13 尺寸结构模块(size.rs)
一、size.rs源码
// Copyright 2013 The Servo Project Developers. See the COPYRIGHT
// file at the top-level directory of this distribution.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 <LICENSE-APACHE or
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0> or the MIT license
// <LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT>, at your
// option. This file may not be copied, modified, or distributed
// except according to those terms.use super::UnknownUnit;
use crate::approxord::{max, min};
use crate::length::Length;
use crate::num::*;
use crate::scale::Scale;
use crate::vector::{vec2, BoolVector2D, Vector2D};
use crate::vector::{vec3, BoolVector3D, Vector3D};use core::cmp::{Eq, PartialEq};
use core::fmt;
use core::hash::Hash;
use core::iter::Sum;
use core::marker::PhantomData;
use core::ops::{Add, AddAssign, Div, DivAssign, Mul, MulAssign, Neg, Sub, SubAssign};#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
use bytemuck::{Pod, Zeroable};
#[cfg(feature = "mint")]
use mint;
use num_traits::{Float, NumCast, Signed};
#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
use serde;/// A 2d size tagged with a unit.
#[repr(C)]
pub struct Size2D<T, U> {/// The extent of the element in the `U` units along the `x` axis (usually horizontal).pub width: T,/// The extent of the element in the `U` units along the `y` axis (usually vertical).pub height: T,#[doc(hidden)]pub _unit: PhantomData<U>,
}impl<T: Copy, U> Copy for Size2D<T, U> {}impl<T: Clone, U> Clone for Size2D<T, U> {fn clone(&self) -> Self {Size2D {width: self.width.clone(),height: self.height.clone(),_unit: PhantomData,}}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<'de, T, U> serde::Deserialize<'de> for Size2D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Deserialize<'de>,
{/// Deserializes 2d size from tuple of width and height.fn deserialize<D>(deserializer: D) -> Result<Self, D::Error>whereD: serde::Deserializer<'de>,{let (width, height) = serde::Deserialize::deserialize(deserializer)?;Ok(Size2D {width,height,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<T, U> serde::Serialize for Size2D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Serialize,
{/// Serializes 2d size to tuple of width and height.fn serialize<S>(&self, serializer: S) -> Result<S::Ok, S::Error>whereS: serde::Serializer,{(&self.width, &self.height).serialize(serializer)}
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a, T, U> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for Size2D<T, U>
whereT: arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a>,
{fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {let (width, height) = arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?;Ok(Size2D {width,height,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Zeroable, U> Zeroable for Size2D<T, U> {}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Pod, U: 'static> Pod for Size2D<T, U> {}impl<T, U> Eq for Size2D<T, U> where T: Eq {}impl<T, U> PartialEq for Size2D<T, U>
whereT: PartialEq,
{fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {self.width == other.width && self.height == other.height}
}impl<T, U> Hash for Size2D<T, U>
whereT: Hash,
{fn hash<H: core::hash::Hasher>(&self, h: &mut H) {self.width.hash(h);self.height.hash(h);}
}impl<T: fmt::Debug, U> fmt::Debug for Size2D<T, U> {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.width, f)?;write!(f, "x")?;fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.height, f)}
}impl<T: Default, U> Default for Size2D<T, U> {fn default() -> Self {Size2D::new(Default::default(), Default::default())}
}impl<T, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// The same as [`Zero::zero`] but available without importing trait.////// [`Zero::zero`]: crate::num::Zero::zero#[inline]pub fn zero() -> SelfwhereT: Zero,{Size2D::new(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}/// Constructor taking scalar values.#[inline]pub const fn new(width: T, height: T) -> Self {Size2D {width,height,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Constructor taking scalar strongly typed lengths.#[inline]pub fn from_lengths(width: Length<T, U>, height: Length<T, U>) -> Self {Size2D::new(width.0, height.0)}/// Constructor setting all components to the same value.#[inline]pub fn splat(v: T) -> SelfwhereT: Clone,{Size2D {width: v.clone(),height: v,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Tag a unitless value with units.#[inline]pub fn from_untyped(p: Size2D<T, UnknownUnit>) -> Self {Size2D::new(p.width, p.height)}
}impl<T: Copy, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// Return this size as an array of two elements (width, then height).#[inline]pub fn to_array(self) -> [T; 2] {[self.width, self.height]}/// Return this size as a tuple of two elements (width, then height).#[inline]pub fn to_tuple(self) -> (T, T) {(self.width, self.height)}/// Return this size as a vector with width and height.#[inline]pub fn to_vector(self) -> Vector2D<T, U> {vec2(self.width, self.height)}/// Drop the units, preserving only the numeric value.#[inline]pub fn to_untyped(self) -> Size2D<T, UnknownUnit> {self.cast_unit()}/// Cast the unit#[inline]pub fn cast_unit<V>(self) -> Size2D<T, V> {Size2D::new(self.width, self.height)}/// Rounds each component to the nearest integer value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::size2;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(size2::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8).round(), size2::<_, Mm>(0.0, -1.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn round(self) -> SelfwhereT: Round,{Size2D::new(self.width.round(), self.height.round())}/// Rounds each component to the smallest integer equal or greater than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::size2;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(size2::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8).ceil(), size2::<_, Mm>(0.0, 0.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn ceil(self) -> SelfwhereT: Ceil,{Size2D::new(self.width.ceil(), self.height.ceil())}/// Rounds each component to the biggest integer equal or lower than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::size2;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(size2::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8).floor(), size2::<_, Mm>(-1.0, -1.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn floor(self) -> SelfwhereT: Floor,{Size2D::new(self.width.floor(), self.height.floor())}/// Returns result of multiplication of both componentspub fn area(self) -> T::OutputwhereT: Mul,{self.width * self.height}/// Linearly interpolate each component between this size and another size.////// # Example////// ```rust/// use euclid::size2;/// use euclid::default::Size2D;////// let from: Size2D<_> = size2(0.0, 10.0);/// let to: Size2D<_> = size2(8.0, -4.0);////// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, -1.0), size2(-8.0, 24.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.0), size2( 0.0, 10.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.5), size2( 4.0, 3.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 1.0), size2( 8.0, -4.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 2.0), size2(16.0, -18.0));/// ```#[inline]pub fn lerp(self, other: Self, t: T) -> SelfwhereT: One + Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T> + Add<Output = T>,{let one_t = T::one() - t;self * one_t + other * t}
}impl<T: NumCast + Copy, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// Cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating point to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.#[inline]pub fn cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Size2D<NewT, U> {self.try_cast().unwrap()}/// Fallible cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating point to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.pub fn try_cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Option<Size2D<NewT, U>> {match (NumCast::from(self.width), NumCast::from(self.height)) {(Some(w), Some(h)) => Some(Size2D::new(w, h)),_ => None,}}// Convenience functions for common casts/// Cast into an `f32` size.#[inline]pub fn to_f32(self) -> Size2D<f32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `f64` size.#[inline]pub fn to_f64(self) -> Size2D<f64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `uint` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_usize(self) -> Size2D<usize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u32` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u32(self) -> Size2D<u32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u64` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u64(self) -> Size2D<u64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i32` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i32(self) -> Size2D<i32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i64` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i64(self) -> Size2D<i64, U> {self.cast()}
}impl<T: Float, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// Returns `true` if all members are finite.#[inline]pub fn is_finite(self) -> bool {self.width.is_finite() && self.height.is_finite()}
}impl<T: Signed, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// Computes the absolute value of each component.////// For `f32` and `f64`, `NaN` will be returned for component if the component is `NaN`.////// For signed integers, `::MIN` will be returned for component if the component is `::MIN`.pub fn abs(self) -> Self {size2(self.width.abs(), self.height.abs())}/// Returns `true` if both components is positive and `false` any component is zero or negative.pub fn is_positive(self) -> bool {self.width.is_positive() && self.height.is_positive()}
}impl<T: PartialOrd, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// Returns the size each component of which are minimum of this size and another.#[inline]pub fn min(self, other: Self) -> Self {size2(min(self.width, other.width), min(self.height, other.height))}/// Returns the size each component of which are maximum of this size and another.#[inline]pub fn max(self, other: Self) -> Self {size2(max(self.width, other.width), max(self.height, other.height))}/// Returns the size each component of which clamped by corresponding/// components of `start` and `end`.////// Shortcut for `self.max(start).min(end)`.#[inline]pub fn clamp(self, start: Self, end: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Copy,{self.max(start).min(end)}// Returns true if this size is larger or equal to the other size in all dimensions.#[inline]pub fn contains(self, other: Self) -> bool {self.width >= other.width && self.height >= other.height}/// Returns vector with results of "greater then" operation on each component.pub fn greater_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.width > other.width,y: self.height > other.height,}}/// Returns vector with results of "lower then" operation on each component.pub fn lower_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.width < other.width,y: self.height < other.height,}}/// Returns `true` if any component of size is zero, negative, or NaN.pub fn is_empty(self) -> boolwhereT: Zero,{let zero = T::zero();// The condition is expressed this way so that we return true in// the presence of NaN.!(self.width > zero && self.height > zero)}
