Linux 正则表达式(basic and extened)
正则表达式(Regular Expressions),整理自:
https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/basedefs/V1_chap09.html
gred
sed
定义
Regular Expressions (REs) provide a mechanism to select specific strings from a set of character strings.
Regular expressions are a context-independent syntax that can represent a wide variety of character sets and character set orderings, where these character sets are interpreted according to the current locale.
什么是 “locale”?
参考自:Locale
A locale is the definition of the subset of a user’s environment that depends on language and cultural conventions.
It is made up from one or more categories.
Each category is identified by its name and controls specific aspects of the behavior of components of the system.
Category names correspond to the following environment variable names:
LC_CTYPE
Character classification and case conversion.
LC_COLLATE
Collation order.
LC_MONETARY
Monetary formatting.
LC_NUMERIC
Numeric, non-monetary formatting.
LC_TIME
Date and time formats.
LC_MESSAGES
Formats of informative and diagnostic messages and interactive responses.
我们常用的是:POSIX Locale
collating element
先回答一个比较容易混淆的概念:什么是collating element?
In many languages, collation (sorting like in a dictionary) is not only done per-character.
For instance, in Czech, ch doesn’t sort between cg and ci like it would in English, but is considered as a whole for sorting.
It is a collating element (we can’t refer to a character here, character are a subset of collating elements) that sorts in between h and i.
也就是说collating element是在某些语言系统中,多个字符组成一个字符的含义。这让我想起音标。
正则表达式中:
What does [[.ch.]] mean in a regex?
When you use [.ch.] in a regexp, you basically say:
“I expect a non-English input sequence with the digraph ch.
I want my regexp to match the single charachter ch.
My programming language/regex engine/keyboard does not allow me to write this digraph’s sign, so I type in [.ch.].
I don’t mean a c followed by an h. Please only find occurences of the digraph as a single charachter.”
[[.ch.]] means that the digraph is part of a a set of characters.
In this case only one character actually. Just standard regexp notation.
参考:https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/basedefs/V1_chap07.html#tag_07_03
multi-character collating element is that of “ch”.
Subject
- Basic Regular Expression
- Extended Regular Expression
Both BREs and EREs are supported by the Regular Expression Matching interface in the System Interfaces volume of POSIX.1-2017 under regcomp(), regexec(), and related functions.
Matched 定义
A sequence of zero or more characters shall be said to be matched by a BRE or ERE when the characters in the sequence correspond to a sequence of characters defined by the pattern.
The search for a matching sequence starts at the beginning of a string and stops when the first sequence matching the expression is found, where “first” is defined to mean “begins earliest in the string”.
If the pattern permits a variable number of matching characters and thus there is more than one such sequence starting at that point, the longest such sequence is matched.
For example, the BRE “bb*” matches the second to fourth characters of the string “abbbc”, and the ERE “(wee|week)(knights|night)” matches all ten characters of the string “weeknights”.
这是采用的是贪心算法。
Consistent with the whole match being the longest of the leftmost matches, each subpattern, from left to right, shall match the longest possible string.
For this purpose, a null string shall be considered to be longer than no match at all.
For example, matching the BRE "\(.*\).*" against “abcdef”, the subexpression "(\1)" is “abcdef”, and matching the BRE "\(a*\)*" against “bc”, the subexpression “(\1)” is the null string.
BRE (ERE) matching a single character 匹配一个字符
A BRE or ERE that shall match either a single character or a single collating element.
Only a BRE or ERE of this type that includes a bracket expression ( RE Bracket Expression) can match a collating element.
BRE (ERE) matching multiple characters 匹配多个字符
A BRE or ERE that shall match a concatenation of single characters or collating elements.
Such a BRE or ERE is made up from a BRE (ERE) matching a single character and BRE (ERE) special characters.
invalid
character class expression
[:alnum:] [:cntrl:] [:lower:] [:space:]
[:alpha:] [:digit:] [:print:] [:upper:]
[:blank:] [:graph:] [:punct:] [:xdigit:]
对应的名字在下面:
LC_CTYPE Category in the POSIX Locale
The minimum character classifications for the POSIX locale follow; the code listing depicts the localedef input, and the table represents the same information, sorted by character. Implementations may add additional characters to the cntrl and punct classifications but shall not make any other additions.LC_CTYPE
# The following is the minimum POSIX locale LC_CTYPE.
# "alpha" is by definition "upper" and "lower"
# "alnum" is by definition "alpha" and "digit"
# "print" is by definition "alnum", "punct", and the <space>
# "graph" is by definition "alnum" and "punct"
#
upper <A>;<B>;<C>;<D>;<E>;<F>;<G>;<H>;<I>;<J>;<K>;<L>;<M>;\<N>;<O>;<P>;<Q>;<R>;<S>;<T>;<U>;<V>;<W>;<X>;<Y>;<Z>
#
lower <a>;<b>;<c>;<d>;<e>;<f>;<g>;<h>;<i>;<j>;<k>;<l>;<m>;\<n>;<o>;<p>;<q>;<r>;<s>;<t>;<u>;<v>;<w>;<x>;<y>;<z>
#
digit <zero>;<one>;<two>;<three>;<four>;<five>;<six>;\<seven>;<eight>;<nine>
#
space <tab>;<newline>;<vertical-tab>;<form-feed>;\<carriage-return>;<space>
#
cntrl <alert>;<backspace>;<tab>;<newline>;<vertical-tab>;\<form-feed>;<carriage-return>;\<NUL>;<SOH>;<STX>;<ETX>;<EOT>;<ENQ>;<ACK>;<SO>;\<SI>;<DLE>;<DC1>;<DC2>;<DC3>;<DC4>;<NAK>;<SYN>;\<ETB>;<CAN>;<EM>;<SUB>;<ESC>;<IS4>;<IS3>;<IS2>;\<IS1>;<DEL>
#
punct <exclamation-mark>;<quotation-mark>;<number-sign>;\<dollar-sign>;<percent-sign>;<ampersand>;<apostrophe>;\<left-parenthesis>;<right-parenthesis>;<asterisk>;\<plus-sign>;<comma>;<hyphen-minus>;<period>;<slash>;\<colon>;<semicolon>;<less-than-sign>;<equals-sign>;\<greater-than-sign>;<question-mark>;<commercial-at>;\<left-square-bracket>;<backslash>;<right-square-bracket>;\<circumflex>;<underscore>;<grave-accent>;<left-curly-bracket>;\<vertical-line>;<right-curly-bracket>;<tilde>
#
xdigit <zero>;<one>;<two>;<three>;<four>;<five>;<six>;<seven>;\<eight>;<nine>;<A>;<B>;<C>;<D>;<E>;<F>;<a>;<b>;<c>;<d>;<e>;<f>
#
blank <space>;<tab>
#
toupper (<a>,<A>);(<b>,<B>);(<c>,<C>);(<d>,<D>);(<e>,<E>);\(<f>,<F>);(<g>,<G>);(<h>,<H>);(<i>,<I>);(<j>,<J>);\(<k>,<K>);(<l>,<L>);(<m>,<M>);(<n>,<N>);(<o>,<O>);\(<p>,<P>);(<q>,<Q>);(<r>,<R>);(<s>,<S>);(<t>,<T>);\(<u>,<U>);(<v>,<V>);(<w>,<W>);(<x>,<X>);(<y>,<Y>);(<z>,<Z>)
#
tolower (<A>,<a>);(<B>,<b>);(<C>,<c>);(<D>,<d>);(<E>,<e>);\(<F>,<f>);(<G>,<g>);(<H>,<h>);(<I>,<i>);(<J>,<j>);\(<K>,<k>);(<L>,<l>);(<M>,<m>);(<N>,<n>);(<O>,<o>);\(<P>,<p>);(<Q>,<q>);(<R>,<r>);(<S>,<s>);(<T>,<t>);\(<U>,<u>);(<V>,<v>);(<W>,<w>);(<X>,<x>);(<Y>,<y>);(<Z>,<z>)
END LC_CTYPE
