Leetcode 1834. Single-Threaded CPU (堆好题)
- Single-Threaded CPU
Medium
You are given n tasks labeled from 0 to n - 1 represented by a 2D integer array tasks, where tasks[i] = [enqueueTimei, processingTimei] means that the ith task will be available to process at enqueueTimei and will take processingTimei to finish processing.
You have a single-threaded CPU that can process at most one task at a time and will act in the following way:
If the CPU is idle and there are no available tasks to process, the CPU remains idle.
If the CPU is idle and there are available tasks, the CPU will choose the one with the shortest processing time. If multiple tasks have the same shortest processing time, it will choose the task with the smallest index.
Once a task is started, the CPU will process the entire task without stopping.
The CPU can finish a task then start a new one instantly.
Return the order in which the CPU will process the tasks.
Example 1:
Input: tasks = [[1,2],[2,4],[3,2],[4,1]]
Output: [0,2,3,1]
Explanation: The events go as follows:
- At time = 1, task 0 is available to process. Available tasks = {0}.
- Also at time = 1, the idle CPU starts processing task 0. Available tasks = {}.
- At time = 2, task 1 is available to process. Available tasks = {1}.
- At time = 3, task 2 is available to process. Available tasks = {1, 2}.
- Also at time = 3, the CPU finishes task 0 and starts processing task 2 as it is the shortest. Available tasks = {1}.
- At time = 4, task 3 is available to process. Available tasks = {1, 3}.
- At time = 5, the CPU finishes task 2 and starts processing task 3 as it is the shortest. Available tasks = {1}.
- At time = 6, the CPU finishes task 3 and starts processing task 1. Available tasks = {}.
- At time = 10, the CPU finishes task 1 and becomes idle.
Example 2:
Input: tasks = [[7,10],[7,12],[7,5],[7,4],[7,2]]
Output: [4,3,2,0,1]
Explanation: The events go as follows:
- At time = 7, all the tasks become available. Available tasks = {0,1,2,3,4}.
- Also at time = 7, the idle CPU starts processing task 4. Available tasks = {0,1,2,3}.
- At time = 9, the CPU finishes task 4 and starts processing task 3. Available tasks = {0,1,2}.
- At time = 13, the CPU finishes task 3 and starts processing task 2. Available tasks = {0,1}.
- At time = 18, the CPU finishes task 2 and starts processing task 0. Available tasks = {1}.
- At time = 28, the CPU finishes task 0 and starts processing task 1. Available tasks = {}.
