值得记忆的STL常用算法,分分钟摆脱容器调用的困境,以vector为例,其余容器写法类似
STL常用算法
概述:
-
算法主要是由头文件
<algorithm><functional><numeric>组成 -
<algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等 -
<nuneric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数 -
<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象
1.常用遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each遍历容器
transform搬运容器到另一个容器
1.for_each
功能描述:
实现遍历容器
函数原型:
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func);
遍历算法 遍历容器中所有元素
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
_func函数或者函数对象
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用遍历算法 for_each
//普通函数
void print01(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}
//仿函数
class print02
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:for_each在实实际开发中是最常用遍历算法,需要熟练掌握
2.transform
功能描述:
搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
tansform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func);
beg1源容器开始迭代器
end1源容器结束迭代器
beg2目标容器开始迭代器
_func函数或者函数对象
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用遍历算法 transform
class Transform
{
public:int operator()(int v){return v;}
};
class print
{
public:int operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>vTarget;//目标容器vTarget.resize(v.size());//目标容器需要提前开辟空间transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}2.常用查找算法
算法简介:
find查找元素
find_if按条件查找
adjacent_find查找相邻重复元素
binary_search二分查找
count统计元素个数
count_if按条件统计元素个数
1.find
功能描述:
查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型:
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
value查找的元素
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//常用的查找算法
//find
//查找 内指数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找 容器中 是否有 5 这个元素vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到了!" << *it << endl;}
}
//查找 自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//重载 == 使底层find知道如何对比person数据类型bool operator==(const Person & p){if(this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("zhangsan",18);Person p2("lisi",19);Person p3("wangwu",20);Person p4("zaholiu",21);Person p5("tangqi",22);//放入容器v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);Person p("wangwu",20);vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p);if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到了:" << "姓名为:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄为:" << it->m_Age << endl; }
}
int main()
{test01();test02();return 0;
}2.find_if
功能描述:
按条件查找元素
函数原型:
find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
_Pred函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用查找算法 find_if
//1.查找内置数据类型
class GreaterFive
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 5;}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到大于5的数字:" << *it << endl;}
}
//2.查找自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
class GreaterT
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p){return p.m_Age > 20;}
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("zhangsan",19);Person p2("lisi",20);Person p3("wangwu",21);Person p4("zhaoliu",22);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);//找年龄大于20岁的vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterT());if(it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到了姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;}
}
int main()
{test01();test02();return 0;
}3.adjacent_find
功能描述:
查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
adjacent_find(iterator beg,iterator end);
查找相邻里复元素返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用查找算法 adjacent_find
void test()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);vector<int>::iterator pos = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if(pos == v.end()){cout << "未找到相邻重复元素" << endl;}else{cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *pos << endl;}
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}4.binary_search
功能描述:
查找指定元素是否存在
函数原型:
bool binary_search(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
查找指定的元素,查到返回true否则false
注意:在无序序列中不可用
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
value查找的元素
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法 binary_search
void test()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找容器中是否有9 元素bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if(ret){cout << "找到了元素" << endl;}else{cout << "没有找到" << endl;}
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:二分查找法查找效率很高,值得注意的是查找的容器中元素必须得是有序序列
5.count
功能描述:
统计元素个数
函数原型:
count(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
统计元素出现次数
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
value统计的元素
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用查找算法 count
//1.统计内置数据类型
void test1()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);cout << "3的元素个数:" << num << endl;
}
//2.统计自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p){if(this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
