Python酷库之旅-第三方库Pandas(051)
目录
一、用法精讲
186、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing属性
186-1、语法
186-2、参数
186-3、功能
186-4、返回值
186-5、说明
186-6、用法
186-6-1、数据准备
186-6-2、代码示例
186-6-3、结果输出
187、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing属性
187-1、语法
187-2、参数
187-3、功能
187-4、返回值
187-5、说明
187-6、用法
187-6-1、数据准备
187-6-2、代码示例
187-6-3、结果输出
188、pandas.Series.value_counts方法
188-1、语法
188-2、参数
188-3、功能
188-4、返回值
188-5、说明
188-6、用法
188-6-1、数据准备
188-6-2、代码示例
188-6-3、结果输出
189、pandas.Series.align方法
189-1、语法
189-2、参数
189-3、功能
189-4、返回值
189-5、说明
189-6、用法
189-6-1、数据准备
189-6-2、代码示例
189-6-3、结果输出
190、pandas.Series.case_when方法
190-1、语法
190-2、参数
190-3、功能
190-4、返回值
190-5、说明
190-6、用法
190-6-1、数据准备
190-6-2、代码示例
190-6-3、结果输出
二、推荐阅读
1、Python筑基之旅
2、Python函数之旅
3、Python算法之旅
4、Python魔法之旅
5、博客个人主页



