路径规划——RRT-Connect算法
路径规划——RRT-Connect算法
算法原理
RRT-Connect算法是在RRT算法的基础上进行的扩展,引入了双树生长,分别以起点和目标点为树的根节点同时扩展随机树从而实现对状态空间的快速搜索。在此算法中以两棵随机树建立连接为路径规划成功的条件。并且,在搜索过程中使用了贪婪搜索的方法,在搜索的过程中,两棵树是交替扩展的,与RRT算法不同的是,RRT-Connect算法并不是每次扩展都会进行随机采样,而是第一棵树先随机采样进而扩展一个新的节点node_new,然后第二棵树利用node_new节点往相同的方向进行多次扩展直到扩展失败才会开始下一轮的交替扩展或者与另一棵树能够建立连接了从而满足路径规划完成的条件。
这种双向的RRT算法比原始RRT算法的搜索速度更快,因为除了使用双树扩展搜索,两棵树在扩展时还是朝着对方的方向进行扩展的,并不是完全随机的。
具体的算法流程可结合上述原理以及RRT算法的实现流程。
算法实现
"""@File: rrt-connect.py@Brief: RRT-Connect algorithm for pathplanning@Author: Benxiaogu@Github: https://github.com/Benxiaogu@CSDN: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51995147?type=blog@Date: 2024-11-13
"""
import numpy as np
import random
import math
from itertools import combinations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import matplotlib.patches as patchesclass RRTConnect:def __init__(self,start,goal,obstacles,board_size,max_try,max_dist,goal_sample_rate,env) -> None:self.start = self.Node(start,None,0)self.goal = self.Node(goal,None,0)self.obstacles = obstaclesself.board_size = board_sizeself.max_try = max_try # Number of iterationsself.max_dist = max_dist # Maximum sampling distanceself.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rateself.env = envself.inflation = 1self.searched = []class Node:def __init__(self,position,parent,cost) -> None:self.position = positionself.parent = parentself.cost = costdef run(self):cost,path,expand = self.plan()self.searched = expandself.visualize(cost,path)def plan(self):nodes_forward = {self.start.position: self.start}nodes_back = {self.goal.position: self.goal}for iter in range(self.max_try):# Generate a random nodenode_rand = self.get_random_node()# Get the nearest neighbor nodenode_near = self.get_nearest_neighbor(list(nodes_forward.values()),node_rand)# Get the new nodenode_new = self.get_new_node(node_rand,node_near)if node_new:nodes_forward[node_new.position] = node_newnode_near_b = self.get_nearest_neighbor(list(nodes_back.values()), node_new)node_new_b = self.get_new_node(node_new,node_near_b)if node_new_b:nodes_back[node_new_b.position] = node_new_b# Greedy extendingwhile True:for node_position, node in nodes_back.items():if node.position == node_new.position:print("final")cost, path = self.extractPath(node_new, nodes_back, nodes_forward)expand = self.get_expand(list(nodes_back.values()), list(nodes_forward.values()))print("Exploring {} nodes.".format(iter))return cost, path, expandnode_new_b2 = self.get_new_node(node_new,node_new_b)if node_new_b2:nodes_back[node_new_b2.position] = node_new_b2node_new_b = node_new_b2else:breakif