数据挖掘流程简单示例10min
数据挖掘流程简单示例10min
套路:
- 准备数据
- 实现算法
- 测试算法
任务1:亲和性分析
如果一个顾客买了商品X,那么他们可能愿意买商品Y衡量方法:
-
支持度support := 所有买X的人数
-
置信度confidence := 所有买X和Y的人数所有买X的人数\frac{ 所有买X和Y的人数 } { 所有买X的人数 }所有买X的人数所有买X和Y的人数
# 引入库
import numpy as np
from operator import itemgetter
# 准备数据# 创造随机生成的数据
X = np.zeros((100, 5), dtype='bool')
for i in range(X.shape[0]):if np.random.random() < 0.3:# A bread winnerX[i][0] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.5:# Who likes milkX[i][1] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.2:# Who likes cheeseX[i][2] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.25:# Who likes applesX[i][3] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.5:# Who likes bananasX[i][4] = 1else:# Not a bread winnerif np.random.random() < 0.5:# Who likes milkX[i][1] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.2:# Who likes cheeseX[i][2] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.25:# Who likes applesX[i][3] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.5:# Who likes bananasX[i][4] = 1else:if np.random.random() < 0.8:# Who likes cheeseX[i][2] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.6:# Who likes applesX[i][3] = 1if np.random.random() < 0.7:# Who likes bananasX[i][4] = 1if X[i].sum() == 0:X[i][4] = 1 # Must buy something, so gets bananas
np.savetxt("./data/affinity_dataset.txt", X, fmt='%d') # 保存# 读取数据
dataset_filename = "./data/affinity_dataset.txt"
X = np.loadtxt(dataset_filename) # 加载数据
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
print(X.shape)
print(X[:5])'''
(100, 5)
[[0. 0. 1. 1. 0.][1. 1. 0. 0. 0.][1. 0. 0. 1. 1.][0. 1. 1. 0. 1.][0. 1. 0. 0. 0.]]'''
我们定义的规则为:买了苹果又买香蕉
下面 rule_valid 表示买了苹果又买香蕉的有多少人
显然支持度 := 所有买X的人数,即支持度=rule_valid
所以置信度=支持度/总人数
# 文件affinity_dataset.txt是生成的数据,得我们来指定列
features = ["bread", "milk", "cheese", "apples", "bananas"]num_apple_purchases = 0 # 计数
for sample in X:if sample[3] == 1: # 记录买 Apples 的有多少人num_apple_purchases += 1
print("买苹果的有{0}人".format(num_apple_purchases))rule_valid = 0
rule_invalid = 0
for sample in X:if sample[3] == 1: # 买了苹果if sample[4] == 1:# 又买香蕉的rule_valid += 1else:# 不买香蕉的rule_invalid += 1
print("买了苹果又买香蕉的有{0}人".format(rule_valid))
print("买了苹果不买香蕉的有{0}人".format(rule_invalid))# 计算支持度support和置信度confidence
support = rule_valid # 支持度是符合“买了苹果又买香蕉”这个规则的人数
confidence = rule_valid / num_apple_purchases
print("支持度support = {0} 置信度confidence = {1:.3f}.".format(support, confidence))
# 置信度的百分比形式
print("置信度confidence的百分比形式为 {0:.1f}%.".format(100 * confidence))'''
买苹果的有39人
买了苹果又买香蕉的有23人
买了苹果不买香蕉的有16人
支持度support = 23 置信度confidence = 0.590.
置信度confidence的百分比形式为 59.0%.
'''
from collections import defaultdict
# 上面"买了苹果又买香蕉"是一种情况,现在把所有可能的情况都做一遍
valid_rules = defaultdict(int)
invalid_rules = defaultdict(int)
num_occurences = defaultdict(int)for sample in X:for premise in range(n_features):if sample[premise] == 0: continue# 先买premise,premise代表一种食物,记做Xnum_occurences[premise] += 1for conclusion in range(n_features):if premise == conclusion: continue # 跳过买X又买X的情况if sample[conclusion] == 1: # 又买了conclusion,conclusion代表一种食物,记做Yvalid_rules[(premise, conclusion)] += 1 # 买X买Yelse: invalid_rules[(premise, conclusion)] += 1 # 买X没买Y
support = valid_rules
confidence = defaultdict(float)
for premise, conclusion in valid_rules.keys():confidence[(premise, conclusion)] = valid_rules[(premise, conclusion)] / num_occurences[premise]
for premise, conclusion in confidence:premise_name = features[premise]conclusion_name = features[conclusion]print("Rule: 买了{0},又买{1}".format(premise_name, conclusion_name))print(" - 置信度Confidence: {0:.3f}".format(confidence[(premise, conclusion)]))print(" - 支持度Support: {0}".format(support[(premise, conclusion)]))print("")'''
