Redis 散列
1. 数据结构
我们自底向上来描述redis散列涉及的数据结构。
首先是负责存储键值的结构,Java 中存储的结构叫 Entry,redis里也差不多,叫dictEntry:
typedef struct dictEntry {void *key; // 键,它是一个指针类型,所以我们可以将其指向sds的指针union { // 这是一个联合类型,也就是你可以选择任意一个字段来存储void *val; // 因为散列也是redis数据库的底层结构,它是使用val字段uint64_t u64; // redis还用散列保存键过期时间,此时就用u64存储过期时间int64_t s64;double d;} v;struct dictEntry *next; // Java中为了处理哈希冲突,是采用拉链法,redis也是一样
} dictEntry;
我们向上,就是 dictEntry 的存储容器,也叫 dictht ,我们就叫他哈希
typedef struct dictht {dictEntry **table; // 指针数组 unsigned long size; // 底层数组长度,或者会所是slot数量unsigned long sizemask; // 它比size小1,位运算比取模快,用它加速定位hash值索引unsigned long used; // 这个是当前哈希表里所有数据的总和,哈希冲突的也算
} dictht;
然后,其实到这里基本可以用了。但是redis依然在 dicthst 之上抽象了 dict 结构,我们叫他散列:
typedef struct dict {dictType *type; // redis将数据和函数分离,dictType 是 API 抽象void *privdata; // 网上说是和 type 一起用的,我们初始化时都是NULLdictht ht[2]; // len=2的dictht数组,主要用0,当rehast时会开放1long rehashidx; // rehashidx == -1 则处于rehashingint16_t pauserehash; /* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */
} dict;
下面是作为数据库键值对存储时候用到的 dictType
/* Db->dict, keys are sds strings, vals are Redis objects. */
dictType dbDictType = {dictSdsHash, /* hash function */NULL, /* key dup */NULL, /* val dup */dictSdsKeyCompare, /* key compare */dictSdsDestructor, /* key destructor */dictObjectDestructor, /* val destructor */dictExpandAllowed /* allow to expand */
};
下面是作为失效控制存储时候用到的 dictType
/* Db->expires */
dictType dbExpiresDictType = {dictSdsHash, /* hash function */NULL, /* key dup */NULL, /* val dup */dictSdsKeyCompare, /* key compare */NULL, /* key destructor */NULL, /* val destructor */dictExpandAllowed /* allow to expand */
};
下面还有针对事务watch专用的 dictType
/* Keylist hash table type has unencoded redis objects as keys and* lists as values. It's used for blocking operations (BLPOP) and to* map swapped keys to a list of clients waiting for this keys to be loaded. */
dictType keylistDictType = {dictObjHash, /* hash function */NULL, /* key dup */NULL, /* val dup */dictObjKeyCompare, /* key compare */dictObjectDestructor, /* key destructor */dictListDestructor, /* val destructor */NULL /* allow to expand */
};
最后,这部分是redis服务器上的DB字段,我们关注散列,就是因为它可以用作数据库的实现,所以这里也列举一下:
struct redisServer {redisDb *db;
}
/* Redis database representation. There are multiple databases identified* by integers from 0 (the default database) up to the max configured* database. The database number is the 'id' field in the structure. */
typedef struct redisDb {dict *dict; // DB 的 keyspace,键空间,当然不是只存储键dict *expires; // DB 中键的过期时间dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */dict *watched_keys; /* 事务中通过watch观察的键int id; // 0-15,redis支持16个数据库long long avg_ttl; // 平均ttl。没啥用unsigned long expires_cursor; // Cursor of the active expire cycle. */list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
需要注意的是,redis 支持的map结构,底层的实现可能是ziplist,即压缩列表,也可能是dict,即散列。我们将名词规范化。
2.生命周期:初始化
我们先看作为数据库键值对存储时的初始化,这是在redis服务器启动时的一部分(DB 里直接使用dict,他压根没想用ziplist):
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {server.db[j].dict = dictCreate(&dbDictType,NULL);server.db[j].expires = dictCreate(&dbExpiresDictType,NULL);server.db[j].expires_cursor = 0;server.db[j].blocking_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);server.db[j].ready_keys = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL);server.db[j].watched_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);server.db[j].id = j;server.db[j].avg_ttl = 0;server.db[j].defrag_later = listCreate();listSetFreeMethod(server.db[j].defrag_later,(void (*)(void*))sdsfree);
}
我们知道redis默认支持16个库,这里就是for循环生成16个数据库,然后我们进入 dictCreate 方法
/* Create a new hash table */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,void *privDataPtr)
{dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d)); // 使用malloc 分配内存,返回指针_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr); // 委托其他方法return d;
}
官方注释也很清晰,这就是创建一个新的哈希表的方法,我们传入了两个参数,一个就是 dictType ,后续针对该哈希表的操作的一些可以自定义的 API,都是由这个结构体来处理的。
我理解这个非常像 Java 里的抽象类里未实现的方法,交给子类去自定义。
/* Initialize the hash table */
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,void *privDataPtr)
{_dictReset(&d->ht[0]); // 初始化 dict.ht[0]_dictReset(&d->ht[1]); // 初始化 dict.ht[1]d->type = type; // 这个玩意就是 dictTyped->privdata = privDataPtr; // 这个玩意是个NULLd->rehashidx = -1; // rehash索引,-1表示没有发生rehashd->pauserehash = 0;return DICT_OK;
}
/* Reset a hash table already initialized with ht_init().* NOTE: This function should only be called by ht_destroy(). */
static void _dictReset(dictht *ht)
{ht->table = NULL; // dictEntry **table 哈希里的字段声明ht->size = 0;ht->sizemask = 0;ht->used = 0;
}
dictCreate 委托给 _dictInit 方法来初始化我们刚生成的 dict,这里的工作,其实很简答,就是初始化,需要注意的是,此时 table 数组是 NULL,等真正 set 值时才会初始化。
3.生命周期:请求
3.1 hset 命令
Redis 负责处理 hset 命令的函数就叫 hsetCommand ,而且redis里的命令都是这个起名法:
typedef struct redisObject {unsigned type:4;unsigned encoding:4;unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency* and most significant 16 bits access time). */int refcount; // 这个字段不用太关注void *ptr; // 指向真实结构体的指针,比如我们现在讲散列,那么它可能指向// ziplist,也可能指向 dict
} robj;
robj 是贯穿 redis 的一个容器类型,你将其想象成 Java 里的 List,Optional。
主要关注type,encoding以及ptr
- type:该对象的类型,字符串,列表,集合,有序集合,map,stream
- encoding:每种type会因为各种性能考虑,在不同场景下有多重编码方式,啥是编码??就是底层数据结构的类型。打个比方,Java 里 List 在底层可以用数组,也可以用链表实现
- ptr:指针结构type+encoding选择出的结构体的指针
void hsetCommand(client *c) {int i, created = 0;robj *o;// 如果参数数量是奇数,那么命令输入错误,这是hset的格式:hset key field valueif ((c->argc % 2) == 1) {addReplyErrorFormat(c,"wrong number of arguments for '%s' command",c->cmd->name);return;}// 查询传入的key对应的散列对象的robj,如果不存在,则创建一个合适的散列对象并返回// 我们提前讲:如果该key不存在,那么会创建一个ziplist,他其实是个char数组的指针// 然后用robj对ziplist做封装if ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c,c->argv[1])) == NULL) return;hashTypeTryConversion(o,c->argv,2,c->argc-1);for (i = 2; i < c->argc; i += 2)created += !hashTypeSet(o,c->argv[i]->ptr,c->argv[i+1]->ptr,HASH_SET_COPY);/* HMSET (deprecated) and HSET return value is different. */char *cmdname = c->argv[0]->ptr;if (cmdname[1] == 's' || cmdname[1] == 'S') {/* HSET */addReplyLongLong(c, created);} else {/* HMSET */addReply(c, shared.ok);}signalModifiedKey(c,c->db,c->argv[1]);notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_HASH,"hset",c->argv[1],c->db->id);server.dirty += (c->argc - 2)/2;
