给PDF添加书签的通解-姜萍同款《偏微分方程》改造手记
背景
网上找了一本姜萍同款的《偏微分方程》,埃文斯,英文版,可惜没有书签,洋洋七百多页,没有书签,怎么读?用福昕编辑器自然能手工一个个加上,可是劳神费力,非程序员所为。
实现
采用pdfbox即可完成,关键是要准备好目录文件。目录文件每行最后一个数字为页码。
package com.icool.command;import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.apache.pdfbox.Loader;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PDDocument;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.PageMode;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.interactive.documentnavigation.destination.PDPageDestination;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.interactive.documentnavigation.destination.PDPageFitWidthDestination;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.interactive.documentnavigation.outline.PDDocumentOutline;
import org.apache.pdfbox.pdmodel.interactive.documentnavigation.outline.PDOutlineItem;import com.beust.jcommander.Parameter;
import com.beust.jcommander.Parameters;
import com.google.auto.service.AutoService;
import com.icool.core.Command;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import static com.icool.command.CLI.MODIFY_CMD;/*** @Author: 西山口小老头* @Date: 2023/8/4 21:17*/class Bookmark {int pageNo;String title;public Bookmark(int pageNo, String title){this.pageNo = pageNo;this.title = title;}
}@AutoService(Command.class)
@Parameters(commandNames = {MODIFY_CMD},commandDescription = "fetch some articles from website."
)
@Slf4j
public class ModifyCommand implements Command{@Parameter(names = { "--pdfFile", "-i" })public String pdfFile;@Parameter(names = { "--output", "-o" })public String outputFile;@Parameter(names = { "--toc", "-t" })public String toc;public List<Bookmark> bookmarks;public ModifyCommand() {bookmarks = new ArrayList<>();}public void loadTOC() {try {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(toc)));String line = null;int offset = 0;int pageNo = 0;String title = null;while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {line = line.trim();log.debug(line);if (line.length() == 0) continue;String pattern = "";String[] fields = line.split(" ");String lastField = fields[fields.length - 1];if (line.startsWith("OFFSET")) {offset = Integer.parseInt(line.split(" ")[1]);} else {// 有的页码号在第一位,有的在最后一位if (StringUtils.isNumeric(lastField)) {pageNo = offset + Integer.parseInt(lastField);//title = line.substring(0, line.lastIndexOf(" ")).trim() + "............" + lastField;title = line.substring(0, line.lastIndexOf(" ")).trim();} else {pageNo = offset + Integer.parseInt(fields[0]);title = line.substring(line.indexOf(" ") + 1).trim();}bookmarks.add(new Bookmark(pageNo, title));}}} catch (Exception ex) {ex.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic void execute() throws CommandException {loadTOC();try(PDDocument document = Loader.loadPDF(new File(pdfFile))) {PDDocumentOutline documentOutline = document.getDocumentCatalog().getDocumentOutline();if (documentOutline == null) {documentOutline = new PDDocumentOutline();document.getDocumentCatalog().setDocumentOutline(documentOutline);}for (Bookmark bookmark: bookmarks) {PDPageDestination pageDestination = new PDPageFitWidthDestination();pageDestination.setPage(document.getPage(bookmark.pageNo));PDOutlineItem bm = new PDOutlineItem();bm.setDestination(pageDestination);bm.setTitle(bookmark.title);documentOutline.addLast(bm);}documentOutline.openNode();document.getDocumentCatalog().setPageMode(PageMode.USE_OUTLINES);document.save(new File(outputFile));}catch (IOException ex) {ex.printStackTrace();}}
}配套的目录文件如下:
OFFSET 12
Preface to second edition 1
Preface to first edition 3
OFFSET 17
1. Introduction 1
1.1. Partial differential equations 1
1.2. Examples 3
1.2.1. Single partial differential equations 3
1.2.2. Systems of partial differential equations 6
1.3. Strategies for studying PDE 6
1.3.1. Well-posed problems, classical solutions 7
1.3.2. Weak solutions and regularity 7
1.3.3. Typical difficulties 9
1.4. Overview 9
1.5. Problems 12
1.6. References 13PART I: REPRESENTATION FORMULAS FOR SOLUTIONS 14
OFFSET 15
2. Four Important Linear PDE 17
2.1. Transport equation 18
2.1.1. Initial-value problem 18
2.1.2. Nonhomogeneous problem 19
2.2. Laplace's equation 20
2.2.1. Fundamental solution 21
2.2.2. Mean-value formulas 25
2.2.3. Properties of harmonic functions 26
2.2.4. Green's function 33
2.2.5. Energy methods 41
2.3. Heat equation 44
