时间不确定度在分布式系统中的说明
On the one hand
时间不确定度问题和影响在分布式系统中
说明
时钟不确定度(Clock Uncertainty)是指在分布式系统中,由于网络延迟、时钟漂移等因素导致系统中各个节点时钟的不同步现象。这种不同步可能会影响到分布式系统的一致性和正确性。为了解决时钟不确定度带来的问题,设计者可以采取一系列的设计思想和策略。
时钟同步算法:时钟同步算法可以帮助系统中的不同节点保持时钟的同步。常见的同步算法包括NTP(Network Time Protocol)和PTP(Precision Time Protocol),它们通过交换时间信息、校正时钟偏差等方式来实现时钟同步。
逻辑时钟:逻辑时钟是一种基于事件顺序的时钟模型,在分布式系统中被广泛应用。逻辑时钟通过给每个事件分配一个全局唯一的时间戳来解决时钟不同步问题。常见的逻辑时钟算法包括Lamport时钟和向量时钟。
异步通信模型:基于消息传递的分布式系统中,采用异步通信模型可以一定程度上减小时钟不确定度。在异步通信模型中,节点之间通过发送和接收消息进行通信,消息的到达时间和顺序可能是不确定的。设计者可以利用异步通信的性质来减小时钟不确定度的影响。
时钟容错机制:时钟容错机制是设计分布式系统中的一种重要策略。通过引入冗余节点、备份机制和数据复制等方式,可以在时钟不同步的情况下保持系统的可靠性和一致性。例如,通过使用主从复制模式,系统可以在主节点时钟不准确的情况下从备份节点获取正确的数据。
基于事件驱动的设计:事件驱动的设计思想可以帮助应对时钟不确定度带来的问题。通过将系统的状态转换和操作与事件的发生相结合,可以更好地处理时钟不同步造成的并发问题。例如,在分布式数据库系统中,可以使用事件驱动的方式来处理并发事务的提交和回滚。
通过合理地应用上述设计思想,可以有效地减小时钟不确定度对分布式系统的影响,提高系统的可靠性和一致性。
在分布式系统中的设计
在分布式系统中,时间不确定度是一个重要的问题,特别是在涉及多个时区的情况下。由于不同时区的计算机可能采用不同的本地时钟,因此在进行数据同步、消息传递、事件处理等分布式操作时,就会面临时间不确定度的挑战。
时间不确定度可能导致以下问题和影响:
- 时间戳不一致:在分布式系统中,不同的计算机可能有不同的本地时间戳,这可能导致在数据同步和一致性维护方面出现问题。例如,如果一个计算机按照其本地时钟给一条数据打上时间戳,而另一个计算机按照其本地时钟进行验证,就可能导致数据的时间戳不一致。
- 事件顺序问题:当涉及到跨时区的事件处理时,由于时钟不一致造成的时间不确定度可能导致事件的顺序不确定。例如,一个跨时区的分布式系统中,可能出现A事件在一个时区先发生,但在另一个时区的计算机上却晚发生的情况,这就会导致事件的顺序混乱。
在设计分布式系统时,需要考虑以下思想来解决时间不确定度带来的问题:
- 使用全局时间戳:可以引入全局时间戳,例如使用NTP(Network Time Protocol)来同步各个计算机的时钟,从而实现全局的时间一致性。这样可以避免因为时间戳不一致而导致的数据同步和一致性问题。
- 事件顺序保证:可以使用分布式一致性协议,如Paxos、Raft等,在分布式系统中保证事件的顺序一致性。这些协议可以通过选举机制和消息传递来确保分布式系统中的事件按特定的顺序被处理。
- 使用逻辑时钟:逻辑时钟是一种基于消息传递的时钟,可以用来解决事件顺序问题。通过为每个事件分配唯一的时间戳,并使用这些时间戳来确定事件的顺序,可以在分布式系统中实现一致的事件顺序。
总之,通过合理设计和采用适当的技术手段,可以解决全球时区之间的时间不确定度问题,并确保分布式系统的正常运行和一致性维护。
TrueTime API
TrueTime API是Google Spanner数据库系统中的一个关键组成部分,它的设计思想是为分布式系统提供高度准确的全局时间,以解决分布式系统中的时间不确定性和一致性问题。
TrueTime API的设计目标是提供一个全局可信赖的时间源,以确保分布式系统中的操作能够按照确定的时间顺序执行。它通过以下方式解决问题:
- GPS和原子钟:TrueTime API使用全球定位系统(GPS)和原子钟来获取高精度的时间信息。每个Spanner服务器节点都有自己的GPS接收器和原子钟,通过与GPS接收器同步时间,并使用原子钟来提供高精度的时间戳。
- 时钟不确定度范围:TrueTime API提供了一个时钟不确定度范围,它表示时间戳的可信度。这个范围由两个值组成,一个是lower bound(下界),表示一个操作一定在此时间之后发生;另一个是upper bound(上界),表示一个操作极有可能在此时间之前发生。
- 两次时间戳的间隙:TrueTime API使用两个连续的时间戳来计算时间戳间的间隙。通过对这个间隙的测量和分析,可以得到一个较为准确的时钟不确定度范围。
- 系统时间调整:TrueTime API还可以对系统时间进行调整,以确保各个节点的时钟保持一致。如果发现某个节点的时钟不准确,TrueTime会通过调整系统时间来纠正。
TrueTime API的设计思想是通过使用高精度的GPS和原子钟来提供全局可信赖的时间源,并结合时钟不确定度范围和时间戳间隙的计算,为分布式系统提供高度准确的全局时间。这使得Spanner数据库系统能够在跨多个数据中心和区域的分布式环境下,实现强一致性和可靠的事务处理。
分布式系统中处理时间
在分布式系统中,时间处理是一个关键的步骤,用于确保各节点的操作按照正确的时间顺序进行,并保持数据的一致性。以下是分布式系统中时间处理的主要步骤:
- 时间同步:首先,为了保证分布式系统中各个节点的时钟保持一致,需要进行时间同步。常用的方法包括使用网络时间协议(NTP)或Google的TrueTime API来同步各个节点的时钟。这样可以确保在整个系统中,各个节点以准确的时间进行操作。
- 时间戳生成:在分布式系统中,为了标记事件的发生顺序,通常会为每个事件生成时间戳。时间戳可以是递增的唯一标识符,也可以是具有时钟信息的值。时间戳的生成应确保在系统中的不同节点上是严格递增的,以便按照正确的时间顺序进行操作。
- 时间戳的传播和比较:当节点之间进行通信时,时间戳通常会随着消息一起传递。接收节点会使用接收到的时间戳与自己的时间戳进行比较,从而确定消息的顺序。如果接收到的时间戳早于自己的时间戳,节点可能会推迟处理该消息,或者在需要时请求重新发送。
- 事件顺序维护:在分布式系统中,经常需要维护事件的顺序,确保它们按照正确的时间顺序执行。通过使用分布式一致性协议,如Paxos、Raft等,可以确保分布式系统中的事件按照一致的顺序被处理。
- 处理时间不确定性:在分布式系统中,由于网络延迟、时钟不一致等原因,时间的不确定性是不可避免的。处理时间不确定性需要一定的策略和算法,例如使用时钟偏差、时钟同步算法等来纠正不准确的时间。
总结起来,分布式系统中的时间处理主要包括时间同步、时间戳生成、时间戳传播和比较、事件顺序维护以及处理时间不确定性等步骤。通过合理的设计和使用适当的时间处理策略,可以确保分布式系统中的操作有序、一致且可靠地进行。
On the other hand
The Problem and Impact of Time Uncertainty in distributed system
Clock Uncertainty refers to the lack of synchronization between clocks in a distributed system, caused by factors such as network latency and clock drift. This asynchrony can affect the consistency and correctness of a distributed system. To address the challenges posed by clock uncertainty, designers can employ a series of design principles and strategies.