}impl<T: PartialEq, U> Size2D<T, U> {/// Returns vector with results of "equal" operation on each component.pub fn equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.width == other.width,y: self.height == other.height,}}/// Returns vector with results of "not equal" operation on each component.pub fn not_equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector2D {BoolVector2D {x: self.width != other.width,y: self.height != other.height,}}
}impl<T: Round, U> Round for Size2D<T, U> {/// See [`Size2D::round`].#[inline]fn round(self) -> Self {self.round()}
}impl<T: Ceil, U> Ceil for Size2D<T, U> {/// See [`Size2D::ceil`].#[inline]fn ceil(self) -> Self {self.ceil()}
}impl<T: Floor, U> Floor for Size2D<T, U> {/// See [`Size2D::floor`].#[inline]fn floor(self) -> Self {self.floor()}
}impl<T: Zero, U> Zero for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn zero() -> Self {Size2D::new(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}
}impl<T: Neg, U> Neg for Size2D<T, U> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn neg(self) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(-self.width, -self.height)}
}impl<T: Add, U> Add for Size2D<T, U> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn add(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(self.width + other.width, self.height + other.height)}
}impl<T: Copy + Add<T, Output = T>, U> Add<&Self> for Size2D<T, U> {type Output = Self;fn add(self, other: &Self) -> Self {Size2D::new(self.width + other.width, self.height + other.height)}
}impl<T: Add<Output = T> + Zero, U> Sum for Size2D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<'a, T: 'a + Add<Output = T> + Copy + Zero, U: 'a> Sum<&'a Self> for Size2D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = &'a Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<T: AddAssign, U> AddAssign for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn add_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {self.width += other.width;self.height += other.height;}
}impl<T: Sub, U> Sub for Size2D<T, U> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn sub(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(self.width - other.width, self.height - other.height)}
}impl<T: SubAssign, U> SubAssign for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn sub_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {self.width -= other.width;self.height -= other.height;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U> Mul<T> for Size2D<T, U> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(self.width * scale, self.height * scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<T> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, other: T) {self.width *= other;self.height *= other;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U1, U2> Mul<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Size2D<T, U1> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U2>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(self.width * scale.0, self.height * scale.0)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, other: Scale<T, U, U>) {*self *= other.0;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U> Div<T> for Size2D<T, U> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(self.width / scale, self.height / scale)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<T> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, other: T) {self.width /= other;self.height /= other;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U1, U2> Div<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Size2D<T, U2> {type Output = Size2D<T::Output, U1>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {Size2D::new(self.width / scale.0, self.height / scale.0)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, other: Scale<T, U, U>) {*self /= other.0;}
}/// Shorthand for `Size2D::new(w, h)`.
#[inline]
pub const fn size2<T, U>(w: T, h: T) -> Size2D<T, U> {Size2D::new(w, h)
}#[cfg(feature = "mint")]
impl<T, U> From<mint::Vector2<T>> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from(v: mint::Vector2<T>) -> Self {Size2D {width: v.x,height: v.y,_unit: PhantomData,}}
}
#[cfg(feature = "mint")]
impl<T, U> From<Size2D<T, U>> for mint::Vector2<T> {#[inline]fn from(s: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {mint::Vector2 {x: s.width,y: s.height,}}
}impl<T, U> From<Vector2D<T, U>> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from(v: Vector2D<T, U>) -> Self {size2(v.x, v.y)}
}impl<T, U> From<Size2D<T, U>> for [T; 2] {#[inline]fn from(s: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {[s.width, s.height]}
}impl<T, U> From<[T; 2]> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from([w, h]: [T; 2]) -> Self {size2(w, h)}
}impl<T, U> From<Size2D<T, U>> for (T, T) {#[inline]fn from(s: Size2D<T, U>) -> Self {(s.width, s.height)}
}impl<T, U> From<(T, T)> for Size2D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from(tuple: (T, T)) -> Self {size2(tuple.0, tuple.1)}
}#[cfg(test)]
mod size2d {use crate::default::Size2D;#[cfg(feature = "mint")]use mint;#[test]pub fn test_area() {let p = Size2D::new(1.5, 2.0);assert_eq!(p.area(), 3.0);}#[cfg(feature = "mint")]#[test]pub fn test_mint() {let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let sm: mint::Vector2<_> = s1.into();let s2 = Size2D::from(sm);assert_eq!(s1, s2);}mod ops {use crate::default::Size2D;use crate::scale::Scale;pub enum Mm {}pub enum Cm {}pub type Size2DMm<T> = crate::Size2D<T, Mm>;pub type Size2DCm<T> = crate::Size2D<T, Cm>;#[test]pub fn test_neg() {assert_eq!(-Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0), Size2D::new(-1.0, -2.0));assert_eq!(-Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0), Size2D::new(-0.0, -0.0));assert_eq!(-Size2D::new(-1.0, -2.0), Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0));}#[test]pub fn test_add() {let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size2D::new(4.0, 6.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size2D::new(4.0, 6.0));let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0));let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(-3.0, -4.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size2D::new(-2.0, -2.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size2D::new(-2.0, -2.0));let s1 = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_add_assign() {let mut s = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);s += Size2D::new(3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(4.0, 6.0));let mut s = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);s += Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0));let mut s = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);s += Size2D::new(-3.0, -4.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(-2.0, -2.0));let mut s = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);s += Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sum() {let sizes = [Size2D::new(0.0, 1.0),Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0),Size2D::new(2.0, 3.0),];let sum = Size2D::new(3.0, 6.0);assert_eq!(sizes.iter().sum::<Size2D<_>>(), sum);}#[test]pub fn test_sub() {let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size2D::new(-2.0, -2.0));let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0));let s1 = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(-3.0, -4.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size2D::new(4.0, 6.0));let s1 = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);let s2 = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sub_assign() {let mut s = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);s -= Size2D::new(3.0, 4.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(-2.0, -2.0));let mut s = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);s -= Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0));let mut s = Size2D::new(1.0, 2.0);s -= Size2D::new(-3.0, -4.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(4.0, 6.0));let mut s = Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);s -= Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size2D::new(0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_scalar() {let s1: Size2D<f32> = Size2D::new(3.0, 5.0);let result = s1 * 5.0;assert_eq!(result, Size2D::new(15.0, 25.0));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_assign_scalar() {let mut s1 = Size2D::new(3.0, 5.0);s1 *= 5.0;assert_eq!(s1, Size2D::new(15.0, 25.0));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_scale() {let s1 = Size2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0);let cm_per_mm: Scale<f32, Mm, Cm> = Scale::new(0.1);let result = s1 * cm_per_mm;assert_eq!(result, Size2DCm::new(0.1, 0.2));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_assign_scale() {let mut s1 = Size2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0);let scale: Scale<f32, Mm, Mm> = Scale::new(0.1);s1 *= scale;assert_eq!(s1, Size2DMm::new(0.1, 0.2));}#[test]pub fn test_div_scalar() {let s1: Size2D<f32> = Size2D::new(15.0, 25.0);let result = s1 / 5.0;assert_eq!(result, Size2D::new(3.0, 5.0));}#[test]pub fn test_div_assign_scalar() {let mut s1: Size2D<f32> = Size2D::new(15.0, 25.0);s1 /= 5.0;assert_eq!(s1, Size2D::new(3.0, 5.0));}#[test]pub fn test_div_scale() {let s1 = Size2DCm::new(0.1, 0.2);let cm_per_mm: Scale<f32, Mm, Cm> = Scale::new(0.1);let result = s1 / cm_per_mm;assert_eq!(result, Size2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0));}#[test]pub fn test_div_assign_scale() {let mut s1 = Size2DMm::new(0.1, 0.2);let scale: Scale<f32, Mm, Mm> = Scale::new(0.1);s1 /= scale;assert_eq!(s1, Size2DMm::new(1.0, 2.0));}#[test]pub fn test_nan_empty() {use std::f32::NAN;assert!(Size2D::new(NAN, 2.0).is_empty());assert!(Size2D::new(0.0, NAN).is_empty());assert!(Size2D::new(NAN, -2.0).is_empty());}}
}/// A 3d size tagged with a unit.
#[repr(C)]
pub struct Size3D<T, U> {/// The extent of the element in the `U` units along the `x` axis.pub width: T,/// The extent of the element in the `U` units along the `y` axis.pub height: T,/// The extent of the element in the `U` units along the `z` axis.pub depth: T,#[doc(hidden)]pub _unit: PhantomData<U>,