2.3.1. Fundamental solution 45
2.3.2. Mean-value formula 51
2.3.3. Properties of solutions 55
2.3.4. Energy methods 62
2.4. Wave equation 65
2.4.1. Solution by spherical means 67
2.4.2. Nonhomogeneous problem 80
2.4.3. Energy methods 82
2.5. Problems 84
2.6. References 90
3. Nonlinear First-Order PDE 91
3.1. Complete integrals, envelopes 92
3.1.1. Complete integrals 92
3.1.2. New solutions from envelopes 94
3.2. Characteristics 96
3.2.1. Derivation of characteristic ODE 96
3.2.2. Examples 99
3.2.3. Boundary conditions 102
3.2.4. Local solution 105
3.2.5. Applications 109
3.3. Introduction to Hamilton-Jacobi equations 114
3.3.1. Calculus of variations, Hamilton's ODE 115
3.3.2. Legendre transform, Hopf-Lax formula 120
3.3.3. Weak solutions, uniqueness 128
3.4. Introduction to conservation laws 135
3.4.1. Shocks, entropy condition 136
3.4.2. Lax-Oleinik formula 143
3.4.3. Weak solutions, uniqueness 148
3.4.4. Riemann's problem 153
3.4.5. Long time behavior 156
3.5. Problems 161
3.6. References 165
4. Other Ways to Represent Solutions 167
4.1. Separation of variables 167
4.1.1. Examples 168
4.1.2. Application: Turing instability 172
4.2. Similarity solutions 176
4.2.1. Plane and traveling waves, solitons 176
4.2.2. Similarity under scaling 185
4.3. Transform methods 187
4.3.1. Fourier transform 187
4.3.2. Radon transform 196
4.3.3. Laplace transform 203
4.4. Converting nonlinear into linear PDE 206
4.4.1. Cole-Hopf transformation 206
4.4.2. Potential functions 208
4.4.3. Hodograph and Legendre transforms 209
4.5. Asymptotics 211
4.5.1. Singular perturbations 211
4.5.2. Laplace's method 216
4.5.3. Geometric optics, stationary phase 218
4.5.4. Homogenization 229
4.6. Power series 232
4.6.1. Noncharacteristic surfaces 232
4.6.2. Real analytic functions 237
4.6.3. Cauchy-Kovalevskaya Theorem 239
4.7. Problems 244
4.8. References 249
OFFSET 13
PART II: THEORY FOR LINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 253
OFFSET 14
5. Sobolev Spaces 253
5.1. Holder spaces 254
5.2. Sobolev spaces 255
5.2.1. Weak derivatives 255
5.2.2. Definition of Sobolev spaces 258
5.2.3. Elementary properties 261
5.3. Approximation 264
5.3.1. Interior approximation by smooth functions . . . 264
5.3.2. Approximation by smooth functions 265
5.3.3. Global approximation by smooth functions .... 266
5.4. Extensions 268
5.5. Traces 271
5.6. Sobolev inequalities 275
5.6.1. Gagliardo-Nirenberg-Sobolev inequality 276
5.6.2. Morrey's inequality 280
5.6.3. General Sobolev inequalities 284
5.7. Compactness 286
5.8. Additional topics 289
5.8.1. Poincare's inequalities 289
5.8.2. Difference quotients 291
5.8.3. Differentiability a.e 295
5.8.4. Hardy's inequality 296
5.8.5. Fourier transform methods 297
5.9. Other spaces of functions 299
5.9.1. The space Я"1 299
5.9.2. Spaces involving time 301
5.10. Problems 305
5.11. References 309
OFFSET 13
6. Second-Order Elliptic Equations 311
6.1. Definitions 311
6.1.1. Elliptic equations 311
6.1.2. Weak solutions 313
6.2. Existence of weak solutions 315
6.2.1. Lax-Milgram Theorem 315
6.2.2. Energy estimates 317
6.2.3. Fredholm alternative 320
6.3. Regularity 326
6.3.1. Interior regularity 327
6.3.2. Boundary regularity 334
6.4. Maximum principles 344
6.4.1. Weak maximum principle 344
6.4.2. Strong maximum principle 347
6.4.3. Harnack's inequality 351
6.5. Eigenvalues and eigenfunctions 354
6.5.1. Eigenvalues of symmetric elliptic operators 354
6.5.2. Eigenvalues of nonsymmetric elliptic operators 360
6.6. Problems 365
6.7. References 370
7. Linear Evolution Equations 371
7.1. Second-order parabolic equations 371
7.1.1. Definitions 372
7.1.2. Existence of weak solutions 375
7.1.3. Regularity 380
7.1.4. Maximum principles 389
7.2. Second-order hyperbolic equations 398
7.2.1. Definitions 398
7.2.2. Existence of weak solutions 401
7.2.3. Regularity 408
7.2.4. Propagation of disturbances 414
7.2.5. Equations in two variables 418
7.3. Hyperbolic systems of first-order equations 421
7.3.1. Definitions 421
7.3.2. Symmetric hyperbolic systems 423
7.3.3. Systems with constant coefficients 429
7.4. Semigroup theory 433
7.4.1. Definitions, elementary properties 434
7.4.2. Generating contraction semigroups 439
7.4.3. Applications 441
7.5. Problems 446
7.6. References 449OFFSET 10PART III: THEORY FOR NONLINEAR PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 453OFFSET 11
