Android Framework——zygote 启动 SystemServer
概述
在Android系统中,所有的应用程序进程以及系统服务进程SystemServer都是由Zygote进程孕育(fork)出来的,这也许就是为什么要把它称为Zygote(受精卵)的原因吧。由于Zygote进程在Android系统中有着如此重要的地位,本文将详细分析它的启动过程
总体时序
先概述一下总体运行流程,当按电源键,首先是加载系统引导程序BootLoader,然后启动linux内核,再启动init进程,最后Zygote进程启动完成。理论上Android系统中的所有应用程序理论上都是由Zygote启动的。Zygote前期启动启动服务,后期主要fork程序。
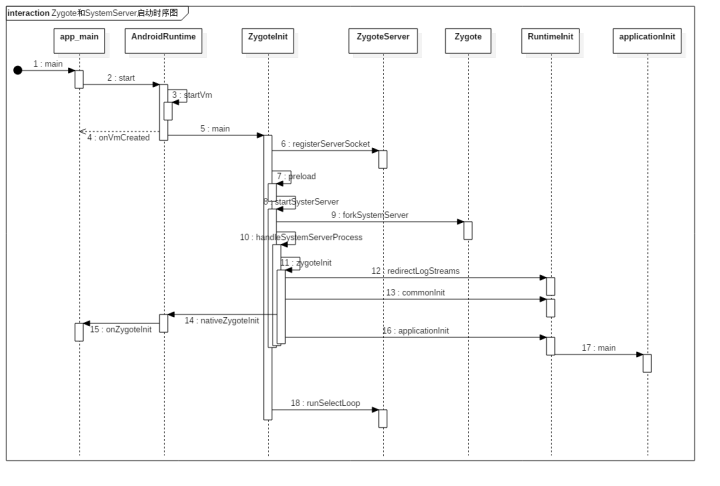
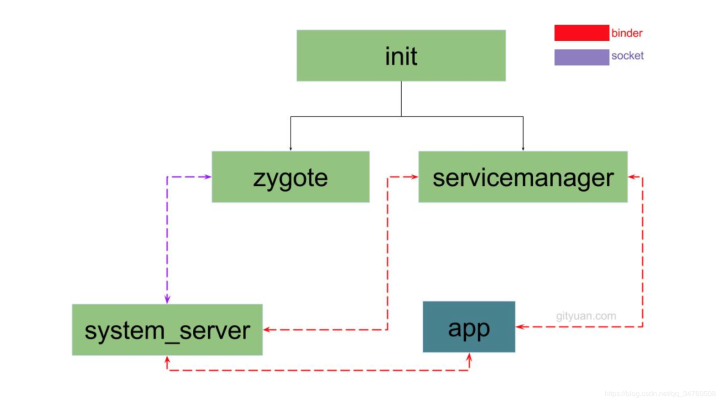
init启动流程
- 用户空间的第一个进程,进程号为1(在《深入理解安卓内核思想》的257页里面写的是0,在这记录一下)
- 职责
- 创建Zygote
- 初始化属性服务
- init文件位于源码目录system/core/init中
init进程的启动三个阶段
- 启动电源以及系统的启动,加载引导程序BootLoader。
- 启动Linux内核
- 启动init进程。
- 启动Zygote进程
- 初始化启动属性服务。
Zygote进程
- 所有App的父进程,ZygoteInit.main
- Zygote进程,是由init进程通过解析init.rc文件后fork生成的,Zygote进程主要包括
- 加载Zygoteinit类,注册Zygote Socket服务端套接字
- 加载虚拟机
- 提前加载类PreloadClasses
- 提前加载资源PreLoadResouces
- system_server进程,是由Zygote fork而来,System Server是Zygote孵化出的第一个进程,System Server 负责启动和管理整个Java FrameWork,包含ActivityManagerService, WorkManagerService,PagerManagerService,PowerManagerService等服务
system_server进程
系统各大服务的载体, SystemServer.main system_server进程从源码角度来看可以分为,引导服务,核心服务和其他服务
- 引导服务(7个):ActivityManagerService、PowerManagerService、LightsService、DisplayManagerService、PackageManagerService、UserManagerService、SensorService;
- 核心服务(3个):BatteryService、UsageStatsService、WebViewUpdateService;
- 其他服务(70个+):AlarmManagerService、VibratorService等。
ServiceManger进程
bInder服务的大管家
ServiceManager 是Binder IPC通信过程中的守护进程,本身也是一个Binder,但是并没有采用多线程模型来跟Binder通信,而是自行编写了binder.c直接和Binder驱动来通信,并且只有一个binder_loop来读取和处理事务,这样做的好处是简单和高效 ServiceManager本身工作相对简单,其工能查询和注册服务
流程图
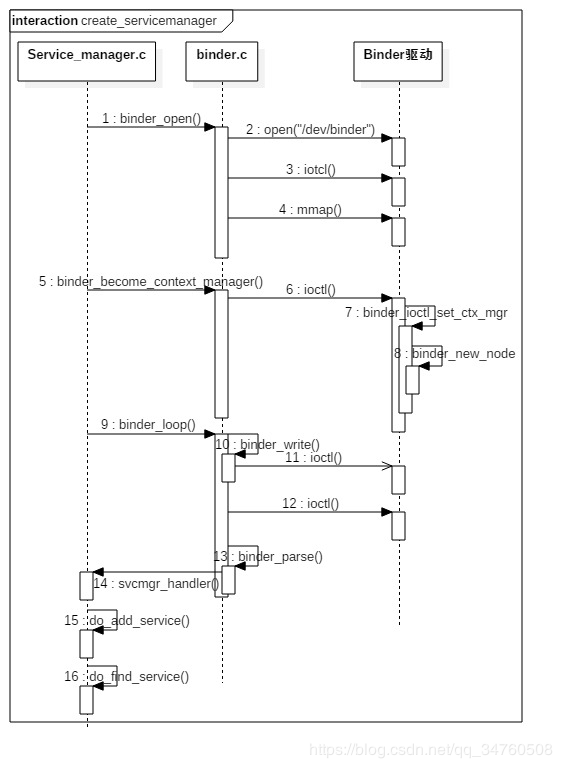
ServiceManager 集中管理系统内的所有服务,通能过权限控制进程是否有权注册服务,通过字符串来查找是否有对应的Service,由于ServiceManager进程注册了Service的死亡通知,那么服务所在的进程死亡后,只需告诉ServiceManager,每个Client通过查询ServiceManager可以获取Service的情况
启动主要包括以下几个阶段
- 打开Binder驱动,并调用mmap()方法分配128k的内存映射空间,binder_open
- 注册成为Binder服务的大管家binder_become_context_manager
- 验证selinux权限,判断进程是否有权注册查看指定服务
- 进入无限循环,处理Client发来的请求 binder_loop
- 根据服务的名称注册服务,重复注册会移除之前的注册信息
- 死亡通知,当所在进程死亡后,调用binder_release方法,然后调用binder_node_release,这个过程发出死亡通知回调
App进程
- 通过Process.start启动的App进程ActivityThread.main
- Zygote 孵化出的第一个App进程是Launcher,这是用户看到的桌面App
- Zygote 还会创建出Browser,Phone,Email等App进程,每个App至少运行在一个进程上
- 所有的App进程都是由Zygote fork而成
3)Zygote进程的启动
Zygote进程, 一个在Android系统中扮演重要角色的进程. 我们知道Android系统中的两个重要服务PackageManagerService和ActivityManagerService, 都是由SystemServer进程启动的, 而这个SystemServer进程本身是Zygote进程在启动的过程中fork出来的. 这样一来, 想必我们就知道Zygote进程在Android系统中的重要地位了.
从图中可得知Android系统中各个进程的先后顺序为:
init进程 –-> Zygote进程 –> SystemServer进程 –>应用进程
链接
- 在init启动Zygote时主要是调用app_main.cpp的main函数中的AppRuntime.start()方法来启动Zygote进程的;
- 接着到AndroidRuntime的start函数:使用JNI调用ZygoteInit的main函数,之所以这里要使用JNI,是因为ZygoteInit是java代码。最终,Zygote就从Native层进入了Java FrameWork层。在此之前,并没有任何代码进入Java FrameWork层面,因此可以认为,Zygote开创了java FrameWork层。
- /frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
@UnsupportedAppUsagepublic static void main(String argv[]) {ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw// an error.ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();// Zygote goes into its own process group.try {Os.setpgid(0, 0);} catch (ErrnoException ex) {throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);}Runnable caller;try {// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restartif (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());}String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");RuntimeInit.enableDdms();boolean startSystemServer = false;String zygoteSocketName = "zygote";String abiList = null;boolean enableLazyPreload = false;for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {startSystemServer = true;} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {enableLazyPreload = true;} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {zygoteSocketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());} else {throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);}}final boolean isPrimaryZygote = zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);if (abiList == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");}// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.if (!enableLazyPreload) {bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,SystemClock.uptimeMillis());preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,SystemClock.uptimeMillis());bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload} else {Zygote.resetNicePriority();}// Do an initial gc to clean up after startupbootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");gcAndFinalize();bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGCbootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from// Zygote.Trace.setTracingEnabled(false, 0);Zygote.initNativeState(isPrimaryZygote);ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);if (startSystemServer) {
