从零构建深度学习推理框架-9 再探Tensor类,算子输入输出的分配
再探Tensor类:
第二节中我们编写的Tensor类其实并不能满足我们的使用需要,我们将在这一节以代码阅读的方式来看看一个完全版本的Tensor应该具备怎样的要素,同时我们对Tensor类的分析来看看在C++中一个设计好的类应该是怎么样的。
Tensor<float>::Tensor(uint32_t channels, uint32_t rows, uint32_t cols) {data_ = arma::fcube(rows, cols, channels);if (channels == 1 && rows == 1) {this->raw_shapes_ = std::vector<uint32_t>{cols};} else if (channels == 1) {this->raw_shapes_ = std::vector<uint32_t>{rows, cols};} else {this->raw_shapes_ = std::vector<uint32_t>{channels, rows, cols};}
}
在这里,raw_shape记录的是另外一个方面的形状信息,主要用于review和flatten层中。
举一个简单的例子,当Tensor将一个大小为(2,16,1)的Tensor reshape到(32,1,1)的大小时,raw_shapes变量会被记录成(32). 将一个大小为(2,16, 2)的Tensor reshape到(2, 64)的大小时,raw_shapes会被记录成(2,64).
那这样做的目的是什么呢?原来的
Tensor不能在逻辑上区分当前的张量是三维的、二维的还是一维的,因为实际的数据存储类arma::fcube总是一个三维数据。所以我们要区分他的逻辑结构,就需要这么一个raw_shape
列优先的Reshape
void Tensor<float>::ReRawshape(const std::vector<uint32_t>& shapes) {CHECK(!this->data_.empty());CHECK(!shapes.empty());const uint32_t origin_size = this->size();uint32_t current_size = 1;for (uint32_t s : shapes) {current_size *= s;}CHECK(shapes.size() <= 3);CHECK(current_size == origin_size);if (shapes.size() == 3) {this->data_.reshape(shapes.at(1), shapes.at(2), shapes.at(0));this->raw_shapes_ = {shapes.at(0), shapes.at(1), shapes.at(2)};} else if (shapes.size() == 2) {this->data_.reshape(shapes.at(0), shapes.at(1), 1);this->raw_shapes_ = {shapes.at(0), shapes.at(1)};} else {this->data_.reshape(shapes.at(0), 1, 1);this->raw_shapes_ = {shapes.at(0)};}
}
我们再来分析一下这个函数,如果传入的shapes是1维的,就相当于将数据展开为(elem_size,1,1),并将逻辑维度赋值为1. 如果传入的shapes,相当于将数据展开为(shapes.at(0), shapes.at(1), 1). 我们来看看下面的这个图例:
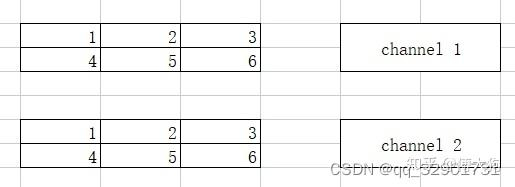
如果把上面的(2,2,3)展平为一维的,那就应该是如下图所示:

而且这也是arma:cube的默认排序(列排序)
行优先的Reshape
那如果我们在某些情况下需要行优先的Reshape呢?
void Tensor<float>::ReView(const std::vector<uint32_t>& shapes) {CHECK(!this->data_.empty());const uint32_t target_channels = shapes.at(0);const uint32_t target_rows = shapes.at(1);const uint32_t target_cols = shapes.at(2);arma::fcube new_data(target_rows, target_cols, target_channels);const uint32_t plane_size = target_rows * target_cols;for (uint32_t c = 0; c < this->data_.n_slices; ++c) {const arma::fmat& channel = this->data_.slice(c);for (uint32_t c_ = 0; c_ < this->data_.n_cols; ++c_) {const float* colptr = channel.colptr(c_);for (uint32_t r = 0; r < this->data_.n_rows; ++r) {const uint32_t pos_index =c * data_.n_rows * data_.n_cols + r * data_.n_cols + c_;const uint32_t ch = pos_index / plane_size;const uint32_t row = (pos_index - ch * plane_size) / target_cols;const uint32_t col = (pos_index - ch * plane_size - row * target_cols);new_data.at(row, col, ch) = *(colptr + r);}}}this->data_ = new_data;
}
我们只能通过位置计算的方式来对逐个元素进行搬运,const uint32_t plane_size = target_rows * target_cols;来计算行数和列数相乘的积。
const uint32_t pos_index = c * data_.n_rows * data_.n_cols + r * data_.n_cols + c_; 得 到调整前的元素下标,随后我们计算调整后的通道下标位置:ch = pos_index / plane_size,plane_size就是和一面,一行乘一列。同理计算row,col等调整位置后的行、列坐标。
计算图关系
内容回顾
我们在回顾一下之前的内容,我们根据pnnx计算图得到了我们的计算图,我们的计算图由两部分组成,分别是kuiper_infer::RuntimeOperator和kuier_infer::RuntimeOperand.
但是作为一个计算图,计算节点之间往往是有连接的,包括从input operator到第一个计算节点再到第二个计算节点,直到最后的输出节点output operator,我们再来回顾一下这两个数据结构的具体定义:
struct RuntimeOperator {int32_t meet_num = 0; /// 计算节点被相连接节点访问到的次数~RuntimeOperator() {for (auto ¶m : this->params) {if (param.second != nullptr) {delete param.second;param.second = nullptr;}}}std::string name; /// 计算节点的名称std::string type; /// 计算节点的类型std::shared_ptr<Layer> layer; /// 节点对应的计算Layerstd::vector<std::string> output_names; /// 节点的输出节点名称std::shared_ptr<RuntimeOperand> output_operands; /// 节点的输出操作数std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<RuntimeOperand>> input_operands; /// 节点的输入操作数std::vector<std::shared_ptr<RuntimeOperand>> input_operands_seq; /// 节点的输入操作数,顺序排列std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<RuntimeOperator>> output_operators; /// 输出节点的名字和节点对应std::map<std::string, RuntimeParameter *> params; /// 算子的参数信息std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<RuntimeAttribute> > attribute; /// 算子的属性信息,内含权重信息
};
- std::map<:string std::shared_ptr>> output_operators; 我们重点来看这个定义,它是当前这个计算节点的下一个计算节点,当数据在当前
RuntimeOperator上计算完成之后,系统会读取output_operators中准备就绪的算子并开始执行。 - std::map<:string std::shared_ptr>> input_operands; 是当前计算节点所需要的输入,它往往来自于上一个
RuntimeOperator的输入。 - std::shared_ptr output_operands; 是当前节点计算得到的输出,它是通过当前的
op计算得到的。
具体的流程是这样的,假设我们在系统中有三个RuntimeOperators,分别为op1,op2和op3. 这三个算子的顺序是依次执行的,分别是op1-->op2-->op3.