8. The Calculus of Variations 453
8.1. Introduction 453
8.1.1. Basic ideas 453
8.1.2. First variation, Euler-Lagrange equation 454
8.1.3. Second variation 458
8.1.4. Systems 459
8.2. Existence of minimizers 465
8.2.1. Coercivity, lower semicontinuity 465
8.2.2. Convexity 467
8.2.3. Weak solutions of Euler-Lagrange equation . . . 472
8.2.4. Systems 475
8.2.5. Local minimizers 480
8.3. Regularity 482
8.3.1. Second derivative estimates 483
8.3.2. Remarks on higher regularity 486
8.4. Constraints 488
8.4.1. Nonlinear eigenvalue problems 488
8.4.2. Unilateral constraints, variational inequalities . 492
8.4.3. Harmonic maps 495
8.4.4. Incompressibility 497
8.5. Critical points 501
8.5.1. Mountain Pass Theorem 501
8.5.2. Application to semilinear elliptic PDE 507
8.6. Invariance, Noether's Theorem 511
8.6.1. Invariant variational problems 512
8.6.2. Noether's Theorem 513
8.7. Problems 520
8.8. References 525 9. Nonvariational Techniques 527
9.1. Monotonicity methods 527
9.2. Fixed point methods 533
9.2.1. Banach's Fixed Point Theorem 534
9.2.2. Schauder's, Schaefer's Fixed Point Theorems . . 538
9.3. Method of subsolutions and supersolutions 543
9.4. Nonexistence of solutions 547
9.4.1. Blow-up 547
9.4.2. Derrick-Pohozaev identity 551
9.5. Geometric properties of solutions 554
9.5.1. Star-shaped level sets 554
9.5.2. Radial symmetry 555
9.6. Gradient flows 560
9.6.1. Convex functions on Hilbert spaces 560
9.6.2. Subdifferentials and nonlinear semigroups .... 565
9.6.3. Applications 571
9.7. Problems 573
9.8. References 577OFFSET 10
10. Hamilton—Jacobi Equations 579
10.1. Introduction, viscosity solutions 579
10.1.1. Definitions 581
10.1.2. Consistency 583
10.2. Uniqueness 586
10.3. Control theory, dynamic programming 590
10.3.1. Introduction to optimal control theory 591
10.3.2. Dynamic programming 592
10.3.3. Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation 594
10.3.4. Hopf-Lax formula revisited 600
10.4. Problems 603
10.5. References 606OFFSET 9
11. Systems of Conservation Laws 609
11.1. Introduction 609
11.1.1. Integral solutions 612
11.1.2. Traveling waves, hyperbolic systems 615
11.2. Riemann's problem 621
11.2.1. Simple waves 621
11.2.2. Rarefaction waves 624
11.2.3. Shock waves, contact discontinuities 625
11.2.4. Local solution of Riemann's problem 632
11.3. Systems of two conservation laws 635
11.3.1. Riemann invariants 635
11.3.2. Nonexistence of smooth solutions 639
11.4. Entropy criteria 641
11.4.1. Vanishing viscosity, traveling waves 642
11.4.2. Entropy/entropy-flux pairs 646
11.4.3. Uniqueness for scalar conservation laws 649
11.5. Problems 654
11.6. References 657OFFSET 8
12. Nonlinear Wave Equations 659
12.1. Introduction 659
12.1.1. Conservation of energy 660
12.1.2. Finite propagation speed 660
12.2. Existence of solutions 663
12.2.1. Lipschitz nonlinearities 663
12.2.2. Short time existence 666
12.3. Semilinear wave equations 670
12.3.1. Sign conditions 670
12.3.2. Three space dimensions 674
12.3.3. Subcritical power nonlinearities 676
12.4. Critical power nonlinearity 679
12.5. Nonexistence of solutions 686
12.5.1. Nonexistence for negative energy 687
12.5.2. Nonexistence for small initial data 689
12.6. Problems 691
12.7. References 696OFFSET 8
APPENDICES 697
Appendix A: Notation 697
A.l. Notation for matrices 697
A.2. Geometric notation 698
A.3. Notation for functions 699
A.4. Vector-valued functions 703
A.5. Notation for estimates 703
A.6. Some comments about notation 704Appendix B: Inequalities 705
B.l. Convex functions 705
B.2. Useful inequalities 706Appendix C: Calculus 710
C.l. Boundaries 710
C.2. Gauss-Green Theorem 711
C.3. Polar coordinates, coarea formula 712
C.4. Moving regions 713
C.5. Convolution and smoothing 713
C.6. Inverse Function Theorem 716
C.7. Implicit Function Theorem 717
C.8. Uniform convergence 718Appendix D: Functional Analysis 719
D.l. Banach spaces 719
D.2. Hilbert spaces 720
D.3. Bounded linear operators 721
D.4. Weak convergence 723
D.5. Compact operators, Fredholm theory 724
D.6. Symmetric operators 728Appendix E: Measure Theory 729
E.l. Lebesgue measure 729
E.2. Measurable functions and integration 730
E.3. Convergence theorems for integrals 731
E.4. Differentiation 732
E.5. Banach space-valued functions 733此TOC文件可以从网上获得,也可以直接从PDF文件拷出来,当然不能是扫描版。主要工作是不断校对OFFSET值。
相关文章:

给PDF添加书签的通解-姜萍同款《偏微分方程》改造手记
背景 网上找了一本姜萍同款的《偏微分方程》,埃文斯,英文版,可惜没有书签,洋洋七百多页,没有书签,怎么读?用福昕编辑器自然能手工一个个加上,可是劳神费力,非程序员所为…...
在寻找电子名片在线制作免费生成?5个软件帮助你快速制作电子名片
在寻找电子名片在线制作免费生成?5个软件帮助你快速制作电子名片 当你需要快速制作电子名片时,有几款免费在线工具可以帮助你实现这个目标。这些工具提供了丰富的设计模板和元素,让你可以轻松地创建个性化、专业水平的电子名片。 1.一键logo…...

Github 2024-06-16 php开源项目日报 Top10
根据Github Trendings的统计,今日(2024-06-16统计)共有10个项目上榜。根据开发语言中项目的数量,汇总情况如下: 开发语言项目数量PHP项目10Livewire: Laravel中构建动态UI组件的全栈框架 创建周期:1818 天开发语言:PHP协议类型:MIT LicenseStar数量:21388 个Fork数量:1…...
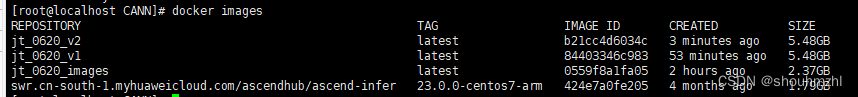
docker将容器打包提交为镜像,再打包成tar包
将容器打包成镜像可以通过以下步骤来实现。这里以 Docker 为例,假设你已经安装了 Docker 并且有一个正在运行的容器。 1. 找到正在运行的容器 首先,你需要找到你想要打包成镜像的容器的 ID 或者名字。可以使用以下命令查看所有正在运行的容器ÿ…...

