排序:插入、选择、交换、归并排序
外部排序:数据元素太多不能同时放在内存中,根据排序过程的要求不能在内外存之间移动数据的排序。

#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <memory.h>
//打印
void PrintArray(int* a, int n);
// 排序实现的接口
// 插入排序
void InsertSort(int* a, int n);
// 希尔排序
void ShellSort(int* a, int n);
// 选择排序
void SelectSort(int* a, int n);
// 堆排序
void AdjustDwon(int* a, int n, int root);
void HeapSort(int* a, int n);
// 冒泡排序
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n);
// 快速排序递归实现
// 快速排序hoare版本
int PartSort1(int* a, int begin, int end);
//三数取中
int GetMidindex(int* a, int begin, int end);
// 快速排序挖坑法
int PartSort2(int* a, int begin, int end);
// 快速排序前后指针法
int PartSort3(int* a, int begin, int end);
void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right);
// 快速排序 非递归实现
void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int left, int right);
// 归并排序递归实现
void MergeSort(int* a, int n);
// 归并排序非递归实现
void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n);
// 计数排序
void CountSort(int* a, int n);
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Sort.h"
#include "Stack.h"
//打印
void PrintArray(int* a, int n)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//插入排序 O(N^2)
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + 1];
//将end+1的数据插入到[0,end]有序数组中
while (end >= 0)
{
if (tmp < a[end])
{
a[end + 1] = a[end];
end--;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + 1] = tmp;
}
}

// 希尔排序 O(N^1.3 N^2)
void ShellSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
//1. gap > 1 相当于预排序,让数组接近有序
//2. gap==1就相当于直接插入排序,保证有序
int gap = n;
while (gap > 1)
{
gap = gap / 3 + 1;//+1是保证最后一次排序gap等于1
//gap==1,最后一次就相当于直接插入排序
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n - gap; i++)
{
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + gap];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (tmp < a[end])
{
a[end + gap] = a[end];
end = end - gap;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + gap] = tmp;
}
//PrintArray(a, n);
}
}
void Swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{
int tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
// 选择排序
// O(N^2)
void SelectSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int begin = 0;
int end = n - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
int maxi = begin;
int mini = begin;
int i = 0;
for (i = begin + 1; i <= end; i++)
{
if (a[i] > a[maxi])
{
maxi = i;
}
if (a[i] < a[mini])
{
mini = i;
}
}
Swap(&a[mini], &a[begin]);
//maxi和begin的位置重叠,maxi的位置需要修正
if (maxi == begin)//max被换走了
{
maxi = mini;//找到max
}
Swap(&a[maxi], &a[end]);
begin++;
end--;
}
}
// 堆排序
void AdjustDwon(int* a, int n, int root)
{
int parent = root;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
//选出较大的孩子
if (a[child + 1] > a[child] && child + 1 < n)
{
child++;
}
if (a[child] > a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{
//排升序,建大堆还是小堆?
int i = 0;
for (i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0 ; i--)
{
AdjustDwon(a, n, i);
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0)
{
Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);
AdjustDwon(a, end, 0);
--end;
}
}

// 冒泡排序 O(N^2)
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
int flag = 1;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (a[j] > a[j + 1])
{
Swap(&a[j], &a[j + 1]);
flag = 0;
}
}
//如果一趟冒泡排序过程中没有发生交换,则已经有序,不需要再进行冒泡排序
if (flag == 1)
{
break;
}
}
}
//三数取中
int GetMidindex(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int mid = (begin + end) / 2 ;
if (a[begin] < a[mid])
{
if (a[mid] < a[end])
{
return mid;
}
else if (a[begin] > a[end])
{
return begin;
}
else
{
return end;
}
}
else//a[begin] > a[mid]
{
if (a[mid] > a[end])
{
return mid;
}
else if (a[begin] < a[end])
{
return begin;
}
else
{
return end;
}
}
}
//左右指针法
int PartSort1(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int mid = GetMidindex(a, begin, end);
Swap(&a[mid], &a[end]);
int keyindex = end;//右边做key
while (begin < end)
{
//左边先走,//left < right防止在++的时候超出,而错过相遇
while (begin < end && a[begin] <= a[keyindex])//左边找比key大,
{
begin++;
}
//右边找比key小
while (begin < end && a[end] >= a[keyindex])
{
end--;
}
//交换left和right位置的值
Swap(&a[begin], &a[end]);
}
//交换key和相遇位置的值
Swap(&a[begin], &a[keyindex]);
return begin;
}
// 快速排序挖坑法
int PartSort2(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int mid = GetMidindex(a, begin, end);
Swap(&a[mid], &a[end]);
//坑
int key = a[end];
while (begin < end)
{
//左边找比key大的
while (begin < end && a[begin] <= key)
{
begin++;
}
//将找到的数填在end位置,然后形成新的坑
a[end] = a[begin];
//右边找比key小的数
while (begin < end && a[end] >= key)
{
end--;
}
//将找到的数填在begin的位置,然后形成新的坑
a[begin] = a[end];
}
//begin和end相遇,循环结束,将key的值填入begin的位置
a[begin] = key;
return begin;
}
// 快速排序前后指针法
int PartSort3(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
int mid = GetMidindex(a, begin, end);
Swap(&a[mid], &a[end]);
int key = a[end];
int keyindex = end;
int cur = begin;
int prev = begin - 1;;
while (cur < end)
{
while (a[cur] <= a[keyindex] && ++prev != cur)
{
Swap(&a[cur], &a[prev]);
}
++cur;
}
Swap(&a[++prev], &a[keyindex]);
return prev;
}
//时间复杂度O(N*log N)
//空间复杂度 O(log N)
void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right)
{
assert(a);
//[left,div-1] , [div+1,right]
if (left >= right)
return;
if ((right - left + 1) > 10)
{
//int div = PartSort1(a, left, right);
//int div = PartSort2(a, left, right);
int div = PartSort3(a, left, right);
//PrintArray(a+left, right-left+1);
//printf("[%d %d] %d [%d %d]", left, div - 1, div, div + 1, right);
//printf("\n");
QuickSort(a, left, div - 1);
QuickSort(a, div + 1, right);
}
else
{
//小于等于10个数,直接选插入排序,不在递归排序
InsertSort(a + left, right - left + 1);
}
}
// 快速排序 非递归实现
//递归改非递归
//-->1.改循环(斐波拉契数列求解),一些简单递归才能改循环
//-->2.栈模拟存储数据非递归
//非递归:1.提高效率(递归建立栈还是有消耗的,但是对于现代的计算机,这个优化微乎其微,可以忽略不计)
// 2.递归的最大缺陷是,如果栈的深度太深,可能会导致栈溢出,因为系统栈空间一般不大,在M级别
// 数据结构模拟非递归,数据是存储在堆上的,堆是G级别的空间
void QuickSortNonR(int* a, int left, int right)
{
assert(a);
//栈来实现快速排序
Stack st;//定义栈
StackInit(&st);
//先入右边,在入左边
StackPush(&st, right);
StackPush(&st, left);
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
int begin = StackTop(&st);//左边
StackPop(&st);//先出一个
int end = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
int div = PartSort1(a, begin, end);
//先处理左边
if (begin < div - 1)//左边至少有两个数据
{
StackPush(&st, div - 1);
StackPush(&st, begin);
}
//处理右边
if (end > div + 1)//至少有两个数据
{
StackPush(&st, end);
StackPush(&st, div + 1);
}
}
//销毁栈,防止内存泄漏
StackDestory(&st);
}
void _MergeArray(int* a, int begin1, int end1, int begin2, int end2, int* tmp)
{
//递归完了得到两个有序数组
//归并
int left = begin1;
int right=end2;
int index = begin1;
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (a[begin1] < a[begin2])
{
tmp[index] = a[begin1];
index++;
begin1++;
}
else
{
tmp[index] = a[begin2];
index++;
begin2++;
}
}
//应该还有一个数组还有剩余元素
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[index++] = a[begin2++];
}
//把归并好的在tmp数组的元素拷贝回原来数组a
int i = 0;
for (i = left; i <= right; i++)
{
a[i] = tmp[i];
}
}
void _MergeSort(int* a, int left, int right, int* tmp)
{
//递归截止条件
if (left >= right)
{
return;
}
//先递归
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
//[left,mid],[mid+1,right]
_MergeSort(a, left, mid, tmp);
_MergeSort(a, mid + 1, right, tmp);
_MergeArray(a, left, mid, mid + 1, right, tmp);
}
// 归并排序递归实现
//时间复杂度 O(N*logN)
//空间复杂度 O(N)
void MergeSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("申请内存失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
_MergeSort(a, 0, n - 1, tmp);
free(tmp);//释放内存,防止内存泄漏
}