- 当我们执行第一个算子
op1的时候,需要将来自于图像的输入填充到op1->input_operands中。 - 第一个算子
op1开始执行,执行的过程中读取op1->input_operands并计算得到相关的输出,放入到op1->output_operands中 - 从
op1的output_operators中读取到ready的op2 - 第二个算子
op2开始执行,执行的过程读取op1->output_operands并拷贝op2->input_operands中,随后op2算子开始执行并计算得到相关的输出,放入到op2->output_operands中。
所以我们可以看到者之间是有一个图关系的,那我们来看一下他是怎么构建这样一个图关系的
怎样构建图关系:
/ 构建图关系for (const auto ¤t_op : this->operators_) {const std::vector<std::string> &output_names = current_op->output_names;for (const auto &next_op : this->operators_) {if (next_op == current_op) {continue;}if (std::find(output_names.begin(), output_names.end(), next_op->name) !=output_names.end()) {current_op->output_operators.insert({next_op->name, next_op});}}}```- **const std::vector\<std::string> &output_names = current_op->output_names;** 存放的是当前`op`的`output_names`,`output_names`也就是当前算子的后一层算子的名字。对于`op1`,它的`output_names`就是`op2`的name.- **const auto &next_op : this->operators_** 我们遍历整个图中的`RuntimeOperators`,如果遇到`next_op`的name和当前`current_op->output_name`是一致的,那么我们就可以认为`next_op`是当前`op`的下一个节点之一。- **current_op->output_operators.insert({next_op->name, next_op});** 将`next_op`插入到`current_op`的下一个节点当中。- 这样一来,当`current_op`执行完成之后就取出`next_op`,并将当前`current_op`的输出`output_opends`(输出)拷贝到`next_op`的`input_operands`(输入)中。因为在初始化的时候就已经约定好了op1的输出是op2,所以只要在接下来的点中不停地寻找op2就好了,找到了之后就把它insert到output_operators里面.这个output_operators是一个map,就可以让输出节点的名字和节点对应。
这么一个计算图也得有输入输出节点吧
作者:傅大狗
链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/604613883
来源:知乎
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
this->input_operators_maps_.clear();this->output_operators_maps_.clear();for (const auto &kOperator : this->operators_) {if (kOperator->type == "pnnx.Input") {this->input_operators_maps_.insert({kOperator->name, kOperator});} else if (kOperator->type == "pnnx.Output") {if (kOperator->name == output_name) {this->output_operators_maps_.insert({kOperator->name, kOperator});} else {LOG(FATAL) << "The graph has two output operator!";}} else {std::shared_ptr<Layer> layer = RuntimeGraph::CreateLayer(kOperator);CHECK(layer != nullptr) << "Layer create failed!";if (layer) {kOperator->layer = layer;}}}
- kOperator->type == "pnnx.Output" 找到
this->operators中的输出节点,但是目前Kuiperinfer只支持一个输出节点,其实也可以多输出,作为一个教学框架我实在不想支持这种corner case - 同理: kOperator->type == "pnnx.Input" 来找到图中,也就是op list中的输入节点
就是在op3结束之后,我们还要把op3的output_operand复制到输出节点的input_operand里面
初始化输入