Regular Expression General Requirements
The requirements in this section shall apply to both basic and extended regular expressions.
The use of regular expressions is generally associated with text processing.
REs (BREs and EREs) operate on text strings, that is, zero or more characters followed by an end-of-string delimiter (typically NUL). Some utilities employing regular expressions limit the processing to lines; that is, zero or more characters followed by a <newline>.
上面提到两个特别的符号NUL和 newline
In the functions processing regular expressions described in System Interfaces volume of POSIX.1-2017, the <newline> is regarded as an ordinary character and both a <period> and a non-matching list can match one.
其实就是一个"."
在 POSIX.1-2017系统接口中 newline是一个常规字符串,同时period 以及 non-matching list都能字面匹配
The Shell and Utilities volume of POSIX.1-2017 specifies within the individual descriptions of those standard utilities employing regular expressions whether they permit matching of <newline> characters; if not stated otherwise, the use of literal <newline> characters or any escape sequence equivalent in either patterns or matched text produces undefined results.
如果是使用正则匹配的工具,就要自己说明是否允许匹配newline。
在有些工具中,一般不处理<newline>,出现<newline>在patterns或者在需要匹配的字符串中,都是为undefined results.
比如说在grep中就不能处理<newline>,grep
If the final byte of an input file is not a newline, grep silently supplies one.
Since newline is also a separator for the list of patterns, there is no way to match newline characters in a text.
Those utilities (like grep) that do not allow <newline> characters to match are responsible for eliminating any <newline> from strings before matching against the RE.
The regcomp() function in the System Interfaces volume of POSIX.1-2017, however, can provide support for such processing without violating the rules of this section.
The interfaces specified in POSIX.1-2017 do not permit the inclusion of a NUL character in an RE or in the string to be matched.
If during the operation of a standard utility a NUL is included in the text designated to be matched, that NUL may designate the end of the text string for the purposes of matching.
下面一段说明要允许有大小写不敏感的匹配。
When a standard utility or function that uses regular expressions specifies that pattern matching shall be performed without regard to the case (uppercase or lowercase) of either data or patterns, then when each character in the string is matched against the pattern, not only the character, but also its case counterpart (if any), shall be matched.
This definition of case-insensitive processing is intended to allow matching of multi-character collating elements as well as characters, as each character in the string is matched using both its cases.
For example, in a locale where “Ch” is a multi-character collating element and where a matching list expression matches such elements, the RE "[[.Ch.]]" when matched against the string “char” is in reality matched against “ch”, “Ch”, “cH”, and “CH”.
The implementation shall support any regular expression that does not exceed 256 bytes in length.
Basic Regular Expression BRE
BREs Matching a Single Character or Collating Element
- A BRE ordinary character, a special character preceded by a
<backslash>, or a<period>shall match a single character. - A bracke expression shall match a single character or a single collating
element.
什么是ordinary character
An ordinary character is a BRE that matches itself: any character in the supported character set, except for the BRE special characters listed in BRE Special Characters.
The interpretation of an ordinary character preceded by an unescaped ( ‘\’ ) is undefined, except for:
- The characters ‘)’, ‘(’, ‘{’, and ‘}’
- The digits 1 to 9 inclusive (see BREs Matching Multiple Characters)
- A character inside a bracket expression.
BRE Special Characters
A BRE special character has special properties in certain contexts.
Outside those contexts, or when preceded by a <backslash>, such a character is a BRE that matches the special character itself.
The BRE special characters and the contexts in which they have their special meaning are as follows:
| special character | usage | literal character (match iteself) | bracket expression (match itself) | notation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | \\. | [.] | The period ‘.’ matches any single character,这个不用加backslach |
| ? | \? | \\? or ? | [?] | The preceding item is optional and is matched at most once. |
| * | \* | \\* or * | [*] | The preceding item is matched zero or more times. |
| + | \+ | \\+ or + | [+] | The preceding item is matched one or more times. |
| {n} | \{n\} | \\{ or \\} or { or } | [{] or [}] | The preceding item is matched exactly n times. |
| {n,} | \{n,\} | 同上 | 同上 | The preceding item is matched n or more times. |
| {,m} | \{,m\} | 同上 | 同上 | The preceding item is matched at most m times. This is a GNU extension. |
| {n,m} | \{n,m\} | 同上 | 同上 | The preceding item is matched at least n times, but not more than m times. |
| ^ | ^ | \\^ | 无 | only sequences starting at the first character of a string shall be matched by the BRE |
| $ | $ | \\$ | [$] | match the end-of-string following the last character |
| \ | \\ | \\\ | [\] | 转义标志是2个\\ |
| | | \| | \\| | [|] | "expression1\|expression2" |
| () | \(\) | ( or ) | [(] or [)] | group expression Groups the inner regexp as a whol |
| [] | [] | \\[ or \\] | [[] or []] | Bracket Expression,不用加\ |
| - | - | \\- | [-] | Bracket Expression range expression 不用加\ |
Note that:
A <period> ( '.' ), a BRE that shall match any character in the supported character set except NUL or <newline> \r\n.
注意上面需要加backslash\的地方,有些地方需要加,有些地方不需要加
如果你需要匹配上面的特殊字符,就需要转义字符
Special Backslash Expressions
The ‘\’ character followed by a special character is a regular expression that matches the special character. The ‘\’ character, when followed by certain ordinary characters, takes a special meaning:
| character | notation |
|---|---|
| ‘\b’ | Match the empty string at the edge of a word. |
| ‘\B’ | Match the empty string provided it’s not at the edge of a word. |
| ‘<’ | Match the empty string at the beginning of a word. |
| ‘>’ | Match the empty string at the end of a word. |
| ‘\w’ | Match word constituent, it is a synonym for [_[:alnum:]]. |
| ‘\W’ | Match non-word constituent, it is a synonym for [^_[:alnum:]]. |
| ‘\s’ | Match whitespace, it is a synonym for [[:space:]]’ |
| ‘\S’ | Match non-whitespace, it is a synonym for [^[:space:]]. |
| ‘]’ | Match ‘]’. |
| ‘}’ | Match ‘}’. |
For example, ‘\brat\b’ matches the separate word ‘rat’, ‘\Brat\B’ matches ‘crate’ but not ‘furry rat’.
The behavior of grep is unspecified if a unescaped backslash is not followed by a special character, a nonzero digit, or a character in the above list. Although grep might issue a diagnostic and/or give the backslash an interpretation now, its behavior may change if the syntax of regular expressions is extended in future versions.
