FFmpeg的AVInputFormat
文章目录
- 结构体定义
- 操作函数
- 支持的AVOutputFormat
通过上面的分析,基本可以看到ffmpeg的套路了,首先一个context上下文,上下文里面一个priv_data 指针,然后再插件结构体中有一个priv_data_size,然后回调函数。
结构体定义
首先肯定是AVFormatContext,这个就是上下文,这个结构体太庞大了。特别要注意里面的AVIOContext,这两个回调可以从自己的内存中读取数据。另外还有一个AVStream的结构体,专门用来存储流。
/*** Format I/O context.* New fields can be added to the end with minor version bumps.* Removal, reordering and changes to existing fields require a major* version bump.* sizeof(AVFormatContext) must not be used outside libav*, use* avformat_alloc_context() to create an AVFormatContext.** Fields can be accessed through AVOptions (av_opt*),* the name string used matches the associated command line parameter name and* can be found in libavformat/options_table.h.* The AVOption/command line parameter names differ in some cases from the C* structure field names for historic reasons or brevity.*/
typedef struct AVFormatContext {/*** A class for logging and @ref avoptions. Set by avformat_alloc_context().* Exports (de)muxer private options if they exist.*/const AVClass *av_class;/*** The input container format.** Demuxing only, set by avformat_open_input().*/const struct AVInputFormat *iformat;/*** The output container format.** Muxing only, must be set by the caller before avformat_write_header().*/const struct AVOutputFormat *oformat;/*** Format private data. This is an AVOptions-enabled struct* if and only if iformat/oformat.priv_class is not NULL.** - muxing: set by avformat_write_header()* - demuxing: set by avformat_open_input()*/void *priv_data;/*** I/O context.** - demuxing: either set by the user before avformat_open_input() (then* the user must close it manually) or set by avformat_open_input().* - muxing: set by the user before avformat_write_header(). The caller must* take care of closing / freeing the IO context.** Do NOT set this field if AVFMT_NOFILE flag is set in* iformat/oformat.flags. In such a case, the (de)muxer will handle* I/O in some other way and this field will be NULL.*/AVIOContext *pb;/* stream info *//*** Flags signalling stream properties. A combination of AVFMTCTX_*.* Set by libavformat.*/int ctx_flags;/*** Number of elements in AVFormatContext.streams.** Set by avformat_new_stream(), must not be modified by any other code.*/unsigned int nb_streams;/*** A list of all streams in the file. New streams are created with* avformat_new_stream().** - demuxing: streams are created by libavformat in avformat_open_input().* If AVFMTCTX_NOHEADER is set in ctx_flags, then new streams may also* appear in av_read_frame().* - muxing: streams are created by the user before avformat_write_header().** Freed by libavformat in avformat_free_context().*/AVStream **streams;/*** input or output URL. Unlike the old filename field, this field has no* length restriction.** - demuxing: set by avformat_open_input(), initialized to an empty* string if url parameter was NULL in avformat_open_input().* - muxing: may be set by the caller before calling avformat_write_header()* (or avformat_init_output() if that is called first) to a string* which is freeable by av_free(). Set to an empty string if it* was NULL in avformat_init_output().** Freed by libavformat in avformat_free_context().*/char *url;/*** Position of the first frame of the component, in* AV_TIME_BASE fractional seconds. NEVER set this value directly:* It is deduced from the AVStream values.** Demuxing only, set by libavformat.*/int64_t start_time;/*** Duration of the stream, in AV_TIME_BASE fractional* seconds. Only set this value if you know none of the individual stream* durations and also do not set any of them. This is deduced from the* AVStream values if not set.** Demuxing only, set by libavformat.*/int64_t duration;/*** Total stream bitrate in bit/s, 0 if not* available. Never set it directly if the file_size and the* duration are known as FFmpeg can compute it automatically.*/int64_t bit_rate;unsigned int packet_size;int max_delay;/*** Flags modifying the (de)muxer behaviour. A combination of AVFMT_FLAG_*.* Set by the user before avformat_open_input() / avformat_write_header().*/int flags;
#define AVFMT_FLAG_GENPTS 0x0001 ///< Generate missing pts even if it requires parsing future frames.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_IGNIDX 0x0002 ///< Ignore index.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NONBLOCK 0x0004 ///< Do not block when reading packets from input.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_IGNDTS 0x0008 ///< Ignore DTS on frames that contain both DTS & PTS
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NOFILLIN 0x0010 ///< Do not infer any values from other values, just return what is stored in the container
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NOPARSE 0x0020 ///< Do not use AVParsers, you also must set AVFMT_FLAG_NOFILLIN as the fillin code works on frames and no parsing -> no frames. Also seeking to frames can not work if parsing to find frame boundaries has been disabled
#define AVFMT_FLAG_NOBUFFER 0x0040 ///< Do not buffer frames when possible
#define AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO 0x0080 ///< The caller has supplied a custom AVIOContext, don't avio_close() it.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_DISCARD_CORRUPT 0x0100 ///< Discard frames marked corrupted
#define AVFMT_FLAG_FLUSH_PACKETS 0x0200 ///< Flush the AVIOContext every packet.
/*** When muxing, try to avoid writing any random/volatile data to the output.* This includes any random IDs, real-time timestamps/dates, muxer version, etc.** This flag is mainly intended for testing.*/
#define AVFMT_FLAG_BITEXACT 0x0400
#define AVFMT_FLAG_SORT_DTS 0x10000 ///< try to interleave outputted packets by dts (using this flag can slow demuxing down)
#if FF_API_LAVF_PRIV_OPT
#define AVFMT_FLAG_PRIV_OPT 0x20000 ///< Enable use of private options by delaying codec open (deprecated, does nothing)
#endif
#define AVFMT_FLAG_FAST_SEEK 0x80000 ///< Enable fast, but inaccurate seeks for some formats
#define AVFMT_FLAG_SHORTEST 0x100000 ///< Stop muxing when the shortest stream stops.
