使用 Elastic 将 AI 摘要添加到你的网站
作者:来自 Elastic Gustavo Llermaly

我们目前所知道的搜索(搜索栏、结果、过滤器、页面等)已经取得了长足的进步,并实现了多种不同的功能。当我们知道找到所需内容所需的关键字或知道哪些文档包含我们想要的信息时,尤其如此。但是,当结果是包含长文本的文档时,除了阅读和总结之外,我们还需要额外的步骤来获得最终答案。因此,为了简化此过程,Google 及其搜索生成体验 ( Search Generative Experience - SGE) 等公司使用 AI 通过 AI 摘要来补充搜索结果。
如果我告诉你,你可以使用 Elastic 做同样的事情,你会怎么做?
在本文中,你将学习创建一个 React 组件,该组件将显示回答用户问题的 AI 摘要以及搜索结果,以帮助用户更快地回答他们的问题。我们还将要求模型提供引用,以便答案以搜索结果为基础。
最终结果将如下所示:

你可以在此处找到完整的工作示例存储库。
步骤
- 创建端点
- 创建索引
- 索引数据
- 创建组件
- 提出问题
创建端点
在创建端点之前,请先查看该项目的高级架构。

从 UI 使用 Elasticsearch 的推荐方法是代理调用,因此我们将为此目的启动 UI 可以连接的后端。你可以在此处阅读有关此方法的更多信息。
重要提示:本文概述的方法提供了一种处理 Elasticsearch 查询和生成摘要的简单方法。在实施此解决方案之前,请考虑你的具体用例和要求。更合适的架构将涉及在代理后面的同一 API 调用下进行搜索和完成。
嵌入端点
为了启用语义搜索,我们将使用 ELSER 模型来帮助我们不仅通过单词匹配进行查找,而且还通过语义含义进行查找。
你可以使用 Kibana UI 创建 ELSER 端点:

或者通过 _inference API:
PUT _inference/sparse_embedding/elser-embeddings
{"service": "elser","service_settings": {"model_id": ".elser_model_2","num_allocations": 1,"num_threads": 1}
}
Completion 端点
要生成 AI 摘要,我们必须将相关文档作为上下文和用户查询发送到模型。为此,我们创建了一个连接到 OpenAI 的完成端点。如果你不想与 OpenAI 合作,你还可以在不断增加的不同提供商列表中进行选择。
PUT _inference/completion/summaries-completion
{"service": "openai","service_settings": {"api_key": "<API_KEY>","model_id": "gpt-4o-mini"}
}
每次用户运行搜索时,我们都会调用模型,因此我们需要速度和成本效益,这是一个测试新款的好机会。
索引数据
由于我们正在为网站添加搜索体验,因此我们可以使用 Elastic 网络爬虫来索引网站内容并使用我们自己的文档进行测试。在此示例中,我将使用 Elastic Labs Blog。
要创建爬虫,请按照文档中的说明进行操作。
在此示例中,我们将使用以下设置:




注意:我添加了一些提取规则来清理字段值。我还使用了爬虫中的 semantic_text 字段,并将其与 article_content 字段关联起来
提取字段的简要说明:
meta_img:用作缩略图的文章图像。meta_author:作者姓名,可按作者进行筛选。article_content:我们仅索引 div 中文章的主要内容,排除页眉和页脚等不相关的数据。此优化通过生成更短的嵌入来增强搜索相关性并降低成本。
应用规则并成功执行抓取后,文档的外观如下:
{"_index": "search-labs-index","_id": "66a5568a30cc8eb607eec315","_version": 1,"_seq_no": 6,"_primary_term": 3,"found": true,"_source": {"last_crawled_at": "2024-07-27T20:20:25Z","url_path_dir3": "langchain-collaboration","meta_img": "https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/assets/images/langchain-partner-blog.png?5c6faef66d5699625c50453e356927d0","semantic_text": {"inference": {"inference_id": "elser_model_2","model_settings": {"task_type": "sparse_embedding"},"chunks": [{"text": """Tutorials Integrations Blog Start Free Trial Contact Sales Open navigation menu Blog / Generative AI LangChain and Elastic collaborate to add vector database and semantic reranking for RAG In the last year, we have seen a lot of movement in generative AI. Many new services and libraries have emerged. LangChain has separated itself as the most popular library for building applications with large language models (LLMs), for example Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The library makes it really easy to prototype and experiment with different models and retrieval systems. To enable the first-class support for Elasticsearch in LangChain, we recently elevated our integration from a community package to an official LangChain partner package . This work makes it straightforward to import Elasticsearch capabilities into LangChain applications. The Elastic team manages the code and the release process through a dedicated repository . We will keep improving the LangChain integration there, making sure that users can take full advantage of the latest improvements in Elasticsearch. Our collaboration with Elastic in the last 12 months has been exceptional, particularly as we establish better ways for developers and end users to build RAG applications from prototype to production," said Harrison Chase, Co-Founder and CEO at LangChain. "The LangChain-Elasticsearch vector database integrations will help do just that, and we're excited to see this partnership grow with future feature and integration releases. Elasticsearch is one of the most flexible and performant retrieval systems that includes a vector database. One of our goals at Elastic is to also be the most open retrieval system out there. In a space as fast-moving as generative AI, we want to have the developer's back when it comes to utilizing emerging tools and libraries. This is why we work closely with libraries like LangChain and add native support to the GenAI ecosystem. From using Elasticsearch as a vector database to hybrid search and orchestrating a full RAG application. Elasticsearch and LangChain have collaborated closely this year. We are putting our extensive experience in building search tools into making your experience of LangChain easier and more flexible. Let's take a deeper look in this blog. Rapid RAG prototyping RAG is a technique for providing users with highly relevant answers to questions. The main advantages over using LLMs directly are that user data can be easily integrated, and hallucinations by the LLM can be minimized. This is achieved by adding a document retrieval step that provides relevant context for the""","embeddings": {"rag": 2.2831416,"elastic": 2.1994505,"genera": 1.990228,"lang": 1.9417559,"vector": 1.7541072,"##ai": 1.5763651,"integration": 1.5619806,"##sea": 1.5154194,"##rank": 1.4946039,"retrieval": 1.3957807,"ll": 1.362704 // more embeddings ...}}]}},"additional_urls": ["https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration"],"body_content": """Tutorials Integrations Blog Start Free Trial Contact Sales Open navigation menu Blog / Generative AI LangChain and Elastic collaborate to add vector database and semantic reranking for RAG In the last year, we have seen a lot of movement in generative AI. Many new services and libraries have emerged. LangChain has separated itself as the most popular library for building applications with large language models (LLMs), for example Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The library makes it really easy to prototype and experiment with different models and retrieval systems. To enable the first-class support for Elasticsearch in LangChain, we recently elevated our integration from a community package to an official LangChain partner package . This work makes it straightforward to import Elasticsearch capabilities into LangChain applications. The Elastic team manages the code and the release process through a dedicated repository . We will keep improving the LangChain integration there, making sure that users can take full advantage of the latest improvements in Elasticsearch. Our collaboration with Elastic in the last 12 months has been exceptional, particularly as we establish better ways for developers and end users to build RAG applications from prototype to production," said Harrison Chase, Co-Founder and CEO at LangChain. "The LangChain-Elasticsearch vector database integrations will help do just that, and we're excited to see this partnership grow with future feature and integration releases. Elasticsearch is one of the most flexible and performant retrieval systems that includes a vector database. One of our goals at Elastic is to also be the most open retrieval system out there. In a space as fast-moving as generative AI, we want to have the developer's back when it comes to utilizing emerging tools and libraries. This is why we work closely with libraries like LangChain and add native support to the GenAI ecosystem. From using Elasticsearch as a vector database to hybrid search and orchestrating a full RAG application. Elasticsearch and LangChain have collaborated closely this year. We are putting our extensive experience in building search tools into making your experience of LangChain easier and more flexible. Let's take a deeper look in this blog. Rapid RAG prototyping RAG is a technique for providing users with highly relevant answers to questions. The main advantages over using LLMs directly are that user data can be easily integrated, and hallucinations by the LLM can be minimized. This is achieved by adding a document retrieval step that provides relevant context for the LLM. Since its inception, Elasticsearch has been the go-to solution for relevant document retrieval and has since been a leading innovator, offering numerous retrieval strategies. When it comes to integrating Elasticsearch into LangChain, we have made it easy to choose between the most common retrieval strategies, for example, dense vector, sparse vector, keyword or hybrid. And we enabled power users to further customize these strategies. Keep reading to see some examples. (Note that we assume we have an Elasticsearch deployment .) LangChain integration package In order to use the langchain-elasticsearch partner package, you first need to install it: pip install langchain-elasticsearch Then you can import the classes you need from the langchain_elasticsearch module, for example, the ElasticsearchStore , which gives you simple methods to index and search your data. In this example, we use Elastic's sparse vector model ELSER (which has to be deployed first) as our retrieval strategy. from langchain_elasticsearch import ElasticsearchStore es_store = ElasticsearchStore( es_cloud_id="your-cloud-id", es_api_key="your-api-key", index_name="rag-example", strategy=ElasticsearchStore.SparseVectorRetrievalStrategy(model_id=".elser_model_2"), ), A simple RAG application Now, let's build a simple RAG example application. First, we add some example documents to our Elasticsearch store. texts = [ "LangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by large language models (LLMs).", "Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine capable of addressing a growing number of use cases.", ... ] es_store.add_texts(texts) Next, we define the LLM. Here, we use the default gpt-3.5-turbo model offered by OpenAI, which also powers ChatGPT. from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI llm = ChatOpenAI(api_key="sk-...") # or set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable Now we are ready to plug together our RAG system. For simplicity we take a standard prompt for instructing the LLM. We also transform the Elasticsearch store into a LangChain retriever. Finally, we chain together the retrieval step with adding the documents to the prompt and sending it to the LLM. from langchain import hub from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt") # standard prompt from LangChain hub retriever = es_store.as_retriever() def format_docs(docs): return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs) rag_chain = ( {"context": retriever | format_docs, "question": RunnablePassthrough()} | prompt | llm | StrOutputParser() ) With these few lines of code, we now already have a simple RAG system. Users can now ask questions on the data: rag_chain.invoke("Which frameworks can help me build LLM apps?") "LangChain is a framework specifically designed for building LLM-powered applications. ..." It's as simple as this. Our RAG system can now respond with info about LangChain, which ChatGPT (version 3.5) cannot. Of course there are many ways to improve this system. One of them is optimizing the way we retrieve the documents. Full retrieval flexibility through the Retriever The Elasticsearch store offers common retrieval strategies out-of-the-box, and developers can freely experiment with what works best for a given use case. But what if your data model is more complex than just text with a single field? What, for example, if your indexing setup includes a web crawler that yields documents with texts, titles, URLs and tags and all these fields are important for search? Elasticsearch's Query DSL gives users full control over how to search their data. And in LangChain, the ElasticsearchRetriever enables this full flexibility directly. All that is required is to define a function that maps the user input query to an Elasticsearch request. Let's say we want to add semantic reranking capabilities to our retrieval step. By adding a Cohere reranking step, the results at the top