- At time = 40, the CPU finishes task 1 and becomes idle.
Constraints:
tasks.length == n
1 <= n <= 105
1 <= enqueueTimei, processingTimei <= 109
解法1:
这题感觉不容易。我一开始想的是把3个变量(enqueueTime, procTime, index)放到一个Node节点里面,然后用minHeap来做。
后来发现不好处理,因为每次CPU处理一个任务完后,会有一些新的curTime >= enqueueTime的任务变得可行,这个只用minHeap来做是不行的,因为我们不能一个个pop出来检查,再把可以的放回去。
参考的网上的做法。用pair<processTime, index>来作为minHeap的Node,用pair<int, pair<int, int>>> // <enQueueTime, pair<processTime, index>>来构成一个数组nodes,并排序。每次我们从minHeap里面取出top来处理后,调整curTime,再把数组nodes里面的可行的任务push到minHeap里面去。注意每次从minHeap里面只能取一个任务,不能用while,因为每个任务处理完以后,又有一些新的任务可行,这些新的任务可能比当前的top还应该先处理。
long long curTime = 0;class Solution {
public:vector<int> getOrder(vector<vector<int>>& tasks) {int n = tasks.size();//priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>> minHeap; //<processTime, index>priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> minHeap; //<processTime, index>vector<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> nodes; // <enQueueTime, pair<processTime, index>>vector<int> res;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {nodes.push_back({tasks[i][0], {tasks[i][1], i}});}sort(nodes.begin(), nodes.end());int index = 0;while (res.size() < n) {if (!minHeap.empty()) { //注意这里不能用while,因为每个任务处理完以后,又有一些新的任务可行,这些新的任务可能比当前的top还应该先处理。auto topNode = minHeap.top();minHeap.pop();res.push_back(topNode.second);curTime += topNode.first;} else if (index < n) {curTime = nodes[index].first;} else break;for (; index < n; index++) {if (curTime >= nodes[index].first) {minHeap.push(nodes[index].second);} else break;}}return res;}
};
相关文章:
)
Leetcode 1834. Single-Threaded CPU (堆好题)
Single-Threaded CPU Medium You are given n tasks labeled from 0 to n - 1 represented by a 2D integer array tasks, where tasks[i] [enqueueTimei, processingTimei] means that the ith task will be available to process at enque…...
21-数据结构-内部排序-交换排序
简介:主要根据两个数据进行比较从而交换彼此位置,以此类推,交换完全部。主要有冒泡和快速排序两种。 目录 一、冒泡排序 1.1简介: 1.2代码: 二、快速排序 1.1简介: 1.2代码: 一、冒泡排序…...
5-k8s-探针介绍
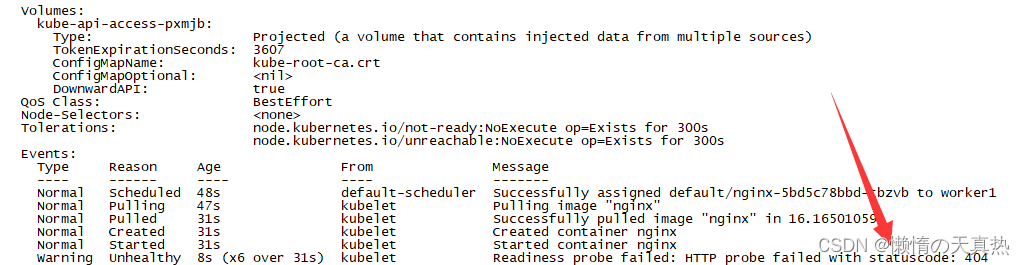
文章目录 一、探针介绍二、探针类型三、探针定义方式四、探针实例五、启动探针测试六、存活探针测试七、就绪探针测试 一、探针介绍 概念 在 Kubernetes 中 Pod 是最小的计算单元,而一个 Pod 又由多个容器组成,相当于每个容器就是一个应用,应…...
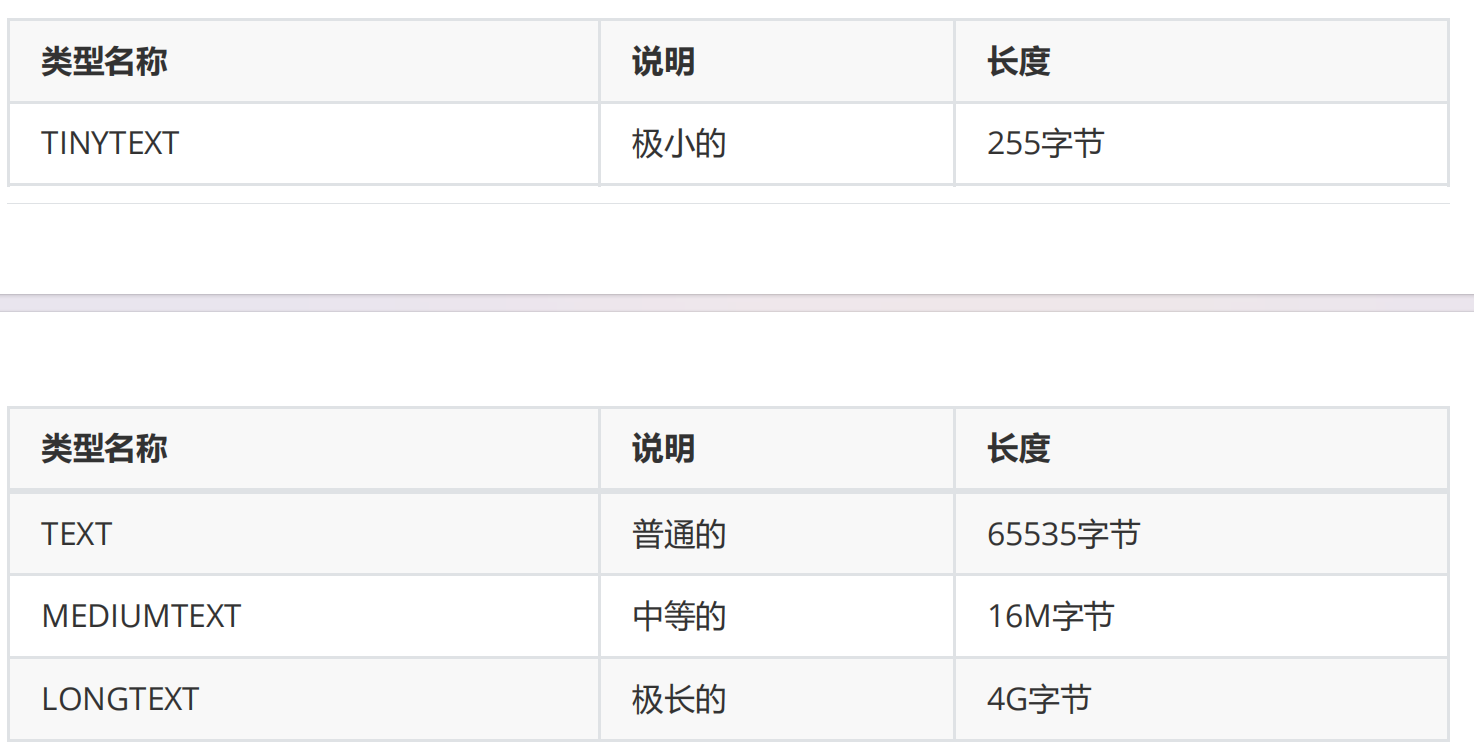
【网络安全 --- MySQL数据库】网络安全MySQL数据库应该掌握的知识,还不收藏开始学习。
四,MySQL 4.1 mysql安装 #centos7默认安装的是MariaDB-5.5.68或者65, #查看版本的指令:[rootweb01 bbs]# rpm -qa| grep mariadb #安装mariadb的最新版,只是更新了软件版本,不会删除之前原有的数据。 #修改yum源的配…...