一、用法精讲
186、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing属性
186-1、语法
# 186、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing属性
property pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing
Return boolean if values in the object are monotonically increasing.Returns:
bool186-2、参数
无
186-3、功能
用于判断系列中的值是否按非递减顺序排列。
186-4、返回值
返回一个布尔值,如果系列中的值是单调递增的(即每个值都大于或等于前一个值),返回True;如果系列中的值不是单调递增的,返回False。
186-5、说明
在数据分析过程中,该属性可以用来快速检查数据的趋势,例如时间序列数据是否按时间递增、价格数据是否持续上升等。
186-6、用法
186-6-1、数据准备
无186-6-2、代码示例
# 186、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing属性
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个单调递增的系列
data_increasing = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# 判断系列中的值是否单调递增
is_monotonic_increasing = data_increasing.is_monotonic_increasing
print(f"系列值是否单调递增: {is_monotonic_increasing}")
# 创建一个非单调递增的系列
data_not_increasing = pd.Series([1, 3, 2, 4, 5])
# 判断系列中的值是否单调递增
is_monotonic_increasing = data_not_increasing.is_monotonic_increasing
print(f"系列值是否单调递增: {is_monotonic_increasing}") 186-6-3、结果输出
# 186、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing属性
# 系列值是否单调递增: True
# 系列值是否单调递增: False187、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing属性
187-1、语法
# 187、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing属性
property pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing
Return boolean if values in the object are monotonically decreasing.Returns:
bool187-2、参数
无
187-3、功能
用于判断系列中的值是否按递减顺序排列。
187-4、返回值
返回一个布尔值,如果系列中的值是单调递减的(即每个值都小于或等于前一个值),返回True;如果系列中的值不是单调递减的,返回False。
187-5、说明
在数据分析过程中,该属性可以用来快速检查数据的趋势,例如库存数据是否持续减少、销售数据是否下降等。
187-6、用法
187-6-1、数据准备
无187-6-2、代码示例
# 187、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing属性
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个单调递减的系列
data_decreasing = pd.Series([5, 4, 3, 2, 1])
# 判断系列中的值是否单调递减
is_monotonic_decreasing = data_decreasing.is_monotonic_decreasing
print(f"系列值是否单调递减: {is_monotonic_decreasing}")
# 创建一个非单调递减的系列
data_not_decreasing = pd.Series([5, 3, 4, 2, 1])
# 判断系列中的值是否单调递减
is_monotonic_decreasing = data_not_decreasing.is_monotonic_decreasing
print(f"系列值是否单调递减: {is_monotonic_decreasing}")
187-6-3、结果输出
# 187、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing属性
# 系列值是否单调递减: True
# 系列值是否单调递减: False188、pandas.Series.value_counts方法
188-1、语法
# 188、pandas.Series.value_counts方法
pandas.Series.value_counts(normalize=False, sort=True, ascending=False, bins=None, dropna=True)
Return a Series containing counts of unique values.The resulting object will be in descending order so that the first element is the most frequently-occurring element. Excludes NA values by default.Parameters:
normalize
bool, default False
If True then the object returned will contain the relative frequencies of the unique values.sort
bool, default True
Sort by frequencies when True. Preserve the order of the data when False.ascending
bool, default False
Sort in ascending order.bins
int, optional
Rather than count values, group them into half-open bins, a convenience for pd.cut, only works with numeric data.dropna
bool, default True
Don’t include counts of NaN.Returns:
Series188-2、参数
188-2-1、normalize(可选,默认值为False):如果设置为True,返回每个唯一值的相对频率;否则返回绝对值的计数。
188-2-2、sort(可选,默认值为True):如果设置为True,结果按计数值排序;如果设置为False,则按唯一值本身排序。
188-2-3、ascending(可选,默认值为False):如果设置为True,结果按升序排序;如果设置为False(默认值),则按降序排序。
188-2-4、bins(可选,默认值为None):如果设置为整数,则会将数据分成相应数量的区间,并返回每个区间的计数。
188-2-5、dropna(可选,默认值为True):如果设置为True(默认值),则不计算NaN值;如果设置为False,则包括NaN值的计数。
188-3、功能
188-3-1、计数每个唯一值的出现次数:默认情况下,返回每个唯一值的绝对频率。
188-3-2、排序:默认按计数值降序排列,但可以通过参数设置为升序或按唯一值本身排序。
188-3-3、相对频率:通过设置normalize=True,可以返回每个唯一值的相对频率(比例)。
188-3-4、分箱:通过设置bins参数,可以将数据分成若干区间,并返回每个区间的计数。
188-3-5、处理缺失值:默认情况下,NaN值不包括在计数中,但可以通过设置dropna=False包括NaN值的计数。
188-4、返回值
返回一个pandas.Series对象,索引是原始Series中的唯一值(或区间),值是每个唯一值(或区间)的计数。
188-5、说明
使用场景:
188-5-1、探索性数据分析(EDA):在数据分析的初始阶段,使用value_counts()可以快速了解数据的分布情况。例如,分析客户年龄分布、产品销售量分布等。
188-5-2、数据清洗:在处理缺失值和重复值时,可以使用value_counts()找出异常值或频次较低的值,从而帮助清洗数据。
188-5-3、分类数据分析:对于分类变量(如性别、地区、职业等),可以使用value_counts()计算每个类别的频次,以便进一步的统计分析或可视化。
188-5-4、数据验证:在数据验证过程中,使用value_counts()可以检查数据是否符合预期分布,例如检查试验组和对照组的样本量是否均衡。
188-5-5、异常检测:通过value_counts()计算频次,识别出频次异常的值,有助于发现数据中的潜在问题或异常情况。
188-5-6、特征工程:在特征工程中,可以使用value_counts()生成新的特征,例如,计算某个特征的出现次数,并将其作为新的特征添加到数据集中。
188-5-7、文本数据分析:在自然语言处理任务中,可以使用value_counts()统计词频,分析文本数据的关键词或常用词。
188-5-8、时间序列分析:对于时间序列数据,可以使用value_counts()统计不同时间段内事件的发生频次,例如统计每月的销售订单数量。
188-5-9、用户行为分析:在用户行为分析中,使用value_counts()可以统计用户的操作频次,例如统计用户登录、点击、购买等行为的次数。
188-6、用法
188-6-1、数据准备
无188-6-2、代码示例
# 188、pandas.Series.value_counts方法
# 188-1、基本用法
import pandas as pd
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4])
counts = data.value_counts()
print(counts, end='\n\n')# 188-2、返回相对频率
import pandas as pd
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4])
counts_normalized = data.value_counts(normalize=True)
print(counts_normalized, end='\n\n')# 188-3、按升序排列
import pandas as pd
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4])
counts_ascending = data.value_counts(ascending=True)
print(counts_ascending, end='\n\n')# 188-4、分箱计数
import pandas as pd
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4])
counts_bins = data.value_counts(bins=3)
print(counts_bins, end='\n\n')# 188-5、包括NaN值的计数
import pandas as pd
data_with_nan = pd.Series([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, None])
counts_with_nan = data_with_nan.value_counts(dropna=False)
print(counts_with_nan)188-6-3、结果输出
# 188、pandas.Series.value_counts方法
# 188-1、基本用法
# 4 4
# 3 3
# 2 2
# 1 1
# Name: count, dtype: int64# 188-2、返回相对频率
# 4 0.4
# 3 0.3
# 2 0.2
# 1 0.1
# Name: proportion, dtype: float64# 188-3、按升序排列
# 1 1
# 2 2
# 3 3
# 4 4
# Name: count, dtype: int64# 188-4、分箱计数
# (3.0, 4.0] 4
# (0.996, 2.0] 3
# (2.0, 3.0] 3
# Name: count, dtype: int64# 188-5、包括NaN值的计数
# 4.0 4
# 3.0 3
# 2.0 2
# 1.0 1
# NaN 1
# Name: count, dtype: int64189、pandas.Series.align方法
189-1、语法
# 189、pandas.Series.align方法
pandas.Series.align(other, join='outer', axis=None, level=None, copy=None, fill_value=None, method=_NoDefault.no_default, limit=_NoDefault.no_default, fill_axis=_NoDefault.no_default, broadcast_axis=_NoDefault.no_default)