Rule: 买了cheese,又买apples- 置信度Confidence: 0.553- 支持度Support: 26Rule: 买了apples,又买cheese- 置信度Confidence: 0.667- 支持度Support: 26Rule: 买了bread,又买milk- 置信度Confidence: 0.619- 支持度Support: 13Rule: 买了milk,又买bread- 置信度Confidence: 0.265- 支持度Support: 13Rule: 买了bread,又买apples- 置信度Confidence: 0.286- 支持度Support: 6Rule: 买了bread,又买bananas- 置信度Confidence: 0.476- 支持度Support: 10Rule: 买了apples,又买bread- 置信度Confidence: 0.154- 支持度Support: 6Rule: 买了apples,又买bananas- 置信度Confidence: 0.590- 支持度Support: 23Rule: 买了bananas,又买bread- 置信度Confidence: 0.185- 支持度Support: 10Rule: 买了bananas,又买apples- 置信度Confidence: 0.426- 支持度Support: 23Rule: 买了milk,又买cheese- 置信度Confidence: 0.204- 支持度Support: 10Rule: 买了milk,又买bananas- 置信度Confidence: 0.429- 支持度Support: 21Rule: 买了cheese,又买milk- 置信度Confidence: 0.213- 支持度Support: 10Rule: 买了cheese,又买bananas- 置信度Confidence: 0.532- 支持度Support: 25Rule: 买了bananas,又买milk- 置信度Confidence: 0.389- 支持度Support: 21Rule: 买了bananas,又买cheese- 置信度Confidence: 0.463- 支持度Support: 25Rule: 买了bread,又买cheese- 置信度Confidence: 0.238- 支持度Support: 5Rule: 买了cheese,又买bread- 置信度Confidence: 0.106- 支持度Support: 5Rule: 买了milk,又买apples- 置信度Confidence: 0.184- 支持度Support: 9Rule: 买了apples,又买milk- 置信度Confidence: 0.231- 支持度Support: 9
'''
# 封装一下方便调用
def print_rule(premise, conclusion, support, confidence, features):premise_name = features[premise]conclusion_name = features[conclusion]print("Rule: 买了{0},又买{1}".format(premise_name, conclusion_name))print(" - 置信度Confidence: {0:.3f}".format(confidence[(premise, conclusion)]))print(" - 支持度Support: {0}".format(support[(premise, conclusion)]))print("")premise = 1
conclusion = 3
print_rule(premise, conclusion, support, confidence, features)'''
Rule: 买了milk,又买apples- 置信度Confidence: 0.184- 支持度Support: 9
'''
# 按支持度support排序
from pprint import pprint
pprint(list(support.items()))'''
[((2, 3), 26),((3, 2), 26),((0, 1), 13),((1, 0), 13),((0, 3), 6),((0, 4), 10),((3, 0), 6),((3, 4), 23),((4, 0), 10),((4, 3), 23),((1, 2), 10),((1, 4), 21),((2, 1), 10),((2, 4), 25),((4, 1), 21),((4, 2), 25),((0, 2), 5),((2, 0), 5),((1, 3), 9),((3, 1), 9)]
'''
sorted_confidence = sorted(confidence.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
for index in range(5): # 打印前5个print("Rule #{0}".format(index + 1))(premise, conclusion) = sorted_confidence[index][0]print_rule(premise, conclusion, support, confidence, features)'''
Rule #1
Rule: 买了apples,又买cheese- 置信度Confidence: 0.667- 支持度Support: 26Rule #2
Rule: 买了bread,又买milk- 置信度Confidence: 0.619- 支持度Support: 13Rule #3
Rule: 买了apples,又买bananas- 置信度Confidence: 0.590- 支持度Support: 23Rule #4
Rule: 买了cheese,又买apples- 置信度Confidence: 0.553- 支持度Support: 26Rule #5
Rule: 买了cheese,又买bananas- 置信度Confidence: 0.532- 支持度Support: 25
'''
任务2:Iris植物分类
给出某一植物部分特征,预测该植物属于哪一类
特征:
- 萼片长宽sepal width, sepal height
- 花瓣长宽petal width, petal height
算法:
- For 给定的每个特征
For 该特征对应的真值(即植物是哪一类) -
- 预测值:基于该特征预测的次数最多的类,即在所有样本里该特征 10 次有 6 次预测了 A 类,那我们对所有样本都预测为 A 类
-
- 计算预测值与真值的误差
- 对上面计算的误差求和
- 使用误差最小的特征作为最终模型
很显然,“在所有样本里该特征 10 次有 6 次预测了 A 类,那我们对所有样本都预测为 A 类”是基于大数据的
不过这样的规则过于简单,下面继续实验会发现准确率只有 60% 左右,当然还是比随机预测 50% 好!
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
#X, y = np.loadtxt("X_classification.txt"), np.loadtxt("y_classification.txt") # 本地加载数据,我先下载好在 data 文件夹里了
dataset = load_iris() # 或者自己亲自下载数据再加载也行
X = dataset.data
y = dataset.target
print(dataset.DESCR) # 打印下数据集介绍
n_samples, n_features = X.shape
# Compute the mean for each attribute计算平均值
attribute_means = X.mean(axis=0)
assert attribute_means.shape == (n_features,)
X_d = np.array(X >= attribute_means, dtype='int')
# 划分训练集和测试集
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split# 设置随机数种子以便复现书里的内容
random_state = 14X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_d, y, random_state=random_state)