void test2()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("aaa",18);Person p2("bbb",19);Person p3("ccc",20);Person p4("ddd",18);Person p5("eee",18);Person p6("fff",18);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);v.push_back(p6);Person p7("ggg",18);int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p7);cout << "和p7年龄一样的有" << num << "个" << endl;
}
int main()
{test1();test2();return 0;
}6.count_if
功能描述:
按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
按条件统计元素出现次数
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
_Pred谓词
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//1.内置数据类型统计
class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 20;}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}
//2.自定义的数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){this->m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person&p){if(this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
class AgeGreater18
{
public:bool operator()(const Person & p){return p.m_Age == 18;}
};
void test1()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("zhangsan",18);Person p2("lisi",18);Person p3("wangwu",19);Person p4("zhaoliu",18);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeGreater18());cout << "18岁的人数:" << num << "个" << endl;
}
int main()
{test();test1();return 0;
}3.常用排序算法
算法简介:
sort对容器内元素进行排序
random_shuffle洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
merge容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
reverse反转指定范围的元素
1.sort
功能描述:
对容器内元素进行排序
函数原型:
sort(iterator beg,iterator end,Pred);按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
_Pred谓词
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);//利用sort进行升序sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;//改为降序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());//greater内建函数for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}2.random_shuffle
功能描述:
洗牌指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:
random_shuffle(iterator beg,iterator end);
指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
//常用排序算法 random_shuffle
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//利用洗牌算法 打乱顺序random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:random_shuffle洗牌算法比较实用,使用时记得加随机数种子
3.merge
功能描述:
两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
函数原型:
merge(iterator beg1,iterator end1,iterator beg2,iterator end2,iterator dest);
容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
注意:两个容器必须是有序的,而且两个均为升序或降序
beg1容器1开始迭代器
end1容器1结束迭代器
beg2容器2开始迭代器
end2客器2结束送代器
dest目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用的排序算法 merge
//仿函数
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v1;vector<int>v2;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i+1);}//目标容器vector<int>vTarget;vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}4.reverse
功能描述:
将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型: reverse(iterator beg,iterator end);
反转指定范围的元素
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用排序算法 reverse
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}cout << "反转前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;reverse(v.begin(), v.end());cout << "反转后:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}4.常用拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
copy容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
replace将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
replace_if容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素
swap互换两个容器的元素
1.swap
功能描述:
容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
函数原型:
copy(iterator beg,iterator end,iterator dest);
按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到就返回结束迭代器位置
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
dest目标超始迭代器
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用拷贝和替换算法 copy
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v1;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);}vector<int>v2;v2.resize(v1.size());copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}2.replace
功能描述:
将容器内指定范围的旧元素核改为新元素
函数原型:
replace(iterator beg,iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue);
将区间内旧元素替换成新元素
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
oldvalue旧元素
newvalue新元素
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用拷贝和替换算法replace
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(20);cout << "替换前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;//将20替换为200replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 20, 200);cout << "替换后:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}3.replace_if
功能描述:
将区间内满足条件的元素,苔换成指定元素
函数原型:
replace_if(iterator beg,iterator end,_pred,newvalue);
按条件换元素,满足条件的替换成指定元素
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
_pred谓词
newvalue替换的新元素
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用拷贝和替换算法replace_if
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
class Greater
