强化学习环境 - robogym - 学习 - 3
强化学习环境 - robogym - 学习 - 3
文章目录
- 强化学习环境 - robogym - 学习 - 3
- 项目地址
- 为什么选择 robogym
- Observation - 观测信息
- Action - 动作信息
- Initialization - 初始状态设置
项目地址
https://github.com/openai/robogym
为什么选择 robogym
-
自己的项目需要做一些机械臂 table-top 级的多任务操作
-
robogym 基于 mujoco 搭建,构建了一个仿真机械臂桌面物体操作(pick-place、stack、rearrange)场景
-
robogym 的例程效果看,支持多个相机示教,包括眼在手上和眼在手外,可以获取多视角视觉信息
-
robogym 的物体支持 YCB 数据集格式
主要是这些原因,当然,看官方 readme.md 文档,它还有其他不错的功能。
国内主流社区对 robogym 的介绍比较少,所以选择写一些文档记录一下,作为参考。
Observation - 观测信息
robogym 的观测一般通过 obs = env.reset() 返回即可得到。爬源码可得到 obs 是一个字典。
把字典的键排序按照值的方法进行了简答的分类,可以得到:仿真环境的 obs 字典是通过:self.mujoco_simulation 、 robot_obs 、 self._goal 、 self._goal_info_dict 和 np.array 四个变量得到的。
obs = {# 读取 self.mujoco_simulation 内部的方法返回作为值"obj_pos": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_pos(),"obj_rel_pos": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_rel_pos(),"obj_vel_pos": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_vel_pos(),"obj_rot": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_rot(),"obj_vel_rot": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_vel_rot(),"qpos": self.mujoco_simulation.qpos,"obj_gripper_contact": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_gripper_contact(),"obj_bbox_size": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_bounding_box_sizes(),"obj_colors": self.mujoco_simulation.get_object_colors(),# 在代码上面实例化了# robot_obs = self.mujoco_simulation.robot.observe()# 这个实例,这部分的键对应的值就是 robot_obs 的方法"robot_joint_pos": robot_obs.joint_positions(),"gripper_pos": robot_obs.tcp_xyz(),"gripper_velp": robot_obs.tcp_vel(),"gripper_controls": robot_obs.gripper_controls(),"gripper_qpos": robot_obs.gripper_qpos(),"gripper_vel": robot_obs.gripper_vel(),"tcp_force": robot_obs.tcp_force(),"tcp_torque": robot_obs.tcp_torque(),# self._goal 从源码来看就是每个物体重排列的位置。"qpos_goal": self._goal["qpos_goal"].copy(),"goal_obj_pos": self._goal["obj_pos"].copy(),"goal_obj_rot": self._goal["obj_rot"].copy(),"rel_goal_obj_pos": self._goal_info_dict["rel_goal_obj_pos"].copy(),"rel_goal_obj_rot": self._goal_info_dict["rel_goal_obj_rot"].copy(),"is_goal_achieved": np.array([self._is_goal_achieved], np.int32),"safety_stop": np.array([robot_obs.is_in_safety_stop()]),}
这里列出了每个键对应的含义。
| observation 键名 | 每个键的意义 |
|---|---|
| object_pos | Get position for all objects. |
| object_rel_pos | Get position for all objects relative to the gripper position. |
| object_vel_pos | Get position velocity for all objects relative to tooltip velocity. |
| object_rot | Get rotation in euler angles for all objects. |
| object_vel_rot | Get rotation velocity for all objects. |
| robot_joint_pos | Array of joint angles (one for each joint). |
| gripper_pos | Tooltip position in the Cartesian coordinate space. |
| gripper_velp | Tooltip velocity in the Cartesian coordinate space. |
| gripper_controls | Gripper’s linear target position. |
| gripper_qpos | Gripper joint positions. |
| gripper_vel | Gripper joint velocities. |
| qpos | Copy of full sim qpos including 3D-position and 4D-quaternion. |
| qpos_goal | Copy of full sim goal qpos including 3D-position and 4D-quaternion. |
| goal_obj_pos | Get current-goal positions for all objects. |
| goal_obj_rot | Get current-goal rotations in euler angles for all objects. |
| is_goal_achieved | Return if current goal is achieved. |
| rel_goal_obj_pos | Get current-goal positions for all objects relative to the gripper position. |
| rel_goal_obj_rot | Get current-goal rotations for all objects relative to the gripper position. |
| obj_gripper_contact | A numpy array of shape [num objects, len(other_geom_ids)], in which each value is binary, 1 meaning having contact and 0 no contact. |
| obj_bbox_size | Returns the bounding box for one objects as a tuple of (positive, half size), where both positive and half size are np.array of shape (3,). |
| obj_colors | This logic works, assuming only assign a single color to one object. |
| safety_stop | True if the arm is in a safety stop, False otherwise. |
| tcp_force | TCP force in world coordinates. |
| tcp_torque | TCP torque in world coordinates. |
根据自己的项目,选择:
object_pos、object_rot,代表了每个物体的位置和姿态;gripper_pos、gripper_controls,代表了机械臂的位置和张开闭合程度;goal_obj_pos、goal_obj_rot,代表了每个物体的目标位置和目标姿态。
需要精简一下观测的信息,有三种思路:
-
爬源码,把不必要的观测信息直接注释掉;
【注意】 一些项目中会在
observation生成后再对里面的键做处理,这样做会导致一些bug!! -
利用 Open AI Gym 的
FilterObservation()这个类过滤掉不想要的键; -
自己写一个函数,把不必要的键过滤掉;
【注意】
.reset()和.step()的返回都需要进行这样的操作!!
这里我选择自己写一个函数。
# create a small util to filter the observation
def filter_obs(raw_obs: dict, name_list: list) -> dict:result = {}for name in name_list:result[name] = copy.copy(raw_obs[name])return result
最后的代码如下。选择 pprint.pprint() 进行输出可以更加格式化。
import copy
import pprint
from robogym.envs.rearrange.ycb import make_env# create a small util to filter the observation
def filter_obs(raw_obs: dict, name_list: list) -> dict:result = {}for name in name_list:result[name] = copy.copy(raw_obs[name])return result# Create an environment with the default number of objects: 5
env = make_env(parameters={'simulation_params': {'num_objects': 3,'max_num_objects': 8,}}
)# Reset to randomly generate an environment with `num_objects: 3`
obs = env.reset()
obs = filter_obs(obs, ["obj_pos", "obj_rot", "gripper_pos", "gripper_controls", "goal_obj_pos", "goal_obj_rot"])
pprint.pprint(obs)while True:a = env.action_space.sample()next_obs, reward, done, info = env.step(a)next_obs = filter_obs(next_obs, ["obj_pos", "obj_rot", "gripper_pos", "gripper_controls", "goal_obj_pos", "goal_obj_rot"])pprint.pprint(next_obs)env.render()
得到结果:
{'goal_obj_pos': array([[1.39363232, 0.86174547, 0.51221652],[1.57460708, 0.70375038, 0.50919097],[1.20793525, 0.8834796 , 0.49350575],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ]]),'goal_obj_rot': array([[ 0. , 0. , -1.79725862],[ 0. , 0. , -1.13518178],[ 0. , 0. , -2.40479252],[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],[ 0. , 0. , 0. ]]),'gripper_controls': array([0.]),'gripper_pos': array([1.23887261, 0.43994768, 0.68622718]),'obj_pos': array([[1.59604171, 0.81327296, 0.51217642],[1.57460711, 0.41286039, 0.50922118],[1.40990736, 0.64130153, 0.49354594],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ],[0. , 0. , 0. ]]),'obj_rot': array([[-8.89659174e-05, -7.47313090e-05, -1.79530140e+00],[-3.00692282e-06, 4.73572520e-06, -1.13518163e+00],[-4.85122664e-02, -4.51887581e-02, -2.40575071e+00],[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00],[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00],[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00],[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00],[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00]])}
为什么 'goal_obj_rot' 这部分只有第三个元素有数值,前面两个没数值?
原因是这是用 rpy 格式描述姿态的。这三个元素依次表示roll 、 pitch 和 yaw 角。如下图所示。

