Habitat环境学习四:Habitat-sim基础用于导航——使用导航网格NavMesh
如何使用导航网格NavMesh
- 官方教程
- 1、NavMesh基础定义
- 1.1 使用NavMesh的原因
- 1.2 什么是NavMesh
- 2、NavMesh的使用方法
- 2.1 获取自上而下Top down view视角地图
- 2.2 在NavMesh中进行查询以及随机产生可导航点
- 2.3 查找最短路径
- 2.4 场景加载NavMesh
- 2.5 重新计算并生成NavMesh
- 2.6 什么是Sliding
官方教程
Habitat是一个高效的真实的3D模拟器,旨在促进具身智能的研究。它相较于其他的仿真环境的优势在于速度非常快,采用单个线程可以达到每秒几千帧。
官方视频教程链接
官方jupyter文件链接
1、NavMesh基础定义
1.1 使用NavMesh的原因
我们默认认为导航约束和碰撞响应是存在的。在我们演示的离散的Habitat-sim行动空间中,默认情况下启用了这些功能。然而,当直接修改代理状态时,代理在执行动作时既不能感知障碍物,也不能感知场景的边界。我们需要引入一种机制,轻便而快速,来强制执行这些约束。本节将详细介绍这种方法。
本教程部分演示了如何加载、重新计算和保存静态场景的导航网格,并明确在离散和连续导航任务中如何使用它。
1.2 什么是NavMesh
导航网格(NavMesh)是由二维凸多边形(即,一个多边形网格)组成的集合,用于定义环境中哪些区域可供具有特定实体的代理自由穿越。换句话说,代理可以在这些区域内自由导航,不受环境中的物体、墙壁、缝隙、悬崖或其他障碍物的阻碍。相邻的多边形在图中彼此连接,从而使得能够使用高效的路径规划算法在导航网格上绘制两点之间的路径。
通过使用导航性的NavMesh近似,代理被具象化为与重力方向对齐的刚性圆柱体。然后,通过对静态场景进行体素化,将在实心体素的顶表面生成多边形,而代理的刚性圆柱体将在这些表面上无交叉或悬垂地放置,并且会遵循配置的约束,如最大可攀爬坡度和步高。
近似将agent视为圆柱体,将agent在场景中可能的位置。这是通过对场景进行体素化,然后在重力方向上重构高度图,然后重构其他的细节,使路径查找变得非常快速和高效。
2、NavMesh的使用方法
可视化导航网格:顶视图地图
PathFinder API使得在场景中生成可行走性的顶视图地图变得简便。由于导航网格是一个3D网格,而场景可以在垂直方向上拥有多个楼层或层次,我们需要在特定的世界高度(y坐标)上切割导航网格。然后,通过以可配置的分辨率(meters_per_pixel)对导航网格进行采样,垂直余量为0.5米,生成地图。
以下示例单元定义了一个matplotlib函数,用于显示带有可选关键点叠加的顶视图地图。然后,使用场景边界框的最小y坐标作为高度,或者选择使用可选配置的自定义高度生成当前场景的顶视图地图。请注意,此高度以场景全局坐标为准,因此我们不能假设0是底层。
2.1 获取自上而下Top down view视角地图
直接调用Habitat Sim中调用api中的PathFinder模块,或者可以从Habitat Labs中的Maps模块执行此操作。
在执行此操作前,稍微区分一下这两个模块,该导航网格实际上是嵌入在3D中的。因此为了获得自上而下的地图,将拥有一个特定的水平切片(Horizontal Slice),并在其中进行可视化,需要设定高度参数。将可视化半米内地导航网络。
有一个单元格,将定义几个将地图上的3D点转为2D点的函数,并使用Matplotlib显示地图。
# convert 3d points to 2d topdown coordinates
# 将定义几个将地图上的3D点转为2D点的函数
def convert_points_to_topdown(pathfinder, points, meters_per_pixel):points_topdown = []bounds = pathfinder.get_bounds()for point in points:# convert 3D x,z to topdown x,ypx = (point[0] - bounds[0][0]) / meters_per_pixelpy = (point[2] - bounds[0][2]) / meters_per_pixelpoints_topdown.append(np.array([px, py]))return points_topdown# 使用Matplotlib显示地图
# display a topdown map with matplotlib
def display_map(topdown_map, key_points=None):plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))ax = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)ax.axis("off")plt.imshow(topdown_map)# plot points on mapif key_points is not None:for point in key_points:plt.plot(point[0], point[1], marker="o", markersize=10, alpha=0.8)plt.show(block=False)# @markdown ###Configure Example Parameters:
# @markdown Configure the map resolution:
# 定义地图的分辨率
meters_per_pixel = 0.1 # @param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:1.0, step:0.01}
# @markdown ---
# @markdown Customize the map slice height (global y coordinate):
custom_height = False # @param {type:"boolean"}
# 定义地图的高度,如果取消设置将设为地图的最低点
height = 1 # @param {type:"slider", min:-10, max:10, step:0.1}
# @markdown If not using custom height, default to scene lower limit.
# @markdown (Cell output provides scene height range from bounding box for reference.)# 从sim.pathfinder.get_bounds()[0][1]获取地图的最低点
print("The NavMesh bounds are: " + str(sim.pathfinder.get_bounds()))
if not custom_height:# get bounding box minumum elevation for automatic heightheight = sim.pathfinder.get_bounds()[0][1]# 如果pathfinder已经加载
if not sim.pathfinder.is_loaded:print("Pathfinder not initialized, aborting.")
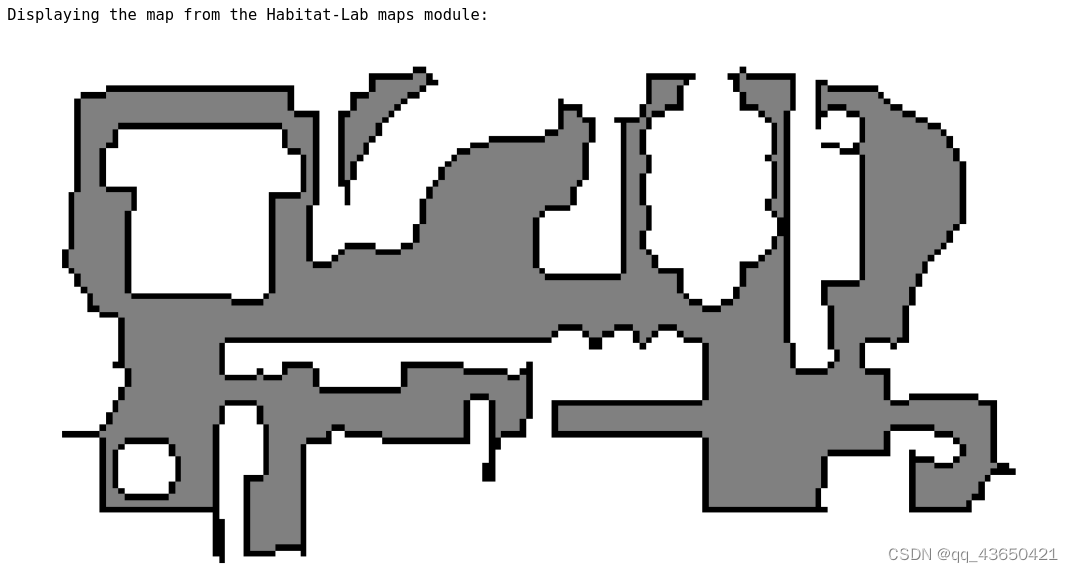
else:# @markdown You can get the topdown map directly from the Habitat-sim API with *PathFinder.get_topdown_view*.# This map is a 2D boolean array# 直接调用sim.pathfinder.get_topdown_view获取自顶向下视图# get_topdown_view的api接受两个参数,分别是分辨率meters_per_pixel和水平切片高度height;sim_topdown_map = sim.pathfinder.get_topdown_view(meters_per_pixel, height)if display:# @markdown Alternatively, you can process the map using the Habitat-Lab [maps module](https://github.com/facebookresearch/habitat-api/blob/master/habitat/utils/visualizations/maps.py)# 同样地可以调用habitat_lab中的maps模块中的get_topdown_map函数hablab_topdown_map = maps.get_topdown_map(sim.pathfinder, height, meters_per_pixel=meters_per_pixel)recolor_map = np.array([[255, 255, 255], [128, 128, 128], [0, 0, 0]], dtype=np.uint8)hablab_topdown_map = recolor_map[hablab_topdown_map]print("Displaying the raw map from get_topdown_view:")display_map(sim_topdown_map)print("Displaying the map from the Habitat-Lab maps module:")display_map(hablab_topdown_map)# easily save a map to file:map_filename = os.path.join(output_path, "top_down_map.png")imageio.imsave(map_filename, hablab_topdown_map)
可以获得如下的输出:
首先打印NavMesh的bounds,可以看到NavMesh的BoundingBox;
因为custom_height为false,直接在最小高度处显示地图;
图一是通过sim.pathfinder.get_topdown_view模块打印的,
图二是通过maps.get_topdown_map模块打印的;
二者的结果非常类似。