// 归并排序非递归实现
void MergeSortNonR(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
int gap = 1;
while (gap < n)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i = i + 2 * gap)
{
//使用闭区间
//[i,i+gap-1],[i+gap,i+2*gap-1]
int begin1 = i;
int end1 = i + gap - 1;
int begin2 = i + gap;
int end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
//1、合并时只有第一组,第二组不需要合并
if (begin2 >= n)
{
break;
}
//2、合并时第二组只有部分数据,需要修改边界值
if (end2 >= n)
{
end2 = n - 1;
}
_MergeArray(a, begin1, end1, begin2, end2, tmp);
}
gap = gap * 2;
PrintArray(a, n);
}
}

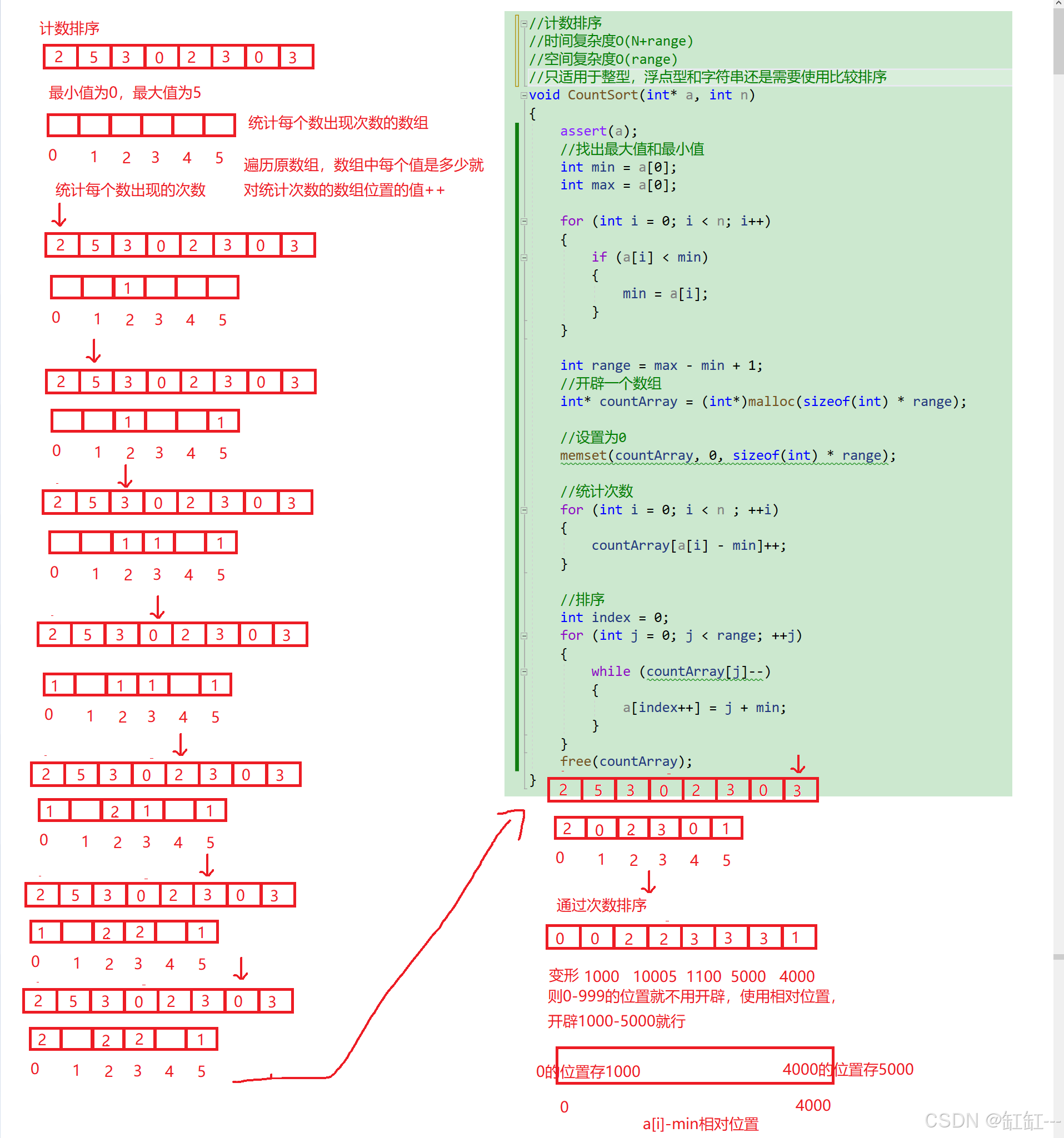
//计数排序
//时间复杂度O(N+range)
//空间复杂度O(range)
//只适用于整型,浮点型和字符串还是需要使用比较排序
void CountSort(int* a, int n)
{
assert(a);
//找出最大值和最小值
int min = a[0];
int max = a[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] > max)
{
max = a[i];
}
if (a[i] < min)
{
min = a[i];
}
}
int range = max - min + 1;
//开辟一个数组
int* countArray = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * range);
//设置为0
memset(countArray, 0, sizeof(int) * range);
//统计次数
for (int i = 0; i < n ; ++i)
{
countArray[a[i] - min]++;
}
//排序
int index = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < range; ++j)
{
while (countArray[j]--)
{
a[index++] = j + min;
}
}
free(countArray);
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Sort.h"
#include "Stack.h"
void TestInsertSort()
{
int a[] = { 2,1,4,3,9,6,4,0,5,8 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
InsertSort(a, sz);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
TestShellSort()
{
int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
ShellSort(a, sz);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestSelectSort()
{
int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
SelectSort(a, sz);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestHeapSort()
{
int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
HeapSort(a, sz);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestBubbleSort()
{
int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
BubbleSort(a, sz);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestQuickSort()
{
//int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int a[] = { 2,1,4,3,9,6,4,0,5,8 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
QuickSort(a, 0,sz-1);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestQuickSortNonR()
{
//int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int a[] = { 2,1,4,3,9,6,4,0,5,8 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
QuickSortNonR(a, 0, sz - 1);
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestMergeSort()
{
//int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int a[] = { 10,6,7,1,3,9,4,2 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
MergeSort(a, sz);//不是sz-1,如果是sz-1,会导致最后一个元素没有排到
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestMergeSortNonR()
{
//int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int a[] = { 10,6,7,1,3,9,4 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
//PrintArray(a, sz);
MergeSortNonR(a, sz);//不是sz-1,如果是sz-1,会导致最后一个元素没有排到
//PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestCountSort()
{
//int a[] = { 20,19,18,17,16,15,14,13,12,11,10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
int a[] = { 10,6,7,1,3,9,4 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
PrintArray(a, sz);
CountSort(a, sz);//不是sz-1,如果是sz-1,会导致最后一个元素没有排到
PrintArray(a, sz);
}
void TestOP()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 100000;
int* a1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
