R语言笔记(五):Apply函数
文章目录
- 一、Apply Family
- 二、`apply()`: rows or columns of a matrix or data frame
- 三、Applying a custom function
- 四、Applying a custom function "on-the-fly"
- 五、Applying a function that takes extra arguments
- 六、What's the return argument?
- 七、Optimized functions for special tasks
- 八、`lapply`: elements of a list or vector
- 九、`sapply()`: elements of a list or vector
- 十、`tapply()`: levels of a factor vector
- 十一、`split()`: split by levels of a factor
一、Apply Family
R offers a family of apply functions, which allow you to apply a function across different chunks of data. Offers an alternative to explicit iteration using for() loop; can be simpler and faster, though not always. Summary of functions:
apply(): apply a function to rows or columns of a matrix or data framelapply(): apply a function to elements of a list or vectorsapply(): same as the above, but simplify the output (if possible)tapply(): apply a function to levels of a factor vector
二、apply(): rows or columns of a matrix or data frame
The apply() function takes inputs of the following form:
apply(x, MARGIN=1, FUN=my.fun), to applymy.fun()across rows of a matrix or data framexapply(x, MARGIN=2, FUN=my.fun), to applymy.fun()across columns of a matrix or data framex
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=sum) # Minimum entry in each column
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 212321.00 221790.00 58.50 3543.93 368.90 2655.40
## Frost Area
## 5223.00 3536794.00colSums(state.x77)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 212321.00 221790.00 58.50 3543.93 368.90 2655.40
## Frost Area
## 5223.00 3536794.00
- When output of the function passed to
FUNis a single value,apply()output a vector across the columns/rows
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=which.max) # Index of the max in each column
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 5 2 18 11 1 44
## Frost Area
## 28 2
- When output of the function passed to
FUNis a vector,apply()output a matrix across the columns/rows
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=summary)

