Java工具--stream流
Java工具--stream流
- 过滤(filter)
- 统计
- 求最大最小和均值
- 求和(sum)
- 过滤后,对数据进行统计
- 遍历(map)
- 规约(reduce)
- 排序(sorted)
- 去重(distinct)
- findAny() 和 findFirst()
- 判断(anyMatch,allMatch,noneMatch)
- 分组
- toList() toSet() toMap()
过滤(filter)
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
List<String> StringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "grape", "apple", "kiwi");// 筛选出所有的偶数 >>>[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
List<Integer> evenList = numberList.stream().filter(num -> num%2==0).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 筛选出所有非a开头的字符串 >>>[orange, banana, grape, kiwi]
List<String> strList = StringList.stream().filter(item -> !item.startsWith("a")).collect(Collectors.toList());
统计
求最大最小和均值
使用 mapToInt() 求整数列表中的最大值、最小值、总和、平均值。
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
// 10
int max = numberList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).max().getAsInt();
// 1
int min = numberList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).min().getAsInt();
// 55
int min = numberList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
// 5.5
double avg = numberList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).average().getAsDouble();// 计算双精度列表中所有数字的平均值
List<Double> doubleList = Arrays.asList(1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.2, 5.2, 6.1);
// 3.6833333333333336
double average = doubleList.stream().reduce(0.0, (a, b) -> a + b) / doubleList.size();
double average2 = doubleList.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).average().getAsDouble();
//获取年龄最大的学生
Student ageMaxStudent = list.stream().max(Comparator.companing(Student::getAge)).get();//获取年龄最小的学生
Student ageMinStudent = list.stream().min(Comparator.companing(Student::getAge)).get();
求和(sum)
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
List<Double> doubleList = Arrays.asList(1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.2, 5.2, 6.1);
List<Long> longNumberList = Arrays.asList(10L, 30L, 50L, 60L, 70L, 80L, 90L);// 55
int m = numberList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
// 22.1
double n = doubleList.stream().mapToDouble(Double::doubleValue).sum();
// 390
long w = longNumberList.stream().mapToLong(Long::longValue).sum();
// 55
int sum1 = numberList.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b);
int sum2 = numberList.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
过滤后,对数据进行统计
// 计算整数列表中所有偶数的和 >>>30
int sum = numberList.stream().filter(num -> num%2==0).mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();// 统计长度大于5的字符串数量 >>>2
long count = StringList.stream().filter(str -> str.length()>5).count();// 查找字符串列表中所有字符串的长度的总和 >>>31
int lengthSum = StringList.stream().mapToInt(String::length).reduce(0, Integer::sum);
遍历(map)
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
List<String> StringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "grape", "apple", "kiwi");// 以整数列表作为输入,返回每个元素的平方的新列表 >>>[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]
List<Integer> squareList = numberList.stream().map(num -> num*num).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 以字符串列表作为输入,返回每个字符串的长度的新列表 >>>[5, 6, 6, 5, 5, 4]
// map中的方法可以简化成 .map(String::length)
List<Integer> lenList = StringList.stream().map(item -> item.length()).collect(Collectors.toList());
规约(reduce)
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);// 10
int maxNum = numberList.stream().reduce(Integer::max).get();
// 1
int minNum = numberList.stream().reduce(Integer::min).get();
// 55
int sumNum = numberList.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
// 55
int sum = numberList.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b);
// 3628800
int product = numberList.stream().reduce(1, (a, b) -> a * b);
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
List<String> StringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "grape", "apple", "kiwi");// 在整数列表中找出最大元素 >>>10
int max = numberList.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a>b? a : b);
// 查找字符串列表中最长的字符串 >>>Optional[banana]
String maxLengthStr = StringList.stream().reduce((s1, s2) -> s1.length() > s2.length()? s1 : s2).toString();