become more relevant without extra manual tuning. For this, we define a Retriever that takes in a function that returns the respective Query DSL structure. def text_similarity_reranking(search_query: str) -> Dict: return { "retriever": { "text_similarity_reranker": { "retriever": { "standard": { "query": { "match": { "text_field": search_query } } } }, "field": "text_field", "inference_id": "cohere-rerank-service", "inference_text": search_query, "window_size": 10 } } } retriever = ElasticsearchRetriever.from_es_params( es_cloud_id="your-cloud-id", es_api_key="your-api-key", index_name="rag-example", content_field=text_field, body_func=text_similarity_reranking, ) (Note that the query structure for similarity reranking is still being finalized. It will be available in an upcoming release.) This retriever can slot seamlessly into the RAG code above. The result is that the retrieval part of our RAG pipeline is much more accurate, leading to more relevant documents being forwarded to the LLM and, most importantly, to more relevant answers. Conclusion Elastic's continued investment into LangChain's ecosystem brings the latest retrieval innovations to one of the most popular GenAI libraries. Through this collaboration, Elastic and LangChain enable developers to rapidly and easily build RAG solutions for end users while providing the necessary flexibility for in-depth tuning of results quality. Ready to try this out on your own? Start a free trial . Looking to build RAG into your apps? Want to try different LLMs with a vector database? Check out our sample notebooks for LangChain, Cohere and more on Github, and join Elasticsearch Relevance Engine training now. Max Jakob 5 min read 11 June 2024 Generative AI Integrations Share Twitter Facebook LinkedIn Recommended Articles Integrations How To Generative AI • 25 July 2024 Protecting Sensitive and PII information in RAG with Elasticsearch and LlamaIndex How to protect sensitive and PII data in a RAG application with Elasticsearch and LlamaIndex. Srikanth Manvi How To Generative AI • 19 July 2024 Build a Conversational Search for your Customer Success Application with Elasticsearch and OpenAI Explore how to enhance your customer success application by implementing a conversational search feature using advanced technologies such as Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Lionel Palacin Integrations How To Generative AI Vector Database • 11 July 2024 semantic_text with Amazon Bedrock Using semantic_text new feature, and AWS Bedrock as inference endpoint service Gustavo Llermaly Integrations How To Generative AI Vector Database • 10 July 2024 Elasticsearch open inference API adds Amazon Bedrock support Elasticsearch open inference API adds support for embeddings generated from models hosted on Amazon Bedrock." Mark Hoy Hemant Malik Vector Database How To Generative AI • 10 July 2024 Playground: Experiment with RAG using Bedrock Anthropic Models and Elasticsearch in minutes Playground is a low code interface for developers to explore grounding LLMs of their choice with their own private data, in minutes. Joe McElroy Aditya Tripathi Max Jakob 5 min read 11 June 2024 Generative AI Integrations Share Twitter Facebook LinkedIn Jump to Rapid RAG prototyping LangChain integration package A simple RAG application Full retrieval flexibility through the Retriever Conclusion Sitemap RSS Feed Search Labs Repo Elastic.co ©2024. Elasticsearch B.V. All Rights Reserved.""","article_content": """In the last year, we have seen a lot of movement in generative AI. Many new services and libraries have emerged. LangChain has separated itself as the most popular library for building applications with large language models (LLMs), for example Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The library makes it really easy to prototype and experiment with different models and retrieval systems. To enable the first-class support for Elasticsearch in LangChain, we recently elevated our integration from a community package to an official LangChain partner package . This work makes it straightforward to import Elasticsearch capabilities into LangChain applications. The Elastic team manages the code and the release process through a dedicated repository . We will keep improving the LangChain integration there, making sure that users can take full advantage of the latest improvements in Elasticsearch. Our collaboration with Elastic in the last 12 months has been exceptional, particularly as we establish better ways for developers and end users to build RAG applications from prototype to production," said Harrison Chase, Co-Founder and CEO at LangChain. "The LangChain-Elasticsearch vector database integrations will help do just that, and we're excited to see this partnership grow with future feature and integration releases. Elasticsearch is one of the most flexible and performant retrieval systems that includes a vector database. One of our goals at Elastic is to also be the most open retrieval system out there. In a space as fast-moving as generative AI, we want to have the developer's back when it comes to utilizing emerging tools and libraries. This is why we work closely with libraries like LangChain and add native support to the GenAI ecosystem. From using Elasticsearch as a vector database to hybrid search and orchestrating a full RAG application. Elasticsearch and LangChain have collaborated closely this year. We are putting our extensive experience in building search tools into making your experience of LangChain easier and more flexible. Let's take a deeper look in this blog. Rapid RAG prototyping RAG is a technique for providing users with highly relevant answers to questions. The main advantages over using LLMs directly are that user data can be easily integrated, and hallucinations by the LLM can be minimized. This is achieved by adding a document retrieval step that provides relevant context for the LLM. Since its inception, Elasticsearch has been the go-to solution for relevant document retrieval and has since been a leading innovator, offering numerous retrieval strategies. When it comes to integrating Elasticsearch into LangChain, we have made it easy to choose between the most common retrieval strategies, for example, dense vector, sparse vector, keyword or hybrid. And we enabled power users to further customize these strategies. Keep reading to see some examples. (Note that we assume we have an Elasticsearch deployment .) LangChain integration package In order to use the langchain-elasticsearch partner package, you first need to install it: pip install langchain-elasticsearch Then you can import the classes you need from the langchain_elasticsearch module, for example, the ElasticsearchStore , which gives you simple methods to index and search your data. In this example, we use Elastic's sparse vector model ELSER (which has to be deployed first) as our retrieval strategy. from langchain_elasticsearch import ElasticsearchStore es_store = ElasticsearchStore( es_cloud_id="your-cloud-id", es_api_key="your-api-key", index_name="rag-example", strategy=ElasticsearchStore.SparseVectorRetrievalStrategy(model_id=".elser_model_2"), ), A simple RAG application Now, let's build a simple RAG example application. First, we add some example documents to our Elasticsearch store. texts = [ "LangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by large language models (LLMs).", "Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine capable of addressing a growing number of use cases.", ... ] es_store.add_texts(texts) Next, we define the LLM. Here, we use the default gpt-3.5-turbo model offered by OpenAI, which also powers ChatGPT. from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI llm = ChatOpenAI(api_key="sk-...") # or set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable Now we are ready to plug together our RAG system. For simplicity we take a standard prompt for instructing the LLM. We also transform the Elasticsearch store into a LangChain retriever. Finally, we chain together the retrieval step with adding the documents to the prompt and sending it to the LLM. from langchain import hub from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt") # standard prompt from LangChain hub retriever = es_store.as_retriever() def format_docs(docs): return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs) rag_chain = ( {"context": retriever | format_docs, "question": RunnablePassthrough()} | prompt | llm | StrOutputParser() ) With these few lines of code, we now already have a simple RAG system. Users can now ask questions on the data: rag_chain.invoke("Which frameworks can help me build LLM apps?") "LangChain is a framework specifically designed for building LLM-powered applications. ..." It's as simple as this. Our RAG system can now respond with info about LangChain, which ChatGPT (version 3.5) cannot. Of course there are many ways to improve this system. One of them is optimizing the way we retrieve the documents. Full retrieval flexibility through the Retriever The Elasticsearch store offers common retrieval strategies out-of-the-box, and developers can freely experiment with what works best for a given use case. But what if your data model is more complex than just text with a single field? What, for example, if your indexing setup includes a web crawler that yields documents with texts, titles, URLs and tags and all these fields are important for search? Elasticsearch's Query DSL gives users full control over how to search their data. And in LangChain, the ElasticsearchRetriever enables this full flexibility directly. All that is required is to define a function that maps the user input query to an Elasticsearch request. Let's say we want to add semantic reranking capabilities to our retrieval step. By adding a Cohere reranking step, the results at the top become more relevant without extra manual tuning. For this, we define a Retriever that takes in a function that returns the respective Query DSL structure. def text_similarity_reranking(search_query: str) -> Dict: return { "retriever": { "text_similarity_reranker": { "retriever": { "standard": { "query": { "match": { "text_field": search_query } } } }, "field": "text_field", "inference_id": "cohere-rerank-service", "inference_text": search_query, "window_size": 