}
3.1.1 hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate
我们先看第一个内部函数,就是根据 hset 传入的 key 查得对应的哈希散列
robj *hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(client *c, robj *key) {// 根据传入的key【robj】查回对应的val【robj】,传入的key就是map的keyrobj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key);// 由于key对应的应该是一个散列,所以这里强制匹配,即robj.type == HASHif (checkType(c,o,OBJ_HASH)) return NULL;// 如果返回的robj是NULL,则说明不存在该散列,那么就创建一个散列。,否则直接返回if (o == NULL) {// 当在db里没有查到这个key,那么创建一个map对象,默认初始化的,都是ziplist编码的o = createHashObject();// 将新创建的robj以及key,设置到db中,key用于定位插槽【slot】的// 而o,也就是新创建的这个map对象,会和key一起,再组成一个dictEntry对象// 存储到db这个大dict中,db.dict[0]dbAdd(c->db,key,o);}return o;
}
里面比较核心的方法是 createHashObject中,这个方法只生成一个空的map对象【robj】,不会向里面设置任何键值对,这里会涉及到散列的编码选择:
robj *createHashObject(void) {unsigned char *zl = ziplistNew();robj *o = createObject(OBJ_HASH, zl);o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST;return o;
}
/* Create a new empty ziplist. */
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void) {unsigned int bytes = ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE+ZIPLIST_END_SIZE;unsigned char *zl = zmalloc(bytes);ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(bytes);ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE);ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = 0;zl[bytes-1] = ZIP_END;return zl;
}
可以看到,默认redis初始化的map,就是 ziplist,然后等真正插入键值对时,再看是否需要转换为哈希。
然后,由于可能是新生成了一个map对象,所以还涉及将其挂到db上的动作:
void dbAdd(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) {// key是hset命令的key,val则是刚生成的map对象【robj】sds copy = sdsdup(key->ptr);// 该函数内部会讲key+val构造为一个dictEntry,挂到db.dict.ht[0]中// 按照顺序看,DB -> dict 散列 -> dictha 哈希 -> dictEntry int retval = dictAdd(db->dict, copy, val);serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,retval == DICT_OK);signalKeyAsReady(db, key, val->type);if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyAdd(key->ptr);
}
这部分代码其实与前面讲的 dictAdd 是基本相同的实现,毕竟db也就是个散列
3.1.2 hashTypeTryConversion
然后我们来看第二个函数 hashTypeTryConversion ,简单的将就是判断插入新的值后,是否可以将原本是 ziplist 存储的散列结构,转换为哈希存储的散列。
散列支持两种编码,即 ziplist 和 hash,当满足下面两个条件时,redis会使用ziplist:
- key-value 结构的所有键值对的字符串长度都小于 hash-max-ziplist-value(默认值64),可以通过配置文件修改
- 散列对象保存的键值对的个数(1个键值对记为1)小于 hash-max-ziplist-entries(默认值512),可以通过配置文件修改
redis 只支持 ziplist 到 hash 的转换,不支持反向。
3.1.3 hashTypeSet
然后我们来看第三个函数 hashTypeSet ,他就是插入键值对的。
#define HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD (1<<0)
#define HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE (1<<1)
#define HASH_SET_COPY 0
int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) {int update = 0;// 如果值【robj】的编码方式是 ziplist 时if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl, *fptr, *vptr;zl = o->ptr;fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, ZIPLIST_HEAD);if (fptr != NULL) {fptr = ziplistFind(zl, fptr, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field), 1);if (fptr != NULL) {/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);serverAssert(vptr != NULL);update = 1;/* Replace value */zl = ziplistReplace(zl, vptr, (unsigned char*)value,sdslen(value));}}if (!update) {/* Push new field/value pair onto the tail of the ziplist */zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)field, sdslen(field),ZIPLIST_TAIL);zl = ziplistPush(zl, (unsigned char*)value, sdslen(value),ZIPLIST_TAIL);}o->ptr = zl;/* Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries)hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// 如果值【robj】的编码方式为哈希时,传入命令里的 field ,查回匹配的entry// 如果没匹配,就设置NULL,需要注意,dictEntry 保存了键【key】和值【val】dictEntry *de = dictFind(o->ptr,field);if (de) {// 如果map里有该field,则进入这段代码,首先获取目前field对应的值并释放内存sdsfree(dictGetVal(de));if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {// 然后将新的val设置到指针上,dictGetVal(de)返回的是指针dictGetVal(de) = value;value = NULL;} else {// 这个是将value复制了一遍,然后设置到val指针上dictGetVal(de) = sdsdup(value);}update = 1;} else {// 如果map中未查得fieldsds f,v;// 构建field结构体if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD) {f = field;field = NULL;} else {f = sdsdup(field);}// 构建value结构体if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE) {v = value;value = NULL;} else {v = sdsdup(value);}// 将field-value设置到map中dictAdd(o->ptr,f,v);}} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}/* Free SDS strings we did not referenced elsewhere if the flags* want this function to be responsible. */if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_FIELD && field) sdsfree(field);if (flags & HASH_SET_TAKE_VALUE && value) sdsfree(value);return update;
}
这里的 dictAdd 负责将键值设到 map 上
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{ // 设置entry,如果entry已存在,这里返回NULLdictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;// 设置值dictSetVal(d, entry, val);return DICT_OK;
}
dictAddRaw 此函数添加条目,但不是设置值,而是向用户返回 dictEntry 结构,这将确保按用户的意愿填充值字段。
这个函数也直接暴露给用户API,主要是为了在哈希值中存储非指针,前面我看到过, dictEntry 里有个联合体,即可以放 *val,也可以放数字等。
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{long index;dictEntry *entry;dictht *ht;if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if* the element already exists. */if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)return NULL;/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry.* Insert the element in top, with the assumption that in a database* system it is more likely that recently added entries are accessed* more frequently. */ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));entry->next = ht->table[index];ht->table[index] = entry;ht->used++;/* Set the hash entry fields. */dictSetKey(d, entry, key);return entry;
}
3.1.4 signalModifiedKey
我们来看第四个函数,signalModifiedKey ,这个函数是后置处理,涉及事物 watck key 和失效。
void signalModifiedKey(client *c, redisDb *db, robj *key) {touchWatchedKey(db,key);trackingInvalidateKey(c,key,1);
}
/* "Touch" a key, so that if this key is being WATCHed by some client the* next EXEC will fail. */
// watch key 检查,这样客户端在执行 exec 时就失败