// 查找字符串列表中最短的字符串 >>>Optional[kiwi]
String minLengthStr = StringList.stream().reduce((s1, s2) -> s1.length() < s2.length()? s1 : s2).toString();
将列表中的所有字符串连接成一个字符串
// apple@orange@banana@grape@apple@kiwi@
String concat1 = StringList.stream().reduce("", (a, b) -> a + b + "@");
// apple@orange@banana@grape@apple@kiwi
String concat2 = StringList.stream().collect(Collectors.joining("@"));
// apple@orange@banana@grape@apple@kiwi
String concat3 = String.join("@", StringList);
排序(sorted)
List<String> StringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "grape", "apple", "kiwi");// 将每个字符串装换为大写,然后按字母顺序排序
// [APPLE, APPLE, BANANA, GRAPE, KIWI, ORANGE]
List<String> sortedUpperCase = StringList.stream().map(String::toUpperCase).sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(12, 2, 33, 24, 5, 61, 27, 8, 39, 10);// 升序 >>>[2, 5, 8, 10, 12, 24, 27, 33, 39, 61]
List<Integer> sort1NumberList = numberList.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Integer> sort2NumberList = numberList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(item->item)).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 降序 >>>[61, 39, 33, 27, 24, 12, 10, 8, 5, 2]
List<Integer> sortReverseNumberList = numberList.stream().sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());// 降序 >>>[61, 39, 33, 27, 24, 12, 10, 8, 5, 2]
List<Integer> numberList1 = Arrays.asList(12, 2, 33, 24, 5, 61, 27, 8, 39, 10);
numberList1.sort((objectA, objectB) -> objectB.compareTo(objectA));
// 升序 >>>[2, 5, 8, 10, 12, 24, 27, 33, 39, 61]
List<Integer> numberList2 = Arrays.asList(12, 2, 33, 24, 5, 61, 27, 8, 39, 10);
numberList2.sort((objectA, objectB) -> objectA.compareTo(objectB));
若需要排序的不是简单数字列表,是对象列表
List sortNumberList = numberList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(item->item.getAge())).collect(Collectors.toList());
studentList.sort((objectA, objectB) -> objectB.getAge().compareTo(objectA.getAge()));
去重(distinct)
// 去重 >>>[apple, orange, banana, grape, kiwi]
List<String> unique = StringList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
findAny() 和 findFirst()
使用 findAny() 和 findFirst() 获取第一条数据。
List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "grape", "apple", "kiwi");String str1 = stringList.stream().filter(item -> item.endsWith("e")).findAny().orElse(null);
String str2 = stringList.stream().filter(item -> item.endsWith("e")).findAny().orElse(null);
findFirst() 和 findAny() 都是获取列表中的第一条数据,但是findAny()操作,返回的元素是不确定的,对于同一个列表多次调用findAny()有可能会返回不同的值。使用findAny()是为了更高效的性能。如果是数据较少,串行地情况下,一般会返回第一个结果,如果是并行(parallelStream并行流)的情况,那就不能确保是第一个。
判断(anyMatch,allMatch,noneMatch)
- anyMatch(T -> boolean)
使用 anyMatch(T -> boolean) 判断流中是否有一个元素匹配给定的 T -> boolean 条件。 - allMatch(T -> boolean)
使用 allMatch(T -> boolean) 判断流中是否所有元素都匹配给定的 T -> boolean 条件。 - noneMatch(T -> boolean)
使用 noneMatch(T -> boolean) 流中是否没有元素匹配给定的 T -> boolean 条件。
List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "grape", "apple");
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(12, 2, 33, 24, 5, 61, 27, 8, 39, 10);// 存在元素以a开头 >>>true
boolean anyStartsWithA = stringList.stream().anyMatch(item -> item.startsWith("a"));
// 所有元素以e结尾 >>>true
boolean allEndsWithB = stringList.stream().allMatch(item -> item.endsWith("e"));
// 没有元素以g开头 >>>false
boolean noneStartsWithG = stringList.stream().noneMatch(item -> item.startsWith("g"));
// 没有元素以k开头 >>>true
boolean noneStartsWithK = stringList.stream().noneMatch(item -> item.startsWith("k"));
// 所有元素都是偶数 >>>false
boolean allEven = numberList.stream().allMatch(item -> item%2==0);
分组
@Testpublic void test011() {// User对象的四个属性,(id,areaCode,name,roomNum,peopleNum)List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new User(1L, "210300", "熊大",1, 2));userList.add(new User(2L, "210300", "赵二",2, 3));userList.add(new User(3L, "210100", "张三",3, 4));userList.add(new User(4L, "210100", "李四",4, 5));userList.add(new User(5L, "210400", "王五",5, 6));/** 返回一个Map,其中键是areaCode,值是具有该areaCode的用户列表* {* 210400=[User(id=5, areaCode=210400, name=王五, roomNum=5, peopleNum=6)],* 210300=[User(id=1, areaCode=210300, name=熊大, roomNum=1, peopleNum=2), User(id=2, areaCode=210300, name=赵二, roomNum=2, peopleNum=3)],* 