【C++】透过STL源代码深度剖析vector的底层


✨ Blog’s 主页: 白乐天_ξ( ✿>◡❛)
🌈 个人Motto:他强任他强,清风拂山冈!
🔥 所属专栏:C++深入学习笔记
💫 欢迎来到我的学习笔记!

参考博客:【C++】透过STL源码深度剖析及模拟实现vector-CSDN博客
一、源码引入
这里我们学习的是基于SGI版本的STL源码。源码如下:
// stl_vector.h/*** Copyright (c) 1994* Hewlett-Packard Company** Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear* in supporting documentation. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no* representations about the suitability of this software for any* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.*** Copyright (c) 1996* Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.** Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear* in supporting documentation. Silicon Graphics makes no* representations about the suitability of this software for any* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.*//* NOTE: This is an internal header file, included by other STL headers.* You should not attempt to use it directly.*/#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_VECTOR_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_VECTOR_H__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE #if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1174
#endiftemplate <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector {
public:typedef T value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type* iterator;typedef const value_type* const_iterator;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATIONtypedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
#else /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator, value_type, const_reference, difference_type> const_reverse_iterator;typedef reverse_iterator<iterator, value_type, reference, difference_type>reverse_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
protected:typedef simple_alloc<value_type, Alloc> data_allocator;iterator start;iterator finish;iterator end_of_storage;void insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x);void deallocate() {if (start) data_allocator::deallocate(start, end_of_storage - start);}void fill_initialize(size_type n, const T& value) {start = allocate_and_fill(n, value);finish = start + n;end_of_storage = finish;}
public:iterator begin() { return start; }const_iterator begin() const { return start; }iterator end() { return finish; }const_iterator end() const { return finish; }reverse_iterator rbegin() { return reverse_iterator(end()); }const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const { return const_reverse_iterator(end()); }reverse_iterator rend() { return reverse_iterator(begin()); }const_reverse_iterator rend() const { return const_reverse_iterator(begin()); }size_type size() const { return size_type(end() - begin()); }size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1) / sizeof(T); }size_type capacity() const { return size_type(end_of_storage - begin()); }bool empty() const { return begin() == end(); }reference operator[](size_type n) { return *(begin() + n); }const_reference operator[](size_type n) const { return *(begin() + n); }vector() : start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0) {}vector(size_type n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }vector(int n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }vector(long n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }explicit vector(size_type n) { fill_initialize(n, T()); }vector(const vector<T, Alloc>& x) {start = allocate_and_copy(x.end() - x.begin(), x.begin(), x.end());finish = start + (x.end() - x.begin());end_of_storage = finish;}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class InputIterator>vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) :start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0){range_initialize(first, last, iterator_category(first));}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */vector(const_iterator first, const_iterator last) {size_type n = 0;distance(first, last, n);start = allocate_and_copy(n, first, last);finish = start + n;end_of_storage = finish;}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */~vector() { destroy(start, finish);deallocate();}vector<T, Alloc>& operator=(const vector<T, Alloc>& x);void reserve(size_type n) {if (capacity() < n) {const size_type old_size = size();iterator tmp = allocate_and_copy(n, start, finish);destroy(start, finish);deallocate();start = tmp;finish = tmp + old_size;end_of_storage = start + n;}}reference front() { return *begin(); }const_reference front() const { return *begin(); }reference back() { return *(end() - 1); }const_reference back() const { return *(end() - 1); }void push_back(const T& x) {if (finish != end_of_storage) {construct(finish, x);++finish;}elseinsert_aux(end(), x);}void swap(vector<T, Alloc>& x) {__STD::swap(start, x.start);__STD::swap(finish, x.finish);__STD::swap(end_of_storage, x.end_of_storage);}iterator insert(iterator position, const T& x) {size_type n = position - begin();if (finish != end_of_storage && position == end()) {construct(finish, x);++finish;}elseinsert_aux(position, x);return begin() + n;}iterator insert(iterator position) { return insert(position, T()); }