RE Bracket Expression
A bracket expression (an expression enclosed in square brackets, “[]” ) is an RE that shall match a specific set of single characters, and may match a specific set of multi-character collating elements, based on the non-empty set of list expressions contained in the bracket expression.
The following rules and definitions apply to bracket expressions:
- A bracket expression is either a matching list expression or a non-matching list expression.
- It consists of one or more expressions: ordinary characters, collating elements, collating symbols, equivalence classes, character classes, or range expressions.
- The
<right-square-bracket> ( ']' )shall lose its special meaning and represent itself in a bracket expression if it occurs first in the list (after an initial ( ‘^’ ), if any).Otherwise, it shall terminate the bracket expression, unless it appears in a collating symbol (such as “[.].]” ) or is the ending for a collating symbol, equivalence class, or character class. - The special characters
'.', '*', '[', and '\\' ( <period>, <asterisk>, <left-square-bracket>, and <backslash>, respectively)shall lose their special meaning within a bracket expression. - The character sequences
"[.", "[=", and "[:" ( <left-square-bracket> followed by a <period>, <equals-sign>, or <colon>)shall be special inside a bracket expression and are used to delimit collating symbols, equivalence class expressions, and character class expressions. These symbols shall be followed by a valid expression and the matching terminating sequence".]", "=]", or ":]",as described in the following items. - A matching list expression specifies a list that shall match any single character that is matched by one of the expressions represented in the list.
- The first character in the list cannot be the
<circumflex>. - An ordinary character in the list should only match that character, but may match any single character that collates equally with that character; for example, “[abc]” is an RE that should only match one of the characters ‘a’, ‘b’, or ‘c’.
- A non-matching list expression begins with a
<circumflex> ( '^' ), and the matching behavior shall be the logical inverse of the corresponding matching list expression (the same bracket expression but without the leading ). For example, if the RE"[abc]"only matches'a', 'b', or 'c', then"[^abc]"is an RE that matches any character except'a', 'b', or 'c'. It is unspecified whether a non-matching list expression matches a multi-character collating element that is not matched by any of the expressions. - 10.The
<circumflex>shall have this special meaning only when it occurs first in the list, immediately following the<left-square-bracket>. - A collating symbol is a collating element enclosed within bracket-period ( “[.” and “.]” ) delimiters. Collating elements are defined as described in Collation Order.
Conforming applications shall represent multi-character collating elements as collating symbols when it is necessary to distinguish them from a list of the individual characters that make up the multi-character collating element. For example, if the string “ch” is a collating element defined using the line:collating-element <ch-digraph> from "<c><h>" - in the locale definition, the expression “[[.ch.]]” shall be treated as an RE containing the collating symbol ‘ch’, while “[ch]” shall be treated as an RE matching ‘c’ or ‘h’.
Collating symbols are recognized only inside bracket expressions. If the string is not a collating element in the current locale, the expression is invalid. - An equivalence class expression shall represent the set of collating elements belonging to an equivalence class, as described in Collation Order.
Only primary equivalence classes shall be recognized.
The class shall be expressed by enclosing any one of the collating elements in the equivalence class within bracket-equal ( “[=” and “=]” ) delimiters.
For example, if ‘a’, ‘à’, and ‘â’ belong to the same equivalence class, then “[[=a=]b]”, “[[=à=]b]”, and “[[=â=]b]” are each equivalent to “[aàâb]”. If the collating element does not belong to an equivalence class, the equivalence class expression shall be treated as a collating symbol. - A character class expression shall represent the union of two sets:
The set of single characters that belong to the character class, as defined in the LC_CTYPE category in the current locale.
An unspecified set of multi-character collating elements.
All character classes specified in the current locale shall be recognized.
A character class expression is expressed as a character class name enclosed within bracket- <colon> ( "[:" and ":]" )delimiters.
The following character class expressions shall be supported in all locales:
[:alnum:] [:cntrl:] [:lower:] [:space:]
[:alpha:] [:digit:] [:print:] [:upper:]
[:blank:] [:graph:] [:punct:] [:xdigit:]
-
In the POSIX locale, a range expression shall be expressed as the starting point and the ending point separated by a
<hyphen-minus> ( '-' ).
In the following, all examples assume the POSIX locale.
eated as invalid.
The interpretation of range expressions where the ending range point is also the starting range point of a subsequent range expression (for example,"[a-m-o]") is undefined. -
The character shall be treated as itself if it occurs first (after an initial ‘^’, if any) or last in the list, or as an ending range point in a range expression.
As examples, the expressions “[-ac]” and “[ac-]” are equivalent and match any of the characters'a', 'c', or '-';
"[^-ac]"and"[^ac-]"are equivalent and match any characters except'a', 'c', or '-'; -
the expression
"[%--]"matches any of the characters between ‘%’ and ‘-’ inclusive; -
the expression “[–@]” matches any of the characters between ‘-’ and ‘@’ inclusive;
-
and the expression
"[a--@]"is either invalid or equivalent to ‘@’, because the letter ‘a’ follows the symbol ‘-’ in the POSIX locale. -
To use a
<hyphen-minus>as the starting range point, it shall either come first in the bracket expression or be specified as a collating symbol; for example,"[][.-.]-0]", which matches either a<right-square-bracket>or any character or collating element that collates between<hyphen-minus>and 0, inclusive. -
If a bracket expression specifies both ‘-’ and ‘]’, the ‘]’ shall be placed first (after the ‘^’, if any) and the ‘-’ last within the bracket expression.
Note:
A future version of this standard may require that an ordinary character in the list only matches that character.
It is unspecified whether a matching list expression matches a multi-character collating element that is matched by one of the expressions.
Anchoring
The caret ‘^’ and the dollar sign ‘$’ are special characters that respectively match the empty string at the beginning and end of a line. They are termed anchors, since they force the match to be “anchored” to beginning or end of a line, respectively.