洛阳水利乙级资质企业在水利科技创新中的作用
洛阳水利乙级资质企业在水利科技创新中扮演着重要的角色,其贡献主要体现在以下几个方面: 一、技术引进与研发 引进先进技术:洛阳水利乙级资质企业积极引进国内外先进的水利工程技术和管理经验,结合本地实际情况,形成独…...

Redis-事务-基本操作-在执行阶段出错不会回滚
文章目录 1、Redis事务控制命令2、Redis事务错误处理3、Redis事务错误处理,在执行阶段出错不会回滚 1、Redis事务控制命令 127.0.0.1:6379> keys * (empty array) 127.0.0.1:6379> multi OK 127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set a1 v1 QUEUED 127.0.0.1:6379(TX)>…...
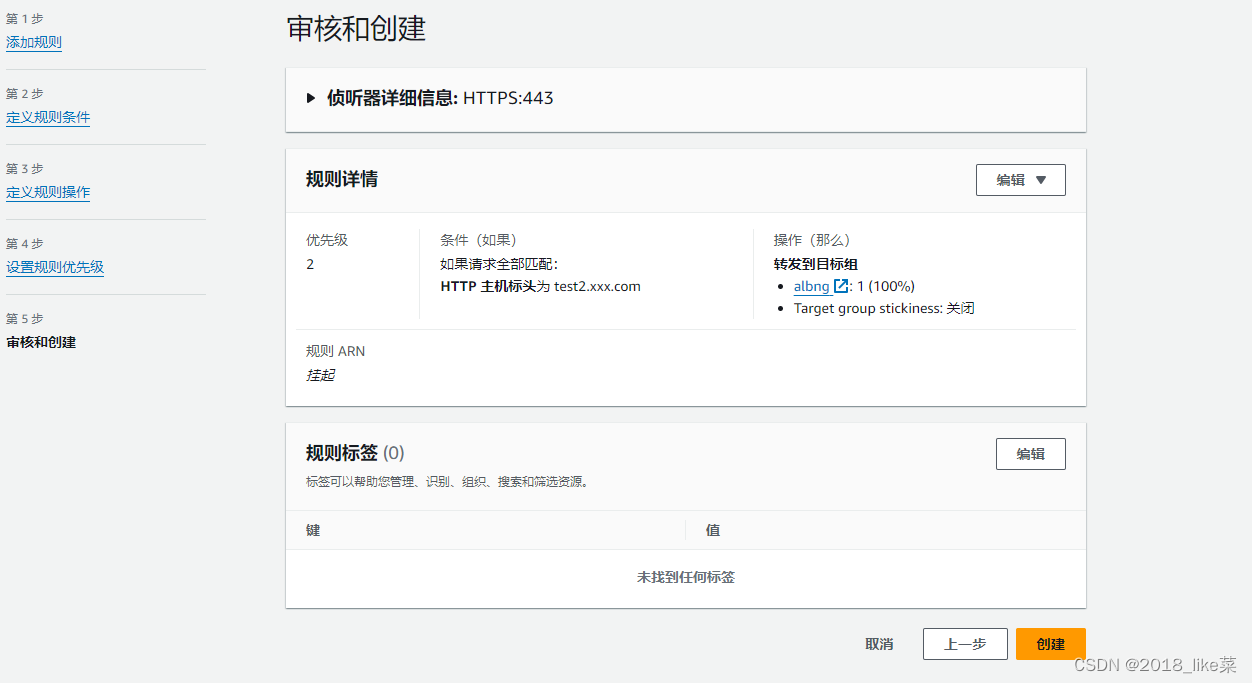
aws的alb,多个域名绑定多个网站实践
例如首次创建的alb负载均衡只有www.xxx.com 需要添加 负载 test2.xxx.com aws的Route 53产品解析到负载均衡 www.xxx.com 添加CNAME,到负载均衡的dns字段axx test2.xxx.com 添加CNAME,到负载均衡的dns字段axx 主要介绍目标组和规则 创建alb就不介…...
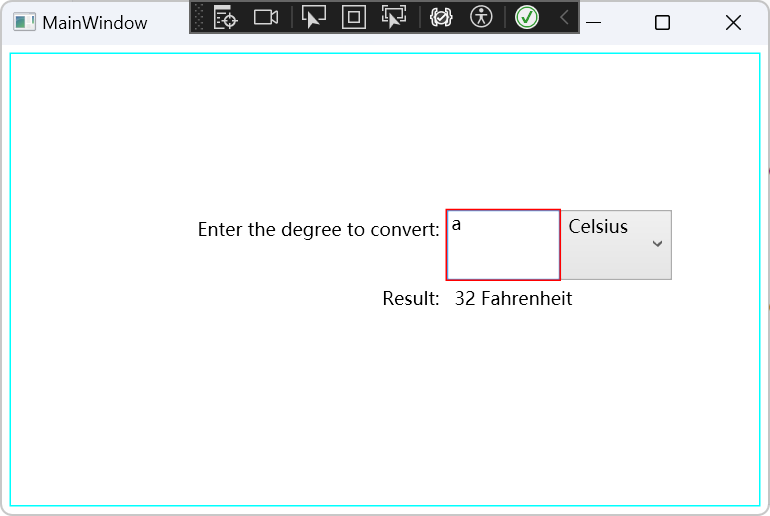
WPF/C#:数据绑定到方法
在WPF Samples中有一个关于数据绑定到方法的Demo,该Demo结构如下: 运行效果如下所示: 来看看是如何实现的。 先来看下MainWindow.xaml中的内容: <Window.Resources><ObjectDataProvider ObjectType"{x:Type local…...
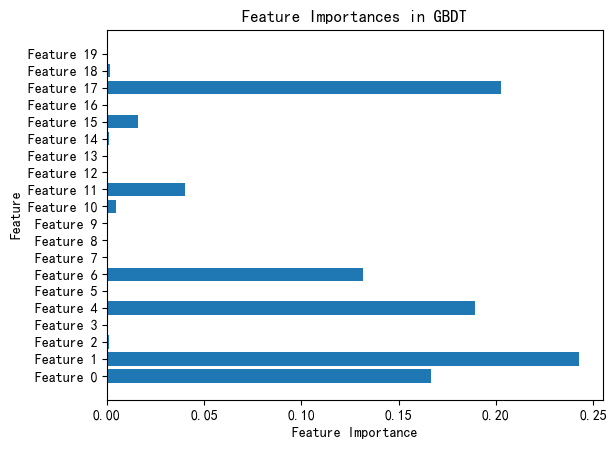
GBDT算法详解
GBDT算法详解 梯度提升决策树(Gradient Boosting Decision Trees,GBDT)是机器学习中一种强大的集成算法。它通过构建一系列的决策树,并逐步优化模型的预测能力,在各种回归和分类任务中取得了显著的效果。本文将详细介…...
51单片机宏定义的例子
代码 demo.c #include "hardware.h"void delay() {volatile unsigned int n;for(n 0; n < 50000; n); }int main(void) {IO_init();while(1){PINSET(LED);delay();PINCLR(LED);delay();}return 0; }cfg.h #ifndef _CFG_H_ #define _CFG_H_// #define F_CPU …...

香港云服务器怎么处理高并发和突发流量?
处理香港云服务器的高并发和突发流量需要综合考虑多种因素,包括服务器配置优化、负载均衡、缓存策略、CDN加速以及监控和自动化调整等措施。以下是处理高并发和突发流量的一些关键步骤和建议: 1. 优化服务器配置 选择高性能实例:根据预期的并…...

c,c++,qt从入门到地狱
前言 1 你所能用的正与你手写的效率相同2 你不需要为你没有用到的特性付出 (无脑的调用函数or公式的空壳人类请出门右转)c 001 scanf and strcpy "_s"bug? 微软官方说明1 Visual Studio 库中的许多函数、成员函数、函数模板和全局变量已弃用,改用微软新增的强化函数…...
iptables(6)扩展匹配条件--tcp-flags、icmp
简介 前面我们已经介绍了不少的扩展模块,例如multiport、iprange、string、time、connlimit模块,但是在tcp扩展模块中只介绍了tcp扩展模块中的”--sport”与--dport”选项,并没有介绍”--tcp-flags”选项,那么这篇文章,我们就来认识一下tcp扩展模块中的”--tcp-flags”和i…...