【MyBatis系列】- 什么是MyBatis
【MyBatis系列】- 什么是MyBatis 文章目录 【MyBatis系列】- 什么是MyBatis一、学习MyBatis知识必备1.1 学习环境准备1.2 学习前掌握知识二、什么是MyBatis三、持久层是什么3.1 为什么需要持久化服务3.2 持久层四、Mybatis的作用五、MyBatis的优点六、参考文档一、学习MyBatis知…...

【Linux】Ubuntu美化bash【教程】
【Linux】Ubuntu美化bash【教程】 文章目录 【Linux】Ubuntu美化bash【教程】1. 查看当前环境中是否有bash2. 安装Synth-Shell3. 配置Synth-Shell4. 取消greeterReference 1. 查看当前环境中是否有bash 查看当前使用的bash echo $SHELL如下所示 sjhsjhR9000X:~$ echo $SHELL…...

微信小程序仿苹果负一屏由弱到强的高斯模糊
进入下面小程序可以体验效果,然后进入更多。查看模糊效果 一、创建小程序组件 二、代码 wxml: <view class"topBar-15"></view> <view class"topBar-14"></view> <view class"topBar-13"></view&…...

js中的new方法
new方法的作用:创建一个实例对象,并继承原对象的属性和方法; new对象内部操作: 1,创建一个新对象,将新对象的proto属性指向原对象的prototype属性; 2,构造函数执行环境中的this指向…...