Back-references and Subexpressions
The back-reference ‘\n’, where n is a single nonzero digit, matches the substring previously matched by the nth parenthesized subexpression of the regular expression.
For example, ‘(a)\1’ matches ‘aa’. If the parenthesized subexpression does not participate in the match, the back-reference makes the whole match fail; for example, ‘(a)*\1’ fails to match ‘a’. If the parenthesized subexpression matches more than one substring, the back-reference refers to the last matched substring; for example, ‘^(ab*)*\1$’ matches ‘ababbabb’ but not ‘ababbab’. When multiple regular expressions are given with -e or from a file (‘-f file’), back-references are local to each expression.
Basic vs Extended Regular Expressions
Basic regular expressions differ from extended regular expressions in the following ways:
- The characters
‘?’, ‘+’, ‘{’, ‘|’, ‘(’, and ‘)’lose their special meaning; instead use the backslashed versions ‘?’, ‘+’, ‘{’, ‘|’, ‘(’, and ‘)’. Also, a backslash is needed before an interval expression’s closing ‘}’. - An unmatched ‘)’ is invalid.
- If an unescaped ‘^’ appears neither first, nor directly after ‘(’ or ‘|’, it is treated like an ordinary character and is not an anchor.
- If an unescaped ‘$’ appears neither last, nor directly before ‘|’ or ‘)’, it is treated like an ordinary character and is not an anchor.
- If an unescaped ‘*’ appears first, or appears directly after ‘(’ or ‘|’ or anchoring ‘^’, it is treated like an ordinary character and is not a repetition operator.
Problematic Regular Expressions
Some strings are invalid regular expressions and cause grep/sed to issue a diagnostic and fail. For example, ‘xy\1’ is invalid because there is no parenthesized subexpression for the back-reference ‘\1’ to refer to.
Also, some regular expressions have unspecified behavior and should be avoided even if grep does not currently diagnose them. For example, ‘xy\0’ has unspecified behavior because ‘0’ is not a special character and ‘\0’ is not a special backslash expression (see Special Backslash Expressions). Unspecified behavior can be particularly problematic because the set of matched strings might be only partially specified, or not be specified at all, or the expression might even be invalid.
The following regular expression constructs are invalid on all platforms conforming to POSIX, so portable scripts can assume that grep rejects these constructs:
- A basic regular expression containing a back-reference ‘\n’ preceded by fewer than n closing parentheses. For example, ‘(a)\2’ is invalid.
- A bracket expression containing ‘[:’ that does not start a character class; and similarly for ‘[=’ and ‘[.’. For example, ‘[a[:b]’ and ‘[a[:ouch:]b]’ are invalid.
GNU grep treats the following constructs as invalid. However, other grep implementations might allow them, so portable scripts should not rely on their being invalid:
- Unescaped ‘\’ at the end of a regular expression.
- Unescaped ‘[’ that does not start a bracket expression.
- A ‘{’ in a basic regular expression that does not start an interval expression.
- A basic regular expression with unbalanced ‘(’ or ‘)’, or an extended regular expression with unbalanced ‘(’.
- In the POSIX locale, a range expression like ‘z-a’ that represents zero elements. A non-GNU grep might treat it as a valid range that never matches.
- An interval expression with a repetition count greater than 32767. (The portable POSIX limit is 255, and even interval expressions with smaller counts can be impractically slow on all known implementations.)
- A bracket expression that contains at least three elements, the first and last of which are both ‘:’, or both ‘.’, or both ‘=’. For example, a non-GNU grep might treat ‘[:alpha:]’ like ‘[[:alpha:]]’, or like ‘[:ahlp]’.
The following constructs have well-defined behavior in GNU grep. However, they have unspecified behavior elsewhere, so portable scripts should avoid them:
- Special backslash expressions like ‘\b’, ‘<’, and ‘]’. See Special Backslash Expressions.
- A basic regular expression that uses ‘?’, ‘+’, or ‘|’.
- An extended regular expression that uses back-references.
- An empty regular expression, subexpression, or alternative. For example, ‘(a|bc|)’ is not portable; a portable equivalent is ‘(a|bc)?’.
- In a basic regular expression, an anchoring ‘^’ that appears directly after ‘(’, or an anchoring ‘$’ that appears directly before ‘)’.
- In a basic regular expression, a repetition operator that directly follows another repetition operator.
- In an extended regular expression, unescaped ‘{’ that does not begin a valid interval expression. GNU grep treats the ‘{’ as an ordinary character.
- A null character or an encoding error in either pattern or input data. See Character Encoding.
- An input file that ends in a non-newline character, where GNU grep silently supplies a newline.
The following constructs have unspecified behavior, in both GNU and other grep implementations. Scripts should avoid them whenever possible.
- A backslash escaping an ordinary character, unless it is a back-reference like ‘\1’ or a special backslash expression like ‘<’ or ‘\b’. See Special Backslash Expressions. For example, ‘\x’ has unspecified behavior now, and a future version of grep might specify ‘\x’ to have a new behavior.
- A repetition operator that appears directly after an anchor, or at the start of a complete regular expression, parenthesized subexpression, or alternative. For example, ‘+|^*(+a|?-b)’ has unspecified behavior, whereas ‘+|^*(+a|?-b)’ is portable.
- A range expression outside the POSIX locale. For example, in some locales ‘[a-z]’ might match some characters that are not lowercase letters, or might not match some lowercase letters, or might be invalid. With GNU grep it is not documented whether these range expressions use native code points, or use the collating sequence specified by the LC_COLLATE category, or have some other interpretation. Outside the POSIX locale, it is portable to use ‘[[:lower:]]’ to match a lower-case letter, or ‘[abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz]’ to match an ASCII lower-case letter.
If a bracket expression contains at least three list elements, where the first and last list elements are the same single-character element of , , or , then it is unspecified whether the bracket expression will be treated as a collating symbol, equivalence class, or character class, respectively; treated as a matching list
Extended Regular Expression ERE
相关文章:
)
Linux 正则表达式(basic and extened)
正则表达式(Regular Expressions),整理自: https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/basedefs/V1_chap09.html gred sed 定义 Regular Expressions (REs) provide a mechanism to select specific strings from a set of character strings.…...