// 使用了forkSystemServer()方法去创建SystemServer进程Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.if (r != null) {r.run();return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// 这里调用了ZygoteServer的runSelectLoop方法来等等ActivityManagerService来请求创建新的应用程序进程
// loops forever in the zygote.caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);}
catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;}
finally
{
if (zygoteServer != null) {zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.if (caller != null) {caller.run();
}
}
其中, 在ZygoteInit的forkSystemServer()方法中启动了SystemServer进程,forkSystemServer()方法核心代码 :
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,ZygoteServer zygoteServer)
{
// 一系统创建SystemServer进程所需参数的准备工作try {...
/* Request to fork the system server process
*/// 3.1pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,parsedArgs.gids,parsedArgs.runtimeFlags,null,parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex)
{throw new RuntimeException(ex);}
/* For child process
*/if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
// 3.2return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}return null;
}
可以看到,forkSystemServer()方法中,注释3.1调用了Zygote的forkSystemServer()方法去创建SystemServer进程,其内部会执行nativeForkSystemServer这个Native方法,它最终会使用fork函数在当前进程创建一个SystemServer进程。如果pid等于0,即当前是处于新创建的子进程ServerServer进程中,则在注释3.2处使用handleSystemServerProcess()方法处理SystemServer进程的一些处理工作。
从以上的分析可以得知,Zygote进程启动中承担的主要职责如下:
- 1、创建AppRuntime,执行其start方法,启动Zygote进程。。
- 2、创建JVM并为JVM注册JNI方法。
- 3、使用JNI调用ZygoteInit的main函数进入Zygote的Java FrameWork层。
- 4、使用registerZygoteSocket方法创建服务器端Socket,并通过runSelectLoop方法等等AMS的请求去创建新的应用进程。
- 5、启动SystemServer进程。
- 调用了handleSystemServerprocess()方法来启动SystemServer进程。handleSystemServerProcess()方法如下所示:
/*** Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
*/
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs) {...
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {...}
else {ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
// 1cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);}
/** Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/// 2return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
}
在注释1处,使用了systemServerClassPath和targetSdkVersion创建了一个PathClassLoader。接着,在注释2处,执行了ZygoteInit的zygoteInit()方法,该方法如下所示:
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
{
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
// 1ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
// 2return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
- zygoteInit()方法的注释2处,这里调用了RuntimeInit 的 applicationInit() 方法,代码如下所示:
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,ClassLoader classLoader) {...
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static mainreturn findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
在applicationInit()方法中最后调用了findStaticMain()方法:
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
// 1cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing class when invoking static main " + className,ex);
}
Method m;try {
// 2m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing static main on " + className, ex);}
catch (SecurityException ex) {throw new RuntimeException("Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException("Main method is not public and static on " + className);}
/** This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/// 3return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
首先,在注释1处,通过发射得到了SystemServer类。接着,在注释2处,找到了SystemServer中的main()方法。最后,在注释3处,会将main()方法传入MethodAndArgsCaller()方法中,这里的MethodAndArgsCaller()方法是一个Runnable实例,它最终会一直返回出去,直到在ZygoteInit的main()方法中被使用,如下所示:
if (startSystemServer) {
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null}
in the parent (zygote) process, and {
@code r != null}
in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
可以看到,最终直接调用了这个Runnable实例的run()方法,代码如下所示:
/*** Helper class which holds a method and arguments and can call them. This is used as part of
* a trampoline to get rid of the initial process setup stack frames.
*/
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
/** method to call
*/private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array
*/private final String[] mArgs;public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;mArgs = args;}
public void run() {try {
// 1mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] {
mArgs });}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