#define AVFMT_FLAG_AUTO_BSF 0x200000 ///< Add bitstream filters as requested by the muxer/*** Maximum number of bytes read from input in order to determine stream* properties. Used when reading the global header and in* avformat_find_stream_info().** Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().** @note this is \e not used for determining the \ref AVInputFormat* "input format"* @sa format_probesize*/int64_t probesize;/*** Maximum duration (in AV_TIME_BASE units) of the data read* from input in avformat_find_stream_info().* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_find_stream_info().* Can be set to 0 to let avformat choose using a heuristic.*/int64_t max_analyze_duration;const uint8_t *key;int keylen;unsigned int nb_programs;AVProgram **programs;/*** Forced video codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user.*/enum AVCodecID video_codec_id;/*** Forced audio codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user.*/enum AVCodecID audio_codec_id;/*** Forced subtitle codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user.*/enum AVCodecID subtitle_codec_id;/*** Maximum amount of memory in bytes to use for the index of each stream.* If the index exceeds this size, entries will be discarded as* needed to maintain a smaller size. This can lead to slower or less* accurate seeking (depends on demuxer).* Demuxers for which a full in-memory index is mandatory will ignore* this.* - muxing: unused* - demuxing: set by user*/unsigned int max_index_size;/*** Maximum amount of memory in bytes to use for buffering frames* obtained from realtime capture devices.*/unsigned int max_picture_buffer;/*** Number of chapters in AVChapter array.* When muxing, chapters are normally written in the file header,* so nb_chapters should normally be initialized before write_header* is called. Some muxers (e.g. mov and mkv) can also write chapters* in the trailer. To write chapters in the trailer, nb_chapters* must be zero when write_header is called and non-zero when* write_trailer is called.* - muxing: set by user* - demuxing: set by libavformat*/unsigned int nb_chapters;AVChapter **chapters;/*** Metadata that applies to the whole file.** - demuxing: set by libavformat in avformat_open_input()* - muxing: may be set by the caller before avformat_write_header()** Freed by libavformat in avformat_free_context().*/AVDictionary *metadata;/*** Start time of the stream in real world time, in microseconds* since the Unix epoch (00:00 1st January 1970). That is, pts=0 in the* stream was captured at this real world time.* - muxing: Set by the caller before avformat_write_header(). If set to* either 0 or AV_NOPTS_VALUE, then the current wall-time will* be used.* - demuxing: Set by libavformat. AV_NOPTS_VALUE if unknown. Note that* the value may become known after some number of frames* have been received.*/int64_t start_time_realtime;/*** The number of frames used for determining the framerate in* avformat_find_stream_info().* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_find_stream_info().*/int fps_probe_size;/*** Error recognition; higher values will detect more errors but may* misdetect some more or less valid parts as errors.* Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().*/int error_recognition;/*** Custom interrupt callbacks for the I/O layer.** demuxing: set by the user before avformat_open_input().* muxing: set by the user before avformat_write_header()* (mainly useful for AVFMT_NOFILE formats). The callback* should also be passed to avio_open2() if it's used to* open the file.*/AVIOInterruptCB interrupt_callback;/*** Flags to enable debugging.*/int debug;
#define FF_FDEBUG_TS 0x0001/*** Maximum buffering duration for interleaving.** To ensure all the streams are interleaved correctly,* av_interleaved_write_frame() will wait until it has at least one packet* for each stream before actually writing any packets to the output file.* When some streams are "sparse" (i.e. there are large gaps between* successive packets), this can result in excessive buffering.** This field specifies the maximum difference between the timestamps of the* first and the last packet in the muxing queue, above which libavformat* will output a packet regardless of whether it has queued a packet for all* the streams.** Muxing only, set by the caller before avformat_write_header().*/int64_t max_interleave_delta;/*** Allow non-standard and experimental extension* @see AVCodecContext.strict_std_compliance*/int strict_std_compliance;/*** Flags indicating events happening on the file, a combination of* AVFMT_EVENT_FLAG_*.** - demuxing: may be set by the demuxer in avformat_open_input(),* avformat_find_stream_info() and av_read_frame(). Flags must be cleared* by the user once the event has been handled.* - muxing: may be set by the user after avformat_write_header() to* indicate a user-triggered event. The muxer will clear the flags for* events it has handled in av_[interleaved]_write_frame().*/int event_flags;
/*** - demuxing: the demuxer read new metadata from the file and updated* AVFormatContext.metadata accordingly* - muxing: the user updated AVFormatContext.metadata and wishes the muxer to* write it into the file*/
#define AVFMT_EVENT_FLAG_METADATA_UPDATED 0x0001/*** Maximum number of packets to read while waiting for the first timestamp.* Decoding only.*/int max_ts_probe;/*** Avoid negative timestamps during muxing.* Any value of the AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_* constants.* Note, this only works when using av_interleaved_write_frame. (interleave_packet_per_dts is in use)* - muxing: Set by user* - demuxing: unused*/int avoid_negative_ts;
#define AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_AUTO -1 ///< Enabled when required by target format
#define AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_MAKE_NON_NEGATIVE 1 ///< Shift timestamps so they are non negative
#define AVFMT_AVOID_NEG_TS_MAKE_ZERO 2 ///< Shift timestamps so that they start at 0/*** Transport stream id.* This will be moved into demuxer private options. Thus no API/ABI compatibility*/int ts_id;/*** Audio preload in microseconds.* Note, not all formats support this and unpredictable things may happen if it is used when not supported.* - encoding: Set by user* - decoding: unused*/int audio_preload;/*** Max chunk time in microseconds.* Note, not all formats support this and unpredictable things may happen if it is used when not supported.* - encoding: Set by user* - decoding: unused*/int max_chunk_duration;/*** Max chunk size in bytes* Note, not all formats support this and unpredictable things may happen if it is used when not supported.* - encoding: Set by user* - decoding: unused*/int max_chunk_size;/*** forces the use of wallclock timestamps as pts/dts of packets* This has undefined results in the presence of B frames.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Set by user*/int use_wallclock_as_timestamps;/*** avio flags, used to force AVIO_FLAG_DIRECT.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Set by user*/int avio_flags;/*** The duration field can be estimated through various ways, and this field can be used* to know how the duration was estimated.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Read by user*/enum AVDurationEstimationMethod duration_estimation_method;/*** Skip initial bytes when opening stream* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Set by user*/int64_t skip_initial_bytes;/*** Correct single timestamp overflows* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Set by user*/unsigned int correct_ts_overflow;/*** Force seeking to any (also non key) frames.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: Set by user*/int seek2any;/*** Flush the I/O context after each packet.* - encoding: Set by user* - decoding: unused*/int flush_packets;/*** format probing score.* The maximal score is AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX, its set when the demuxer probes* the format.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by avformat, read by user*/int probe_score;/*** Maximum number of bytes read from input in order to identify the* \ref AVInputFormat "input format". Only used when the format is not set* explicitly by the caller.** Demuxing only, set by the caller before avformat_open_input().** @sa probesize*/int format_probesize;/*** ',' separated list of allowed decoders.* If NULL then all are allowed* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/char *codec_whitelist;/*** ',' separated list of allowed demuxers.* If NULL then all are allowed* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/char *format_whitelist;/*** IO repositioned flag.* This is set by avformat when the underlaying IO context read pointer* is repositioned, for example when doing byte based seeking.* Demuxers can use the flag to detect such changes.*/int io_repositioned;/*** Forced video codec.* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with* the same codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user*/const AVCodec *video_codec;/*** Forced audio codec.* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with* the same codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user*/const AVCodec *audio_codec;/*** Forced subtitle codec.* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with* the same codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user*/const AVCodec *subtitle_codec;/*** Forced data codec.* This allows forcing a specific decoder, even when there are multiple with* the same codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user*/const AVCodec *data_codec;/*** Number of bytes to be written as padding in a metadata header.* Demuxing: Unused.* Muxing: Set by user via av_format_set_metadata_header_padding.*/int metadata_header_padding;/*** User data.* This is a place for some private data of the user.*/void *opaque;/*** Callback used by devices to communicate with application.*/av_format_control_message control_message_cb;/*** Output timestamp offset, in microseconds.* Muxing: set by user*/int64_t output_ts_offset;/*** dump format separator.* can be ", " or "\n " or anything else* - muxing: Set by user.* - demuxing: Set by user.*/uint8_t *dump_separator;/*** Forced Data codec_id.* Demuxing: Set by user.*/enum AVCodecID data_codec_id;/*** ',' separated list of allowed protocols.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/char *protocol_whitelist;/*** A callback for opening new IO streams.