而 table-top 级的物体都是“平躺”的,所以默认 yaw 角有姿态。
在上述打印出来的字典可以看到,当忽略很小的小数(-3.00692282e-06)时,目标姿态和当前物体姿态差别不大,这说明在当前环境中,只需要机械臂做细致的平移就行。
Action - 动作信息
robogym 的动作空间比较特殊:它通过一层 wrapper 把原本 [ − 1 , 1 ] [-1,1] [−1,1] 数值的动作空间给离散化了:在 ~/robogym/robogym/wrappers/utils.py 里面 DiscretizeActionWrapper 把奖励值做了封装,通过离散数值索引一个列表 [-1. -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0. 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1. ] ,获得机械臂TCP末端的偏移量,前面三维度分别是 xyz,后面两个维度是姿态角,最后一个维度是夹爪的开闭(但是测试效果是夹爪开闭似乎无效,可能是因为这是 rearrange 环境,对物体的操作更多是“push”而不是“pick-and-place”)。
【注意】在这样的默认包装下,保持机械臂末端位姿不动的动作向量是:a = np.asarray([5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5]) 可以设置一个全局参数保存这个动作向量。
【注意】a = np.asarray([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) 不是静止的向量,相反,它是偏移最大的动作向量!
Initialization - 初始状态设置
好的初始状态既能完成更好的实验,也能在做成视频的时候更美观些。对于机械臂 rearrange 环境,设置初始状态的函数是在 ~/robogym/robogym/envs/rearrange/common/base.py 文件里面 RearrangeEnv 类的 _randomize_robot_initial_position() 函数中。函数中是通过设置末端TCP的初始位姿来进行状态初始化的。
action = self.action_space.sample()
if self.parameters.n_random_initial_steps < 1:return
for _ in range(self.parameters.n_random_initial_steps):self._set_action(action)self.mujoco_simulation.step()
self._set_action(action * 0.0)
for _ in range(100):# calling set_action each tick is necessary # for the robot to reach stability with relative actionsself._set_action(action * 0.0)self.mujoco_simulation.step()print(self.mujoco_simulation.get_qpos('robot0:arm_joint_angles'))
里面用到了这个类中实例过的mujoco接口 mujoco_simulation 。这里的mujoco接口保留了大量 mujoco-py 的方法,可以爬源码看到都有哪些函数方法可以调用。
class SimulationInterface:"""Base class for domain-specific simulation interfaces tied to particular XML.Goal is to transform code interfacing with generic `MjSim` that looks like that:hand_angles = sim.data.qpos[hand_angle_idx]cube_pos = sim.data.qpos[cube_pos_idx]sim.model.actuator_gainprm[actuator_idx] = actuator_kpssim.model.actuator_biasprm[actuator_idx] = actuator_kpsInto more high-level and domain-specific version:hand_angles = sim.hand.get_angles()cube_pos = sim.get_cube_pos()sim.set_actuator_kp(actuator_kps)Etc.This is a base class that just exposes a few generic utilities to help the subclassesimplement the abovementioned functionality. By convention, the subclasses should be named<Something>Simulation."""__slots__ = ["sim","qpos_idxs","qvel_idxs","synchronization_points","_mujoco_viewer",]def __init__(self, sim: MjSim):self.sim = simself.qpos_idxs: Dict[str, List[int]] = {}self.qvel_idxs: Dict[str, List[int]] = {}self.synchronization_points = [] # type: ignoreself._mujoco_viewer = None@propertydef mj_sim(self):""" MuJoCo simulation object - alias to make it clearer """return self.sim@propertydef mujoco_viewer(self):"""Get a nicely-interactive version of the mujoco viewer"""if self._mujoco_viewer is None:# Inline import since this is only relevant on platforms# which have GLFW support.from mujoco_py.mjviewer import MjViewer # noqaself._mujoco_viewer = MjViewer(self.sim)return self._mujoco_viewerdef enable_pid(self):""" Enable our custom PID controller code for the actuators with 'user' type """cymj.set_pid_control(self.sim.model, self.sim.data)######################################################################################### SUBCLASS REGISTRATIONdef register_joint_group(self, group_name, prefix):""" Finds and collect joint ids for given joint name prefix or a list of prefixes. """if isinstance(prefix, str):self.qpos_idxs[group_name] = joint_qpos_ids_from_prefix(self.sim.model, prefix)self.qvel_idxs[group_name] = joint_qvel_ids_from_prefix(self.sim.model, prefix)elif isinstance(prefix, list):self.qpos_idxs[group_name] = list(it.chain.from_iterable(joint_qpos_ids_from_prefix(self.sim.model, p) for p in prefix))self.qvel_idxs[group_name] = list(it.chain.from_iterable(joint_qvel_ids_from_prefix(self.sim.model, p) for p in prefix))def register_joint_group_by_name(self, group_name, name):""" Finds and collect joint ids for given joint name or list of