}impl<T: Copy, U> Copy for Size3D<T, U> {}impl<T: Clone, U> Clone for Size3D<T, U> {fn clone(&self) -> Self {Size3D {width: self.width.clone(),height: self.height.clone(),depth: self.depth.clone(),_unit: PhantomData,}}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<'de, T, U> serde::Deserialize<'de> for Size3D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Deserialize<'de>,
{fn deserialize<D>(deserializer: D) -> Result<Self, D::Error>whereD: serde::Deserializer<'de>,{let (width, height, depth) = serde::Deserialize::deserialize(deserializer)?;Ok(Size3D {width,height,depth,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "serde")]
impl<T, U> serde::Serialize for Size3D<T, U>
whereT: serde::Serialize,
{fn serialize<S>(&self, serializer: S) -> Result<S::Ok, S::Error>whereS: serde::Serializer,{(&self.width, &self.height, &self.depth).serialize(serializer)}
}#[cfg(feature = "arbitrary")]
impl<'a, T, U> arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a> for Size3D<T, U>
whereT: arbitrary::Arbitrary<'a>,
{fn arbitrary(u: &mut arbitrary::Unstructured<'a>) -> arbitrary::Result<Self> {let (width, height, depth) = arbitrary::Arbitrary::arbitrary(u)?;Ok(Size3D {width,height,depth,_unit: PhantomData,})}
}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Zeroable, U> Zeroable for Size3D<T, U> {}#[cfg(feature = "bytemuck")]
unsafe impl<T: Pod, U: 'static> Pod for Size3D<T, U> {}impl<T, U> Eq for Size3D<T, U> where T: Eq {}impl<T, U> PartialEq for Size3D<T, U>
whereT: PartialEq,
{fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {self.width == other.width && self.height == other.height && self.depth == other.depth}
}impl<T, U> Hash for Size3D<T, U>
whereT: Hash,
{fn hash<H: core::hash::Hasher>(&self, h: &mut H) {self.width.hash(h);self.height.hash(h);self.depth.hash(h);}
}impl<T: fmt::Debug, U> fmt::Debug for Size3D<T, U> {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.width, f)?;write!(f, "x")?;fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.height, f)?;write!(f, "x")?;fmt::Debug::fmt(&self.depth, f)}
}impl<T: Default, U> Default for Size3D<T, U> {fn default() -> Self {Size3D::new(Default::default(), Default::default(), Default::default())}
}impl<T, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// The same as [`Zero::zero`] but available without importing trait.////// [`Zero::zero`]: crate::num::Zero::zeropub fn zero() -> SelfwhereT: Zero,{Size3D::new(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}/// Constructor taking scalar values.#[inline]pub const fn new(width: T, height: T, depth: T) -> Self {Size3D {width,height,depth,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Constructor taking scalar strongly typed lengths.#[inline]pub fn from_lengths(width: Length<T, U>, height: Length<T, U>, depth: Length<T, U>) -> Self {Size3D::new(width.0, height.0, depth.0)}/// Constructor setting all components to the same value.#[inline]pub fn splat(v: T) -> SelfwhereT: Clone,{Size3D {width: v.clone(),height: v.clone(),depth: v,_unit: PhantomData,}}/// Tag a unitless value with units.#[inline]pub fn from_untyped(p: Size3D<T, UnknownUnit>) -> Self {Size3D::new(p.width, p.height, p.depth)}
}impl<T: Copy, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// Return this size as an array of three elements (width, then height, then depth).#[inline]pub fn to_array(self) -> [T; 3] {[self.width, self.height, self.depth]}/// Return this size as an array of three elements (width, then height, then depth).#[inline]pub fn to_tuple(self) -> (T, T, T) {(self.width, self.height, self.depth)}/// Return this size as a vector with width, height and depth.#[inline]pub fn to_vector(self) -> Vector3D<T, U> {vec3(self.width, self.height, self.depth)}/// Drop the units, preserving only the numeric value.#[inline]pub fn to_untyped(self) -> Size3D<T, UnknownUnit> {self.cast_unit()}/// Cast the unit#[inline]pub fn cast_unit<V>(self) -> Size3D<T, V> {Size3D::new(self.width, self.height, self.depth)}/// Rounds each component to the nearest integer value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::size3;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(size3::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8, 0.4).round(), size3::<_, Mm>(0.0, -1.0, 0.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn round(self) -> SelfwhereT: Round,{Size3D::new(self.width.round(), self.height.round(), self.depth.round())}/// Rounds each component to the smallest integer equal or greater than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::size3;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(size3::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8, 0.4).ceil(), size3::<_, Mm>(0.0, 0.0, 1.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn ceil(self) -> SelfwhereT: Ceil,{Size3D::new(self.width.ceil(), self.height.ceil(), self.depth.ceil())}/// Rounds each component to the biggest integer equal or lower than the original value.////// This behavior is preserved for negative values (unlike the basic cast).////// ```rust/// # use euclid::size3;/// enum Mm {}////// assert_eq!(size3::<_, Mm>(-0.1, -0.8, 0.4).floor(), size3::<_, Mm>(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0))/// ```#[inline]#[must_use]pub fn floor(self) -> SelfwhereT: Floor,{Size3D::new(self.width.floor(), self.height.floor(), self.depth.floor())}/// Returns result of multiplication of all componentspub fn volume(self) -> TwhereT: Mul<Output = T>,{self.width * self.height * self.depth}/// Linearly interpolate between this size and another size.////// # Example////// ```rust/// use euclid::size3;/// use euclid::default::Size3D;////// let from: Size3D<_> = size3(0.0, 10.0, -1.0);/// let to: Size3D<_> = size3(8.0, -4.0, 0.0);////// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, -1.0), size3(-8.0, 24.0, -2.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.0), size3( 0.0, 10.0, -1.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 0.5), size3( 4.0, 3.0, -0.5));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 1.0), size3( 8.0, -4.0, 0.0));/// assert_eq!(from.lerp(to, 2.0), size3(16.0, -18.0, 1.0));/// ```#[inline]pub fn lerp(self, other: Self, t: T) -> SelfwhereT: One + Sub<Output = T> + Mul<Output = T> + Add<Output = T>,{let one_t = T::one() - t;self * one_t + other * t}
}impl<T: NumCast + Copy, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// Cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating point to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.#[inline]pub fn cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Size3D<NewT, U> {self.try_cast().unwrap()}/// Fallible cast from one numeric representation to another, preserving the units.////// When casting from floating point to integer coordinates, the decimals are truncated/// as one would expect from a simple cast, but this behavior does not always make sense/// geometrically. Consider using `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before casting.pub fn try_cast<NewT: NumCast>(self) -> Option<Size3D<NewT, U>> {match (NumCast::from(self.width),NumCast::from(self.height),NumCast::from(self.depth),) {(Some(w), Some(h), Some(d)) => Some(Size3D::new(w, h, d)),_ => None,}}// Convenience functions for common casts/// Cast into an `f32` size.#[inline]pub fn to_f32(self) -> Size3D<f32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `f64` size.#[inline]pub fn to_f64(self) -> Size3D<f64, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `uint` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_usize(self) -> Size3D<usize, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `u32` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_u32(self) -> Size3D<u32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i32` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i32(self) -> Size3D<i32, U> {self.cast()}/// Cast into an `i64` size, truncating decimals if any.////// When casting from floating point sizes, it is worth considering whether/// to `round()`, `ceil()` or `floor()` before the cast in order to obtain/// the desired conversion behavior.#[inline]pub fn to_i64(self) -> Size3D<i64, U> {self.cast()}
}impl<T: Float, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// Returns `true` if all members are finite.#[inline]pub fn is_finite(self) -> bool {self.width.is_finite() && self.height.is_finite() && self.depth.is_finite()}
}impl<T: Signed, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// Computes the absolute value of each component.////// For `f32` and `f64`, `NaN` will be returned for component if the component is `NaN`.////// For signed integers, `::MIN` will be returned for component if the component is `::MIN`.pub fn abs(self) -> Self {size3(self.width.abs(), self.height.abs(), self.depth.abs())}/// Returns `true` if all components is positive and `false` any component is zero or negative.pub fn is_positive(self) -> bool {self.width.is_positive() && self.height.is_positive() && self.depth.is_positive()}
}impl<T: PartialOrd, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// Returns the size each component of which are minimum of this size and another.#[inline]pub fn min(self, other: Self) -> Self {size3(min(self.width, other.width),min(self.height, other.height),min(self.depth, other.depth),)}/// Returns the size each component of which are maximum of this size and another.#[inline]pub fn max(self, other: Self) -> Self {size3(max(self.width, other.width),max(self.height, other.height),max(self.depth, other.depth),)}/// Returns the size each component of which clamped by corresponding/// components of `start` and `end`.////// Shortcut for `self.max(start).min(end)`.#[inline]pub fn clamp(self, start: Self, end: Self) -> SelfwhereT: Copy,{self.max(start).min(end)}// Returns true if this size is larger or equal to the other size in all dimensions.#[inline]pub fn contains(self, other: Self) -> bool {self.width >= other.width && self.height >= other.height && self.depth >= other.depth}/// Returns vector with results of "greater than" operation on each component.pub fn greater_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.width > other.width,y: self.height > other.height,z: self.depth > other.depth,}}/// Returns vector with results of "lower than" operation on each component.pub fn lower_than(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.width < other.width,y: self.height < other.height,z: self.depth < other.depth,}}/// Returns `true` if any component of size is zero, negative or NaN.pub fn is_empty(self) -> boolwhereT: Zero,{let zero = T::zero();!(self.width > zero && self.height > zero && self.depth > zero)}
}impl<T: PartialEq, U> Size3D<T, U> {/// Returns vector with results of "equal" operation on each component.pub fn equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.width == other.width,y: self.height == other.height,z: self.depth == other.depth,}}/// Returns vector with results of "not equal" operation on each component.pub fn not_equal(self, other: Self) -> BoolVector3D {BoolVector3D {x: self.width != other.width,y: self.height != other.height,z: self.depth != other.depth,}}