struct RuntimeOperand {std::string name; /// 操作数的名称std::vector<int32_t> shapes; /// 操作数的形状std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Tensor<float>>> datas; /// 存储操作数 为什么是vector,因为是一个batch,如果batch是2的话,那就存储的是两个RuntimeDataType type = RuntimeDataType::kTypeUnknown; /// 操作数的类型,一般是float
};
可以看到这里的RuntimeOperand::datas就是存储具体数据的地方,我们初始化输入输出的空间也就是要在推理之前先根据shapes来初始化好这里datas的空间
代码位于runtime_ir.cpp的InitOperatorInputTensor中 RuntimeGraphShape::InitOperatorInputTensor(operators_) 这个函数的输入是operator list, 所以将在这个函数中对所有的op进行输入和输出空间的初始化。
- 得到一个
op的输入空间input_operands
const std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<RuntimeOperand>> &input_operands_map = op->input_operands;
- 如果初始的是空就continue
for (const auto &op : operators) {if (op->input_operands.empty()) {continue;} - 得到
input_operands中记录的数据应有大小input_operand_shape和存储数据的变量input_datas
auto &input_datas = input_operand->datas;CHECK(!input_operand_shape.empty());
const int32_t batch = input_operand_shape.at(0);
CHECK(batch >= 0) << "Dynamic batch size is not supported!";
CHECK(input_operand_shape.size() == 2 ||input_operand_shape.size() == 4 ||input_operand_shape.size() == 3)
- 我们需要根据
input_operand_shape中记录的大小去初始化input_datas. 而input_operand_shape可能是三维的,二维的以及一维的,如下方所示 - input_operand_shape : (batch, elemsize) 一维的
- input_operand_shape : (batch, rows,cols) 二维的
- input_operand_shape : (batch, rows,cols, channels) 三维的
如果当前input_operand_shape是二维的数据,也就是说输入维度是(batch,rows,cols)的. 我们首先对batch进行遍历,对一个batch的中的数据input_datas= op->input_operand(输入)进行初始化。
input_datas.resize(batch);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < batch; ++i) {
}
在for循环内,它会调用如下的方法去初始化一个二维的张量:
input_datas.at(i) = std::make_shared<Tensor<float>>(1, input_operand_shape.at(1), input_operand_shape.at(2));
这一块不太清楚,我们实际代码看一遍:
for (int32_t i = 0; i < batch; ++i) {if (input_operand_shape.size() == 4) {input_datas.at(i) = std::make_shared<Tensor<float>>(input_operand_shape.at(1), input_operand_shape.at(2),input_operand_shape.at(3));也就是如果是shape == 4 , 那就是三维的,那么1就是channel,2就是row,3就是col
那么如果输入的channel == 1,或者row == 1
Tensor<float>::Tensor(uint32_t channels, uint32_t rows, uint32_t cols) {data_ = arma::fcube(rows, cols, channels);if (channels == 1 && rows == 1) {this->raw_shapes_ = std::vector<uint32_t>{cols};} else if (channels == 1) {this->raw_shapes_ = std::vector<uint32_t>{rows, cols};} else {this->raw_shapes_ = std::vector<uint32_t>{channels, rows, cols};}
}
那就正好被初始化为了我们之前的raw_shape 这样的一个逻辑维度
这就和我们上面的课程内容对应上了,Tensor<float>原本是一个三维数据,我们怎么在逻辑上给他表现成一个二维的张量呢?这就要用到我们上面说到的raw_shapes了。