int* a2 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
int* a3 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
int* a4 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
int* a5 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
int* a6 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
a1[i] = rand();
a2[i] = a1[i];
a3[i] = a1[i];
a4[i] = a1[i];
a5[i] = a1[i];
a6[i] = a1[i];
}
int begin1 = clock();
InsertSort(a1, N);
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
ShellSort(a2, N);
int end2 = clock();
int begin3 = clock();
SelectSort(a3, N);
int end3 = clock();
int begin4 = clock();
HeapSort(a4, N);
int end4 = clock();
int begin5 = clock();
BubbleSort(a5, N);
int end6 = clock();
int begin7 = clock();
QuickSort(a5, 0, N-1);
int end8 = clock();
int begin9 = clock();
QuickSortNonR(a5, 0, N - 1);
int end10 = clock();
/*int begin5 = clock();
QuickSort(a5, 0, N - 1);
int end5 = clock();
int begin6 = clock();
MergeSort(a6, N);
int end6 = clock();*/
//printf("InsertSort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("ShellSort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
printf("SelectSort:%d\n", end3 - begin3);
printf("HeapSort:%d\n", end4 - begin4);
//printf("BubbleSort:%d\n", end6 - begin5);
printf("QuickSort:%d\n", end8 - begin7);
printf("QuickSortNonR:%d\n", end10 - begin9);
/*printf("QuickSort:%d\n", end5 - begin5);
printf("MergeSort:%d\n", end6 - begin6);
free(a1);
free(a2);
free(a3);
free(a4);
free(a5);
free(a6);*/
}
int main()
{
//TestInsertSort();
//TestShellSort();
//TestSelectSort();
//TestHeapSort();
//TestBubbleSort();
//TestQuickSort();
//TestQuickSortNonR();
//TestMergeSort();
//TestMergeSortNonR();
//MergeSortFile("Sort.txt");
TestCountSort();
//TestOP();
return 0;
}
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
//用数组来实现
//静态的数组
//#define N 10
//struct Stack
//{
// int _a[N];
// int _top;
//};
//动态的数组
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top;//栈顶下标
int _capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst);
//销毁
void StackDestory(Stack* pst);
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x);
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst);
//获取数据个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst);
//返回1是空,返回0是非空
int StackEmpty(Stack* pst);
//获取栈顶的数据
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Stack.h"
//初始化
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//pst->_a = NULL;
//pst->_top = 0;
//pst->_capacity = 0;
pst->_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
pst->_top = 0;
pst->_capacity = 4;
}
//销毁
void StackDestory(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->_a);
pst->_a = NULL;
pst->_top = 0;
pst->_capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->_top == pst->_capacity)//满了需要增容
{
pst->_capacity *= 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->_a, pst->_capacity*sizeof(STDataType) );
if (tmp == NULL)//增容失败
{
printf("增容失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
else//将tmp给pst->_a,指向它
{
pst->_a = tmp;
}
}
pst->_a[pst->_top] = x;
pst->_top++;
}
//出栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);
--pst->_top;
}
//获取数据个数
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->_top;
}
//返回1是空,返回0是非空
int StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->_top == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
//获取栈顶的数据
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);
return pst->_a[pst->_top - 1];//pst->_top是元素的个数
}
相关文章:

排序:插入、选择、交换、归并排序
排序 :所谓排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作。 稳定性 :假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,…...
认识+安装ElasticSearch
1. 为什么要学习ElasticSearch? 一般的来说,项目中的搜索功能尤其是电商项目,商品的搜索肯定是访问频率最高的页面之一。目前搜索功能是基于数据库的模糊搜索来实现的,存在很多问题。 1.1 数据库搜索所存在的问题 1.1.1 查询效率较低 由于数据库模糊查询不走索引&…...
一个模块实现期货分钟 K 线计算、主连行情合成
由于不同期货品种的交易时间存在差异,且不同期货合约的活跃度各不相同,因此基于期货快照行情数据合成分钟K线的计算方法在时间对齐上需要进行不同的处理。 本教程旨在提升 DolphinDB 在具体业务场景中的应用效率,并降低其在实际业务中的开发…...
和.max(0)的使用)
PyTorch:.max(1)和.max(0)的使用
目录 1).max(1)的使用: 2).max(0)的使用: 1).max(1)的使用: 假设有一个形状为 ( m , n ) 的 Tensor x ,其中m表示行数,n表示列数。 x.max(1) ,相当于x.max(dim1) 。作…...

ASP.NET Core 中使用 Cookie 身份验证
在 ASP.NET Core 中使用 Cookie 身份验证,通常是为了实现用户的登录和授权。以下是配置 Cookie 身份验证的步骤。 1. 安装必要的 NuGet 包 首先,确保项目中包含 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies 包。你可以通过 NuGet 包管理器或命令行安…...
Ollama私有化部署大语言模型LLM
目录 一、Ollama介绍 二、安装Ollama 1、标准安装 2、国内加速 三、升级Ollama版本 四、使用Ollama 1、启动ollama服务 systemctl start ollama.service ollama serve 2、使用ollama命令 ollama run 运行模型 ollama ps 查看正在运行的模型 ollama list 查看(本地)…...

安卓app抓包总结(精)
前言 这里简单记录一下相关抓包工具证书的安装 burp证书安装 安装证书到移动设备(安卓7以后必须上传到设备系统根证书上) 导出证书 openssl x509 -inform DER -in cacert.der -out cacert.pem 转换格式 openssl x509 -inform PEM -subject_hash_old -in cacert.pem …...

Three.js 性能优化:打造流畅高效的3D应用
文章目录 前言一、减少几何体复杂度(Reduce Geometry Complexity)二、合并几何体(Merge Geometries)三、使用缓冲区几何体(Use BufferGeometries)四、纹理压缩与管理(Texture Compression and M…...