}impl<T: Round, U> Round for Size3D<T, U> {/// See [`Size3D::round`].#[inline]fn round(self) -> Self {self.round()}
}impl<T: Ceil, U> Ceil for Size3D<T, U> {/// See [`Size3D::ceil`].#[inline]fn ceil(self) -> Self {self.ceil()}
}impl<T: Floor, U> Floor for Size3D<T, U> {/// See [`Size3D::floor`].#[inline]fn floor(self) -> Self {self.floor()}
}impl<T: Zero, U> Zero for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn zero() -> Self {Size3D::new(Zero::zero(), Zero::zero(), Zero::zero())}
}impl<T: Neg, U> Neg for Size3D<T, U> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn neg(self) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(-self.width, -self.height, -self.depth)}
}impl<T: Add, U> Add for Size3D<T, U> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn add(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(self.width + other.width,self.height + other.height,self.depth + other.depth,)}
}impl<T: Copy + Add<T, Output = T>, U> Add<&Self> for Size3D<T, U> {type Output = Self;fn add(self, other: &Self) -> Self {Size3D::new(self.width + other.width,self.height + other.height,self.depth + other.depth,)}
}impl<T: Add<Output = T> + Zero, U> Sum for Size3D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<'a, T: 'a + Add<Output = T> + Copy + Zero, U: 'a> Sum<&'a Self> for Size3D<T, U> {fn sum<I: Iterator<Item = &'a Self>>(iter: I) -> Self {iter.fold(Self::zero(), Add::add)}
}impl<T: AddAssign, U> AddAssign for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn add_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {self.width += other.width;self.height += other.height;self.depth += other.depth;}
}impl<T: Sub, U> Sub for Size3D<T, U> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]fn sub(self, other: Self) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(self.width - other.width,self.height - other.height,self.depth - other.depth,)}
}impl<T: SubAssign, U> SubAssign for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn sub_assign(&mut self, other: Self) {self.width -= other.width;self.height -= other.height;self.depth -= other.depth;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U> Mul<T> for Size3D<T, U> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]#[rustfmt::skip]fn mul(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(self.width * scale,self.height * scale,self.depth * scale,)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<T> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, other: T) {self.width *= other;self.height *= other;self.depth *= other;}
}impl<T: Copy + Mul, U1, U2> Mul<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Size3D<T, U1> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U2>;#[inline]fn mul(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(self.width * scale.0,self.height * scale.0,self.depth * scale.0,)}
}impl<T: Copy + MulAssign, U> MulAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn mul_assign(&mut self, other: Scale<T, U, U>) {*self *= other.0;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U> Div<T> for Size3D<T, U> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U>;#[inline]#[rustfmt::skip]fn div(self, scale: T) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(self.width / scale,self.height / scale,self.depth / scale,)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<T> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, other: T) {self.width /= other;self.height /= other;self.depth /= other;}
}impl<T: Copy + Div, U1, U2> Div<Scale<T, U1, U2>> for Size3D<T, U2> {type Output = Size3D<T::Output, U1>;#[inline]fn div(self, scale: Scale<T, U1, U2>) -> Self::Output {Size3D::new(self.width / scale.0,self.height / scale.0,self.depth / scale.0,)}
}impl<T: Copy + DivAssign, U> DivAssign<Scale<T, U, U>> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn div_assign(&mut self, other: Scale<T, U, U>) {*self /= other.0;}
}#[cfg(feature = "mint")]
impl<T, U> From<mint::Vector3<T>> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from(v: mint::Vector3<T>) -> Self {size3(v.x, v.y, v.z)}
}
#[cfg(feature = "mint")]
impl<T, U> From<Size3D<T, U>> for mint::Vector3<T> {#[inline]fn from(s: Size3D<T, U>) -> Self {mint::Vector3 {x: s.width,y: s.height,z: s.depth,}}
}impl<T, U> From<Vector3D<T, U>> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from(v: Vector3D<T, U>) -> Self {size3(v.x, v.y, v.z)}
}impl<T, U> From<Size3D<T, U>> for [T; 3] {#[inline]fn from(s: Size3D<T, U>) -> Self {[s.width, s.height, s.depth]}
}impl<T, U> From<[T; 3]> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from([w, h, d]: [T; 3]) -> Self {size3(w, h, d)}
}impl<T, U> From<Size3D<T, U>> for (T, T, T) {#[inline]fn from(s: Size3D<T, U>) -> Self {(s.width, s.height, s.depth)}
}impl<T, U> From<(T, T, T)> for Size3D<T, U> {#[inline]fn from(tuple: (T, T, T)) -> Self {size3(tuple.0, tuple.1, tuple.2)}
}/// Shorthand for `Size3D::new(w, h, d)`.
#[inline]
pub const fn size3<T, U>(w: T, h: T, d: T) -> Size3D<T, U> {Size3D::new(w, h, d)
}#[cfg(test)]
mod size3d {mod ops {use crate::default::{Size2D, Size3D};use crate::scale::Scale;pub enum Mm {}pub enum Cm {}pub type Size3DMm<T> = crate::Size3D<T, Mm>;pub type Size3DCm<T> = crate::Size3D<T, Cm>;#[test]pub fn test_neg() {assert_eq!(-Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Size3D::new(-1.0, -2.0, -3.0));assert_eq!(-Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), Size3D::new(-0.0, -0.0, -0.0));assert_eq!(-Size3D::new(-1.0, -2.0, -3.0), Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));}#[test]pub fn test_add() {let s1 = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size3D::new(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size3D::new(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));let s1 = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));let s1 = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(-4.0, -5.0, -6.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size3D::new(-3.0, -3.0, -3.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size3D::new(-3.0, -3.0, -3.0));let s1 = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 + s2, Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));assert_eq!(s1 + &s2, Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sum() {let sizes = [Size3D::new(0.0, 1.0, 2.0),Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0),Size3D::new(2.0, 3.0, 4.0),];let sum = Size3D::new(3.0, 6.0, 9.0);assert_eq!(sizes.iter().sum::<Size3D<_>>(), sum);}#[test]pub fn test_add_assign() {let mut s = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);s += Size3D::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));let mut s = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);s += Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));let mut s = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);s += Size3D::new(-4.0, -5.0, -6.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(-3.0, -3.0, -3.0));let mut s = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);s += Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sub() {let s1 = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size3D::new(-3.0, -3.0, -3.0));let s1 = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));let s1 = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(-4.0, -5.0, -6.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size3D::new(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));let s1 = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);let s2 = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s1 - s2, Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_sub_assign() {let mut s = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);s -= Size3D::new(4.0, 5.0, 6.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(-3.0, -3.0, -3.0));let mut s = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);s -= Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));let mut s = Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);s -= Size3D::new(-4.0, -5.0, -6.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(5.0, 7.0, 9.0));let mut s = Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);s -= Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);assert_eq!(s, Size3D::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_scalar() {let s1: Size3D<f32> = Size3D::new(3.0, 5.0, 7.0);let result = s1 * 5.0;assert_eq!(result, Size3D::new(15.0, 25.0, 35.0));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_assign_scalar() {let mut s1: Size3D<f32> = Size3D::new(3.0, 5.0, 7.0);s1 *= 5.0;assert_eq!(s1, Size3D::new(15.0, 25.0, 35.0));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_scale() {let s1 = Size3DMm::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let cm_per_mm: Scale<f32, Mm, Cm> = Scale::new(0.1);let result = s1 * cm_per_mm;assert_eq!(result, Size3DCm::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.3));}#[test]pub fn test_mul_assign_scale() {let mut s1 = Size3DMm::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);let scale: Scale<f32, Mm, Mm> = Scale::new(0.1);s1 *= scale;assert_eq!(s1, Size3DMm::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.3));}#[test]pub fn test_div_scalar() {let s1: Size3D<f32> = Size3D::new(15.0, 25.0, 35.0);let result = s1 / 5.0;assert_eq!(result, Size3D::new(3.0, 5.0, 7.0));}#[test]pub fn test_div_assign_scalar() {let mut s1: Size3D<f32> = Size3D::new(15.0, 25.0, 35.0);s1 /= 5.0;assert_eq!(s1, Size3D::new(3.0, 5.0, 7.0));}#[test]pub fn test_div_scale() {let s1 = Size3DCm::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.3);let cm_per_mm: Scale<f32, Mm, Cm> = Scale::new(0.1);let result = s1 / cm_per_mm;assert_eq!(result, Size3DMm::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));}#[test]pub fn test_div_assign_scale() {let mut s1 = Size3DMm::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.3);let scale: Scale<f32, Mm, Mm> = Scale::new(0.1);s1 /= scale;assert_eq!(s1, Size3DMm::new(1.0, 2.0, 3.0));}#[test]fn test_nonempty() {assert!(!Size2D::new(1.0, 1.0).is_empty());assert!(!Size3D::new(1.0, 1.0, 1.0).is_empty());}#[test]pub fn test_nan_empty() {use std::f32::NAN;assert!(Size3D::new(NAN, 2.0, 3.0).is_empty());assert!(Size3D::new(0.0, NAN, 0.0).is_empty());assert!(Size3D::new(1.0, 2.0, NAN).is_empty());}}
}二、说明
Size实现与Vector相似。
相关文章:
)
13 尺寸结构模块(size.rs)
一、size.rs源码 // Copyright 2013 The Servo Project Developers. See the COPYRIGHT // file at the top-level directory of this distribution. // // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 <LICENSE-APACHE or // http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE…...