10 } } } retriever = ElasticsearchRetriever.from_es_params( es_cloud_id="your-cloud-id", es_api_key="your-api-key", index_name="rag-example", content_field=text_field, body_func=text_similarity_reranking, ) (Note that the query structure for similarity reranking is still being finalized. It will be available in an upcoming release.) This retriever can slot seamlessly into the RAG code above. The result is that the retrieval part of our RAG pipeline is much more accurate, leading to more relevant documents being forwarded to the LLM and, most importantly, to more relevant answers. Conclusion Elastic's continued investment into LangChain's ecosystem brings the latest retrieval innovations to one of the most popular GenAI libraries. Through this collaboration, Elastic and LangChain enable developers to rapidly and easily build RAG solutions for end users while providing the necessary flexibility for in-depth tuning of results quality.""","domains": ["https://www.elastic.co"],"title": "LangChain and Elastic collaborate to add vector database and semantic reranking for RAG — Search Labs","meta_author": ["Max Jakob"],"url": "https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration","url_scheme": "https","meta_description": "Learn how LangChain and Elasticsearch can accelerate your speed of innovation in the LLM and GenAI space.","headings": ["LangChain and Elastic collaborate to add vector database and semantic reranking for RAG","Rapid RAG prototyping","LangChain integration package","A simple RAG application","Full retrieval flexibility through the Retriever","Conclusion","Protecting Sensitive and PII information in RAG with Elasticsearch and LlamaIndex","Build a Conversational Search for your Customer Success Application with Elasticsearch and OpenAI","semantic_text with Amazon Bedrock","Elasticsearch open inference API adds Amazon Bedrock support","Playground: Experiment with RAG using Bedrock Anthropic Models and Elasticsearch in minutes"],"links": ["https://cloud.elastic.co/registration?onboarding_token=search&cta=cloud-registration&tech=trial&plcmt=navigation&pg=search-labs","https://discuss.elastic.co/c/search/84","https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch-labs","https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain-elastic","https://pypi.org/project/langchain-elasticsearch/","https://python.langchain.com/v0.2/docs/integrations/providers/elasticsearch/","https://search.elastic.co/?location%5B0%5D=Search+Labs&referrer=https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration","https://www.elastic.co/contact","https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/query-dsl.html","https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/machine-learning/current/ml-nlp-elser.html#download-deploy-elser","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/category/generative-ai","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/elasticsearch-cohere-rerank","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration#a-simple-rag-application","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration#conclusion","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration#full-retrieval-flexibility-through-the-retriever","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration#langchain-integration-package","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration#rapid-rag-prototyping","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/retrieval-augmented-generation-rag","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/semantic-reranking-with-retrievers","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/integrations","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/tutorials","https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/tutorials/install-elasticsearch"],"id": "66a5568a30cc8eb607eec315","url_port": 443,"url_host": "www.elastic.co","url_path_dir2": "blog","url_path": "/search-labs/blog/langchain-collaboration","url_path_dir1": "search-labs"}}
创建代理
要设置代理服务器,我们将使用 express.js。我们将按照最佳实践创建两个端点:一个用于处理 _search 调用,另一个用于 completion 调用。
首先创建一个名为 es-proxy 的新目录,使用 cd es-proxy 导航到该目录,然后使用 npm init 初始化你的项目。
接下来,使用以下命令安装必要的依赖项:
yarn add express axios dotenv cors以下是每个包的简要说明:
express:用于创建代理服务器,该服务器将处理传入的请求并将其转发到 Elasticsearch。axios:一种流行的 HTTP 客户端,可简化对 Elasticsearch API 的请求。dotenv:允许你通过将敏感数据存储在环境变量中来管理它们,例如 API 密钥。cors:通过处理跨源资源共享 (CORS),使你的 UI 能够向不同的域(在本例中为代理服务器)发出请求。当你的前端和后端托管在不同的域或端口上时,这对于避免出现问题至关重要。
现在,创建一个 .env 文件来安全地存储你的 Elasticsearch URL 和 API 密钥:
ELASTICSEARCH_URL=https://<your_elasticsearch_url>
API_KEY=<your_api_key>
确保你创建的 API 密钥仅限于所需的索引,并且是只读的
最后,创建一个 index.js 文件,内容如下:
index.js
require("dotenv").config();const express = require("express");
const cors = require("cors");
const app = express();
const axios = require("axios");app.use(express.json());
app.use(cors());const { ELASTICSEARCH_URL, API_KEY } = process.env;// Handle all _search requests
app.post("/api/:index/_search", async (req, res) => {try {const response = await axios.post(`${ELASTICSEARCH_URL}/${req.params.index}/_search`,req.body,{headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json",Authorization: `ApiKey ${API_KEY}`,},});res.json(response.data);} catch (error) {res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });}
});// Handle all _completion requests
app.post("/api/completion", async (req, res) => {try {const response = await axios.post(`${ELASTICSEARCH_URL}/_inference/completion/summaries-completion`,req.body,{headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json",Authorization: `ApiKey ${API_KEY}`,},});res.json(response.data);} catch (error) {res.status(500).json({ error: error.message });}
});// Start the server
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 1337;
app.listen(PORT, () => {console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});现在,通过运行 node index.js 启动服务器。这将默认在端口 1337 上启动服务器,或者在 .env 文件中定义的端口上启动服务器。
创建组件
对于 UI 组件,我们将使用 Search UI React 库 search-ui。我们将创建一个自定义组件,以便每次用户运行搜索时,它都会使用我们创建的 completion 推理端点将最佳结果发送到 LLM,然后将答案显示给用户。
你可以在此处找到有关配置实例的完整教程。你可以在计算机上运行 search-ui,也可以在此处使用我们的在线沙盒。
运行示例并连接到数据后,在启动应用程序文件夹中的终端中运行以下安装步骤:
yarn add axios antd html-react-parser安装其他依赖项后,为新组件创建一个新的 AiSummary.js 文件。这将包括一个简单的提示,用于向 AI 提供说明和规则。
AiSummary.js
import { withSearch } from "@elastic/react-search-ui";
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
import { Card } from "antd";
import parse from "html-react-parser";const formatSearchResults = (results) => {return results.slice(0, 3).map((result) => `Article Author(s): ${result.meta_author.raw.join(",")}Article URL: ${result.url.raw}Article title: ${result.title.raw}Article content: ${result.article_content.raw}`).join("\n");
};const fetchAiSummary = async (searchTerm, results) => {const prompt = `You are a search assistant. Your mission is to complement search results with an AI Summary to address the user request.User request: ${searchTerm}Top search results: ${formatSearchResults(results)}Rules:- The answer must be short. No more than one paragraph.- Use HTML- Use content from the most relevant search results only to answer the user request- Add highlights wrapping in <i><b></b></i> tags the most important phrases of your answer- At the end of the answer add a citations section with links to the articles you got the answer on this format:<h4>Citations</h4><ul><li><a href="{url}"> {title} </a></li></ul>- Only provide citations from the top search results I showed you, and only if they are relevant to the user request.`;const responseData = await axios.post("http://localhost:1337/api/completion",{ input: prompt },{headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json",},});return responseData.data.completion[0].result;
};const AiSummary = ({ results, searchTerm, resultSearchTerm }) => {const [aiSummary, setAiSummary] = useState("");const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);useEffect(() => {if (searchTerm) {setIsLoading(true);fetchAiSummary(searchTerm, results).then((summary) => {setAiSummary(summary);setIsLoading(false);});}}, [resultSearchTerm]);return (<Card style={{ width: "100%" }} loading={isLoading}><div><h2>AI Summary</h2>{!resultSearchTerm ? "Ask anything!" : parse(aiSummary)}</div></Card>);
};export default withSearch(({ results, searchTerm, resultSearchTerm }) => ({results,searchTerm,resultSearchTerm,AiSummary,
}))(AiSummary);
更新 App.js
现在我们创建了自定义组件,是时候将其添加到应用程序中了。你的 App.js 应如下所示:
App.js
import React from "react";
import ElasticsearchAPIConnector from "@elastic/search-ui-elasticsearch-connector";
import {ErrorBoundary,SearchProvider,SearchBox,Results,Facet,
} from "@elastic/react-search-ui";
import { Layout } from "@elastic/react-search-ui-views";
import "@elastic/react-search-ui-views/lib/styles/styles.css";
import AiSummary from "./AiSummary";const connector = new ElasticsearchAPIConnector({host: "http://localhost:1337/api",index: "search-labs-index",},(requestBody, requestState) => {if (!requestState.searchTerm) return requestBody;requestBody.query = {semantic: {query: requestState.searchTerm,field: "semantic_text",},};return requestBody;}
);const config = {debug: true,searchQuery: {search_fields: {semantic_text: {},},result_fields: {title: {snippet: {},},article_content: {snippet: {size: 10,},},meta_description: {},url: {},meta_author: {},meta_img: {},},facets: {"meta_author.enum": { type: "value" },},},apiConnector: connector,alwaysSearchOnInitialLoad: false,
};export default function App() {return (<SearchProvider config={config}><div className="App"><ErrorBoundary><Layoutheader={<SearchBox />}bodyHeader={<AiSummary />}bodyContent={<ResultstitleField="title"thumbnailField="meta_img"urlField="url"/>}sideContent={<Facet key={"1"} field={"meta_author.enum"} label={"author"} />}/></ErrorBoundary></div></SearchProvider>);
}
请注意,在连接器实例中我们如何覆盖默认查询以使用语义查询并利用我们创建的 semantic_text 映射。
提出问题
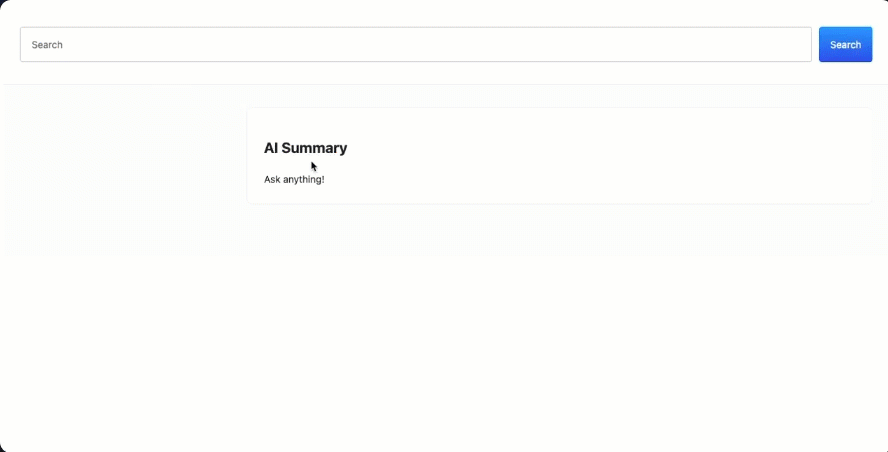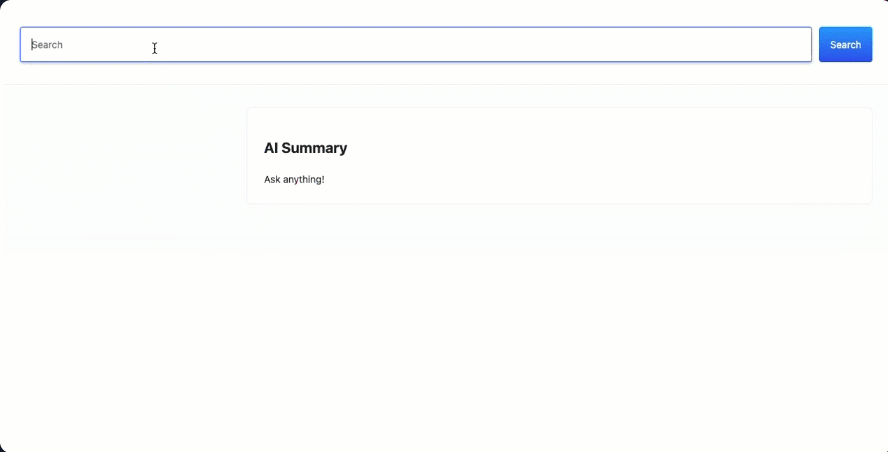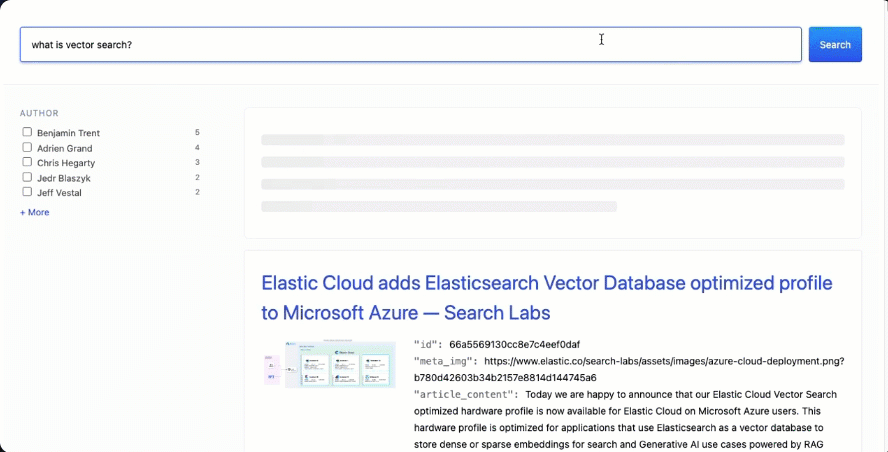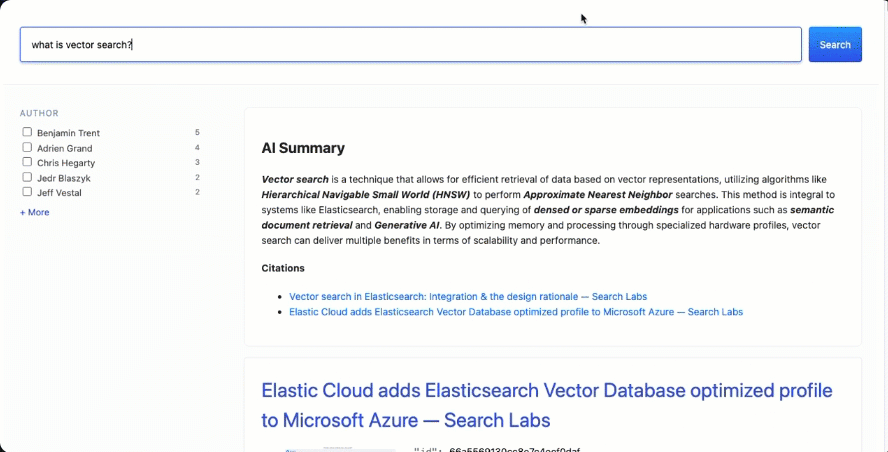
现在是时候测试它了。提出有关你索引的文档的任何问题,在搜索结果上方,你应该会看到一张带有 AI 摘要的卡片:
结论
重新设计你的搜索体验对于保持用户的参与度非常重要,并节省他们浏览结果以找到问题答案的时间。借助 Elastic 开放推理服务和搜索用户界面,设计此类体验比以往任何时候都更容易。你准备好尝试了吗?
准备好自己尝试了吗?开始免费试用。
Elasticsearch 集成了 LangChain、Cohere 等工具。加入我们的 Beyond RAG Basics 网络研讨会,构建你的下一个 GenAI 应用程序!
原文:Generate AI summaries with Elastic — Search Labs
相关文章:

使用 Elastic 将 AI 摘要添加到你的网站
作者:来自 Elastic Gustavo Llermaly 我们目前所知道的搜索(搜索栏、结果、过滤器、页面等)已经取得了长足的进步,并实现了多种不同的功能。当我们知道找到所需内容所需的关键字或知道哪些文档包含我们想要的信息时,尤…...
dOOv:Java 数据验证与映射库(简化业务逻辑)
dOOv 是一个为 Java 开发人员设计的轻量化库,专注于数据验证和对象间的映射。与传统的验证框架不同,dOOv 通过提供简洁、声明式的 API,使得开发者可以轻松地编写、扩展和维护验证和映射规则。其设计灵感源自领域驱动设计(DDD&…...

Arthas sc(查看JVM已加载的类信息 )
文章目录 二、命令列表2.2 class/classloader相关命令2.2.5 sc(查看JVM已加载的类信息 )举例1:模糊搜索,xx包下所有的类举例2:打印类的详细信息举例3:打印出类的Field信息 本人其他相关文章链接 二、命令列…...
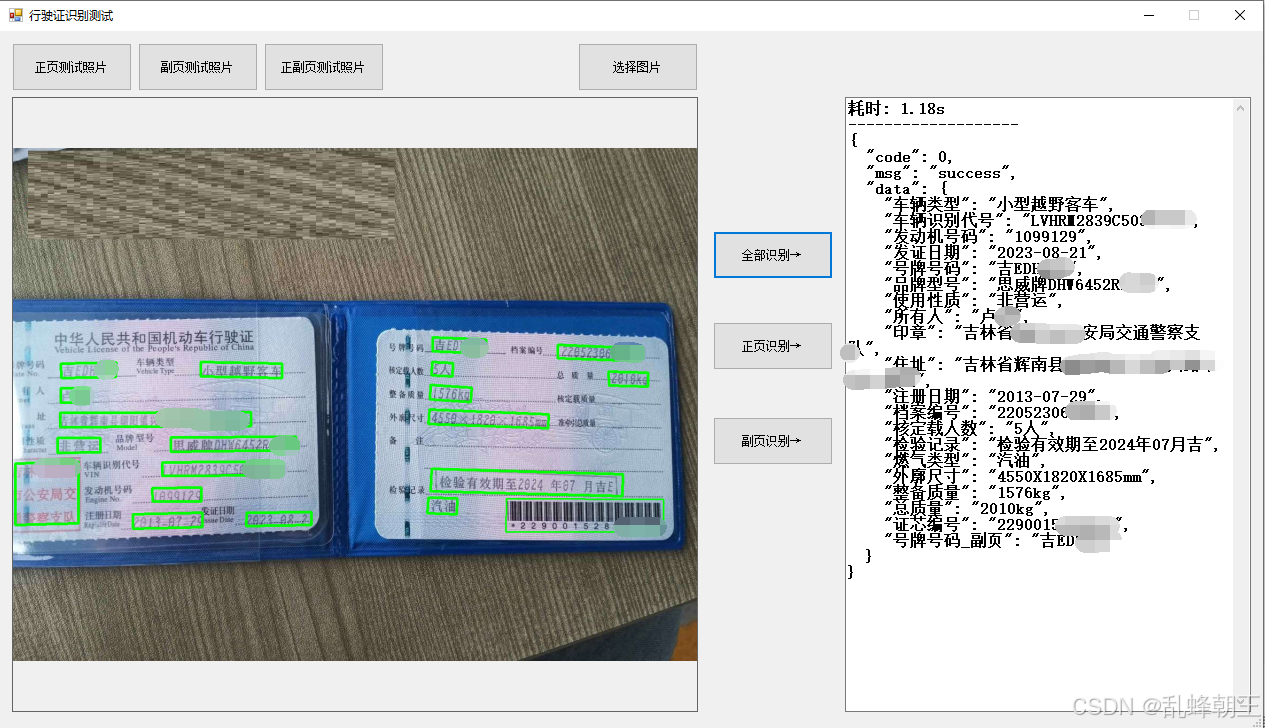
OCR 行驶证识别 离线识别
目录 正页识别 副页识别 全部识别 OCR 行驶证识别 离线识别 正页识别 副页识别 全部识别...

