What Are Docker Image Layers?
Docker images consist of multiple layers that collectively provide the content you see in your containers. But what actually is a layer, and how does it differ from a complete image?
In this article you’ll learn how to distinguish these two concepts and why the difference matters. While you can use Docker without a thorough understanding of layers, having an awareness of their purpose will help you identify optimization opportunities.
What’s an Image?
A Docker “image” behaves like a template from which consistent containers can be created. If Docker was a traditional virtual machine, the image could be likened to the ISO used to install your VM. This isn’t a robust comparison, as Docker differs from VMs in terms of both concept and implementation, but it’s a useful starting point nonetheless.
Images define the initial filesystem state of new containers. They bundle your application’s source code and its dependencies into a self-contained package that’s ready to use with a container runtime. Within the image, filesystem content is represented as multiple independent layers.
What are Layers?
Layers are a result of the way Docker images are built. Each step in a Dockerfile creates a new “layer” that’s essentially a diff of the filesystem changes since the last step. Metadata instructions such as LABEL and MAINTAINER do not create layers because they don’t affect the filesystem.
This image has two instructions (COPY and RUN) so it’ll create two layers:
FROM ubuntu:latest
COPY foo.txt /foo.txt
RUN date > /built-on.txt
- The first step copies foo.txt into a new layer that’s based on the ubuntu:latest image.
- The second step runs the date command and pipes its output into a file. This creates a second layer that’s based on the previous one.
Create foo.txt in your working directory:
$ echo "Hello World" > foo.txt
Now build the sample image:
$ docker build . -t demo:latest
Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.56kB
Step 1/3 : FROM ubuntu:latest---> df5de72bdb3b
Step 2/3 : COPY foo.txt /foo.txt---> 4932aede6a15
Step 3/3 : RUN date > /built-on.txt---> Running in 91d260fc2e68
Removing intermediate container 91d260fc2e68---> 6f653c6a60fa
Successfully built 6f653c6a60fa
Successfully tagged foo:latest
Each build step emits the ID of the created layer. The last step’s layer becomes the final image so it gets tagged with foo:latest.
The sequence reveals that layers are valid Docker images. Although the term “layer” isn’t normally used to refer to a tagged image, all tagged images are technically just layers with an identifier assigned.
You can start a container from an intermediate layer’s image:
$ docker run -it 4932aede6a15 sh
# cat /foo.txt
Hello World
# cat /built-on.txt
cat: /built-on.txt: No such file or directory
This example starts a container from the layer created by the second build step. foo.txt is available in the container but built-on.txt doesn’t exist because it’s not added until the third step. That file’s only available in the filesystems of subsequent layers.
The Role of Layers
Layers contain the changes created by a build step, relative to the previous layer in the Dockerfile. FROM instructions are a special case that reference the final layer of an existing image.
Layers allow build steps to be cached to avoid redundant work. Docker can skip unchanged instructions in your Dockerfile by reusing the previously created layer. It bases the next step on that existing layer, instead of building a new one.
You can see this by modifying your Dockerfile as follows:
FROM ubuntu:latest
COPY foo.txt /foo.txt
RUN date +%Y-%m-%d > /built-on.txt
The third build step has changed. Now rebuild your image:
$ docker build . -t demo:latest
Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.584kB
Step 1/3 : FROM ubuntu:latest---> df5de72bdb3b
Step 2/3 : COPY foo.txt /foo.txt---> Using cache---> 4932aede6a15
Step 3/3 : RUN date +%Y-%m-%d > /built-on.txt---> Running in 2b91ec0462c4
Removing intermediate container 2b91ec0462c4---> c6647ff378c1
Successfully built c6647ff378c1
Successfully tagged demo:latest
The second build step shows as Using cache and produces the same layer ID. Docker could skip building this layer as it was already created earlier and foo.txt hasn’t changed since the first build.
This caching only works up to the point a layer is modified. All the steps after that layer will need to be rebuilt too so they’re based on the new filesystem revision.
Layers and Pull Operations
Another benefit of layers is how they enable partial image pulls. Once you’ve downloaded a few images to your machine, you’ll often find new pulls can skip some layers that you already have. This image contains 13 layers but only six had to be downloaded by the pull operation:
docker pull php:8.0-apache
8.0-apache: Pulling from library/php
7a6db449b51b: Already exists
ad2afdb99a9d: Already exists
dbc5aa907229: Already exists
82f252ab4ad1: Already exists
bf5b34fc9894: Already exists
6161651d3d95: Already exists
cf2adf296ef1: Already exists
f0d7c5221e44: Pull complete
f647198f6316: Pull complete
c37afe1da4e5: Pull complete
09c93531cbca: Pull complete
fef371007dd3: Pull complete
52043dbb1c06: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:429889e8f9eac0a806a005b0728a004303b0d49d77b09496d39158707abd6280
Status: Downloaded newer image for php:8.0-apache
docker.io/library/php:8.0-apache
The other layers were already present on the Docker host so they could be reused. This improves performance and avoids wasting network bandwidth.
Inspecting Image Layers
You can list the layers within an image by running the docker image history command. Each layer displays the ID of the created image and the Dockerfile instruction that caused the change. You can see the total size of the content within the layer too.
$ docker image history
IMAGE CREATED CREATED BY SIZE COMMENT
6f653c6a60fa 4 minutes ago /bin/sh -c date > /built-on.txt 29B
f8420d1a96f3 4 minutes ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) COPY file:a5630a7506b26a37... 0B
df5de72bdb3b 4 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) CMD ["bash"] 0B
<missing> 4 weeks ago /bin/sh -c #(nop) ADD file:396eeb65c8d737180... 77.8MB
The last layer displays as because it refers to a layer within the ubuntu:latest base image. This is not available locally, as only the final layer of the base image (df5de72bdb3b) gets pulled down during builds. There’s no need to independently pull all the intermediate layers when you want to use a specific image.
Summary
Docker images and layers are generally interchangeable terms. A layer is an image and an image is formed from one or more layers. The major difference lies in tags: an image will be tagged and designed for end users, while the term “layer” normally refers to the untagged intermediate images created as part of a build operation. These aren’t visible unless you go looking for them.
There’s one more topic that relates to layers: running containers add an extra writable layer on top of their image. Layers sourced from the container’s image are read-only so filesystem modifications made by the container target its ephemeral writable layer. The writable layer gets discarded when the container’s stopped or deleted.
相关文章:

What Are Docker Image Layers?
Docker images consist of multiple layers that collectively provide the content you see in your containers. But what actually is a layer, and how does it differ from a complete image? In this article you’ll learn how to distinguish these two concepts and…...
范数详解-torch.linalg.norm计算实例
文章目录 二范数F范数核范数无穷范数L1范数L2范数 前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。点击跳转到网站。 范数是一种数学概念,可以将向量或矩阵映射到非负实数上,通常被…...

postgresdb备份脚本
以下是一个简单的postgresdb备份脚本示例: 复制 #!/bin/bash # 设置备份目录和文件名 BACKUP_DIR/path/to/backup BACKUP_FILEdb_backup_$(date %F_%H-%M-%S).sql # 设置数据库连接参数 DB_HOSTlocalhost DB_PORT5432 DB_NAMEmydatabase DB_USERmyusername DB_PA…...

MATLAB程序员投简历的技巧解析,如何写出有亮点的简历
如果你想在简历中展示你的项目经验,一定要有亮点。一个导出的 Excel 文件过大导致浏览器卡顿的例子就是一个很好的亮点。你可以在简历中写明这个例子。如果面试官问起,可以用浏览器的原理来解释。浏览器内核可以简单地分为以下 5 个线程:GUI …...
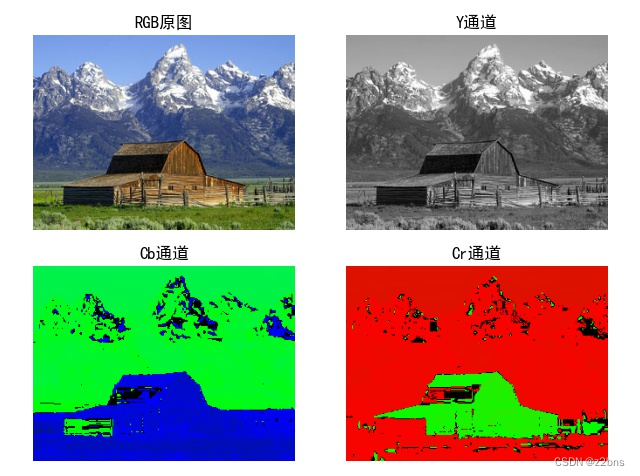
颜色空间转换RGB-YCbCr
颜色空间 颜色空间(Color Space)是描述颜色的一种方式,它是一个由数学模型表示的三维空间,通常用于将数字表示的颜色转换成可见的颜色。颜色空间的不同取决于所选的坐标轴和原点,以及用于表示颜色的色彩模型。在计算机…...