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 30;}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(20);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(10);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(20);cout << "替换前:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;//将大于30的替换为100replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater(), 100);cout << "替换后:" << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:replace_if按条件查找,可以利用仿函数灵活筛选满足的条件
4.swap
功能描述:
互换两个容器的元素
函数原型: swap(container c1,container c2);互换两个容器的元素
c1容器1
c2容器2
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用拷贝和替换算法 swap
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v1;vector<int>v2;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 100);}cout << "交换前:" << endl;for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print());cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print());cout << endl;cout << "--------------------------" << endl;cout << "交换后:" << endl;swap(v1, v2);for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print());cout << endl;for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}5.常用算法生成算法
注意:
算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为include<numeric>
算法简介: accumulate计算容器元素累计总和
fill向容器中添加元素
1.accumulate
功能描述:
计算区间内容器元素累计总和
函数原型: accumulate(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
计算容器元素累计总和
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
value起始值
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>
using namespace std;
//常用算法生成算法
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;for(int i = 0;i <= 100; i++){v.push_back(i);}int total = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);cout << "累计求和值为:" << total << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:accumulate使用时头文件注意是numeric,这个算法很实用
2.fill
功能描述:
向容器中填充相定的元素
函数原型:
fill(iterator beg,iterator end,value);
向容器中填充元素
beg开始迭代器
end结束迭代器
value填充的值
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<numeric>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用算法生成算法
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v;v.resize(10);//后期重新填充fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 100);for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}6.常用集合算法
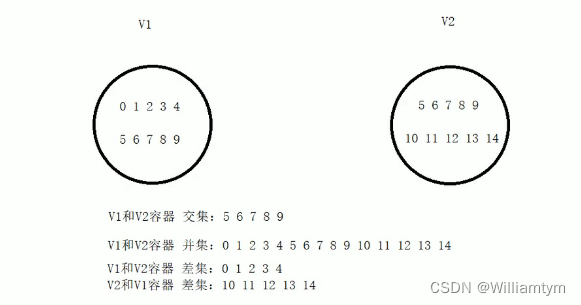
算法简介:
set_intersection求两个容器的交集
set_union求两个容器的并集
set_difference求两个容器的差集
1.set_intersection
功能描述:
求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);求两个集合的交集
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用集合算法
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v1;vector<int>v2;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 5);}vector<int>vTarget;//目标容器需要提前开辟空间//最特殊情况就是大容器包含小容器,开辟空间取小容器的size即可vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));//获取交集vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print());
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:
求交集的两个集合必须的有序序列
目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值
set_intersection返回值既是交集中最后一个元素的位置
2.set_union
功能描述:
求两个集合的并集
函数原型:
set_union(iterator begl, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
求两个集合的并集I
注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
beg1 容器1开始迭代器
end1 容器1结束迭代器
beg2 容器2开始迭代器
end2 容器2结束迭代器
dest目标容器开始迭代器
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用集合算法
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v1;vector<int>v2;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 5);}vector<int>vTarget;vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print());
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}总结:
求并集的两个集合必须的有序序列
目标容器开辟空间需要两个容器相加
set_union返回值既是并集中最后一个元素的位置
3.set_difference
功能描述:
求两个集合的差集
函数原型:
set_difference(iterator beg1,iterator end1,iterator beg2,iterator end2,iterator dest);
求两个集合的差集
注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
beg1容器1开始迭代器
end1容器1结束迭代器
beg2容器2开始迭代器
end2容器2结束迭代器
dest目标容器开始迭代器
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//常用集合算法
class print
{
public:operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test()
{vector<int>v1;vector<int>v2;for(int i = 0;i < 10; i++){v1.push_back(i);v2.push_back(i + 5);}vector<int>vTarget;vTarget.resize(max(v1.size(),v2.size()));vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());cout << "v1和v2的差集:" << endl;for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print());cout << endl;itEnd = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());cout << "v2和v1的差集:" << endl;for_each(vTarget.begin(), itEnd, print());cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test();return 0;
}
相关文章:

值得记忆的STL常用算法,分分钟摆脱容器调用的困境,以vector为例,其余容器写法类似
STL常用算法 概述: 算法主要是由头文件<algorithm> <functional> <numeric>组成 <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等 <nuneric>体积很小,只包括…...
java如何手动导jar包
今天用IDEA,需要导入一个Jar包,因为以前都是用eclipse的,所以对这个idea还不怎么上手,连打个Jar包都是谷歌了一下。 但是发现网上谷歌到的做法一般都是去File –> Project Structure中去设置,有没有如同eclipse一样…...

怎么防止SQL注入?
首先SQL注入是一种常见的安全漏洞,黑客可以通过注入恶意代码来攻击数据库和应用程序。以下是一些防止SQL注入的基本措施: 数据库操作层面 使用参数化查询:参数化查询可以防止SQL注入,因为参数化查询会对用户输入的数据进行过滤和…...