三、Applying a custom function
For a custom function, we can just define it before hand, and the use apply() as usual
# Our custom function: second largest value
second.max = function(v) { sorted.v = sort(v,decreasing = T)return(sorted.v[2])
}apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=second.max)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 18076.00 5348.00 2.40 72.96 13.90 66.70
## Frost Area
## 186.00 262134.00apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=max)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 21198.0 6315.0 2.8 73.6 15.1 67.3
## Frost Area
## 188.0 566432.0
四、Applying a custom function “on-the-fly”
Instead of defining a custom function before hand, we can define it “on-the-fly”.
# Compute trimmed means, defining this on-the-fly
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=function(v) { sorted.v = sort(v,decreasing = T)return(sorted.v[2])
})## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 18076.00 5348.00 2.40 72.96 13.90 66.70
## Frost Area
## 186.00 262134.00
- When the custom function is simple, this can be more convenient
# Compute trimmed means, defining this on-the-fly
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=function(v) {sort(v,decreasing = T)[2]})## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 18076.00 5348.00 2.40 72.96 13.90 66.70
## Frost Area
## 186.00 262134.00
五、Applying a function that takes extra arguments
Can tell apply() to pass extra arguments to the function in question. E.g., can use: apply(x, MARGIN=1, FUN=my.fun, extra.arg.1, extra.arg.2), for two extra arguments extra.arg.1, extra.arg.2 to be passed to my.fun()
# Our custom function: trimmed mean, with user-specified percentiles
kth.max = function(v,k) { sorted.v = sort(v,decreasing = T)return(sorted.v[k])
}apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=kth.max, k=10)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 5814.00 4903.00 1.80 72.13 11.10 59.90
## Frost Area
## 155.00 96184.00
六、What’s the return argument?
What kind of data type will apply() give us? Depends on what function we pass. Summary, say, with FUN=my.fun():
- If
my.fun()returns a single value, thenapply()will return a vector - If
my.fun()returns k values, thenapply()will return a matrix with k rows (note: this is true regardless of whetherMARGIN=1orMARGIN=2) - If
my.fun()returns different length outputs for different inputs, thenapply()will return a list - If
my.fun()returns a list, thenapply()will return a list
七、Optimized functions for special tasks
Don’t overuse the apply paradigm! There’s lots of special functions that optimized are will be both simpler and faster than using apply(). E.g.,
rowSums(),colSums(): for computing row, column sums of a matrixrowMeans(),colMeans(): for computing row, column means of a matrixmax.col(): for finding the maximum position in each row of a matrix
Combining these functions with logical indexing and vectorized operations will enable you to do quite a lot. E.g., how to count the number of positives in each row of a matrix?
x = matrix(rnorm(9), 3, 3)
# Don't do this (much slower for big matrices)
apply(x, MARGIN=1, function(v) { return(sum(v > 0)) })
## [1] 2 2 1# Do this insted (much faster, simpler)
rowSums(x > 0)
## [1] 2 2 1
八、lapply: elements of a list or vector
The lapply() function takes inputs as in: lapply(x, FUN=my.fun), to apply my.fun() across elements of a list or vector x. The output is always a list
my.list## $nums
## [1] 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
##
## $chars
## [1] "a" "b" "c" "d" "e" "f" "g" "h" "i" "j" "k" "l"
##
## $bools
## [1] TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE
lapply(my.list, FUN=mean) # Get a warning: mean() can't be applied to chars
## Warning in mean.default(X[[i]], ...): argument is not numeric or
## logical: returning NA
## $nums
## [1] 0.35
##
## $chars
## [1] NA
##
## $bools
## [1] 0.5lapply(my.list, FUN=summary)
## $nums
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.100 0.225 0.350 0.350 0.475 0.600
##
## $chars
## Length Class Mode
## 12 character character
##
## $bools
## Mode FALSE TRUE
## logical 3 3
九、sapply(): elements of a list or vector
The sapply() function works just like lapply(), but tries to simplify the return value whenever possible. E.g., most common is the conversion from a list to a vector
sapply(my.list, FUN=mean) # Simplifies the result, now a vector
## Warning in mean.default(X[[i]], ...): argument is not numeric or
## logical: returning NA
## nums chars bools
## 0.35 NA 0.50
sapply(my.list, FUN=summary) # Can't simplify, so still a list
## $nums
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.100 0.225 0.350 0.350 0.475 0.600
##
## $chars
## Length Class Mode
## 12 character character
##
## $bools
## Mode FALSE TRUE
## logical 3 3
十、tapply(): levels of a factor vector
The function tapply() takes inputs as in: tapply(x, INDEX=my.index, FUN=my.fun), to apply my.fun() to subsets of entries in x that share a common level in my.index
# Compute the mean and sd of the Frost variable, within each region
tapply(state.x77[,"Frost"], INDEX=state.region, FUN=mean)
## Northeast South North Central West
## 132.7778 64.6250 138.8333 102.1538tapply(state.x77[,"Frost"], INDEX=state.region, FUN=sd)
## Northeast South North Central West
## 30.89408 31.30682 23.89307 68.87652
十一、split(): split by levels of a factor
The function split() split up the rows of a data frame by levels of a factor, as in: split(x, f=my.index) to split a data frame x according to levels of my.index
# Split up the state.x77 matrix according to region
state.by.reg = split(data.frame(state.x77), f=state.region)class(state.by.reg) # The result is a list
## [1] "list"names(state.by.reg) # This has 4 elements for the 4 regions
## [1] "Northeast" "South" "North Central" "West"class(state.by.reg[[1]]) # Each element is a data frame
## [1] "data.frame"
相关文章:

R语言笔记(五):Apply函数
文章目录 一、Apply Family二、apply(): rows or columns of a matrix or data frame三、Applying a custom function四、Applying a custom function "on-the-fly"五、Applying a function that takes extra arguments六、Whats the return argument?七、Optimized…...

Newsqueak:在 Go 之前的一门语言
写在前面 学习一个东西的一种很好的方法,就是去了解这个东西的历史。在我们学习 Go 的过程中,同样也可以去了解下在 Go 之前的一些事情。 内容 Rob Pike 是 Go 语言的作者之一,早年他在贝尔实验室工作,也是 Unix 团队的成员。 …...

世界酒中国菜与另可数字平台达成战略合作
世界酒中国菜与另可数字平台达成战略合作,共推行业发展新高度 近日,在行业内引起广泛关注的“世界酒中国菜”项目,与“另可”数字平台成功举行了战略合作签约仪式。这一重要合作不仅是双方发展历程中的重要里程碑,更是继世界酒中…...