年薪40万程序员辞职炒股,把一年工资亏光了,得了抑郁症,太惨了
年薪40万的程序员辞职全职炒股 把一年的工资亏光了 得了抑郁症 刚才在网上看了一篇文章 是一位北京的一位在互联网 大厂上班的程序员 在去年就是股市行情比较好的时候 他买了30多万股票 结果连续三个月都赚钱 然后呢 他是就把每天就996这种工作就辞掉了 然后在家全是炒股 感觉炒…...
10分钟如何轻松掌握JMeter使用方法?
目录 引言 安装jmeter HTTP信息头管理器 JMeter断言 HTTP请求默认值来代替所有的域名与端口 JSON提取器来替换变量 结语 引言 想要了解网站或应用程序的性能极限,JMeter是一个不可或缺的工具。但是,对于初学者来说,该如何上手使用JMe…...
[NLP]如何训练自己的大型语言模型
简介 大型语言模型,如OpenAI的GPT-4或Google的PaLM,已经席卷了人工智能领域。然而,大多数公司目前没有能力训练这些模型,并且完全依赖于只有少数几家大型科技公司提供技术支持。 在Replit,我们投入了大量资源来建立从…...
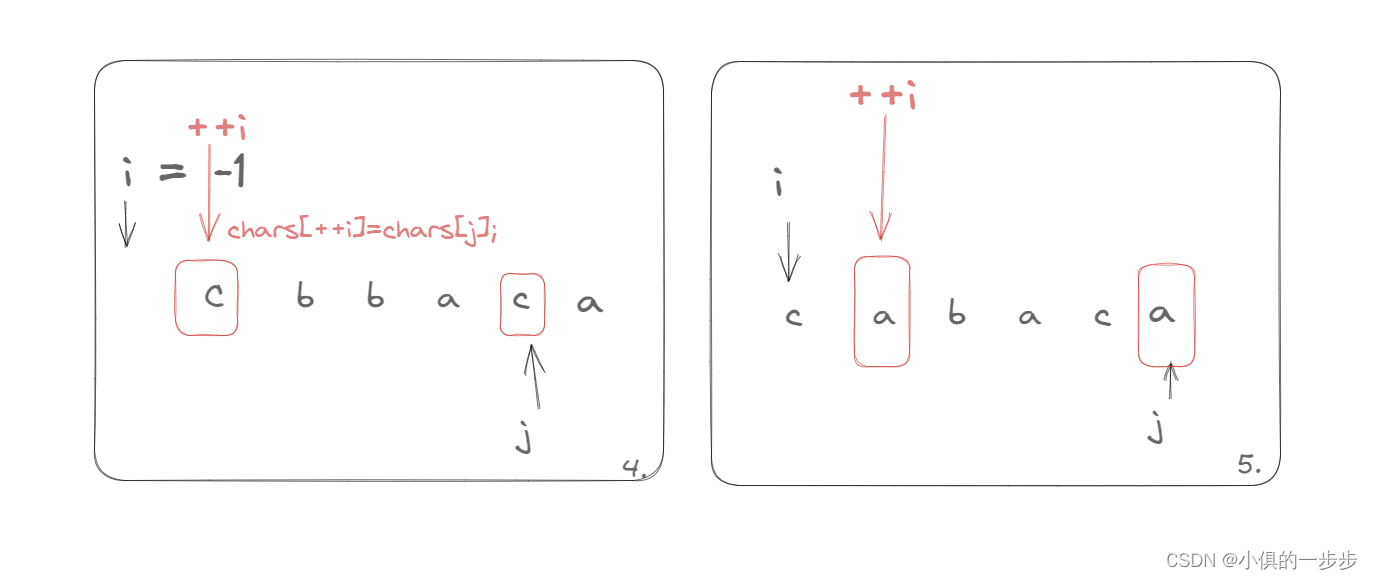
LeetCode1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项 给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。 在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。 在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一…...
)
3。数据结构(3)
嵌入式软件开发第三部分,各类常用的数据结构及扩展,良好的数据结构选择是保证程序稳定运行的关键,(1)部分包括数组,链表,栈,队列。(2)部分包括树,…...