** Whenever a muxer or a demuxer needs to open an IO stream (typically from* avformat_open_input() for demuxers, but for certain formats can happen at* other times as well), it will call this callback to obtain an IO context.** @param s the format context* @param pb on success, the newly opened IO context should be returned here* @param url the url to open* @param flags a combination of AVIO_FLAG_** @param options a dictionary of additional options, with the same* semantics as in avio_open2()* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure** @note Certain muxers and demuxers do nesting, i.e. they open one or more* additional internal format contexts. Thus the AVFormatContext pointer* passed to this callback may be different from the one facing the caller.* It will, however, have the same 'opaque' field.*/int (*io_open)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext **pb, const char *url,int flags, AVDictionary **options);/*** A callback for closing the streams opened with AVFormatContext.io_open().*/void (*io_close)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb);/*** ',' separated list of disallowed protocols.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/char *protocol_blacklist;/*** The maximum number of streams.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/int max_streams;/*** Skip duration calcuation in estimate_timings_from_pts.* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/int skip_estimate_duration_from_pts;/*** Maximum number of packets that can be probed* - encoding: unused* - decoding: set by user*/int max_probe_packets;/*** A callback for closing the streams opened with AVFormatContext.io_open().** Using this is preferred over io_close, because this can return an error.* Therefore this callback is used instead of io_close by the generic* libavformat code if io_close is NULL or the default.** @param s the format context* @param pb IO context to be closed and freed* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure*/int (*io_close2)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb);
} AVFormatContext;
下面的结构体就是需要插件实现的回调函数。
/*** @addtogroup lavf_encoding* @{*/
typedef struct AVOutputFormat {const char *name;/*** Descriptive name for the format, meant to be more human-readable* than name. You should use the NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL() macro* to define it.*/const char *long_name;const char *mime_type;const char *extensions; /**< comma-separated filename extensions *//* output support */enum AVCodecID audio_codec; /**< default audio codec */enum AVCodecID video_codec; /**< default video codec */enum AVCodecID subtitle_codec; /**< default subtitle codec *//*** can use flags: AVFMT_NOFILE, AVFMT_NEEDNUMBER,* AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER, AVFMT_NOTIMESTAMPS, AVFMT_VARIABLE_FPS,* AVFMT_NODIMENSIONS, AVFMT_NOSTREAMS, AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH,* AVFMT_TS_NONSTRICT, AVFMT_TS_NEGATIVE*/int flags;/*** List of supported codec_id-codec_tag pairs, ordered by "better* choice first". The arrays are all terminated by AV_CODEC_ID_NONE.*/const struct AVCodecTag * const *codec_tag;const AVClass *priv_class; ///< AVClass for the private context/****************************************************************** No fields below this line are part of the public API. They* may not be used outside of libavformat and can be changed and* removed at will.* New public fields should be added right above.******************************************************************//*** size of private data so that it can be allocated in the wrapper*/int priv_data_size;/*** Internal flags. See FF_FMT_FLAG_* in internal.h.*/int flags_internal;int (*write_header)(struct AVFormatContext *);/*** Write a packet. If AVFMT_ALLOW_FLUSH is set in flags,* pkt can be NULL in order to flush data buffered in the muxer.* When flushing, return 0 if there still is more data to flush,* or 1 if everything was flushed and there is no more buffered* data.*/int (*write_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *, AVPacket *pkt);int (*write_trailer)(struct AVFormatContext *);/*** A format-specific function for interleavement.* If unset, packets will be interleaved by dts.** @param s An AVFormatContext for output. pkt will be added to* resp. taken from its packet buffer.* @param[in,out] pkt A packet to be interleaved if has_packet is set;* also used to return packets. If no packet is returned* (e.g. on error), pkt is blank on return.* @param flush 1 if no further packets are available as input and* all remaining packets should be output.* @param has_packet If set, pkt contains a packet to be interleaved* on input; otherwise pkt is blank on input.* @return 1 if a packet was output, 0 if no packet could be output,* < 0 if an error occurred*/int (*interleave_packet)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt,int flush, int has_packet);/*** Test if the given codec can be stored in this container.** @return 1 if the codec is supported, 0 if it is not.* A negative number if unknown.* MKTAG('A', 'P', 'I', 'C') if the codec is only supported as AV_DISPOSITION_ATTACHED_PIC*/int (*query_codec)(enum AVCodecID id, int std_compliance);void (*get_output_timestamp)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int stream,int64_t *dts, int64_t *wall);/*** Allows sending messages from application to device.*/int (*control_message)(struct AVFormatContext *s, int type,void *data, size_t data_size);/*** Write an uncoded AVFrame.** See av_write_uncoded_frame() for details.** The library will free *frame afterwards, but the muxer can prevent it* by setting the pointer to NULL.*/int (*write_uncoded_frame)(struct AVFormatContext *, int stream_index,AVFrame **frame, unsigned flags);/*** Returns device list with it properties.* @see avdevice_list_devices() for more details.*/int (*get_device_list)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVDeviceInfoList *device_list);enum AVCodecID data_codec; /**< default data codec *//*** Initialize format. May allocate data here, and set any AVFormatContext or* AVStream parameters that need to be set before packets are sent.* This method must not write output.** Return 0 if streams were fully configured, 1 if not, negative AVERROR on failure** Any allocations made here must be freed in deinit().*/int (*init)(struct AVFormatContext *);/*** Deinitialize format. If present, this is called whenever the muxer is being* destroyed, regardless of whether or not the header has been written.** If a trailer is being written, this is called after write_trailer().** This is called if init() fails as well.*/void (*deinit)(struct AVFormatContext *);/*** Set up any necessary bitstream filtering and extract any extra data needed* for the global header.** @note pkt might have been directly forwarded by a meta-muxer; therefore* pkt->stream_index as well as the pkt's timebase might be invalid.* Return 0 if more packets from this stream must be checked; 1 if not.*/int (*check_bitstream)(struct AVFormatContext *s, struct AVStream *st,const AVPacket *pkt);
} AVOutputFormat;
操作函数
/*** Allocate an AVFormatContext.* avformat_free_context() can be used to free the context and everything* allocated by the framework within it.*/
AVFormatContext *avformat_alloc_context(void);/*** Free an AVFormatContext and all its streams.* @param s context to free*/
void avformat_free_context(AVFormatContext *s);/*** Add a new stream to a media file.** When demuxing, it is called by the demuxer in read_header(). If the* flag AVFMTCTX_NOHEADER is set in s.ctx_flags, then it may also* be called in read_packet().** When muxing, should be called by the user before avformat_write_header().** User is required to call avformat_free_context() to clean up the allocation* by avformat_new_stream().** @param s media file handle* @param c unused, does nothing** @return newly created stream or NULL on error.*/
AVStream *avformat_new_stream(AVFormatContext *s, const AVCodec *c);/*** Wrap an existing array as stream side data.** @param st stream* @param type side information type* @param data the side data array. It must be allocated with the av_malloc()* family of functions. The ownership of the data is transferred to* st.* @param size side information size* @return zero on success, a negative AVERROR code on failure. On failure,* the stream is unchanged and the data remains owned by the caller.*/
int av_stream_add_side_data(AVStream *st, enum AVPacketSideDataType type,uint8_t *data, size_t size);/*** Allocate new information from stream.** @param stream stream* @param type desired side information type* @param size side information size* @return pointer to fresh allocated data or NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t *av_stream_new_side_data(AVStream *stream,enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t size);
/*** Get side information from stream.** @param stream stream* @param type desired side information type* @param size If supplied, *size will be set to the size of the side data* or to zero if the desired side data is not present.* @return pointer to data if present or NULL otherwise*/
uint8_t *av_stream_get_side_data(const AVStream *stream,enum AVPacketSideDataType type, size_t *size);/*** Allocate an AVFormatContext for an output format.* avformat_free_context() can be used to free the context and* everything allocated by the framework within it.** @param *ctx is set to the created format context, or to NULL in* case of failure* @param oformat format to use for allocating the context, if NULL* format_name and filename are used instead* @param format_name the name of output format to use for allocating the* context, if NULL filename is used instead* @param filename the name of the filename to use for allocating the* context, may be NULL* @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative AVERROR code in case of* failure*/
int avformat_alloc_output_context2(AVFormatContext **ctx, const AVOutputFormat *oformat,const char *format_name, const char *filename);/*** @addtogroup lavf_decoding* @{*//*** Find AVInputFormat based on the short name of the input format.*/
const AVInputFormat *av_find_input_format(const char *short_name);/*** Guess the file format.** @param pd data to be probed* @param is_opened Whether the file is already opened; determines whether* demuxers with or without AVFMT_NOFILE are probed.*/
const AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format(const AVProbeData *pd, int is_opened);/*** Guess the file format.** @param pd data to be probed* @param is_opened Whether the file is already opened; determines whether* demuxers with or without AVFMT_NOFILE are probed.* @param score_max A probe score larger that this is required to accept a* detection, the variable is set to the actual detection* score afterwards.* If the score is <= AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX / 4 it is recommended* to retry with a larger probe buffer.*/
const AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format2(const AVProbeData *pd,int is_opened, int *score_max);/*** Guess the file format.** @param is_opened Whether the file is already opened; determines whether* demuxers with or without AVFMT_NOFILE are probed.* @param score_ret The score of the best detection.*/
const AVInputFormat *av_probe_input_format3(const AVProbeData *pd,int is_opened, int *score_ret);/*** Probe a bytestream to determine the input format. Each time a probe returns* with a score that is too low, the probe buffer size is increased and another* attempt is made. When the maximum probe size is reached, the input format* with the highest score is returned.** @param pb the bytestream to probe* @param fmt the input format is put here* @param url the url of the stream* @param logctx the log context* @param offset the offset within the bytestream to probe from* @param max_probe_size the maximum probe buffer size (zero for default)* @return the score in case of success, a negative value corresponding to an* the maximal score is AVPROBE_SCORE_MAX* AVERROR code otherwise*/
int av_probe_input_buffer2(AVIOContext *pb, const AVInputFormat **fmt,const char *url, void *logctx,unsigned int offset, unsigned int max_probe_size);/*** Like av_probe_input_buffer2() but returns 0 on success*/
int av_probe_input_buffer(AVIOContext *pb, const AVInputFormat **fmt,const char *url, void *logctx,unsigned int offset, unsigned int max_probe_size);/*** Open an input stream and read the header. The codecs are not opened.* The stream must be closed with avformat_close_input().** @param ps Pointer to user-supplied AVFormatContext (allocated by avformat_alloc_context).* May be a pointer to NULL, in which case an AVFormatContext is allocated by this* function and written into ps.* Note that a user-supplied AVFormatContext will be freed on failure.* @param url URL of the stream to open.* @param fmt If non-NULL, this parameter forces a specific input format.* Otherwise the format is autodetected.* @param options A dictionary filled with AVFormatContext and demuxer-private options.* On return this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with a dict containing* options that were not found. May be NULL.** @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure.** @note If you want to use custom IO, preallocate the format context and set its pb field.*/
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *url,const AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options);/*** Read packets of a media file to get stream information. This* is useful for file formats with no headers such as MPEG. This* function also computes the real framerate in case of MPEG-2 repeat* frame mode.* The logical file position is not changed by this function;* examined packets may be buffered for later processing.** @param ic media file handle* @param options If non-NULL, an ic.nb_streams long array of pointers to* dictionaries, where i-th member contains options for* codec corresponding to i-th stream.* On return each dictionary will be filled with options that were not found.* @return >=0 if OK, AVERROR_xxx on error** @note this function isn't guaranteed to open all the codecs, so* options being non-empty at return is a perfectly normal behavior.** @todo Let the user decide somehow what information is needed so that* we do not waste time getting stuff the user does not need.*/
int avformat_find_stream_info(AVFormatContext *ic, AVDictionary **options);/*** Find the programs which belong to a given stream.** @param ic media file handle* @param last the last found program, the search will start after this* program, or from the beginning if it is NULL* @param s stream index* @return the next program which belongs to s, NULL if no program is found or* the last program is not among the programs of ic.*/
AVProgram *av_find_program_from_stream(AVFormatContext *ic, AVProgram *last, int s);void av_program_add_stream_index(AVFormatContext *ac, int progid, unsigned int idx);/*** Find the "best" stream in the file.* The best stream is determined according to various heuristics as the most* likely to be what the user expects.* If the decoder parameter is non-NULL, av_find_best_stream will find the* default decoder for the stream's codec; streams for which no decoder can* be found are ignored.** @param ic media file handle* @param type stream type: video, audio, subtitles, etc.* @param wanted_stream_nb user-requested stream number,* or -1 for automatic selection* @param related_stream try to find a stream related (eg. in the same* program) to this one, or -1 if none* @param decoder_ret if non-NULL, returns the decoder for the* selected stream* @param flags flags; none are currently defined* @return the non-negative stream number in case of success,* AVERROR_STREAM_NOT_FOUND if no stream with the requested type* could be found,* AVERROR_DECODER_NOT_FOUND if streams were found but no decoder* @note If av_find_best_stream returns successfully and decoder_ret is not* NULL, then *decoder_ret is guaranteed to be set to a valid AVCodec.*/
int av_find_best_stream(AVFormatContext *ic,enum AVMediaType type,int wanted_stream_nb,int related_stream,const AVCodec **decoder_ret,int flags);
其实想要说明的一些函数是下面的,这些函数可以用来控制输入流的播放,暂停,跳转,等,特别是在rtsp等流媒体服务器上,非常有用。
就这些吧,等到后面分析rtsp和rtmp的客户端的时候,我们再来详细的讲一下这些函数的调用流程,今天就先列出来吧。
/*** Return the next frame of a stream.* This function returns what is stored in the file, and does not validate* that what is there are valid frames for the decoder. It will split what is* stored in the file into frames and return one for each call. It will not* omit invalid data between valid frames so as to give the decoder the maximum* information possible for decoding.** On success, the returned packet is reference-counted (pkt->buf is set) and* valid indefinitely. The packet must be freed with av_packet_unref() when* it is no longer needed. For video, the packet contains exactly one frame.* For audio, it contains an integer number of frames if each frame has* a known fixed size (e.g. PCM or ADPCM data). If the audio frames have* a variable size (e.g. MPEG audio), then it contains one frame.** pkt->pts, pkt->dts and pkt->duration are always set to correct* values in AVStream.time_base units (and guessed if the format cannot* provide them). pkt->pts can be AV_NOPTS_VALUE if the video format* has B-frames, so it is better to rely on pkt->dts if you do not* decompress the payload.** @return 0 if OK, < 0 on error or end of file. On error, pkt will be blank* (as if it came from av_packet_alloc()).** @note pkt will be initialized, so it may be uninitialized, but it must not* contain data that needs to be freed.*/
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt);/*** Seek to the keyframe at timestamp.* 'timestamp' in 'stream_index'.** @param s media file handle* @param stream_index If stream_index is (-1), a default* stream is selected, and timestamp is automatically converted* from AV_TIME_BASE units to the stream specific time_base.* @param timestamp Timestamp in AVStream.time_base units* or, if no stream is specified, in AV_TIME_BASE units.* @param flags flags which select direction and seeking mode* @return >= 0 on success*/
int av_seek_frame(AVFormatContext *s, int stream_index, int64_t timestamp,int flags);/*** Seek to timestamp ts.* Seeking will be done so that the point from which all active streams* can be presented successfully will be closest to ts and within min/max_ts.* Active streams are all streams that have AVStream.discard < AVDISCARD_ALL.** If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_BYTE, then all timestamps are in bytes and* are the file position (this may not be supported by all demuxers).* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME, then all timestamps are in frames* in the stream with stream_index (this may not be supported by all demuxers).* Otherwise all timestamps are in units of the stream selected by stream_index* or if stream_index is -1, in AV_TIME_BASE units.* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_ANY, then non-keyframes are treated as* keyframes (this may not be supported by all demuxers).* If flags contain AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD, it is ignored.** @param s media file handle* @param stream_index index of the stream which is used as time base reference* @param min_ts smallest acceptable timestamp* @param ts target timestamp* @param max_ts largest acceptable timestamp* @param flags flags* @return >=0 on success, error code otherwise** @note This is part of the new seek API which is still under construction.*/
int avformat_seek_file(AVFormatContext *s, int stream_index, int64_t min_ts, int64_t ts, int64_t max_ts, int flags);/*** Discard all internally buffered data. This can be useful when dealing with* discontinuities in the byte stream. Generally works only with formats that* can resync. This includes headerless formats like MPEG-TS/TS but should also* work with NUT, Ogg and in a limited way AVI for example.** The set of streams, the detected duration, stream parameters and codecs do* not change when calling this function. If you want a complete reset, it's* better to open a new AVFormatContext.** This does not flush the AVIOContext (s->pb). If necessary, call* avio_flush(s->pb) before calling this function.** @param s media file handle* @return >=0 on success, error code otherwise*/
int avformat_flush(AVFormatContext *s);/*** Start playing a network-based stream (e.g. RTSP stream) at the* current position.*/
int av_read_play(AVFormatContext *s);/*** Pause a network-based stream (e.g. RTSP stream).** Use av_read_play() to resume it.*/
int av_read_pause(AVFormatContext *s);/*** Close an opened input AVFormatContext. Free it and all its contents* and set *s to NULL.*/
void avformat_close_input(AVFormatContext **s);
/*** @}*/
支持的AVOutputFormat
相关文章:

FFmpeg的AVInputFormat
文章目录 结构体定义操作函数支持的AVOutputFormat 通过上面的分析,基本可以看到ffmpeg的套路了,首先一个context上下文,上下文里面一个priv_data 指针,然后再插件结构体中有一个priv_data_size,然后回调函数。 结构体…...