ElasticSearch基础篇——概念讲解,部署搭建,使用RestClient操作索引库和文档数据
目录 一、概念介绍 二、Elasticsearch的Docker容器安装 2.1拉取elasticsearch的镜像文件 2.2运行docker命令启动容器 2.3通过访问端口地址查看部署情况 三、安装Kibana容器 3.1拉取Kibana镜像容器指令(默认拉取最新版本): 3.2拉取完…...
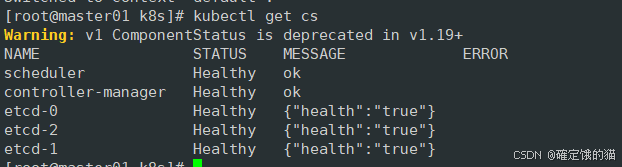
k8s 二进制部署安装(一)
目录 环境准备 初始化操作系统 部署docker 引擎 部署 etcd 集群 准备签发证书环境 部署 Master01 服务器相关组件 apiserver scheduler controller-manager.sh admin etcd 存储了 Kubernetes 集群的所有配置数据和状态信息,包括资源对象、集群配置、元数据…...
115页PPT华为管理变革:制度创新与文化塑造的核心实践
集成供应链(ISC)体系 集成供应链(ISC)体系是英文Integrated Supply Chain的缩写,是一种先进的管理思想,它指的是由相互间提供原材料、零部件、产品和服务的供应商、合作商、制造商、分销商、零售商、顾客等…...

ubuntu限制网速方法
sudo apt-get install trickle sudo trickle -d <下载速度> -u <上传速度> <命令>例如git clone sudo trickle -d 1024 git clone http://xxxxxxxxxx.git如果想简化指令可以在bashrc中添加如下指令 alias gitttrickle -u 1024 gitgitt为自定义 使用方法&am…...

三品PLM研发管理系统:企业产品研发过程的得力助手
三品PLM系统:全方位赋能企业产品生命周期管理的优选方案 在当今竞争激烈的市场环境中,产品生命周期管理PLM系统已成为企业实现高效、灵活和创新产品开发的关键工具。PLM系统集成了信息技术、先进管理思想与企业业务流程,旨在帮助企业优化产品…...

PyCharm 添加不了 Anaconda 环境
经常会遇到 PyCharm 无法添加新创建的 Anaconda 环境, Setting --> Python Interpreter --> Add Python Interperter --> Conda Environment 中为空,即使打开右侧文件夹路径按钮,选择新创建的 conda 环境,也无法找到 pyt…...

Leetcode 二叉树的右视图
好的,我来用中文详细解释这段代码的算法思想。 问题描述 题目要求给定一个二叉树的根节点,从树的右侧看过去,按从上到下的顺序返回看到的节点值。即,我们需要找到每一层的最右侧节点并将其加入结果中。 算法思想 这道题可以通…...

console.log(“res.data = “ + JSON.stringify(res.data));
res.data[object Object] 说明你在控制台打印 res.data 时,它是一个 JavaScript 对象,而不是字符串。这种情况下,console.log 输出的 [object Object] 表示它无法直接显示对象的内容。 要查看 res.data 的实际内容,你需要将其转换…...

node和npm
背景(js) 1、为什么js能操作DOM和BOM? 原因:每个浏览器都内置了DOM、BOM这样的API函数 2、浏览器中的js运行环境? v8引擎:负责解析和执行js代码 内置API:由运行环境提供的特殊接口,只能在所…...

通过四元数求机器人本体坐标旋转量
是的,通过两次姿态数据(以四元数表示)的差值,可以确定机器人在两个时刻之间的旋转角度变化。具体步骤如下: 获取四元数:假设两个时刻的四元数分别为 ( q_1 ) 和 ( q_2 )。计算四元数的差值: 将…...
-QL语法(递归))
CodeQL学习笔记(2)-QL语法(递归)
最近在学习CodeQL,对于CodeQL就不介绍了,目前网上一搜一大把。本系列是学习CodeQL的个人学习笔记,根据个人知识库笔记修改整理而来的,分享出来共同学习。个人觉得QL的语法比较反人类,至少与目前主流的这些OOP语言相比&…...