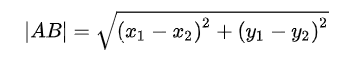
【千题案例】TypeScript获取两点之间的距离 | 中点 | 补点 | 向量 | 角度
我们在编写一些瞄准、绘制、擦除等功能函数时,经常会遇到计算两点之间的一些参数,那本篇文章就来讲一下两点之间的一系列参数计算。 目录 1️⃣ 两点之间的距离 ①实现原理 ②代码实现及结果 2️⃣两点之间的中点 ①实现原理 ②代码实现及结果 3…...
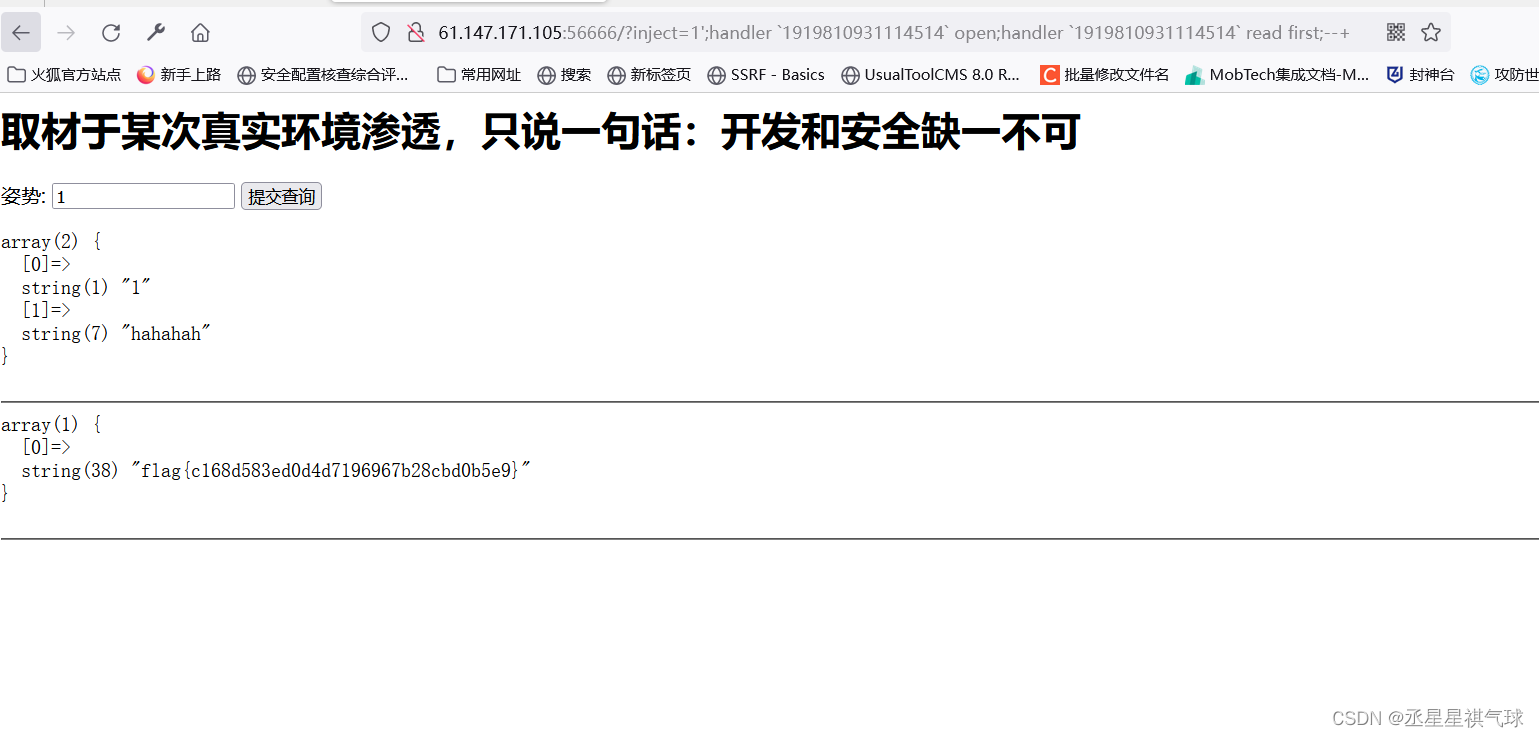
堆叠注入--攻防世界CTF赛题学习
在一次联系CTF赛题中才了解到堆叠注入,在这里简单介绍一下。 堆叠注入的原理什么的一搜一大堆,我就不引用百度了,直接进入正题。 这个是攻防世界的一道CTF赛题。 采用寻常思路来寻找sql注入漏洞。 payload:1 and 11-- 利用payload: and 12…...