C#-Json文件的读写
文章速览 命名空间读取Json核心代码示例 写入Json核心代码示例 坚持记录实属不易,希望友善多金的码友能够随手点一个赞。 共同创建氛围更加良好的开发者社区! 谢谢~ 命名空间 using Newtonsoft.Json;读取Json 核心代码 //核心代码using (StreamReader…...

【2023级研究生《人工智能》课程考试说明】
一.试题范围 考试题共包括4道大题: 第一大题:分类和回归----(8选1) 第二大题:降维和聚类----(7选1) 第三大题:API调用(课程中学习过的所有云平台)…...

C语言队列操作及其安全问题
在C语言中,队列是一种常用的数据结构,特别适用于嵌入式开发中的任务调度、缓冲区管理等场景。下面是一个简单的循环队列的模板代码,它使用数组来实现队列,并提供了基本的入队(enqueue)和出队(de…...
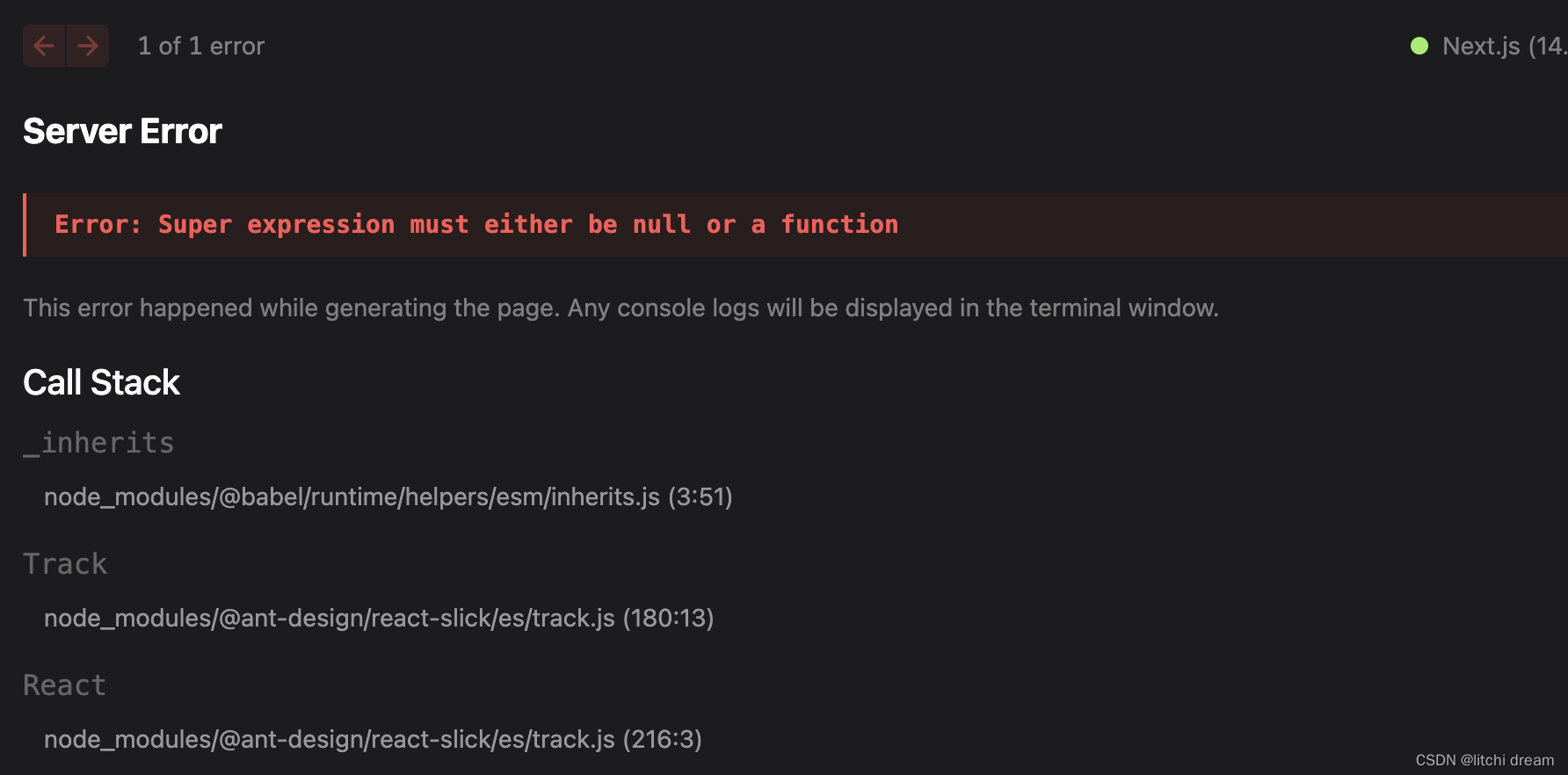
next.js v14 升级全步骤|迁移 pages Router 到 App Router
【概括】本文升级整体按照官网文档指引进行,在迁移 pages Router 前先看了官网的实操视频。 【注意】文章内对 .babel.ts、next.config.js 进行了多次更改,最终配置可见 报错3: Server Error ReferenceError: React is not defined 一、升级 Next.js 版…...