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class InputIterator>void insert(iterator position, InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {range_insert(position, first, last, iterator_category(first));}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */void insert(iterator position,const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */void insert (iterator pos, size_type n, const T& x);void insert (iterator pos, int n, const T& x) {insert(pos, (size_type) n, x);}void insert (iterator pos, long n, const T& x) {insert(pos, (size_type) n, x);}void pop_back() {--finish;destroy(finish);}iterator erase(iterator position) {if (position + 1 != end())copy(position + 1, finish, position);--finish;destroy(finish);return position;}iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last) {iterator i = copy(last, finish, first);destroy(i, finish);finish = finish - (last - first);return first;}void resize(size_type new_size, const T& x) {if (new_size < size()) erase(begin() + new_size, end());elseinsert(end(), new_size - size(), x);}void resize(size_type new_size) { resize(new_size, T()); }void clear() { erase(begin(), end()); }protected:iterator allocate_and_fill(size_type n, const T& x) {iterator result = data_allocator::allocate(n);__STL_TRY {uninitialized_fill_n(result, n, x);return result;}__STL_UNWIND(data_allocator::deallocate(result, n));}#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class ForwardIterator>iterator allocate_and_copy(size_type n,ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last) {iterator result = data_allocator::allocate(n);__STL_TRY {uninitialized_copy(first, last, result);return result;}__STL_UNWIND(data_allocator::deallocate(result, n));}
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */iterator allocate_and_copy(size_type n,const_iterator first, const_iterator last) {iterator result = data_allocator::allocate(n);__STL_TRY {uninitialized_copy(first, last, result);return result;}__STL_UNWIND(data_allocator::deallocate(result, n));}
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class InputIterator>void range_initialize(InputIterator first, InputIterator last,input_iterator_tag) {for ( ; first != last; ++first)push_back(*first);}// This function is only called by the constructor. We have to worry// about resource leaks, but not about maintaining invariants.template <class ForwardIterator>void range_initialize(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,forward_iterator_tag) {size_type n = 0;distance(first, last, n);start = allocate_and_copy(n, first, last);finish = start + n;end_of_storage = finish;}template <class InputIterator>void range_insert(iterator pos,InputIterator first, InputIterator last,input_iterator_tag);template <class ForwardIterator>void range_insert(iterator pos,ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last,forward_iterator_tag);#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */
};template <class T, class Alloc>
inline bool operator==(const vector<T, Alloc>& x, const vector<T, Alloc>& y) {return x.size() == y.size() && equal(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin());
}template <class T, class Alloc>
inline bool operator<(const vector<T, Alloc>& x, const vector<T, Alloc>& y) {return lexicographical_compare(x.begin(), x.end(), y.begin(), y.end());
}#ifdef __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDERtemplate <class T, class Alloc>
inline void swap(vector<T, Alloc>& x, vector<T, Alloc>& y) {x.swap(y);
}#endif /* __STL_FUNCTION_TMPL_PARTIAL_ORDER */template <class T, class Alloc>
vector<T, Alloc>& vector<T, Alloc>::operator=(const vector<T, Alloc>& x) {if (&x != this) {if (x.size() > capacity()) {iterator tmp = allocate_and_copy(x.end() - x.begin(),x.begin(), x.end());destroy(start, finish);deallocate();start = tmp;end_of_storage = start + (x.end() - x.begin());}else if (size() >= x.size()) {iterator i = copy(x.begin(), x.end(), begin());destroy(i, finish);}else {copy(x.begin(), x.begin() + size(), start);uninitialized_copy(x.begin() + size(), x.end(), finish);}finish = start + x.size();}return *this;