STM32 ADC+定时器+DMA+FFT
本次实现的功能为单片机DAC输出一个正弦波,然后ADC定时采样用DMA输出,最后对DAC输出的波形进行FFT。单片机STM32F103ZET6内部时钟一、配置ADCADC端口为PA1,采用DMA输出,定时器3触发定时器时钟64M,分频后为102.4KHzADC采…...
)
用Node.js实现一个HTTP服务器程序(文件服务器)
http Node.js开发的目的就是为了用JavaScript编写Web服务器程序。因为JavaScript实际上已经统治了浏览器端的脚本,其优势就是有世界上数量最多的前端开发人员。如果已经掌握了JavaScript前端开发,再学习一下如何将JavaScript应用在后端开发,就是名副其实的全栈了。 HTTP协…...

Python实现人脸识别检测, 对美女主播照片进行评分排名
前言 嗨喽,大家好呀~这里是爱看美女的茜茜呐 素材、视频、代码、插件安装教程我都准备好了,直接在文末名片自取就可点击此处跳转 开发环境: Python 3.8 Pycharm 2021.2 模块使用: requests >>> pip install requests tqdm >…...
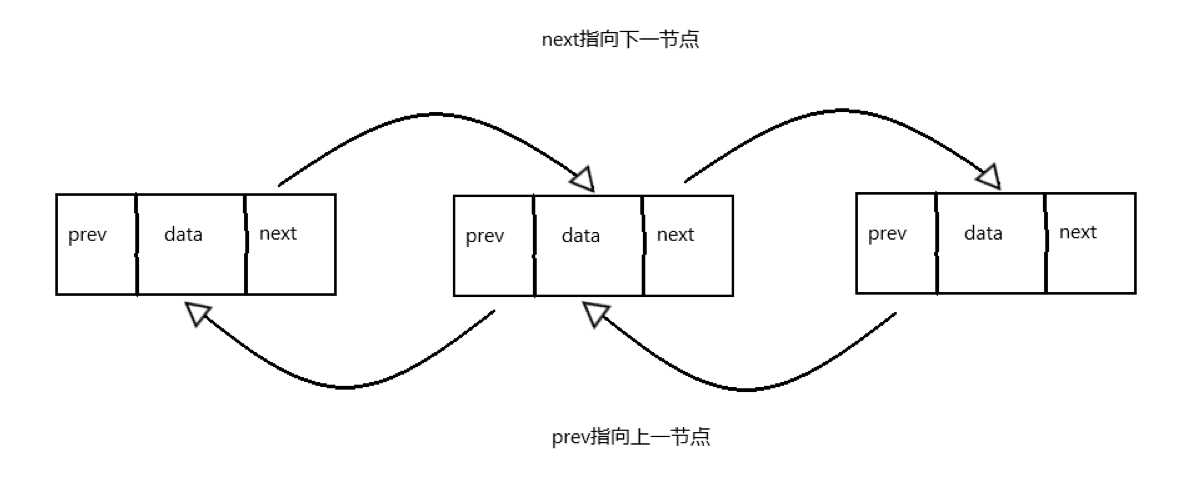
【数据结构与算法】什么是双向链表?并用代码手动实现一个双向链表
文章目录一、什么是双向链表二、双向链表的简单实现一、什么是双向链表 我们来看一下这个例子: 在一个教室里,所有的课桌排成一列,如图 相信在你们的读书生涯中,老师肯定有要求你们记住自己的前后桌是谁。所以该例子中&#x…...