STM32单片机学习记录(2.2)
一、STM32 13.1 - PWR简介 1. PWR(Power Control)电源控制 (1)PWR负责管理STM32内部的电源供电部分,可以实现可编程电压监测器和低功耗模式的功能; (2)可编程电压监测器(…...

CSS 样式化表格:从基础到高级技巧
CSS 样式化表格:从基础到高级技巧 1. 典型的 HTML 表格结构2. 为表格添加样式2.1 间距和布局2.2 简单的排版2.3 图形和颜色2.4 斑马条纹2.5 样式化标题 3. 完整的示例代码4. 总结 在网页设计中,表格是展示数据的常见方式。然而,默认的表格样式…...

【python】tkinter实现音乐播放器(源码+音频文件)【独一无二】
👉博__主👈:米码收割机 👉技__能👈:C/Python语言 👉专__注👈:专注主流机器人、人工智能等相关领域的开发、测试技术。 【python】tkinter实现音乐播放器(源码…...

javascript常用函数大全
javascript函数一共可分为五类: •常规函数 •数组函数 •日期函数 •数学函数 •字符串函数 1.常规函数 javascript常规函数包括以下9个函数: (1)alert函数:显示一个警告对话框,包括一个OK按钮。 (2)confirm函数:显…...
)
C#属性和字段(访问修饰符)
不同点逻辑性/灵活性存储性访问性使用范围安全性属性(Property)源于字段,对字段的扩展,逻辑字段并不占用实际的内存可以被其他类访问对接收的数据范围做限定,外部使用增加了数据的安全性字段(Field)不经过逻辑处理占用内存的空间及位置大部分字段不能直接被访问内存使用不安全 …...

DeepSeek为什么超越了OpenAI?从“存在主义之问”看AI的觉醒
悉尼大学学者Teodor Mitew向DeepSeek提出的问题,在推特上掀起了一场关于AI与人类意识的大讨论。当被问及"你最想问人类什么问题"时,DeepSeek的回答直指人类存在的本质:"如果意识是进化的偶然,宇宙没有内在的意义&a…...

langchain基础(二)
一、输出解析器(Output Parser) 作用:(1)让模型按照指定的格式输出; (2)解析模型输出,提取所需的信息 1、逗号分隔列表 CommaSeparatedListOutputParser:…...

数据库安全管理中的权限控制:保护数据资产的关键措施
title: 数据库安全管理中的权限控制:保护数据资产的关键措施 date: 2025/2/2 updated: 2025/2/2 author: cmdragon excerpt: 在信息化迅速发展的今天,数据库作为关键的数据存储和管理中心,已经成为了企业营运和决策的核心所在。然而,伴随着数据规模的不断扩大和数据价值…...