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x) {if (finish != end_of_storage) {construct(finish, *(finish - 1));++finish;T x_copy = x;copy_backward(position, finish - 2, finish - 1);*position = x_copy;}else {const size_type old_size = size();const size_type len = old_size != 0 ? 2 * old_size : 1;iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);iterator new_finish = new_start;__STL_TRY {new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);construct(new_finish, x);++new_finish;new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);}# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS catch(...) {destroy(new_start, new_finish); data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);throw;}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */destroy(begin(), end());deallocate();start = new_start;finish = new_finish;end_of_storage = new_start + len;}
}template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position, size_type n, const T& x) {if (n != 0) {if (size_type(end_of_storage - finish) >= n) {T x_copy = x;const size_type elems_after = finish - position;iterator old_finish = finish;if (elems_after > n) {uninitialized_copy(finish - n, finish, finish);finish += n;copy_backward(position, old_finish - n, old_finish);fill(position, position + n, x_copy);}else {uninitialized_fill_n(finish, n - elems_after, x_copy);finish += n - elems_after;uninitialized_copy(position, old_finish, finish);finish += elems_after;fill(position, old_finish, x_copy);}}else {const size_type old_size = size(); const size_type len = old_size + max(old_size, n);iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);iterator new_finish = new_start;__STL_TRY {new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);new_finish = uninitialized_fill_n(new_finish, n, x);new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS catch(...) {destroy(new_start, new_finish);data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);throw;}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */destroy(start, finish);deallocate();start = new_start;finish = new_finish;end_of_storage = new_start + len;}}
}#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class T, class Alloc> template <class InputIterator>
void vector<T, Alloc>::range_insert(iterator pos,InputIterator first, InputIterator last,input_iterator_tag) {for ( ; first != last; ++first) {pos = insert(pos, *first);++pos;}
}template <class T, class Alloc> template <class ForwardIterator>
void vector<T, Alloc>::range_insert(iterator position,ForwardIterator first,ForwardIterator last,forward_iterator_tag) {if (first != last) {size_type n = 0;distance(first, last, n);if (size_type(end_of_storage - finish) >= n) {const size_type elems_after = finish - position;iterator old_finish = finish;if (elems_after > n) {uninitialized_copy(finish - n, finish, finish);finish += n;copy_backward(position, old_finish - n, old_finish);copy(first, last, position);}else {ForwardIterator mid = first;advance(mid, elems_after);uninitialized_copy(mid, last, finish);finish += n - elems_after;uninitialized_copy(position, old_finish, finish);finish += elems_after;copy(first, mid, position);}}else {const size_type old_size = size();const size_type len = old_size + max(old_size, n);iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);iterator new_finish = new_start;__STL_TRY {new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);new_finish = uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_finish);new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONScatch(...) {destroy(new_start, new_finish);data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);throw;}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */destroy(start, finish);deallocate();start = new_start;finish = new_finish;end_of_storage = new_start + len;}}
}#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert(iterator position, const_iterator first, const_iterator last) {if (first != last) {size_type n = 0;distance(first, last, n);if (size_type(end_of_storage - finish) >= n) {const size_type elems_after = finish - position;iterator old_finish = finish;if (elems_after > n) {uninitialized_copy(finish - n, finish, finish);finish += n;copy_backward(position, old_finish - n, old_finish);copy(first, last, position);}else {uninitialized_copy(first + elems_after, last, finish);finish += n - elems_after;uninitialized_copy(position, old_finish, finish);finish += elems_after;copy(first, first + elems_after, position);}}else {const size_type old_size = size();const size_type len = old_size + max(old_size, n);iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);iterator new_finish = new_start;__STL_TRY {new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);new_finish = uninitialized_copy(first, last, new_finish);new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONScatch(...) {destroy(new_start, new_finish);data_allocator::deallocate(new_start, len);throw;}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */destroy(start, finish);deallocate();start = new_start;finish = new_finish;end_of_storage = new_start + len;}}