23种设计模式
参考链接: 【狂神说Java】通俗易懂的23种设计模式教学(停更)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 23种设计模式【狂神说】_狂神说设计模式_miss_you1213的博客-CSDN博客 1. 单例模式 参考链接: 【狂神说Java】单例模式-23种设计模式系列_哔哩哔哩…...

20美刀一个月的ChatGPT架构师,性价比逆天了
文章目录20美刀一个月的ChatGPT架构师,性价比逆天了1.角色设定2.基本描述3.解决方案4.物理网络蓝图5.系统集成接口5.1 系统集成接口设计5.1.1 前端服务器与后端服务器接口:5.1.2 后端服务器与去背景处理服务接口:5.2 系统集成接口展示6.部署环…...

海门区教育科学规划课题2020年度成果鉴定书
海门区教育科学规划课题2020年度成果鉴定书 课题编号:HMGZ2020007 课题名称 中学历史核心素养校本化实施的培育研究 主持人 徐彬 工作单位 南通市海门证大中学 核心组成员 (包括主持人) 姓名 研究任务完成情况 (获得的主要成果、…...

大数据专业应该怎么学习
大数据学习不能停留在理论的层面上,大数据方向切入应是全方位的,基础语言的学习只是很小的一个方面,编程落实到最后到编程思想。学习前一定要对大数据有一个整体的认识。 大数据是数据量多吗?其实并不是,通过Hadoop其…...
学习黑客十余年,如何成为一名高级的安全工程师?
1. 前言 说实话,一直到现在,我都认为绝大多数看我这篇文章的读者最后终究会放弃,原因很简单,自学终究是一种适合于极少数人的学习方法,而且非常非常慢,在这个过程中的变数过大,稍有不慎&#…...
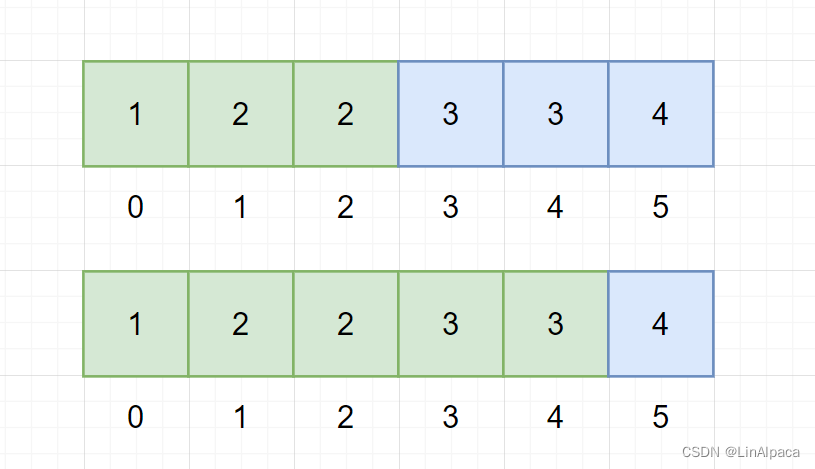
【算法】手把手学会二分查找
目录 简介 基本步骤 第一种二分 第二种二分 例题 搜索插入位置 数的范围 总结 简介 🥥二分查找,又叫折半查找,通过找到数据二段性每次都能将原来的数据筛选掉一半,通过这个算法我们能够将一个一个查找的 O(n) 的时间复杂…...

SVO、vinsmono、 OKVIS系统比较
几个经典视觉slam系统的比较 SVO 高翔链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/39904950/answer/138644975处理的各个线程: tracking部分-frame to frame 、frame to map 金字塔的处理。这一步估计是从金字塔的顶层开始,把上一层的结果作为下一层估计的初…...