Align two objects on their axes with the specified join method.Join method is specified for each axis Index.Parameters:
otherDataFrame or Series
join{‘outer’, ‘inner’, ‘left’, ‘right’}, default ‘outer’
Type of alignment to be performed.left: use only keys from left frame, preserve key order.right: use only keys from right frame, preserve key order.outer: use union of keys from both frames, sort keys lexicographically.inner: use intersection of keys from both frames, preserve the order of the left keys.axisallowed axis of the other object, default None
Align on index (0), columns (1), or both (None).levelint or level name, default None
Broadcast across a level, matching Index values on the passed MultiIndex level.copybool, default True
Always returns new objects. If copy=False and no reindexing is required then original objects are returned.NoteThe copy keyword will change behavior in pandas 3.0. Copy-on-Write will be enabled by default, which means that all methods with a copy keyword will use a lazy copy mechanism to defer the copy and ignore the copy keyword. The copy keyword will be removed in a future version of pandas.You can already get the future behavior and improvements through enabling copy on write pd.options.mode.copy_on_write = Truefill_valuescalar, default np.nan
Value to use for missing values. Defaults to NaN, but can be any “compatible” value.method{‘backfill’, ‘bfill’, ‘pad’, ‘ffill’, None}, default None
Method to use for filling holes in reindexed Series:pad / ffill: propagate last valid observation forward to next valid.backfill / bfill: use NEXT valid observation to fill gap.Deprecated since version 2.1.limitint, default None
If method is specified, this is the maximum number of consecutive NaN values to forward/backward fill. In other words, if there is a gap with more than this number of consecutive NaNs, it will only be partially filled. If method is not specified, this is the maximum number of entries along the entire axis where NaNs will be filled. Must be greater than 0 if not None.Deprecated since version 2.1.fill_axis{0 or ‘index’} for Series, {0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’} for DataFrame, default 0
Filling axis, method and limit.Deprecated since version 2.1.broadcast_axis{0 or ‘index’} for Series, {0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’} for DataFrame, default None
Broadcast values along this axis, if aligning two objects of different dimensions.Deprecated since version 2.1.Returns:
tuple of (Series/DataFrame, type of other)
Aligned objects.189-2、参数
189-2-1、other(必须):Series或DataFrame,表示需要与调用该方法的对象对齐的另一个对象。
189-2-2、join(可选,默认值为'outer'):{'outer', 'inner', 'left', 'right'},指定对齐方式。
189-2-2-1、'outer': 返回两个对象的并集,包含所有索引。
189-2-2-2、'inner': 返回两个对象的交集,仅包含共同的索引。
189-2-2-3、'left': 返回左侧对象的所有索引,缺失的右侧对象的索引用NaN填充。
189-2-2-4、'right': 返回右侧对象的所有索引,缺失的左侧对象的索引用NaN填充。
189-2-3、axis(可选,默认值为None):整数或字符串,仅在DataFrame中有效,指明对齐的轴,0表示行,1表示列。
189-2-4、level(可选,默认值为None):整数或字符串,如果对象是多层索引,可以使用此参数指定对齐的层次。
189-2-5、copy(可选,默认值为None):如果为True,则返回的对象会复制;如果为False,则返回的对象可能共享数据;如果为None,则根据数据的情况决定是否复制。
189-2-6、fill_value(可选,默认值为None):标量值,如果需要填充缺失的值,可以指定一个填充值。
189-2-7、method(可选):字符串,指定用于填充缺失数据的方法,如'pad'(前向填充)或者'backfill'(后向填充),如果不提供,默认不填充。
189-2-8、limit(可选):整数,用于限制填充的最大数量。
189-2-9、fill_axis(可选):整数或字符串,指定用于填充缺失值的轴,仅在DataFrame中有效。
189-2-10、broadcast_axis(可选):整数或字符串,指定用于广播操作的轴。
189-3、功能
对齐两个对象,使它们的索引对齐,并允许用户选择如何处理缺失的值。
189-4、返回值
返回一个元组,包含对齐后的两个对象,形如(left, right):
left是对齐后的左侧对象。right是对齐后的右侧对象。
如果fill_value被指定,而某些索引无法对齐,则缺失的部分将被填充为指定的值。
189-5、说明
使用场景:
189-5-1、数据合并与连接:在处理来自不同数据源的数据时,可能需要将它们合并成一个统一的格式,使用align可以确保所有数据都以相同的索引对齐,从而方便后续处理。
189-5-2、时间序列分析:在时间序列数据中,不同的时间序列可能会有不同的时间索引,使用align方法可以对齐它们,使得每个时间点的值能够方便地进行比较和计算。
189-5-3、数据补齐与填充:当某些数据缺失时,可以使用align方法结合fill_value进行补齐,确保后续分析时不会因为缺失值而出现错误。
189-5-4、计算与比较:在进行计算(如差异计算、比例计算等)时,需要对齐各个数据列的索引,使用align方法可以保证参与计算的数据都是对齐的,从而得到合理的结果。
189-5-5、处理多层索引:对于具有多层索引的Series或DataFrame,可以利用level参数对特定层次进行对齐,便于复杂数据结构的操作。
189-5-6、数据清理:在清理数据时,需要处理不一致的索引,在删减或重塑数据时,使用align可以确保所有列都有相同的索引结构。
189-6、用法
189-6-1、数据准备
无189-6-2、代码示例
# 189、pandas.Series.align方法
# 189-1、合并不同客户的销售数据
import pandas as pd
# 创建两个不同的销售数据 Series
sales_jan = pd.Series([200, 300], index=['Alice', 'Bob'])
sales_feb = pd.Series([150, 400, 250], index=['Alice', 'Charlie', 'Bob'])
# 使用align方法对齐两个Series
aligned_jan, aligned_feb = sales_jan.align(sales_feb, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("对齐后的1月销售数据:")
print(aligned_jan)
print("\n对齐后的2月销售数据:")
print(aligned_feb)
# 计算每个客户在1月和2月的销售总额
total_sales = aligned_jan + aligned_feb
print("\n客户总销售额:")
print(total_sales, end='\n\n')# 189-2、时间序列对比
import pandas as pd
# 创建两个时间序列数据Series
temperature = pd.Series([22, 24, 23], index=pd.date_range('2023-01-01', periods=3))
humidity = pd.Series([30, 32], index=pd.date_range('2023-01-01', periods=2))
# 使用align方法对齐两个时间序列
aligned_temp, aligned_hum = temperature.align(humidity, join='inner')
print("对齐后的温度数据:")
print(aligned_temp)
print("\n对齐后的湿度数据:")
print(aligned_hum)
# 计算温度与湿度的关系
correlation = aligned_temp.corr(aligned_hum)
print(f"\n温度与湿度的相关性:{correlation}", end='\n\n')# 189-3、处理多层索引
import pandas as pd
# 创建多层索引的Series
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('A', 1), ('A', 2), ('B', 1), ('B', 2)])
data1 = pd.Series([10, 20, 30, 40], index=index)
index2 = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('A', 1), ('B', 1), ('B', 3)])
data2 = pd.Series([5, 25, 15], index=index2)
# 对齐多层索引的Series
aligned_data1, aligned_data2 = data1.align(data2, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("对齐后的第一组数据:")
print(aligned_data1)
print("\n对齐后的第二组数据:")
print(aligned_data2)
# 计算对齐后数据的和
sum_data = aligned_data1 + aligned_data2
print("\n对齐后数据的和:")
print(sum_data, end='\n\n')# 189-4、数据清理与补齐
import pandas as pd
# 创建带有缺失值的Series
data1 = pd.Series([1, 2, None, 4], index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
data2 = pd.Series([None, 2, 3, None], index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'E'])
# 对齐两个Series,使用fill_value填充缺失值
aligned_data1, aligned_data2 = data1.align(data2, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("对齐后的数据1:")
print(aligned_data1)
print("\n对齐后的数据2:")
print(aligned_data2)
# 计算补齐后的总和
total = aligned_data1 + aligned_data2
print("\n补齐后的数据总和:")