names. """if isinstance(name, str):self.qpos_idxs[group_name] = joint_qpos_ids(self.sim.model, name)self.qvel_idxs[group_name] = joint_qvel_ids(self.sim.model, name)elif isinstance(name, list):self.qpos_idxs[group_name] = list(it.chain.from_iterable(joint_qpos_ids(self.sim.model, n) for n in name))self.qvel_idxs[group_name] = list(it.chain.from_iterable(joint_qvel_ids(self.sim.model, n) for n in name))######################################################################################### GET DATA OUT OF SIMdef get_qpos(self, group_name):""" Gets qpos for a particular group. """return self.sim.data.qpos[self.qpos_idxs[group_name]]def get_qpos_dict(self, group_names):""" Gets qpos dictionary for multiple groups. """return {k: self.get_qpos(k) for k in group_names}def get_qvel(self, group_name):""" Gets qvel for a particular group. """return self.sim.data.qvel[self.qvel_idxs[group_name]]def get_qvel_dict(self, group_names):""" Gets qpos dictionary for multiple groups. """return {k: self.get_qvel(k) for k in group_names}@propertydef qpos(self):""" Returns. copy of full sim qpos. """return self.sim.data.qpos.copy()@propertydef qvel(self):""" Returns copy of full sim qvel. """return self.sim.data.qvel.copy()def get_state(self) -> MjSimState:return self.sim.get_state()######################################################################################### SET DATA IN SIMdef set_qpos(self, group_name, value):""" Sets qpos for a given group. """self.sim.data.qpos[self.qpos_idxs[group_name]] = valuedef set_qvel(self, group_name, value):""" Sets qpos for a given group. """self.sim.data.qvel[self.qvel_idxs[group_name]] = valuedef add_qpos(self, group_name, value):""" Sets qpos for a given group. """self.sim.data.qpos[self.qpos_idxs[group_name]] += valuedef set_state(self, state: MjSimState):self.sim.set_state(state)######################################################################################### INTERFACE TO UNDERLYING SIMdef step(self, with_udd=True):"""Advances the simulation by calling ``mj_step``.If ``qpos`` or ``qvel`` have been modified directly, the user is required to call:meth:`.forward` before :meth:`.step` if their ``udd_callback`` requires access to MuJoCostate set during the forward dynamics."""self.sim.step(with_udd=with_udd)self.sim.forward()# To potentially communicate with other processesfor point in self.synchronization_points:point.synchronize()def reset(self):"""Resets the simulation data and clears buffers."""self.sim.reset()def set_constants(self):"""Sets the derived constants of the mujoco simulation."""self.sim.set_constants()def forward(self):"""Computes the forward kinematics. Calls ``mj_forward`` internally."""self.sim.forward()def render(self,width=None,height=None,*,camera_name=None,depth=False,mode="offscreen",device_id=-1):"""Renders view from a camera and returns image as an `numpy.ndarray`.Args:- width (int): desired image width.- height (int): desired image height.- camera_name (str): name of camera in model. If None, the freecamera will be used.- depth (bool): if True, also return depth buffer- device (int): device to use for rendering (only for GPU-backedrendering).Returns:- rgb (uint8 array): image buffer from camera- depth (float array): depth buffer from camera (only returnedif depth=True)"""return self.sim.render(width=width,height=height,camera_name=camera_name,depth=depth,mode=mode,device_id=device_id,)######################################################################################### PROPERTIES@propertydef n_substeps(self):""" Number of substeps in the mujoco sim """return self.sim.nsubsteps
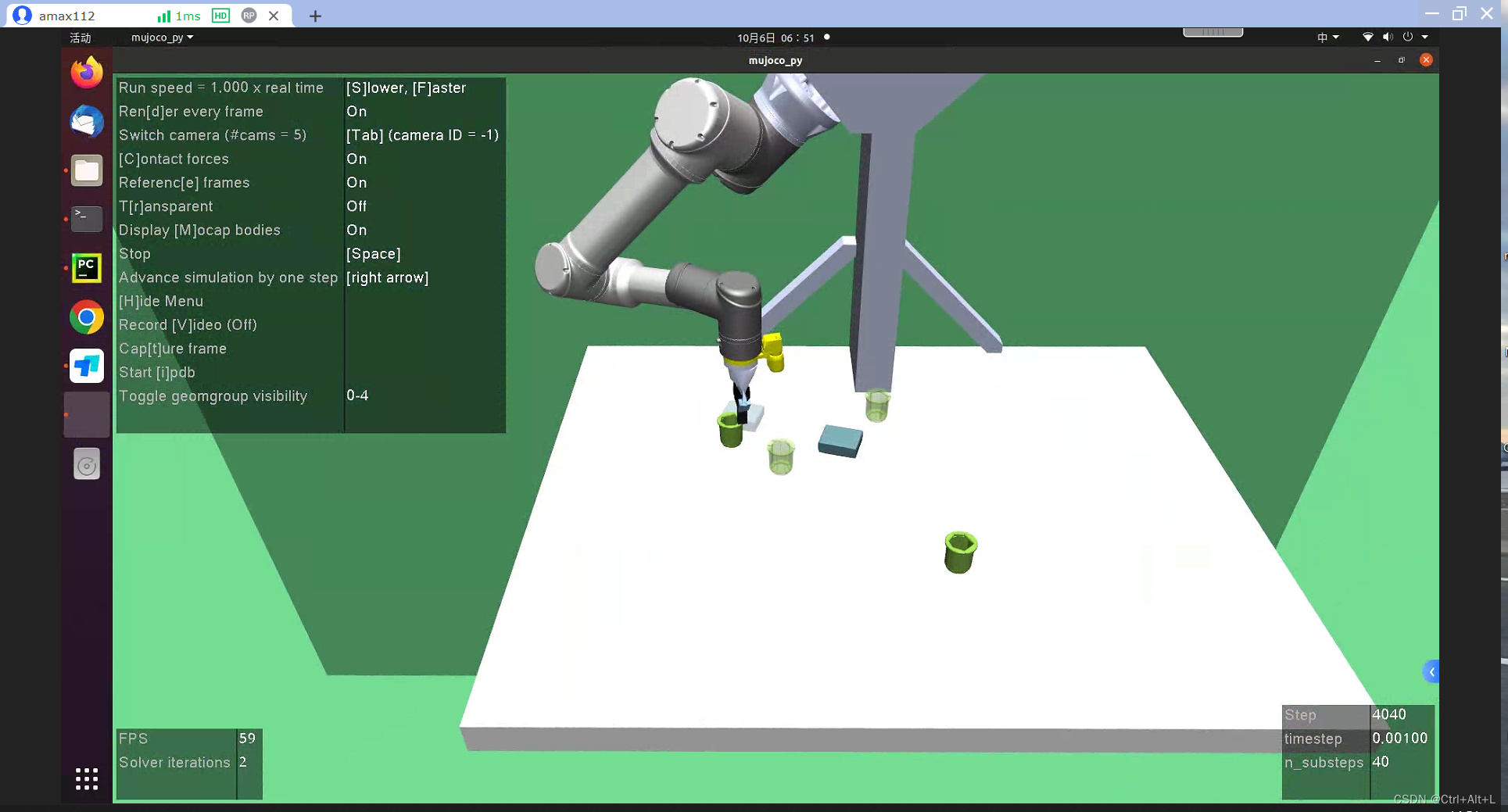
在这里,我主要通过单步调试,实现一个关节角的初始化。具体做法是:注释掉上面初始化状态的代码,写入自己的代码:
from math import piprint(self.mujoco_simulation.qpos_idxs.keys())
self.mujoco_simulation.set_qpos('robot0:arm_joint_angles',np.asarray([1.5 * 0.5 * pi, -0.5 * pi, 1.5 * 0.5 * pi,-1.74529567, -4.18881842, 2.35619837]))self.mujoco_simulation.step()
结果现实,代码可以运行。效果如下:
相关文章:

强化学习环境 - robogym - 学习 - 3
强化学习环境 - robogym - 学习 - 3 文章目录 强化学习环境 - robogym - 学习 - 3项目地址为什么选择 robogymObservation - 观测信息Action - 动作信息Initialization - 初始状态设置 项目地址 https://github.com/openai/robogym 为什么选择 robogym 自己的项目需要做一些机…...
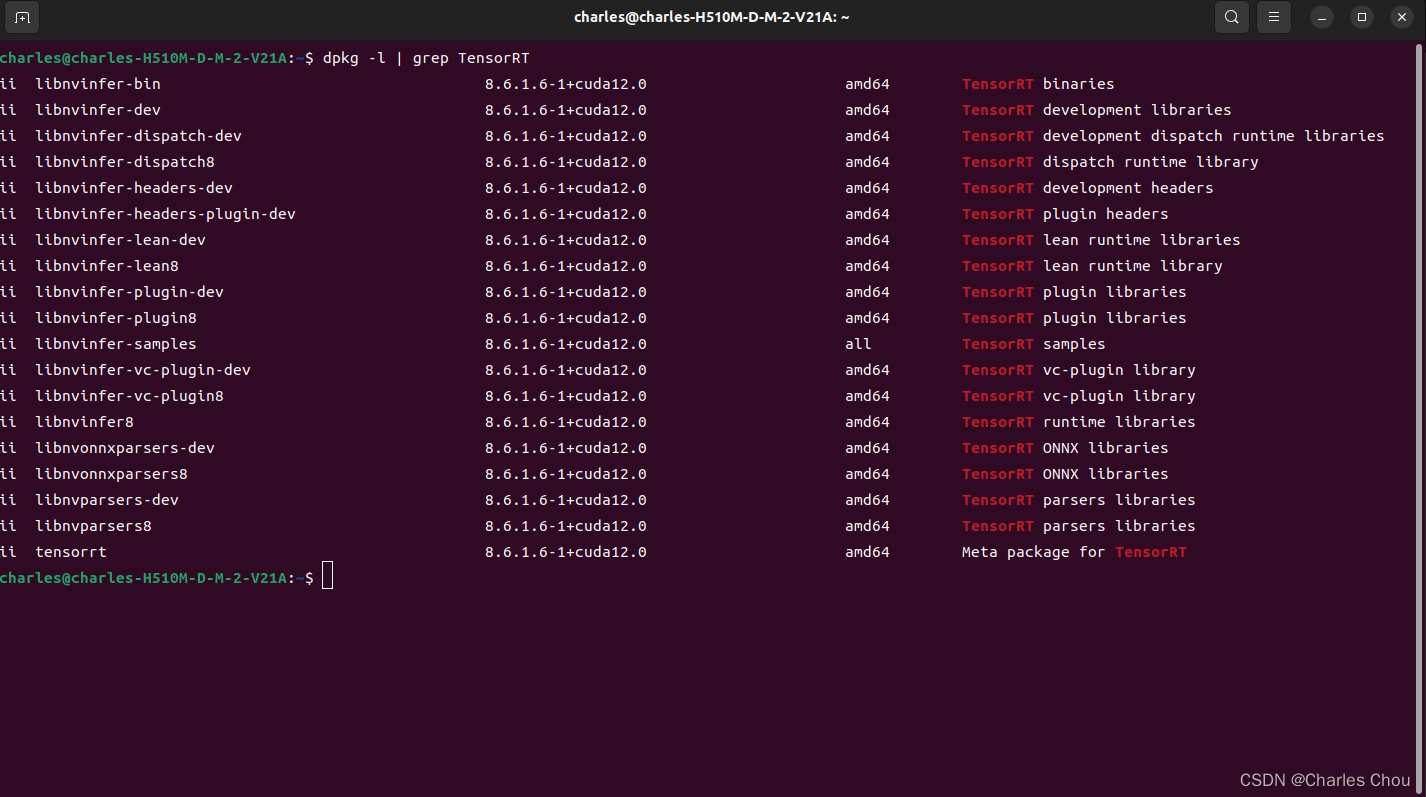
CUDA+cuDNN+TensorRT 配置避坑指南
深度学习模型加速部署的环境配置,需要在本地安装NVIDIA的一些工具链和软件包,这是一个些许繁琐的过程,而且一步错,步步错。笔者将会根据自己的经验来提供建议,减少踩坑几率。当然可以完全按照官方教程操作,…...
关于PointHeadBox类的理解
forward函数 def forward(self, batch_dict):"""Args:batch_dict:batch_size:point_features: (N1 N2 N3 ..., C) or (B, N, C)point_features_before_fusion: (N1 N2 N3 ..., C)point_coords: (N1 N2 N3 ..., 4) [bs_idx, x, y, z]point_labels (opti…...
ajax的使用)
javascript二维数组(10)ajax的使用
在JQuery中,使用AJAX的方法主要有以下几种: $.ajax():这是JQuery中最通用的AJAX请求方法。它需要一个包含各种参数的对象,其中包括请求的URL、请求方式、数据类型、请求参数等。请求成功后执行的回调函数也是通过参数来定义的。 …...