QT停靠窗口QDockWidget类
QT停靠窗口QDockWidget类 QDockWidget类简介函数和方法讲解 QDockWidget类简介 QDockWidget 类提供了一个部件,它可以停靠在 QMainWindow 内或作为桌面上的顶级窗口浮动。 QDockWidget 提供了停靠窗口部件的概念,也称为工具面板或实用程序窗口。 停靠窗…...

【LeetCode】139. 单词拆分
139. 单词拆分(中等) 思路 首先将大问题分解成小问题: 前 i 个字符的子串,能否分解成单词;剩余子串,是否为单个单词; 动态规划的四个步骤: 确定 dp 数组以及下标的含义 dp[i] 表示 s…...

【三维重建】NeRF原理+代码讲解
文章目录 一、技术原理1.概览2.基于神经辐射场(Neural Radiance Field)的体素渲染算法3.体素渲染算法4.位置信息编码(Positional encoding)5.多层级体素采样 二、代码讲解1.数据读入2.创建nerf1.计算焦距focal与其他设置2.get_emb…...
IntelliJ IDEA 社区版2021.3配置SpringBoot项目详细教程及错误解决方法
目录 一、SpringBoot的定义 二、Spring Boot 优点 三、创建一个springboot的项目 四、使用IDEA创建SpringBoot失败案例 一、SpringBoot的定义 Spring 的诞⽣是为了简化 Java 程序的开发的,⽽ Spring Boot 的诞⽣是为了简化 Spring 程序开发的。 Spring Boot 翻…...
Qt中QDebug的使用
QDebug类为调试信息(debugging information)提供输出流。它的声明在<QDebug>中,实现在Core模块中。将调试或跟踪信息(debugging or tracing information)写出到device, file, string or console时都会使用QDebug。 此类的成员函数参考:https://doc…...
vue使用路由的query配置项时如何清除地址栏的参数
写vue项目时,如果想通过路由的query配置项把参数从一个组件传到另一个组件,但是又不希望?idxxx显示在地址栏(如:http://localhost:8080/test?idxxx的?idxxx),该怎么做: 举一个案例࿱…...
)
Redis-列表(List)
Redis列表(List) 介绍 单键多值Redis 列表是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。你可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边)它的底层实际是个双向链表,对两端的操作性能很高,通过索…...

ripro主题修改教程-首页搜索框美化教程
先看效果图: 我们来看怎么实现: 1、找到wp-content/themes/ripro/assets/css/diy.css并将下面的内容整体复制进去并保存 /*首页搜索框*/ .bgcolor-fff {background-color: #fff; } .row,.navbar .menu-item-mega>.sub-menu{margin-left:-10px;margin-right:-10px;} .home…...

写作业用白光还是暖光?盘点色温4000K的护眼台灯
台灯的白光或者暖光指的是台灯的色温,低色温的光线看起来发黄发红,高色温的光线发白发蓝。 如果灯光的光源是高品质光源,本身没有蓝光问题,那么色温的选择对护眼的影响是比较少的,更多的是对人学习工作状态,…...
-- SimpleDateFormat类)
Java时间类(一)-- SimpleDateFormat类
目录 1. SimpleDateFormat的构造方法: 时间模式字母: 2. SimpleDateFormat的常用方法: “工欲善其事,必先利其器”。学习时间类之前,需要先学习SimpleDateFormat类。 java.text.SimpleDateFormat类是以与语言环境有关的方式来格式...

