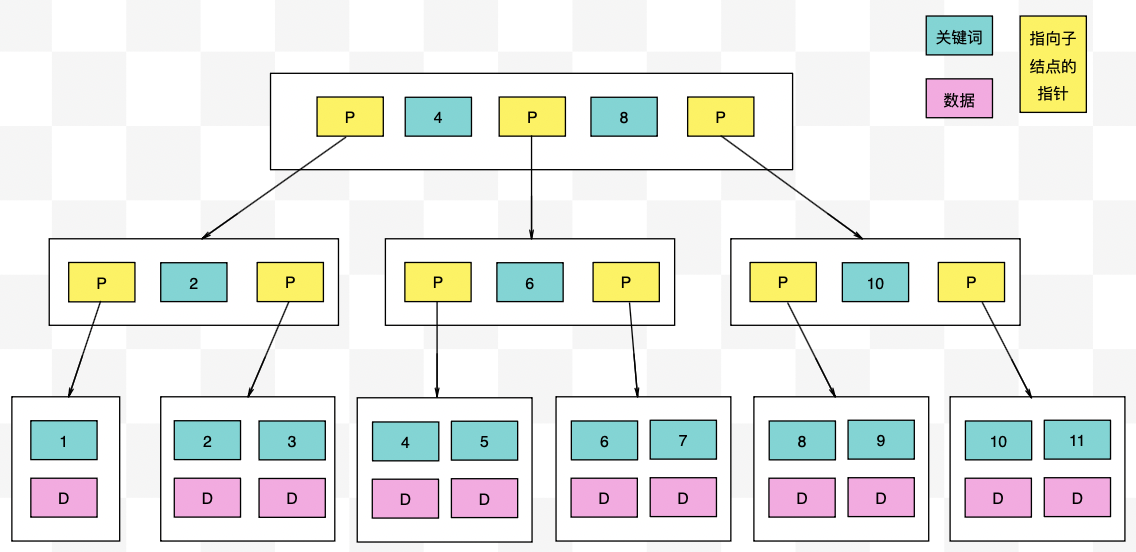
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...
【JavaWeb】Docker项目部署
引言 之前学习了Linux操作系统的常见命令,在Linux上安装软件,以及如何在Linux上部署一个单体项目,大多数同学都会有相同的感受,那就是麻烦。 核心体现在三点: 命令太多了,记不住 软件安装包名字复杂&…...

Pinocchio 库详解及其在足式机器人上的应用
Pinocchio 库详解及其在足式机器人上的应用 Pinocchio (Pinocchio is not only a nose) 是一个开源的 C 库,专门用于快速计算机器人模型的正向运动学、逆向运动学、雅可比矩阵、动力学和动力学导数。它主要关注效率和准确性,并提供了一个通用的框架&…...
群晖NAS如何在虚拟机创建飞牛NAS
套件中心下载安装Virtual Machine Manager 创建虚拟机 配置虚拟机 飞牛官网下载 https://iso.liveupdate.fnnas.com/x86_64/trim/fnos-0.9.2-863.iso 群晖NAS如何在虚拟机创建飞牛NAS - 个人信息分享...

Caliper 配置文件解析:fisco-bcos.json
config.yaml 文件 config.yaml 是 Caliper 的主配置文件,通常包含以下内容: test:name: fisco-bcos-test # 测试名称description: Performance test of FISCO-BCOS # 测试描述workers:type: local # 工作进程类型number: 5 # 工作进程数量monitor:type: - docker- pro…...

Bean 作用域有哪些?如何答出技术深度?
导语: Spring 面试绕不开 Bean 的作用域问题,这是面试官考察候选人对 Spring 框架理解深度的常见方式。本文将围绕“Spring 中的 Bean 作用域”展开,结合典型面试题及实战场景,帮你厘清重点,打破模板式回答,…...

人工智能--安全大模型训练计划:基于Fine-tuning + LLM Agent
安全大模型训练计划:基于Fine-tuning LLM Agent 1. 构建高质量安全数据集 目标:为安全大模型创建高质量、去偏、符合伦理的训练数据集,涵盖安全相关任务(如有害内容检测、隐私保护、道德推理等)。 1.1 数据收集 描…...