print(total, end='\n\n')# 189-5、数据比较
import pandas as pd
# 创建两个带有不同客户的销售数据Series
sales_last_month = pd.Series([300, 500, 200], index=['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'])
sales_this_month = pd.Series([350, 450, 300, 100], index=['Alice', 'Bob', 'David', 'Charlie'])
# 对齐两个Series
aligned_last_month, aligned_this_month = sales_last_month.align(sales_this_month, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("上个月的销售数据:")
print(aligned_last_month)
print("\n这个月的销售数据:")
print(aligned_this_month)
# 计算销售增长
sales_growth = aligned_this_month - aligned_last_month
print("\n销售增长(这个月 - 上个月):")
print(sales_growth, end='\n\n')# 189-6、索引重命名与对齐
import pandas as pd
# 创建两个带有不同索引的Series
data_a = pd.Series([5, 10, 15], index=['x', 'y', 'z'])
data_b = pd.Series([1, 2, 3], index=['y', 'z', 'w'])
# 重命名索引以便于理解
data_a.index = ['Item_A1', 'Item_A2', 'Item_A3']
data_b.index = ['Item_B1', 'Item_B2', 'Item_B3']
# 使用align方法对齐
aligned_a, aligned_b = data_a.align(data_b, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("对齐后的数据A:")
print(aligned_a)
print("\n对齐后的数据B:")
print(aligned_b)
# 计算A和B的和
total_data = aligned_a + aligned_b
print("\n对齐后数据A和B的和:")
print(total_data, end='\n\n')# 189-7、填补缺失数据
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个带有缺失值的Series
series_a = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, None], index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
series_b = pd.Series([None, 2, None, 4, 5], index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'E', 'F'])
# 对齐两个Series,使用fill_value填充缺失值
aligned_a, aligned_b = series_a.align(series_b, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("对齐后的数据A:")
print(aligned_a)
print("\n对齐后的数据B:")
print(aligned_b)
# 计算合并后的序列总和
filled_data = aligned_a + aligned_b
print("\n填补缺失值后的数据总和:")
print(filled_data, end='\n\n')# 189-8、在数据科学项目中的应用
import pandas as pd
# 创建Product价格数据和销量数据
prices = pd.Series([100, 150, 200], index=['Product_A', 'Product_B', 'Product_C'])
sales = pd.Series([10, 5, 8, 3], index=['Product_A', 'Product_B', 'Product_D', 'Product_C'])
# 对齐价格和销量数据
aligned_prices, aligned_sales = prices.align(sales, join='outer', fill_value=0)
print("对齐后的价格数据:")
print(aligned_prices)
print("\n对齐后的销量数据:")
print(aligned_sales)
# 计算每个产品的销售收入
revenue = aligned_prices * aligned_sales
print("\n每个产品的销售收入:")
print(revenue, end='\n\n')189-6-3、结果输出
# 189、pandas.Series.align方法
# 189-1、合并不同客户的销售数据
# 对齐后的1月销售数据:
# Alice 200.0
# Bob 300.0
# Charlie 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后的2月销售数据:
# Alice 150
# Bob 250
# Charlie 400
# dtype: int64
#
# 客户总销售额:
# Alice 350.0
# Bob 550.0
# Charlie 400.0
# dtype: float64# 189-2、时间序列对比
# 对齐后的温度数据:
# 2023-01-01 22
# 2023-01-02 24
# Freq: D, dtype: int64
#
# 对齐后的湿度数据:
# 2023-01-01 30
# 2023-01-02 32
# Freq: D, dtype: int64
#
# 温度与湿度的相关性:0.9999999999999999# 189-3、处理多层索引
# 对齐后的第一组数据:
# A 1 10.0
# 2 20.0
# B 1 30.0
# 2 40.0
# 3 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后的第二组数据:
# A 1 5.0
# 2 0.0
# B 1 25.0
# 2 0.0
# 3 15.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后数据的和:
# A 1 15.0
# 2 20.0
# B 1 55.0
# 2 40.0
# 3 15.0
# dtype: float64# 189-4、数据清理与补齐
# 对齐后的数据1:
# A 1.0
# B 2.0
# C 0.0
# D 4.0
# E 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后的数据2:
# A 0.0
# B 2.0
# C 3.0
# D 0.0
# E 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 补齐后的数据总和:
# A 1.0
# B 4.0
# C 3.0
# D 4.0
# E 0.0
# dtype: float64# 189-5、数据比较
# 上个月的销售数据:
# Alice 300.0
# Bob 500.0
# Charlie 200.0
# David 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 这个月的销售数据:
# Alice 350
# Bob 450
# Charlie 100
# David 300
# dtype: int64
#
# 销售增长(这个月 - 上个月):
# Alice 50.0
# Bob -50.0
# Charlie -100.0
# David 300.0
# dtype: float64# 189-6、索引重命名与对齐
# 对齐后的数据A:
# Item_A1 5.0
# Item_A2 10.0
# Item_A3 15.0
# Item_B1 0.0
# Item_B2 0.0
# Item_B3 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后的数据B:
# Item_A1 0.0
# Item_A2 0.0
# Item_A3 0.0
# Item_B1 1.0
# Item_B2 2.0
# Item_B3 3.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后数据A和B的和:
# Item_A1 5.0
# Item_A2 10.0
# Item_A3 15.0
# Item_B1 1.0
# Item_B2 2.0
# Item_B3 3.0
# dtype: float64# 189-7、填补缺失数据
# 对齐后的数据A:
# A 1.0
# B 2.0
# C 3.0
# D 0.0
# E 0.0
# F 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后的数据B:
# A 0.0
# B 2.0
# C 0.0
# D 0.0
# E 4.0
# F 5.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 填补缺失值后的数据总和:
# A 1.0
# B 4.0
# C 3.0
# D 0.0
# E 4.0
# F 5.0
# dtype: float64# 189-8、在数据科学项目中的应用
# 对齐后的价格数据:
# Product_A 100.0
# Product_B 150.0
# Product_C 200.0
# Product_D 0.0
# dtype: float64
#
# 对齐后的销量数据:
# Product_A 10
# Product_B 5
# Product_C 3
# Product_D 8
# dtype: int64
#
# 每个产品的销售收入:
# Product_A 1000.0
# Product_B 750.0
# Product_C 600.0
# Product_D 0.0
# dtype: float64190、pandas.Series.case_when方法
190-1、语法
# 190、pandas.Series.case_when方法
pandas.Series.case_when(caselist)
Replace values where the conditions are True.Parameters:
caselistA list of tuples of conditions and expected replacements
Takes the form: (condition0, replacement0), (condition1, replacement1), … . condition should be a 1-D boolean array-like object or a callable. If condition is a callable, it is computed on the Series and should return a boolean Series or array. The callable must not change the input Series (though pandas doesn`t check it). replacement should be a 1-D array-like object, a scalar or a callable. If replacement is a callable, it is computed on the Series and should return a scalar or Series. The callable must not change the input Series (though pandas doesn`t check it).New in version 2.2.0.Returns:
Series190-2、参数
190-2-1、caselist(必须):一个包含条件和值的列表,每个元素都是一个元组(condition, value),其中,condition是一个返回布尔值的表达式或函数,用于判断条件是否满足;value是当条件满足时返回的值。
190-3、功能
根据一系列条件来设置Series中每个元素的值,并返回一个新的Series。
190-4、返回值
返回一个新的Series对象。
190-5、说明
无
190-6、用法
190-6-1、数据准备
无190-6-2、代码示例
# 190、pandas.Series.case_when方法
import pandas as pd
c = pd.Series([6, 7, 8, 9], name='c')
a = pd.Series([0, 0, 1, 2])
b = pd.Series([0, 3, 4, 5])
c.case_when(caselist=[(a.gt(0), a), (b.gt(0), b)])
print(c)190-6-3、结果输出
# 190、pandas.Series.case_when方法
# 0 6
# 1 7
# 2 8
# 3 9
# Name: c, dtype: int64二、推荐阅读
1、Python筑基之旅
2、Python函数之旅
3、Python算法之旅
4、Python魔法之旅
5、博客个人主页
相关文章:

Python酷库之旅-第三方库Pandas(051)
目录 一、用法精讲 186、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_increasing属性 186-1、语法 186-2、参数 186-3、功能 186-4、返回值 186-5、说明 186-6、用法 186-6-1、数据准备 186-6-2、代码示例 186-6-3、结果输出 187、pandas.Series.is_monotonic_decreasing属性 187…...

linux timestamp
驱动或应用中获取时间戳的接口。 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <time.h> #include <sys/time.h> #if 0 #include <linux/ktime.h> /* 内核驱动中获取时间戳 */ static ktime_t get_kernel_time…...

Vue.js 搭建大屏可视化项目
引言 在数字化转型的时代背景下,大屏可视化项目因其直观的数据展示和实时的业务监控能力而变得日益重要。Vue.js,以其简洁的语法、高效的虚拟DOM和强大的组件化能力,成为了构建大屏可视化应用的首选框架之一。本文将从零开始,引导…...
Linux:进程信号(二.信号的保存与处理、递达、volatile关键字、SIGCHLD信号)
上次介绍了:(Linux:进程信号(一.认识信号、信号的产生及深层理解、Term与Core))[https://blog.csdn.net/qq_74415153/article/details/140624810] 文章目录 1.信号保存1.1递达、未决、阻塞等概念1.2再次理解信号产生与保存1.3信号…...
最值得推荐的5个AI大模型API
在这个以人工智能为主导的新时代,选择一个卓越的AI模型API接口,对于企业和个人在AI驱动的商业和技术革新中取得成功至关重要。 在人工智能的浪潮中,大型AI模型API接口正成为推动技术创新和业务发展的重要力量。随着2024年技术的持续进步和应用…...
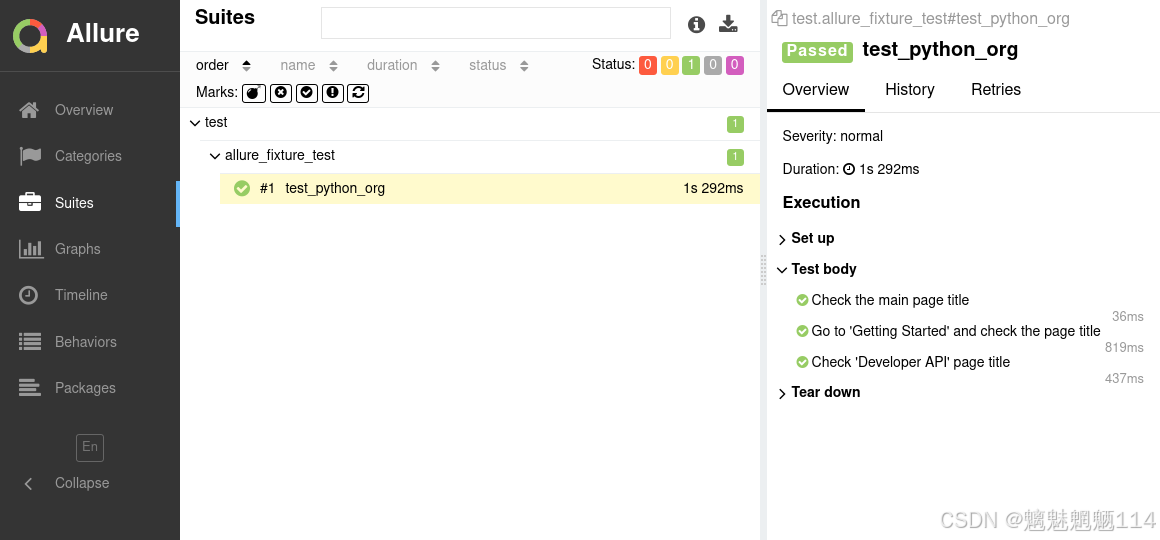
PyTest+Allure生成测试报告
一、官网文档(权威) 1. Allure Report 官网:Allure Report Docs — Introduction 2. Allure GitHub地址:GitHub - allure-framework/allure2: Allure Report is a flexible, lightweight multi-language test reporting tool. It …...
 - 编写接收程序、添加frame - Linux)
ROS2教程(10) - 编写接收程序、添加frame - Linux
注意 : 本篇文章接上节 (点击此处跳转到上节) 编写接收程序 cpp <the_work_ws>/src/learning_tf2_cpp/src/turtle_tf2_listener.cpp #include <chrono> #include <functional> #include <memory> #include <string>#include "geometry_…...

Arraylist与LinkedList的区别
Arraylist 概念 Arraylist非线程安全Arraylist 底层使用的是Object数组ArrayList 采用数组存储,插入和删除元素的时间复杂度受元素位置的影响ArrayList 支持快速随机访问,就是通过元素的序号快速获取元素对象ArrayList的空间浪费主要体现在列表的结尾会预留一定的容…...