print("训练集数据有 {} 条".format(y_train.shape))
print("测试集数据有 {} 条".format(y_test.shape))'''
训练集数据有 (112,) 条
测试集数据有 (38,) 条
'''
from collections import defaultdict
from operator import itemgetterdef train(X, y_true, feature):"""Computes the predictors and error for a given feature using the OneR algorithmParameters----------X: array [n_samples, n_features]The two dimensional array that holds the dataset. Each row is a sample, each columnis a feature.y_true: array [n_samples,]The one dimensional array that holds the class values. Corresponds to X, such thaty_true[i] is the class value for sample X[i].feature: intAn integer corresponding to the index of the variable we wish to test.0 <= variable < n_featuresReturns-------predictors: dictionary of tuples: (value, prediction)For each item in the array, if the variable has a given value, make the given prediction.error: floatThe ratio of training data that this rule incorrectly predicts."""# 1.一些等下要用的变量(数据的形状如上)n_samples, n_features = X.shapeassert 0 <= feature < n_featuresvalues = set(X[:,feature])predictors = dict()errors = []# 2.算法(对照上面的算法流程)# 已经给定特征 feature,作为函数参数传过来了for current_value in values: # For 该特征对应的真值(即植物是哪一类)most_frequent_class, error = train_feature_value(X, y_true, feature, current_value) # 预测值:基于该特征预测的次数最多的类,即在所有样本里该特征 10 次有 6 次预测了 A 类,那我们对所有样本都预测为 A 类predictors[current_value] = most_frequent_classerrors.append(error)# 计算预测值与真值的误差total_error = sum(errors)# 对上面计算的误差求和# python里求和函数 sum([1, 2, 3]) == 1 + 2 + 3 == 6return predictors, total_error# Compute what our predictors say each sample is based on its value
#y_predicted = np.array([predictors[sample[feature]] for sample in X])def train_feature_value(X, y_true, feature, value):# 预测值:基于该特征预测的次数最多的类,即在所有样本里该特征 10 次有 6 次预测了 A 类,那我们对所有样本都预测为 A 类# 我们需要一个字典型变量存每个变量预测正确的次数class_counts = defaultdict(int)# 对每个二元组(类别,真值)迭代计数for sample, y in zip(X, y_true):if sample[feature] == value:class_counts[y] += 1# 现在选被预测最多的类别,需要排序。(我们认为被预测最多的类别就是正确的)sorted_class_counts = sorted(class_counts.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse=True)most_frequent_class = sorted_class_counts[0][0]# 误差定义为分类“错误”的次数,这里“错误”指样本中没有分类为我们预测的值,即样本的真实类别不是“被预测最多的类别”n_samples = X.shape[1]error = sum([class_count for class_value, class_count in class_counts.items()if class_value != most_frequent_class])return most_frequent_class, error
# For 给定的每个特征,计算所有预测值(这里 for 写到 list 里面是 python 的语法糖)
all_predictors = {variable: train(X_train, y_train, variable) for variable in range(X_train.shape[1])}
errors = {variable: error for variable, (mapping, error) in all_predictors.items()}
# 现在选择最佳模型并保存为 "model"
# 按误差排序
best_variable, best_error = sorted(errors.items(), key=itemgetter(1))[0]
print("最佳模型基于第 {0} 个变量,误差为 {1:.2f}".format(best_variable, best_error))# 选最好的模型,也就是误差最小的模型
model = {'variable': best_variable,'predictor': all_predictors[best_variable][0]}
print(model)'''
最佳模型基于第 2 个变量,误差为 37.00
{'variable': 2, 'predictor': {0: 0, 1: 2}}
'''
def predict(X_test, model):variable = model['variable']predictor = model['predictor']y_predicted = np.array([predictor[int(sample[variable])] for sample in X_test])return y_predicted
y_predicted = predict(X_test, model)
print(y_predicted)
accuracy = np.mean(y_predicted == y_test) * 100
print("在测试集上的准确率 {:.1f}%".format(accuracy))
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(y_test, y_predicted))'''
[0 0 0 2 2 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 2 2 0 2 0 2 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 22]
在测试集上的准确率 65.8%precision recall f1-score support0 0.94 1.00 0.97 171 0.00 0.00 0.00 132 0.40 1.00 0.57 8avg / total 0.51 0.66 0.55 38
'''
在测试集上的准确率 65.8%,比完全随机预测 50% 好一点点。
相关文章:

数据挖掘流程简单示例10min
数据挖掘流程简单示例10min 套路: 准备数据实现算法测试算法 任务1:亲和性分析 如果一个顾客买了商品X,那么他们可能愿意买商品Y衡量方法: 支持度support : 所有买X的人数 置信度confidence : 所有买X和Y的人数所有买X的人数…...
KDJB1200六相继电保护测试仪
一、概述 KDJB1200继电保护测试仪是在参照电力部颁发的《微机型继电保护试验装置技术条件(讨论稿)》的基础上,广泛听取用户意见,总结目前国内同类产品优缺点,充分使用现代新的的微电子技术和器件实现的一种新型小型化微机继电保护测试仪。可…...
从WEB到PWA 开发-发布-安装
见意如题!本文主要来说说PWA开发!作为一个前端程序员,在没有任何Android/IOS的开发情况下,想想我们有多少种方法来开发一个原生移动应用程序!我们可以有非原生、混合开发,PWA等等手段。类似uniappÿ…...

FPGA纯vhdl实现MIPI CSI2 RX视频解码输出,OV13850采集,提供工程源码和技术支持
目录1、前言2、Xilinx官方主推的MIPI解码方案3、纯Vhdl方案解码MIPI4、vivado工程介绍5、上板调试验证6、福利:工程代码的获取1、前言 FPGA图像采集领域目前协议最复杂、技术难度最高的应该就是MIPI协议了,MIPI解码难度之高,令无数英雄竞折腰…...