}
else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
在注释1处,这个mMethod就是指的SystemServer的main()方法,这里动态调用了SystemServer的main()方法,最终,SystemServer进程就进入了SystemServer的main()方法中了。这里还有个遗留问题,为什么不直接在findStaticMain()方法中直接动态调用SystemServer的main()方法呢?原因就是这种递归返回后再执行入口方法的方式会让SystemServer的main()方法看起来像是SystemServer的入口方法,而且,这样也会清除之前所有SystemServer相关设置过程中需要的堆栈帧。
--------走到 SystemService 进程
- /frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
接下来我们看看SystemServer的main()方法:
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new SystemServer().run();
}
main()方法中调用了SystemServer的run()方法,如下所示:
private void run() {try {...
// 1Looper.prepareMainLooper();...
// Initialize native services.
// 2System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.performPendingShutdown();
// Initialize the system context.createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
// 3mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelizedSystemServerInitThreadPool.get();}
finally {traceEnd();
// InitBeforeStartServices}
// Start services.try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
// 4startBootstrapServices();
// 5startCoreServices();
//6startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();}
catch (Throwable ex) {Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;}
finally {
traceEnd();
}...
// Loop forever.
// 7Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
在注释1处,创建了消息Looper。
在注释2处,加载了动态库libandroid_servers.so。
在注释3处,创建了SystemServerManager,它的作用是对系统服务进行创建、启动和生命周期管理。
在注释4处的startBootstarpServices()方法中使用SystemServiceManager启动了ActivityManagerService、PackageManagerService、PowerManagerService等引导服务。
在注释5处的startCoreServices()方法中则启动了BatteryService、WebViewUpdateService、DropBoxManagerService、UsageStatsService4个核心服务。
在注释6处的startOtherServices()方法中启动了WindowManagerService、InputManagerService、CameraService等其它服务。这些服务的父类都是SystemService。
可以看到,上面把系统服务分成了三种类型:引导服务、核心服务、其它服务。这些系统服务共有100多个,其中对于我们来说比较关键的有:
- 引导服务:ActivityManagerService,负责四大组件的启动、切换、调度。
- 引导服务:PackageManagerService,负责对APK进行安装、解析、删除、卸载等操作。
- 引导服务:PowerManagerService,负责计算系统中与Power相关的计算,然后决定系统该如何反应。
- 核心服务:BatteryService,管理电池相关的服务。
- 其它服务:WindowManagerService,窗口管理服务。
- 其它服务:InputManagerService,管理输入事件。
很多系统服务的启动逻辑都是类似的,这里我以启动ActivityManagerService服务来进行举例,代码如下所示:
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
SystemServiceManager 的 startService() 方法启动了ActivityManagerService,该启动方法如下所示:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {final String name = serviceClass.getName();
...try {Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
// 1service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
}
catch (InstantiationException ex) {...
// 2startService(service);return service;
}
finally {Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
在注释1处使用反射创建了ActivityManagerService实例,并在注释2处调用了另一个startService()重载方法,如下所示:
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
// 1mServices.add(service);
// Start it.long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
// 2service.onStart();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex)
{
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
在注释1处,首先会将ActivityManagerService添加在mServices中,它是一个存储SystemService类型的ArrayList,这样就完成了ActivityManagerService的注册。
在注释2处,调用了ActivityManagerService的onStart()方法完成了启动ActivityManagerService服务。
除了使用SystemServiceManager的startService()方法来启动系统服务外,也可以直接调用服务的main()方法来启动系统服务,如PackageManagerService:
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
这里直接调用了PackageManagerService的main()方法:
public static PackageManagerService main(Context context, Installer installer,boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
// Self-check for initial settings.PackageManagerServiceCompilerMapping.checkProperties();
// 1PackageManagerService m = new PackageManagerService(context, installer,factoryTest, onlyCore);
m.enableSystemUserPackages();
// 2ServiceManager.addService("package", m);
// 3final PackageManagerNative pmn = m.new PackageManagerNative();
ServiceManager.addService("package_native", pmn);
return m;
}
在注释1处,直接新建了一个PackageManagerService实例,
注释2处将PackageManagerService注册到服务大管家ServiceManager中,ServiceManager用于管理系统中的各种Service,用于系统C/S架构中的Binder进程间通信,即如果Client端需要使用某个Servcie,首先应该到ServiceManager查询Service的相关信息,然后使用这些信息和该Service所在的Server进程建立通信通道,这样Client端就可以服务端进程的Service进行通信了。
7. SystemService 进程总结
SystemService的启动流程分析至此已经完结,经过以上的分析可知,SystemService进程被创建后,主要的处理如下:
- 1、启动Binder线程池,这样就可以与其他进程进行Binder跨进程通信。
- 2、创建SystemServiceManager,它用来对系统服务进行创建、启动和生命周期管理。
- 3、启动各种系统服务:引导服务、核心服务、其他服务,共100多种。应用开发主要关注引导服务ActivityManagerService、PackageManagerService和其他服务WindowManagerService、InputManagerService即可。
相关文章:

Android Framework——zygote 启动 SystemServer
概述 在Android系统中,所有的应用程序进程以及系统服务进程SystemServer都是由Zygote进程孕育(fork)出来的,这也许就是为什么要把它称为Zygote(受精卵)的原因吧。由于Zygote进程在Android系统中有着如此重…...
在ubuntu上搭建SSH和FTP和NFS和TFTP
一、SSH服务搭建使用如下命令安装 SSH 服务;ssh 的配置文件为/etc/ssh/sshd_config,使用默认配置即可。sudo apt-get install openssh-server开启 SSH 服务以后我们就可以在 Windwos 下使用终端软件登陆到 Ubuntu,比如使用 Mobaxterm。二、FT…...

ThinkPHP 6.1 模板篇之文件加载
本文主要讲述模板中如何使用包含文件、引入css/js文件及路径优化。 包含文件 使用{include}标签来加载公用重复的文件,比如头部、尾部和导航部分 包含用法 1.创建公用文件 在模版 view 目录创建一个 common公共目录,分别创建 header、footer 和 nav …...

操作系统内核与安全分析课程笔记【1】链表、汇编与makefile
文章目录链表循环双向链表哈希链表其他链表汇编内联汇编扩展内联汇编makefile链表 链表是linux内核中关键的数据结构。在第二次课中,重点介绍了循环双向链表和哈希链表。这两种链表都在传统的双向链表的基础之上进行了针对效率的优化。(ps:这部分可以通…...
| 机考必刷)
华为OD机试题 - 九宫格按键输入(JavaScript)| 机考必刷
更多题库,搜索引擎搜 梦想橡皮擦华为OD 👑👑👑 更多华为OD题库,搜 梦想橡皮擦 华为OD 👑👑👑 更多华为机考题库,搜 梦想橡皮擦华为OD 👑👑👑 华为OD机试题 最近更新的博客使用说明本篇题解:九宫格按键输入题目输入输出示例一输入输出说明示例二输入输出说…...