GB 35114-2017 学习笔记(规避版权阉割版)
GB 35114-2017 学习笔记(规避版权阉割版) openstd.samr.gov.cn 国家标准全文公开系统 这个政府网站提供GB 35114-2017标准的的预览和下载,有需要的自行下载 GB 35114-2017作为一个国家强制标准,在国家标准全文公开系统 自己做个…...

YOLO-FaceV2: A Scale and Occlusion Aware Face Detector
《YOLO-FaceV2:一种尺度与遮挡感知的人脸检测器》 1.引言2.相关工作3.YOLO-FaceV23.1网络结构3.2尺度感知RFE模型3.3遮挡感知排斥损失3.4遮挡感知注意力网络3.5样本加权函数3.6Anchor设计策略3.7 归一化高斯Wasserstein距离 4.实验4.1 数据集4.2 训练4.3 消融实验4.3.1 SEAM块4…...

进程间通信--详解
目录 前言一、进程间通信介绍1、进程间通信目的2、进程间通信发展3、进程间通信的分类4、进程间通信的必要性5、进程间通信的技术背景6、进程间通信的本质理解 二、管道1、什么是管道2、匿名管道pipe(1)匿名管道的原理(2)pipe函数…...
零基础上手WebGIS+智慧校园实例(1)【html by js】
请点个赞收藏关注支持一下博主喵!!! 等下再更新一下1. WebGIS矢量图形的绘制(超级详细!!),2. WebGIS计算距离, 以及智慧校园实例 with 3个例子!!…...
【Github】如何使用Git将本地项目上传到Github
【Github】如何使用Git将本地项目上传到Github 写在最前面1. 注册Github账号2. 安装Git工具配置用户名和邮箱仅为当前项目配置(可选) 3. 创建Github仓库4. 获取仓库地址5. 本地操作(1)进入项目文件夹(2)克隆…...