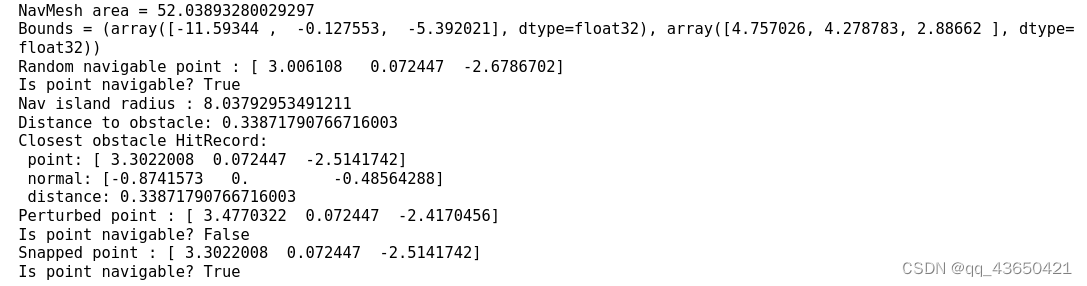
2.2 在NavMesh中进行查询以及随机产生可导航点
# @markdown ## Querying the NavMeshif not sim.pathfinder.is_loaded:print("Pathfinder not initialized, aborting.")
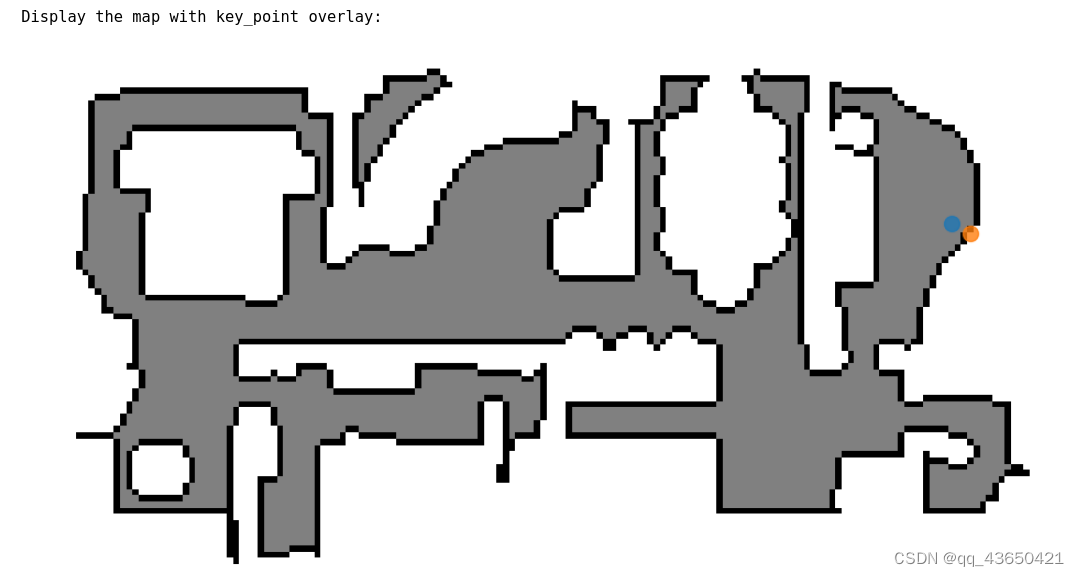
else:# @markdown NavMesh area and bounding box can be queried via *3navigable_area* and *get_bounds* respectively.print("NavMesh area = " + str(sim.pathfinder.navigable_area)) # 打印所有的可导航区域print("Bounds = " + str(sim.pathfinder.get_bounds())) # 可以查询边界# @markdown A random point on the NavMesh can be queried with *get_random_navigable_point*.pathfinder_seed = 1 # @param {type:"integer"}sim.pathfinder.seed(pathfinder_seed) nav_point = sim.pathfinder.get_random_navigable_point() # 可以获取一个随机点,即蓝色点print("Random navigable point : " + str(nav_point))print("Is point navigable? " + str(sim.pathfinder.is_navigable(nav_point)))# @markdown The radius of the minimum containing circle (with vertex centroid origin) for the isolated navigable island of a point can be queried with *island_radius*.# @markdown This is analogous to the size of the point's connected component and can be used to check that a queried navigable point is on an interesting surface (e.g. the floor), rather than a small surface (e.g. a table-top).# 这段代码的目的是帮助用户理解如何使用 island_radius 查询导航点的孤立可行走区域的最小包围圆的半径print("Nav island radius : " + str(sim.pathfinder.island_radius(nav_point)))# @markdown The closest boundary point can also be queried (within some radius).# 在max_search_radius的搜索半径内查找距离nav_point最近的点max_search_radius = 2.0 # @param {type:"number"}print("Distance to obstacle: "+ str(sim.pathfinder.distance_to_closest_obstacle(nav_point, max_search_radius)))hit_record = sim.pathfinder.closest_obstacle_surface_point( # 查找最近的障碍物点nav_point, max_search_radius)print("Closest obstacle HitRecord:")print(" point: " + str(hit_record.hit_pos))print(" normal: " + str(hit_record.hit_normal))print(" distance: " + str(hit_record.hit_dist))vis_points = [nav_point]# HitRecord will have infinite distance if no valid point was found:if math.isinf(hit_record.hit_dist):print("No obstacle found within search radius.")else:# @markdown Points near the boundary or above the NavMesh can be snapped onto it.# 扰动该点,将其延长至边界外perturbed_point = hit_record.hit_pos - hit_record.hit_normal * 0.2print("Perturbed point : " + str(perturbed_point))print("Is point navigable? " + str(sim.pathfinder.is_navigable(perturbed_point)))# 计算边界内距离该扰动后点最近的点,这是采用snap_point方法snapped_point = sim.pathfinder.snap_point(perturbed_point)print("Snapped point : " + str(snapped_point))print("Is point navigable? " + str(sim.pathfinder.is_navigable(snapped_point)))vis_points.append(snapped_point)# @markdown ---# @markdown ### Visualization# @markdown Running this cell generates a topdown visualization of the NavMesh with sampled points overlayed.meters_per_pixel = 0.1 # @param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:1.0, step:0.01}if display:xy_vis_points = convert_points_to_topdown(sim.pathfinder, vis_points, meters_per_pixel)# use the y coordinate of the sampled nav_point for the map height slicetop_down_map = maps.get_topdown_map(sim.pathfinder, height=nav_point[1], meters_per_pixel=meters_per_pixel)recolor_map = np.array([[255, 255, 255], [128, 128, 128], [0, 0, 0]], dtype=np.uint8)top_down_map = recolor_map[top_down_map]print("\nDisplay the map with key_point overlay:")display_map(top_down_map, key_points=xy_vis_points)
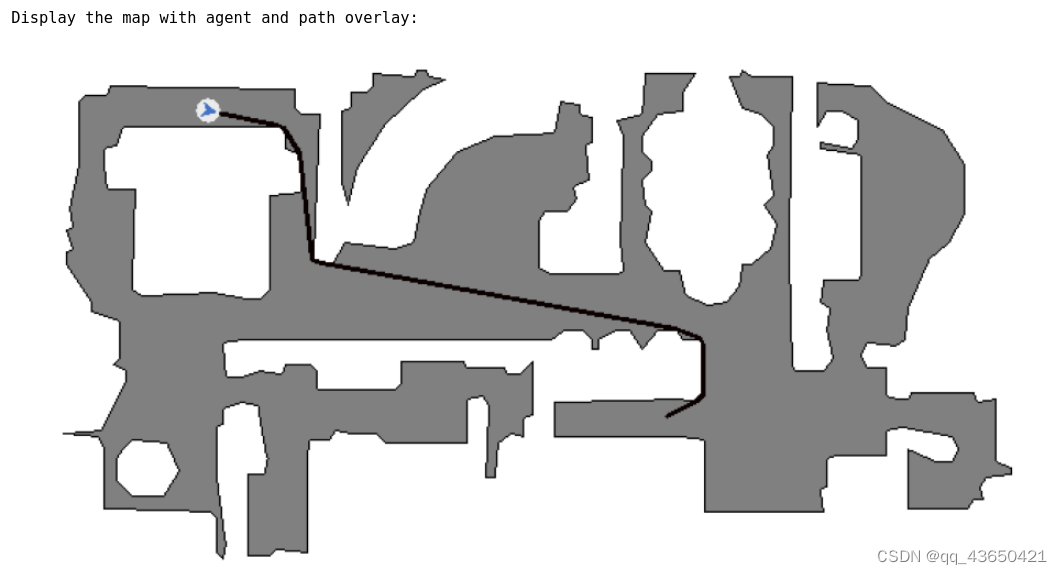
蓝色点是产生的随机点,
2.3 查找最短路径
查收随机点并采用Habitat_sim中的api查找最短路径。