PMSM控制_foc 控制环路
整个系统的控制过程有以下部分,以无感FOC,双电阻电流采样,控制周期为 10KHz 为例: 1、在每隔一个 PWM 周期采样一次两相电流 2、进行 FOC 的计算 (1)clarke 变换,将电流变换至静止坐标系下的 Ia…...

Linux 练习七 (IPC 共享内存)
文章目录System V 共享内存机制:shmget shmat shmdt shmctl案例一:有亲缘关系的进程通信案例二:非亲缘关系的进程通信内存写端write1.c内存读端read1.c案例三:不同程序之间的进程通信程序一,写者shmwr.c程序二…...

【数据库原理复习】ch4 完整性约束 SQL定义
这里写目录标题基本概念实体完整性参照完整性违规处理用户自定义完整性约束条件定义完整性约束命名字句基本概念 完整性约束主要包括 实体完整性参照完整性用户自定义完整性 实体完整性 关系模型中实体完整性通常在建表时候添加primary key完成 # primary key定义 create …...

【2023年的就业形势依旧严峻】
2023年口罩放开的第一年,也是第一个招聘会,挤满了求职者和用人单位,大多数都是想着重新开始,抓住金三银四的好时机,找到心仪的工作和符合岗位要求的人才,一起整装出发。我们理想的状态是,经济已…...
Linux下LED灯驱动模板详解
一、地址映射我们先了解MMU,全称是Memory Manage Unit。在老版本的Linux中要求处理器必须有MMU,但是现在Linux内核已经支持五MMU。MMU主要完成的功能如下:1、完成虚拟空间到物理空间的映射2、内存保护,设置存储器的访问权限&#…...
【C++】你不得不爱的——继承
凡是面向对象的语言,都有三大特性,继承,封装和多态,但并不是只有这三个特性,是因为者三个特性是最重要的特性,那今天我们一起来看继承! 目录 1.继承的概念及定义 1.概念 2.继承的定义 2.基类…...