CMMI5认证哪些企业可以申请
CMMI5认证哪些企业可以申请 什么是CMMI5认证 CMMI(Capability Maturity Model Integration)是一种用于评估组织的软件工程能力的国际标准。CMMI模型包括5个等级,其中CMMI5是最高等级,代表组织具有达到持续优化和创新的能力。获得…...
【iptables 实战】9 docker网络原理分析
在开始本章阅读之前,需要提前了解以下的知识 阅读本节需要一些docker的基础知识,最好是在linux上安装好docker环境。提前掌握iptables的基础知识,前文参考【iptables 实战】 一、docker网络模型 docker网络模型如下图所示 说明࿱…...
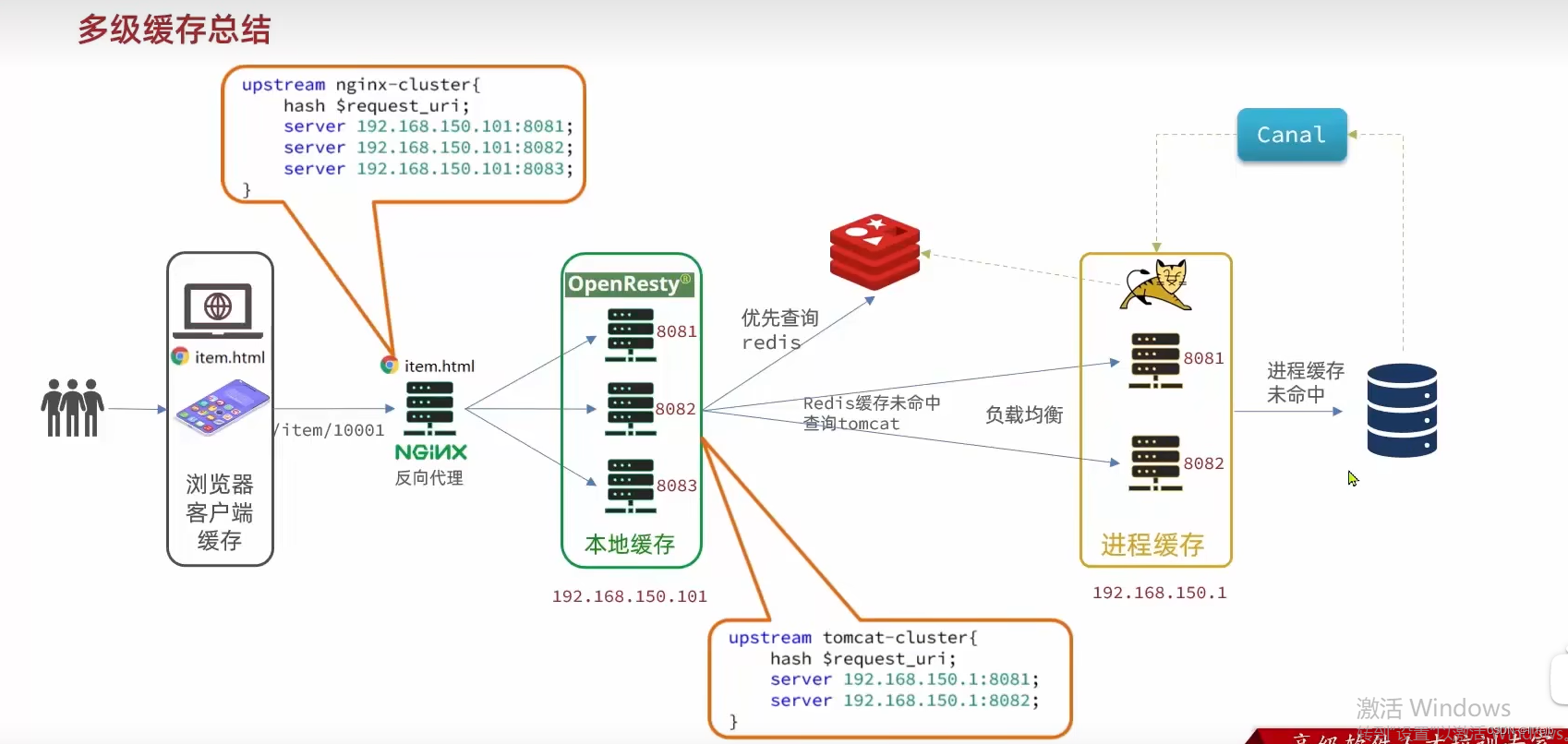
【多级缓存】
文章目录 1. JVM进程缓存2. Lua语法3. 实现多级缓存3.1 反向代理流程3.2 OpenResty快速入门 4. 查询Tomcat4.1 发送http请求的API4.2 封装http工具4.3 基于ID负载均衡4.4 流程小结 5. Redis缓存查询5.1 实现Redis查询 6. Nginx本地缓存6.1 本地缓存API6.2 实现本地缓存查询 7. …...
第五课 树与图
文章目录 第五课 树与图lc94.二叉树的中序遍历--简单题目描述代码展示 lc589.N叉树的层序遍历--中等题目描述代码展示 lc297.二叉树的序列化和反序列化--困难题目描述代码展示 lc105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树--中等题目描述代码展示 lc106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉…...