len(nodes_back) < len(nodes_forward):nodes_forward, nodes_back = nodes_back, nodes_forwardreturn 0, None, Nonedef get_random_node(self):"""Return a random node."""if random.random()>self.goal_sample_rate:node = self.Node((random.uniform(0,self.env.height),random.uniform(0,self.env.width)),None,0)else:node = self.goalreturn nodedef get_nearest_neighbor(self,node_list,node):"""Return node that is nearest to 'node' in node_list"""dist = [self.distance(node, n) for n in node_list]node_near = node_list[int(np.argmin(dist))]return node_neardef get_new_node(self,node_rand,node_near):"""Return node found based on node_near and node_rand."""dx = node_rand.position[0] - node_near.position[0]dy = node_rand.position[1] - node_near.position[1]dist = math.hypot(dx,dy)theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)d = min(self.max_dist,dist)position = ((node_near.position[0]+d*math.cos(theta)),node_near.position[1]+d*math.sin(theta))node_new = self.Node(position,node_near,node_near.cost+d)if self.isCollision(node_new, node_near):return Nonereturn node_newdef isCollision(self,node1,node2):"""Judge collision from node1 to node2 """if self.isInObstacles(node1) or self.isInObstacles(node2):return Truefor rect in self.env.obs_rectangle:if self.isInterRect(node1,node2,rect):return Truefor circle in self.env.obs_circle:if self.isInterCircle(node1,node2,circle):return Truereturn Falsedef distance(self,node1,node2):dx = node2.position[0] - node1.position[0]dy = node2.position[1] - node1.position[1]return math.hypot(dx,dy)def isInObstacles(self,node):"""Determine whether it is in obstacles or not."""x,y = node.position[0],node.position[1]for (ox,oy,w,h) in self.env.boundary:if ox-self.inflation<x<ox+w+self.inflation and oy-self.inflation<y<oy+h+self.inflation:return Truefor (ox,oy,w,h) in self.env.obs_rectangle:if ox-self.inflation<x<ox+w+self.inflation and oy-self.inflation<y<oy+h+self.inflation:return Truefor (ox,oy,r) in self.env.obs_circle:if math.hypot(x-ox,y-oy)<=r+self.inflation:return Truereturn Falsedef isInterRect(self,node1,node2,rect):""""Judge whether it will cross the rectangle when moving from node1 to node2"""ox,oy,w,h = rectvertex = [[ox-self.inflation,oy-self.inflation],[ox+w+self.inflation,oy-self.inflation],[ox+w+self.inflation,oy+h+self.inflation],[ox-self.inflation,oy+h+self.inflation]]x1,y1 = node1.positionx2,y2 = node2.positiondef cross(p1,p2,p3):x1 = p2[0]-p1[0]y1 = p2[1]-p1[1]x2 = p3[0]-p1[0]y2 = p3[1]-p1[0]return x1*y2 - x2*y1for v1,v2 in combinations(vertex,2):if max(x1,x2) >= min(v1[0],v2[0]) and min(x1,x2)<=max(v1[0],v2[0]) and \max(y1,y2) >= min(v1[1],v2[1]) and min(y1,y2) <= max(v1[1],v2[1]):if cross(v1,v2,node1.position) * cross(v1,v2,node2.position)<=0 and \cross(node1.position,node2.position,v1) * cross(node1.position,node2.position,v2)<=0:return Truereturn Falsedef isInterCircle(self,node1,node2,circle):"""Judge whether it will cross the circle when moving from node1 to node2"""ox,oy,r = circledx = node2.position[0] - node1.position[0]dy = node2.position[1] - node1.position[1]# print("isInterCircle-dx:",dx)# print("isInterCircle-dy:",dy)d = dx * dx + dy * dyif d==0:return False# Projectiont = ((ox - node1.position[0]) * dx + (oy - node1.position[1]) * dy) / d# The projection point is on line segment ABif 0 <= t <= 1:closest_x = node1.position[0] + t * dxclosest_y = node1.position[1] + t * dy# Distance from center of the circle to line segment ABdistance = math.hypot(ox-closest_x,oy-closest_y)return distance <= r+self.inflationreturn Falsedef extractPath(self, node_middle, nodes_back, nodes_forward):""""Extract the path based on the closed set."""if self.start.position in nodes_back:nodes_forward, nodes_back = nodes_back, nodes_forward# forwardnode = nodes_forward[node_middle.position]path_forward = [node.position]cost = node.costwhile node.position != self.start.position:node_parent = nodes_forward[node.parent.position]node = node_parentpath_forward.append(node.position)# backwardnode = nodes_back[node_middle.position]path_back = []cost += node.costwhile node.position != self.goal.position:node_parent = nodes_back[node.parent.position]node = node_parentpath_back.append(node.position)path = list(reversed(path_forward))+path_backreturn cost, pathdef get_expand(self, nodes_back, nodes_forward):expand = []tree_size = max(len(nodes_forward), len(nodes_back))for tr in range(tree_size):if tr < len(nodes_forward):expand.append(nodes_forward[tr])if tr < len(nodes_back):expand.append(nodes_back[tr])return expanddef visualize(self, cost, path):"""Plot the map."""...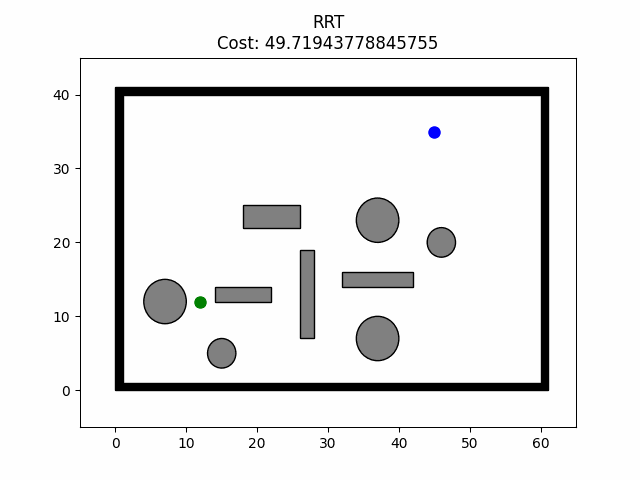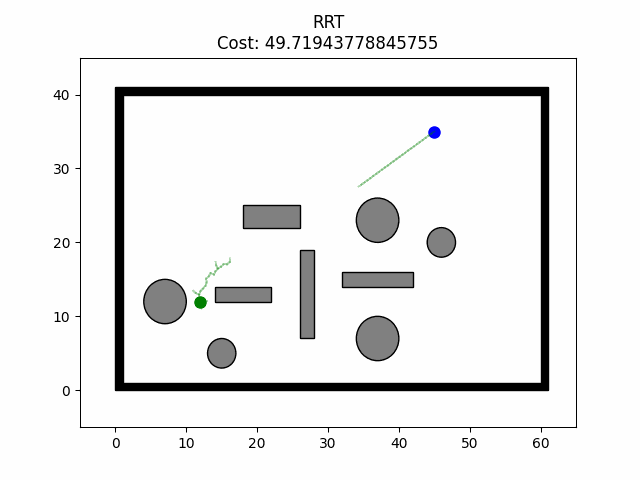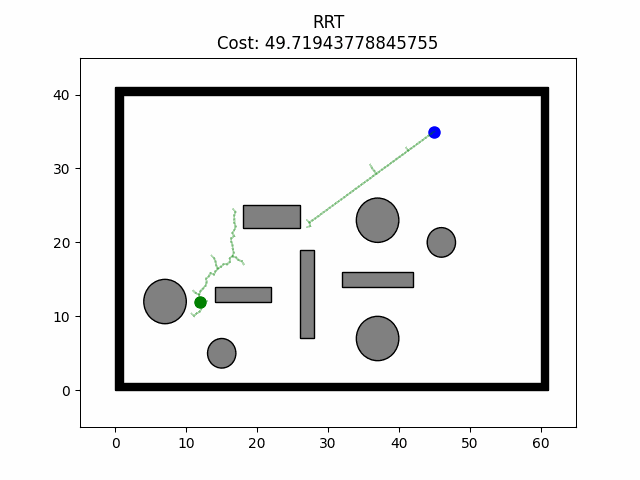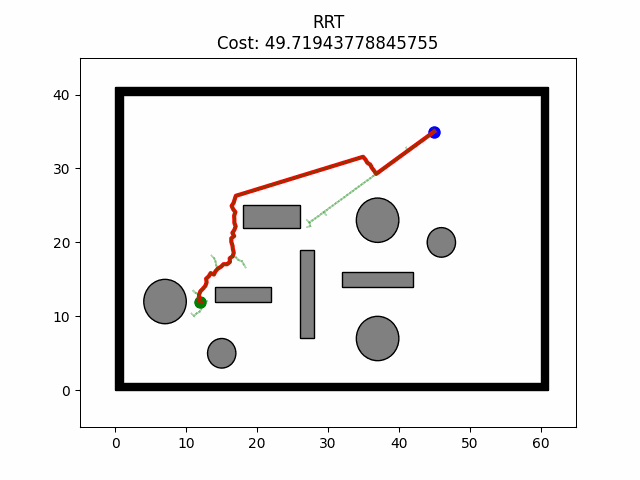
完整代码:PathPlanning
相关文章:

路径规划——RRT-Connect算法
路径规划——RRT-Connect算法 算法原理 RRT-Connect算法是在RRT算法的基础上进行的扩展,引入了双树生长,分别以起点和目标点为树的根节点同时扩展随机树从而实现对状态空间的快速搜索。在此算法中以两棵随机树建立连接为路径规划成功的条件。并且&…...

数据科学与SQL:如何计算排列熵?| 基于SQL实现
目录 0 引言 1 排列熵的计算原理 2 数据准备 3 问题分析 4 小结 0 引言 把“熵”应用在系统论中的信息管理方法称为熵方法。熵越大,说明系统越混乱,携带的信息越少;熵越小,说明系统越有序,携带的信息越多。在传感…...

Redis/Codis性能瓶颈揭秘:网卡软中断的影响与优化
目录 现象回顾 问题剖析 现场分析 解决方案 总结与反思 1.调整中断亲和性(IRQ Affinity): 2.RPS(Receive Packet Steering)和 RFS(Receive Flow Steering): 近期,…...