# @markdown ## Pathfinding Queries on NavMesh# @markdown The shortest path between valid points on the NavMesh can be queried as shown in this example.# @markdown With a valid PathFinder instance:
if not sim.pathfinder.is_loaded:print("Pathfinder not initialized, aborting.")
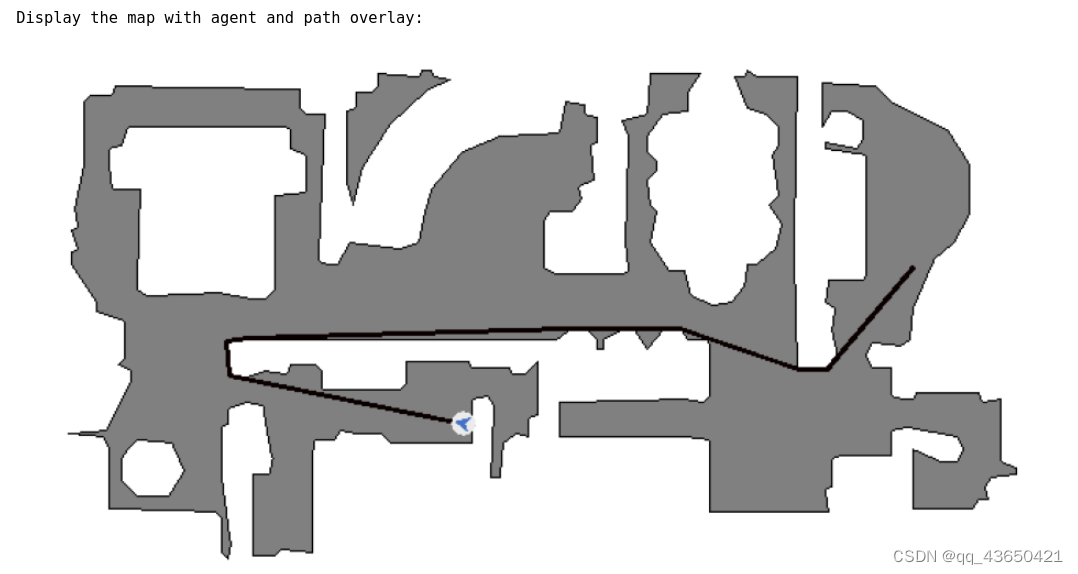
else:seed = 4 # @param {type:"integer"}sim.pathfinder.seed(seed)# fmt off# @markdown 1. Sample valid points on the NavMesh for agent spawn location and pathfinding goal.# fmt on# 获得两个随机点sample1 = sim.pathfinder.get_random_navigable_point()sample2 = sim.pathfinder.get_random_navigable_point()# @markdown 2. Use ShortestPath module to compute path between samples.# 初始化habitat_sim.ShortestPath()的实例path = habitat_sim.ShortestPath()# 将起始点设置为产生的随机点path.requested_start = sample1path.requested_end = sample2# 通过sim.pathfinder.find_path查找最短路径,found_path是一个布尔值found_path = sim.pathfinder.find_path(path)# 返回该路径的距离geodesic_distance = path.geodesic_distancepath_points = path.points# @markdown - Success, geodesic path length, and 3D points can be queried.print("found_path : " + str(found_path))print("geodesic_distance : " + str(geodesic_distance))print("path_points : " + str(path_points))# @markdown 3. Display trajectory (if found) on a topdown map of ground floorif found_path:meters_per_pixel = 0.025# 获取场景的bounding boxscene_bb = sim.get_active_scene_graph().get_root_node().cumulative_bb# 获得最小高度height = scene_bb.y().minif display:# 获取自上而下地图top_down_map = maps.get_topdown_map(sim.pathfinder, height, meters_per_pixel=meters_per_pixel)# 地图重新着色recolor_map = np.array([[255, 255, 255], [128, 128, 128], [0, 0, 0]], dtype=np.uint8)top_down_map = recolor_map[top_down_map]# 获取网格尺寸grid_dimensions = (top_down_map.shape[0], top_down_map.shape[1])# convert world trajectory points to maps module grid points# 对于场景上的轨迹,将3D点转为地图上的2D点trajectory = [maps.to_grid(path_point[2],path_point[0],grid_dimensions,pathfinder=sim.pathfinder,)for path_point in path_points]# 计算初始的切线来设置agentgrid_tangent = mn.Vector2(trajectory[1][1] - trajectory[0][1], trajectory[1][0] - trajectory[0][0])# 获取初始的朝向path_initial_tangent = grid_tangent / grid_tangent.length()initial_angle = math.atan2(path_initial_tangent[0], path_initial_tangent[1])# draw the agent and trajectory on the map# 使用draw_agent在自上而下地图上绘制轨迹maps.draw_path(top_down_map, trajectory)# 使用draw_agent函数绘制agentmaps.draw_agent(top_down_map, trajectory[0], initial_angle, agent_radius_px=8)print("\nDisplay the map with agent and path overlay:")display_map(top_down_map)# @markdown 4. (optional) Place agent and render images at trajectory points (if found).display_path_agent_renders = True # @param{type:"boolean"}if display_path_agent_renders:print("Rendering observations at path points:")tangent = path_points[1] - path_points[0]agent_state = habitat_sim.AgentState()# 遍历每个轨迹点,计算切线并设置agent以及渲染for ix, point in enumerate(path_points):if ix < len(path_points) - 1:tangent = path_points[ix + 1] - point# 设置agent当前的位置agent_state.position = point# 这段代码使用Magnum库来计算代理在路径上某个点的观察矩阵,从而确定代理的旋转状态,并将该旋转状态应用到代理的状态中,以便在仿真环境中正确地朝向路径上的下一个点tangent_orientation_matrix = mn.Matrix4.look_at(point, point + tangent, np.array([0, 1.0, 0]))tangent_orientation_q = mn.Quaternion.from_matrix(tangent_orientation_matrix.rotation())agent_state.rotation = utils.quat_from_magnum(tangent_orientation_q)agent.set_state(agent_state)# 获取agent在此刻的观测observations = sim.get_sensor_observations()rgb = observations["color_sensor"]semantic = observations["semantic_sensor"]depth = observations["depth_sensor"]if display:display_sample(rgb, semantic, depth)
首先打印是否找到路径;
路径的测地距离;
路径上的点;
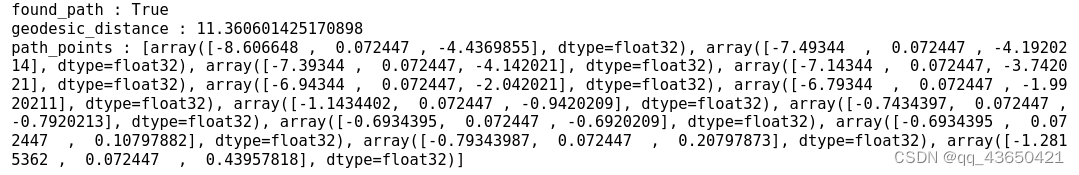
在地图中agent的行驶路线:
打印agent的观测,