在软件开发中正确使用MySQL日期时间类型的深度解析
在日常软件开发场景中,时间信息的存储是底层且核心的需求。从金融交易的精确记账时间、用户操作的行为日志,到供应链系统的物流节点时间戳,时间数据的准确性直接决定业务逻辑的可靠性。MySQL作为主流关系型数据库,其日期时间类型的…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...

linux 错误码总结
1,错误码的概念与作用 在Linux系统中,错误码是系统调用或库函数在执行失败时返回的特定数值,用于指示具体的错误类型。这些错误码通过全局变量errno来存储和传递,errno由操作系统维护,保存最近一次发生的错误信息。值得注意的是,errno的值在每次系统调用或函数调用失败时…...
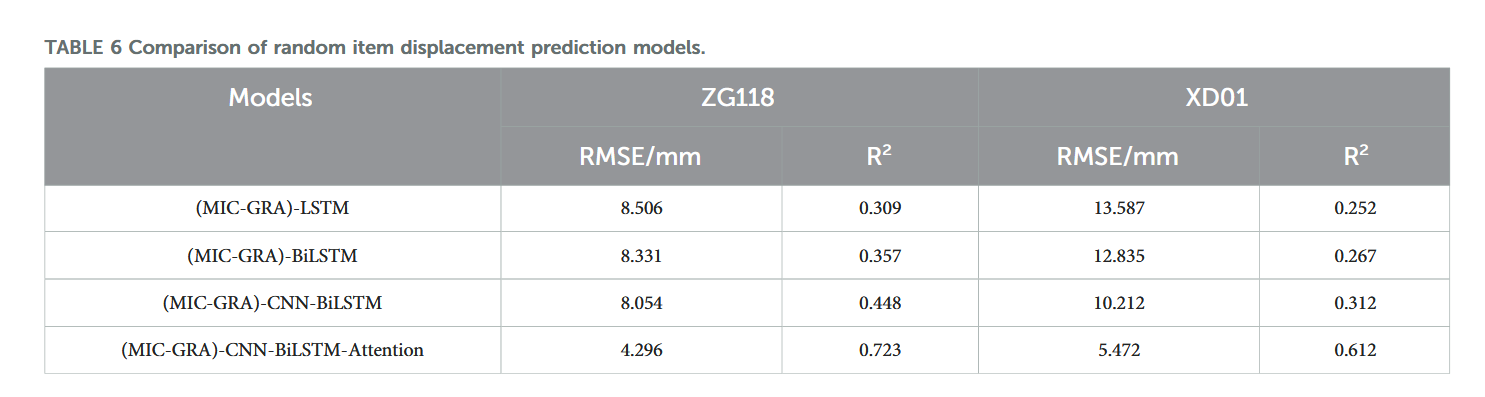
【论文阅读28】-CNN-BiLSTM-Attention-(2024)
本文把滑坡位移序列拆开、筛优质因子,再用 CNN-BiLSTM-Attention 来动态预测每个子序列,最后重构出总位移,预测效果超越传统模型。 文章目录 1 引言2 方法2.1 位移时间序列加性模型2.2 变分模态分解 (VMD) 具体步骤2.3.1 样本熵(S…...
AI书签管理工具开发全记录(十九):嵌入资源处理
1.前言 📝 在上一篇文章中,我们完成了书签的导入导出功能。本篇文章我们研究如何处理嵌入资源,方便后续将资源打包到一个可执行文件中。 2.embed介绍 🎯 Go 1.16 引入了革命性的 embed 包,彻底改变了静态资源管理的…...

MySQL 8.0 事务全面讲解
以下是一个结合两次回答的 MySQL 8.0 事务全面讲解,涵盖了事务的核心概念、操作示例、失败回滚、隔离级别、事务性 DDL 和 XA 事务等内容,并修正了查看隔离级别的命令。 MySQL 8.0 事务全面讲解 一、事务的核心概念(ACID) 事务是…...

Git 3天2K星标:Datawhale 的 Happy-LLM 项目介绍(附教程)
引言 在人工智能飞速发展的今天,大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)已成为技术领域的焦点。从智能写作到代码生成,LLM 的应用场景不断扩展,深刻改变了我们的工作和生活方式。然而,理解这些模型的内部…...

wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像
wpf在image控件上快速显示内存图像https://www.cnblogs.com/haodafeng/p/10431387.html 如果你在寻找能够快速在image控件刷新大图像(比如分辨率3000*3000的图像)的办法,尤其是想把内存中的裸数据(只有图像的数据,不包…...