集合Queue、Deque、LinkedList、ArrayDeque、PriorityQueue详解
1、 Queue与Deque的区别 在研究java集合源码的时候,发现了一个很少用但是很有趣的点:Queue以及Deque; 平常在写leetcode经常用LinkedList向上转型Deque作为栈或者队列使用,但是一直都不知道Queue的作用,于是就直接官方…...

谈一下开源生态对 AI人工智能大模型的促进作用
谈一下开源生态对 AI人工智能大模型的促进作用 作者:开源呼叫中心系统 FreeIPCC,Github地址:https://github.com/lihaiya/freeipcc 开源生态对大模型的促进作用是一个多维度且深远的话题,它不仅加速了技术创新的速度,…...

基于python的机器学习(四)—— 聚类(一)
目录 一、聚类的原理与实现 1.1 聚类的概念和类型 1.2 如何度量距离 1.2.1 数据的类型 1.2.2 连续型数据的距离度量方法 1.2.3 离散型数据的距离度量方法 1.3 聚类的基本步骤 二、层次聚类算法 2.1 算法原理和实例 2.2 算法的Sklearn实现 2.2.1 层次聚类法的可视化实…...

实时数据开发 | 怎么通俗理解Flink容错机制,提到的checkpoint、barrier、Savepoint、sink都是什么
今天学Flink的关键技术–容错机制,用一些通俗的比喻来讲这个复杂的过程。参考自《离线和实时大数据开发实战》 需要先回顾昨天发的Flink关键概念 检查点(checkpoint) Flink容错机制的核心是分布式数据流和状态的快照,从而当分布…...

C++设计模式-策略模式-StrategyMethod
动机(Motivation) 在软件构建过程中,某些对象使用的算法可能多种多样,经常改变,如果将这些算法都编码到对象中,将会使对象变得异常复杂;而且有时候支持不使用的算法也是一个性能负担。 如何在运…...

小程序免备案:快速部署与优化的全攻略
小程序免备案为开发者提供了便捷高效的解决方案,省去繁琐的备案流程,同时通过优化网络性能和数据传输,保障用户体验。本文从部署策略、应用场景到技术实现,全面解析小程序免备案的核心优势。 小程序免备案:快速部署与优…...
Jmeter中的定时器
4)定时器 1--固定定时器 功能特点 固定延迟:在每个请求之间添加固定的延迟时间。精确控制:可以精确控制请求的发送频率。简单易用:配置简单,易于理解和使用。 配置步骤 添加固定定时器 右键点击需要添加定时器的请求…...
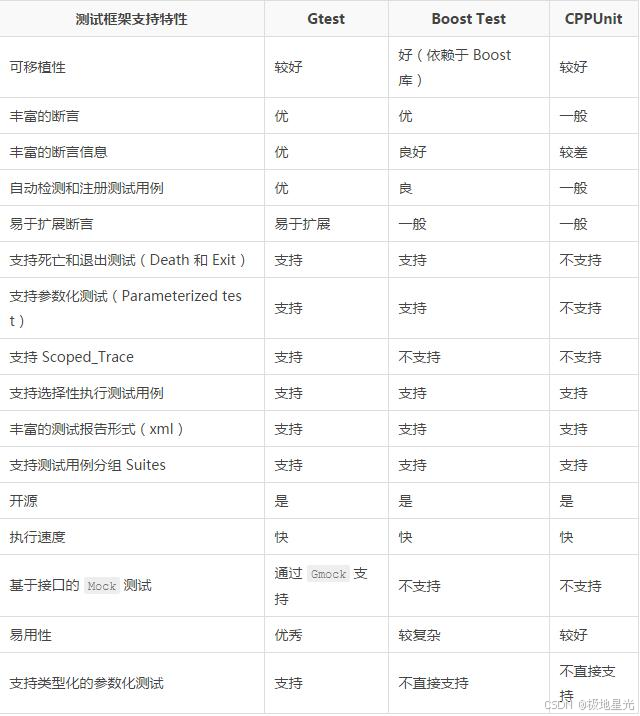
C++自动化测试:GTest 与 GitLab CI/CD 的完美融合
在现代软件开发中,自动化测试是保证代码质量和稳定性的关键手段。对于C项目而言,自动化测试尤为重要,它能有效捕捉代码中的潜在缺陷,提高代码的可维护性和可靠性。本文将重点介绍如何在C项目中结合使用Google Test(GTe…...