PHP 在 2025 年的现状与展望
PHP 在 2025 年依然强劲,继续为超过 77% 使用已知服务器端编程语言的网站提供动力。这并非仅仅依靠遗留代码,像 WordPress、Shopify 和 Laravel 这样的主流平台持续推动 PHP 的发展,使其保持着 актуальность 并不断进化。 为什么…...
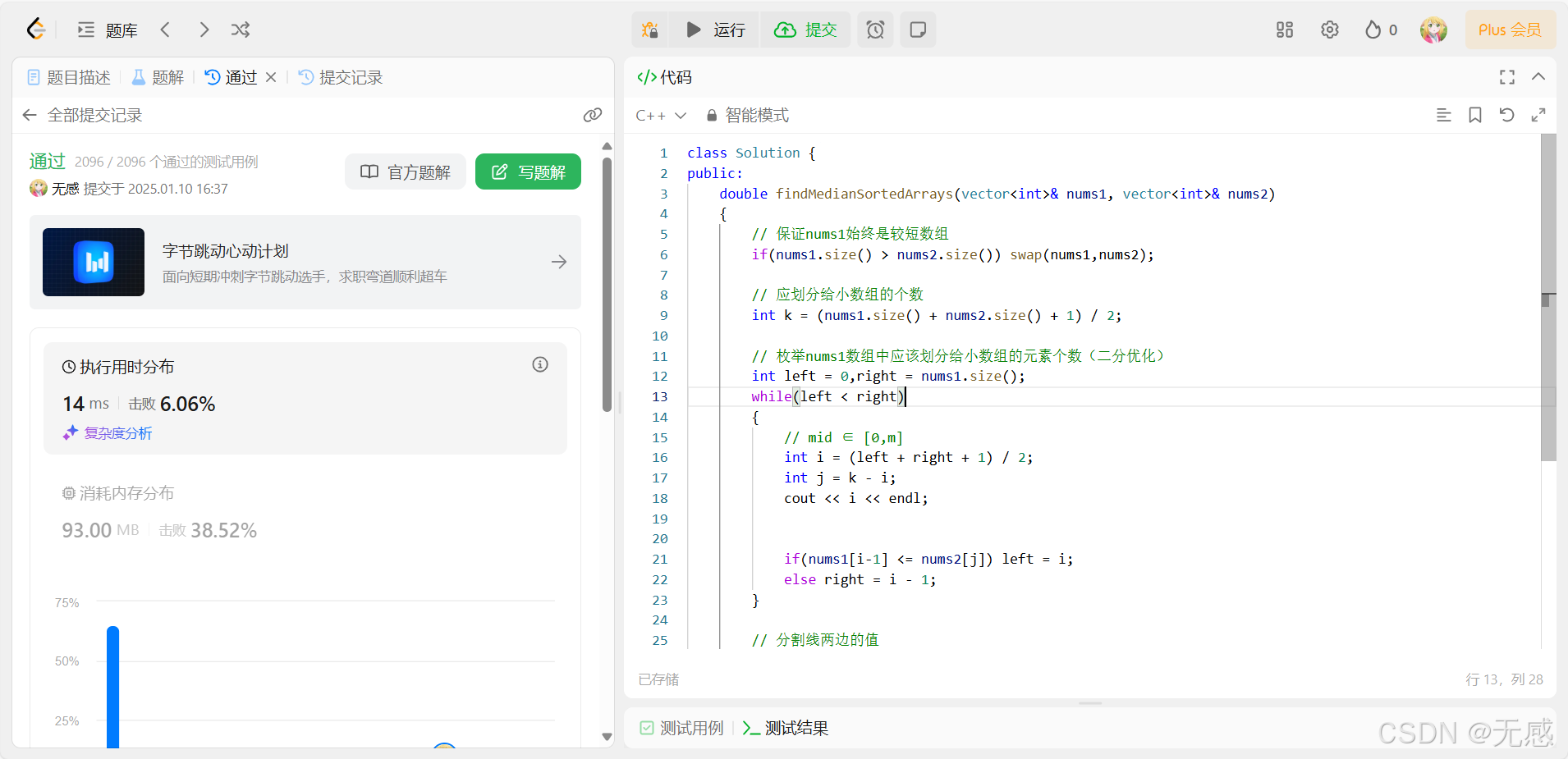
力扣经典二分题:4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
题目链接:4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode) 一、题目分析 这道题目是让我们在 两个正序的数组中寻找中位数已知两个数组的大小分别是:int m nums1.size(),n nums2.size();中位数性质1:中位数左侧元素 …...
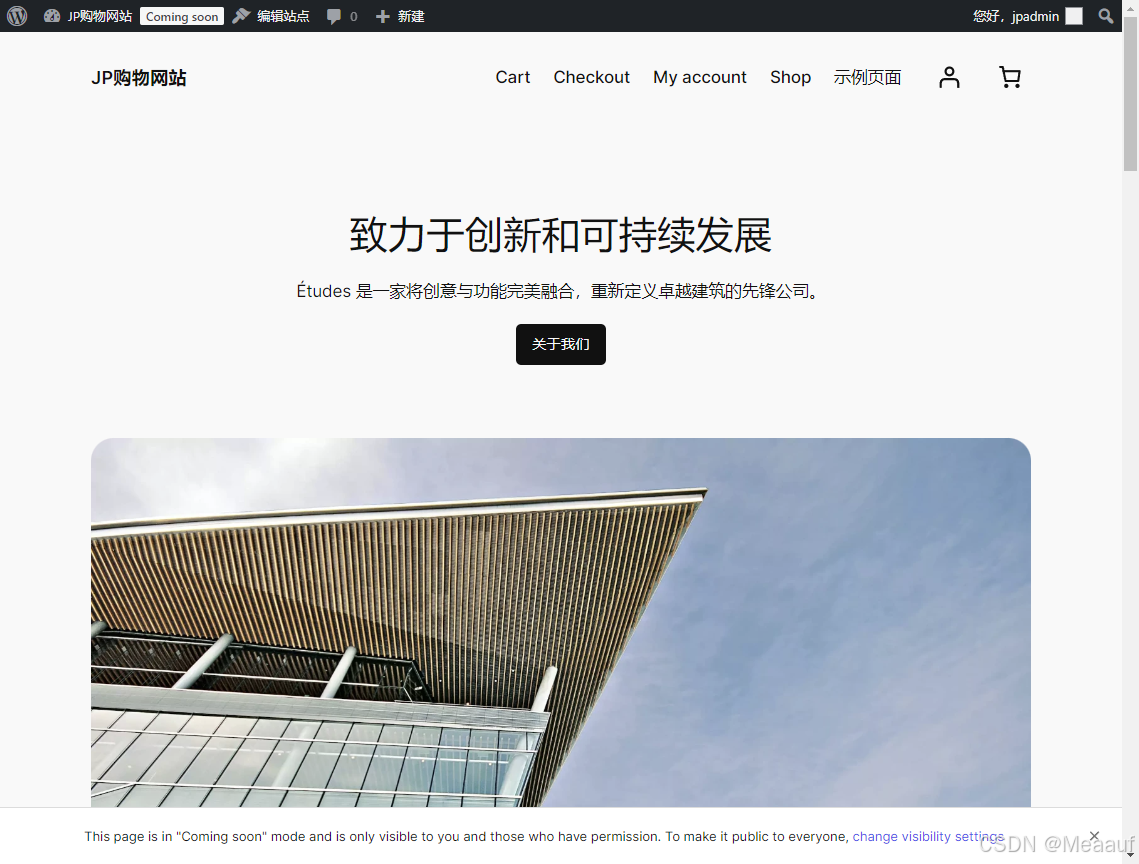
解决WordPress出现Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: ftp_nlist()致命问题
错误背景 WordPress版本:wordpress-6.6.2-zh_CN WooCommerce版本:woocommerce.9.5.1 WordPress在安装了WooCommerce插件后,安装的过程中没有问题,在安装完成后提示: 此站点遇到了致命错误,请查看您站点管理…...
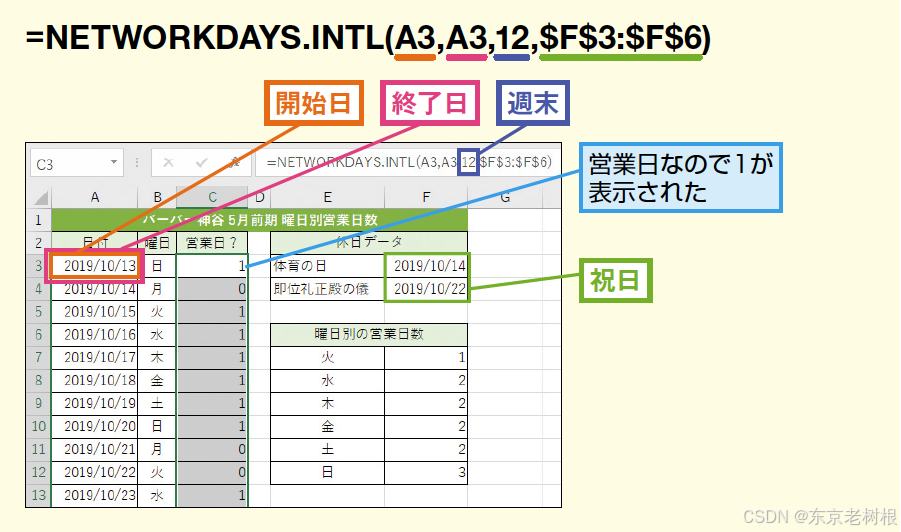
Excel 技巧07 - 如何计算到两个日期之间的工作日数?(★)如何排除节假日计算两个日期之间的工作日数?
本文讲了如何在Excel中计算两个日期之间的工作日数,以及如何排除节假日计算两个日期之间的工作日数。 1,如何计算到两个日期之间的工作日数? 其实就是利用 NETWORKDAYS.INTL 函数 - weekend: 1 - 星期六,星期日 2,如…...