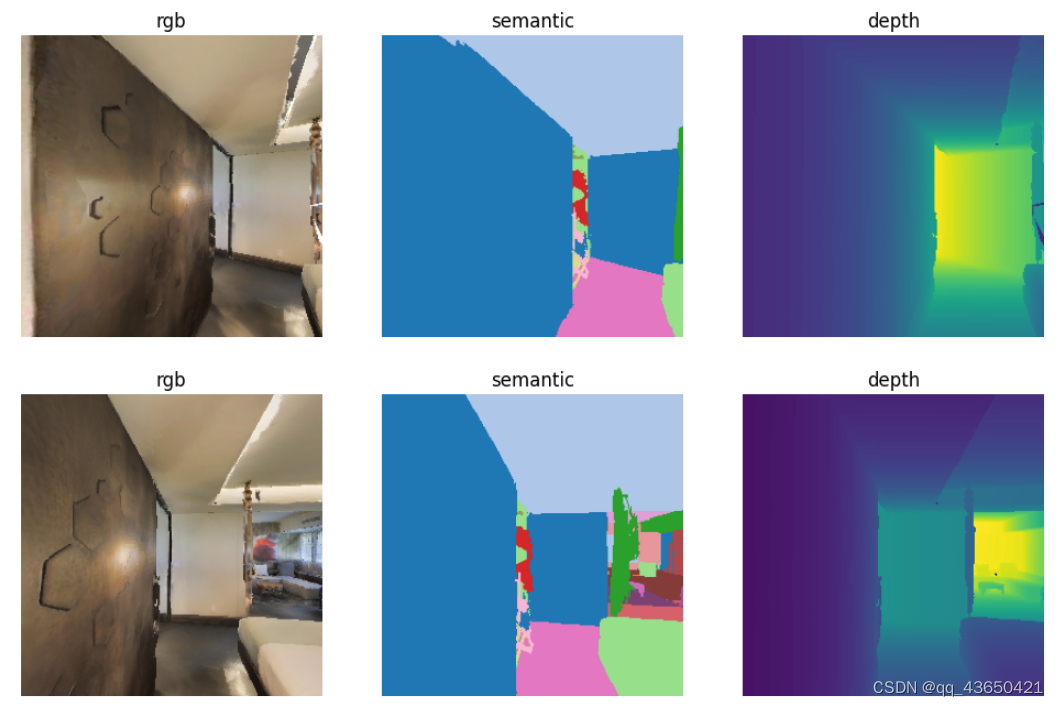
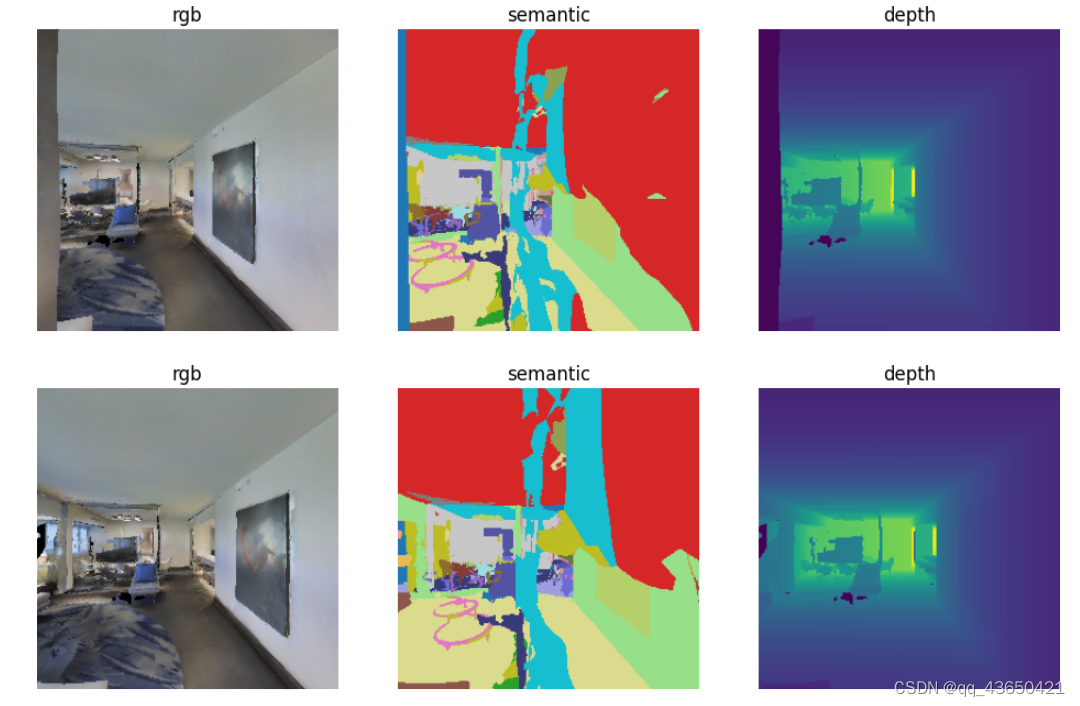
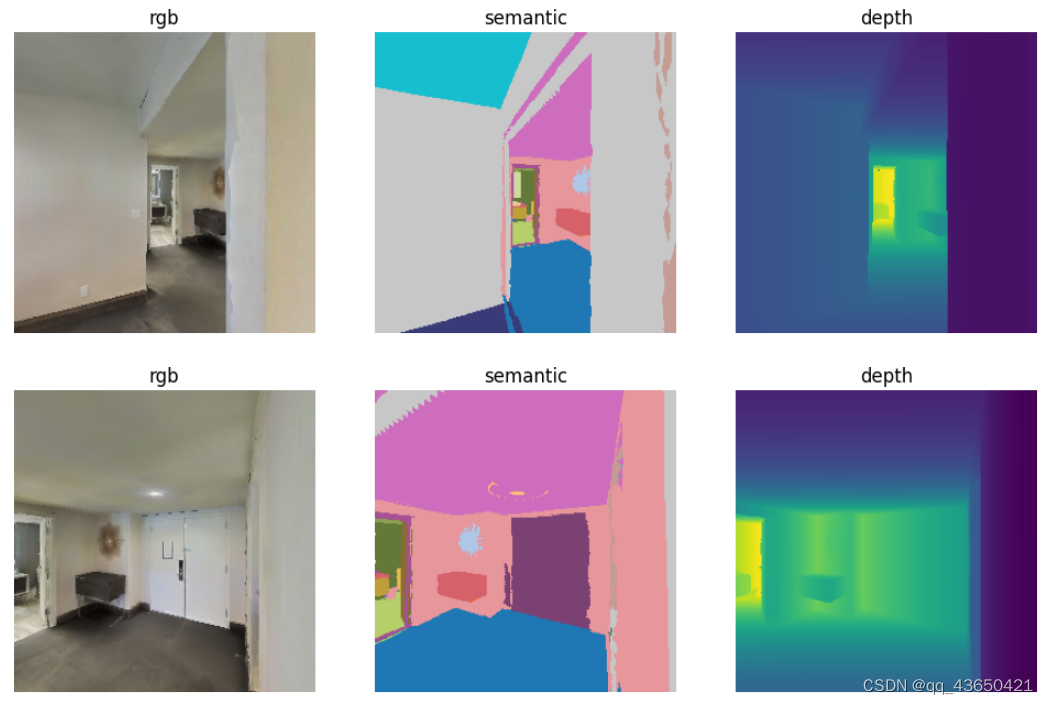
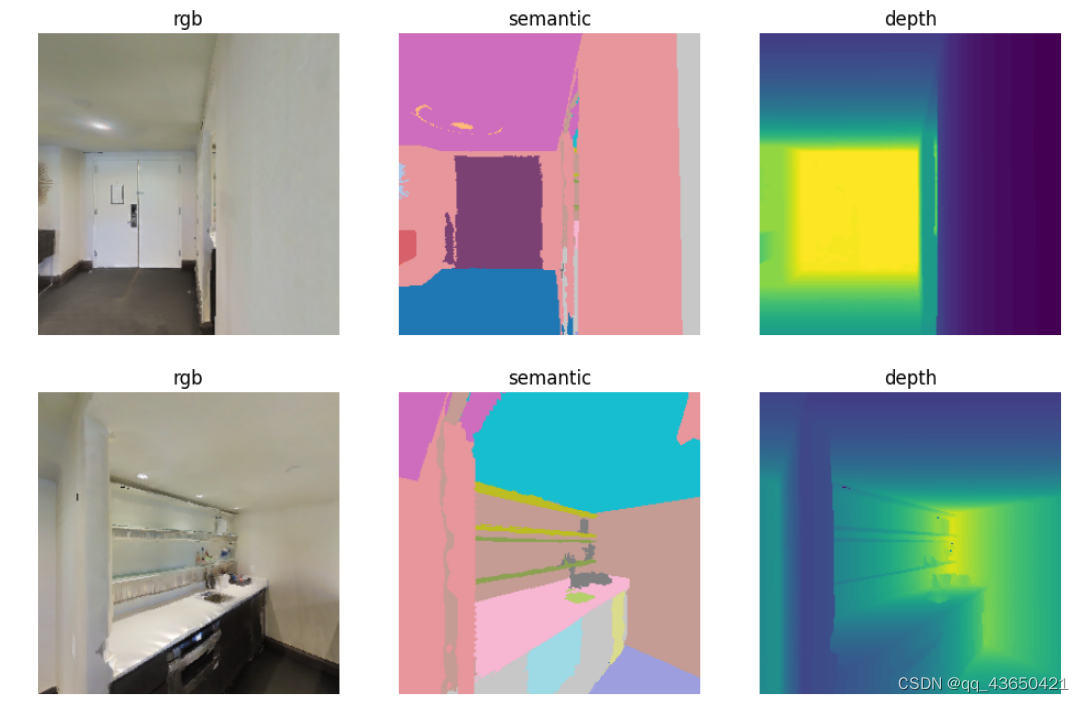