如何在Ubuntu上安装WordPress
如何在Ubuntu上安装WordPress 执行系统更新 apt update && apt upgrade第一步 安装 Apache apt install apache2确认 Apache 安装是否成功. systemctl status apache2安装成功后 打开浏览器输入 http://server-ip-address 第二步 安装 MySQL apt install mariad…...

处理导入Excel文件过大导致Zip bomb detected的问题
处理导入Excel文件过大导致Zip bomb detected的问题 处理导入Excel文件过大导致Zip bomb detected的问题解决方案完整示例代码处理内存溢出问题优化处理大文件的策略 处理导入Excel文件过大导致Zip bomb detected的问题 在Java应用中导入Excel文件时,可能会遇到文件…...

【FFmpeg】AVIOContext结构体
【FFmpeg】AVIOContext结构体 1.AVIOContext结构体的定义 参考: FFMPEG结构体分析:AVIOContext 示例工程: 【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库实现264软编 【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库实现264软解 【FFmpeg】调用ffmpeg库进行RTMP推流和拉流 【FFmpeg】调用…...
: K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?)
云原生核心技术 (7/12): K8s 核心概念白话解读(上):Pod 和 Deployment 究竟是什么?
大家好,欢迎来到《云原生核心技术》系列的第七篇! 在上一篇,我们成功地使用 Minikube 或 kind 在自己的电脑上搭建起了一个迷你但功能完备的 Kubernetes 集群。现在,我们就像一个拥有了一块崭新数字土地的农场主,是时…...

DockerHub与私有镜像仓库在容器化中的应用与管理
哈喽,大家好,我是左手python! Docker Hub的应用与管理 Docker Hub的基本概念与使用方法 Docker Hub是Docker官方提供的一个公共镜像仓库,用户可以在其中找到各种操作系统、软件和应用的镜像。开发者可以通过Docker Hub轻松获取所…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...
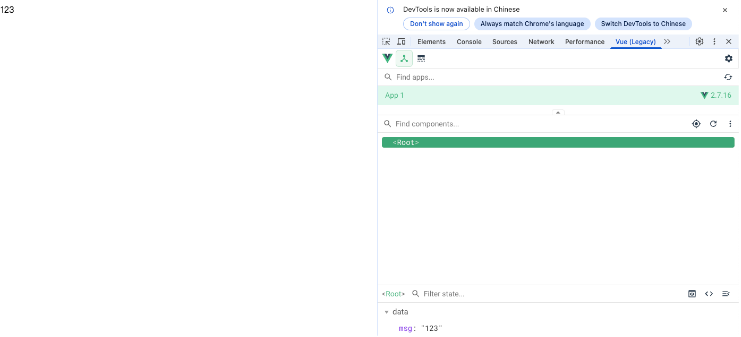
Vue2 第一节_Vue2上手_插值表达式{{}}_访问数据和修改数据_Vue开发者工具
文章目录 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染2. 插值表达式{{}}3. 访问数据和修改数据4. vue响应式5. Vue开发者工具--方便调试 1.Vue2上手-如何创建一个Vue实例,进行初始化渲染 准备容器引包创建Vue实例 new Vue()指定配置项 ->渲染数据 准备一个容器,例如: …...
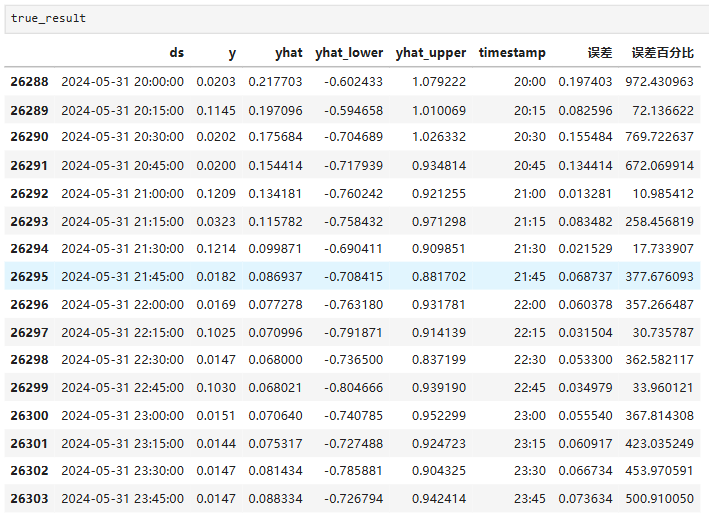
Python实现prophet 理论及参数优化
文章目录 Prophet理论及模型参数介绍Python代码完整实现prophet 添加外部数据进行模型优化 之前初步学习prophet的时候,写过一篇简单实现,后期随着对该模型的深入研究,本次记录涉及到prophet 的公式以及参数调优,从公式可以更直观…...

linux 错误码总结
1,错误码的概念与作用 在Linux系统中,错误码是系统调用或库函数在执行失败时返回的特定数值,用于指示具体的错误类型。这些错误码通过全局变量errno来存储和传递,errno由操作系统维护,保存最近一次发生的错误信息。值得注意的是,errno的值在每次系统调用或函数调用失败时…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个医院查看报告小程序
一、开发环境准备 工具安装: 下载安装DevEco Studio 4.0(支持HarmonyOS 5)配置HarmonyOS SDK 5.0确保Node.js版本≥14 项目初始化: ohpm init harmony/hospital-report-app 二、核心功能模块实现 1. 报告列表…...