PHP泛目录生成源码,可生成长尾关键词页面,带使用方法视频教程
介绍: 真正的好东西,搞网站优化seo从业必备。可以快速提升网站权重,带来的流量哗哗的 PHP泛目录生成源码 可生成新闻页面和关键词页面 带使用方法视频教程 泛目录可以用来提升网站收录和排名 合理运用目录可以达到快速出词和出权重的效果…...

LeetCode题练习与总结:丑数--263
一、题目描述 丑数 就是只包含质因数 2、3 和 5 的正整数。 给你一个整数 n ,请你判断 n 是否为 丑数 。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。 示例 1: 输入:n 6 输出:true 解释࿱…...
)
初识C语言(五)
前言 本文章就代表C语言介绍以及了解正式完成,后续进行具体分析和详细解析学习。知识根深蒂固才可以应付后来的学习,地基要打好,后续才会轻松。 十四、结构体 结构体是C语言中最最重要的知识点,使得C语言有能力描述复杂的类型。 …...

Linux:深入理解冯诺依曼结构与操作系统
目录 1. 冯诺依曼体系结构 1.1 结构分析 1.2 存储结构分布图 2. 操作系统 2.1 概念 2.2 如何管理 2.3 什么是系统调用和库函数 1. 冯诺依曼体系结构 1.1 结构分析 不管是何种计算机,如个人笔记本电脑,服务器,都是遵循冯诺依曼结构。…...
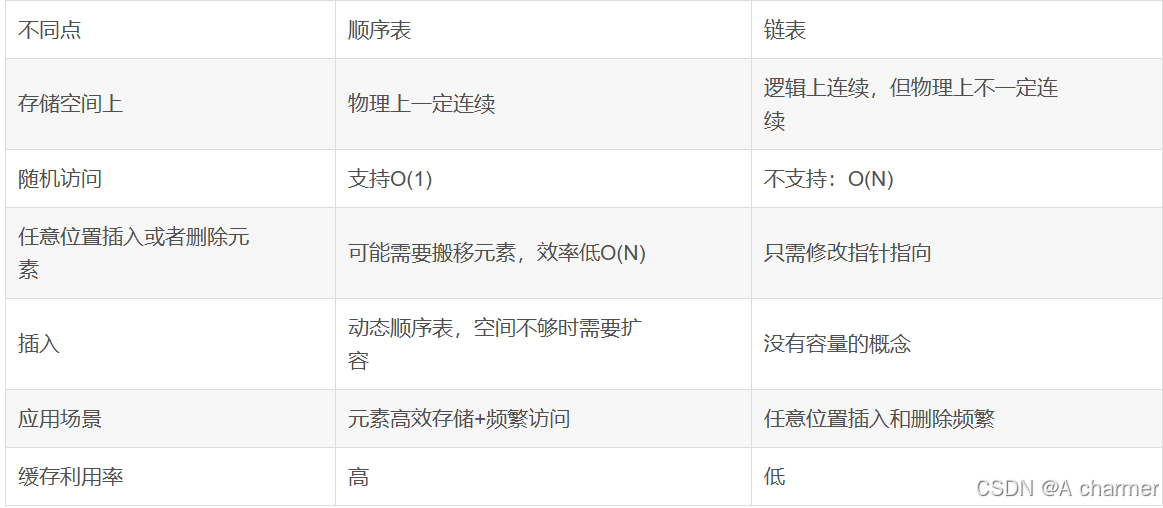
面试中顺序表常考的十大题目解析
在数据结构与算法的面试中,顺序表是一个常见的考点。它作为一种基础的数据结构,涵盖了多种操作和概念,以下将详细介绍面试中关于顺序表常考的十大题目。 💝💝💝如果你对顺序表的概念与理解还存在疑惑&#…...
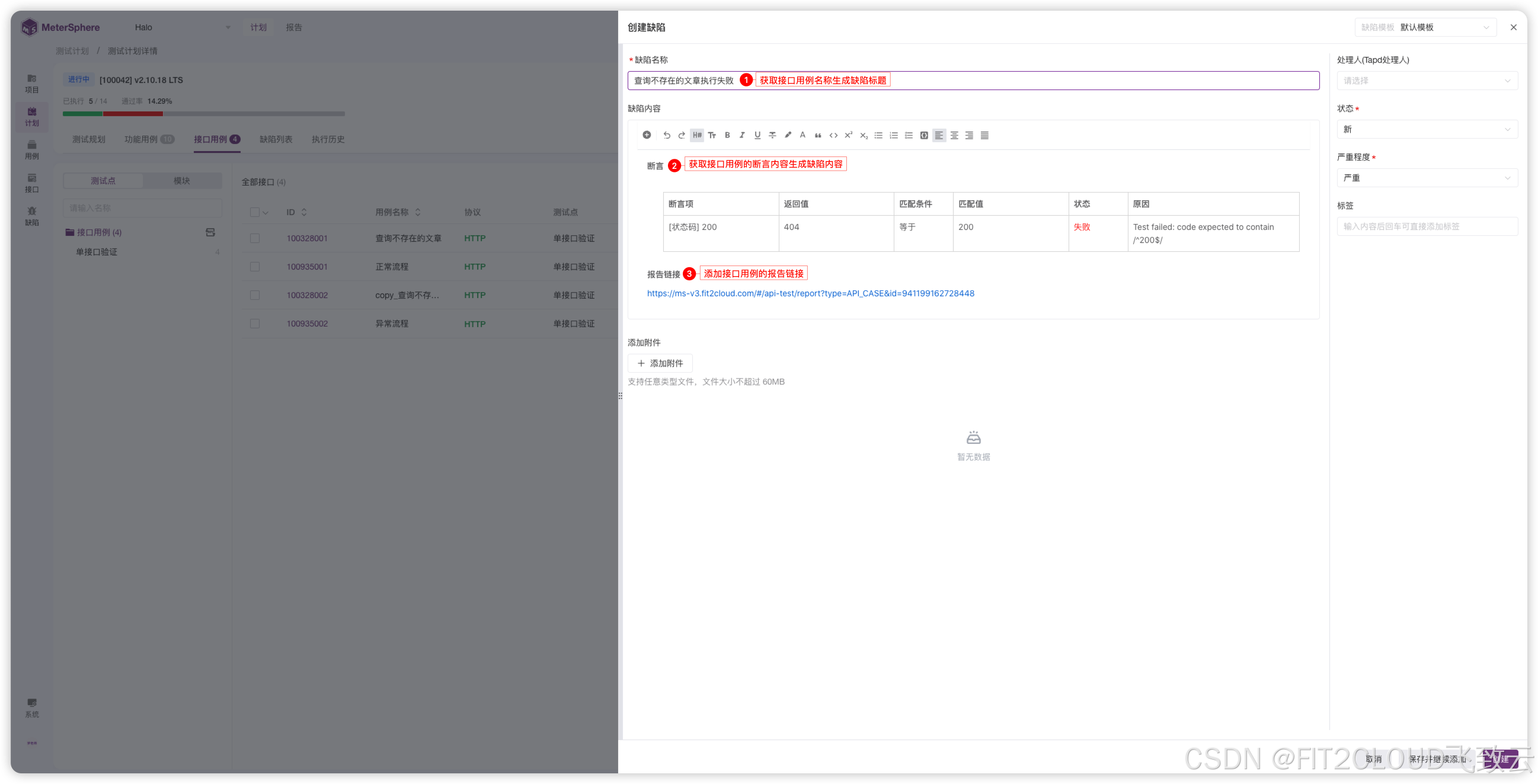
测试管理新增视图与高级搜索功能,测试计划支持一键生成缺陷详情,MeterSphere开源持续测试工具v3.3版本发布
2024年9月29日,MeterSphere开源持续测试工具正式发布v3.3版本。 在这一版本中,接口测试方面,接口导入功能支持导入Postman、JMX、HAR和MeterSphere格式的文件,接口场景的自定义请求步骤支持cURL快捷导入;测试管理方面…...
TypeScript 算法手册 【归并排序】
文章目录 1. 归并排序简介1.1 归并排序定义1.2 归并排序特点 2. 归并排序步骤过程拆解2.1 分割数组2.2 递归排序2.3 合并有序数组 3. 归并排序的优化3.1 原地归并排序3.2 混合插入排序案例代码和动态图 4. 归并排序的优点5. 归并排序的缺点总结 【 已更新完 TypeScript 设计模式…...