- 调用并初始化一维的数据也同理, 在初始化的过程中会调用(channels==1&&rows==1) 这个条件判断,并将
raw_shapes这个维度定义成一维。
input_datas.at(i) = std::make_shared<Tensor<float>>(1, input_operand_shape.at(1), 1)避免第二次初始化
那么在计算的过程中,我们只需要一次初始化就可以。
所以在第二次遇到她的时候,只需要去检查空间是否发生改变就可以啦
if (!input_datas.empty()) {CHECK(input_datas.size() == batch) << "Batch size is wrong!";for (int32_t i = 0; i < batch; ++i) {const std::vector<uint32_t> &input_data_shape =input_datas.at(i)->shapes();CHECK(input_data_shape.size() == 3)<< "THe origin shape size of operator input data do not equals ""to three";if (input_operand_shape.size() == 4) {CHECK(input_data_shape.at(0) == input_operand_shape.at(1) &&input_data_shape.at(1) == input_operand_shape.at(2) &&input_data_shape.at(2) == input_operand_shape.at(3));} else if (input_operand_shape.size() == 2) {CHECK(input_data_shape.at(1) == input_operand_shape.at(1) &&input_data_shape.at(0) == 1 && input_data_shape.at(2) == 1);} else {// current shape size = 3CHECK(input_data_shape.at(1) == input_operand_shape.at(1) &&input_data_shape.at(0) == 1 &&input_data_shape.at(2) == input_operand_shape.at(2));}}} CHECK(input_data_shape.at(0) == input_operand_shape.at(1) &&input_data_shape.at(1) == input_operand_shape.at(2) &&input_data_shape.at(2) == input_operand_shape.at(3));上面这一部分,左边是我们实际有的shape,也就是我们第一次初始化的shape,而右边的是我们再次遇到的时候应该具有的shape,所以这一次就是check这两个shape是否一致,如果check不通过,那就代表输入空间的大小被改变了。那这样的话就会报错,退出这个程序
示例:
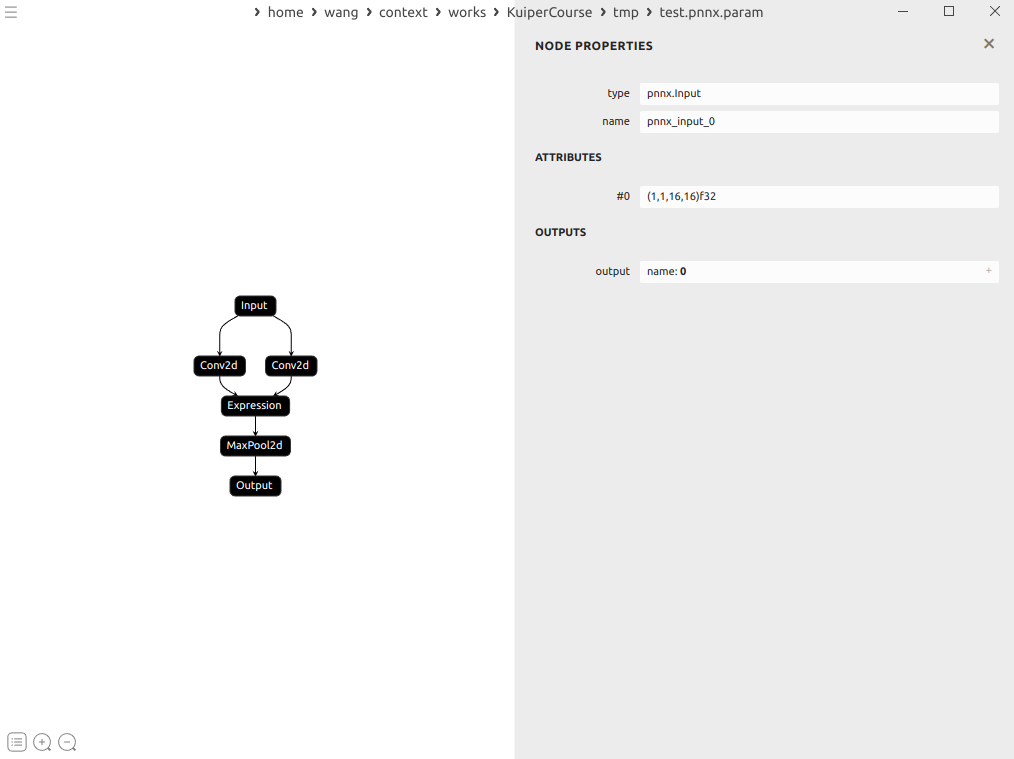
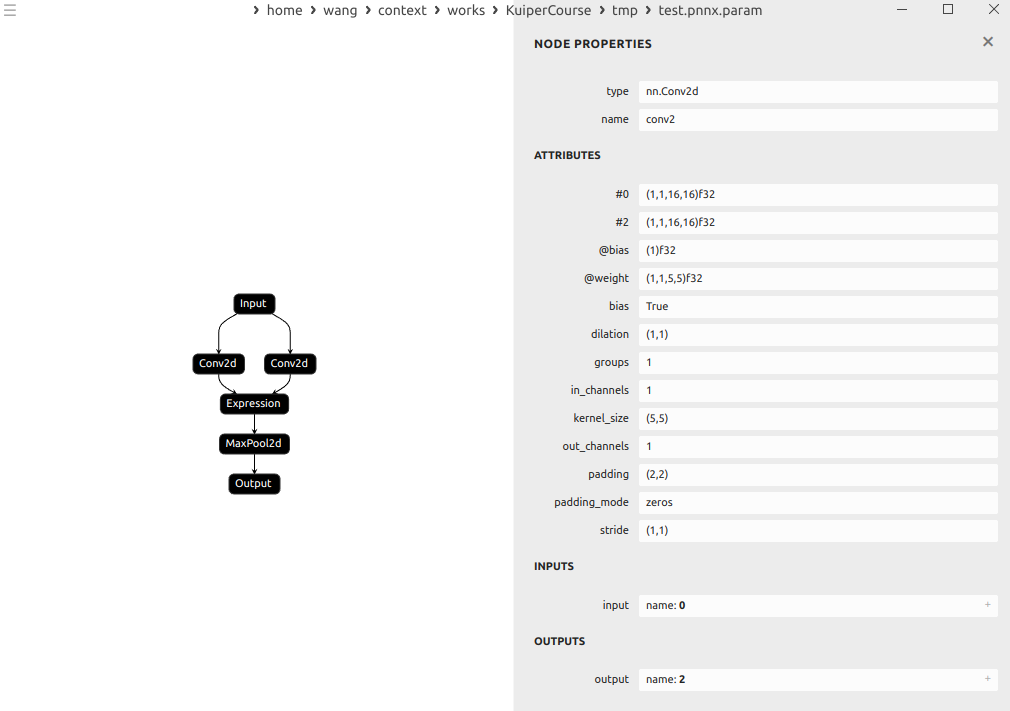
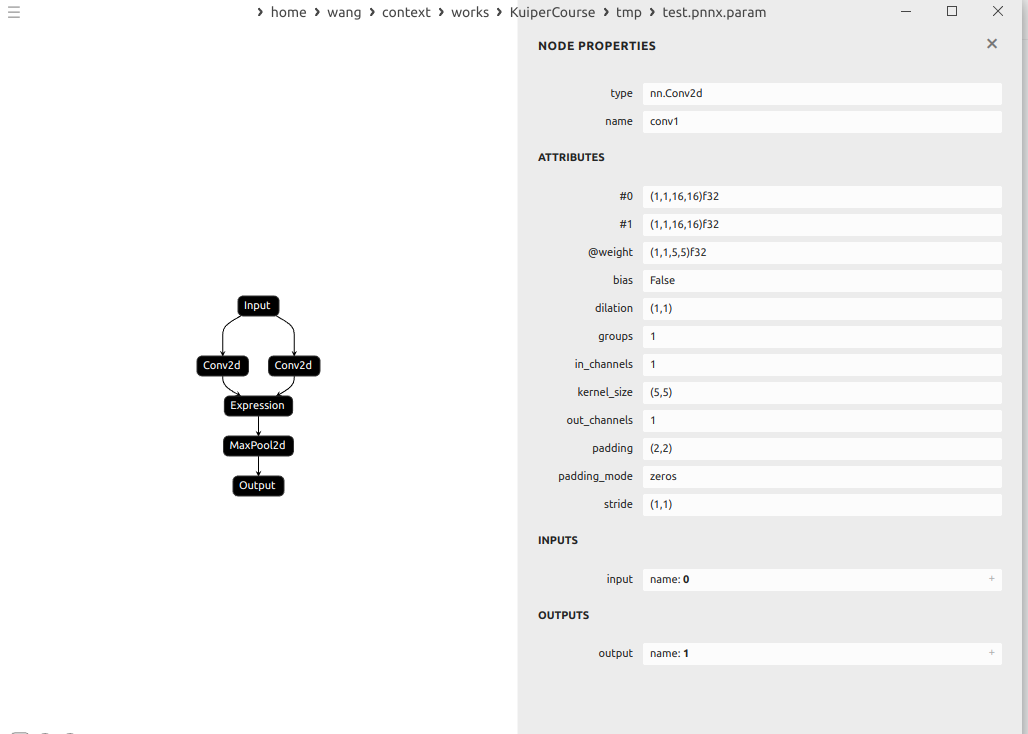
这里的conv的输出分别是1和2
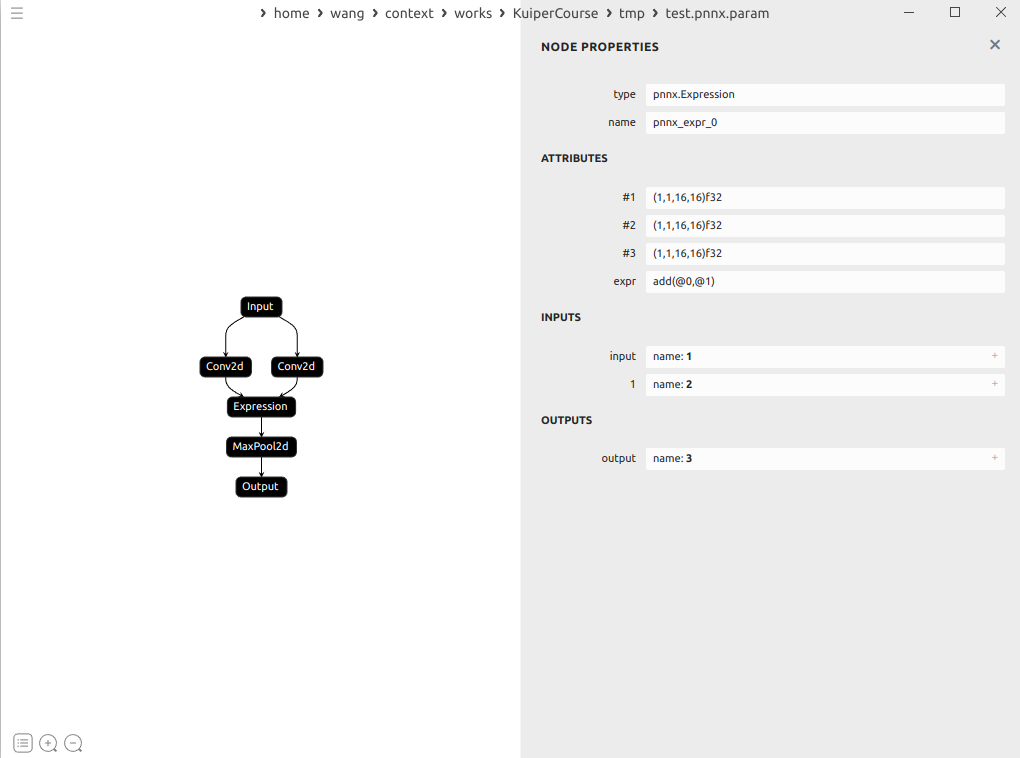
expression就接受了1和2为输入
最近在忙老师布置的任务,就耽误了这方面的进度,慢慢补把
相关文章:

从零构建深度学习推理框架-9 再探Tensor类,算子输入输出的分配
再探Tensor类: 第二节中我们编写的Tensor类其实并不能满足我们的使用需要,我们将在这一节以代码阅读的方式来看看一个完全版本的Tensor应该具备怎样的要素,同时我们对Tensor类的分析来看看在C中一个设计好的类应该是怎么样的。 Tensor<fl…...

Vue使用element-ui
main.js配置 //引入Vue import Vue from vue //引入App import App from ./App.vue//完整引入 //引入ElementUI组件库 // import ElementUI from element-ui; //引入ElementUI全部样式 // import element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css;//按需引入 import { Button,Row,DatePi…...

使用ApplicationRunner简化Spring Boot应用程序的初始化和启动
ApplicationRunner这个接口,我们一起来了解这个组件,并简单使用它吧。🤭 引言 在开发Spring Boot应用程序时,应用程序的初始化和启动是一个重要的环节。ApplicationRunner是Spring Boot提供的一个有用的接口,可以帮助…...

Vue 2.x 项目升级到 Vue 3详细指南【修改清单】
文章目录 前言0.迁移过程1. 安装 Vue 32. 逐一处理迁移中的警告3. 迁移全局和内部 API4. 迁移 Vue Router 和 Vuex5. 处理其他的不兼容变更 1. Vue3特性1. Composition API2. 更好的性能3. 更好的 TypeScript 支持4. 多个根元素5. Suspense 组件6. Teleport 组件7. 全局 API 的…...