void touchWatchedKey(redisDb *db, robj *key) {list *clients;listIter li;listNode *ln;// 如果db的watched_keys(它也是一个散列)为空,则返回,没有事物在watchif (dictSize(db->watched_keys) == 0) return;// 查询watch了该key的客户端,这里返回的是个list,这里查询很简单,就是哈希取模再比较keyclients = dictFetchValue(db->watched_keys, key);if (!clients) return;// 将所有watch了该key的客户端的flag标签,都或等 CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS/* Mark all the clients watching this key as CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS *//* Check if we are already watching for this key */listRewind(clients,&li);while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);c->flags |= CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS;}
}
// 我也不知道这个函数是干嘛的
void trackingInvalidateKey(client *c, robj *keyobj, int bcast) {if (TrackingTable == NULL) return;unsigned char *key = (unsigned char*)keyobj->ptr;size_t keylen = sdslen(keyobj->ptr);if (bcast && raxSize(PrefixTable) > 0)trackingRememberKeyToBroadcast(c,(char *)key,keylen);rax *ids = raxFind(TrackingTable,key,keylen);if (ids == raxNotFound) return;raxIterator ri;raxStart(&ri,ids);raxSeek(&ri,"^",NULL,0);while(raxNext(&ri)) {uint64_t id;memcpy(&id,ri.key,sizeof(id));client *target = lookupClientByID(id);/* Note that if the client is in BCAST mode, we don't want to* send invalidation messages that were pending in the case* previously the client was not in BCAST mode. This can happen if* TRACKING is enabled normally, and then the client switches to* BCAST mode. */if (target == NULL ||!(target->flags & CLIENT_TRACKING)||target->flags & CLIENT_TRACKING_BCAST){continue;}/* If the client enabled the NOLOOP mode, don't send notifications* about keys changed by the client itself. */if (target->flags & CLIENT_TRACKING_NOLOOP &&target == server.current_client){continue;}/* If target is current client and it's executing a command, we need schedule key invalidation.* As the invalidation messages may be interleaved with command* response and should after command response. */if (target == server.current_client && server.fixed_time_expire) {incrRefCount(keyobj);listAddNodeTail(server.tracking_pending_keys, keyobj);} else {sendTrackingMessage(target,(char *)keyobj->ptr,sdslen(keyobj->ptr),0);}}raxStop(&ri);/* Free the tracking table: we'll create the radix tree and populate it* again if more keys will be modified in this caching slot. */TrackingTableTotalItems -= raxSize(ids);raxFree(ids);raxRemove(TrackingTable,(unsigned char*)key,keylen,NULL);
}
3.2 hlen 命令
hlen 命令是由下面这个函数来处理的
void hlenCommand(client *c) {robj *o;// 这行很简单,就是从数据库里查询key对应的robj对象,其中,因为这map结构的方法,// 所以检查robj头里的type是否是HASH,否则命令就用错了if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.czero)) == NULL ||checkType(c,o,OBJ_HASH)) return;// hashTypeLength 返回一个长度,然后addReplyLongLong将结果写到buf中addReplyLongLong(c,hashTypeLength(o));
}
所以核心的方法都是在下面这个函数内:
/* Return the number of elements in a hash. */
unsigned long hashTypeLength(const robj *o) {unsigned long length = ULONG_MAX;// 如果是ziplist编码的,那么这里有优点特殊了// 当 zllen 小于65535时,那么ziplist的len=zllen// 当 zllen 等于 65535,那么就得一个个算,直到END标记处if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {// 这里使用ziplistLen函数,该函数就是直接拿ziplist数据结构的zllen字段// 这里除以2,是因为这是保存的键值对,是成对出现的length = ziplistLen(o->ptr) / 2;} else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// 如果时hash编码,其dictht里的used字段记录了当前有多少键值对length = dictSize((const dict*)o->ptr);} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}return length;
}
下面引用ziplist的内存布局图
area |<---- ziplist header ---->|<----------- entries ------------->|<-end->|size 4 bytes 4 bytes 2 bytes ? ? ? ? 1 byte+---------+--------+-------+--------+--------+--------+--------+-------+ component | zlbytes | zltail | zllen | entry1 | entry2 | ... | entryN | zlend |+---------+--------+-------+--------+--------+--------+--------+-------+^ ^ ^ address | | |ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD | ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END|ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL
| 域 | 长度/类型 | 域的值 |
|---|---|---|
zlbytes | uint32_t | 整个 ziplist 占用的内存字节数,对 ziplist 进行内存重分配,或者计算末端时使用。 |
zltail | uint32_t | 到达 ziplist 表尾节点的偏移量。 通过这个偏移量,可以在不遍历整个 ziplist 的前提下,弹出表尾节点。 |
zllen | uint16_t | ziplist 中节点的数量。 当这个值小于 UINT16_MAX (65535)时,这个值就是 ziplist 中节点的数量; 当这个值等于 UINT16_MAX 时,节点的数量需要遍历整个 ziplist 才能计算得出。 |
entryX | ? | ziplist 所保存的节点,各个节点的长度根据内容而定。 |
zlend | uint8_t | 255 的二进制值 1111 1111 (UINT8_MAX) ,用于标记 ziplist 的末端。 |
3.3 增量rehash
增量式rehash是redis时间事件处理函数中的一部分:
/* Rehash */
if (server.activerehashing) {// dbs_per_call 这个值是min(16,你设置的数据库数量)for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) {// 增量式rehashint work_done = incrementallyRehash(rehash_db);// work_done 标识该在rehash过程中是否真的干活了if (work_done) {/* If the function did some work, stop here, we'll do* more at the next cron loop. */break;} else {/* If this db didn't need rehash, we'll try the next one. */// 如果该库没有做任何工作,那说明该库无需rehash,那++处理下一个数据// 这里取了个模,好实现环型处理,0,1,2,3...15,0,1,2...rehash_db++;rehash_db %= server.dbnum;}}
}
我们主要关注下面这个增量式rehash核心方法:
int incrementallyRehash(int dbid) {/* Keys dictionary */// 如果键空间在rehash,那么就执行1ms的if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].dict)) {dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].dict,1);return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */}/* Expires */// 如果键空间没有rehash,则检查失效空间是否在rehash,是的话也执行1ms的if (dictIsRehashing(server.db[dbid].expires)) {dictRehashMilliseconds(server.db[dbid].expires,1);return 1; /* already used our millisecond for this loop... */}return 0;
}
如果检测到该db处于散列中,那么就调用下面这个方法,执行1ms的任务:
/* Rehash in ms+"delta" milliseconds. The value of "delta" is larger * than 0, and is smaller than 1 in most cases. The exact upper bound * depends on the running time of dictRehash(d,100).*/
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms) {// 如果 dict 的 pauserehash>0,那么就暂停rehashif (d->pauserehash > 0) return 0;long long start = timeInMilliseconds();int rehashes = 0;// while循环,调用 dictRehash,每次执行100任务量,执行完后就计算下剩余时间,不够就结束while(dictRehash(d,100)) {rehashes += 100;if (timeInMilliseconds()-start > ms) break;}return rehashes;
}
核心方法,rehash,我们送进来的n=100