《NFL橄榄球》:卡罗来纳黑豹·橄榄1号位
卡罗来纳黑豹(英语:Carolina Panthers)是一支位于北卡罗来纳州夏洛特的职业美式橄榄球球队。他们是国家美式橄榄球联合会的南区其中一支球队。他们与杰克逊维尔美洲虎在1995年加入NFL,成为扩充球队。 2018年球队市值为23亿美元&am…...
我说我为什么抽不到SSR,原来是这段代码在作祟...
本文是龚国玮所写,熊哥有所新增修改删减,原文见文末。 我说我为什么抽不到SSR,原来是加权随机算法在作祟 阅读本文需要做好心理准备,建议带着深究到底的决心和毅力进行学习! 灵魂拷问 为什么有 50% 的几率获得金币&a…...

MySQL MGR 集群新增节点
前言 服务器规划现状(CentOS7.x) IP地址主机名部署角色192.168.x.101mysql01mysql192.168.x.102mysql02mysql192.168.x.103mysql03mysql192.168.x.104proxysql01proxysql、keepalived192.168.x.105proxysql02proxysql、keepalived 新增服务器IP&#x…...

【单目标优化算法】蜣螂优化算法(Dung beetle optimizer,DBO)(Matlab代码实现)
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥 🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。 ⛳️座右铭&a…...
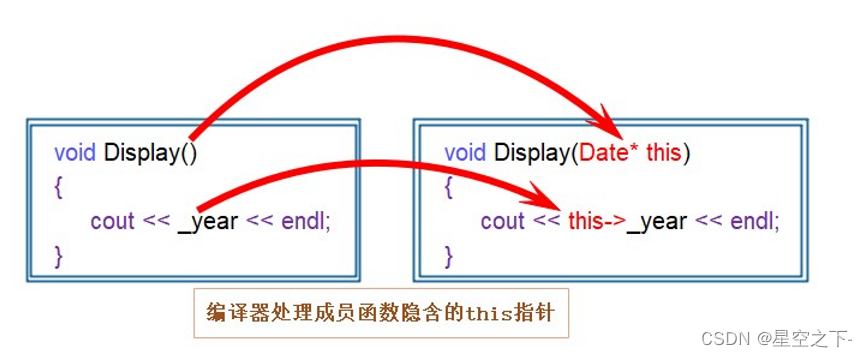
【C++】类和对象入门必知
面向过程和面向对象的初步认识类的引入类的定义类的访问限定符封装类的作用域类的实例化类对象模型this指针C语言和C实现Stack的对比面向过程和面向对象的初步认识 C语言是面向过程的,关注的是过程,分析出求解问题的步骤,通过函数调用逐步解…...

day38 动态规划 | 509、斐波那契数 70、爬楼梯 746、使用最小花费爬楼梯
题目 509、斐波那契数 斐波那契数,通常用 F(n) 表示,形成的序列称为 斐波那契数列 。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是: F(0) 0,F(1) 1 F(n) F(n - 1) F(n - 2),其…...

2023年备考软考必须知道的6件事
不知不觉,距离2023年上半年软考也只有不到100天的时间了,报名入口也将在3月13日正式开通,你是正在犹豫是否参加考试? 还是已经开始着手准备复习? 关于软考考试你还有哪些疑问? 2023年备考软考必须知道的6件事,建议收藏…...

GLOG如何控制输出的小数点位数
1 问题 在小白的蹩脚翻译演绎型博文《GLOG从入门到入门》中,有位热心读者提问说:在保存日志时,浮点型变量的小数位数如何设置? 首先感谢这位“嘻嘻哈哈的地球人”赏光阅读了小白这不太通顺的博客文章,并提出了一个很…...
2022年全国职业院校技能大赛(中职组)网络安全竞赛试题A(6)
目录 模块A 基础设施设置与安全加固 一、项目和任务描述: 二、服务器环境说明 三、具体任务(每个任务得分以电子答题卡为准) A-1任务一:登录安全加固(Windows) 1.密码策略 a.密码策略必须同时满足大小…...