2023-10-07 事业-代号z-副业-CQ私服-调研与分析
摘要: CQ作为一款运营了20年的游戏, 流传出的私服可以说是层出不穷, 到了现在我其实对这款游戏的长线运营的前景很悲观. 但是作为商业的一部分, 对其做谨慎的分析还是很有必要的. 传奇调研的来源: 一. 各种售卖私服的网站 传奇服务端版本库-传奇手游源码「免费下载」传奇GM论…...
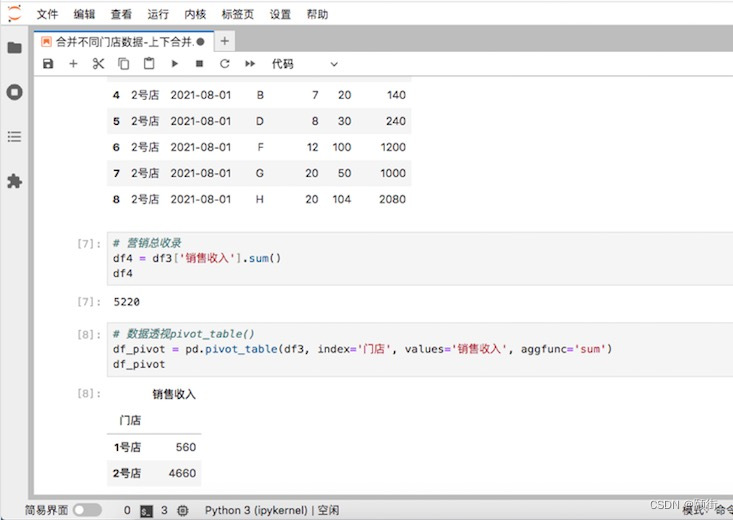
合并不同门店数据-上下合并
项目背景:线下超市分店,统计产品的销售数量和销售额,并用透视表计算求和 merge()函数可以根据链接键横向连接两张不同表,concat()函数可以上下合并和左右合并2种不同的合并方式。merge()函数只能横向连接两张表,而con…...