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {// n * 100,这是最大允许访问的空插槽int empty_visits = n*10; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */unsigned long s0 = d->ht[0].size;unsigned long s1 = d->ht[1].size;if (dict_can_resize == DICT_RESIZE_FORBID || !dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0;if (dict_can_resize == DICT_RESIZE_AVOID && ((s1 > s0 && s1 / s0 < dict_force_resize_ratio) ||(s1 < s0 && s0 / s1 < dict_force_resize_ratio))){return 0;}// while循环,迭代次数最大为n,同时确保ht[0]剩余简键值对>0while(n-- && d->ht[0].used != 0) {dictEntry *de, *nextde;assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);// 需要注意的是rehashidx是插槽索引,简单说就是dictht结构体数组指针这个数组的索引while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {// 当插槽位置为NULL,那么rehashidx++d->rehashidx++;// 如果空插槽碰到的太多,超过100*n,也不做了,怕时间花销太大if (--empty_visits == 0) return 1;}// 取出rehashidx处的头部dictEntryde = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx];// 将该插槽下所有的dictEntry迁移到ht[1]中while(de) {uint64_t h;nextde = de->next;// 从dictEntry中取出key,然后与ht[1]的sizemask做取模得到索引h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask;// 这里怕迷糊,de是当前entry,nextde是下一个entry// 首先将de设置到当前entry的next指针设置为ht[1]中插槽头entryde->next = d->ht[1].table[h];// 然后将ht[1]的头entry换成当前entryd->ht[1].table[h] = de;// used 统计计算d->ht[0].used--;d->ht[1].used++;// 然后重用de变量,存储下一个entry,然后循环起来,直刀最后一个冲突键为止de = nextde;}// 将当前rehashidx位置设置NULL(毕竟都迁移完了),然后 rehashidx++d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;d->rehashidx++;}// 如果整个表都被rehash完了,那么释放内存,然后ht[0]和ht[1]对掉,并下掉rehashidx标志if (d->ht[0].used == 0) {zfree(d->ht[0].table);d->ht[0] = d->ht[1];_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);d->rehashidx = -1;return 0;}/* More to rehash... */return 1;
}
3.4 单步rehash
其实,除了定时时间任务里的增量rehash之外,在正常命令处理时,也会随时做一点rehash,我称呼它为单步rehahs,主要是为了贴合它起的名字:
/* This function performs just a step of rehashing, and only if hashing has* not been paused for our hash table. When we have iterators in the* middle of a rehashing we can't mess with the two hash tables otherwise* some element can be missed or duplicated.** This function is called by common lookup or update operations in the* dictionary so that the hash table automatically migrates from H1 to H2* while it is actively used. */
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {if (d->pauserehash == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
该函数与前面增量rehahs不同的点在于,他n 不是100次,而是 1次。除此之外,没啥任何区别。
我们下面大概列举一下会出发单步rehash的场景:
- 向db中插入新的键值对
- 向db删除一个键
- 向db发起查询操作
3.5 迭代器
Jababoy 应该比较数据,首先就是获取迭代器,Redis 中有好多种 iterator,我们首先介绍散列类型的,就是db内的某个map上的hkeys
hashTypeIterator *hashTypeInitIterator(robj *subject) {// 函数传入的subject,就是我们的迭代目标,比方我们这里时在处理散列结构// 那么送入的就可能是ziplist,也可能是hash编码的hashTypeIterator *hi = zmalloc(sizeof(hashTypeIterator));hi->subject = subject;hi->encoding = subject->encoding;if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {// 如果是ziplist编码hi->fptr = NULL;hi->vptr = NULL;} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// 如果是hash编码hi->di = dictGetIterator(subject->ptr);} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}return hi;
}
dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d)
{// 初始化一个dictIterator结构dictIterator *iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter));iter->d = d;iter->table = 0;iter->index = -1;iter->safe = 0;iter->entry = NULL;iter->nextEntry = NULL;return iter;
}
我们看一下迭代器的数据结构:hashTypeIterator 内部嵌套了一个 dictIterator结构,原因是因为map有两种编码,所以为了给使用者一个公共API,就出现了hashTypeIterator,由它来负责调度是走ziplist的迭代器,还是hash的迭代器。
typedef struct {robj *subject;int encoding;unsigned char *fptr, *vptr;dictIterator *di;dictEntry *de;
} hashTypeIterator;
typedef struct dictIterator {dict *d;long index;int table, safe;dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry;/* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */unsigned long long fingerprint;
} dictIterator;
初始化完,我们继续看下一个函数 hashTypeNext,对应 Java 的就是 next() 方法
int hashTypeNext(hashTypeIterator *hi) {// 如果是ziplist编码的迭代器if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST) {unsigned char *zl;unsigned char *fptr, *vptr;// hi 是迭代器,subject是ziplist的robj,用ptr可以直接指针到ziplistzl = hi->subject->ptr;// 下面这俩玩意吃实话时就是NULLfptr = hi->fptr;vptr = hi->vptr;if (fptr == NULL) {// 初始化cursorserverAssert(vptr == NULL);fptr = ziplistIndex(zl, 0);} else {/* Advance cursor */serverAssert(vptr != NULL);fptr = ziplistNext(zl, vptr);}if (fptr == NULL) return C_ERR;/* Grab pointer to the value (fptr points to the field) */vptr = ziplistNext(zl, fptr);serverAssert(vptr != NULL);/* fptr, vptr now point to the first or next pair */// hi->fptr = fptr;hi->vptr = vptr;} else if (hi->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {// 如果是哈希编码的迭代器if ((hi->de = dictNext(hi->di)) == NULL) return C_ERR;} else {serverPanic("Unknown hash encoding");}return C_OK;
}
由于ziplist本身就是有序的,它是按照插入顺序存储的,所以如果是ziplis编码的话,迭代器就是直接使用了ziplist本身的特性进行迭代。
而对于hash编码的case,我们需要重点研究dictNex函数的实现:
dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter)
{while (1) {if (iter->entry == NULL) {// 初始化时,iter->table 就是0,表示选择ht[0]开始dictht *ht = &iter->d->ht[iter->table];// 其实下面这俩判断,就是index和table的初始值,当首次执行时,会根据// 迭代饿模式,来区别设置,如果是安全模式,则设置dict的pasuerRehash,// 如果是非安全模式,则计算一个词是dict各个状态字段汇聚出来的一个指纹哈希值if (iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0) {if (iter->safe)dictPauseRehashing(iter->d);elseiter->fingerprint = dictFingerprint(iter->d);}// index++,开始扫描哈希,它就像rehash里的rehashidxiter->index++;// 这个条件是判断是否当前index已经超过当前扫描的dictht的size最大插槽数了if (iter->index >= (long) ht->size) {// 当dict处于rehash中,且现在是扫描0号表,那么就切换到1号表,index归零if (dictIsRehashing(iter->d) && iter->table == 0) {iter->table++;iter->index = 0;ht = &iter->d->ht[1];} else {break;}}// 将该插槽处的dictEntry设置到entry上,然后iter->entry = ht->table[iter->index];} else {// 这种case是因为之前设置过entry,这里又进入循环了iter->entry = iter->nextEntry;}// 如果entry非null,则设置好nextEntry,就可以返回了// 如果entry位null,会进入while循环,继续查找if (iter->entry) {/* We need to save the 'next' here, the iterator user* may delete the entry we are returning. */iter->nextEntry = iter->entry->next;return iter->entry;}}return NULL;
}
我们需要理解 dictIterator 的内部字段的含义:
- d 就是本迭代的 dict 对象【robj】
- entry 当前迭代到的元素
- nextEntry 下一个元素
- safe 是否安全模式迭代,安全模式会暂停rehash
- fingerprint 指纹,当不是安全模式时,redis将dict里的used,size等字段进行哈希计算,得到一个指纹
我理解这个迭代器很容易理解,线循环哈希插槽,然后在插槽内再循环链表。
相关文章:

Redis 散列
1. 数据结构 我们自底向上来描述redis散列涉及的数据结构。 首先是负责存储键值的结构,Java 中存储的结构叫 Entry,redis里也差不多,叫dictEntry: typedef struct dictEntry {void *key; // 键,它是一个指针类型…...

ip地址错误无法上网怎么修复
在数字化日益普及的今天,网络已经成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。然而,当遇到IP地址错误导致无法上网的问题时,很多人可能会感到手足无措。那么,IP地址错误无法上网怎么修复?下面跟着虎观代理小二一起来了解一下吧。…...

数据库管理的艺术(MySQL):DDL、DML、DQL、DCL及TPL的实战应用(上:数据定义与控制)
文章目录 DDL数据定义语言1、创建数据库2、创建表3、修改表结构4、删除5、数据类型 列的约束主键约束(primary key)唯一约束(unique key)非空约束检查约束(check)外键约束(foreign keyÿ…...

成为CMake砖家(5): VSCode CMake Tools 插件基本使用
大家好,我是白鱼。 之前提到过,白鱼的主力 编辑器/IDE 是 VSCode, 也提到过使用 CMake Language Support 搭配 dotnet 执行 CMakeLists.txt 语法高亮。 对于阅读 CMakeLists.txt 脚本, 这足够了。 而在 C/C 开发过程中ÿ…...

【简洁明了】调节大模型的prompt的方法【带案例】
简明调节大模型的prompt的方法【简洁明了带案例】 1. 明确任务目标2. 提供上下文3. 指定格式4. 限制输出长度5. 使用示例6. 逐步引导7. 提供反面例子8. 使用CoT思维链9. 反复试验和调整方法九解释:乔哈里窗检视 最后 因为网上给出的调节prompt都 过于详细ÿ…...

【操作系统】文件管理——文件存储空间管理(个人笔记)
学习日期:2024.7.17 内容摘要:文件存储空间管理、文件的基本操作 在上一章中,我们学习了文件物理结构的管理,重点学习了操作系统是如何实现逻辑结构到物理结构的映射,这显然是针对已经存储了文件的磁盘块的࿰…...

微软GraphRAG +本地模型+Gradio 简单测试笔记
安装 pip install graphragmkdir -p ./ragtest/input#将文档拷贝至 ./ragtest/input/ 下python -m graphrag.index --init --root ./ragtest修改settings.yaml encoding_model: cl100k_base skip_workflows: [] llm:api_key: ${GRAPHRAG_API_KEY}type: openai_chat # or azu…...
)
数学建模-Topsis(优劣解距离法)
介绍 TOPSIS法(Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution) 可翻译为逼近理想解排序法,国内常简称为优劣解距离法 TOPSIS 法是一种常用的综合评价方法,其能充分利用原始数据的信息, 其结果能精…...

嵌入式linux相机 转换模块
convert_manager.c #include <config.h> #include <convert_manager.h> #include <string.h>static PT_VideoConvert g_ptVideoConvertHead NULL;/*********************************************************************** 函数名称: Register…...

【自学安全防御】二、防火墙NAT智能选路综合实验
任务要求: (衔接上一个实验所以从第七点开始,但与上一个实验关系不大) 7,办公区设备可以通过电信链路和移动链路上网(多对多的NAT,并且需要保留一个公网IP不能用来转换) 8,分公司设备可以通过总…...

【Android】传给后端的Url地址被转码问题处理
一、问题 为什么使用Gson().toJson的时候,字符串中的会被转成\u003d 在 Gson 中,默认情况下会对某些特殊字符进行 HTML 转义,以确保生成的 JSON 字符串在 HTML 中是安全的。因此,字符 会被转义为 \u003d。你可以通过禁用 HTML 转…...

1.厦门面试
1.Vue的生命周期阶段 vue生命周期分为四个阶段 第一阶段(创建阶段):beforeCreate,created 第二阶段(挂载阶段):beforeMount(render),mounted 第三阶段&#…...
)
设计模式使用场景实现示例及优缺点(行为型模式——状态模式)
在一个遥远的国度中,有一个被称为“变幻之城”的神奇城堡。这座城堡有一种特殊的魔法,能够随着王国的需求改变自己的形态和功能。这种神奇的变化是由一个古老的机制控制的,那就是传说中的“状态宝石”。 在变幻之城中,有四颗宝石&…...

抖音短视频seo矩阵系统源码(搭建技术开发分享)
#抖音矩阵系统源码开发 #短视频矩阵系统源码开发 #短视频seo源码开发 一、 抖音短视频seo矩阵系统源码开发,需要掌握以下技术: 网络编程:能够使用Python、Java或其他编程语言进行网络编程,比如使用爬虫技术从抖音平台获取数据。…...