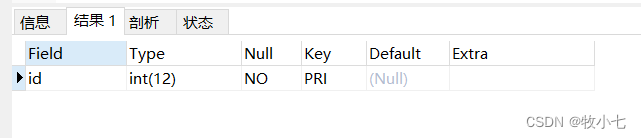
SQL命令---删除字段
介绍 使用sql语句删除表字段。 命令 alter table 表名 drop 字段名;例子 删除a表中的name字段。 alter table a drop name;下面是执行删除后的表结构:...

深入探讨 Python 中的装饰器和上下文管理器
Python 作为一门灵活而强大的语言,提供了许多高级特性,其中装饰器(Decorators)和上下文管理器(Context Managers)是其中两个非常有用的概念。这两个功能性特性提供了对代码结构和行为进行修改和控制的强大工…...

比whatsapp效果好---Google Messages RCS协议消息推送
这段时间由于使用谷歌手机Pixel 7 ( Android13)研究改机room,看了很多相关的资料,测试研究了谷歌生态很多软件功能。结果就是改机Room还没编译成功,反而是测试出Google Messages群发功能的bug,算是一个惊喜…...
HBuilder X
选择一款编程软件有以下几个好处: (1)提高效率:编程软件通常强调代码编辑和自动完成,可以帮助程序员更快速、更准确地输入代码。 (2)降低错误率:编程软件还可以检测代码中的错误&a…...
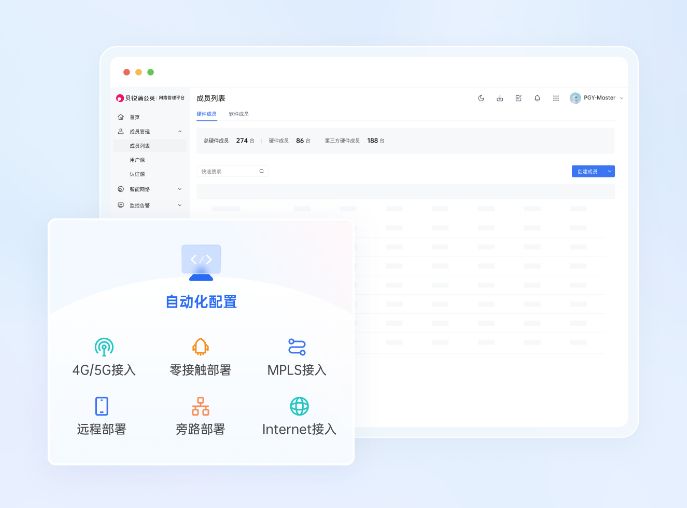
异地现场工控设备,如何实现远程配置、调试?
南京某企业专注于工业物联领域,在相关项目中往往会在各个点位部署基于Linux系统的中控主机,实现各类物联设备信息的采集、汇总。但是,由于各点位分散多地,且数量达到了上百个,虽然中控主机具备4G物联网接入能力&#x…...
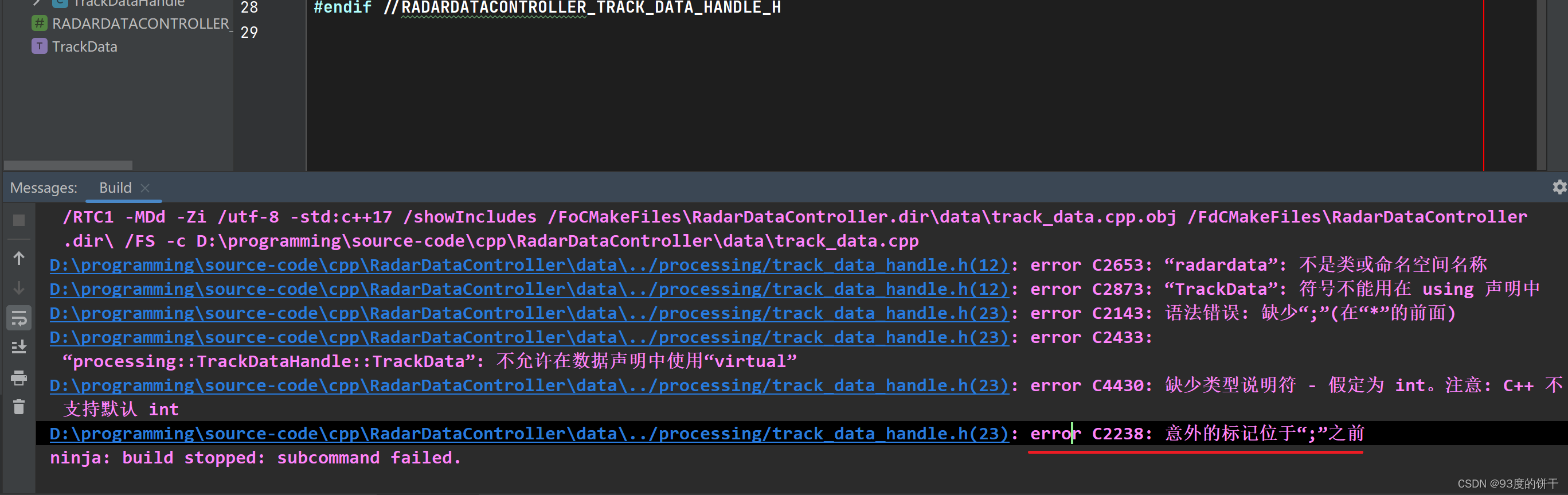
C++报错:error C2238: 意外的标记位于“;”之前
报错信息如下: 编译遇见这样的错误信息主要有一下几种: 情况一: 多数情况下出现这种问题的原因是因为头文件重复包含:即头文件A包含了B,头文件B又包含了A,导致编译器在加载头文件时陷入死循环。 解决办法…...
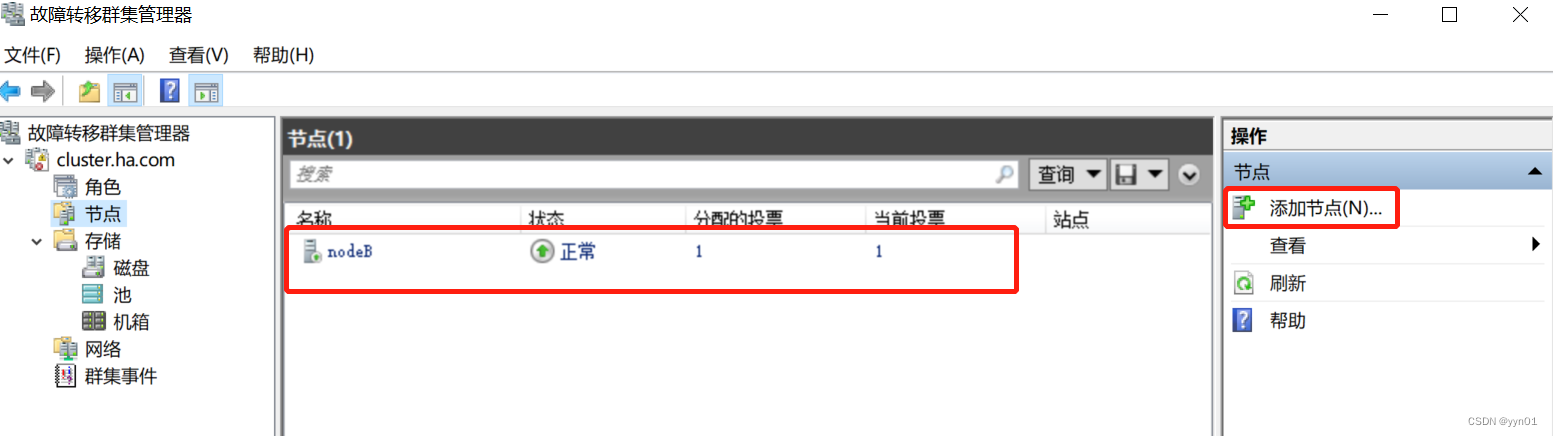
五、Microsoft群集服务(MSCS)环境的搭建
一、【目的】 学会利用Windows Server布置群集环境。 二、【设备】 FreeNAS11.2,Windows Server 2019 三、【要求】 学会利用Windows Server布置群集环境,掌握处理问题的能力。 配置表: 节点公网IP(public)内网IP(private)群集IP(clust…...