vscode连接远程开发机报错
远程开发机更新,vscode连接失败 报错信息 "install" terminal command done Install terminal quit with output: Host key verification failed. Received install output: Host key verification failed. Failed to parse remote port from server ou…...
模型)
神经网络12-Time-Series Transformer (TST)模型
Time-Series Transformer (TST) 是一种基于 Transformer 架构的深度学习模型,专门用于时序数据的建模和预测。TST 是 Transformer 模型的一个变种,针对传统时序模型(如 RNN、LSTM)在处理长时间依赖、复杂数据关系时的限制而提出的…...
IDEA 2024安装指南(含安装包以及使用说明 cannot collect jvm options 问题 四)
汉化 setting 中选择插件 完成 安装出现问题 1.可能是因为之前下载过的idea,找到连接中 文件,卸载即可。...
Fakelocation Server服务器/专业版 Centos7
前言:需要Centos7系统 Fakelocation开源文件系统需求 Centos7 | Fakelocation | 任务一 更新Centos7 (安装下载不再赘述) sudo yum makecache fastsudo yum update -ysudo yum install -y kernelsudo reboot//如果遇到错误提示为 Another app is curre…...
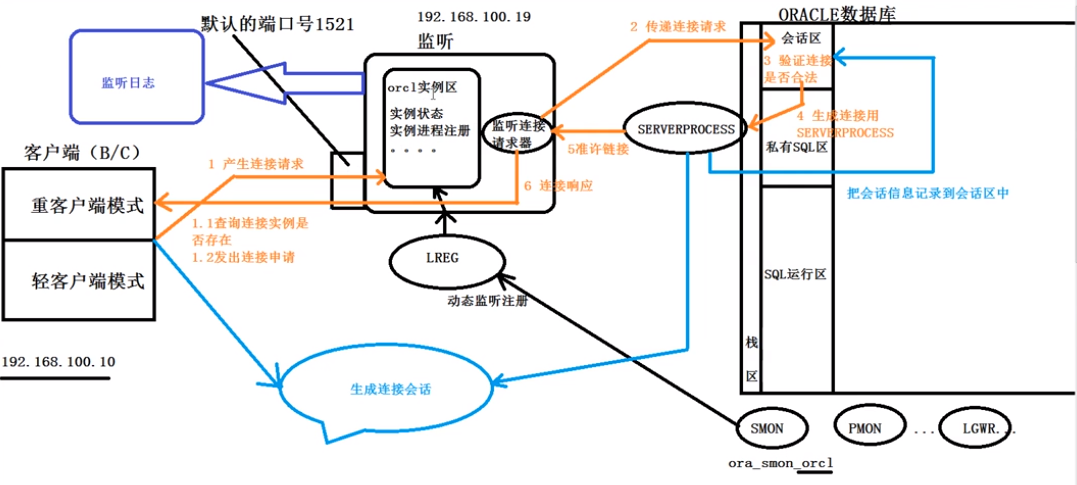
oracle的静态注册和动态注册
oracle的静态注册和动态注册 静态注册: 静态注册 : 指将实例的相关信息手动告知 listener 侦 听 器 , 可以使用netmgr,netca,oem 以及直接 vi listener.ora 文件来实现静态注册,在动态注册不稳定时使用,特点是:稳定&…...
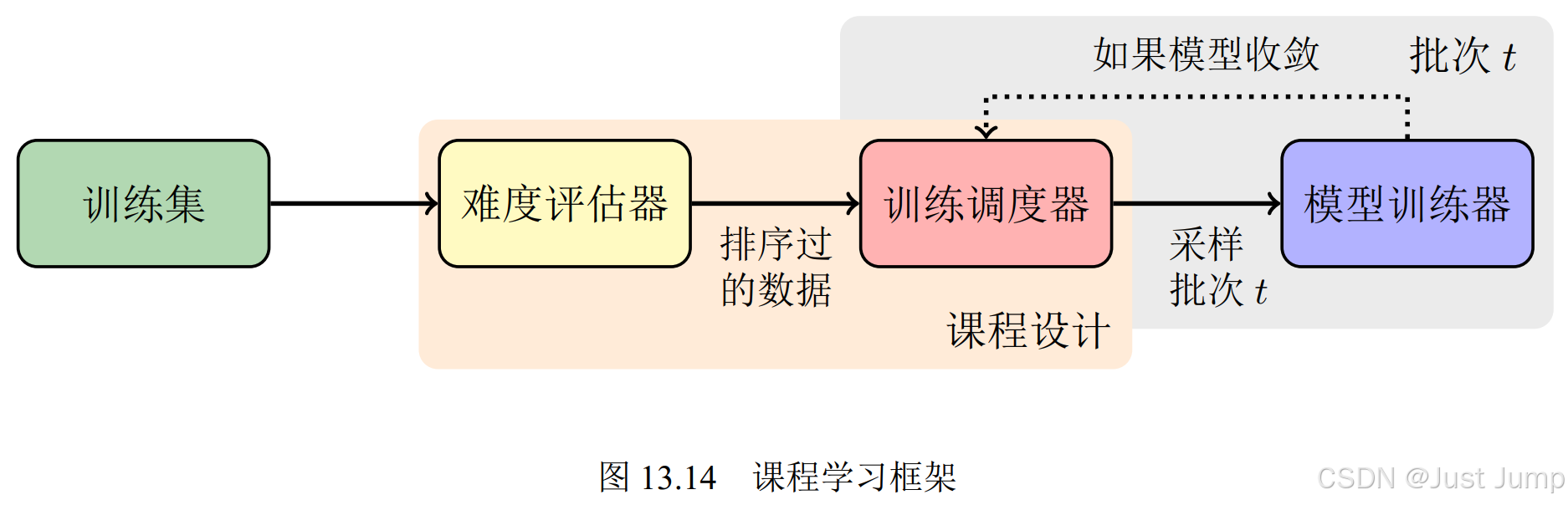
机器翻译基础与模型 之四:模型训练
1、开放词表 1.1 大词表和未登陆词问题 理想情况下,机器翻译应该是一个开放词表(Open Vocabulary)的翻译任务。也就是,无论测试数据中包含什么样的词,机器翻译系统都应该能够正常翻译。 现实的情况是即使不断扩充词…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...
)
【服务器压力测试】本地PC电脑作为服务器运行时出现卡顿和资源紧张(Windows/Linux)
要让本地PC电脑作为服务器运行时出现卡顿和资源紧张的情况,可以通过以下几种方式模拟或触发: 1. 增加CPU负载 运行大量计算密集型任务,例如: 使用多线程循环执行复杂计算(如数学运算、加密解密等)。运行图…...
项目部署到Linux上时遇到的错误(Redis,MySQL,无法正确连接,地址占用问题)
Redis无法正确连接 在运行jar包时出现了这样的错误 查询得知问题核心在于Redis连接失败,具体原因是客户端发送了密码认证请求,但Redis服务器未设置密码 1.为Redis设置密码(匹配客户端配置) 步骤: 1).修…...