快速实现一个快递物流管理系统:实时更新与状态追踪
物流管理是电商、仓储和配送等行业的重要组成部分。随着电子商务的快速发展,快递物流的高效管理和实时状态更新变得尤为关键。本文将演示如何使用Node.js、Express、MongoDB等技术快速构建一个简单的快递物流管理系统,该系统支持快递订单的实时更新和追踪…...
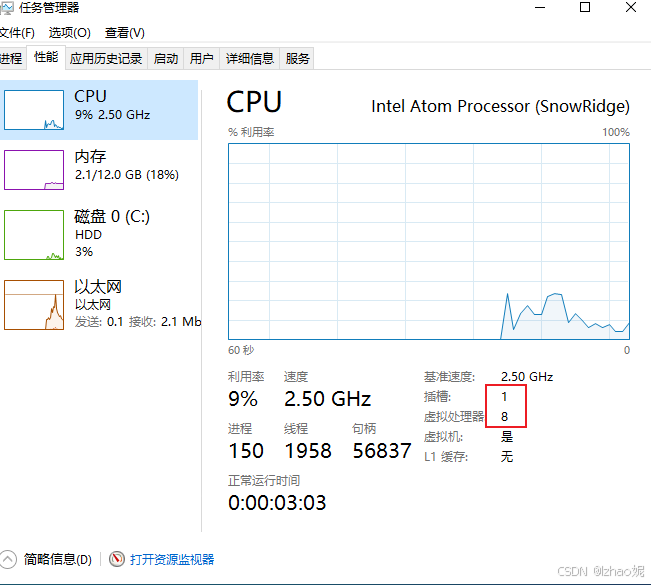
kvm 解决 安装windows 虚拟机cpu 核数问题
通过lscpu命令查到我本机的cpu信息如下 CPU(s): 12 —— 系统的总逻辑处理单元数量(包括所有核心和逻辑处理器)。Thread(s) per core: 2 —— 每个物理核心支持 2 个线程(表示启用了超线程技术)。Core(s) per socket: 6 —— 每个…...
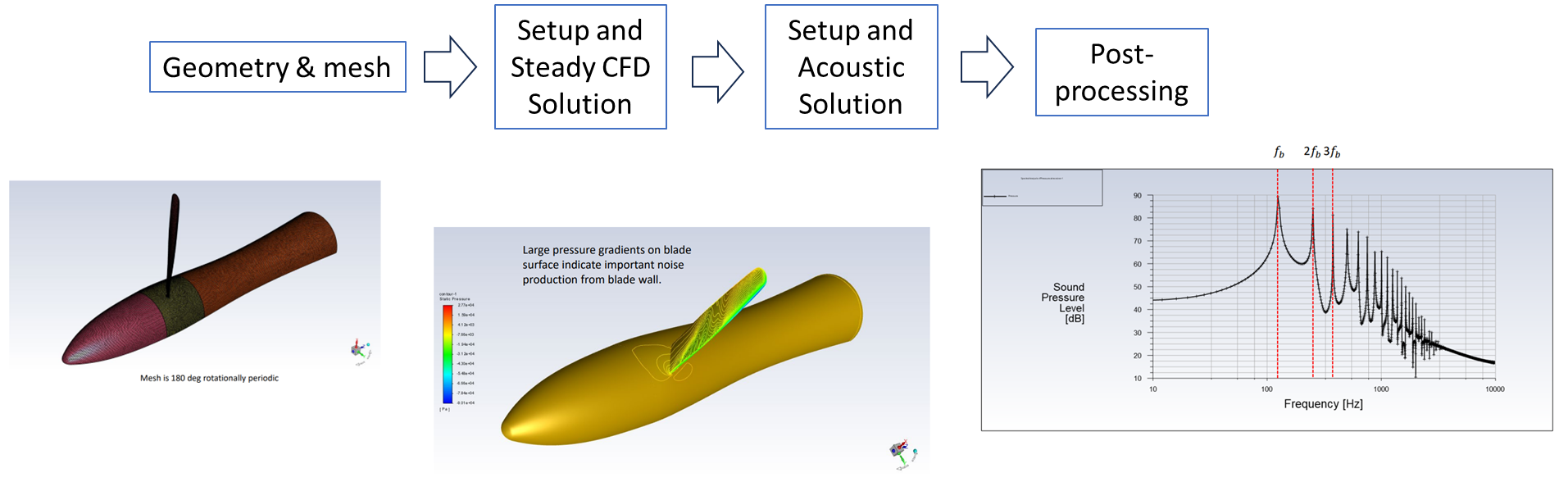
Ansys Fluent Aeroacoustics 应用
探索 Ansys Fluent 在气动声学领域的前沿功能,彻底改变各行各业解决降噪和提高音质的方式。 了解气动声学 气动声学是声学的一个分支,它处理湍流流体运动产生的噪声以及这些声音通过流体介质(如空气)的传播。这个领域在工程中至…...