}#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif__STL_END_NAMESPACE #endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_VECTOR_H */// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End:二、分析源码
源码的分析方法:先看框架,再分析细节,最好要学会画图直观的展现清楚类内部、类之间的关系!例如分析一个类:先分析它的大致框架,功能是什么、核心成员是什么、核心函数是什么、该类的大致方向是做什么。然后再分析类与类之间是什么关系。
2.1 捋顺牵头框架
切记不要看细节,不要一行一行地看;例如这里就是先找到一个大类vector。
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector {
public:typedef T value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type* iterator;typedef const value_type* const_iterator;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;#ifdef __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATIONtypedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;typedef reverse_iterator<iterator> reverse_iterator;
#else /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */typedef reverse_iterator<const_iterator, value_type, const_reference, difference_type> const_reverse_iterator;typedef reverse_iterator<iterator, value_type, reference, difference_type>reverse_iterator;
#endif /* __STL_CLASS_PARTIAL_SPECIALIZATION */
protected:typedef simple_alloc<value_type, Alloc> data_allocator;iterator start;iterator finish;iterator end_of_storage;void insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x);void deallocate() {if (start) data_allocator::deallocate(start, end_of_storage - start);}
2.2 分析成员变量
在上一步找到的一个大类里面,开始查找成员变量,成员变量一般在private或者protected里面。
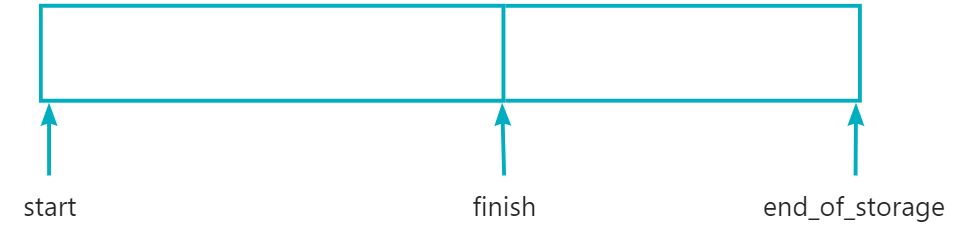
protected:iterator start;iterator finish;iterator end_of_storage;
可以发现这里定义两三个迭代器,在此之前(【链接】string的模拟实现)我们就已经知道迭代器名称是typedef来的,因此在这里我们可以找一下它的typedef,在public位置找到了iterator的重定义位置。这里就找到了iterator最根本的面貌。
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* iterator;
在找到成员变量后我们要学会“猜”它的作用:例如猜测start是空间内存的开始位置或者数据开始的位置;猜测finish是数据结束位置;猜测end_of_storage是空间结束位置。猜测是基于自己的学习经验,有依据的进行推测,而并非是乱猜。合理的猜测有助于我们更加顺利的理解源码,但也容易误导我们自己。猜测需要使用后面的步骤进行证实!
注意:细节不要硬扣,这里不能涉及太多的细节,我们目前的目标主要是学习它的基本框架。源码的细节都是一层套着一层,关注细节容易绕晕自己,我们应该知道:不要让本应该读绘本的幼儿园小朋友去读《水浒》,即俗语“少不读水浒,老不读三国”。
2.3 分析构造函数
在分析完成员函数后,我们开始分析构造函数vector(……),看看该类的对象初始化以后是什么样的结果。
vector() : start(0), finish(0), end_of_storage(0) {}
vector(size_type n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }
vector(int n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }
vector(long n, const T& value) { fill_initialize(n, value); }
在这里我们可以发现vector()是初始化为无参的构造函数,接下来我们开始分析核心的接口。
2.4 分析核心接口
一个类的实现会调用很多的接口,我们要关注核心接口、常用接口。例如这里我们查找一下常用的push_back接口。在这里开始证实我们方才的猜测是否正确。
void push_back(const T& x) {if (finish != end_of_storage) {construct(finish, x);++finish;}elseinsert_aux(end(), x);}
按照我们的猜测以及push_back接口进行画图:
在这里有一个construct函数,我们没有经验时你就会不知道它的作用。在有些项目里面会考虑使用内 存池提高效率,STL的六大组件之一空间配置器(内存池)出来的数据只开辟了空间,并没有进行初始化。
这里就使用了内存池里面的空间,自然是没有进行初始化。它使用了construct进行初始化,头文件是stl_construct.h。 construct是一个类模板的定位new,定位new相当于显示调用构造函数。
// stl_construct.h
template <class T1, class T2>
inline void construct(T1* p, const T2& value) {new (p) T1(value);
}
分析到这里就基本印证了我们方才的猜测。如果不确定,还可以继续往下分析。else里面的一种清况:
insert_aux(end(), x);
我们可以右击insert_aux()转到定义:
template <class T, class Alloc>
void vector<T, Alloc>::insert_aux(iterator position, const T& x) {if (finish != end_of_storage) {construct(finish, *(finish - 1)); // 空间不满,走此处++finish;T x_copy = x;copy_backward(position, finish - 2, finish - 1);*position = x_copy;}else {const size_type old_size = size();// 在这里转到定义const size_type len = old_size != 0 ? 2 * old_size : 1;iterator new_start = data_allocator::allocate(len);// 这里使用的是内存池开辟的空间iterator new_finish = new_start;__STL_TRY {new_finish = uninitialized_copy(start, position, new_start);construct(new_finish, x);++new_finish;new_finish = uninitialized_copy(position, finish, new_finish);}
根据上面的定义代码,我们可以大概知道if是判断空间足够后的插入数据的操作,else是空间不够、中间插入数据时,后面的数据需要往后挪动,可能会出现抛出异常的清况,就使用了__STL_TRY这一段宏定义过的内容,在抛异常的时候进行捕获。
下面这几句代码就是最终确定我们的猜测的关键代码。
// stl_vector.h
public:iterator begin() { return start; }//const_iterator begin() const { return start; }iterator end() { return finish; }//const_iterator end() const { return finish; }size_type size() const { return size_type(end() - begin()); }size_type capacity() const { return size_type(end_of_storage - begin()); }
通过对 SGI 版本 STL 中vector源码的分析,我们了解了其框架结构、成员变量、构造函数和核心接口的实现原理。vector容器通过巧妙地使用迭代器和内存管理技术,提供了高效的动态数组功能。我们也可以根据现在所掌握的东西,进行vector的模拟实现。