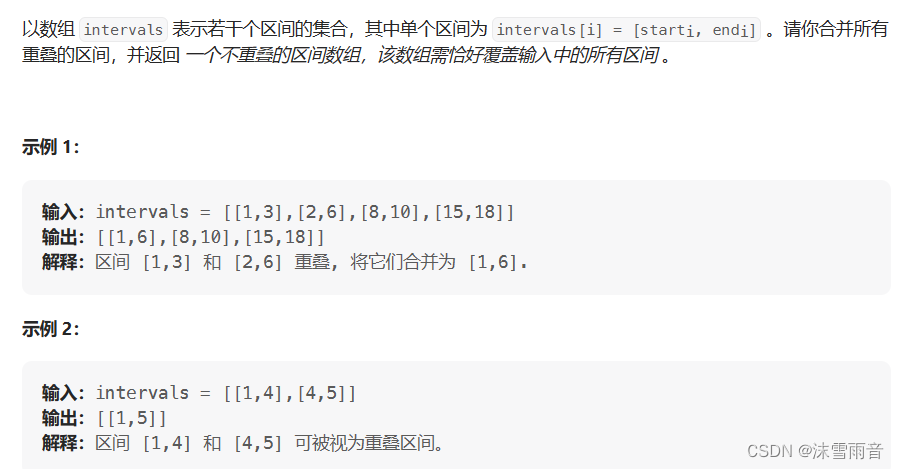
【算法日志】贪心算法刷题:重叠区问题(day31)
代码随想录刷题60Day 目录 前言 无重叠区间(筛选区间) 划分字母区间(切割区间) 合并区间 前言 今日的重点是掌握重叠区问题。 无重叠区间(筛选区间) int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector<vector<in…...
基于Jenkins构建生产CICD环境、jenkins安装
目录 Jenkins简介 安装配置Jenkins Jenkins简介 Jenkins是一个用Java编写的开源的持续集成工具。在与Oracle发生争执后,项目从Hudson项目独立。官方网站:https://jenkins.io/。 Jenkins提供了软件开发的持续集成服务。它运行在Servlet容器中ÿ…...
基于Java SpringBoot+vue+html 的地方美食系统(2.0版本)
博主介绍:✌程序员徐师兄、7年大厂程序员经历。全网粉丝30W,csdn、博客专家、掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域和毕业项目实战✌ 文章目录 1 简介2 技术栈3 系统流程的分析3.1 用户管理的流程3.2个人中心管理流程3.3登录流程 4系统设计…...
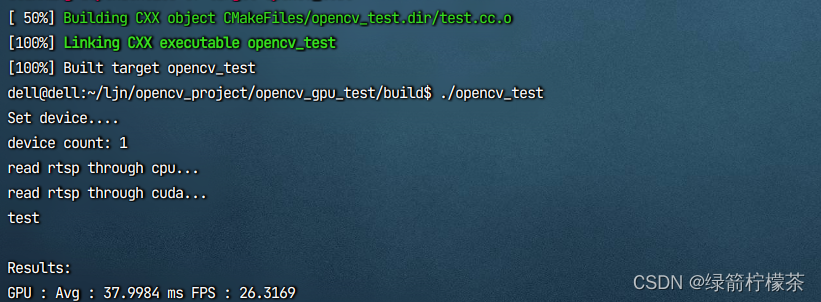
opencv-gpu版本编译(添加java支持,可选)实现硬解码
目录 opencv gpu版本编译,实现硬解码,加速rtsp视频流读取1、准备文件2、复制 NVCUVID 头文件到 cuda 安装目录 include3、安装相关依赖4、 执行cmake5、编译安装6、测试 opencv gpu版本编译,实现硬解码,加速rtsp视频流读取 前置条…...
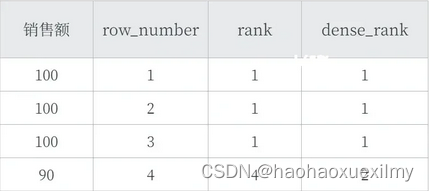
数据分析问答总结
一、SQL窗口函数 1.是什么 OLAP(Online Anallytical Processing联机分析处理),对数据库数据进行实时分析处理。 2.基本语法: <窗口函数>OVER (PARTITION BY <用于分组的列名> ORDER BY <用于排序的…...
Python学习笔记_实战篇(二)_django多条件筛选搜索
多条件搜索在很多网站上都有用到,比如京东,淘宝,51cto,等等好多购物教育网站上都有,当然网上也有很多开源的比楼主写的好的多了去了,仅供参考,哈哈 先来一张效果图吧,不然幻想不出来…...

【生态经济学】利用R语言进行经济学研究技术——从数据的收集与清洗、综合建模评价、数据的分析与可视化、因果推断等方面入手
查看原文>>>如何快速掌握利用R语言进行经济学研究技术——从数据的收集与清洗、综合建模评价、数据的分析与可视化、因果推断等方面入手 近年来,人工智能领域已经取得突破性进展,对经济社会各个领域都产生了重大影响,结合了统计学、…...

xml中的vo是干什么用的
在Java中,VO(Value Object)是一种常见的设计模式,用于表示纯粹的数据对象。VO 通常用于在不同层或模块之间传递数据,并且它们的主要目的是封装和组织数据,而不包含业务逻辑。 VO 在Java中的具体作用有以下…...

现代企业数据泄露的原因分析与建议
近年来,随着信息技术的飞速发展,数据已经成为现代企业不可或缺的发展资源。然而,随之而来的数据泄露危机,给个人、企业甚至整个社会带来了巨大的风险与威胁。本文将综合探讨企业数据泄露的主要途径和原因,并提出防护建…...