Video-XL:面向小时级视频理解的超长视觉语言模型
在人工智能领域,视频理解一直是一个挑战性的任务,尤其是对于长时间视频内容的理解。现在,Video-XL的问世标志着我们在这一领域迈出了重要的一步。Video-XL是一个专为小时级视频理解设计的超长视觉语言模型,它能够处理超长视频序列…...

postgresql subtransaction以及他的效能
文章目录 什么是subtransaction使用子事务PL/pgSQL 中的子事务与其他数据库的兼容性运行性能测试Subtransaction的实现子事务和可见性解释测试结果诊断子事务过多的问题结论 什么是subtransaction 在 PostgreSQL 中,当处于自动提交模式时,必须使用 BEGI…...

新手逆向实战三部曲之二——通过更改关键跳注册软件(爆破)
教程开始: 软件已无壳,具体脱壳请移步"新手逆向实战三部曲之一",这里略去查壳脱壳。 先用OD打开软件试运行了解下注册流程,以便找到突破口 经过对软件的了解,本次教程采用的是下bp MessageBoxA断点的方法找…...

高级SQL技巧:提升数据查询与分析能力的关键
高级SQL技巧:提升数据查询与分析能力的关键 在数据驱动的时代,SQL(结构化查询语言)是数据分析和数据库管理的基础工具。掌握高级SQL技巧不仅能提高查询效率,还能优化数据库结构,使数据分析和报告更加精准高…...

IntelliJ IDEA 安装 Maven 工具并更换阿里源
Maven是一个强大的项目管理工具,可以帮助Java开发者管理项目依赖、构建项目等。在IntelliJ IDEA中安装Maven工具并将其源更改为阿里源的步骤如下: 1. 安装 Maven 通过 IntelliJ IDEA 自带 Maven 打开 IntelliJ IDEA。创建或打开一个项目。点击菜单栏中…...

MIT 6.824 Lab1记录
MapReduce论文阅读 1. 编程模型 Map 函数(kv -> kv) Map 函数将输入的键值对处理为一系列中间值(键值对),并将所有的中间结果传递给 Reduce 处理。 map(String key, String value):// key: document name// val…...

基于Uniapp开发HarmonyOS 5.0旅游应用技术实践
一、技术选型背景 1.跨平台优势 Uniapp采用Vue.js框架,支持"一次开发,多端部署",可同步生成HarmonyOS、iOS、Android等多平台应用。 2.鸿蒙特性融合 HarmonyOS 5.0的分布式能力与原子化服务,为旅游应用带来…...

Linux云原生安全:零信任架构与机密计算
Linux云原生安全:零信任架构与机密计算 构建坚不可摧的云原生防御体系 引言:云原生安全的范式革命 随着云原生技术的普及,安全边界正在从传统的网络边界向工作负载内部转移。Gartner预测,到2025年,零信任架构将成为超…...