相关文章:

【C++】透过STL源代码深度剖析vector的底层
✨ Blog’s 主页: 白乐天_ξ( ✿>◡❛) 🌈 个人Motto:他强任他强,清风拂山冈! 🔥 所属专栏:C深入学习笔记 💫 欢迎来到我的学习笔记! 参考博客:【C】透过STL源…...

ubuntu 开启root
sudo passwd root#输入以下命令来给root账户设置密码 sudo passwd -u root#启用root账户 su - root#要登录root账户 root 开启远程访问: 小心不要改到这里了:sudo nano /etc/ssh/ssh_config 而是:/etc/ssh/sshd_config sudo nano /etc/ssh…...
使用 Llama 3.1 和 Qdrant 构建多语言医疗保健聊天机器人的步骤
长话短说: 准备好深入研究: 矢量存储的复杂性以及如何利用 Qdrant 进行高效数据摄取。掌握 Qdrant 中的集合管理以获得最佳性能。释放上下文感知响应的相似性搜索的潜力。精心设计复杂的 LangChain 工作流程以增强聊天机器人的功能。将革命性的 Llama …...

【Linux-基础IO】如何理解Linux下一切皆文件磁盘的介绍
目录 如何理解Linux系统上一切皆文件 1.物理角度认识磁盘 2.对磁盘的存储进行逻辑抽象 磁盘寻址 3.磁盘中的寄存器 如何理解Linux系统上一切皆文件 计算机中包含大量外设,操作系统想要管理好这些外设,就必须对这些外设进行先描述再组织,…...

Golang | Leetcode Golang题解之第436题寻找右区间
题目: 题解: func findRightInterval(intervals [][]int) []int {n : len(intervals)type pair struct{ x, i int }starts : make([]pair, n)ends : make([]pair, n)for i, p : range intervals {starts[i] pair{p[0], i}ends[i] pair{p[1], i}}sort.…...