Safety-Gym环境配置与安
官网: https://github.com/openai/safety-gym https://github.com/openai/safety-starter-agents 一、安装依赖环境配置 建议使用python 3.7及以下环境,因为官方的safety-rl是基于tensorflow1.13.1实现,而tensorflow1.13.1只能支持python…...
3月再不跳槽,就晚了
从时间节点上来看,3月、4月是每年跳槽的黄金季! 以 BAT 为代表的互联网大厂,无论是薪资待遇、还是平台和福利,都一直是求职者眼中的香饽饽,“大厂经历” 在国内就业环境中无异于一块金子招牌。在这金三银四的时间里&a…...
HTTP cookie格式与约束
cookie是前端编程当中经常要使用到的概念,我们可以使用cookie利用浏览器来存放用户的状态信息保存用户做了一些什么事情。session是服务器端维护的状态。session又是如何和cookie关联起来。后面介绍cookie和session的使用。Cookie 是什么?RFC6265, HTTP …...

docker基础
docker基础 docker概述 docker的出现?docker解决思想docker历史docker链接docker能干什么?开发-运维 docker安装 镜像(image)容器(container)仓库(repository)底层原理 docker命令 帮助命令镜像命令 docker-images查看所有本地主机上的镜像docker-searc…...

【微信小程序】--JSON 配置文件作用(三)
💌 所属专栏:【微信小程序开发教程】 😀 作 者:我是夜阑的狗🐶 🚀 个人简介:一个正在努力学技术的CV工程师,专注基础和实战分享 ,欢迎咨询! &#…...

EDA-课设
EDA-课程设计-电子闹钟 一、实验目的 1.掌握多层电路在 QuartusII 集成开发环境中的实现; 2.熟练掌握基于 QuartusII 集成开发环境的组合逻辑电路设计流程; 3.掌握基于 QuartusII 集成开发环境的时序逻辑电路设计流程; 4.理解有限状态机设计…...

C/C++每日一练(20230222)
目录 1. 部分复制字符串(★) 2. 按字典顺序排列问题(★★) 3. 地下城游戏(★★★) 附录 动态规划 1. 部分复制字符串 将字符串2小写字母复制到字符串1:编写程序,输入字符串s2,将其中所有小写字母复制到字符串数组strl中。例如:aal1bb22cc33de4AA55…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...

生成xcframework
打包 XCFramework 的方法 XCFramework 是苹果推出的一种多平台二进制分发格式,可以包含多个架构和平台的代码。打包 XCFramework 通常用于分发库或框架。 使用 Xcode 命令行工具打包 通过 xcodebuild 命令可以打包 XCFramework。确保项目已经配置好需要支持的平台…...
)
rknn优化教程(二)
文章目录 1. 前述2. 三方库的封装2.1 xrepo中的库2.2 xrepo之外的库2.2.1 opencv2.2.2 rknnrt2.2.3 spdlog 3. rknn_engine库 1. 前述 OK,开始写第二篇的内容了。这篇博客主要能写一下: 如何给一些三方库按照xmake方式进行封装,供调用如何按…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...