基于 asp.net家庭财务管理系统设计与实现
博主介绍:专注于Java .net php phython 小程序 等诸多技术领域和毕业项目实战、企业信息化系统建设,从业十五余年开发设计教学工作 ☆☆☆ 精彩专栏推荐订阅☆☆☆☆☆不然下次找不到哟 我的博客空间发布了1000毕设题目 方便大家学习使用感兴趣的可以先…...

allure_pytest:AttributeError: ‘str‘ object has no attribute ‘iter_parents‘
踩坑记录 问题描述: 接口自动化测试时出现报错,报错文件是allure_pytest库 问题分析: 自动化测试框架是比较成熟的代码,报错也不是自己写的文件,而是第三方库,首先推测是allure_pytest和某些库有版本不兼…...

C语言 反转链表
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/?envTypestudy-plan-v2&envIdselected-coding-interview 完整代码: /*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/// 反转链表…...

MFC CRectTracker 类用法详解
CRectTracker 类并非 Microsoft Foundation Class (MFC) 库中应用很广泛的一个类,一般教科书中很少有提到。在编程中如果需编写选择框绘制以及选择框大小调整、移动等程序时,用CRectTracker 类就会做到事半而功倍。下面详细介绍MFC CRectTracker 类。 M…...

好玩的调度技术-场景编辑器
好玩的调度技术-场景编辑器 文章目录 好玩的调度技术-场景编辑器前言一、演示一、代码总结好玩系列 前言 这两天写前端写上瘾了,顺手做了个好玩的东西,好玩系列也好久没更新,正好作为素材写一篇文章,我真的觉得蛮好玩的ÿ…...