微服务SpringSession解析部署使用全流程
目录 1、SpringSession简介 2、实现session共享的三种方式 1、修改Tomcat配置文件 2、Nginx负载均衡策略 3、redis统一存储 0、准备工作 1、本地服务添加依赖 2、修改本地服务配置文件 3、添加application.properties文件 4、添加nacos - redis配置 5、修改本地项目…...

自动驾驶 3DGS 学习笔记
目录 street_gaussians gsplat依赖项 运行报错: python>3.9 SGD: Street View Synthesis with Gaussian Splatting and Diffusion Prior 差分高斯光栅化 diff-gaussian-rasterization street_gaussians https://github.com/zju3dv/street_gaussians gsp…...

【C++笔试强训】如何成为算法糕手Day5
学习编程就得循环渐进,扎实基础,勿在浮沙筑高台 循环渐进Forward-CSDN博客 目录 循环渐进Forward-CSDN博客 第一题:游游的you 思路: 第二题:腐烂的苹果 思路: 第三题:孩子们的游戏 思路&…...

【Qt】无IDE的Gui程序快速开始
Qt安装 在 Windows 上安装 Qt 的步骤如下: 下载 Qt 安装程序 访问 Qt 的官方网站:Qt Downloads。点击“Download”按钮,下载 Qt Online Installer(在线安装程序)。 运行安装程序 双击下载的 QtInstaller.exe 文件…...

Python编码系列—Python备忘录模式:掌握对象状态保存与恢复技术
🌟🌟 欢迎来到我的技术小筑,一个专为技术探索者打造的交流空间。在这里,我们不仅分享代码的智慧,还探讨技术的深度与广度。无论您是资深开发者还是技术新手,这里都有一片属于您的天空。让我们在知识的海洋中…...
)
linux常用命令汇编(持续更新)
一、用户提示符 # root账号提示符 $ 普通用户提示符 二、关闭计算机 shutdown(安全有序地关闭计算机) 语法:shutdown [options] [time] [message] shutdown -h now #立即关机(--halt/终止) shutdown -r now #重…...

AI面试指南:AI工具总结评测,助力求职季
AI面试指南:AI工具总结评测,助力求职季 摘要: 在竞争激烈的AI领域秋招季,准备充分并借助高效工具是提升面试通过率的关键。本文主要介绍一些针对秋招的AI面试工具和学习资源,分为简历优化、面试助手、手撕代码练习三个…...

大二考核题解
大二考核题解 题号题目考察知识点A有意思的监考二分答案B海绵宝宝的数独DFSC走楼梯递推D碱基配对kmpE好简单的题啊,写它!最短路 写在前面: 整体难度不大,代码能力需要一些,正常来说至少要会3题以上 A 有意思的监考 …...

深入解析:Kubernetes 如何使用 etcd 作为配置中心和注册中心
在 Kubernetes 中,etcd 是核心的分布式存储组件,负责存储和管理集群的所有配置信息、状态数据以及服务注册信息。etcd 的高可用性和强一致性使得它成为 Kubernetes 的 “source of truth”,确保集群能够动态、高效地管理资源,并保…...