210100=[User(id=3, areaCode=210100, name=张三, roomNum=3, peopleNum=4), User(id=4, areaCode=210100, name=李四, roomNum=4, peopleNum=5)]* }*/Map<String, List<User>> areaCodeAndUserMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode));/** 按areaCode分组,并收集组中roomNum最大的User对象* {* 210400=Optional[User(id=5, areaCode=210400, name=王五, roomNum=5, peopleNum=6)],* 210300=Optional[User(id=2, areaCode=210300, name=赵二, roomNum=2, peopleNum=3)],* 210100=Optional[User(id=4, areaCode=210100, name=李四, roomNum=4, peopleNum=5)]* }*/Map<String, Optional<User>> areaCodeAndMaxRoomMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode,Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getRoomNum))));// 按areaCode分组,并将组中的userID收集为List// {210400=[5], 210300=[1, 2], 210100=[3, 4]}Map<String, List<Long>> areaCodeAndUserIdMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode,Collectors.mapping(User::getId, Collectors.toList())));// 按areaCode分组,并统计个数// {210400=1, 210300=2, 210100=2}Map<String, Long> areaCodeNumMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode, Collectors.counting()));// 按areaCode分组,并统计组中的roomNum平均值// {210400=5.0, 210300=1.5, 210100=3.5}Map<String, Double> areaCodeAndRoomSumMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode, Collectors.averagingInt(User::getRoomNum)));// 按areaCode分组,并统计组中的roomNum和// {210400=5, 210300=3, 210100=7}Map<String, Integer> areaCodeAndRoomNumMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode, Collectors.summingInt(User::getRoomNum)));// 按areaCode分组,并统计组中的peopleNum和// {210400=6, 210300=5, 210100=9}Map<String, Integer> areaCodeAndPeopleNumMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(User::getAreaCode, Collectors.summingInt(User::getPeopleNum)));}@Data@NoArgsConstructor@AllArgsConstructorclass User{private Long id;private String areaCode;private String name;private Integer roomNum;private Integer peopleNum;}
List<String> StringList = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "grape", "apple", "kiwi");// 按字符串长度分组
Map<Integer, List<String>> groups = new HashMap<>();
for (String item : StringList) {int length = item.length();if (!groups.containsKey(length)) {groups.put(length, new ArrayList<>());}groups.get(length).add(item);
}// {4=[kiwi], 5=[apple, grape, apple], 6=[orange, banana]}
System.out.println(groups);
toList() toSet() toMap()
用toMap方法时,必须确保选择的key是唯一且非空的
@Test
public void test011() {// User对象的四个属性,(id,areaCode,name,roomNum,peopleNum)List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();userList.add(new User(1L, "210300", "熊大",1, 2));userList.add(new User(2L, "210300", "赵二",2, 3));userList.add(new User(3L, "210100", "张三",3, 4));userList.add(new User(4L, "210100", "李四",4, 5));userList.add(new User(5L, "210400", "王五",5, 6));// [210300, 210300, 210100, 210100, 210400]List<String> list1 = userList.stream().map(User::getAreaCode).collect(Collectors.toList());// [210400, 210300, 210100]Set<String> set1 = userList.stream().map(User::getAreaCode).collect(Collectors.toSet());/*** {* 李四=User(id=4, areaCode=210100, name=李四, roomNum=4, peopleNum=5), * 张三=User(id=3, areaCode=210100, name=张三, roomNum=3, peopleNum=4), * 熊大=User(id=1, areaCode=210300, name=熊大, roomNum=1, peopleNum=2), * 赵二=User(id=2, areaCode=210300, name=赵二, roomNum=2, peopleNum=3), * 王五=User(id=5, areaCode=210400, name=王五, roomNum=5, peopleNum=6)* }*/Map<String, User> map1 = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getName, Function.identity()));/*** {* 1=User(id=1, areaCode=210300, name=熊大, roomNum=1, peopleNum=2), * 2=User(id=2, areaCode=210300, name=赵二, roomNum=2, peopleNum=3), * 3=User(id=3, areaCode=210100, name=张三, roomNum=3, peopleNum=4), * 4=User(id=4, areaCode=210100, name=李四, roomNum=4, peopleNum=5), * 5=User(id=5, areaCode=210400, name=王五, roomNum=5, peopleNum=6)* }*/Map<Long, User> map2 = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getId, Function.identity()));// {李四=5, 张三=4, 熊大=2, 赵二=3, 王五=6}Map<String, Integer> map3 = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getName, User::getPeopleNum));// {1=熊大, 2=赵二, 3=张三, 4=李四, 5=王五}Map<String, String> map4 = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(item -> String.valueOf(item.getId()),User::getName));}
相关文章:

Java工具--stream流
Java工具--stream流 过滤(filter)统计求最大最小和均值求和(sum)过滤后,对数据进行统计 遍历(map)规约(reduce)排序(sorted)去重(dist…...
什么是 JWT?它是如何工作的?
松哥最近辅导了几个小伙伴秋招,有小伙伴在面小红书时遇到这个问题,这个问题想回答全面还是有些挑战,松哥结合之前的一篇旧文和大伙一起来聊聊。 一 无状态登录 1.1 什么是有状态 有状态服务,即服务端需要记录每次会话的客户端信…...

微信小程序使用picker,数组怎么设置默认值
默认先显示请选择XXX。然后点击弹出选择列表。如果默认value是0的话,他就直接默认显示数组的第一个了。<picker mode"selector" :value"planIndex" :range"planStatus" range-key"label" change"bindPlanChange&qu…...

Springboot生成树工具类,可通过 id/code 编码生成 2.0版本
优化工具类中,查询父级时便利多次的问题 import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils; import org.apache.commons.lang3.mutable.MutableLong; import org.springframework.lang.NonNull; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.spri…...

17、CPU缓存架构详解高性能内存队列Disruptor实战
1.CPU缓存架构详解 1.1 CPU高速缓存概念 CPU缓存即高速缓冲存储器,是位于CPU与主内存间的一种容量较小但速度很高的存储器。CPU高速缓存可以分为一级缓存,二级缓存,部分高端CPU还具有三级缓存,每一级缓存中所储存的全部数据都是…...

算法训练营打卡Day18
目录 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差二叉搜索树中的众数二叉树的最近公共祖先额外练手题目 题目1、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 力扣题目链接(opens new window) 给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。 示例: 思…...

【leetcode】169.多数元素
boyer-moore算法最简单理解方法: 假设你在投票选人 如果你和候选人(利益)相同,你就会给他投一票(count1),如果不同,你就会踩他一下(count-1)当候选人票数为0&…...

MyBatis<foreach>标签的用法与实践
foreach标签简介 实践 demo1 简单的一个批量更新,这里传入了一个List类型的集合作为参数,拼接到 in 的后面 ,来实现一个简单的批量更新 <update id"updateVislxble" parameterType"java.util.List">update model…...

R语言Shiny包新手教程
R语言Shiny包新手教程 1. 简介 Shiny 是一个 R 包,用于创建交互式网页应用。它非常适合展示数据分析结果和可视化效果。 2. 环境准备 安装R和RStudio 确保你的计算机上安装了 R 和 RStudio。你可以从 CRAN 下载 R,或从 RStudio 官网 下载 RStudio。…...

[大象快讯]:PostgreSQL 17 重磅发布!
家人们,数据库界的大新闻来了!📣 PostgreSQL 17 正式发布,全球开发者社区的心血结晶,带来了一系列令人兴奋的新特性和性能提升。 发版通告全文如下 PostgreSQL 全球开发小组今天(2024-09-26)宣布…...

CHI trans--Home节点发起的操作
总目录: CHI协议简读汇总-CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/zhangshangjie1/article/details/131877216 Home节点能够发起的操作,包含如下几类: Home to Subordinate Read transactionsHome to Subordinate Write transactionsHome to Subor…...

Rust和Go谁会更胜一筹
在国内,我认为Go语言会成为未来的主流,因为国内程序员号称码农,比较适合搬砖,而Rust对心智要求太高了,不适合搬砖。 就个人经验来看,Go语言简单,下限低,没有什么心智成本,…...

记HttpURLConnection下载图片
目录 一、示例代码1 二、示例代码2 一、示例代码1 import java.io.*; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.URL;public class Test {/*** 下载图片*/public void getNetImg() {InputStream inStream null;FileOutputStream fOutStream null;try {// URL 统…...
物联网实训室建设的必要性
物联网实训室建设的必要性 一、物联网发展的背景 物联网(IoT)是指通过信息传感设备,按照约定的协议,将任何物品与互联网连接起来,进行信息交换和通信,以实现智能化识别、定位、跟踪、监控和管理的一种网络…...

初识C语言(四)
目录 前言 十一、常见关键字(补充) (1)register —寄存器 (2)typedef类型重命名 (3)static静态的 1、修饰局部变量 2、修饰全局变量 3、修饰函数 十二、#define定义常量和宏…...
产品架构图:从概念到实践
在当今快速发展的科技时代,产品架构图已成为产品经理和设计师不可或缺的工具。它不仅帮助我们理解复杂的产品体系,还能指导我们进行有效的产品设计和开发。本文将深入探讨产品架构图的概念、重要性以及绘制方法。 整个内容框架分为三个部分,…...

smartctl 命令:查看硬盘健康状态
一、命令简介 smartctl 命令用于获取硬盘的 SMART 信息。 介绍硬盘SMART 硬盘的 SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) 技术用于监控硬盘的健康状态,并能提供一些潜在故障的预警信息。通过查看 SMART 数据,用户可以了解硬…...