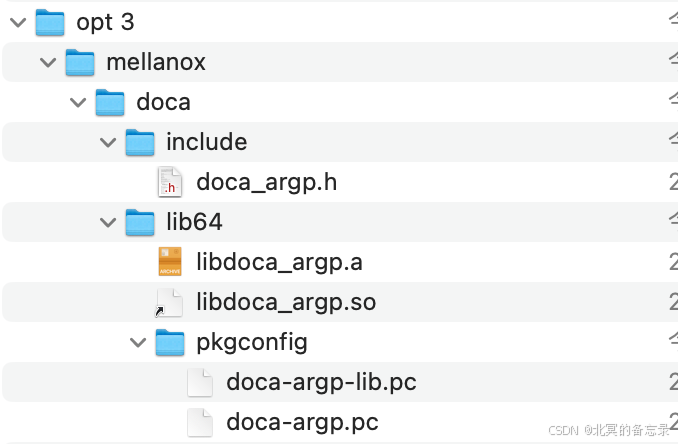
微知-DOCA ARGP参数模块的相关接口和用法(config单元、params单元,argp pipe line,回调)
文章目录 1. 背景2. 设置参数的主要流程2.1 初始化2.2 注册某个params的处理方式以及回调函数2.4 定义好前面的params以及init指定config地点后start处理argv 3. 其他4. DOCA ARGP包相关4.1 主要接口4.2 DOCA ARGP的2个rpm包4.2.1 doca-sdk-argp-2.9.0072-1.el8.x86_64.rpm4.2.…...
)
PostgreSQL高可用Patroni安装(超详细)
目录 一 安装Patroni 0 Patroni 对Python的版本要求 1 卸载原来的Python 3.6 版本 2 安装Python 3.7 之上版本 3 安装依赖 psycopg3 4 安装patroni 5 卸载 patroni 二 安装ETCD 1 使用 yum 安装 etcd 2 etcd 配置文件 3 管理 etcd 4 设置密码 5 常用命令 三 安装…...
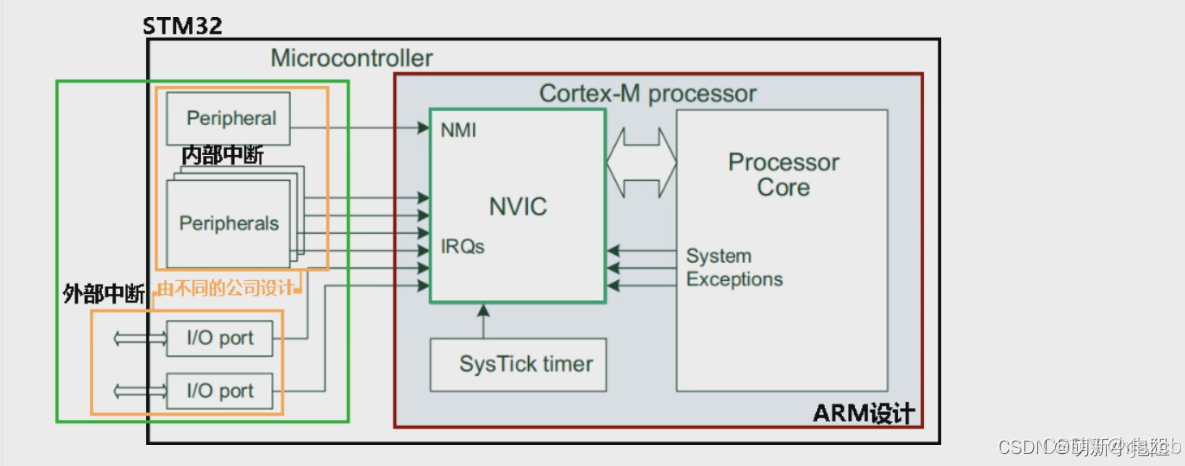
mcu之,armv7架构,contex-M4系列,时钟树,中断,IO架构(一)
写这篇文章的目的,是记录一下arm架构的32mcu,方便记忆芯片架构原理,方便我展开对,BootLoader的研究。 arm架构,时钟树,先做个记录,有空写。...
)
论文解析:基于区块链的去中心化服务选择,用于QoS感知的云制造(四区)
目录 论文解析:基于区块链的去中心化服务选择,用于QoS感知的云制造(四区) 基于区块链的去中心化云制造服务选择方法 一、核心内容概述 二、核心创新点及原理与理论 三、实验与理论分析 PBFT(实用拜占庭容错) 论文解析:基于区块链的去中心化服务选择,用于QoS感知的…...