MQ高级:RabbitMQ小细节
在之前的学习中,我们只介绍了消息的发送,但是没有考虑到异常的情况,今天我们就介绍一些异常情况,和细节的部分。 目录 生产者可靠性 生产者重连 生产者确认 MQ可靠性 持久化 Lazy Queue 消费者可靠性 消费者确认机制 失…...
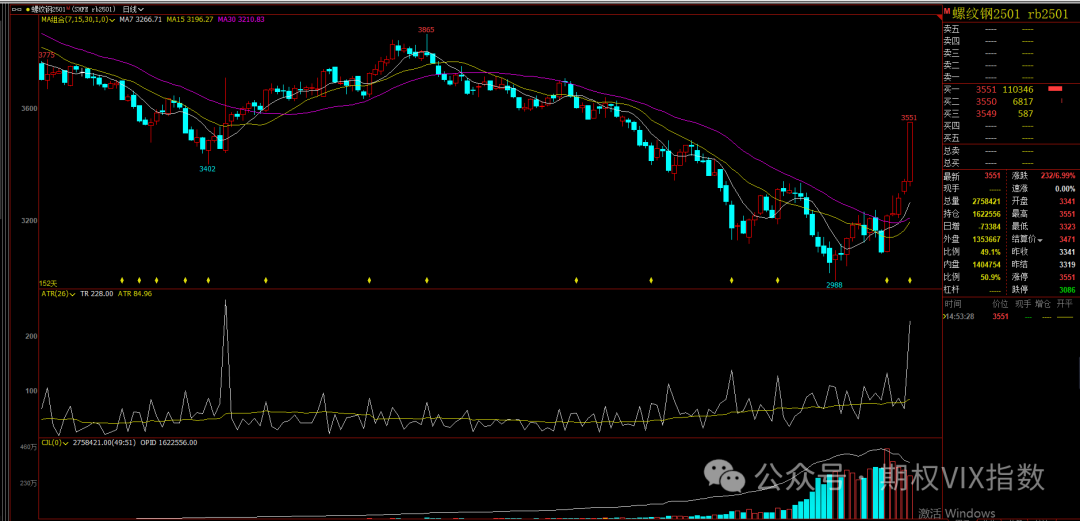
期权卖方怎么选择权利金高的品种,期货VIX高低对行情有什么影响
VIX指数——全称为芝加哥期权交易所市场波动率指数,俗称恐慌指数。 是衡量波动性的重要指标。VIX指数上升,预期未来市场波动性会增加。VIX指数下降,预期未来市场波动性会降低。 期货VIX指数最新价格排序 期权卖方尽量选择期货VIX指数在25以…...

内存对齐的原理和使用
1. 什么是内存对齐? 内存对齐是指将数据存储在内存中时,按照数据类型的大小,将数据放在特定的内存边界上。例如,4 字节的 int 通常放在能够被 4 整除的地址上,8 字节的 double 则放在能被 8 整除的地址上。 2. 为什么…...

搭建企业级私有仓库harbor
华子目录 harbor简介实验环境准备下载软件包安装docker-cehosts解析 实验步骤配置https加密传输解压进入解压目录,修改文件配置启动harbor 测试客户端配置harbor本地加速器注意 通过docker compose管理harbor harbor简介 harbor是由wmware公司开源的企业级docker r…...

互联网前后端分离的开发场景,一般会员和数据权限的判断是放在前端还是后端?
推荐学习文档 golang应用级os框架,欢迎stargolang应用级os框架使用案例,欢迎star案例:基于golang开发的一款超有个性的旅游计划app经历golang实战大纲golang优秀开发常用开源库汇总想学习更多golang知识,这里有免费的golang学习笔…...

李宏毅机器学习2022-HW8-Anomaly Detection
文章目录 TaskBaselineReportQuestion2 Code Link Task 异常检测Anomaly Detection 将data经过Encoder,在经过Decoder,根据输入和输出的差距来判断异常图像。training data是100000张人脸照片,testing data有大约10000张跟training data相同…...
【Axure高保真原型】引导弹窗
今天和大家中分享引导弹窗的原型模板,载入页面后,会显示引导弹窗,适用于引导用户使用页面,点击完成后,会显示下一个引导弹窗,直至最后一个引导弹窗完成后进入首页。具体效果可以点击下方视频观看或打开下方…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

golang循环变量捕获问题
在 Go 语言中,当在循环中启动协程(goroutine)时,如果在协程闭包中直接引用循环变量,可能会遇到一个常见的陷阱 - 循环变量捕获问题。让我详细解释一下: 问题背景 看这个代码片段: fo…...