ETLCloud可能遇到的问题有哪些?常见坑位解析
数据集成平台ETLCloud,主要用于支持数据的抽取(Extract)、转换(Transform)和加载(Load)过程。提供了一个简洁直观的界面,以便用户可以在不同的数据源之间轻松地进行数据迁移和转换。…...
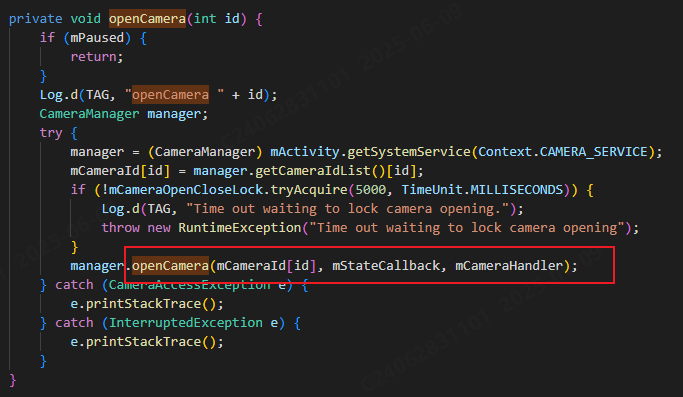
相机从app启动流程
一、流程框架图 二、具体流程分析 1、得到cameralist和对应的静态信息 目录如下: 重点代码分析: 启动相机前,先要通过getCameraIdList获取camera的个数以及id,然后可以通过getCameraCharacteristics获取对应id camera的capabilities(静态信息)进行一些openCamera前的…...
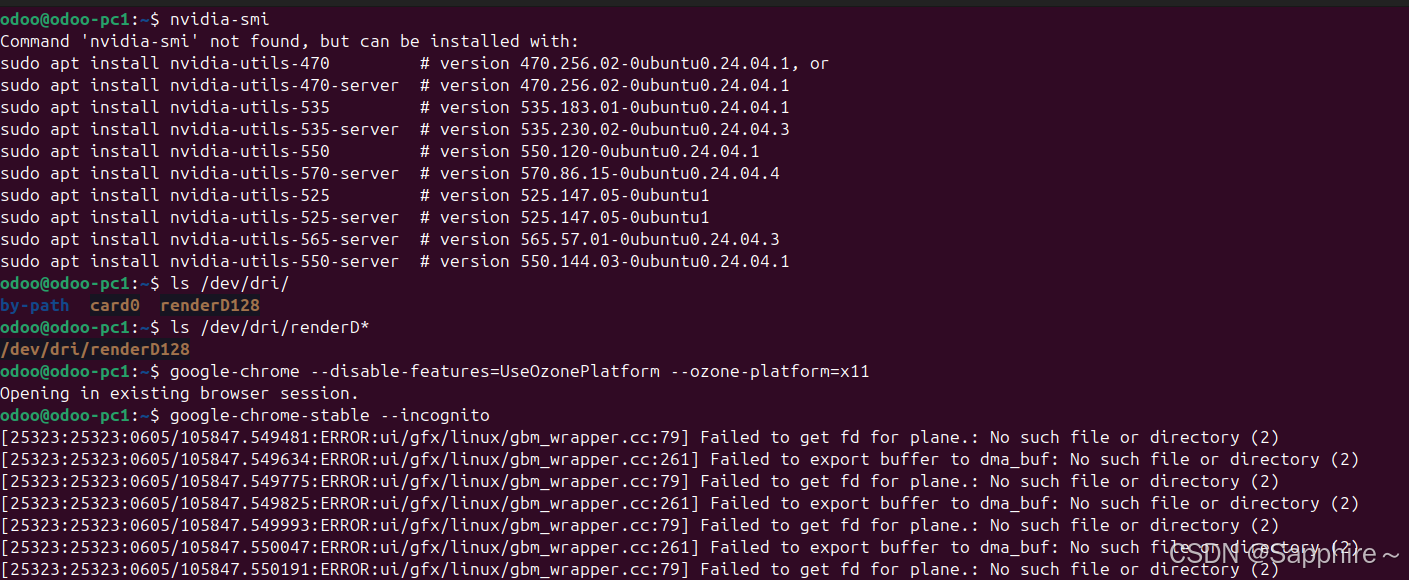
Linux-07 ubuntu 的 chrome 启动不了
文章目录 问题原因解决步骤一、卸载旧版chrome二、重新安装chorme三、启动不了,报错如下四、启动不了,解决如下 总结 问题原因 在应用中可以看到chrome,但是打不开(说明:原来的ubuntu系统出问题了,这个是备用的硬盘&a…...