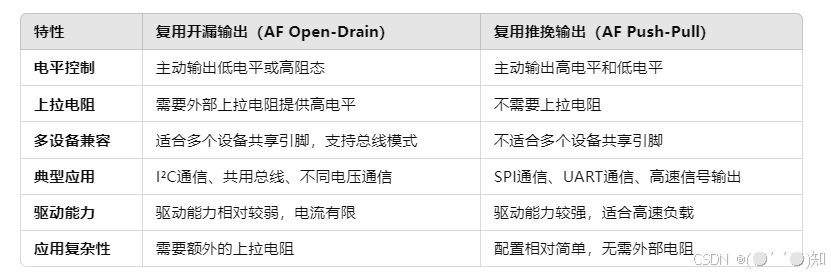
详细解析STM32 GPIO引脚的8种模式
目录 一、输入浮空(Floating Input):GPIO引脚不连接任何上拉或下拉电阻,处于高阻态 1.浮空输入的定义 2.浮空输入的特点 3.浮空输入的应用场景 4.浮空输入的缺点 5.典型配置方式 6.注意事项 二、输入上拉(Inpu…...

【hacker送书第16期】Python数据分析、挖掘与可视化、AI全能助手ChatGPT职场工作效率提升技巧与案例
解锁数据分析与AI应用的双重秘密:全面推广《Python数据分析、挖掘与可视化从入门到精通》与《AI全能助手ChatGPT职场工作效率提升技巧与案例》 前言Python数据分析、挖掘与可视化从入门到精通💕内容简介获取方式 AI全能助手ChatGPT职场工作效率提升技巧与…...

翼鸥教育:从OceanBase V3.1.4 到 V4.2.1,8套核心集群升级实践
引言:自2021年起,翼鸥教育便开始应用OceanBase社区版,两年间,先后部署了总计12套生产集群,其中核心集群占比超过四分之三,所承载的数据量已突破30TB。自2022年10月,OceanBase 社区发布了4.2.x 版…...

WebGIS开发中不同坐标系坐标转换问题
在 JavaScript 中,使用 proj4 库进行坐标系转换是一个非常常见的操作。proj4 是一个支持多种坐标系的 JavaScript 库,提供了从一种坐标系到另一种坐标系的转换功能。 以下是使用 proj4 进行坐标系转换的基本步骤: 1. 安装 proj4 你可以通过…...
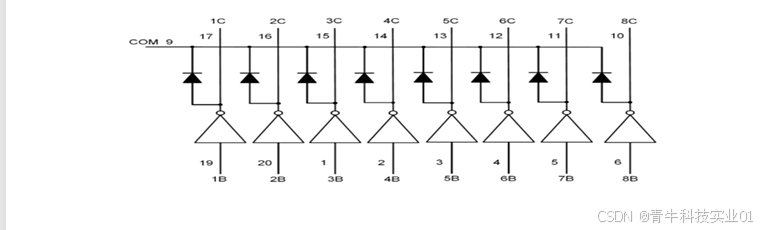
【青牛科技】视频监控器应用
1、简介: 我司安防产品广泛应用在视频监控器上,产品具有性能优良,可 靠性高等特点。 2、图示: 实物图如下: 3、具体应用: 标题:视频监控器应用 简介:视频监控器工作原理是光&#x…...
AWTK-WIDGET-WEB-VIEW 实现笔记 (3) - MacOS
MacOS 上实现 AWTK-WIDGET-WEB-VIEW 有点麻烦,主要原因是没有一个简单的办法将一个 WebView 嵌入到一个窗口中。所以,我们只能通过创建一个独立的窗口来实现。 1. 创建窗口 我对 Object-C 不熟悉,也不熟悉 Cocoa 框架,在 ChatGPT…...
PgSQL即时编译JIT | 第1期 | JIT初识
PgSQL即时编译JIT | 第1期 | JIT初识 JIT是Just-In-Time的缩写,也就是说程序在执行的时候生成可以执行的代码,然后执行它。在介绍JIT之前,需要说下两种执行方式:解释执行和编译执行。其中解释执行是通过解释器,将代码逐…...

Go小记:使用Go实现ssh客户端
一、前言 SSH(Secure Shell)是一种用于在不安全网络上安全访问远程计算机的网络协议。它通过加密的方式提供远程登录会话和其他网络服务,保证通信的安全性和数据的完整性。 本文使用golang.org/x/crypto/ssh包来实现SSH客户端 可以通过go …...

Nginx Spring boot指定域名跨域设置
1、Nginx配置跨域: server {listen 80;server_name your-backend-service.com;location / {proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; # Spring Boot应用的内部地址proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-F…...

深入理解Redis(七)----Redis实现分布式锁
基于Redis的实现方式 1、选用Redis实现分布式锁原因: (1)Redis有很高的性能; (2)Redis命令对此支持较好,实现起来比较方便 2、使用命令介绍: (1)SETNX SETNX …...