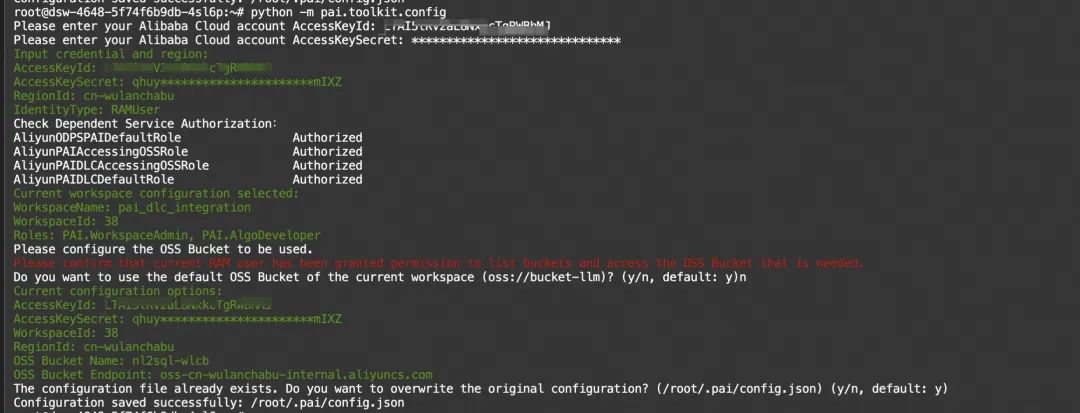
通义千问 Qwen-72B-Chat在PAI-DSW的微调推理实践
01 引言 通义千问-72B(Qwen-72B)是阿里云研发的通义千问大模型系列的720亿参数规模模型。Qwen-72B的预训练数据类型多样、覆盖广泛,包括大量网络文本、专业书籍、代码等。Qwen-72B-Chat是在Qwen-72B的基础上,使用对齐机制打造的…...
web应用体系以及windows网络常见操作应用
本课程目标 1.Dos命令(必须掌握) 2.网络体系(笔试选择填空题) 3.搭建windows测试环境 一、Dos命令 1.DOS窗口启动 启动方式1.进入DOS页面:win+R,键入cmd 启动方式2.开始-运行--输入cmd-回车,此时将出现一个显示命令提示符的窗口,如下图 2、常见的Dos命令: 1、cd…...

FFmpeg 安装配置
FFmpeg 安装配置 依赖包 sudo apt-get install -y autoconf automake bzip2 cmake freetype-devel gcc gcc-c git libtool make mercurial pkgconfig zlib-devel x264-develsudo apt-get install yasm -y安装 wget https://ffmpeg.org/releases/ffmpeg-4.2.3.tar.bz2tar -…...
14:00面试,14:08就出来了,问的问题有点变态。。。。。。
从小厂出来,没想到在另一家公司又寄了。 到这家公司开始上班,加班是每天必不可少的,看在钱给的比较多的份上,就不太计较了。没想到5月一纸通知,所有人不准加班,加班费不仅没有了,薪资还要降40%…...
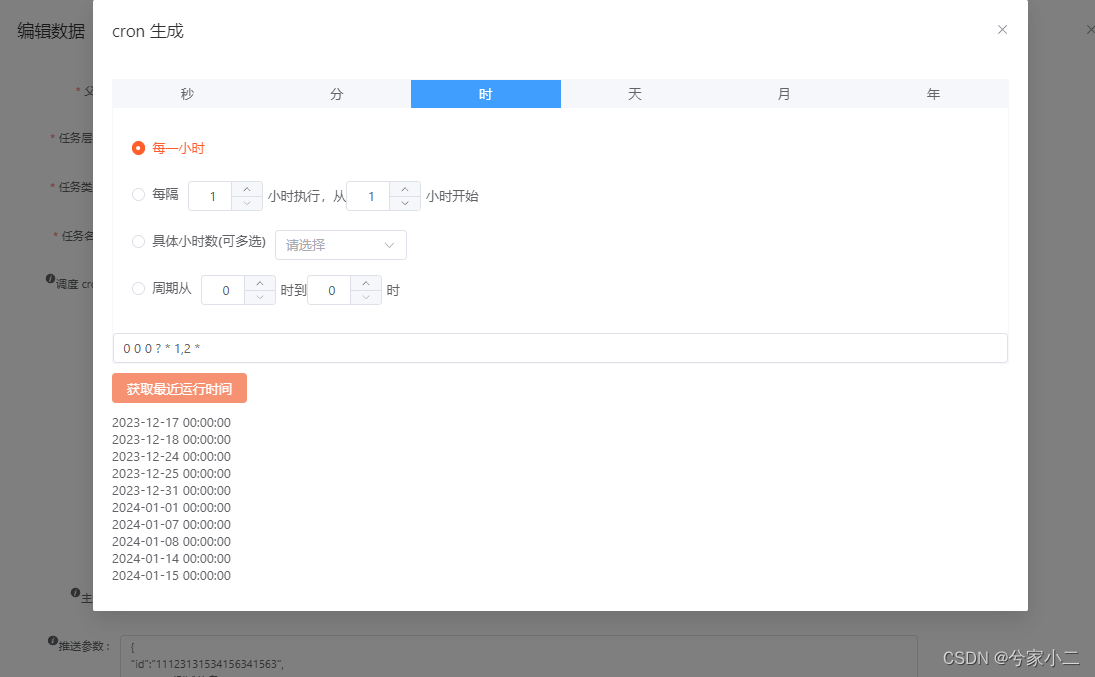
vue3 添加编辑页使用 cron 表达式生成
示例效果图 1、添加组件 <template><div class"v3c"><ul class"v3c-tab"><li class"v3c-tab-item" :class"{ v3c-active: tabActive 1 }" click"onHandleTab(1)">秒</li><li class&qu…...
洛谷P1722 矩阵Ⅱ——卡特兰数
传送门: P1722 矩阵 II - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1722 用不需要除任何数的公式来求。 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #includ…...
Unity | Shader基础知识(第六集:语法<如何加入外部颜色资源>)
目录 一、本节介绍 1 上集回顾 2 本节介绍 二、语法结构 1 复习 2 理论知识 3 Shader里声明的写法 4 Properties和SubShader毕竟不是一家人 三、 片元着色器中使用资源 四、代码实现 五、全部代码 六、下集介绍 相关阅读 Unity - Manual: Writing Surface Shaders…...