学习记忆——数学篇——案例——算术——整除特点
理解记忆法 对于数的整除特征大家都比较熟悉:比如4看后两位(因为100是4的倍数),8看后三位(因为1000是8的倍数),5末尾是0或5,3与9看各位数字和等等,今天重点研究一下3,9,…...

PHP8中的魔术方法-PHP8知识详解
在PHP 8中,魔术方法是一种特殊的方法,它们以两个下划线(__)开头。魔术方法允许您定义类的行为,例如创建对象、调用其他方法或访问和修改类的属性。以下是一些常见的魔术方法: __construct(): 类的构造函数…...

[图论]哈尔滨工业大学(哈工大 HIT)学习笔记23-31
视频来源:4.1.1 背景_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 目录 1. 哈密顿图 1.1. 背景 1.2. 哈氏图 2. 邻接矩阵/邻接表 3. 关联矩阵 3.1. 定义 4. 带权图 1. 哈密顿图 1.1. 背景 (1)以地球为建模,从一个大城市开始遍历其他大城市并且返回…...

Nginx+Keepalived实现服务高可用
Nginx 和 Keepalived 是常用于构建高可用性(High Availability)架构的工具。Nginx 是一款高性能的Web服务器和反向代理服务器,而Keepalived则提供了对Nginx服务的健康状态监测和故障切换功能。 下载Nginx 在服务器1和服务器2分别下载nginx …...
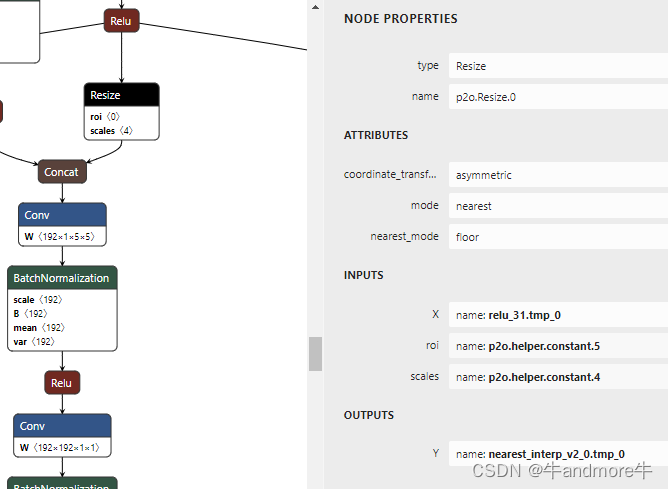
picodet onnx转其它芯片支持格式时遇到
文章目录 报错信息解决方法两模型精度对比 报错信息 报错信息为: Upsample(resize) Resize_0 not support attribute coordinate_transformation_mode:half_pixel. 解决方法 整个模型转换过程是:paddle 动态模型转成静态,再用paddle2onnx…...