改变seed=5可以获得截然不同的轨迹。
2.4 场景加载NavMesh
加载一个预先计算好的场景导航网格,只需将其与正在加载的场景资产一起包含,使用.navmesh文件扩展名。
如果在.glb文件中存在.navmesh文件,则会自动进行加载。
否则可以用load_nav_mesh指定路径手动进行加载。
# initialize a new simulator with the apartment_1 scene
# this will automatically load the accompanying .navmesh file
sim_settings["scene"] = "/home/lu/Desktop/embodied_ai/habitat-sim-0.2.1/data/scene_datasets/mp3d_example/17DRP5sb8fy/17DRP5sb8fy.glb"
cfg = make_cfg(sim_settings)
try: # Got to make initialization idiot proofsim.close()
except NameError:pass
sim = habitat_sim.Simulator(cfg)# the navmesh can also be explicitly loaded
sim.pathfinder.load_nav_mesh("/home/lu/Desktop/embodied_ai/habitat-sim-0.2.1/data/scene_datasets/mp3d_example/17DRP5sb8fy/17DRP5sb8fy.navmesh"
)
2.5 重新计算并生成NavMesh
- Voxelization parameters:
Decrease these for better accuracy at the cost of higher compute cost.
用于控制初始网格到体素网格的转换;
Note: most continuous parameters are converted to multiples of cell dimensions, so these should be compatible values for best accuracy.
cell_size - xz-plane voxel dimensions. [Limit: >= 0]
cell_height - y-axis voxel dimension. [Limit: >= 0]
可以根据Agent实例参数化导航网格本身,根据agent的上坡能力将有坡度的区域也可视为可通行区域 。
- Agent parameters:
agent_height - Height of the agent. Used to cull navigable cells with obstructions.
agent_radius - Radius of the agent. Used as distance to erode/shrink the computed heightfield. [Limit: >=0]
agent_max_climb - Maximum ledge height that is considered to still be traversable. [Limit: >=0]
agent_max_slope - The maximum slope that is considered navigable. [Limits: 0 <= value < 85] [Units: Degrees] - Navigable area filtering options (default active):
filter_low_hanging_obstacles - Marks navigable spans as non-navigable if the clearence above the span is less than the specified height.
filter_ledge_spans - Marks spans that are ledges as non-navigable. This filter reduces the impact of the overestimation of conservative voxelization so the resulting mesh will not have regions hanging in the air over ledges.
filter_walkable_low_height_spans - Marks navigable spans as non-navigable if the clearence above the span is less than the specified height. Allows the formation of navigable regions that will flow over low lying objects such as curbs, and up structures such as stairways. - Detail mesh generation parameters:
region_min_size - Minimum number of cells allowed to form isolated island areas.
region_merge_size - Any 2-D regions with a smaller span (cell count) will, if possible, be merged with larger regions. [Limit: >=0]
edge_max_len - The maximum allowed length for contour edges along the border of the mesh. Extra vertices will be inserted as needed to keep contour edges below this length. A value of zero effectively disables this feature. [Limit: >=0] [ / cell_size]
edge_max_error - The maximum distance a simplfied contour’s border edges should deviate the original raw contour. [Limit: >=0]
verts_per_poly - The maximum number of vertices allowed for polygons generated during the contour to polygon conversion process.[Limit: >= 3]
detail_sample_dist - Sets the sampling distance to use when generating the detail mesh. (For height detail only.) [Limits: 0 or >= 0.9] [x cell_size]
detail_sample_max_error - The maximum distance the detail mesh surface should deviate from heightfield data. (For height detail only.) [Limit: >=0] [x cell_height]
在这个单元格中,实际上能够包含配置整个导航网格的所有设置。重建它并可视化它。
# @markdown ## Recompute NavMesh:# @markdown Take a moment to edit some parameters and visualize the resulting NavMesh. Consider agent_radius and agent_height as the most impactful starting point. Note that large variations from the defaults for these parameters (e.g. in the case of very small agents) may be better supported by additional changes to cell_size and cell_height.
navmesh_settings = habitat_sim.NavMeshSettings()# @markdown Choose Habitat-sim defaults (e.g. for point-nav tasks), or custom settings.
use_custom_settings = False # @param {type:"boolean"}
sim.navmesh_visualization = True # @param {type:"boolean"}
navmesh_settings.set_defaults()
if use_custom_settings:# fmt: off#@markdown ---#@markdown ## Configure custom settings (if use_custom_settings):#@markdown Configure the following NavMeshSettings for customized NavMesh recomputation.#@markdown **Voxelization parameters**:navmesh_settings.cell_size = 0.05 #@param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:0.2, step:0.01}#default = 0.05navmesh_settings.cell_height = 0.2 #@param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:0.4, step:0.01}#default = 0.2#@markdown **Agent parameters**:navmesh_settings.agent_height = 1.5 #@param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:3.0, step:0.01}#default = 1.5navmesh_settings.agent_radius = 0.1 #@param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:0.5, step:0.01}#default = 0.1navmesh_settings.agent_max_climb = 0.2 #@param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:0.5, step:0.01}#default = 0.2navmesh_settings.agent_max_slope = 45 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:85, step:1.0}# default = 45.0# fmt: on# @markdown **Navigable area filtering options**:navmesh_settings.filter_low_hanging_obstacles = True # @param {type:"boolean"}# default = Truenavmesh_settings.filter_ledge_spans = True # @param {type:"boolean"}# default = Truenavmesh_settings.filter_walkable_low_height_spans = True # @param {type:"boolean"}# default = True# fmt: off#@markdown **Detail mesh generation parameters**:#@markdown For more details on the effectsnavmesh_settings.region_min_size = 20 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:50, step:1}#default = 20navmesh_settings.region_merge_size = 20 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:50, step:1}#default = 20navmesh_settings.edge_max_len = 12.0 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:50, step:1}#default = 12.0navmesh_settings.edge_max_error = 1.3 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:5, step:0.1}#default = 1.3navmesh_settings.verts_per_poly = 6.0 #@param {type:"slider", min:3, max:6, step:1}#default = 6.0navmesh_settings.detail_sample_dist = 6.0 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:10.0, step:0.1}#default = 6.0navmesh_settings.detail_sample_max_error = 1.0 #@param {type:"slider", min:0, max:10.0, step:0.1}# default = 1.0# fmt: onnavmesh_success = sim.recompute_navmesh(sim.pathfinder, navmesh_settings, include_static_objects=False
)if not navmesh_success:print("Failed to build the navmesh! Try different parameters?")
else:# @markdown ---# @markdown **Agent parameters**:agent_state = sim.agents[0].get_state()set_random_valid_state = False # @param {type:"boolean"}seed = 5 # @param {type:"integer"}sim.seed(seed)orientation = 0if set_random_valid_state:agent_state.position = sim.pathfinder.get_random_navigable_point()orientation = random.random() * math.pi * 2.0# @markdown Optionally configure the agent state (overrides random state):set_agent_state = True # @param {type:"boolean"}try_to_make_valid = True # @param {type:"boolean"}if set_agent_state:pos_x = 0 # @param {type:"number"}pos_y = 0 # @param {type:"number"}pos_z = 0.0 # @param {type:"number"}# @markdown Y axis rotation (radians):orientation = 1.56 # @param {type:"number"}agent_state.position = np.array([pos_x, pos_y, pos_z])if try_to_make_valid:snapped_point = np.array(sim.pathfinder.snap_point(agent_state.position))if not np.isnan(np.sum(snapped_point)):print("Successfully snapped point to: " + str(snapped_point))agent_state.position = snapped_pointif set_agent_state or set_random_valid_state:agent_state.rotation = utils.quat_from_magnum(mn.Quaternion.rotation(-mn.Rad(orientation), mn.Vector3(0, 1.0, 0)))sim.agents[0].set_state(agent_state)agent_state = sim.agents[0].get_state()print("Agent state: " + str(agent_state))print(" position = " + str(agent_state.position))print(" rotation = " + str(agent_state.rotation))print(" orientation (about Y) = " + str(orientation))observations = sim.get_sensor_observations()rgb = observations["color_sensor"]semantic = observations["semantic_sensor"]depth = observations["depth_sensor"]if display:display_sample(rgb, semantic, depth)# @markdown **Map parameters**:# fmt: offmeters_per_pixel = 0.025 # @param {type:"slider", min:0.01, max:0.1, step:0.005}# fmt: onagent_pos = agent_state.position# topdown map at agent positiontop_down_map = maps.get_topdown_map(sim.pathfinder, height=agent_pos[1], meters_per_pixel=meters_per_pixel)recolor_map = np.array([[255, 255, 255], [128, 128, 128], [0, 0, 0]], dtype=np.uint8)top_down_map = recolor_map[top_down_map]grid_dimensions = (top_down_map.shape[0], top_down_map.shape[1])# convert world agent position to maps module grid pointagent_grid_pos = maps.to_grid(agent_pos[2], agent_pos[0], grid_dimensions, pathfinder=sim.pathfinder)agent_forward = utils.quat_to_magnum(sim.agents[0].get_state().rotation).transform_vector(mn.Vector3(0, 0, -1.0))agent_orientation = math.atan2(agent_forward[0], agent_forward[2])# draw the agent and trajectory on the mapmaps.draw_agent(top_down_map, agent_grid_pos, agent_orientation, agent_radius_px=8)print("\nDisplay topdown map with agent:")display_map(top_down_map)