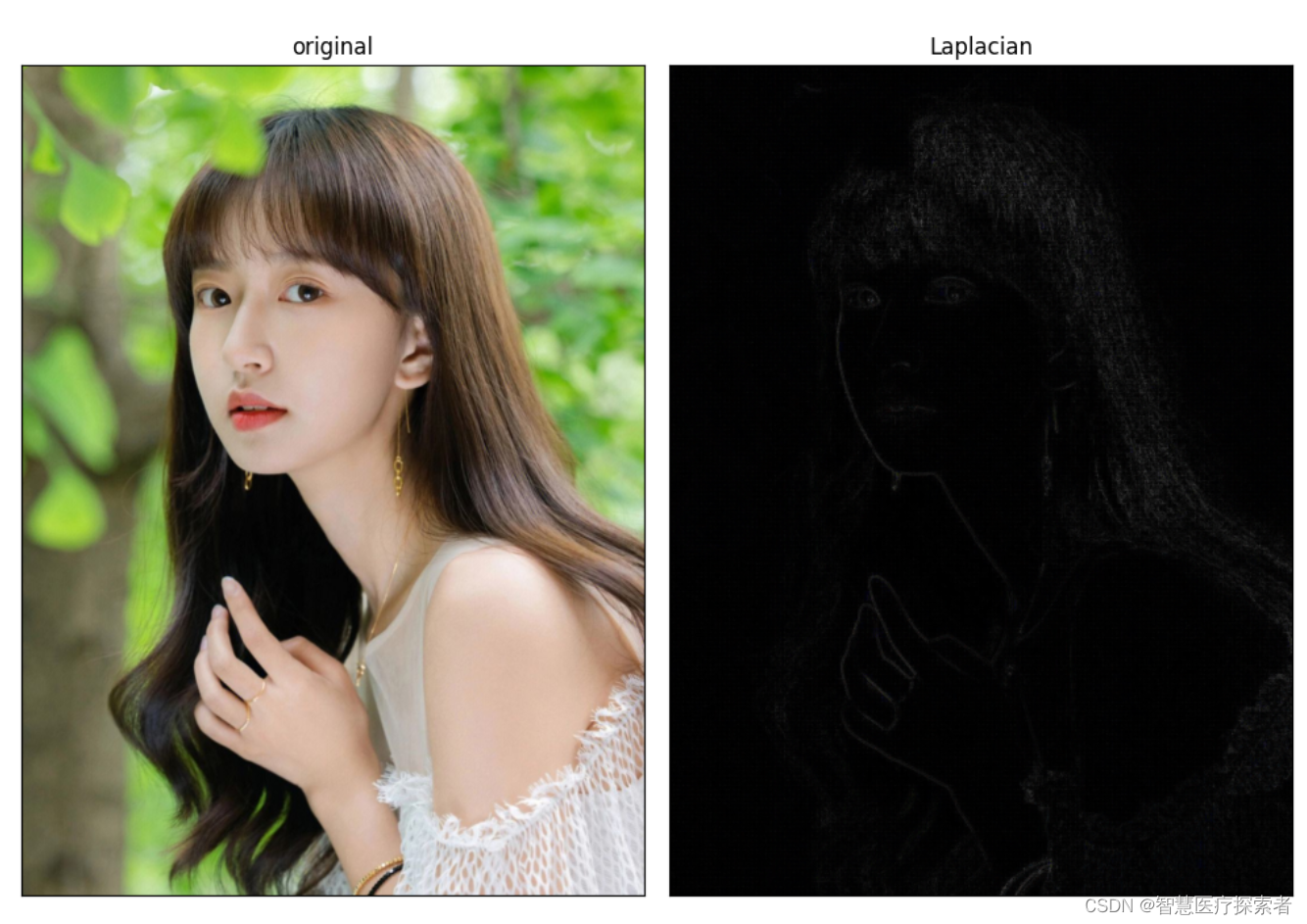

使用opencv的Laplacian算子实现图像边缘检测
1 边缘检测介绍 图像边缘检测技术是图像处理和计算机视觉等领域最基本的问题,也是经典的技术难题之一。如何快速、精确地提取图像边缘信息,一直是国内外的研究热点,同时边缘的检测也是图像处理中的一个难题。早期的经典算法包括边缘算子方法…...

5. PyTorch——数据处理模块
1.数据加载 在PyTorch中,数据加载可通过自定义的数据集对象。数据集对象被抽象为Dataset类,实现自定义的数据集需要继承Dataset,并实现两个Python魔法方法: __getitem__:返回一条数据,或一个样本。obj[in…...
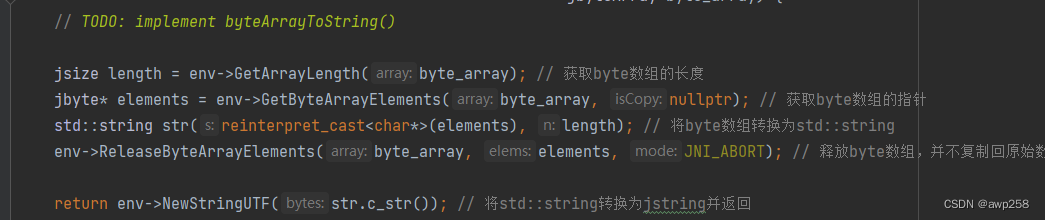
Android 移动端编译 cityhash动态库
最近做项目, 硬件端 需要 用 cityhash 编译一个 动态库 提供给移动端使用,l 记录一下 编译过程 city .cpp // // Created by Administrator on 2023/12/12. // // Copyright (c) 2011 Google, Inc. // // Permission is hereby granted, free of charg…...
IO流学习
IO流:存储和读取数据的解决方案 import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建对象//写出 输入流 OutputStream//本地文件fileFileOutputStream fos new FileOutputS…...

新手HTML和CSS的常见知识点
目录 1.HTML标题标签(到)用于定义网页中的标题,并按照重要性递减排列。例如: 2.HTML段落标签()用于定义网页中的段落。例如: 3.HTML链接标签()用于创建链接…...
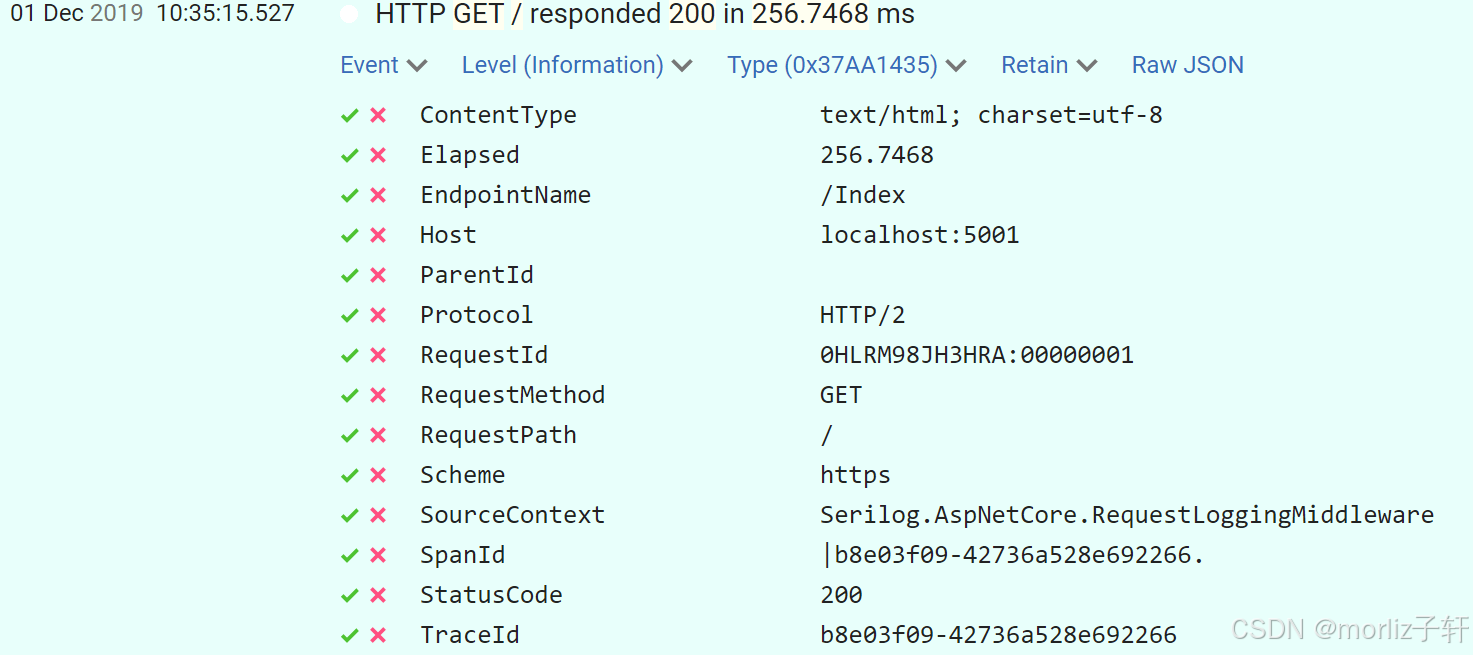
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...