)
Database Advantages (数据库系统的优点)
数据库管理系统(DBMS)提供了一种结构化的方式来存储、管理和访问数据,与传统的文件处理系统相比,数据库提供了许多显著的优点。以下是数据库系统的主要优势: 1. Data Integrity (数据完整性) 概念:数据完整…...
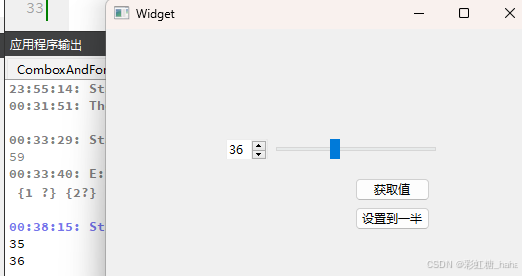
Qt桌面应用开发 第五天(常用控件)
目录 1.QPushButton和ToolButton 1.1QPushButton 1.2ToolButton 2.RadioButton和CheckBox 2.1RadioButton单选按钮 2.2CheckBox多选按钮 3.ListWidget 4.TreeWidget控件 5.TableWidget控件 6.Containers控件 6.1QScrollArea 6.2QToolBox 6.3QTabWidget 6.4QStacke…...
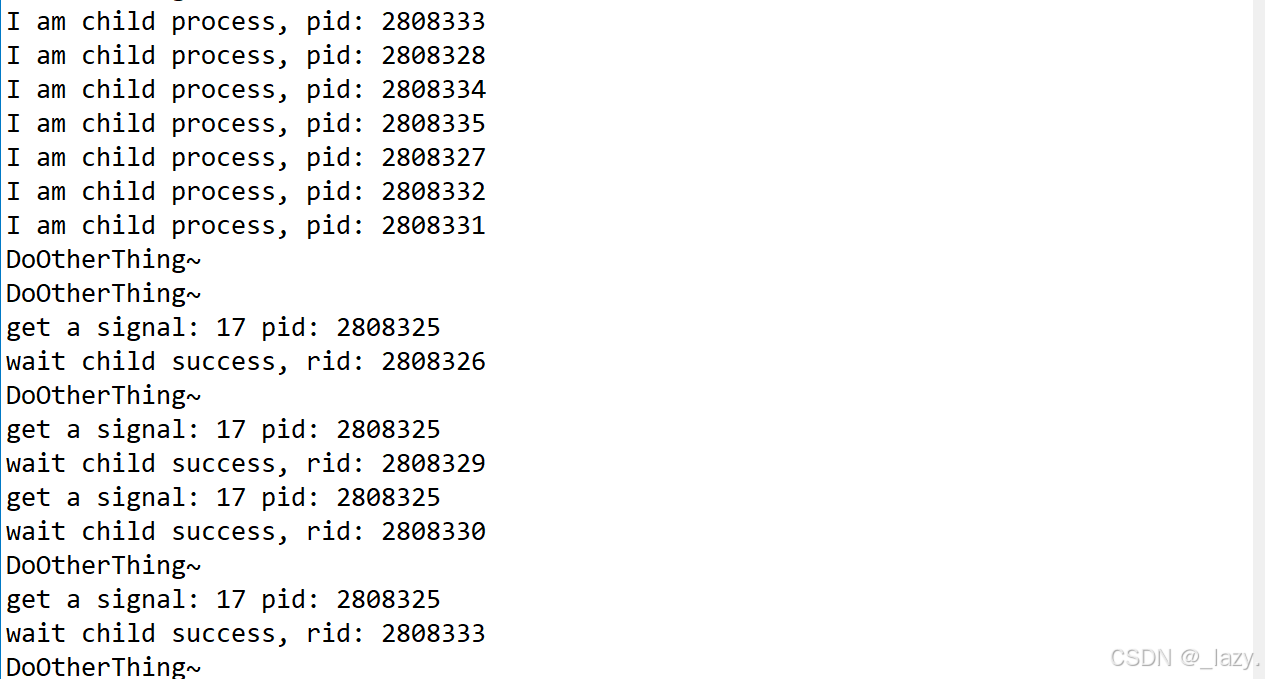
初识Linux · 信号处理 · 续
目录 前言: 可重入函数 重谈进程等待和优化 前言: 在前文,我们已经介绍了信号产生,信号保存,信号处理的主题内容,本文作为信号处理的续篇,主要是介绍一些不那么重要的内容,第一个…...