机器学习-无监督算法之降维
降维:将训练数据中的样本从高维空间转换到低维空间,降维是对原始数据线性变换实现的。为什么要降维?高维计算难,泛化能力差,防止维数灾难优点:减少冗余特征,方便数据可视化,减少内存…...
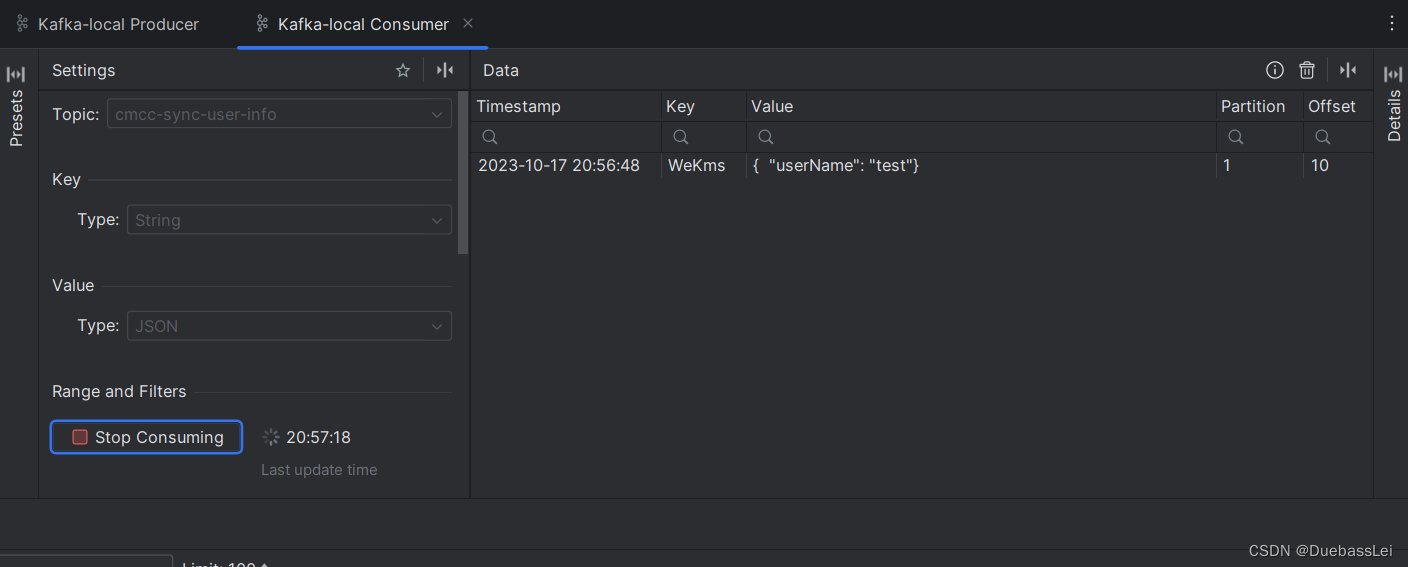
ubuntu20.04下Kafka安装部署及基础使用
Ubuntu安装kafka基础使用 kafka 安装环境基础安装下载kafka解压文件修改配置文件启动kafka创建主题查看主题发送消息接收消息 工具测试kafka Assistant 工具连接测试基础连接连接成功查看topic查看消息查看分区查看消费组 Idea 工具测试基础信息配置信息当前消费组发送消息消费…...

汉得欧洲x甄知科技 | 携手共拓全球化布局,助力出海中企数智化发展
HAND Europe 荣幸获得华为云颁发的 GrowCloud 合作伙伴奖项,进一步巩固了其在企业数字化领域的重要地位。于 2023 年 10 月 5 日,HAND Europe 参加了华为云荷比卢峰会,并因其在全球拓展方面的杰出贡献而荣获 GrowCloud 合作伙伴奖项的认可。 …...

【Javascript保姆级教程】显示类型转换和隐式类型转换
文章目录 前言一、显式类型转换1.1 字符串转换1.2 数字转换1.3 布尔值转换 二、隐式类型转换2.1 数字与字符串相加2.2 布尔值与数字相乘 总结 前言 JavaScript是一种灵活的动态类型语言,这意味着变量的数据类型可以在运行时自动转换,或者通过显式类型转…...