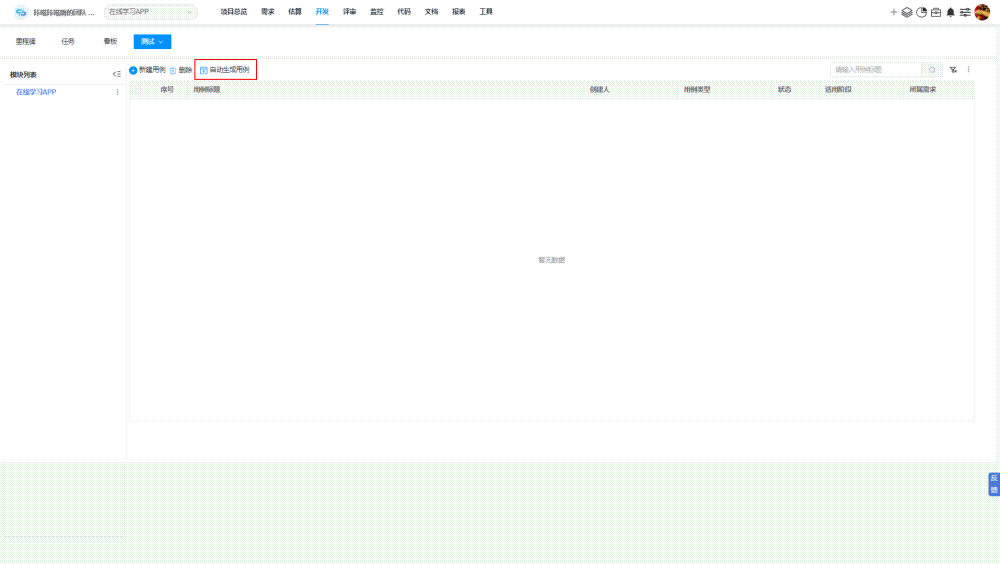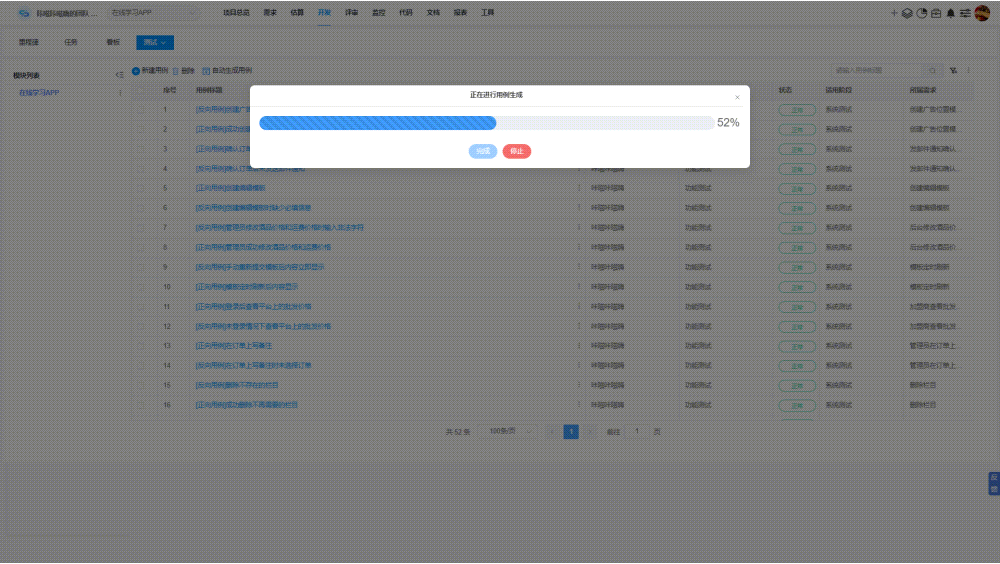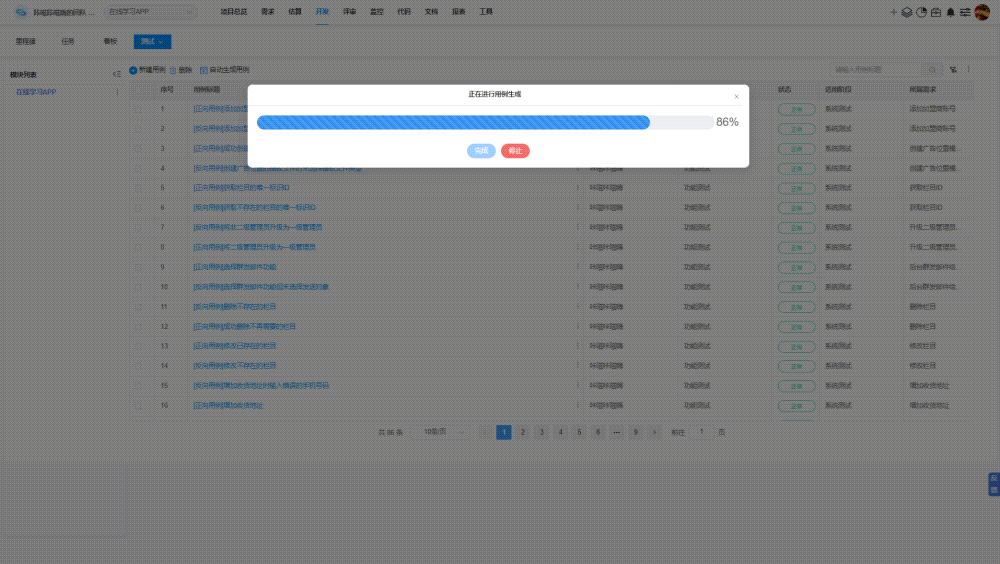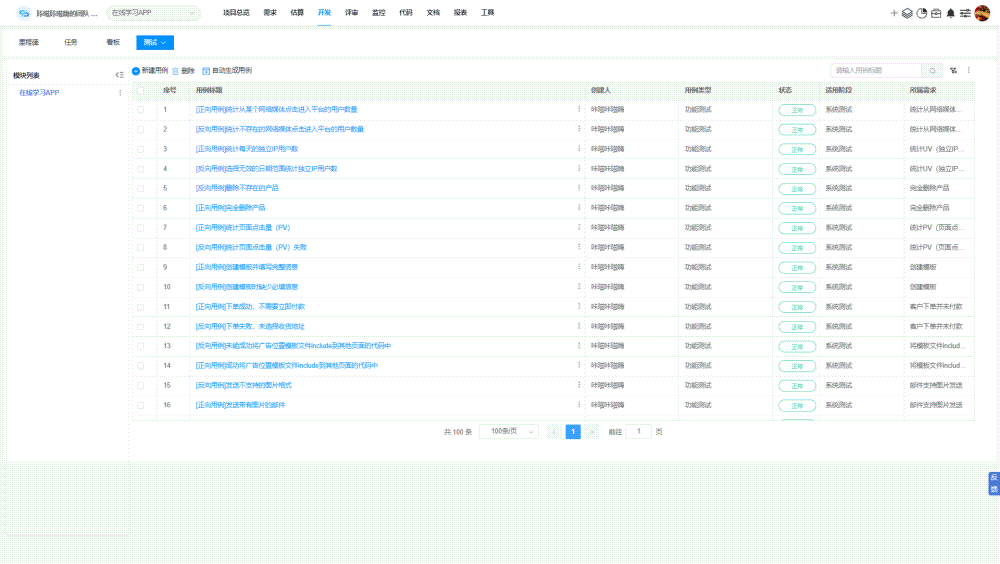
提高自动化测试脚本编写效率 5大关键注意事项
提高自动化测试脚本编写效率能加速测试周期,减少人工错误,提升软件质量,促进项目按时交付,增强团队生产力和项目成功率。而自动化测试脚本编写效率低下,往往会导致测试周期延长,增加项目成本,延…...
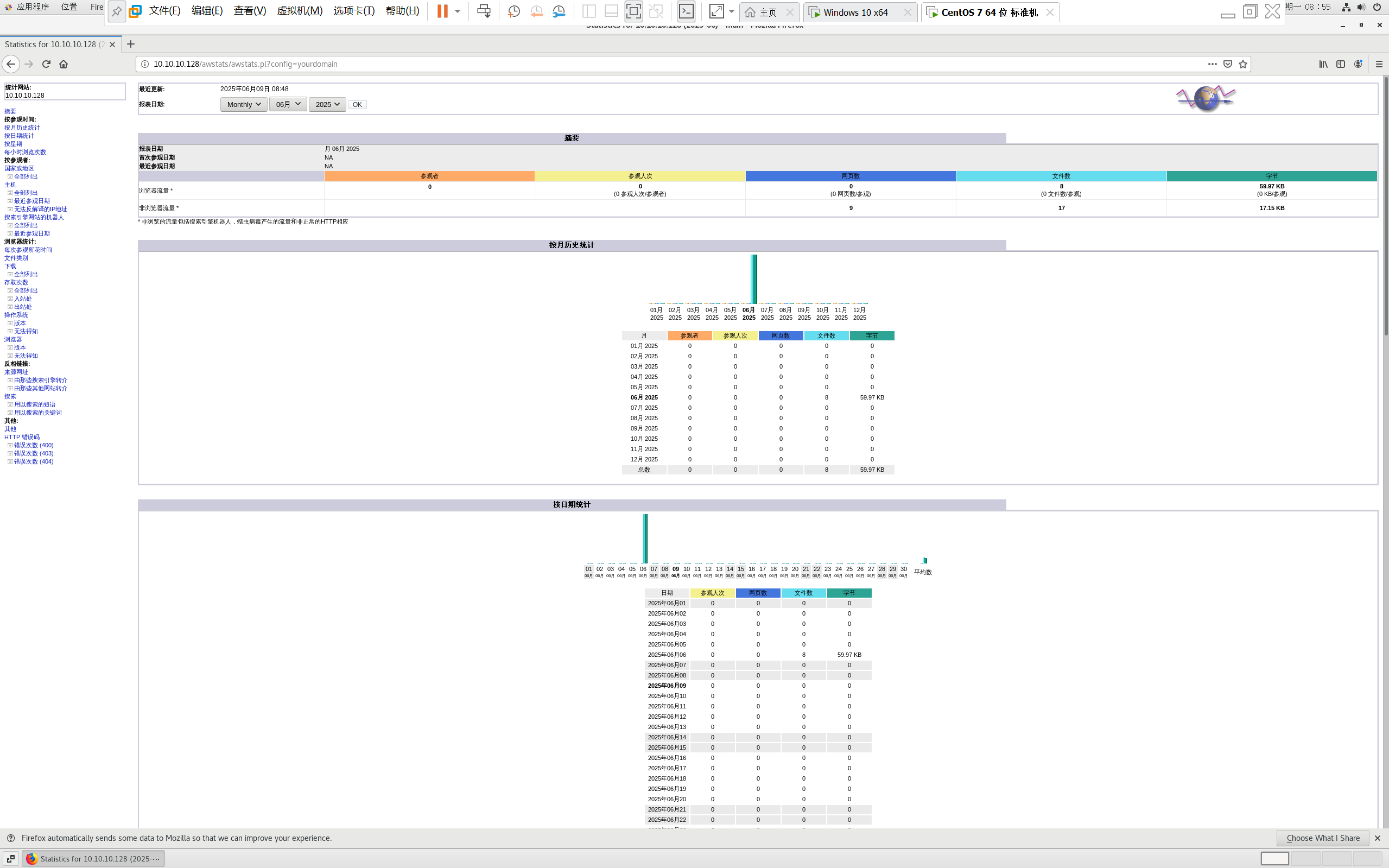
centos 7 部署awstats 网站访问检测
一、基础环境准备(两种安装方式都要做) bash # 安装必要依赖 yum install -y httpd perl mod_perl perl-Time-HiRes perl-DateTime systemctl enable httpd # 设置 Apache 开机自启 systemctl start httpd # 启动 Apache二、安装 AWStats࿰…...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...

Frozen-Flask :将 Flask 应用“冻结”为静态文件
Frozen-Flask 是一个用于将 Flask 应用“冻结”为静态文件的 Python 扩展。它的核心用途是:将一个 Flask Web 应用生成成纯静态 HTML 文件,从而可以部署到静态网站托管服务上,如 GitHub Pages、Netlify 或任何支持静态文件的网站服务器。 &am…...