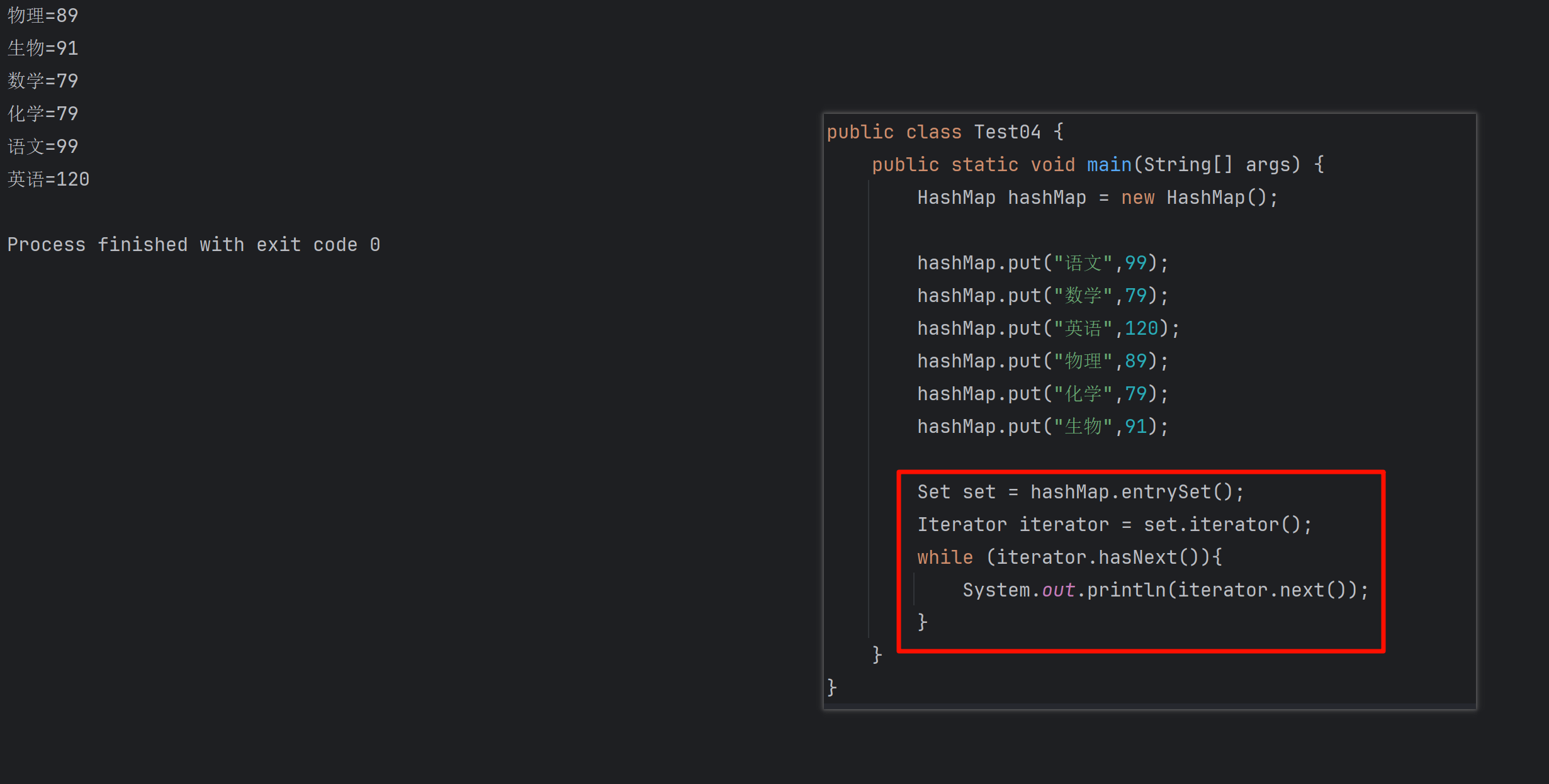
遍历 Map 类型集合的方法汇总
1 方法一 先用方法 keySet() 获取集合中的所有键。再通过 gey(key) 方法用对应键获取值 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap hashMap new HashMap();hashMap.put("语文",99);has…...

Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility
Cilium动手实验室: 精通之旅---20.Isovalent Enterprise for Cilium: Zero Trust Visibility 1. 实验室环境1.1 实验室环境1.2 小测试 2. The Endor System2.1 部署应用2.2 检查现有策略 3. Cilium 策略实体3.1 创建 allow-all 网络策略3.2 在 Hubble CLI 中验证网络策略源3.3 …...

Spring是如何解决Bean的循环依赖:三级缓存机制
1、什么是 Bean 的循环依赖 在 Spring框架中,Bean 的循环依赖是指多个 Bean 之间互相持有对方引用,形成闭环依赖关系的现象。 多个 Bean 的依赖关系构成环形链路,例如: 双向依赖:Bean A 依赖 Bean B,同时 Bean B 也依赖 Bean A(A↔B)。链条循环: Bean A → Bean…...