C++算法前缀和的应用:分割数组的最大值的原理、源码及测试用例
分割数组的最大值 相关知识点 C算法:前缀和、前缀乘积、前缀异或的原理、源码及测试用例:付视频课程 二分 过些天整理基础知识 题目 给定一个非负整数数组 nums 和一个整数 m ,你需要将这个数组分成 m 个非空的连续子数组。 设计一个算法…...
gitlab自编译 源码下载
网上都是怎么用 gitlab,但是实际开发中有需要针对 gitlab 进行二次编译自定义实现功能的想法。 搜索了网上的资料以及在官网的查找,查到了如下 gitlab 使用 ruby 开发。 gitlab 下载包 gitlab/gitlab-ce - Packages packages.gitlab.com gitlab/gitl…...
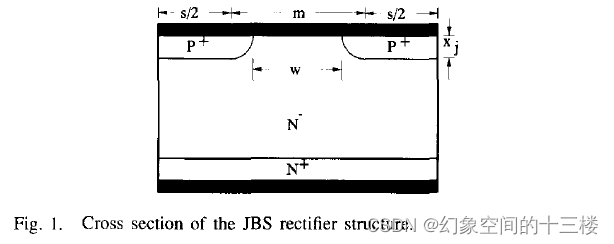
SBD(Schottky Barrier Diode)与JBS(Junction Barrier Schottky)
SBD和JBS二极管都是功率二极管,具有单向导电性,在电路中主要用于整流、箝位、续流等应用。两者的主要区别在于结构和性能。 结构 SBD是肖特基二极管的简称,其结构由一个金属和一个半导体形成的金属-半导体结构成。 JBS是结势垒肖特基二极…...
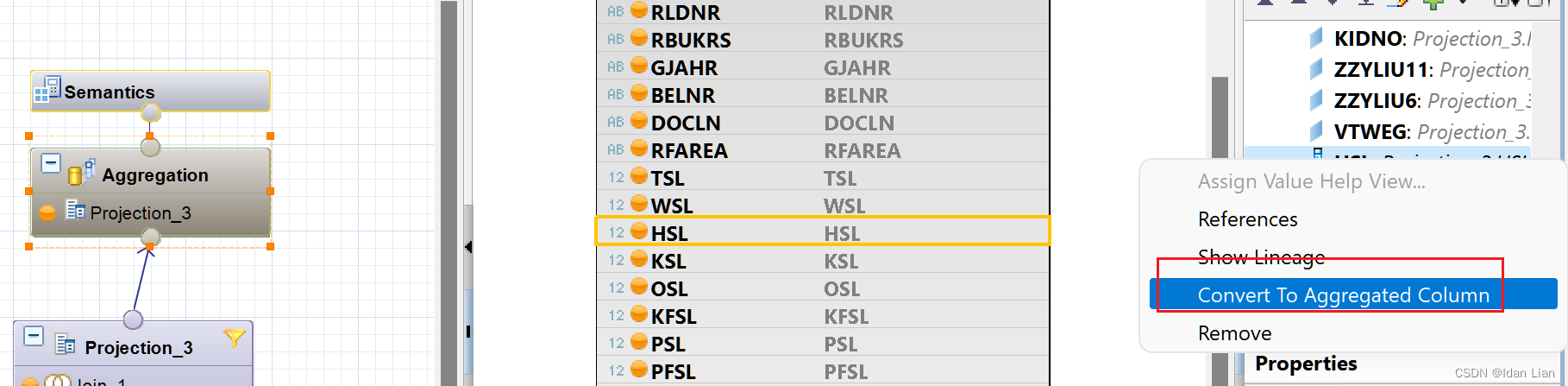
HANA:计算视图-图形化Aggregation组件-踩坑小记(注意事项)
今天遇到在做HANA视图开发的时候,遇到一个事,一直以为是个BUG,可把我气坏了,具体逻辑是这样的,是勇图形化处理的,ACDOCA innerjoin 一个时间维度表,就这么简单,完全按照ACDOCA的主键…...
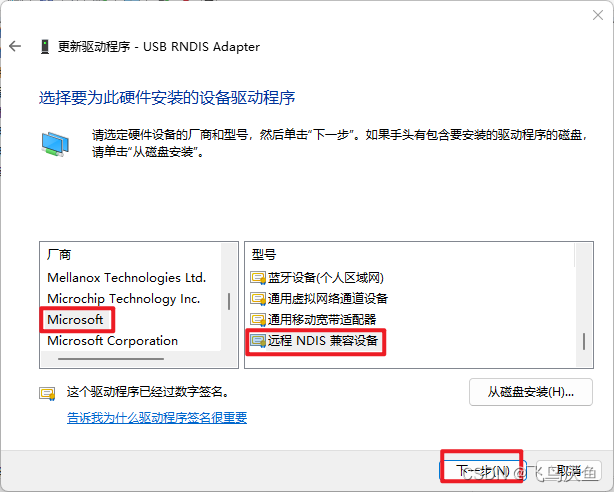
【milkv】更新rndis驱动
问题 由于windows升级到了11,导致rndis驱动无法识别到。 解决 打开设备管理器,查看网络适配器,没有更新会显示黄色的图标。 右击选择更新驱动...