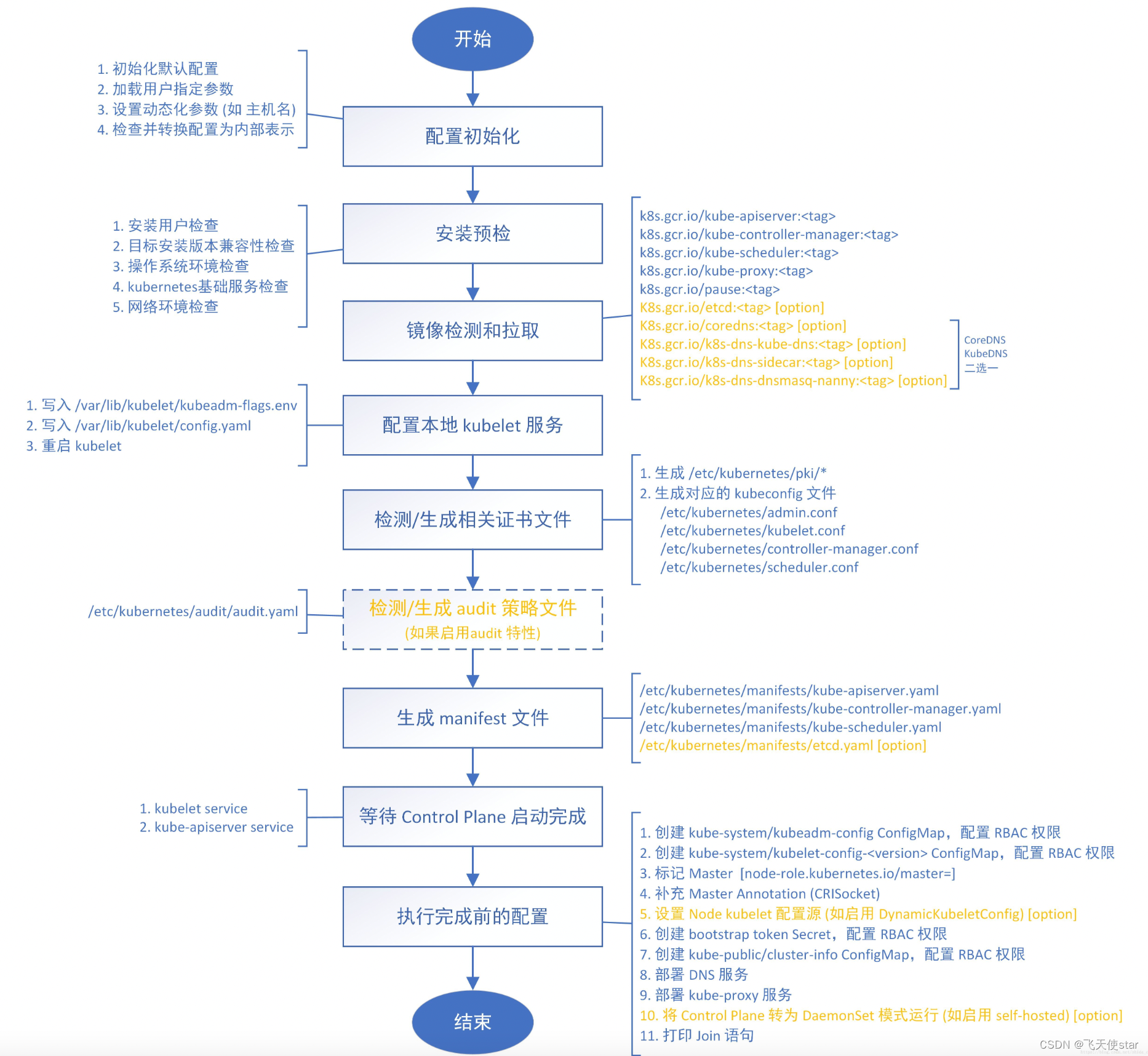
飞天使-kubeadm安装一主一从集群
文章目录 安装前准备安装前准备配置yum源等安装前准备docker安装 安装kubeadm配置kubeadm验证集群 参考链接 安装前准备 cat >> /etc/hosts <<EOF 192.168.100.30 k8s-01 192.168.100.31 k8s-02 EOF hostnamectl set-hostname k8s-01 #所有机器按照要求修改 ho…...

string类写时拷贝
文章目录 1.string类拷贝构造函数的现代写法2.string类写时拷贝vs和g下string结构的不同vs下string的结构:g下string的结构 3.总结 1.string类拷贝构造函数的现代写法 string类拷贝构造函数的传统写法: string(const string& s){if (this ! &s)…...
QT VS编译环境无法打开包括文件type_traits
这问题,别人给的处理方法都是: 添加环境变量执行vsvars32.bat/vcvarsall.bat/vsdevcmd.bat重新安装QT项目:执行qmake。。。。 个人不推荐配置环境编译,除非你非常熟,因为配置环境变量需要你知道有哪些路径需要添加&a…...
深入浅出 TCP/IP 协议栈
TCP/IP 协议栈是一系列网络协议的总和,是构成网络通信的核心骨架,它定义了电子设备如何连入因特网,以及数据如何在它们之间进行传输。TCP/IP 协议采用4层结构,分别是应用层、传输层、网络层和链路层,每一层都呼叫它的下…...

Servlet+JDBC实战开发书店项目讲解第13讲:库存管理功能
ServletJDBC实战开发书店项目讲解第13讲:库存管理功能 在第13讲中,我们将讲解如何实现书店项目中的库存管理功能。该功能包括图书的添加、编辑、删除和查询等核心功能。下面是实现该功能的主要思路: 显示库存列表: 创建一个管理页…...

Shepherd: A Critic for Language Model Generation
本文是LLM系列的相关文章,针对《Shepherd: A Critic for Language Model Generation》的翻译。 Shepherd:语言模型生成的评价 摘要1 引言2 数据收集3 Shepherd模型4 评估反馈5 结果6 相关工作7 结论不足 摘要 随着大型语言模型的改进,人们对…...
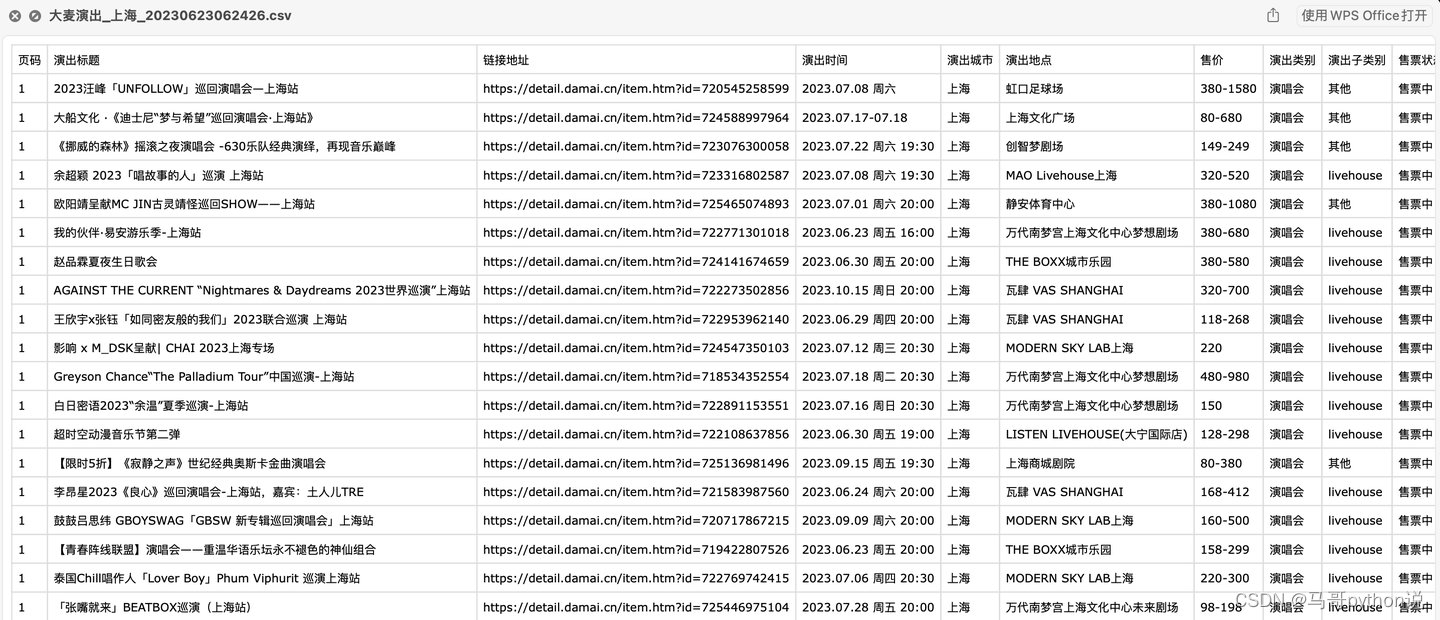
【Python爬虫案例】爬取大麦网任意城市的近期演出!