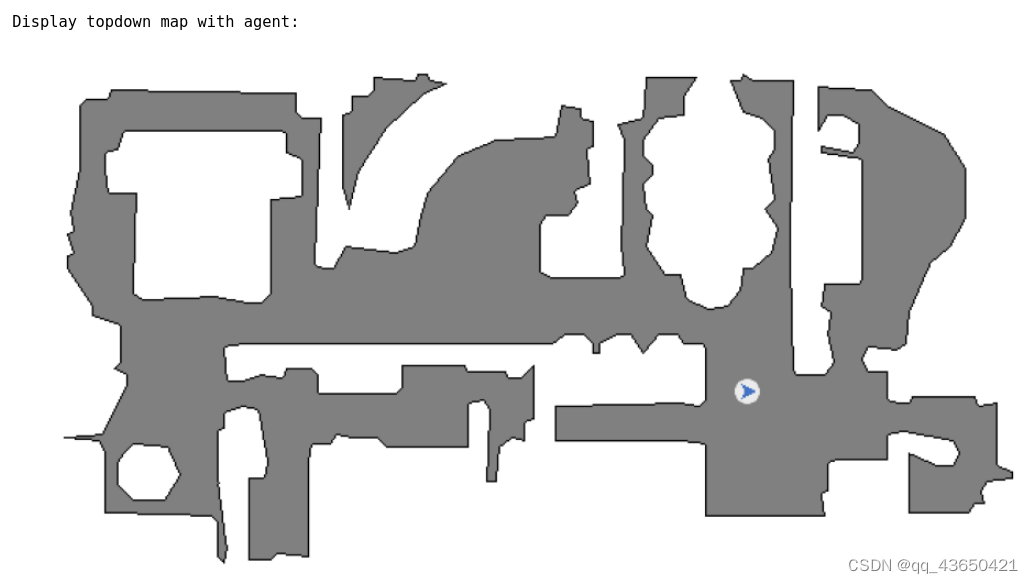
2.6 什么是Sliding
大多数游戏引擎允许代理在执行与环境碰撞的动作时沿障碍物滑动。虽然这在游戏中是合理的行为,但它并不准确反映机器人代理与环境之间的碰撞结果。
我们注意到允许滑动会使训练变得更容易,并导致更高的仿真性能,但它损害了经过训练的策略在模拟与实际环境之间的迁移。
有关此主题的更详细阐述,请参阅我们的论文:Are We Making Real Progress in Simulated Environments? Measuring the Sim2Real Gap in Embodied Visual Navigation。
将其打开以后在现实世界中可以获得更好的表现,但会让训练更加困难。
# @title Discrete and Continuous Navigation:# @markdown Take moment to run this cell a couple times and note the differences between discrete and continuous navigation with and without sliding.# @markdown ---
# @markdown ### Set example parameters:
seed = 7 # @param {type:"integer"}
# @markdown Optionally navigate on the currently configured scene and NavMesh instead of re-loading with defaults:
use_current_scene = False # @param {type:"boolean"}sim_settings["seed"] = seed
if not use_current_scene:# reload a default nav scenesim_settings["scene"] = "./data/scene_datasets/mp3d_example/17DRP5sb8fy/17DRP5sb8fy.glb" # agent启动的位置cfg = make_cfg(sim_settings)try: # make initialization Colab cell order proofsim.close()except NameError:passsim = habitat_sim.Simulator(cfg)
random.seed(sim_settings["seed"])
sim.seed(sim_settings["seed"])
# set new initial state
sim.initialize_agent(agent_id=0)
agent = sim.agents[0]# @markdown Seconds to simulate: 仿真的时间
sim_time = 10 # @param {type:"integer"}# @markdown Optional continuous action space parameters:启用连续模式或是离散模式
continuous_nav = True # @param {type:"boolean"}# defaults for discrete control
# control frequency (actions/sec):控制频率,离散控制采用3Hz的控制频率,无跳帧
control_frequency = 3
# observation/integration frames per action
frame_skip = 1
# 而对于连续的情况每秒70个步骤
if continuous_nav:control_frequency = 5 # @param {type:"slider", min:1, max:30, step:1}frame_skip = 12 # @param {type:"slider", min:1, max:30, step:1}fps = control_frequency * frame_skip
print("fps = " + str(fps))
control_sequence = []
for _action in range(int(sim_time * control_frequency)):if continuous_nav:# allow forward velocity and y rotation to vary# 计算连续时可行的前进速度和旋转速度control_sequence.append({"forward_velocity": random.random() * 2.0, # [0,2)"rotation_velocity": (random.random() - 0.5) * 2.0, # [-1,1)})else:control_sequence.append(random.choice(action_names))# create and configure a new VelocityControl structure
# 设置速度控制结构
vel_control = habitat_sim.physics.VelocityControl()
vel_control.controlling_lin_vel = True
vel_control.lin_vel_is_local = True
vel_control.controlling_ang_vel = True
vel_control.ang_vel_is_local = True# try 2 variations of the control experiment
# 循环是否采用滑动
for iteration in range(2):# reset observations and robot stateobservations = []video_prefix = "nav_sliding"sim.config.sim_cfg.allow_sliding = True# turn sliding off for the 2nd passif iteration == 1:sim.config.sim_cfg.allow_sliding = Falsevideo_prefix = "nav_no_sliding"print(video_prefix)# manually control the object's kinematic state via velocity integrationtime_step = 1.0 / (frame_skip * control_frequency)print("time_step = " + str(time_step))for action in control_sequence:# apply actionsif continuous_nav:# update the velocity control# local forward is -z# 连续操作,采用预先计算好的动作vel_control.linear_velocity = np.array([0, 0, -action["forward_velocity"]])# local up is yvel_control.angular_velocity = np.array([0, action["rotation_velocity"], 0])else: # discrete action navigationdiscrete_action = agent.agent_config.action_space[action]did_collide = False# 采用身体动作检查碰撞 if agent.controls.is_body_action(discrete_action.name):did_collide = agent.controls.action(agent.scene_node,discrete_action.name,discrete_action.actuation,apply_filter=True,)else:for _, v in agent._sensors.items():habitat_sim.errors.assert_obj_valid(v)agent.controls.action(v.object,discrete_action.name,discrete_action.actuation,apply_filter=False,)# simulate and collect framesfor _frame in range(frame_skip):if continuous_nav:# Integrate the velocity and apply the transform.# Note: this can be done at a higher frequency for more accuracy# 连续导航,首先获取agent的状态agent_state = agent.stateprevious_rigid_state = habitat_sim.RigidState(utils.quat_to_magnum(agent_state.rotation), agent_state.position)# manually integrate the rigid state# 使用速度控制积分器在时间补长内进行显式欧拉积分# 可以获得一个新的目标状态target_rigid_state = vel_control.integrate_transform(time_step, previous_rigid_state)# snap rigid state to navmesh and set state to object/agent# calls pathfinder.try_step or self.pathfinder.try_step_no_sliding# 使用导航网格强制导航性约束获取新的end_positionend_pos = sim.step_filter(previous_rigid_state.translation, target_rigid_state.translation)# set the computed state# 设置当前状态agent_state.position = end_posagent_state.rotation = utils.quat_from_magnum(target_rigid_state.rotation)agent.set_state(agent_state)# Check if a collision occured# 检查filter的前后距离前置是否发生碰撞dist_moved_before_filter = (target_rigid_state.translation - previous_rigid_state.translation).dot()dist_moved_after_filter = (end_pos - previous_rigid_state.translation).dot()# NB: There are some cases where ||filter_end - end_pos|| > 0 when a# collision _didn't_ happen. One such case is going up stairs. Instead,# we check to see if the the amount moved after the application of the filter# is _less_ than the amount moved before the application of the filterEPS = 1e-5# 检查距离是否大于某个阈值collided = (dist_moved_after_filter + EPS) < dist_moved_before_filter# run any dynamics simulation# 进行仿真sim.step_physics(time_step)# render observationobservations.append(sim.get_sensor_observations())print("frames = " + str(len(observations)))# video rendering with embedded 1st person viewif do_make_video:# use the vieo utility to render the observationsvut.make_video(observations=observations,primary_obs="color_sensor",primary_obs_type="color",video_file=output_directory + "continuous_nav",fps=fps,open_vid=show_video,)sim.reset()# [/embodied_agent_navmesh]
在开启sliding,agent在碰撞后会沿着障碍物进行滑动;
而如果关闭sliding,agent在碰撞后会被障碍区卡住。
视频展示的是连续导航的情况:
nav_outputcontinuous_nav
相关文章:

Habitat环境学习四:Habitat-sim基础用于导航——使用导航网格NavMesh
如何使用导航网格NavMesh 官方教程1、NavMesh基础定义1.1 使用NavMesh的原因1.2 什么是NavMesh 2、NavMesh的使用方法2.1 获取自上而下Top down view视角地图2.2 在NavMesh中进行查询以及随机产生可导航点2.3 查找最短路径2.4 场景加载NavMesh2.5 重新计算并生成NavMesh2.6 什么…...

python学习笔记 -- 字符串
目录 一、输出字符串的格式 二、字符串的一些函数 1、len函数:字符串长度 2、查找字符所在位置index 3、某字符在字符串中的个数count 4、字符切片 对字符串进行翻转 -- 利用步长 5、修改大小写字母: 6、判断开头和结尾 7、拆分字符串 一、输出…...

2024年GPT如何发展?
2023 年,人工智能领域最具影响的莫过于 GPT-4、ChatGPT 了。 ChatGPT 凭一己之力掀起了 AI 领域的热潮,火爆全球,似乎开启了第四次工业革命。 ChatGPT 入选《Nature》2023 年度十大人物(Nature’s 10),这…...
从REPR设计模式看 .NET的新生代类库FastEndpoints的威力
📢欢迎点赞 :👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 如有错误敬请指正,赐人玫瑰,手留余香!📢本文作者:由webmote 原创📢作者格言:新的征程,我们面对的不仅仅是技术还有人心,人心不可测,海水不可量,唯有技术,才是深沉黑夜中的一座闪烁的灯塔 !序言 又到了一年年末,春节将至…...
JavaScript 续)
前端入门:(五)JavaScript 续
10. 浏览器存储 10.1 Cookie的概念和使用 Cookie是一种存储在用户计算机上的小型文本文件,用于跟踪和识别用户。Cookie通常用于存储用户的偏好设置、会话信息等,可以通过JavaScript进行读取和设置。 // 示例:设置和读取Cookie document.co…...
研究多态恶意软件,探讨网络安全与AI
前言 近期ChatGPT火遍全球,AI技术被应用到了全球各行各业当中,国内外各大厂商也开始推出自己的ChatGPT,笔者所在公司在前段时间也推出了自研的安全GPT,AI技术在网络安全行业得到了很多的应用,不管是网络安全研究人员、…...

linux驱动工作原理
linux或者windows驱动是如何对上和对下工作的,请用中文回答 在Linux系统中,设备驱动程序通过在/dev目录下创建文件系统条目与硬件通信。应用程序通过打开这些文件来获取描述符,以此来与设备交互。驱动程序内部使用主次设备号来标识设备。而在…...
)
Rust语言入门(第3篇)
引用与借用 上一篇中,我们介绍了rust的所有权概念,若直接传递变量做函数参数,堆上的变量就会失去所有权,而栈上变量则由于复制,仍有所有权。 fn main(){let b 3;makes_copy(b);println!("after using a variab…...
电脑服务器离线安装.net framework 3.5解决方案(错误:0x8024402c )(如何确定当前系统是否安装NET Framework 3.5)
问题环境: 日常服务的搭建或多或少都会有需要到NET Framework 3.5的微软程序运行框架,本次介绍几种不同的安装方式主要解决运行在Windows 2012 以上的操作系统的服务。 NET Framework 3.5 是什么? .NET Framework是微软公司推出的程序运行框架…...
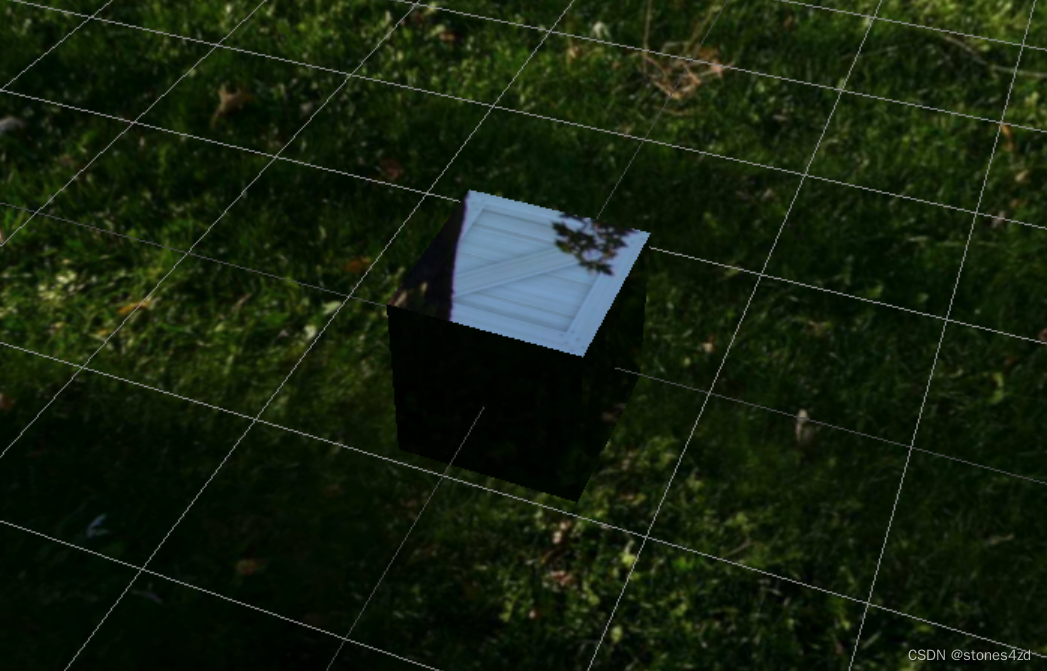

Three.js学习8:基础贴图
一、贴图 贴图(Texture Mapping),也翻译为纹理映射,“贴图”这个翻译更直观。 贴图,就是把图片贴在 3D 物体材质的表面,让它具有一定的纹理,来为 3D 物体添加细节的一种方法。这使我们能够添加…...
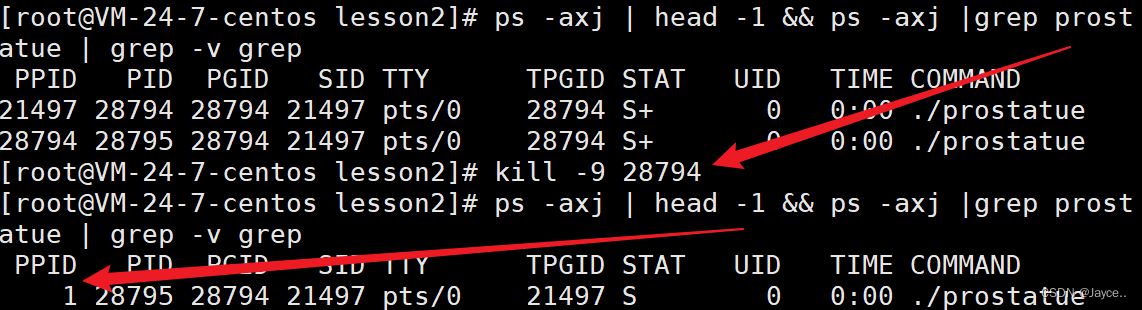
【Linux】进程学习(二):进程状态
目录 1.进程状态1.1 阻塞1.2 挂起 2. 进程状态2.1 运行状态-R进一步理解运行状态 2.2 睡眠状态-S2.3 休眠状态-D2.4 暂停状态-T2.5 僵尸状态-Z僵尸进程的危害 2.6 死亡状态-X2.7 孤儿进程 1.进程状态 1.1 阻塞 阻塞:进程因为等待某种条件就绪,而导致的…...