分布式增量爬虫实现方案
之前我们在讨论的是分布式爬虫如何实现增量爬取。增量爬虫的目标是只爬取新产生或发生变化的页面,避免重复抓取,以节省资源和时间。 在分布式环境下,增量爬虫的实现需要考虑多个爬虫节点之间的协调和去重。 另一种思路:将增量判…...

MySQL 8.0 事务全面讲解
以下是一个结合两次回答的 MySQL 8.0 事务全面讲解,涵盖了事务的核心概念、操作示例、失败回滚、隔离级别、事务性 DDL 和 XA 事务等内容,并修正了查看隔离级别的命令。 MySQL 8.0 事务全面讲解 一、事务的核心概念(ACID) 事务是…...

离线语音识别方案分析
随着人工智能技术的不断发展,语音识别技术也得到了广泛的应用,从智能家居到车载系统,语音识别正在改变我们与设备的交互方式。尤其是离线语音识别,由于其在没有网络连接的情况下仍然能提供稳定、准确的语音处理能力,广…...

Vue3 PC端 UI组件库我更推荐Naive UI
一、Vue3生态现状与UI库选择的重要性 随着Vue3的稳定发布和Composition API的广泛采用,前端开发者面临着UI组件库的重新选择。一个好的UI库不仅能提升开发效率,还能确保项目的长期可维护性。本文将对比三大主流Vue3 UI库(Naive UI、Element …...

HTML版英语学习系统
HTML版英语学习系统 这是一个完全免费、无需安装、功能完整的英语学习工具,使用HTML CSS JavaScript实现。 功能 文本朗读练习 - 输入英文文章,系统朗读帮助练习听力和发音,适合跟读练习,模仿学习;实时词典查询 - 双…...
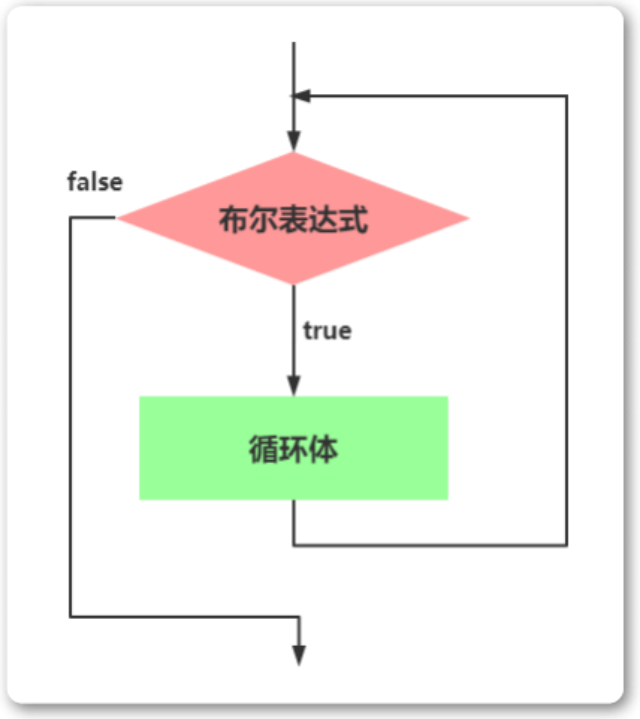
循环语句之while
While语句包括一个循环条件和一段代码块,只要条件为真,就不断 循环执行代码块。 1 2 3 while (条件) { 语句 ; } var i 0; while (i < 100) {console.log(i 当前为: i); i i 1; } 下面的例子是一个无限循环,因…...
Web APIS Day01
1.声明变量const优先 那为什么一开始前面就不能用const呢,接下来看几个例子: 下面这张为什么可以用const呢?因为复杂数据的引用地址没变,数组还是数组,只是添加了个元素,本质没变,所以可以用con…...