多模态大语言模型arxiv论文略读(108)
CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文标题:CROME: Cross-Modal Adapters for Efficient Multimodal LLM ➡️ 论文作者:Sayna Ebrahimi, Sercan O. Arik, Tejas Nama, Tomas Pfister ➡️ 研究机构: Google Cloud AI Re…...
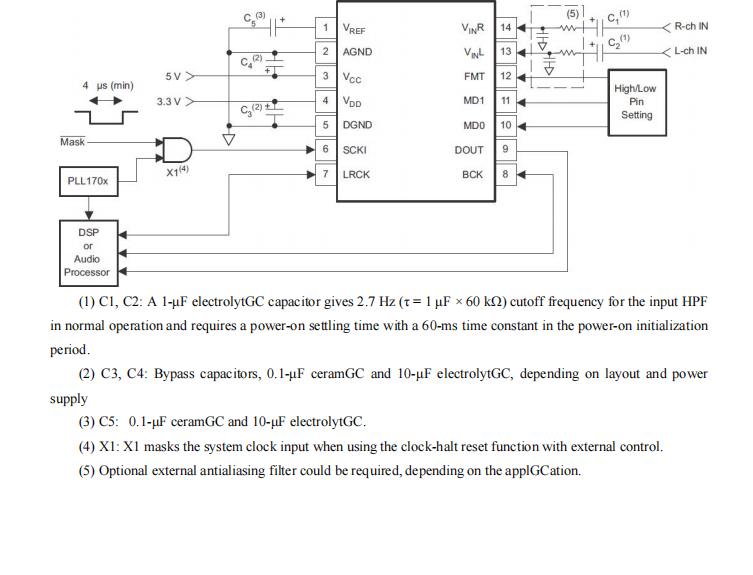
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...

AI,如何重构理解、匹配与决策?
AI 时代,我们如何理解消费? 作者|王彬 封面|Unplash 人们通过信息理解世界。 曾几何时,PC 与移动互联网重塑了人们的购物路径:信息变得唾手可得,商品决策变得高度依赖内容。 但 AI 时代的来…...
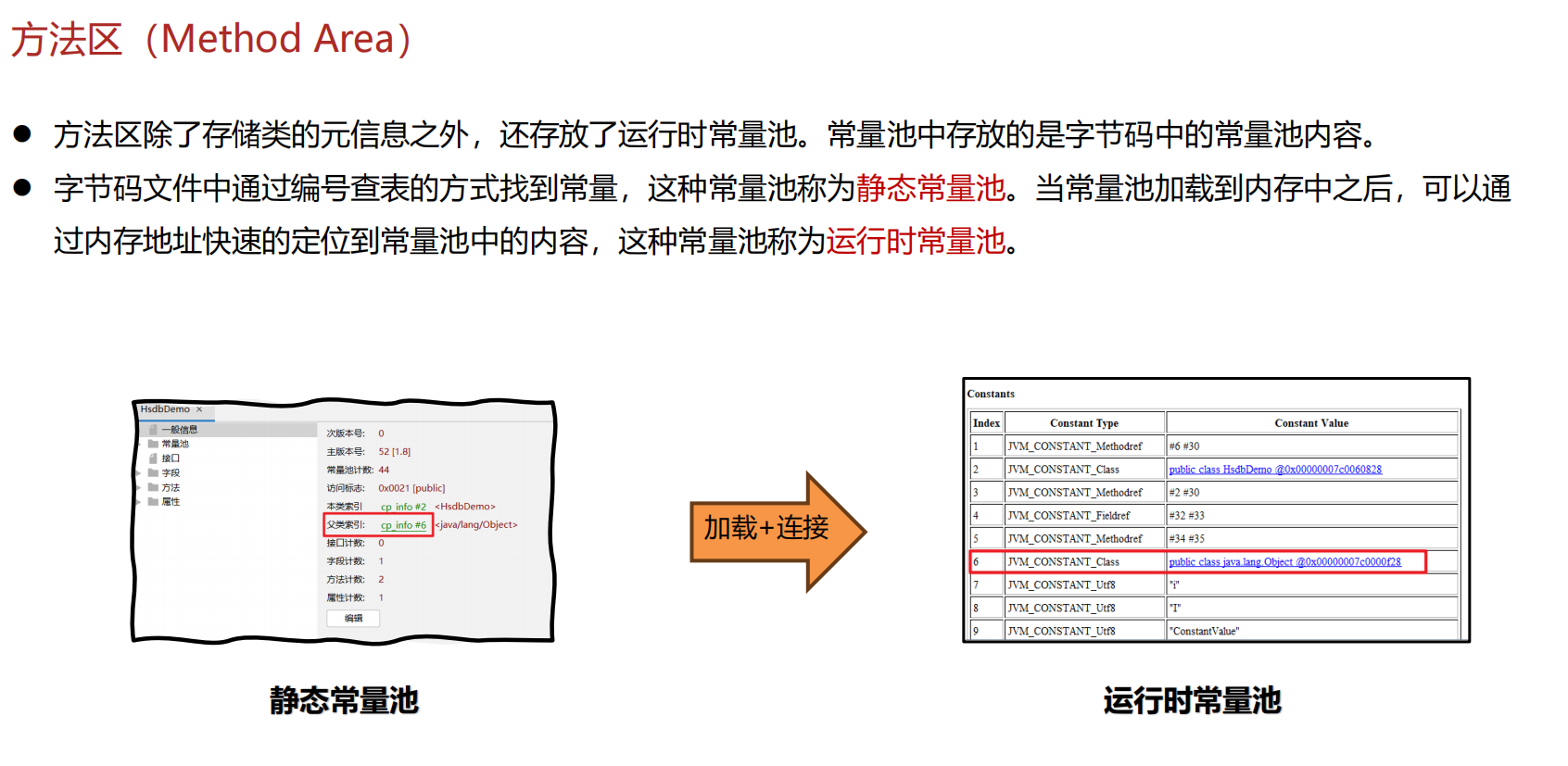
JVM 内存结构 详解
内存结构 运行时数据区: Java虚拟机在运行Java程序过程中管理的内存区域。 程序计数器: 线程私有,程序控制流的指示器,分支、循环、跳转、异常处理、线程恢复等基础功能都依赖这个计数器完成。 每个线程都有一个程序计数…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...

6.计算机网络核心知识点精要手册
计算机网络核心知识点精要手册 1.协议基础篇 网络协议三要素 语法:数据与控制信息的结构或格式,如同语言中的语法规则语义:控制信息的具体含义和响应方式,规定通信双方"说什么"同步:事件执行的顺序与时序…...

用js实现常见排序算法
以下是几种常见排序算法的 JS实现,包括选择排序、冒泡排序、插入排序、快速排序和归并排序,以及每种算法的特点和复杂度分析 1. 选择排序(Selection Sort) 核心思想:每次从未排序部分选择最小元素,与未排…...