基于混沌博弈优化的BP神经网络(分类应用) - 附代码
基于混沌博弈优化的BP神经网络(分类应用) - 附代码 文章目录 基于混沌博弈优化的BP神经网络(分类应用) - 附代码1.鸢尾花iris数据介绍2.数据集整理3.混沌博弈优化BP神经网络3.1 BP神经网络参数设置3.2 混沌博弈算法应用 4.测试结果…...
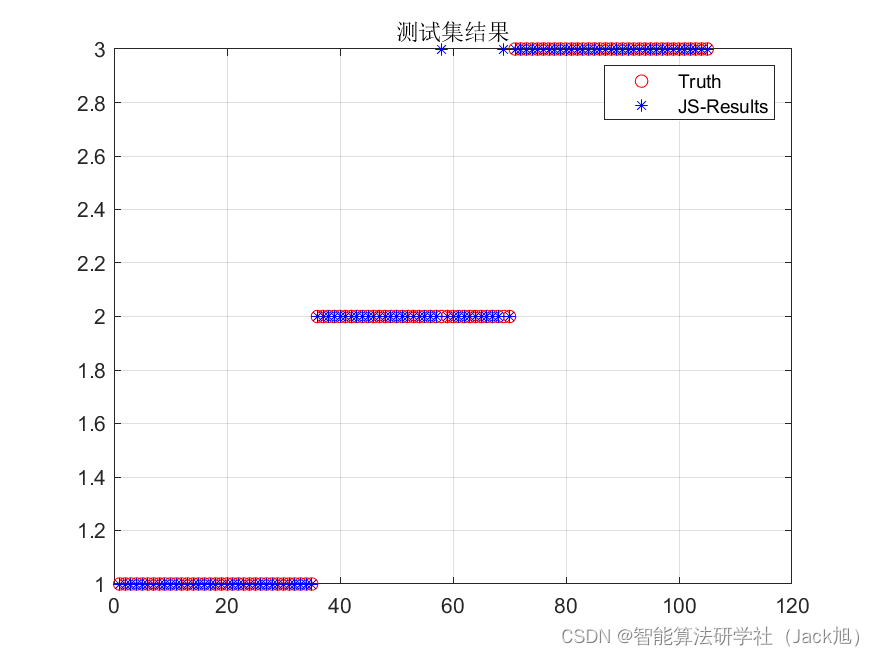
基于人工水母优化的BP神经网络(分类应用) - 附代码
基于人工水母优化的BP神经网络(分类应用) - 附代码 文章目录 基于人工水母优化的BP神经网络(分类应用) - 附代码1.鸢尾花iris数据介绍2.数据集整理3.人工水母优化BP神经网络3.1 BP神经网络参数设置3.2 人工水母算法应用 4.测试结果…...