前端开发规范
一、开发工具 开发工具统一使用 VSCode代码格式化插件使用 Prettier代码格式校验使用 ESLintVSCode 需安装的插件有:ESLint、Prettier、Vetur 二、命名规范 项目命名使用小写字母,以连字符分隔 正确:fe-project 错误:FE PROJECT…...
不用科学上网,免费的GPT-4 IDE工具Cursor保姆级使用教程
大家好,我是可乐。 过去的一周,真是疯狂的一周。 GPT-4 震撼发布,拥有了多模态能力,不仅能和GPT3一样进行文字对话,还能读懂图片; 然后斯坦福大学发布 Alpaca 7 B,性能匹敌 GPT-3.5ÿ…...

【艾特淘】抖音小店物流体验分提升的6个维度,新手做店必看
抖音小店体验分,考核的内容包括商品、物流以及服务。大部分人会把重心放在商品评价和服务上,忽略了物流体验。但其实,抖音小店物流体验占比有20%,比服务分的占比还高一点。如果你的订单物流出了问题,很有可能会导致用户…...

数据结构——二叉树与堆
作者:几冬雪来 时间: 内容:二叉树与堆内容讲解 目录 前言: 1.完全二叉树的存储: 2.堆的实现: 1.创建文件: 2.定义结构体: 3.初始化结构体: 4.扩容空间与扩容…...
大数据学习栈记——Neo4j的安装与使用
本文介绍图数据库Neofj的安装与使用,操作系统:Ubuntu24.04,Neofj版本:2025.04.0。 Apt安装 Neofj可以进行官网安装:Neo4j Deployment Center - Graph Database & Analytics 我这里安装是添加软件源的方法 最新版…...

css实现圆环展示百分比,根据值动态展示所占比例
代码如下 <view class""><view class"circle-chart"><view v-if"!!num" class"pie-item" :style"{background: conic-gradient(var(--one-color) 0%,#E9E6F1 ${num}%),}"></view><view v-else …...
)
rknn优化教程(二)
文章目录 1. 前述2. 三方库的封装2.1 xrepo中的库2.2 xrepo之外的库2.2.1 opencv2.2.2 rknnrt2.2.3 spdlog 3. rknn_engine库 1. 前述 OK,开始写第二篇的内容了。这篇博客主要能写一下: 如何给一些三方库按照xmake方式进行封装,供调用如何按…...
)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解)
React Native 开发环境搭建(全平台详解) 在开始使用 React Native 开发移动应用之前,正确设置开发环境是至关重要的一步。本文将为你提供一份全面的指南,涵盖 macOS 和 Windows 平台的配置步骤,如何在 Android 和 iOS…...
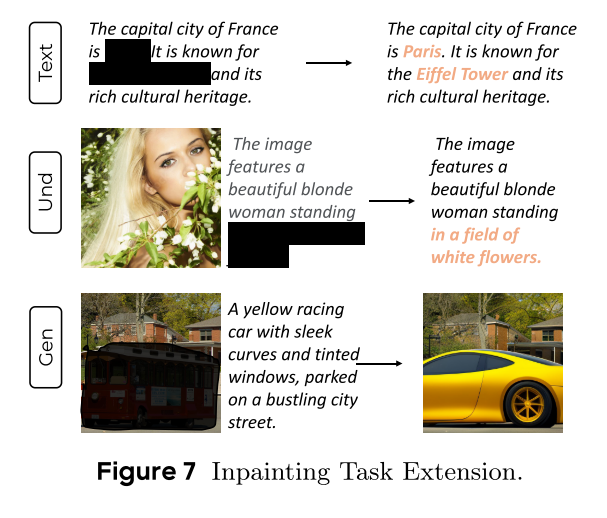
MMaDA: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models
CODE : https://github.com/Gen-Verse/MMaDA Abstract 我们介绍了一种新型的多模态扩散基础模型MMaDA,它被设计用于在文本推理、多模态理解和文本到图像生成等不同领域实现卓越的性能。该方法的特点是三个关键创新:(i) MMaDA采用统一的扩散架构…...