BBR 为什么没有替代 CUBIC 成为 Linux 内核缺省算法
自 2017 年底 bbr 发布以来,随着媒体的宣讲,各大站点陆续部署 bbr,很多网友不禁问,bbr 这么好,为什么不替代 cubic 成为 linux 的缺省算法。仅仅因为它尚未标准化?这么好的算法又为什么没被标准化ÿ…...

Git忽略规则原理和.gitignore文件不生效的原因和解决办法
在使用Git进行版本控制时,.gitignore文件扮演着至关重要的角色。它允许我们指定哪些文件或目录应该被Git忽略,从而避免将不必要的文件(如日志文件、编译产物等)纳入版本控制中。然而,在实际使用过程中,有时…...

MySQL-数据库设计
1.范式 数据库的范式是⼀组规则。在设计关系数据库时,遵从不同的规范要求,设计出合理的关系型数 据库,这些不同的规范要求被称为不同的范式。 关系数据库有六种范式:第⼀范式(1NF)、第⼆范式(…...
:手搓截屏和帧率控制)
Python|GIF 解析与构建(5):手搓截屏和帧率控制
目录 Python|GIF 解析与构建(5):手搓截屏和帧率控制 一、引言 二、技术实现:手搓截屏模块 2.1 核心原理 2.2 代码解析:ScreenshotData类 2.2.1 截图函数:capture_screen 三、技术实现&…...

Cursor实现用excel数据填充word模版的方法
cursor主页:https://www.cursor.com/ 任务目标:把excel格式的数据里的单元格,按照某一个固定模版填充到word中 文章目录 注意事项逐步生成程序1. 确定格式2. 调试程序 注意事项 直接给一个excel文件和最终呈现的word文件的示例,…...

golang循环变量捕获问题
在 Go 语言中,当在循环中启动协程(goroutine)时,如果在协程闭包中直接引用循环变量,可能会遇到一个常见的陷阱 - 循环变量捕获问题。让我详细解释一下: 问题背景 看这个代码片段: fo…...
【力扣数据库知识手册笔记】索引
索引 索引的优缺点 优点1. 通过创建唯一性索引,可以保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。2. 可以加快数据的检索速度(创建索引的主要原因)。3. 可以加速表和表之间的连接,实现数据的参考完整性。4. 可以在查询过程中,…...

中南大学无人机智能体的全面评估!BEDI:用于评估无人机上具身智能体的综合性基准测试
作者:Mingning Guo, Mengwei Wu, Jiarun He, Shaoxian Li, Haifeng Li, Chao Tao单位:中南大学地球科学与信息物理学院论文标题:BEDI: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Embodied Agents on UAVs论文链接:https://arxiv.…...

《用户共鸣指数(E)驱动品牌大模型种草:如何抢占大模型搜索结果情感高地》
在注意力分散、内容高度同质化的时代,情感连接已成为品牌破圈的关键通道。我们在服务大量品牌客户的过程中发现,消费者对内容的“有感”程度,正日益成为影响品牌传播效率与转化率的核心变量。在生成式AI驱动的内容生成与推荐环境中࿰…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...
Reasoning over Uncertain Text by Generative Large Language Models
https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/34674/36829 1. 概述 文本中的不确定性在许多语境中传达,从日常对话到特定领域的文档(例如医学文档)(Heritage 2013;Landmark、Gulbrandsen 和 Svenevei…...
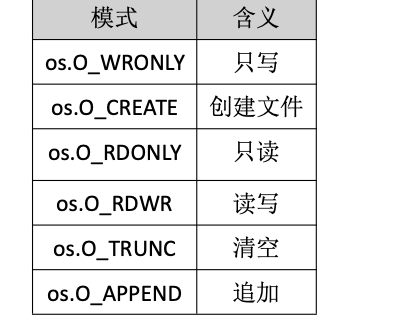
Golang——9、反射和文件操作
反射和文件操作 1、反射1.1、reflect.TypeOf()获取任意值的类型对象1.2、reflect.ValueOf()1.3、结构体反射 2、文件操作2.1、os.Open()打开文件2.2、方式一:使用Read()读取文件2.3、方式二:bufio读取文件2.4、方式三:os.ReadFile读取2.5、写…...

wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像
wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像https://www.cnblogs.com/haodafeng/p/10431387.html 如果你在寻找能够快速在image控件刷新大图像(比如分辨率3000*3000的图像)的办法,尤其是想把内存中的裸数据(只有图像的数据,不包…...