Nestjs使用Redis的最佳实践
前几天在项目中有用到Redis JWT实现服务端对token的主动删除(退出登录功能)。故此介绍下如何在Nestjs中使用Redis,并做下总结。 知识准备 了解Redis - 网上很多简介。了解Nestjs如何使用jwt生成token - 可移步看下我之前的文章 效果展示 一、mac安装与使用 示…...
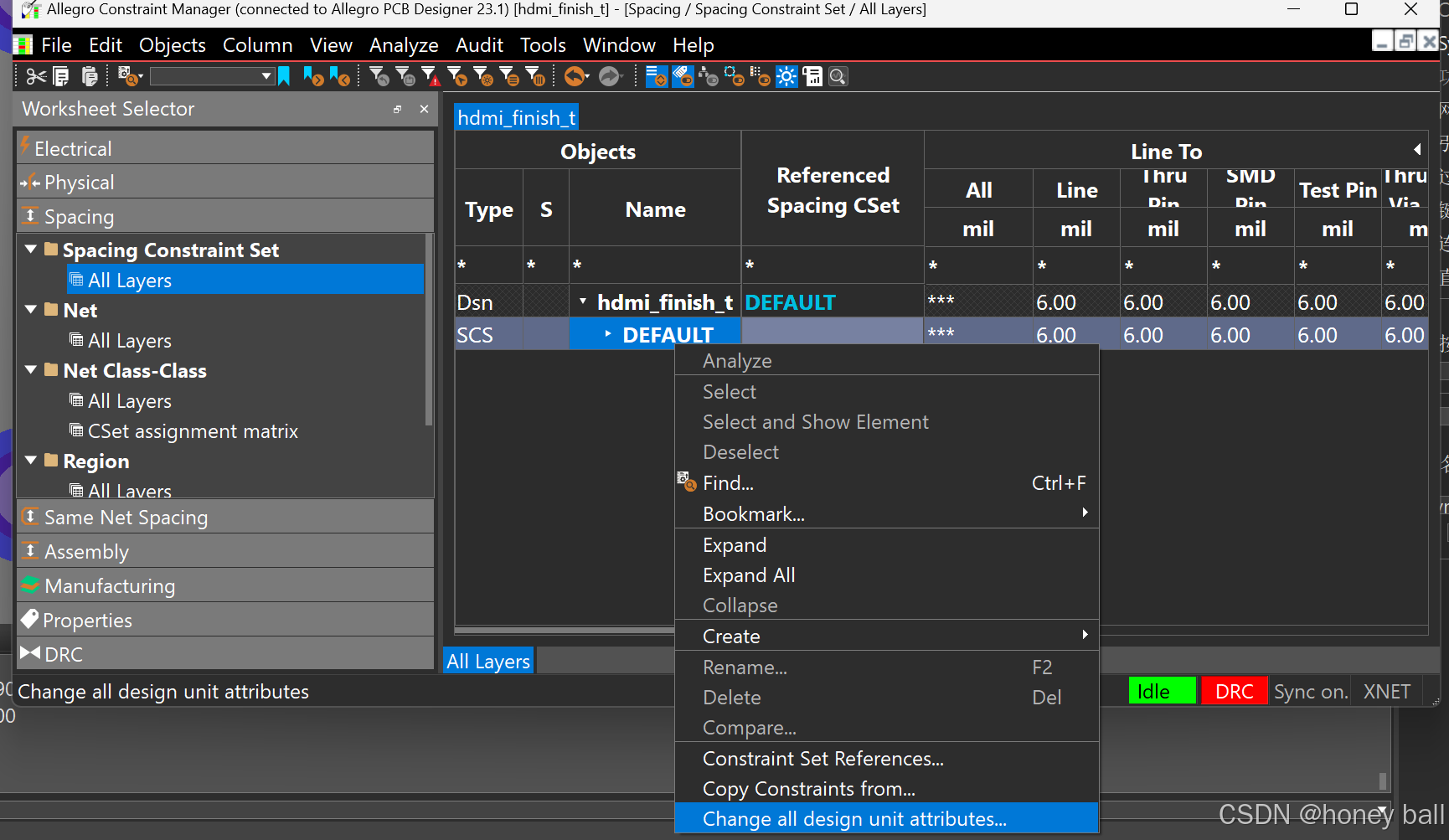
Cadence23学习笔记(十四)
ARC就是圆弧走线的意思: 仅打开网络的话可以只针对net进行修改走线的属性: 然后现在鼠标左键点那个走线,那个走线就会变为弧形: 添加差分对: 之后,分别点击两条线即可分配差分对: 选完差分对之后…...
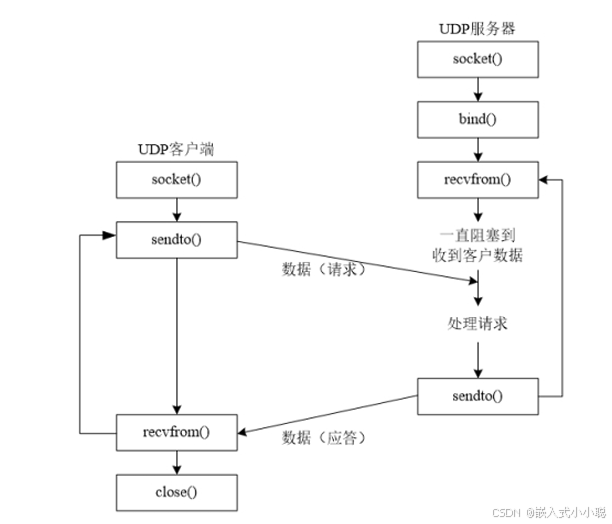
socket 编程
1. socket 套接字 Socket 是一个用于网络通信的技术。Socket 通信允许客户端——服务器之间进行双向通信。它可以使任何客户端机器连接到任何服务器,安装在客户端和服务器两侧的程序就可以实现双向的通信。Socket的作用就是把连接两个计算机的通信软件“中间接”起来…...