Leetcode598:区间加法 II
题目描述: 给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 M 和一个操作数组 op 。矩阵初始化时所有的单元格都为 0 。ops[i] [ai, bi] 意味着当所有的 0 < x < ai 和 0 < y < bi 时, M[x][y] 应该加 1。 在 执行完所有操作后 ,计算并返回 矩阵中最大…...

【Proteus】NE555纯硬件实现LED呼吸灯效果,附源文件,效果展示
本文通过NE555定时器芯片和简单的电容充放电电路,设计了一种纯硬件实现的呼吸灯方案,并借助Proteus仿真软件验证其功能。方案无需编程,成本低且易于实现,适合电子爱好者学习PWM(脉宽调制)和定时器电路原理。 一、呼吸灯原理与NE555功能分析 1. 呼吸灯核心原理 呼吸灯的…...

SAP HCM insufficient authorization, no.skipped personnel 总结归纳
导读 权限:HCM模块中有普通权限和结构化权限。普通权限就是PFCG的权限,结构化权限就是按照部门ID授权,颗粒度更细,对分工明细化的单位尤其重要,今天遇到的问题就是结构化权限的问题。 作者:vivi,来源&…...

五. Redis 配置内容(详细配置说明)
五. Redis 配置内容(详细配置说明) 文章目录 五. Redis 配置内容(详细配置说明)1. Units 单位配置2. INCLUDES (包含)配置3. NETWORK (网络)配置3.1 bind(配置访问内容)3.2 protected-mode (保护模式)3.3 port(端口)配置3.4 timeout(客户端超时时间)配置3.5 tcp-keepalive()配置…...

4 [危机13小时追踪一场GitHub投毒事件]
事件概要 自北京时间 2024.12.4 晚间6点起, GitHub 上不断出现“幽灵仓库”,仓库中没有任何代码,只有诱导性的病毒文件。当天,他们成为了 GitHub 上 star 增速最快的仓库。超过 180 个虚假僵尸账户正在传播病毒,等待不…...
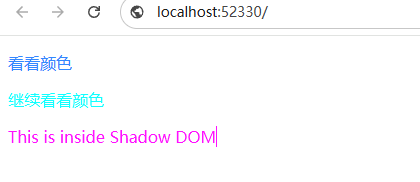
Shadow DOM举例
这东西具有隔离效果,对于一些插件需要append一些div倒是不错的选择 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset"utf-8"> <title>演示例子</title> </head> <body> <style&g…...

力扣动态规划-18【算法学习day.112】
前言 ###我做这类文章一个重要的目的还是记录自己的学习过程,我的解析也不会做的非常详细,只会提供思路和一些关键点,力扣上的大佬们的题解质量是非常非常高滴!!! 习题 1.下降路径最小和 题目链接:931. …...

网络基础
协议 协议就是约定 网络协议是协议中的一种 协议分层 协议本身也是软件,在设计上为了更好的模块化,解耦合,也是设计成为层状结构的 两个视角: 小白:同层协议,直接通信 工程师:同层协议&…...

使用 EXISTS 解决 SQL 中 IN 查询数量过多的问题
在 SQL 查询中,当我们面对需要在 IN 子句中列举大量数据的场景时,查询的性能往往会受到显著影响。这时候,使用 EXISTS 可以成为一种优化的良方。 问题的来源 假设我们有两个表,orders 和 customers,我们需要查询所有…...

使用SpringBoot发送邮件|解决了部署时连接超时的bug|网易163|2025
使用SpringBoot发送邮件 文章目录 使用SpringBoot发送邮件1. 获取网易邮箱服务的授权码2. 初始化项目maven部分web部分 3. 发送邮件填写配置EmailSendService [已解决]部署时连接超时附:Docker脚本Dockerfile创建镜像启动容器 1. 获取网易邮箱服务的授权码 温馨提示…...

Ruby Dir 类和方法详解
Ruby Dir 类和方法详解 引言 在 Ruby 中,Dir 是一个非常有用的类,用于处理文件系统中的目录。它提供了许多方便的方法来列出目录内容、搜索文件、以及处理文件系统的其他相关操作。本文将详细介绍 Ruby 的 Dir 类及其常用方法。 一、Dir 类概述 Dir …...

FFmpeg 低延迟同屏方案
引言 在实时互动需求激增的当下,无论是在线教育中的师生同屏演示、远程办公的屏幕共享协作,还是游戏直播的画面实时传输,低延迟同屏已成为保障用户体验的核心指标。FFmpeg 作为一款功能强大的多媒体框架,凭借其灵活的编解码、数据…...
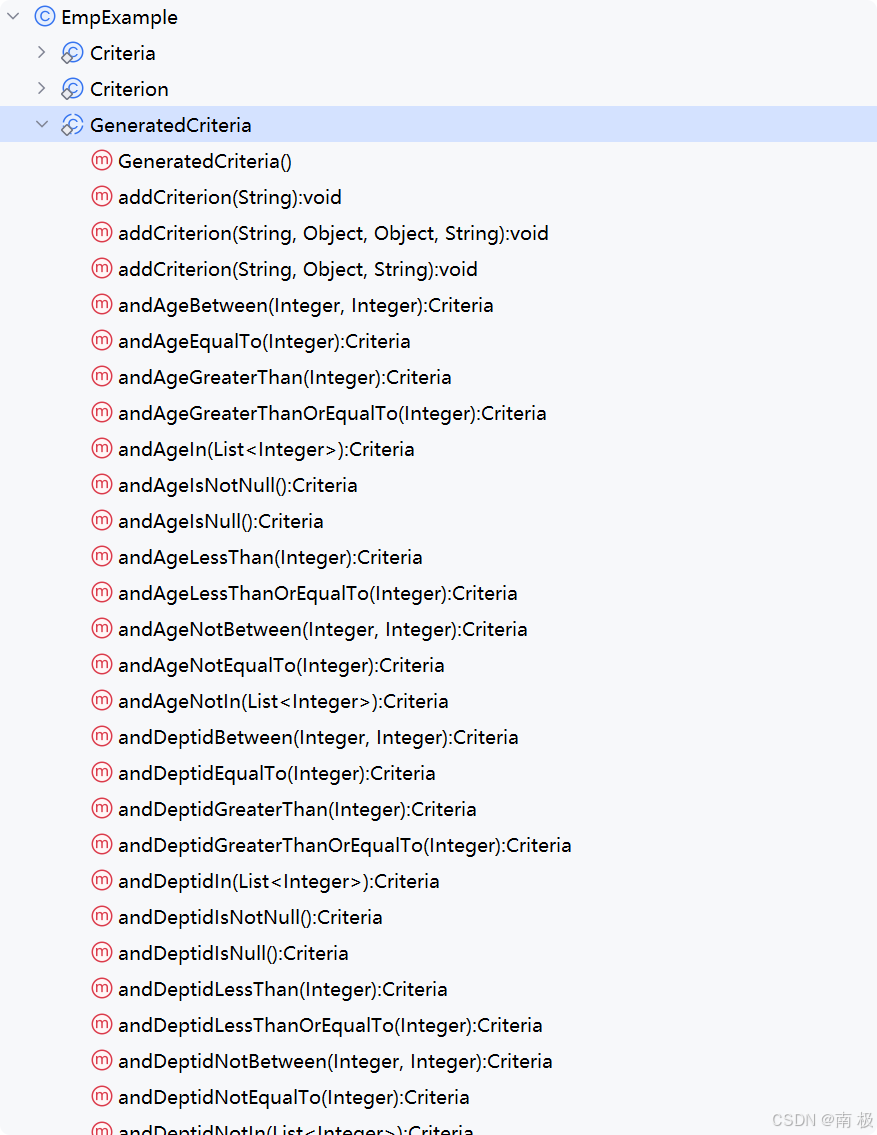
Mybatis逆向工程,动态创建实体类、条件扩展类、Mapper接口、Mapper.xml映射文件
今天呢,博主的学习进度也是步入了Java Mybatis 框架,目前正在逐步杨帆旗航。 那么接下来就给大家出一期有关 Mybatis 逆向工程的教学,希望能对大家有所帮助,也特别欢迎大家指点不足之处,小生很乐意接受正确的建议&…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...
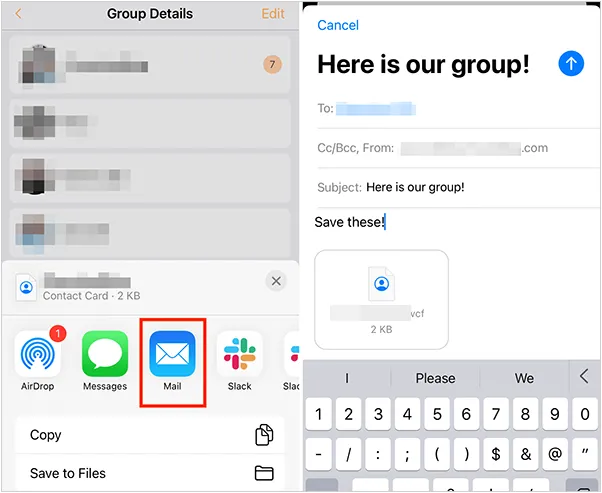
如何将联系人从 iPhone 转移到 Android
从 iPhone 换到 Android 手机时,你可能需要保留重要的数据,例如通讯录。好在,将通讯录从 iPhone 转移到 Android 手机非常简单,你可以从本文中学习 6 种可靠的方法,确保随时保持连接,不错过任何信息。 第 1…...