3403. 从盒子中找出字典序最大的字符串 I
3403. 从盒子中找出字典序最大的字符串 I 题目链接:3403. 从盒子中找出字典序最大的字符串 I 代码如下: class Solution { public:string answerString(string word, int numFriends) {if (numFriends 1) {return word;}string res;for (int i 0;i &…...
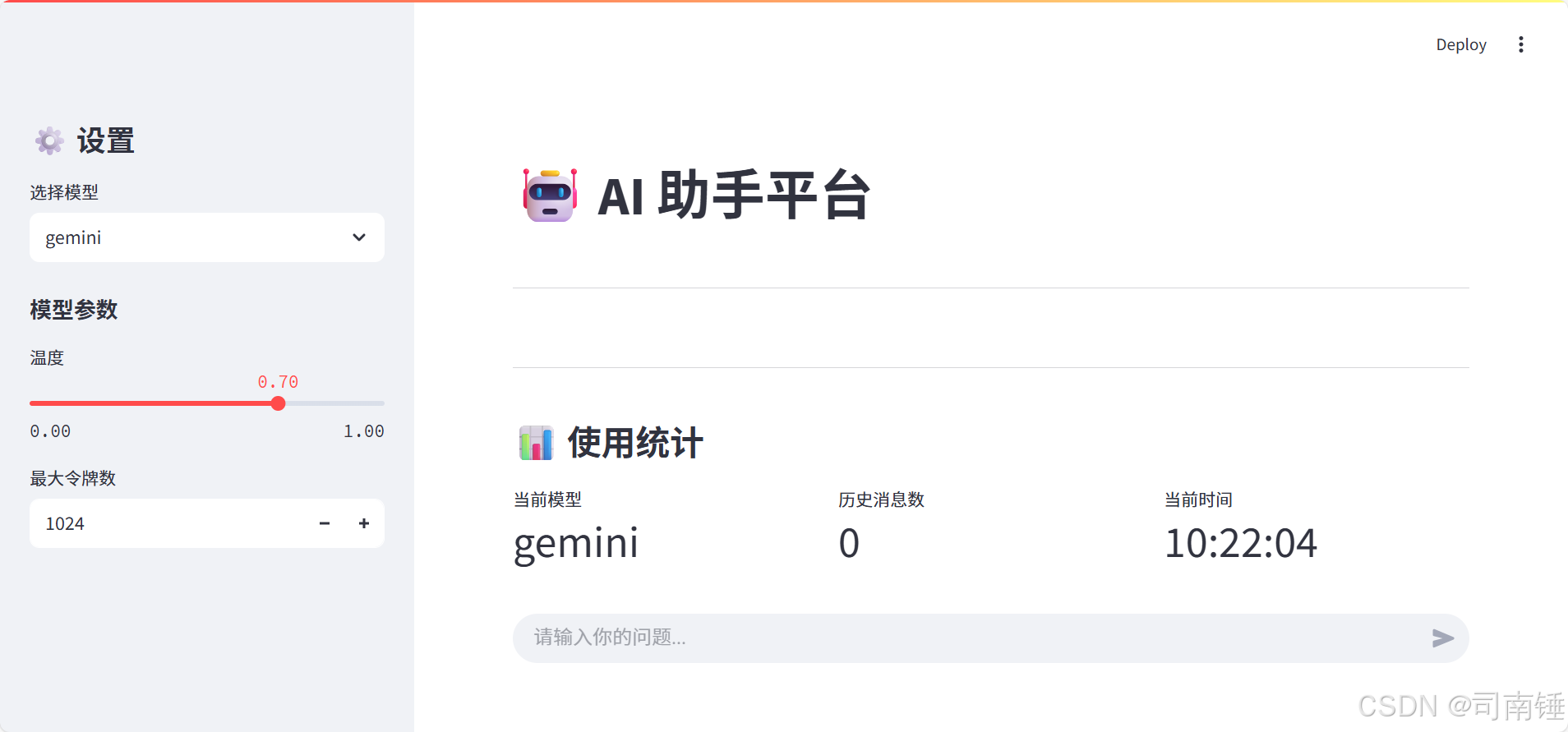
使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台
🎯 使用 Streamlit 构建支持主流大模型与 Ollama 的轻量级统一平台 📌 项目背景 随着大语言模型(LLM)的广泛应用,开发者常面临多个挑战: 各大模型(OpenAI、Claude、Gemini、Ollama)接口风格不统一;缺乏一个统一平台进行模型调用与测试;本地模型 Ollama 的集成与前…...