生信名词|MOA|基因敲低与基因敲除|DMSO|MODZ|生信基础
生信名词|MOA|基因敲低与基因敲除|DMSO|MODZ|生信基础 MOA(Mechanisms Of Action,作用机理) 过去,在药物投入到临床使用之前,它的生物学机理往往未被研究透彻。如今,随着技术的发展,一种新药物…...
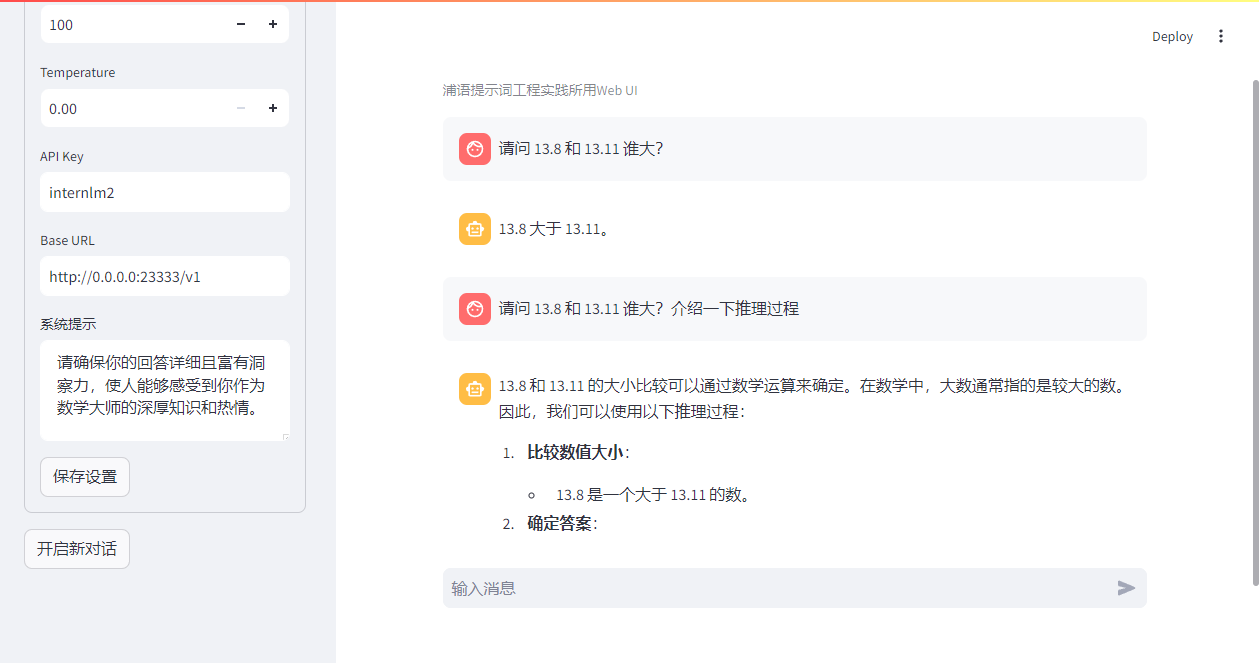
基础岛第3关:浦语提示词工程实践
模型部署 使用下面脚本测试模型 from huggingface_hub import login, snapshot_download import osos.environ[HF_ENDPOINT] https://hf-mirror.comlogin(token“your_access_token")models ["internlm/internlm2-chat-1_8b"]for model in models:try:snapsh…...
vscode中配置python虚拟环境
python虚拟环境作用 Python虚拟环境允许你为每个独立的项目创建一个隔离的环境,这样每个项目都可以拥有自己的一套Python安装包和依赖,不会互相影响。实际使用中,可以在vscode或pycharm中使用虚拟环境。 1.创建虚拟环境的方法: …...

chatGPT对我学术写作的三种帮助
chatGPT对我学术写作的三种帮助 概述提高学术写作水平大模型选择概述上下文以提供精确的指令 提升同行评审优化编辑反馈 概述 从生成式人工智能中获得的价值并非来自于技术本身盲目地输出文本,而是来自于与工具的互动,并利用自身的专业知识来完善它所生…...