如何使用 HTTPie 进行高效的 HTTP 请求
如何使用 HTTPie 进行高效的 HTTP 请求 引言 HTTPie 是一个命令行 HTTP 客户端,它以其简洁的语法和人性化的输出格式赢得了广大开发者的喜爱。与 curl 相比,HTTPie 提供了更加直观和用户友好的接口,使得执行 HTTP 请求变得轻松愉快。本文将…...
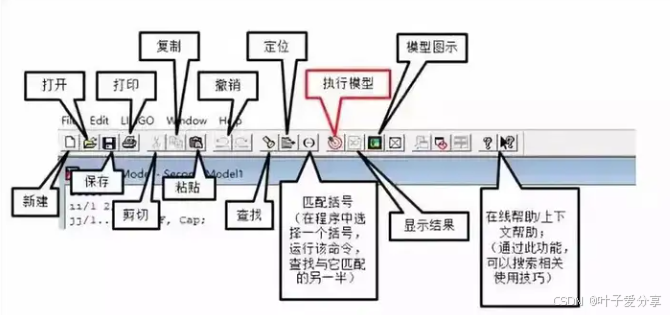
Lingo求解器百度云下载 ling 8.0/lingo 18安装包资源分享
如大家所熟悉的,Lingo是Linear Interaction and General Optimizer的缩写,中文名称为“交互式线性和通用优化求解器”,是一套专门用于求解最优化问题的软件包。 在大部分人认知里,Lingo可用于求解线性规划、二次规划、整数规划、…...
文献综述如何为研究的理论框架做出贡献
VersaBot一键生成文献综述 文献综述在几个关键方面对塑造和巩固研究的理论框架起着至关重要的作用; 1. 识别相关理论和概念: 通过对现有研究的探索,您将遇到与您的主题相关的突出理论和概念。这些可以作为您自己的理论框架的构建块。 2. 理…...
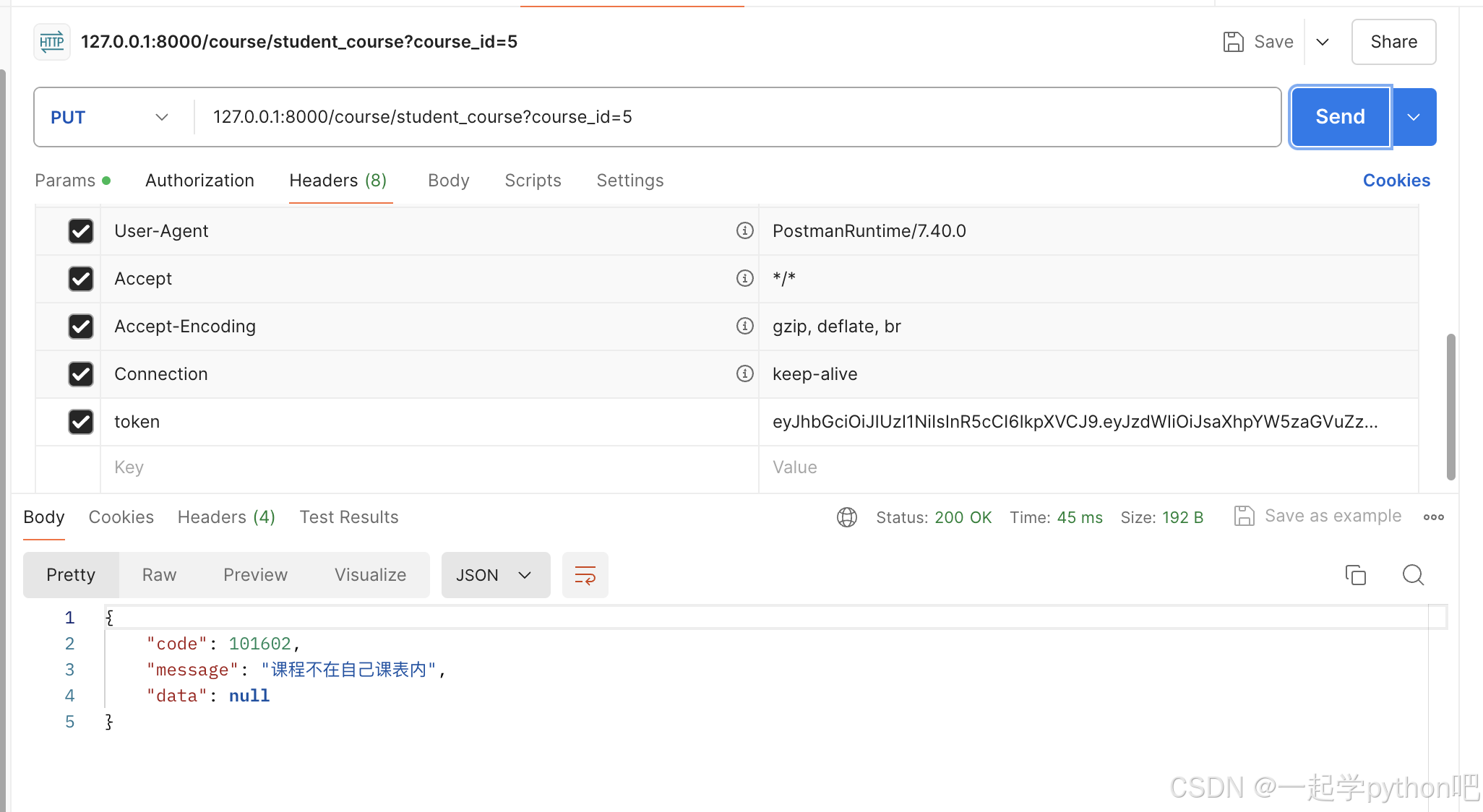
FastAPI(七十九)实战开发《在线课程学习系统》接口开发-- 加入课程和退出课程
源码见:"fastapi_study_road-learning_system_online_courses: fastapi框架实战之--在线课程学习系统" 加入课程 我们先看下加入课程 1.是否登录 2.课程是否存在 3.是否已经存在 4.添加 首先实现逻辑 def get_student_course(db: Session, course: int…...

【赛事推荐】2024中国高校计算机大赛人工智能创意赛
“中国高校计算机大赛”(China Collegiate Computing Contest,简称C4)是面向全国高校各专业在校学生的科技类竞赛活动,于2016年由教育部高等学校计算机类专业教学指导委员会、教育部高等学校大学软件工程专业教学指导委员会、教育…...

C++沉思:预处理和编译
预处理和编译 条件编译源代码使用方式典型示例原理 使用static_assert执行编译时断言检查使用方式原理 在C中,编译是将源代码转换为机器代码并组织在目标文件中,然后将目标文件链接在一起生成可执行文件的过程。编译器实际上一次只处理一个文件ÿ…...

交通数据处理-计算途径某些路段的车辆数
根据车辆的运行轨迹,计算先经过某些路段,再经过某些路段的车辆数。 欢迎关注本人公众号--交通数据探索师 如下表, 其中:vehicle: 车辆编号;route: 车辆轨迹。 以第一行为例,车辆car1按顺序经过了路段123…...

从0到1入门系列 | 崖山公开课再加码,三小时带你入门崖山数据库!
对不断更新的技术心生迷茫 不知如何正确的提升自己? 对新兴的国产数据库领域充满好奇 却不知从何入手? 崖山专家团队精心筹备 《从0到1入门》系列直播课 6节课 三小时 助力数据库小白变身技术高手 掌握最前沿的数据库技术 现在开始 开启职场“金…...