数据库系统概论
文章目录前言基础篇:1-5章第 1 章 绪论1.1 数据库系统概述1.2 数据模型1.3 数据库系统的结构1.4 数据库系统的组成1.5 小结第 2 章 关系数据库1.关系模型1.1 关系数据结构1.2 关系完整性约束实体完整性、参照完整性、用户定义完整性2.关系代数8种关系代数运算符并 ∪…...
32位处理器AM6528BACDXEA、AM6548BACDXEAF基于Arm Cortex-A53内核【工业4.0嵌入式产品应用】
AM6528BACDXEA、AM6548BACDXEAF 处理器是专为满足工业4.0嵌入式产品对处理性能的复杂需求而设计的Arm应用处理器。AM654x和AM652x器件将四个或两个Arm Cortex-A53内核与一个双Arm Cortex-R5F MCU子系统结合在一起。这些包含的功能旨在帮助客户实现终端产品的功能安全目标。它还…...

多图片怎么转换成PDF?这招教你轻松转换
多图片怎么转换成PDF?我们经常会传输图片文件给同事或者朋友,但是多张图片的传输比较麻烦,有的时候传输比较慢,而且也不便于查看,所以我们就可以将需要传输的多张图片转换成一个PDF文件,这样查看文件时就可…...
kali双网卡
先单独开启一个网卡,配置/etc/network/interfaces 修改为如下配置 This file describes the network interfaces available on your system and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5). source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* The loopb…...
【wed前端初级课程】第一章 什么是HTML
什么是WEB前端? 简单来说就是网页,只是这个网页它是由多种技术参与制作的,用来向用户展示的页面。 HTML(超文本标签语言):它决定了网页的结构。 CSS:网页的装饰器。 JavaScript:JavaScrip最初是因为校验…...
sd卡格式化后数据恢复怎么操作
有时候我们需要清空SD卡数据文件,有时候则是因为需要修复SD卡所以需要格式化,但是却被提示无法格式化SD卡。这种情况往往是由于平时SD卡使用时的一些不良习惯或是SD卡中病毒,病毒在运行SD卡中的软件所造成的。那么sd卡格式化后数据恢复怎么操…...

论文阅读笔记|大规模多标签文本分类
多标签文本分类(Extreme Multi Label Classification, MLTC)是自然语言处理领域中一个十分重要的任务,其旨在从一个给定的标签集合中选取出与文本相关的若干个标签。MLTC可以广泛应用于网页标注,话题识别和情感分析等场景。大规模…...