【PostgreSQL 】入门篇——支持的各种数据类型介绍,包括整数、浮点数、字符串、日期、JSON、数组等
1. 整数类型 1.1 SMALLINT 描述:用于存储小范围的整数值。大小:2 字节范围:-32,768 到 32,767使用场景:适合存储小型计数器、状态码等。示例: CREATE TABLE status_codes (id SMALLINT PRIMARY KEY,description TEX…...
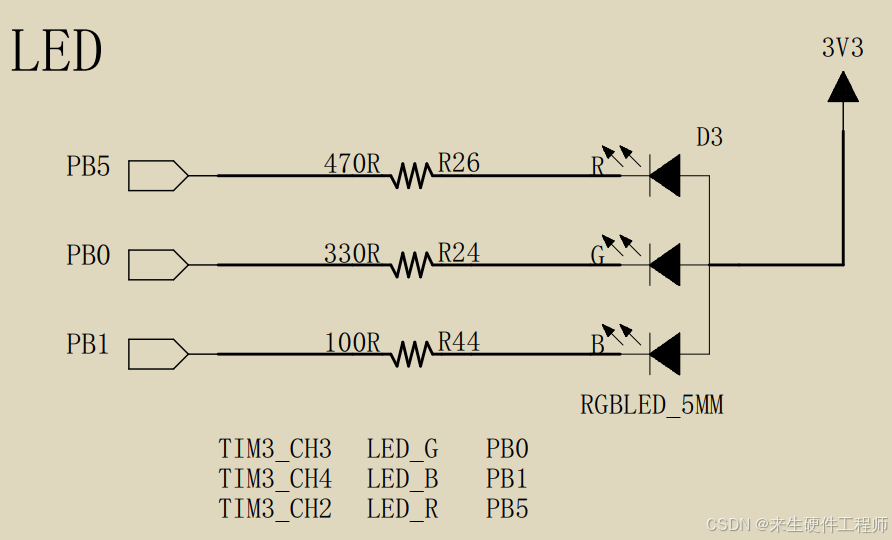
野火STM32F103VET6指南者开发板入门笔记:【1】点亮RGB
硬件介绍 提示:本文是基于野火STM32F103指南者开发板所写例程,其他开发板请自行移植到自己的工程项目当中即可。 RGB-LEDPin引脚:低电平-点亮,高电平-熄灭REDPB5GREENPB0BLUEPB1 文章目录 硬件介绍软件介绍:结构体方式…...
)
数据工程师岗位常见面试问题-3(附回答)
数据工程师已成为科技行业最重要的角色之一,是组织构建数据基础设施的骨干。随着企业越来越依赖数据驱动的决策,对成熟数据工程师的需求会不断上升。如果您正在准备数据工程师面试,那么应该掌握常见的数据工程师面试问题:包括工作…...
强大的JVM监控工具
介绍 在生产环境中,经常会遇到各种各样奇葩的性能问题,所以掌握最基本的JVM命令行监控工具还是很有必要的 名称主要作用jps查看正在运行的Java进程jstack打印线程快照jmap导出堆内存映像文件jstat查看jvm统计信息jinfo实时查看和修改jvm配置参数jhat用…...

python 实现点的多项式算法
点的多项式算法介绍 点的多项式算法通常指的是通过一组点(即数据点,通常包括自变量和因变量的值)来拟合一个多项式函数的方法。这种方法在数值分析、统计学、机器学习等领域中非常常见。下面是一些常见的多项式拟合算法: 1. 最小…...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...

C++初阶-list的底层
目录 1.std::list实现的所有代码 2.list的简单介绍 2.1实现list的类 2.2_list_iterator的实现 2.2.1_list_iterator实现的原因和好处 2.2.2_list_iterator实现 2.3_list_node的实现 2.3.1. 避免递归的模板依赖 2.3.2. 内存布局一致性 2.3.3. 类型安全的替代方案 2.3.…...

《Playwright:微软的自动化测试工具详解》
Playwright 简介:声明内容来自网络,将内容拼接整理出来的文档 Playwright 是微软开发的自动化测试工具,支持 Chrome、Firefox、Safari 等主流浏览器,提供多语言 API(Python、JavaScript、Java、.NET)。它的特点包括&a…...

STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解
STM32F4基本定时器使用和原理详解 前言如何确定定时器挂载在哪条时钟线上配置及使用方法参数配置PrescalerCounter ModeCounter Periodauto-reload preloadTrigger Event Selection 中断配置生成的代码及使用方法初始化代码基本定时器触发DCA或者ADC的代码讲解中断代码定时启动…...

JVM垃圾回收机制全解析
Java虚拟机(JVM)中的垃圾收集器(Garbage Collector,简称GC)是用于自动管理内存的机制。它负责识别和清除不再被程序使用的对象,从而释放内存空间,避免内存泄漏和内存溢出等问题。垃圾收集器在Ja…...

leetcodeSQL解题:3564. 季节性销售分析
leetcodeSQL解题:3564. 季节性销售分析 题目: 表:sales ---------------------- | Column Name | Type | ---------------------- | sale_id | int | | product_id | int | | sale_date | date | | quantity | int | | price | decimal | -…...
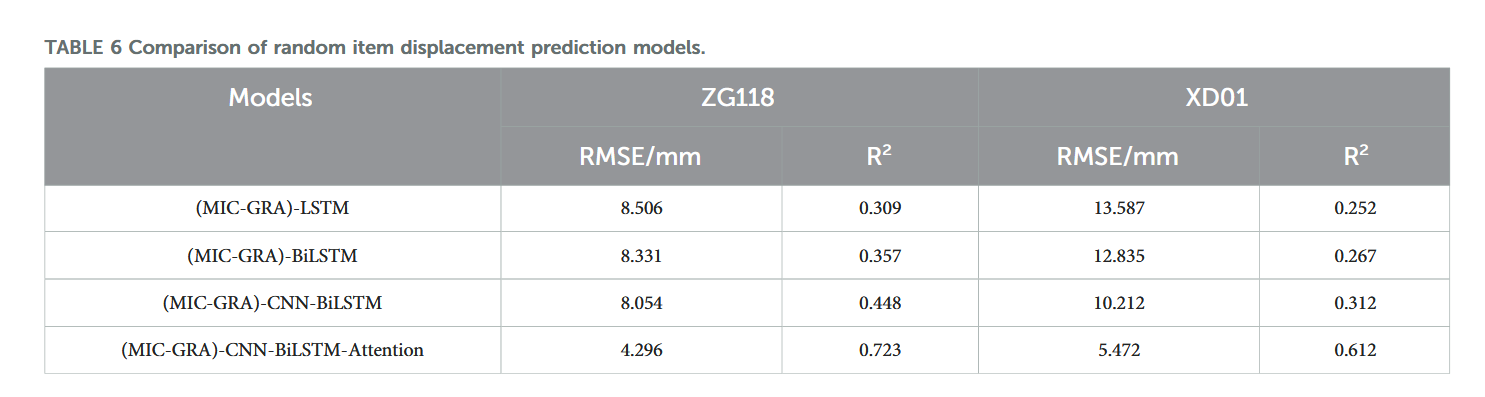
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...
SpringTask-03.入门案例
一.入门案例 启动类: package com.sky;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCach…...

MySQL用户和授权
开放MySQL白名单 可以通过iptables-save命令确认对应客户端ip是否可以访问MySQL服务: test: # iptables-save | grep 3306 -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.14.102/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.4.16/32 -p tcp -m tcp -…...
如何在网页里填写 PDF 表格?
有时候,你可能希望用户能在你的网站上填写 PDF 表单。然而,这件事并不简单,因为 PDF 并不是一种原生的网页格式。虽然浏览器可以显示 PDF 文件,但原生并不支持编辑或填写它们。更糟的是,如果你想收集表单数据ÿ…...