Powershell自定义带参数的别名
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 前言一、函数二、使用步骤总结 前言 之前写了一篇文章定义别名让powershell尽可能接近Unix风格,增强两者的互操作性,今天给出方法可以定义带…...
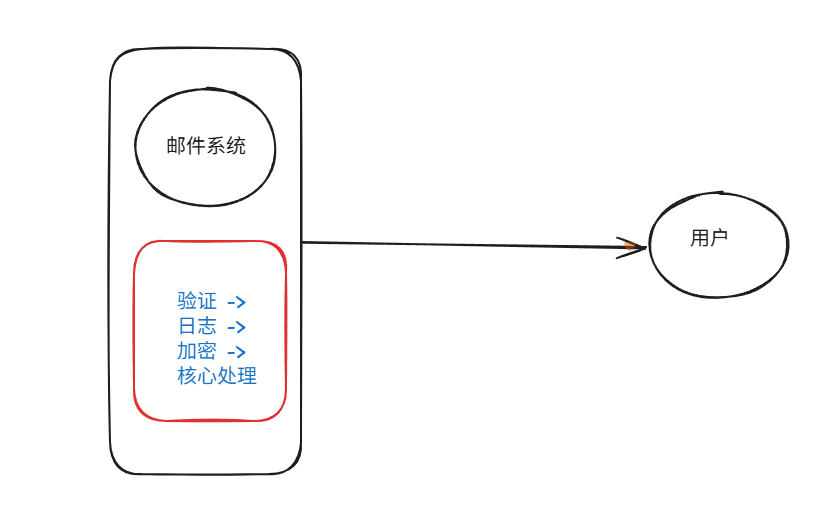
装饰模式(Decorator Pattern)重构java邮件发奖系统实战
前言 现在我们有个如下的需求,设计一个邮件发奖的小系统, 需求 1.数据验证 → 2. 敏感信息加密 → 3. 日志记录 → 4. 实际发送邮件 装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其…...

iOS 26 携众系统重磅更新,但“苹果智能”仍与国行无缘
美国西海岸的夏天,再次被苹果点燃。一年一度的全球开发者大会 WWDC25 如期而至,这不仅是开发者的盛宴,更是全球数亿苹果用户翘首以盼的科技春晚。今年,苹果依旧为我们带来了全家桶式的系统更新,包括 iOS 26、iPadOS 26…...
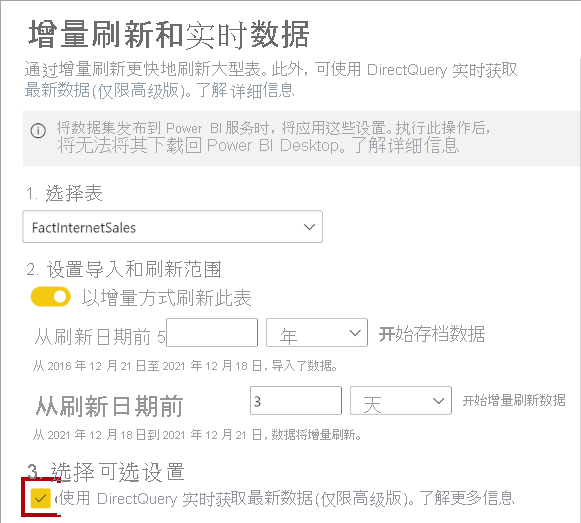
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-选择 Power BI 模型框架【附练习数据】
微软PowerBI考试 PL300-选择 Power BI 模型框架 20 多年来,Microsoft 持续对企业商业智能 (BI) 进行大量投资。 Azure Analysis Services (AAS) 和 SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) 基于无数企业使用的成熟的 BI 数据建模技术。 同样的技术也是 Power BI 数据…...

Auto-Coder使用GPT-4o完成:在用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来3天涨跌的分类任务
通过akshare库,获取股票数据,并生成TabPFN这个模型 可以识别、处理的格式,写一个完整的预处理示例,并构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务 用TabPFN这个模型构建一个预测未来 3 天股价涨跌的分类任务,进行预测并输…...

【ROS】Nav2源码之nav2_behavior_tree-行为树节点列表
1、行为树节点分类 在 Nav2(Navigation2)的行为树框架中,行为树节点插件按照功能分为 Action(动作节点)、Condition(条件节点)、Control(控制节点) 和 Decorator(装饰节点) 四类。 1.1 动作节点 Action 执行具体的机器人操作或任务,直接与硬件、传感器或外部系统…...
ArcGIS Pro制作水平横向图例+多级标注
今天介绍下载ArcGIS Pro中如何设置水平横向图例。 之前我们介绍了ArcGIS的横向图例制作:ArcGIS横向、多列图例、顺序重排、符号居中、批量更改图例符号等等(ArcGIS出图图例8大技巧),那这次我们看看ArcGIS Pro如何更加快捷的操作。…...

Java面试专项一-准备篇
一、企业简历筛选规则 一般企业的简历筛选流程:首先由HR先筛选一部分简历后,在将简历给到对应的项目负责人后再进行下一步的操作。 HR如何筛选简历 例如:Boss直聘(招聘方平台) 直接按照条件进行筛选 例如:…...
)
.Net Framework 4/C# 关键字(非常用,持续更新...)
一、is 关键字 is 关键字用于检查对象是否于给定类型兼容,如果兼容将返回 true,如果不兼容则返回 false,在进行类型转换前,可以先使用 is 关键字判断对象是否与指定类型兼容,如果兼容才进行转换,这样的转换是安全的。 例如有:首先创建一个字符串对象,然后将字符串对象隐…...
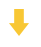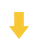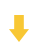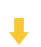
初探Service服务发现机制
1.Service简介 Service是将运行在一组Pod上的应用程序发布为网络服务的抽象方法。 主要功能:服务发现和负载均衡。 Service类型的包括ClusterIP类型、NodePort类型、LoadBalancer类型、ExternalName类型 2.Endpoints简介 Endpoints是一种Kubernetes资源…...
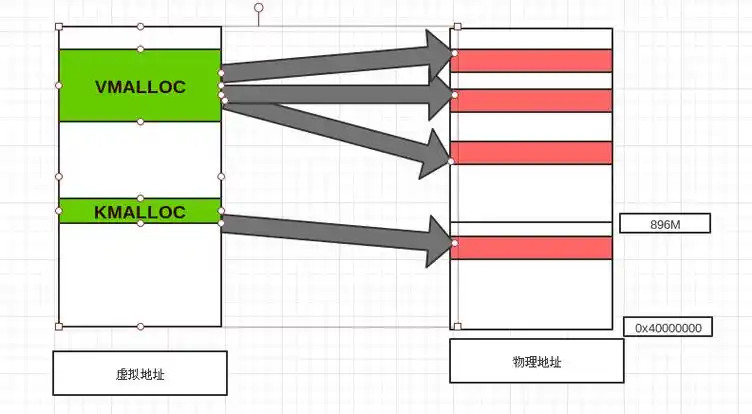
Linux 内存管理实战精讲:核心原理与面试常考点全解析
Linux 内存管理实战精讲:核心原理与面试常考点全解析 Linux 内核内存管理是系统设计中最复杂但也最核心的模块之一。它不仅支撑着虚拟内存机制、物理内存分配、进程隔离与资源复用,还直接决定系统运行的性能与稳定性。无论你是嵌入式开发者、内核调试工…...