【学习笔记】CF704B Ant Man
智商不够啊,咋想到贪心的😅 非常经典的贪心模型🤔 首先,从小到大将每个 i i i插入到排列中,用 D P DP DP记录还有多少个位置可以插入,可以通过钦定新插入的位置左右两边是否继续插入数来提前计算贡献。注…...

SQLines数据迁移工具
Data and Analytics Platform Migration - SQLines Tools SQLines提供的工具可以帮助您在不同的数据库平台之间传输数据、转换数据库模式(DDL)、视图、存储过程、包、用户定义函数(udf)、触发器、SQL查询和SQL脚本。 SQLines SQL Converter OverviewCommand LineConfigurati…...
)
pkl文件与打开(使用numpy和pickle)
文章目录 1. 什么是pkl文件2. 如何打开?Reference 1. 什么是pkl文件 1)python中有一种存储方式,可以存储为.pkl文件。 2)该存储方式,可以将python项目过程中用到的一些暂时变量、或者需要提取、暂存的字符串、列表、…...

3d渲染农场全面升级,好用的渲染平台值得了解
什么是渲染农场? 渲染农场是专门从事 3D 渲染的大型机器集合,称为渲染节点,这些机器组合在一起执行一项任务(渲染 3D 帧和动画)。通过将渲染工作分配给数百台机器,可以显着减少渲染时间,从而使…...

1.5 JAVA程序运行的机制
**1.5 Java程序的运行机制** --- **简介:** Java程序的运行涉及两个主要步骤:编译和运行。这种机制确保了Java的跨平台特性。 **主要内容:** 1. **Java程序的执行过程**: - **编译**:首先,扩展名为.jav…...

C++初阶-list的底层
目录 1.std::list实现的所有代码 2.list的简单介绍 2.1实现list的类 2.2_list_iterator的实现 2.2.1_list_iterator实现的原因和好处 2.2.2_list_iterator实现 2.3_list_node的实现 2.3.1. 避免递归的模板依赖 2.3.2. 内存布局一致性 2.3.3. 类型安全的替代方案 2.3.…...

【Linux】shell脚本忽略错误继续执行
在 shell 脚本中,可以使用 set -e 命令来设置脚本在遇到错误时退出执行。如果你希望脚本忽略错误并继续执行,可以在脚本开头添加 set e 命令来取消该设置。 举例1 #!/bin/bash# 取消 set -e 的设置 set e# 执行命令,并忽略错误 rm somefile…...

Golang dig框架与GraphQL的完美结合
将 Go 的 Dig 依赖注入框架与 GraphQL 结合使用,可以显著提升应用程序的可维护性、可测试性以及灵活性。 Dig 是一个强大的依赖注入容器,能够帮助开发者更好地管理复杂的依赖关系,而 GraphQL 则是一种用于 API 的查询语言,能够提…...
从零开始打造 OpenSTLinux 6.6 Yocto 系统(基于STM32CubeMX)(九)
设备树移植 和uboot设备树修改的内容同步到kernel将设备树stm32mp157d-stm32mp157daa1-mx.dts复制到内核源码目录下 源码修改及编译 修改arch/arm/boot/dts/st/Makefile,新增设备树编译 stm32mp157f-ev1-m4-examples.dtb \stm32mp157d-stm32mp157daa1-mx.dtb修改…...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...
Unsafe Fileupload篇补充-木马的详细教程与木马分享(中国蚁剑方式)
在之前的皮卡丘靶场第九期Unsafe Fileupload篇中我们学习了木马的原理并且学了一个简单的木马文件 本期内容是为了更好的为大家解释木马(服务器方面的)的原理,连接,以及各种木马及连接工具的分享 文件木马:https://w…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...

#Uniapp篇:chrome调试unapp适配
chrome调试设备----使用Android模拟机开发调试移动端页面 Chrome://inspect/#devices MuMu模拟器Edge浏览器:Android原生APP嵌入的H5页面元素定位 chrome://inspect/#devices uniapp单位适配 根路径下 postcss.config.js 需要装这些插件 “postcss”: “^8.5.…...

处理vxe-table 表尾数据是单独一个接口,表格tableData数据更新后,需要点击两下,表尾才是正确的
修改bug思路: 分别把 tabledata 和 表尾相关数据 console.log() 发现 更新数据先后顺序不对 settimeout延迟查询表格接口 ——测试可行 升级↑:async await 等接口返回后再开始下一个接口查询 ________________________________________________________…...

Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析
Java求职者面试指南:计算机基础与源码原理深度解析 第一轮提问:基础概念问题 1. 请解释什么是进程和线程的区别? 面试官:进程是程序的一次执行过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位;而线程是进程中的…...