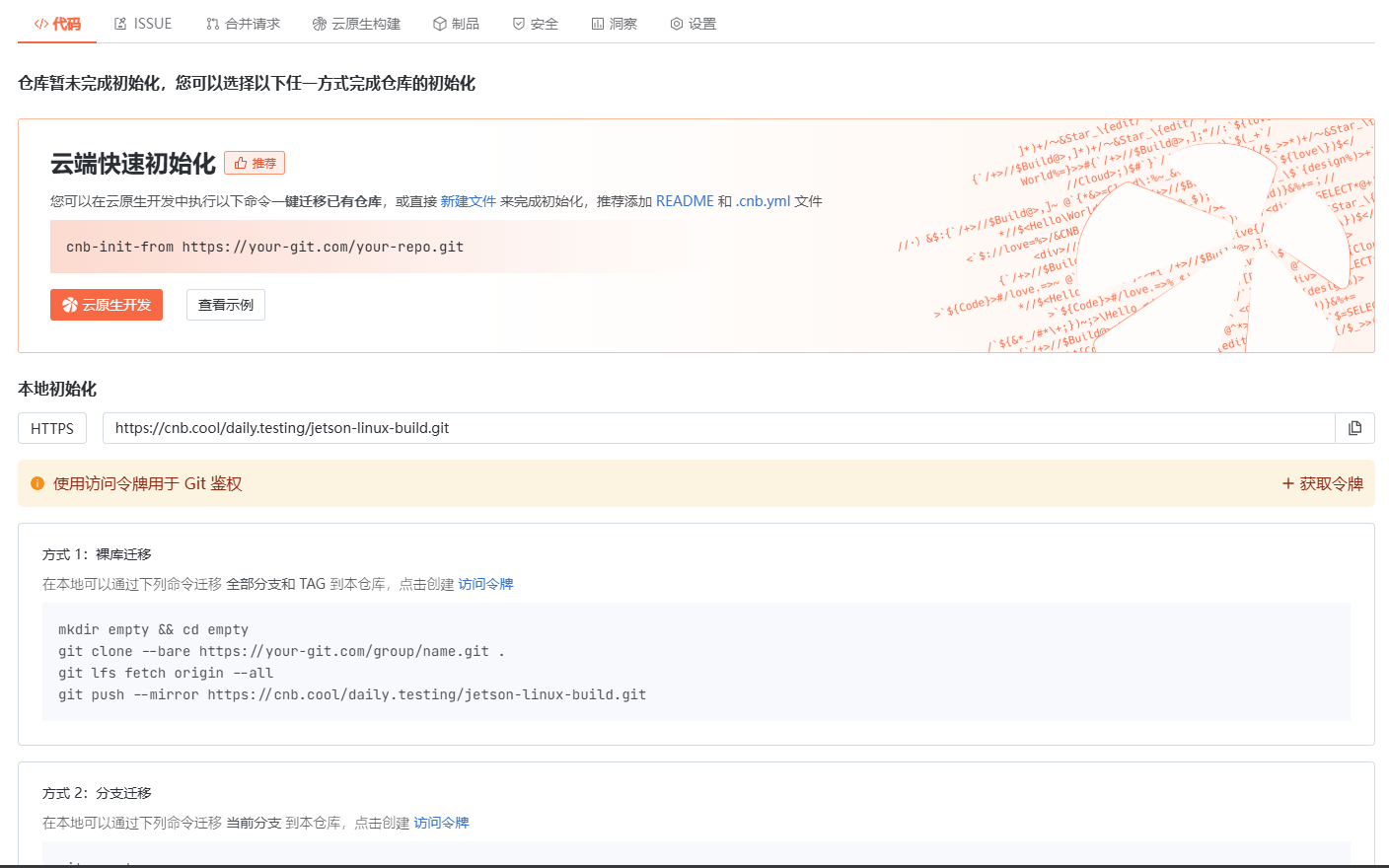
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境
云原生玩法三问:构建自定义开发环境 引言 临时运维一个古董项目,无文档,无环境,无交接人,俗称三无。 运行设备的环境老,本地环境版本高,ssh不过去。正好最近对 腾讯出品的云原生 cnb 感兴趣&…...
保姆级教程:在无网络无显卡的Windows电脑的vscode本地部署deepseek
文章目录 1 前言2 部署流程2.1 准备工作2.2 Ollama2.2.1 使用有网络的电脑下载Ollama2.2.2 安装Ollama(有网络的电脑)2.2.3 安装Ollama(无网络的电脑)2.2.4 安装验证2.2.5 修改大模型安装位置2.2.6 下载Deepseek模型 2.3 将deepse…...