Spring Boot 笔记 003 Bean注册
使用Idea导入第三方jar包 在porn.xml种添加的第三方jar包依赖,并刷新 可以在启动类中尝试调用 以上放到启动类中,不推荐,建议创建一个专门定义的类 package com.geji.config;import cn.itcast.pojo.Country; import cn.itcast.pojo.Province;…...
PCIE 参考时钟架构
一、PCIe架构组件 首先先看下PCIE架构组件,下图中主要包括: ROOT COMPLEX (RC) (CPU); PCIE PCI/PCI-X Bridge; PCIE SWITCH; PCIE ENDPOINT (EP) (pcie设备); BUFFER; 各个器件的时钟来源都是由100MHz经过Buffer后提供。一个PCIE树上最多可以有256…...

【开源】JAVA+Vue.js实现在线课程教学系统
目录 一、摘要1.1 系统介绍1.2 项目录屏 二、研究内容2.1 课程类型管理模块2.2 课程管理模块2.3 课时管理模块2.4 课程交互模块2.5 系统基础模块 三、系统设计3.1 用例设计3.2 数据库设计 四、系统展示4.1 管理后台4.2 用户网页 五、样例代码5.1 新增课程类型5.2 网站登录5.3 课…...
复习提纲29)
计算机网络(第六版)复习提纲29
第六章:应用层 SS6.1 域名系统DNS 1 DNS被设计为一个联机分布式数据库系统,并采用客户服务器方式(C/S) 2 域名的体系结构 3 域名服务器及其体系结构 A 域名服务器的分类 1 根域名服务器 2 顶级域名服务器(TLD服务器&a…...

有道ai写作,突破免费限制,无限制使用
预览效果 文末提供源码包及apk下载地址 有道ai写作python版 import hashlib import time import json import ssl import base64 import uuidfrom urllib.parse import quote import requests from requests_toolbelt.multipart.encoder import MultipartEncoder from Crypto…...

node.js 使用 elementtree 生成思维导图 Freemind 文件
请参阅: java : pdfbox 读取 PDF文件内书签 请注意:书的目录.txt 编码:UTF-8,推荐用 Notepad 转换编码。 npm install elementtree --save 编写 txt_etree_mm.js 如下 // 读目录.txt文件,使用 elementtree 生成思维导图 Free…...

Vue中路由守卫的详细应用
作为一名web前端开发者,我们肯定经常使用Vue框架来构建我们的项目。而在Vue中,路由是非常重要的一部分,它能够实现页面的跳转和导航,提供更好的用户体验。然而,有时我们需要在路由跳转前或跳转后执行一些特定的逻辑&am…...
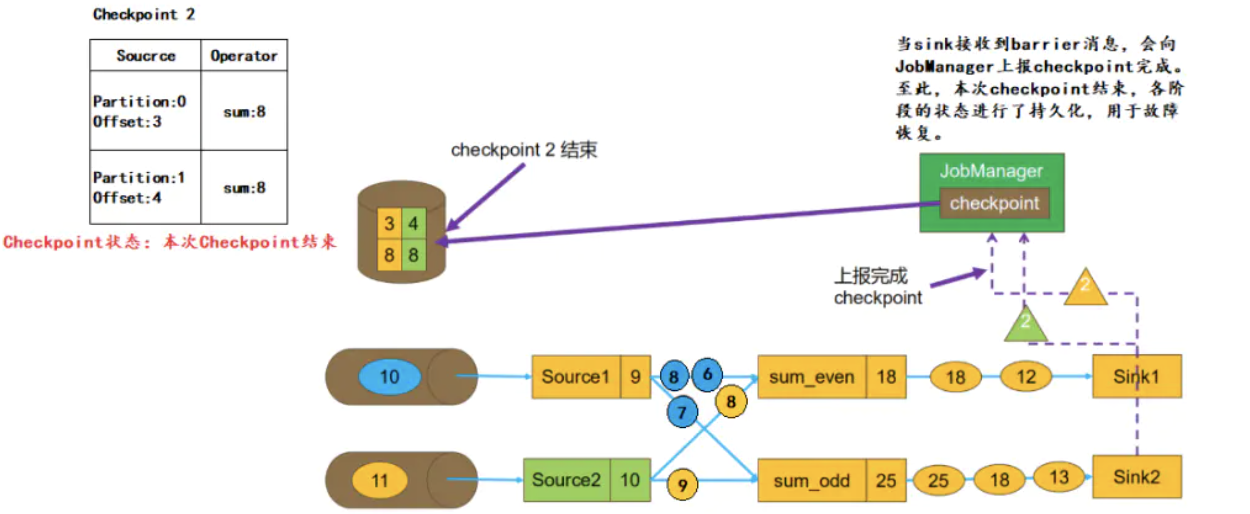
Flink Checkpoint过程
Checkpoint 使用了 Chandy-Lamport 算法 流程 1. 正常流式处理(尚未Checkpoint) 如下图,Topic 有两个分区,并行度也为 2,根据奇偶数 我们假设任务从 Kafka 的某个 Topic 中读取数据,该Topic 有 2 个 Pa…...

【Java程序代理与系统代理关系】Java程序代理与系统代理关系优先级及覆盖关系
前言 使用Apache HttpClient工具包中的HttpClients.createDefault()方法创建的默认HTTP客户端会根据操作系统当前的设置来决定是否使用代理。 具体来说,当创建默认HTTP客户端时,它会检查系统的代理设置。如果操作系统当前设置了系统级代理,…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

vscode里如何用git
打开vs终端执行如下: 1 初始化 Git 仓库(如果尚未初始化) git init 2 添加文件到 Git 仓库 git add . 3 使用 git commit 命令来提交你的更改。确保在提交时加上一个有用的消息。 git commit -m "备注信息" 4 …...

TRS收益互换:跨境资本流动的金融创新工具与系统化解决方案
一、TRS收益互换的本质与业务逻辑 (一)概念解析 TRS(Total Return Swap)收益互换是一种金融衍生工具,指交易双方约定在未来一定期限内,基于特定资产或指数的表现进行现金流交换的协议。其核心特征包括&am…...

大模型多显卡多服务器并行计算方法与实践指南
一、分布式训练概述 大规模语言模型的训练通常需要分布式计算技术,以解决单机资源不足的问题。分布式训练主要分为两种模式: 数据并行:将数据分片到不同设备,每个设备拥有完整的模型副本 模型并行:将模型分割到不同设备,每个设备处理部分模型计算 现代大模型训练通常结合…...

3403. 从盒子中找出字典序最大的字符串 I
3403. 从盒子中找出字典序最大的字符串 I 题目链接:3403. 从盒子中找出字典序最大的字符串 I 代码如下: class Solution { public:string answerString(string word, int numFriends) {if (numFriends 1) {return word;}string res;for (int i 0;i &…...
保姆级教程:在无网络无显卡的Windows电脑的vscode本地部署deepseek
文章目录 1 前言2 部署流程2.1 准备工作2.2 Ollama2.2.1 使用有网络的电脑下载Ollama2.2.2 安装Ollama(有网络的电脑)2.2.3 安装Ollama(无网络的电脑)2.2.4 安装验证2.2.5 修改大模型安装位置2.2.6 下载Deepseek模型 2.3 将deepse…...
RabbitMQ入门4.1.0版本(基于java、SpringBoot操作)
RabbitMQ 一、RabbitMQ概述 RabbitMQ RabbitMQ最初由LShift和CohesiveFT于2007年开发,后来由Pivotal Software Inc.(现为VMware子公司)接管。RabbitMQ 是一个开源的消息代理和队列服务器,用 Erlang 语言编写。广泛应用于各种分布…...

JS手写代码篇----使用Promise封装AJAX请求
15、使用Promise封装AJAX请求 promise就有reject和resolve了,就不必写成功和失败的回调函数了 const BASEURL ./手写ajax/test.jsonfunction promiseAjax() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) > {const xhr new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.open("get&quo…...

C++--string的模拟实现
一,引言 string的模拟实现是只对string对象中给的主要功能经行模拟实现,其目的是加强对string的底层了解,以便于在以后的学习或者工作中更加熟练的使用string。本文中的代码仅供参考并不唯一。 二,默认成员函数 string主要有三个成员变量,…...