大语言模型如何处理长文本?常用文本分割技术详解
为什么需要文本分割? 引言:为什么需要文本分割?一、基础文本分割方法1. 按段落分割(Paragraph Splitting)2. 按句子分割(Sentence Splitting)二、高级文本分割策略3. 重叠分割(Sliding Window)4. 递归分割(Recursive Splitting)三、生产级工具推荐5. 使用LangChain的…...
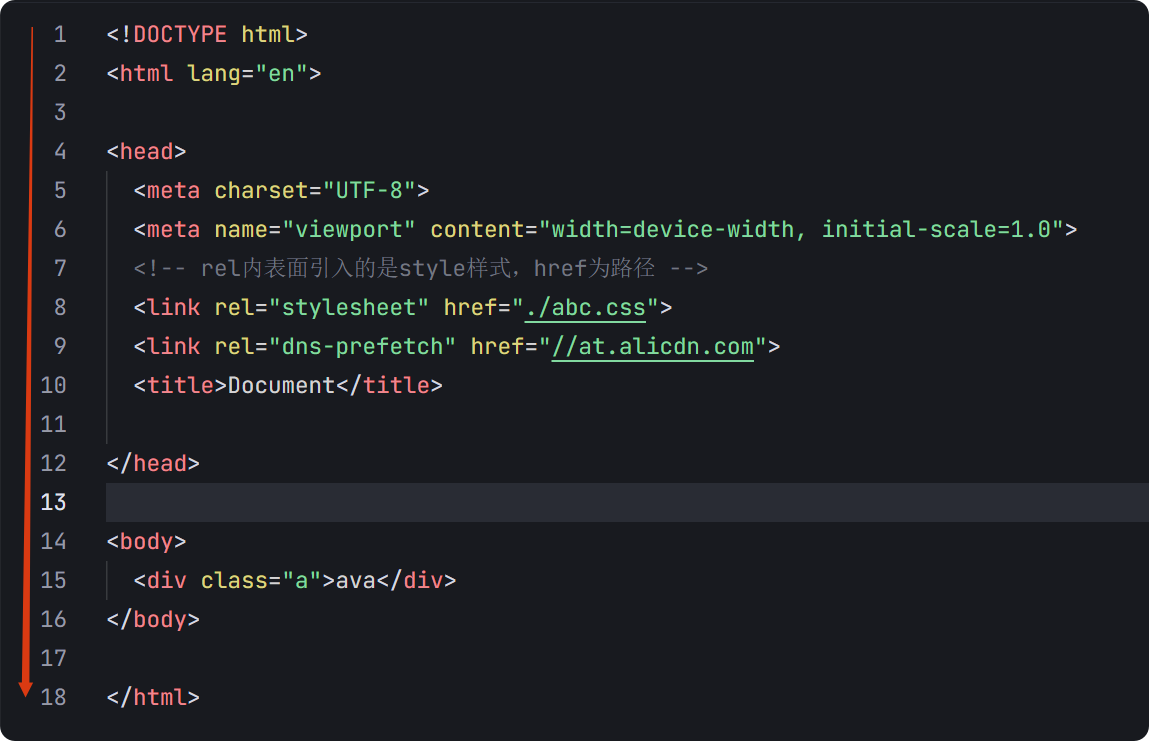
04-初识css
一、css样式引入 1.1.内部样式 <div style"width: 100px;"></div>1.2.外部样式 1.2.1.外部样式1 <style>.aa {width: 100px;} </style> <div class"aa"></div>1.2.2.外部样式2 <!-- rel内表面引入的是style样…...

鸿蒙中用HarmonyOS SDK应用服务 HarmonyOS5开发一个生活电费的缴纳和查询小程序
一、项目初始化与配置 1. 创建项目 ohpm init harmony/utility-payment-app 2. 配置权限 // module.json5 {"requestPermissions": [{"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"},{"name": "ohos.permission.GET_NETWORK_INFO"…...

Device Mapper 机制
Device Mapper 机制详解 Device Mapper(简称 DM)是 Linux 内核中的一套通用块设备映射框架,为 LVM、加密磁盘、RAID 等提供底层支持。本文将详细介绍 Device Mapper 的原理、实现、内核配置、常用工具、操作测试流程,并配以详细的…...
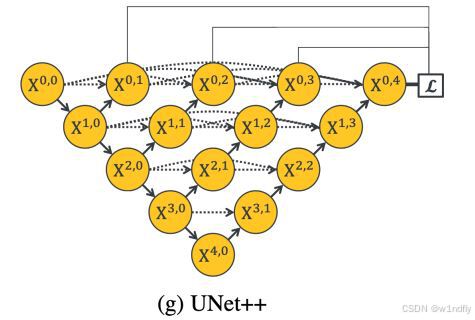
nnUNet V2修改网络——暴力替换网络为UNet++
更换前,要用nnUNet V2跑通所用数据集,证明nnUNet V2、数据集、运行环境等没有问题 阅读nnU-Net V2 的 U-Net结构,初步了解要修改的网络,知己知彼,修改起来才能游刃有余。 U-Net存在两个局限,一是网络的最佳深度因应用场景而异,这取决于任务的难度和可用于训练的标注数…...

git: early EOF
macOS报错: Initialized empty Git repository in /usr/local/Homebrew/Library/Taps/homebrew/homebrew-core/.git/ remote: Enumerating objects: 2691797, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (1760/1760), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (636/636…...