Go 语言并发编程基础:无缓冲与有缓冲通道
在上一章节中,我们了解了 Channel 的基本用法。本章将重点分析 Go 中通道的两种类型 —— 无缓冲通道与有缓冲通道,它们在并发编程中各具特点和应用场景。 一、通道的基本分类 类型定义形式特点无缓冲通道make(chan T)发送和接收都必须准备好࿰…...
C++:多态机制详解
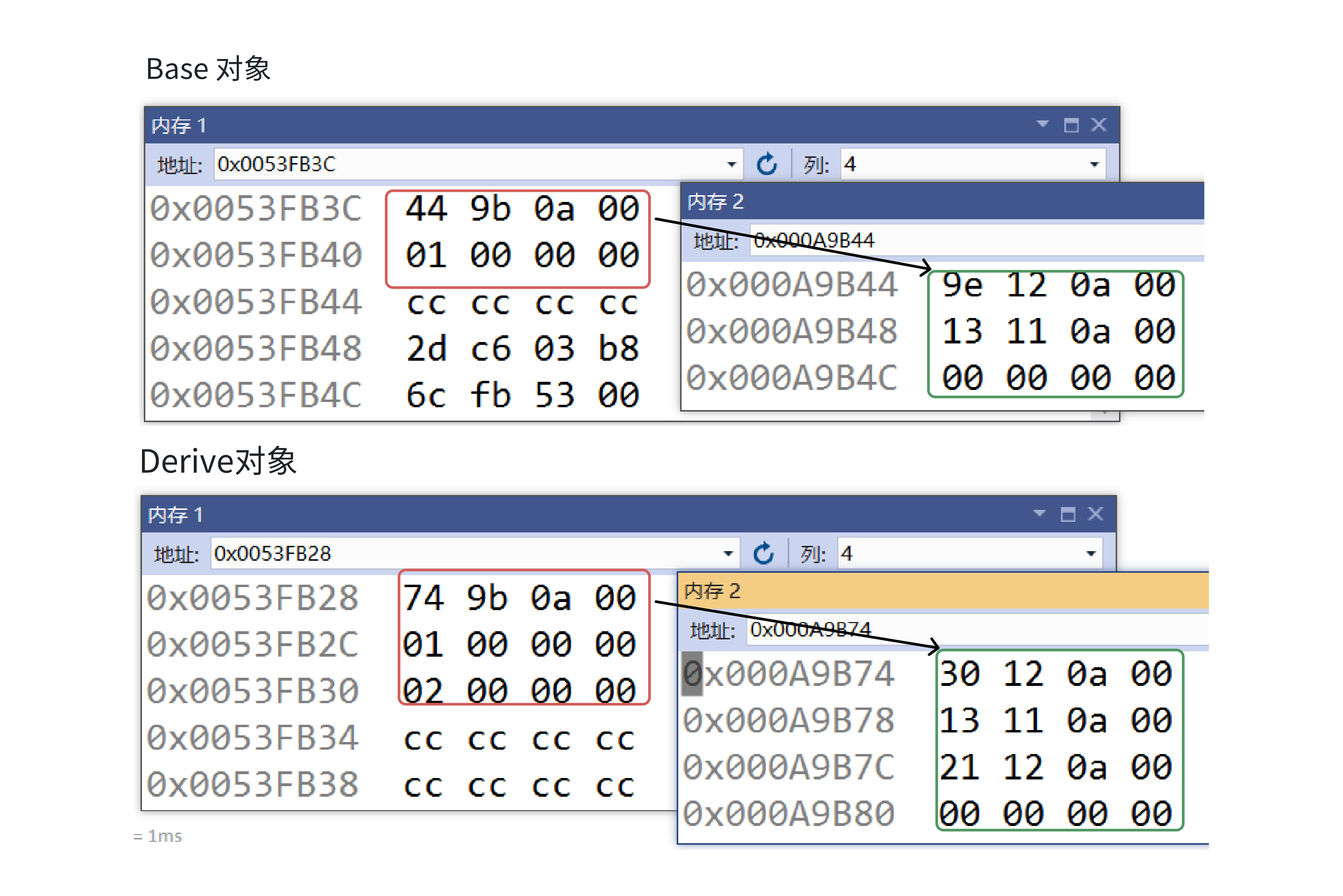
目录 一. 多态的概念 1.静态多态(编译时多态) 二.动态多态的定义及实现 1.多态的构成条件 2.虚函数 3.虚函数的重写/覆盖 4.虚函数重写的一些其他问题 1).协变 2).析构函数的重写 5.override 和 final关键字 1&#…...

A2A JS SDK 完整教程:快速入门指南
目录 什么是 A2A JS SDK?A2A JS 安装与设置A2A JS 核心概念创建你的第一个 A2A JS 代理A2A JS 服务端开发A2A JS 客户端使用A2A JS 高级特性A2A JS 最佳实践A2A JS 故障排除 什么是 A2A JS SDK? A2A JS SDK 是一个专为 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者设计的强大库ÿ…...

【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的“no matching...“系列算法协商失败问题
【SSH疑难排查】轻松解决新版OpenSSH连接旧服务器的"no matching..."系列算法协商失败问题 摘要: 近期,在使用较新版本的OpenSSH客户端连接老旧SSH服务器时,会遇到 "no matching key exchange method found", "n…...