设计模式和设计原则回顾
设计模式和设计原则回顾 23种设计模式是设计原则的完美体现,设计原则设计原则是设计模式的理论基石, 设计模式 在经典的设计模式分类中(如《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》一书中),总共有23种设计模式,分为三大类: 一、创建型模式(5种) 1. 单例模式(Sing…...
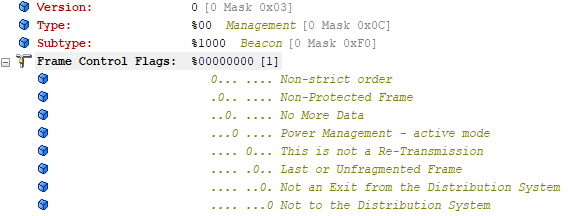
【WiFi帧结构】
文章目录 帧结构MAC头部管理帧 帧结构 Wi-Fi的帧分为三部分组成:MAC头部frame bodyFCS,其中MAC是固定格式的,frame body是可变长度。 MAC头部有frame control,duration,address1,address2,addre…...

PHP和Node.js哪个更爽?
先说结论,rust完胜。 php:laravel,swoole,webman,最开始在苏宁的时候写了几年php,当时觉得php真的是世界上最好的语言,因为当初活在舒适圈里,不愿意跳出来,就好比当初活在…...

Admin.Net中的消息通信SignalR解释
定义集线器接口 IOnlineUserHub public interface IOnlineUserHub {/// 在线用户列表Task OnlineUserList(OnlineUserList context);/// 强制下线Task ForceOffline(object context);/// 发布站内消息Task PublicNotice(SysNotice context);/// 接收消息Task ReceiveMessage(…...
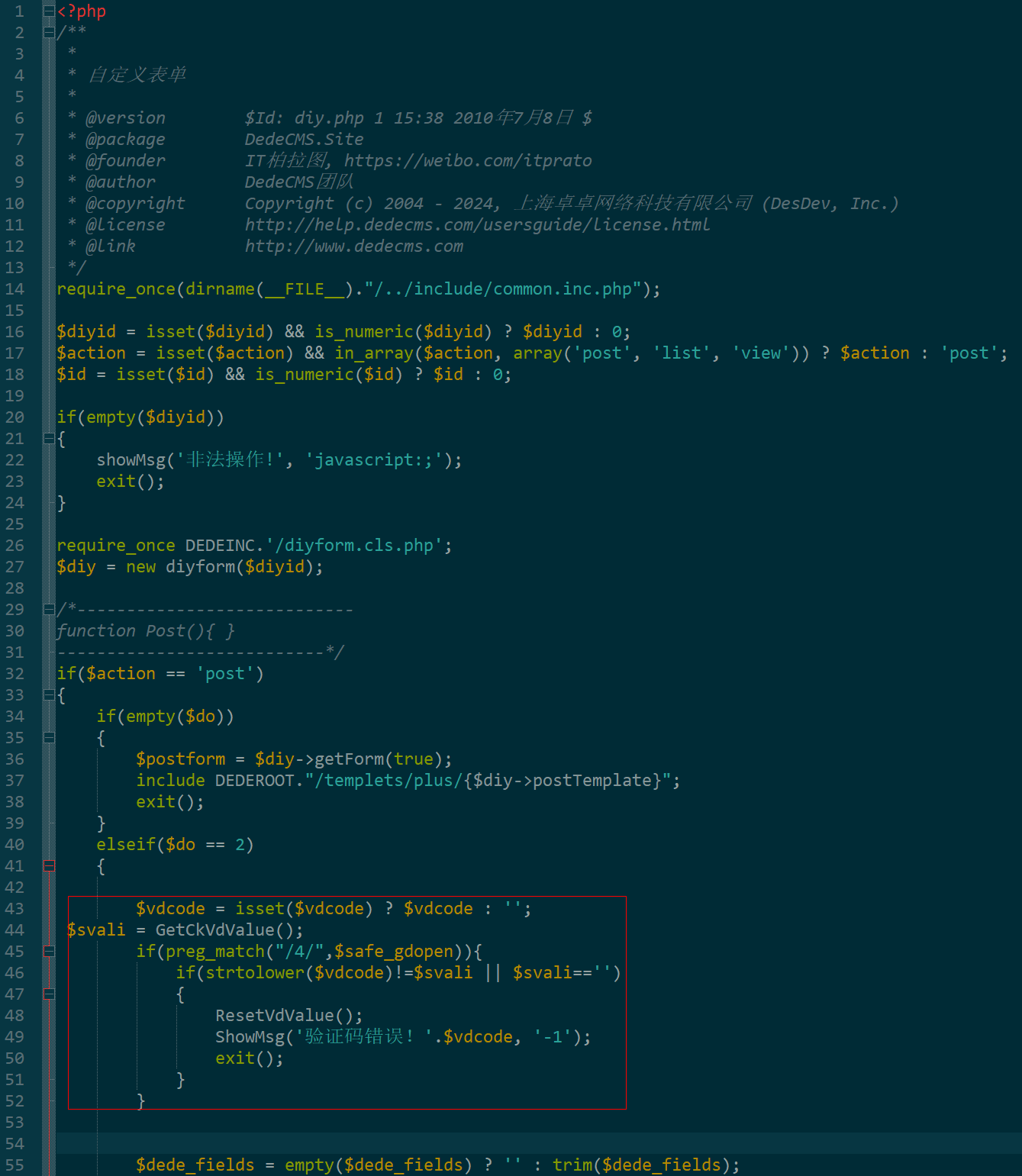
dedecms 织梦自定义表单留言增加ajax验证码功能
增加ajax功能模块,用户不点击提交按钮,只要输入框失去焦点,就会提前提示验证码是否正确。 一,模板上增加验证码 <input name"vdcode"id"vdcode" placeholder"请输入验证码" type"text&quo…...
2025 后端自学UNIAPP【项目实战:旅游项目】6、我的收藏页面
代码框架视图 1、先添加一个获取收藏景点的列表请求 【在文件my_api.js文件中添加】 // 引入公共的请求封装 import http from ./my_http.js// 登录接口(适配服务端返回 Token) export const login async (code, avatar) > {const res await http…...
)
Java入门学习详细版(一)
大家好,Java 学习是一个系统学习的过程,核心原则就是“理论 实践 坚持”,并且需循序渐进,不可过于着急,本篇文章推出的这份详细入门学习资料将带大家从零基础开始,逐步掌握 Java 的核心概念和编程技能。 …...
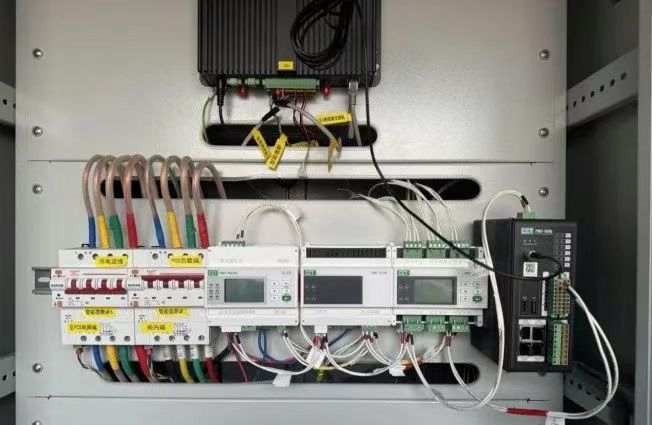
IT供电系统绝缘监测及故障定位解决方案
随着新能源的快速发展,光伏电站、储能系统及充电设备已广泛应用于现代能源网络。在光伏领域,IT供电系统凭借其持续供电性好、安全性高等优势成为光伏首选,但在长期运行中,例如老化、潮湿、隐裂、机械损伤等问题会影响光伏板绝缘层…...

CMake控制VS2022项目文件分组
我们可以通过 CMake 控制源文件的组织结构,使它们在 VS 解决方案资源管理器中以“组”(Filter)的形式进行分类展示。 🎯 目标 通过 CMake 脚本将 .cpp、.h 等源文件分组显示在 Visual Studio 2022 的解决方案资源管理器中。 ✅ 支持的方法汇总(共4种) 方法描述是否推荐…...