【C++】哈希学习
哈希学习 unordered系列关联式容器哈希结构除留余数法哈希冲突闭散列线性探测二次探测 负载因子开散列开散列增容 闭散列 VS 开散列字符串哈希算法 线性探测 & 二次探测实现拉链法实现 unordered系列关联式容器 unordered系列关联式容器是从C11开始,STL提供的。…...

题目2267:蓝桥杯2016年第七届真题-取球博弈
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; int n[5], vis[1000][2][2];int dfs(int x, int f, int s) {if(vis[x][f%2][s%2] ! 2) {return vis[x][f%2][s%2];}if(x < n[1]) { // 不能取球了if((f%2 1) && (s%2 0)) return 1;els…...

【以太网PHY实战】SR8201F硬件设计与调试避坑指南
1. 初识SR8201F:一款高性价比的国产百兆PHY芯片 大家好,我是老张,在嵌入式硬件和网络通信这块摸爬滚打了十几年,用过不少以太网PHY芯片。今天想和大家聊聊一款让我印象深刻的国产芯片——和芯德润的SR8201F。说实话,第…...

从原理到调参:Torch-Pruning中的TaylorImportance剪枝算法深度解析
从原理到调参:深入解析Torch-Pruning中的TaylorImportance剪枝算法 在模型部署和优化的实际工作中,我们常常面临一个核心矛盾:如何在保持模型精度的同时,显著降低其计算复杂度和存储开销?对于算法工程师和模型优化人员…...

PyCaret与FastAPI集成:构建机器学习API服务的完整指南
PyCaret与FastAPI集成:构建机器学习API服务的完整指南 【免费下载链接】pycaret An open-source, low-code machine learning library in Python 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/py/pycaret PyCaret是一个开源的低代码机器学习库,通过…...

ollama部署本地大模型|embeddinggemma-300m在金融研报相似度分析应用
ollama部署本地大模型|embeddinggemma-300m在金融研报相似度分析应用 金融分析师每天需要阅读大量研报,如何快速找到相似内容、发现关联信息?本文将手把手教你用ollama部署embeddinggemma-300m模型,构建金融研报智能分析系统。 1.…...

鸿蒙常见问题分析四十二:PanGesture拖动手势eventOffset为空
一个“拖不动”的组件引发的调试困局这周,团队里的小张在为一个工具类应用开发一个可自由拖拽的“悬浮球”功能。这个悬浮球可以放在屏幕任意位置,方便用户快速启动常用操作。为了实现流畅的拖拽,他毫不犹豫地选择了PanGesture(拖…...

Llama-3.2V-11B-cot完整教程:从零构建支持WebRTC实时流推理的视觉服务
Llama-3.2V-11B-cot完整教程:从零构建支持WebRTC实时流推理的视觉服务 想不想让AI不仅能看懂图片,还能像人一样,对着视频流进行一步步的思考和分析?今天,我们就来手把手教你,如何从零开始,把一…...

无锁编程与原子操作
1、非修改序列算法这些算法不会改变它们所操作的容器中的元素。1.1 find 和 find_iffind(begin, end, value):查找第一个等于 value 的元素,返回迭代器(未找到返回 end)。find_if(begin, end, predicate):查找第一个满…...

赤井一号开发板:国产8051嵌入式机电控制平台
1. 项目概述“赤井一号开发板”是一款面向嵌入式学习与小型机电控制场景设计的多功能硬件平台,核心控制器采用国产高性能8位单片机STC32G12K128(LQFP48封装)。该芯片基于增强型8051内核,主频最高可达48 MHz,内置128 KB…...

3小时解锁桌面效率提升:零代码基础掌握RobotJS自动化工具
3小时解锁桌面效率提升:零代码基础掌握RobotJS自动化工具 【免费下载链接】robotjs Node.js Desktop Automation. 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/ro/robotjs 开篇:被重复劳动困住的三个真实场景 场景一:客服日常的机械重…...