JS手写代码篇----使用Promise封装AJAX请求
15、使用Promise封装AJAX请求 promise就有reject和resolve了,就不必写成功和失败的回调函数了 const BASEURL ./手写ajax/test.jsonfunction promiseAjax() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {const xhr new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open("get&quo…...

前端开发者常用网站
Can I use网站:一个查询网页技术兼容性的网站 一个查询网页技术兼容性的网站Can I use:Can I use... Support tables for HTML5, CSS3, etc (查询浏览器对HTML5的支持情况) 权威网站:MDN JavaScript权威网站:JavaScript | MDN...
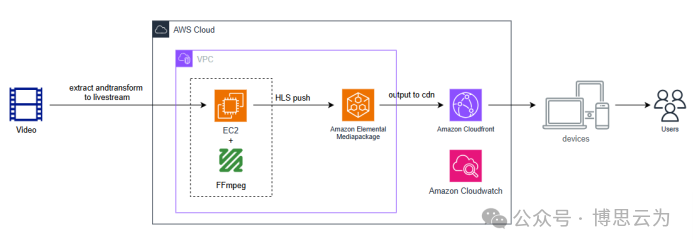
客户案例 | 短视频点播企业海外视频加速与成本优化:MediaPackage+Cloudfront 技术重构实践
01技术背景与业务挑战 某短视频点播企业深耕国内用户市场,但其后台应用系统部署于东南亚印尼 IDC 机房。 随着业务规模扩大,传统架构已较难满足当前企业发展的需求,企业面临着三重挑战: ① 业务:国内用户访问海外服…...

基于Uniapp的HarmonyOS 5.0体育应用开发攻略
一、技术架构设计 1.混合开发框架选型 (1)使用Uniapp 3.8版本支持ArkTS编译 (2)通过uni-harmony插件调用原生能力 (3)分层架构设计: graph TDA[UI层] -->|Vue语法| B(Uniapp框架)B --&g…...
)
iOS 项目怎么构建稳定性保障机制?一次系统性防错经验分享(含 KeyMob 工具应用)
崩溃、内存飙升、后台任务未释放、页面卡顿、日志丢失——稳定性问题,不一定会立刻崩,但一旦积累,就是“上线后救不回来的代价”。 稳定性保障不是某个工具的功能,而是一套贯穿开发、测试、上线全流程的“观测分析防范”机制。 …...
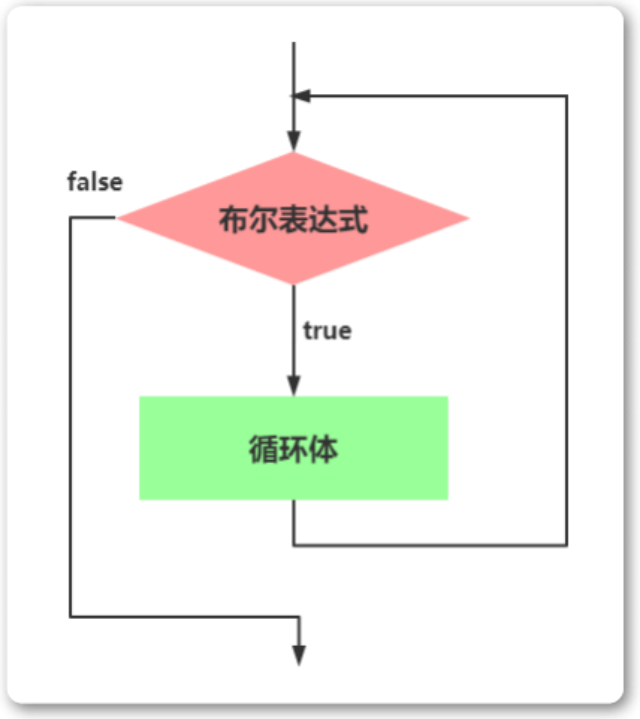
循环语句之while
While语句包括一个循环条件和一段代码块,只要条件为真,就不断 循环执行代码块。 1 2 3 while (条件) { 语句 ; } var i 0; while (i < 100) {console.log(i 当前为: i); i i 1; } 下面的例子是一个无限循环,因…...
)
Vue3学习(接口,泛型,自定义类型,v-for,props)
一,前言 继续学习 二,TS接口泛型自定义类型 1.接口 TypeScript 接口(Interface)是一种定义对象形状的强大工具,它可以描述对象必须包含的属性、方法和它们的类型。接口不会被编译成 JavaScript 代码,仅…...