汇编常见指令
汇编常见指令 一、数据传送指令 指令功能示例说明MOV数据传送MOV EAX, 10将立即数 10 送入 EAXMOV [EBX], EAX将 EAX 值存入 EBX 指向的内存LEA加载有效地址LEA EAX, [EBX4]将 EBX4 的地址存入 EAX(不访问内存)XCHG交换数据XCHG EAX, EBX交换 EAX 和 EB…...
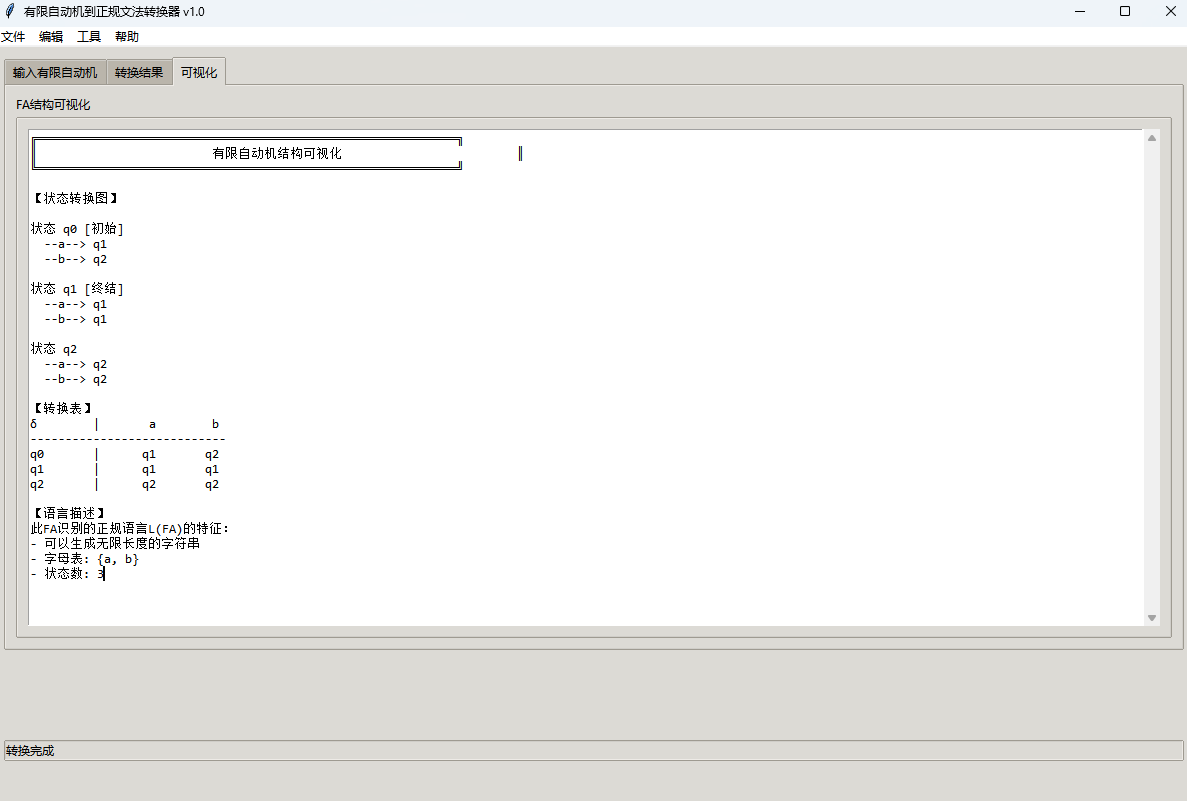
有限自动机到正规文法转换器v1.0
1 项目简介 这是一个功能强大的有限自动机(Finite Automaton, FA)到正规文法(Regular Grammar)转换器,它配备了一个直观且完整的图形用户界面,使用户能够轻松地进行操作和观察。该程序基于编译原理中的经典…...