老规矩,先上结果: 含10个字段: 页码,演出标题,链接地址,演出时间,演出城市,演出地点,售价,演出类别,演出子类别,售票状态。 代码演示…...
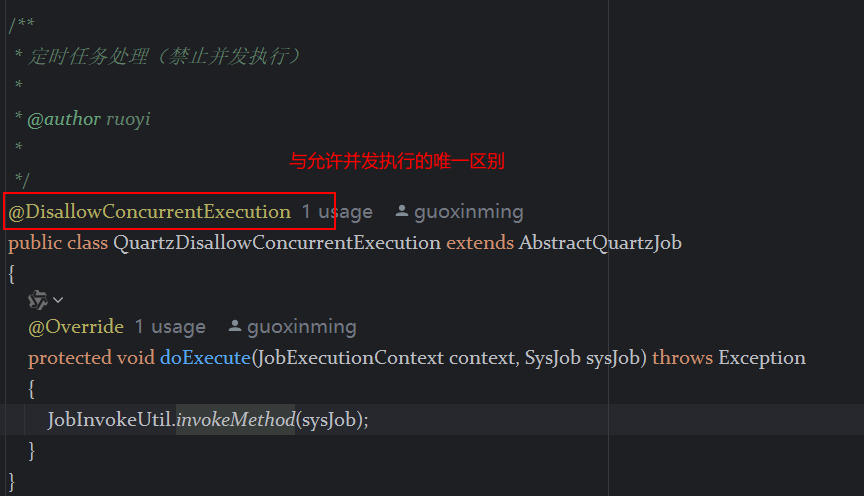
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
Module Federation 和 Native Federation 的比较
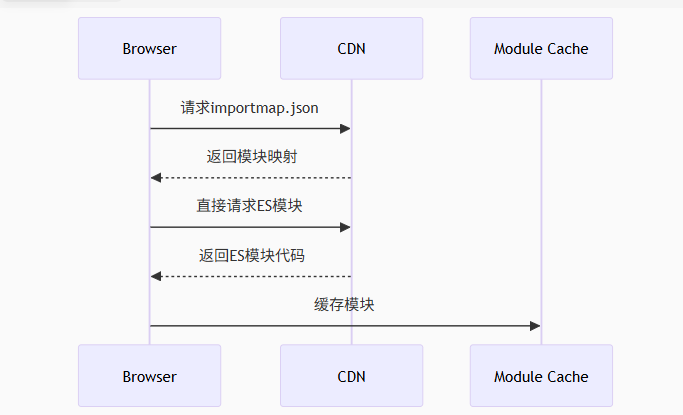
前言 Module Federation 是 Webpack 5 引入的微前端架构方案,允许不同独立构建的应用在运行时动态共享模块。 Native Federation 是 Angular 官方基于 Module Federation 理念实现的专为 Angular 优化的微前端方案。 概念解析 Module Federation (模块联邦) Modul…...

成都鼎讯硬核科技!雷达目标与干扰模拟器,以卓越性能制胜电磁频谱战
在现代战争中,电磁频谱已成为继陆、海、空、天之后的 “第五维战场”,雷达作为电磁频谱领域的关键装备,其干扰与抗干扰能力的较量,直接影响着战争的胜负走向。由成都鼎讯科技匠心打造的雷达目标与干扰模拟器,凭借数字射…...
自然语言处理——循环神经网络
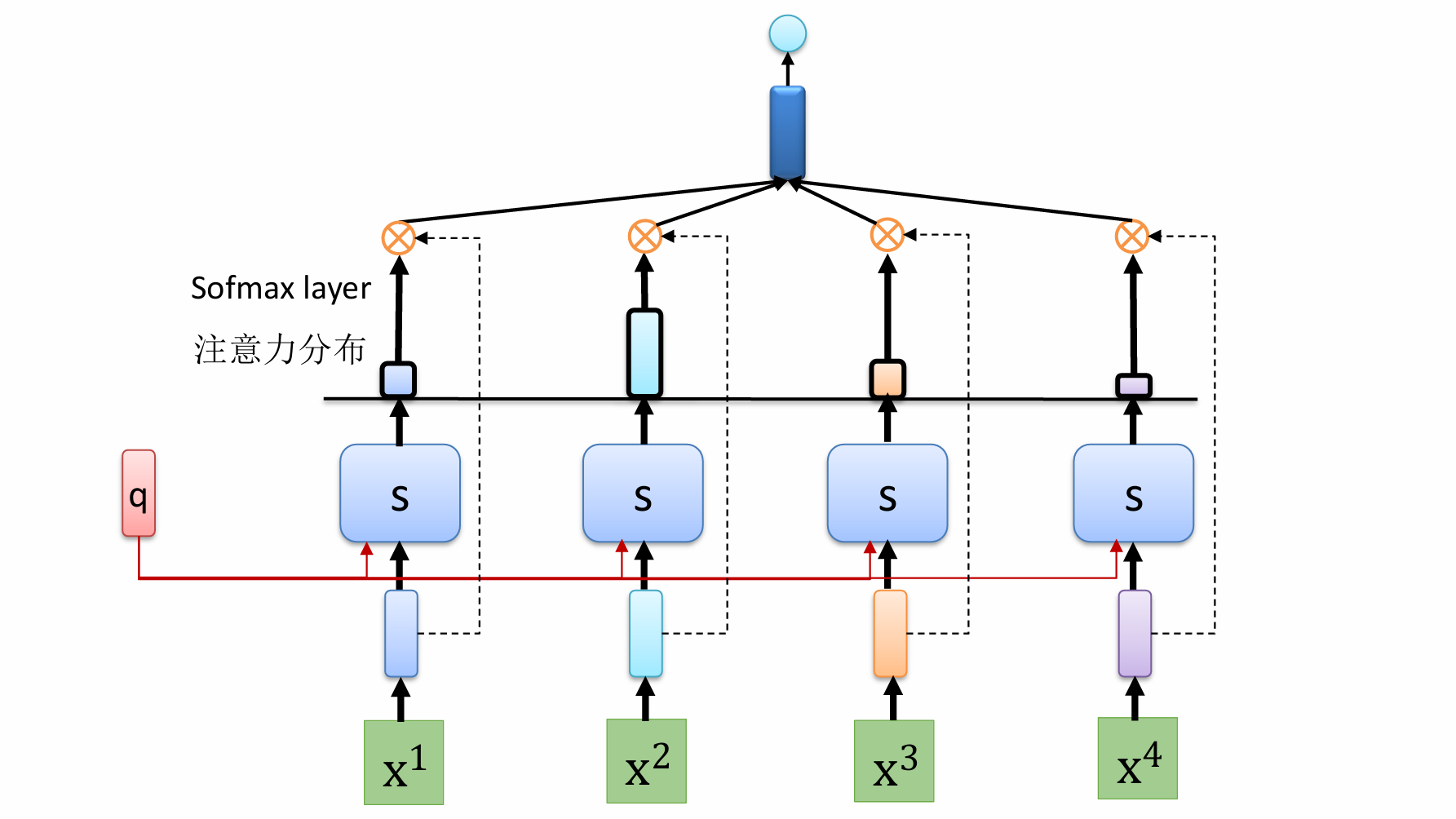
自然语言处理——循环神经网络 循环神经网络应用到基于机器学习的自然语言处理任务序列到类别同步的序列到序列模式异步的序列到序列模式 参数学习和长程依赖问题基于门控的循环神经网络门控循环单元(GRU)长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)…...