性能优化中,多面体模型基本原理
1)多面体编译技术是一种基于多面体模型的程序分析和优化技术,它将程序 中的语句实例、访问关系、依赖关系和调度等信息映射到多维空间中的几何对 象,通过对这些几何对象进行几何操作和线性代数计算来进行程序的分析和优 化。 其中࿰…...
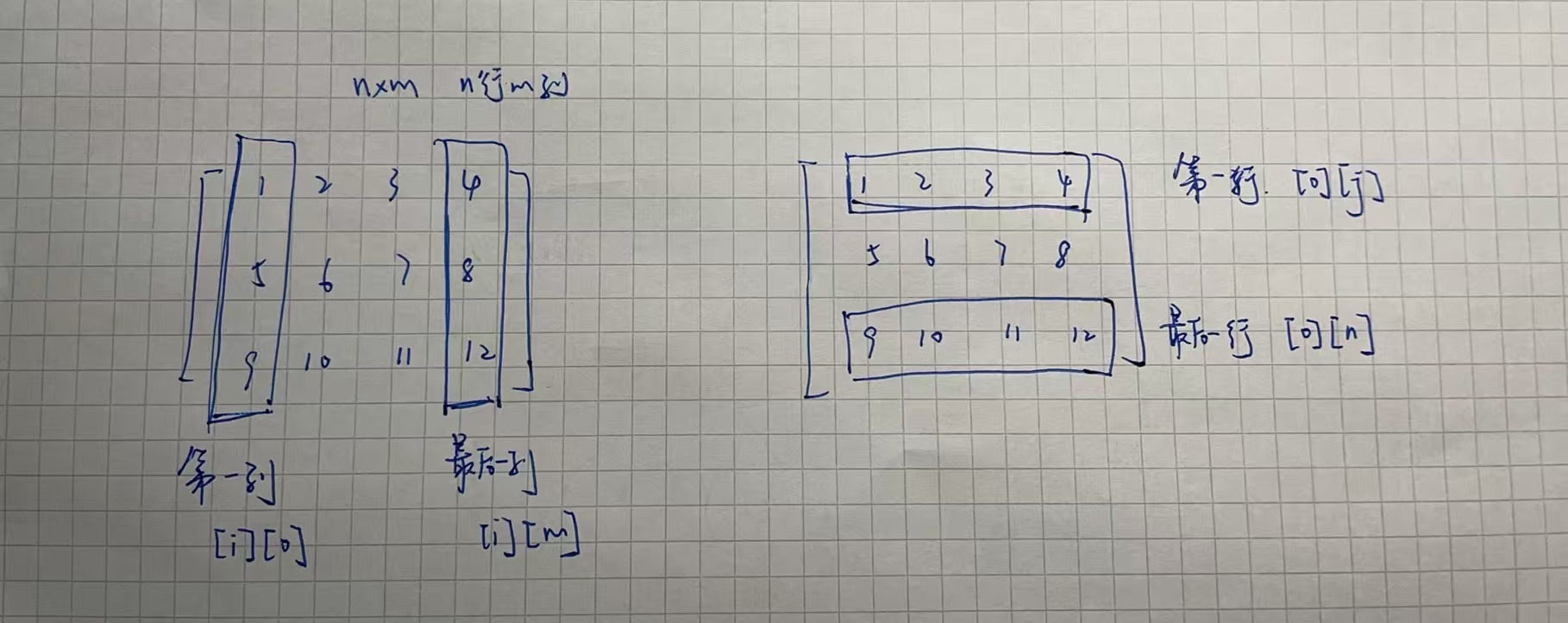
二维数组 行列混淆区分 js
二维数组定义 行 row:是“横着的一整行” 列 column:是“竖着的一整列” 在 JavaScript 里访问二维数组 grid[i][j] 表示 第i行第j列的元素 let grid [[1, 2, 3], // 第0行[4, 5, 6], // 第1行[7, 8, 9] // 第2行 ];// grid[i][j] 表示 第i行第j列的…...