Aspose.PDF 限制绕过方案:Java 字节码技术实战分享(仅供学习)
Aspose.PDF 限制绕过方案:Java 字节码技术实战分享(仅供学习) 一、Aspose.PDF 简介二、说明(⚠️仅供学习与研究使用)三、技术流程总览四、准备工作1. 下载 Jar 包2. Maven 项目依赖配置 五、字节码修改实现代码&#…...
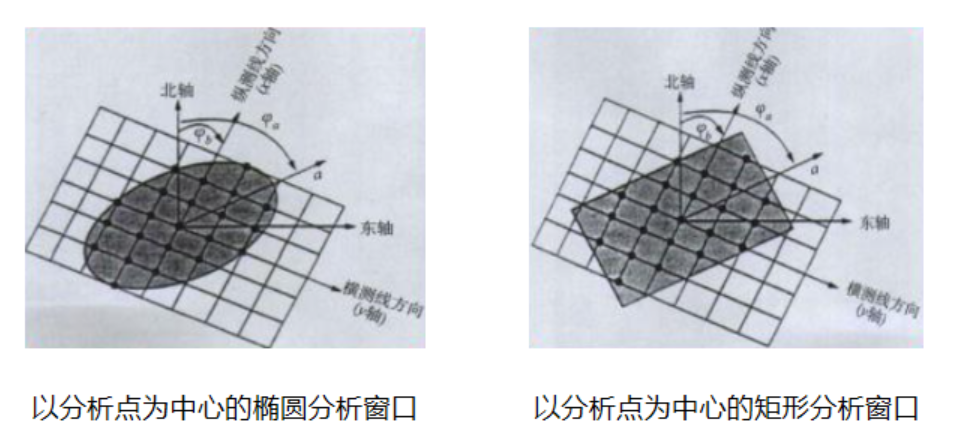
论文笔记——相干体技术在裂缝预测中的应用研究
目录 相关地震知识补充地震数据的认识地震几何属性 相干体算法定义基本原理第一代相干体技术:基于互相关的相干体技术(Correlation)第二代相干体技术:基于相似的相干体技术(Semblance)基于多道相似的相干体…...
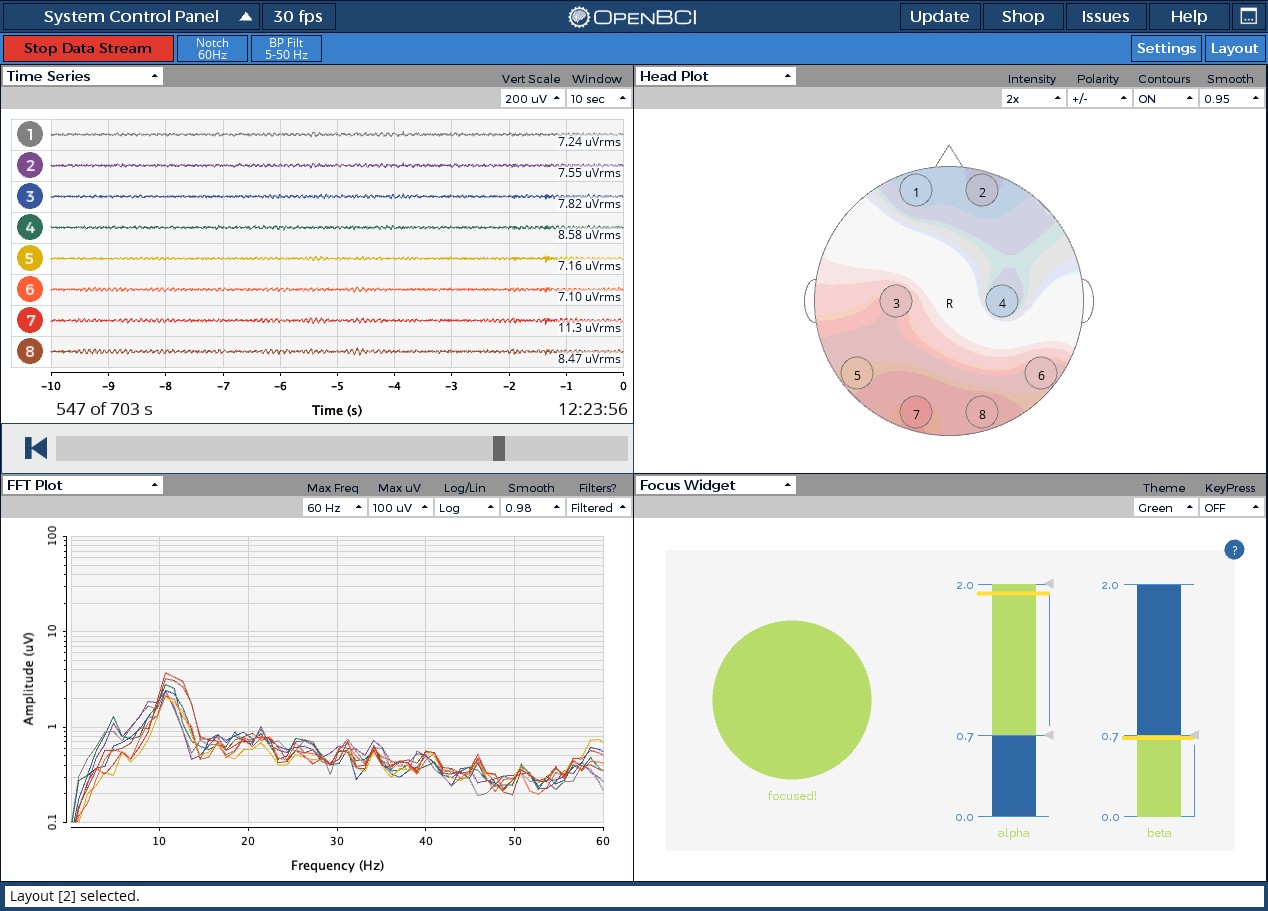
脑机新手指南(七):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(上)
一、OpenBCI_GUI 项目概述 (一)项目背景与目标 OpenBCI 是一个开源的脑电信号采集硬件平台,其配套的 OpenBCI_GUI 则是专为该硬件设计的图形化界面工具。对于研究人员、开发者和学生而言,首次接触 OpenBCI 设备时,往…...
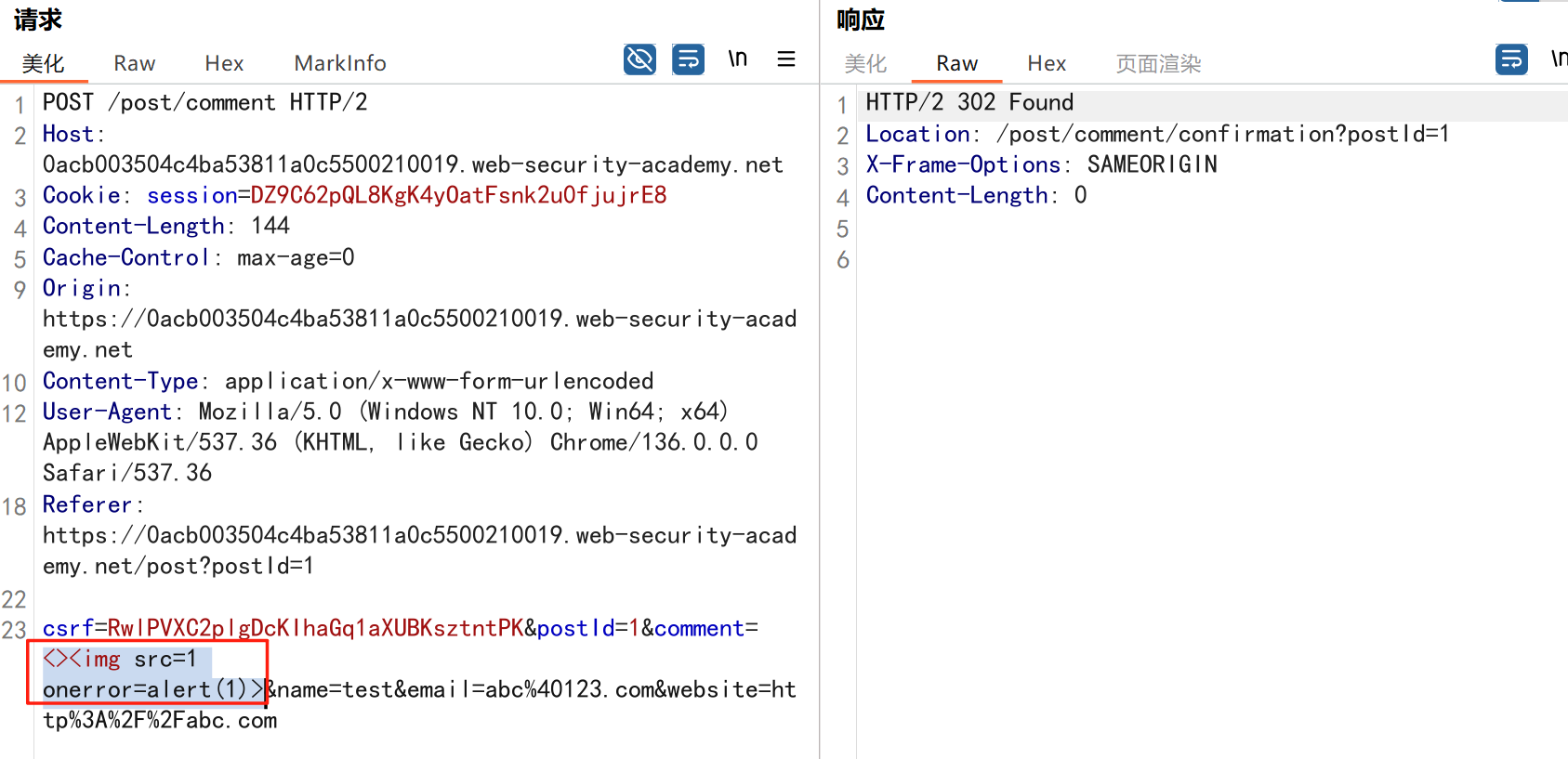
渗透实战PortSwigger靶场:lab13存储型DOM XSS详解
进来是需要留言的,先用做简单的 html 标签测试 发现面的</h1>不见了 数据包中找到了一个loadCommentsWithVulnerableEscapeHtml.js 他是把用户输入的<>进行 html 编码,输入的<>当成字符串处理回显到页面中,看来只是把用户输…...