119.使用AI Agent解决问题:Jenkins build Pipeline时,提示npm ERR! errno FETCH_ERROR
目录 1.Jenkins Build时的错误 2.百度文心快码AI智能体帮我解决 提问1:jenkins中如何配置npm的源 提问2:jenkins pipeline 类型为pipeline script from SCM时,如何配置npm源 3.最终解决方法-Jenkinsfile的修改 4.感触 1.Jenkins Build时…...

istio-proxy内存指标
在 Istio 环境中,istio-proxy 是 Envoy 的边车代理容器。通过运行命令 curl localhost:15000/memory,或者curl localhost:15000/stats 可以查询 Envoy 的内存统计信息。以下是典型返回结果的结构和意义: 返回结果单位是bytes,需/…...

List详解 - 双向链表的操作
在C中,std::list是标准模板库(STL)中的一个容器,它实现了双向链表的数据结构。与数组或向量(std::vector)不同,std::list允许在常数时间内进行插入和删除操作,尤其是在链表的任意位置…...
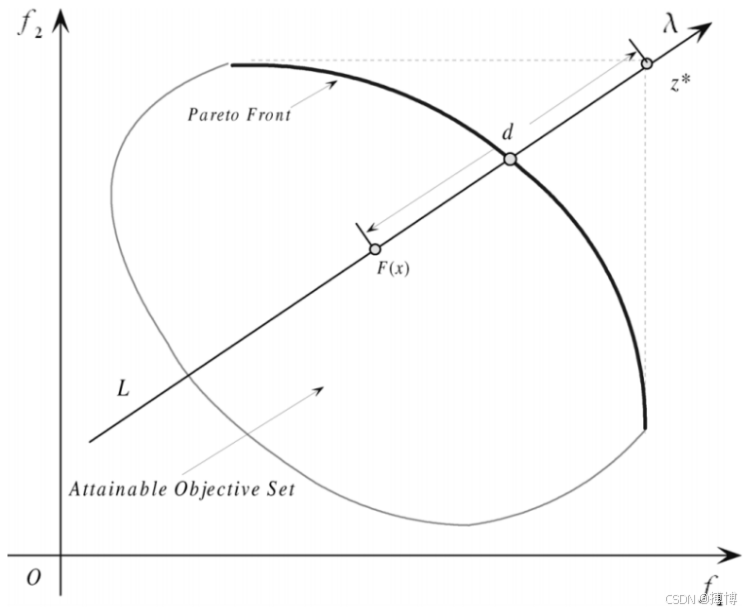
多目标优化算法之一:基于分解的方法
在多目标优化算法中,“基于分解的方法”通常指的是将多目标优化问题(MOP)分解为多个单目标优化子问题,并同时优化这些子问题。这种方法的核心思想是通过引入权重向量或参考点,将多目标问题转化为多个标量优化问题,每个子问题都关注于原始问题的一个特定方面或视角。这样可…...

conntrack iptables 安全组
centos 安装yum install conntrack-tools 1. conntrack状态 NEW: 新建连接(第一次包)。 ESTABLISHED: 已建立连接,正在传输数据。 RELATED: 与已有连接相关的连接,如 FTP 数据连接。 INVALID: 无效连接,无法识别或不…...
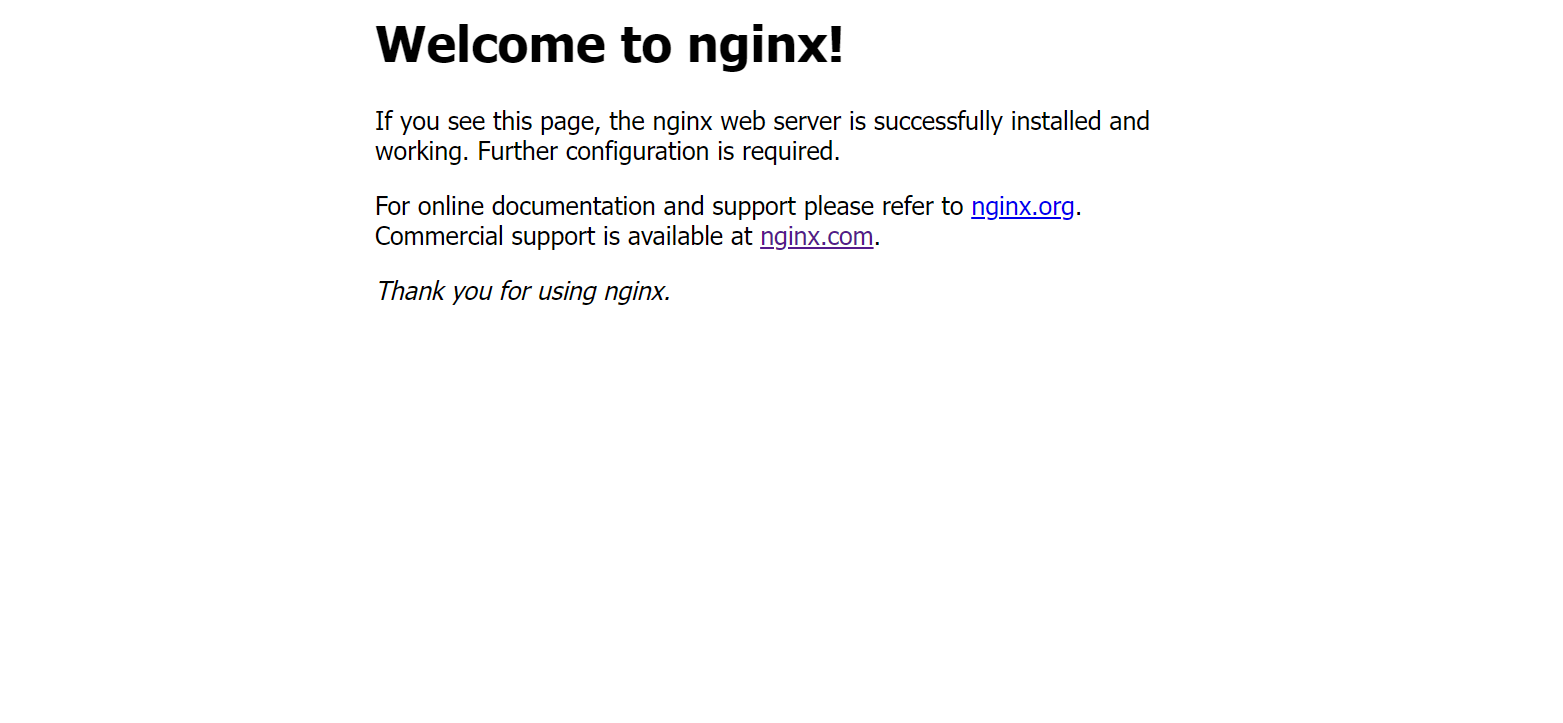
linux之kylin系统nginx的安装
一、nginx的作用 1.可做高性能的web服务器 直接处理静态资源(HTML/CSS/图片等),响应速度远超传统服务器类似apache支持高并发连接 2.反向代理服务器 隐藏后端服务器IP地址,提高安全性 3.负载均衡服务器 支持多种策略分发流量…...