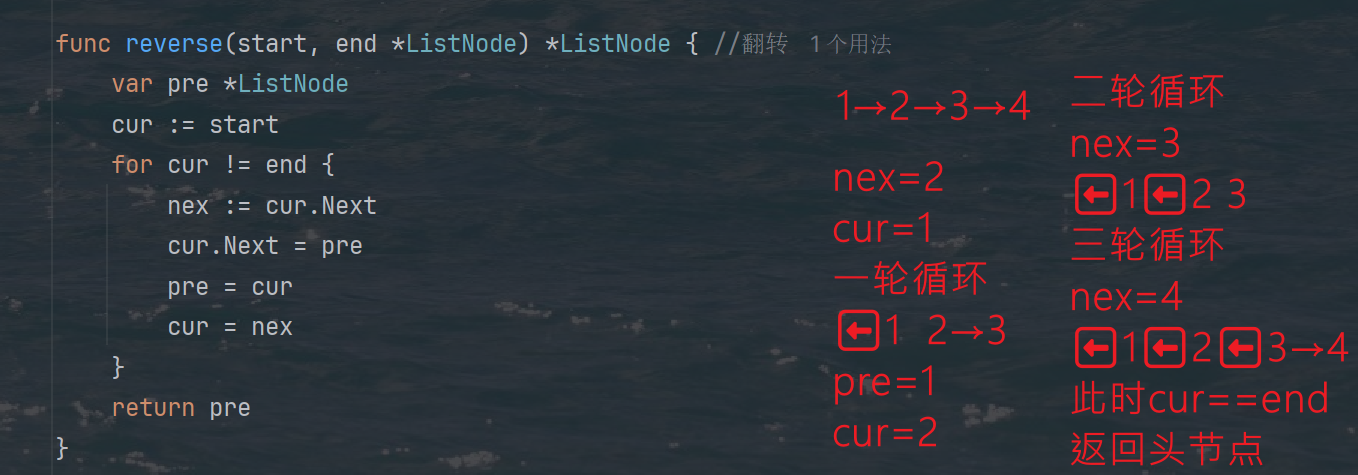
力扣热题100 k个一组反转链表题解
题目: 代码: func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {cur : headfor i : 0; i < k; i {if cur nil {return head}cur cur.Next}newHead : reverse(head, cur)head.Next reverseKGroup(cur, k)return newHead }func reverse(start, end *ListNode) *ListN…...

适应性Java用于现代 API:REST、GraphQL 和事件驱动
在快速发展的软件开发领域,REST、GraphQL 和事件驱动架构等新的 API 标准对于构建可扩展、高效的系统至关重要。Java 在现代 API 方面以其在企业应用中的稳定性而闻名,不断适应这些现代范式的需求。随着不断发展的生态系统,Java 在现代 API 方…...
windows系统MySQL安装文档
概览:本文讨论了MySQL的安装、使用过程中涉及的解压、配置、初始化、注册服务、启动、修改密码、登录、退出以及卸载等相关内容,为学习者提供全面的操作指导。关键要点包括: 解压 :下载完成后解压压缩包,得到MySQL 8.…...

Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫
Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫 构建坚不可摧的数字堡垒 引言:攻防对抗的新纪元 在日益复杂的网络威胁环境中,Linux系统安全已从被动防御转向主动免疫。2023年全球网络安全报告显示,高级持续性威胁(APT)攻击同比增长65%,平均入侵停留时间缩短至48小时。本章将从…...

数据结构:泰勒展开式:霍纳法则(Horner‘s Rule)
目录 🔍 若用递归计算每一项,会发生什么? Horners Rule(霍纳法则) 第一步:我们从最原始的泰勒公式出发 第二步:从形式上重新观察展开式 🌟 第三步:引出霍纳法则&…...