Springboot社区养老保险系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,社区养老保险系统小程序被用户普遍使用,为方…...
Selenium常用函数介绍
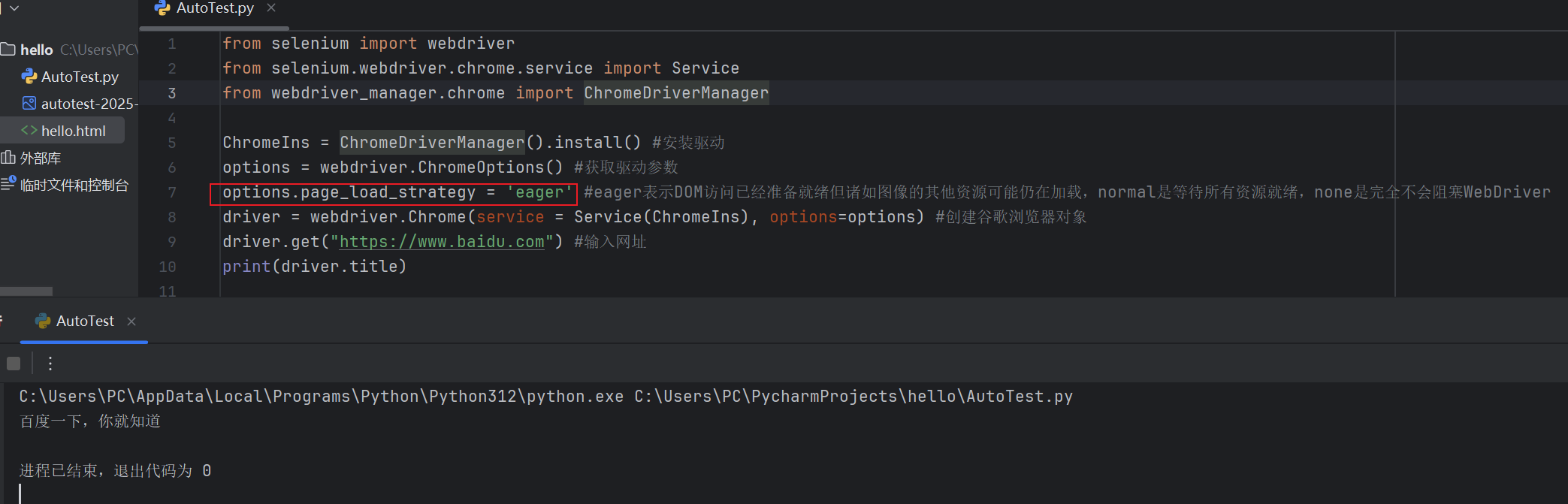
目录 一,元素定位 1.1 cssSeector 1.2 xpath 二,操作测试对象 三,窗口 3.1 案例 3.2 窗口切换 3.3 窗口大小 3.4 屏幕截图 3.5 关闭窗口 四,弹窗 五,等待 六,导航 七,文件上传 …...

Python+ZeroMQ实战:智能车辆状态监控与模拟模式自动切换
目录 关键点 技术实现1 技术实现2 摘要: 本文将介绍如何利用Python和ZeroMQ消息队列构建一个智能车辆状态监控系统。系统能够根据时间策略自动切换驾驶模式(自动驾驶、人工驾驶、远程驾驶、主动安全),并通过实时消息推送更新车…...
群晖NAS如何在虚拟机创建飞牛NAS
套件中心下载安装Virtual Machine Manager 创建虚拟机 配置虚拟机 飞牛官网下载 https://iso.liveupdate.fnnas.com/x86_64/trim/fnos-0.9.2-863.iso 群晖NAS如何在虚拟机创建飞牛NAS - 个人信息分享...
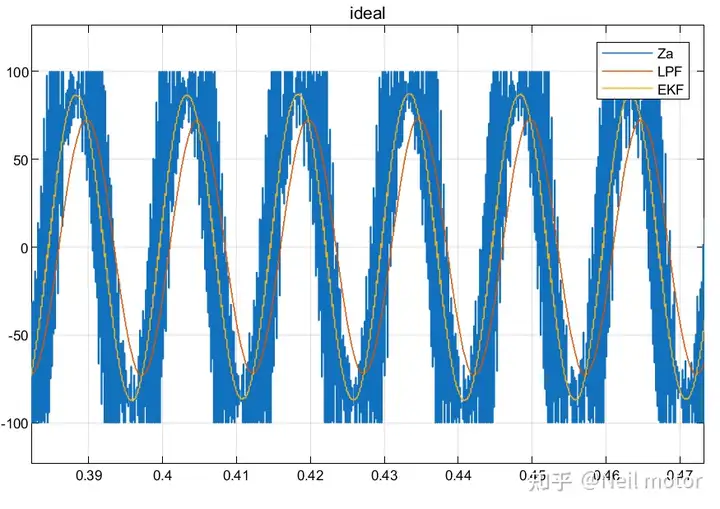
永磁同步电机无速度算法--基于卡尔曼滤波器的滑模观测器
一、原理介绍 传统滑模观测器采用如下结构: 传统SMO中LPF会带来相位延迟和幅值衰减,并且需要额外的相位补偿。 采用扩展卡尔曼滤波器代替常用低通滤波器(LPF),可以去除高次谐波,并且不用相位补偿就可以获得一个误差较小的转子位…...

实战三:开发网页端界面完成黑白视频转为彩色视频
一、需求描述 设计一个简单的视频上色应用,用户可以通过网页界面上传黑白视频,系统会自动将其转换为彩色视频。整个过程对用户来说非常简单直观,不需要了解技术细节。 效果图 二、实现思路 总体思路: 用户通过Gradio界面上…...