golang循环变量捕获问题
在 Go 语言中,当在循环中启动协程(goroutine)时,如果在协程闭包中直接引用循环变量,可能会遇到一个常见的陷阱 - 循环变量捕获问题。让我详细解释一下: 问题背景 看这个代码片段: fo…...
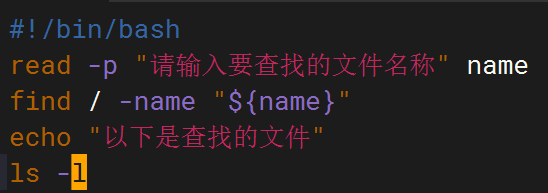
shell脚本--常见案例
1、自动备份文件或目录 2、批量重命名文件 3、查找并删除指定名称的文件: 4、批量删除文件 5、查找并替换文件内容 6、批量创建文件 7、创建文件夹并移动文件 8、在文件夹中查找文件...

解锁数据库简洁之道:FastAPI与SQLModel实战指南
在构建现代Web应用程序时,与数据库的交互无疑是核心环节。虽然传统的数据库操作方式(如直接编写SQL语句与psycopg2交互)赋予了我们精细的控制权,但在面对日益复杂的业务逻辑和快速迭代的需求时,这种方式的开发效率和可…...
linux arm系统烧录
1、打开瑞芯微程序 2、按住linux arm 的 recover按键 插入电源 3、当瑞芯微检测到有设备 4、松开recover按键 5、选择升级固件 6、点击固件选择本地刷机的linux arm 镜像 7、点击升级 (忘了有没有这步了 估计有) 刷机程序 和 镜像 就不提供了。要刷的时…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...
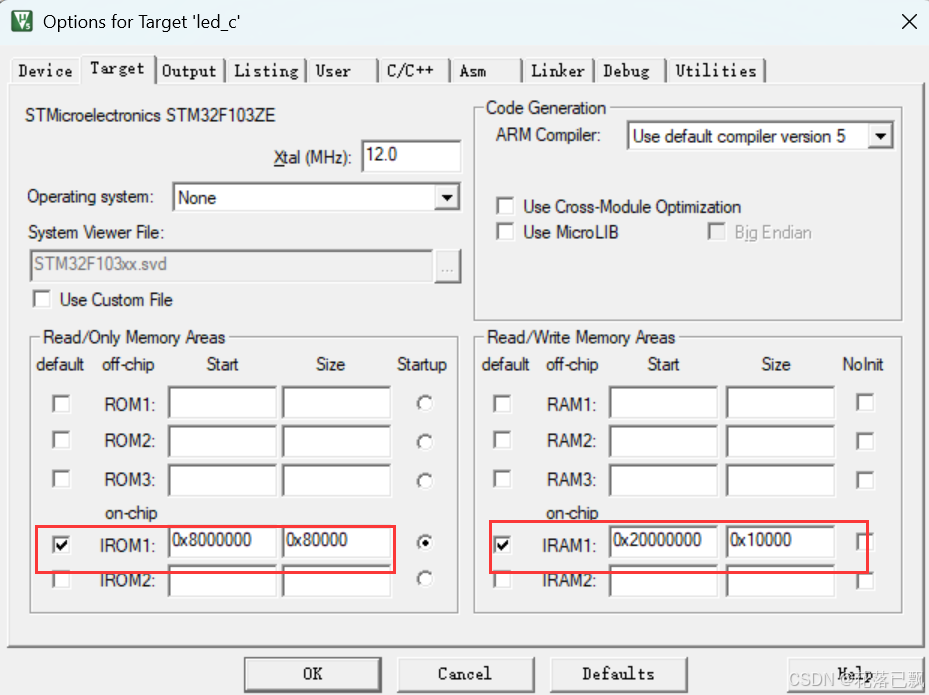
Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解
文章目录 Keil 中设置 STM32 Flash 和 RAM 地址详解一、Flash 和 RAM 配置界面(Target 选项卡)1. IROM1(用于配置 Flash)2. IRAM1(用于配置 RAM)二、链接器设置界面(Linker 选项卡)1. 勾选“Use Memory Layout from Target Dialog”2. 查看链接器参数(如果没有勾选上面…...

C++中string流知识详解和示例
一、概览与类体系 C 提供三种基于内存字符串的流,定义在 <sstream> 中: std::istringstream:输入流,从已有字符串中读取并解析。std::ostringstream:输出流,向内部缓冲区写入内容,最终取…...

九天毕昇深度学习平台 | 如何安装库?
pip install 库名 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --user 举个例子: 报错 ModuleNotFoundError: No module named torch 那么我需要安装 torch pip install torch -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple --user pip install 库名&#x…...
VM虚拟机网络配置(ubuntu24桥接模式):配置静态IP
编辑-虚拟网络编辑器-更改设置 选择桥接模式,然后找到相应的网卡(可以查看自己本机的网络连接) windows连接的网络点击查看属性 编辑虚拟机设置更改网络配置,选择刚才配置的桥接模式 静态ip设置: 我用的ubuntu24桌…...