国际化翻译navigator.language与语种对照表
代码(navigator.language) 语种 字段名 "zh-CN", 中文 Chinese "zh-SG" 马新简体 Chinese_SG "zh-TW","zh-HK", 繁体中文 Chinese_TW "en", "en-US"(美国), "en-EG"…...
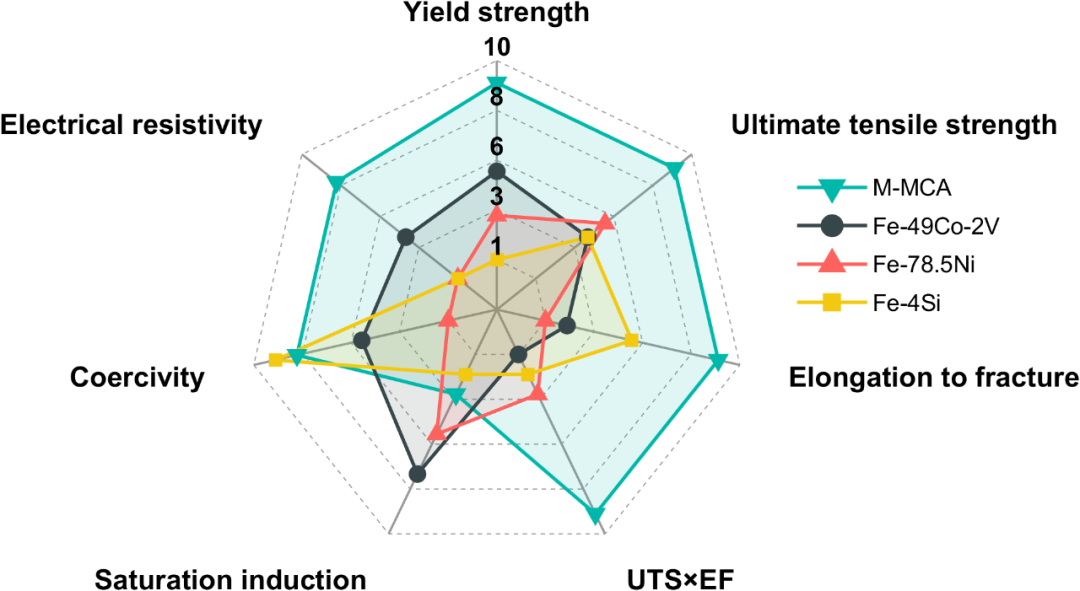
Matlab进阶绘图第6期—雷达图/蜘蛛图/星图
雷达图(Radar Chart),又称星图、蜘蛛图、蜘蛛网图、网络图、Kiviat图等,是一种以从同一点开始的轴上表示的三个以上变量的二维图表的形式,来显示多变量数据的图形方法。 雷达图可以直观地对多维数据集目标对象的性能、…...
解决Ubuntu22.04 VMware失败的问题 ubuntu入门之二十八
现象1 打开VMware失败 Ubuntu升级之后打开VMware上报需要安装vmmon和vmnet,点击确认后如下提示 最终上报fail 解决方法 内核升级导致,需要在新内核下重新下载编译安装 查看版本 $ vmware -v VMware Workstation 17.5.1 build-23298084$ lsb_release…...
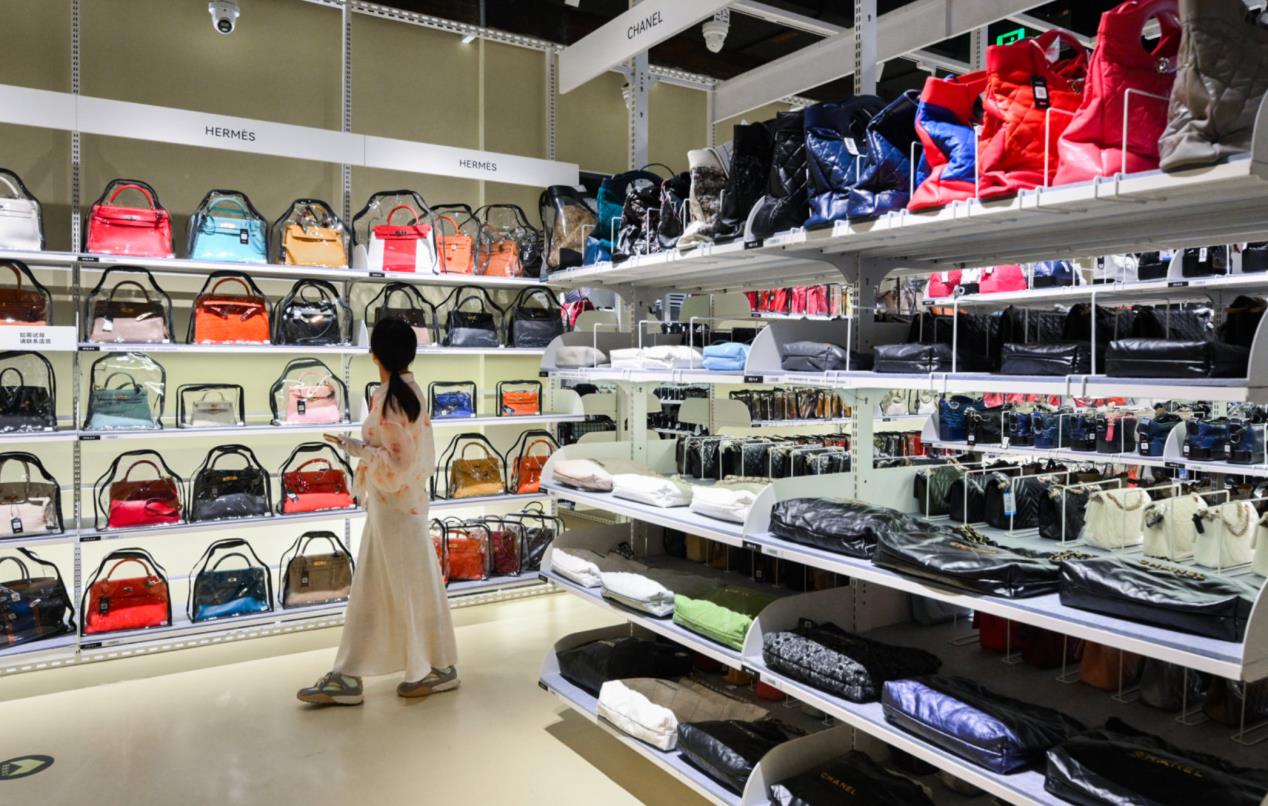

转转集团旗下首家二手多品类循环仓店“超级转转”开业
6月9日,国内领先的循环经济企业转转集团旗下首家二手多品类循环仓店“超级转转”正式开业。 转转集团创始人兼CEO黄炜、转转循环时尚发起人朱珠、转转集团COO兼红布林CEO胡伟琨、王府井集团副总裁祝捷等出席了开业剪彩仪式。 据「TMT星球」了解,“超级…...
指令的指南)
在Ubuntu中设置开机自动运行(sudo)指令的指南
在Ubuntu系统中,有时需要在系统启动时自动执行某些命令,特别是需要 sudo权限的指令。为了实现这一功能,可以使用多种方法,包括编写Systemd服务、配置 rc.local文件或使用 cron任务计划。本文将详细介绍这些方法,并提供…...