回溯算法学习
一、电话号码的字母组合 import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;import javax.management.loading.PrivateClassLoader;public class letterCombinations {private static final String[] KEYPAD {"", //0"", //1"abc", //2"…...
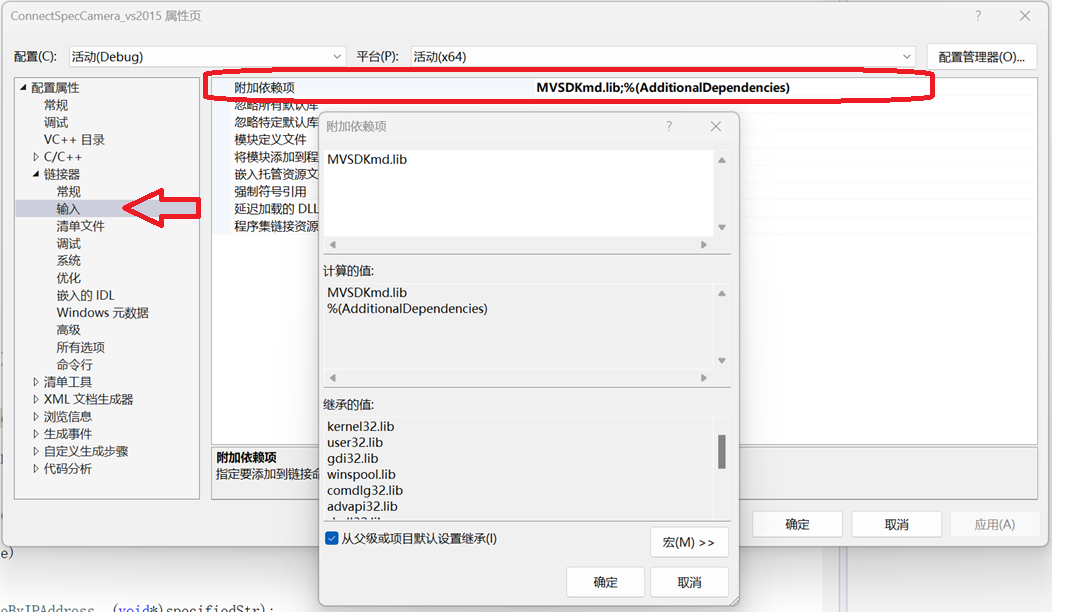
C/C++ 中附加包含目录、附加库目录与附加依赖项详解
在 C/C 编程的编译和链接过程中,附加包含目录、附加库目录和附加依赖项是三个至关重要的设置,它们相互配合,确保程序能够正确引用外部资源并顺利构建。虽然在学习过程中,这些概念容易让人混淆,但深入理解它们的作用和联…...

[免费]微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端+Vue管理端)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】
大家好,我是java1234_小锋老师,看到一个不错的微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端)【论文源码SQL脚本】,分享下哈。 项目视频演示 【免费】微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端) Java毕业设计_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 项…...

NPOI Excel用OLE对象的形式插入文件附件以及插入图片
static void Main(string[] args) {XlsWithObjData();Console.WriteLine("输出完成"); }static void XlsWithObjData() {// 创建工作簿和单元格,只有HSSFWorkbook,XSSFWorkbook不可以HSSFWorkbook workbook new HSSFWorkbook();HSSFSheet sheet (HSSFSheet)workboo…...
Golang——9、反射和文件操作
反射和文件操作 1、反射1.1、reflect.TypeOf()获取任意值的类型对象1.2、reflect.ValueOf()1.3、结构体反射 2、文件操作2.1、os.Open()打开文件2.2、方式一:使用Read()读取文件2.3、方式二:bufio读取文件2.4、方式三:os.ReadFile读取2.5、写…...
Golang——7、包与接口详解
包与接口详解 1、Golang包详解1.1、Golang中包的定义和介绍1.2、Golang包管理工具go mod1.3、Golang中自定义包1.4、Golang中使用第三包1.5、init函数 2、接口详解2.1、接口的定义2.2、空接口2.3、类型断言2.4、结构体值接收者和指针接收者实现接口的区别2.5、一个结构体实现多…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...