Matlab | matlab常用命令总结
常用命令 一、 基础操作与环境二、 矩阵与数组操作(核心)三、 绘图与可视化四、 编程与控制流五、 符号计算 (Symbolic Math Toolbox)六、 文件与数据 I/O七、 常用函数类别重要提示这是一份 MATLAB 常用命令和功能的总结,涵盖了基础操作、矩阵运算、绘图、编程和文件处理等…...

ip子接口配置及删除
配置永久生效的子接口,2个IP 都可以登录你这一台服务器。重启不失效。 永久的 [应用] vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0修改文件内内容 TYPE"Ethernet" BOOTPROTO"none" NAME"eth0" DEVICE"eth0" ONBOOT&q…...
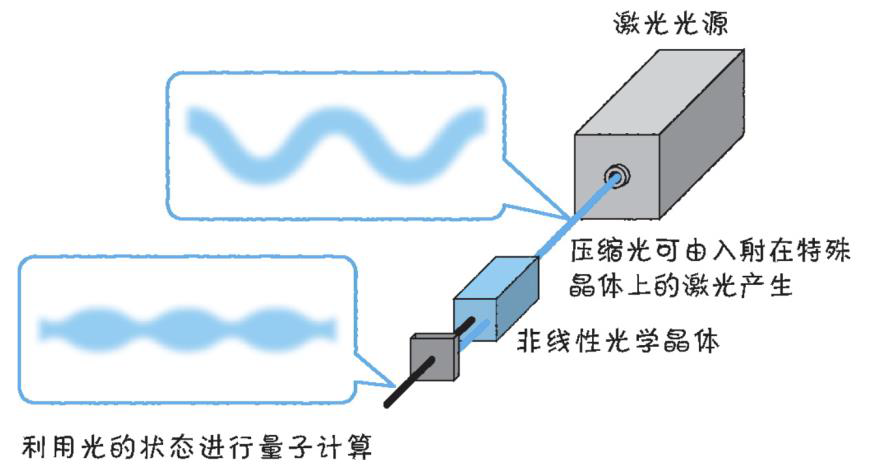
以光量子为例,详解量子获取方式
光量子技术获取量子比特可在室温下进行。该方式有望通过与名为硅光子学(silicon photonics)的光波导(optical waveguide)芯片制造技术和光纤等光通信技术相结合来实现量子计算机。量子力学中,光既是波又是粒子。光子本…...
提供了哪些便利?)
现有的 Redis 分布式锁库(如 Redisson)提供了哪些便利?
现有的 Redis 分布式锁库(如 Redisson)相比于开发者自己基于 Redis 命令(如 SETNX, EXPIRE, DEL)手动实现分布式锁,提供了巨大的便利性和健壮性。主要体现在以下几个方面: 原子性保证 (Atomicity)ÿ…...
windows系统MySQL安装文档
概览:本文讨论了MySQL的安装、使用过程中涉及的解压、配置、初始化、注册服务、启动、修改密码、登录、退出以及卸载等相关内容,为学习者提供全面的操作指导。关键要点包括: 解压 :下载完成后解压压缩包,得到MySQL 8.…...
 error)
【前端异常】JavaScript错误处理:分析 Uncaught (in promise) error
在前端开发中,JavaScript 异常是不可避免的。随着现代前端应用越来越多地使用异步操作(如 Promise、async/await 等),开发者常常会遇到 Uncaught (in promise) error 错误。这个错误是由于未正确处理 Promise 的拒绝(r…...

从零开始了解数据采集(二十八)——制造业数字孪生
近年来,我国的工业领域正经历一场前所未有的数字化变革,从“双碳目标”到工业互联网平台的推广,国家政策和市场需求共同推动了制造业的升级。在这场变革中,数字孪生技术成为备受关注的关键工具,它不仅让企业“看见”设…...