Clock synchronization algorithms assist in maintaining clock synchronization among different nodes in a system. Common synchronization algorithms include NTP (Network Time Protocol) and PTP (Precision Time Protocol), which exchange time information and correct clock deviations to achieve clock synchronization.
Logical clocks are extensively used in distributed systems as a clock model based on event order. Logical clocks assign a globally unique timestamp to each event to resolve clock asynchrony. Common logical clock algorithms include Lamport clocks and vector clocks.
Asynchronous communication model can mitigate the impact of clock uncertainty in message-passing-based distributed systems. In an asynchronous communication model, message arrival time and order may be uncertain. Designers can leverage the asynchrony property to minimize the influence of clock uncertainty.
Clock fault-tolerance mechanisms are essential strategies for designing distributed systems. By introducing redundant nodes, backup mechanisms, and data replication, system reliability and consistency can be maintained even in the presence of clock asynchrony. For example, using a master-slave replication model, a system can retrieve correct data from a backup node when the master node’s clock is inaccurate.
Event-driven design is an approach that helps address the challenges posed by clock uncertainty. By combining system state transitions and operations with event occurrences, concurrency issues caused by clock asynchrony can be better handled. In distributed database systems, for example, an event-driven approach can be used to handle concurrent transaction commits and rollbacks.
By applying these design principles, clock uncertainty can be effectively mitigated, improving the reliability and consistency of distributed systems.
Dealing with Time in Distributed Systems
In distributed systems, time handling is a crucial aspect to ensure operations across nodes occur in the correct order and maintain data consistency. The main steps involved in time handling in distributed systems are as follows:
1. Time synchronization : Ensuring clock synchronization among different nodes in the distributed system is the first step. Common methods include using Network Time Protocol (NTP) or the TrueTime API developed by Google, which provide mechanisms to synchronize clocks across nodes, ensuring accurate timekeeping throughout the system.
2. Timestamp generation : In distributed systems, generating timestamps is essential for marking the order of events. Timestamps can be unique identifiers that increment over time, or they may contain clock information. Generating timestamps must ensure strict order across system nodes, enabling correct sequencing of operations.
3. Timestamp propagation and comparison : When communicating between nodes, timestamps often accompany messages. Receiving nodes compare these timestamps with their own clocks to determine the order of events. If a received timestamp is earlier than the local timestamp, the node may delay processing the message or request retransmission if necessary.
4. Event sequencing : Maintaining event order is frequently required in distributed systems to ensure events are processed in the correct time order. By using distributed consensus protocols such as Paxos or Raft, events can be consistently ordered and processed in a distributed system.
5. Handling time uncertainty : In distributed systems, time uncertainty is unavoidable due to network latency, clock inconsistencies, and other factors. Mitigating the impact of time uncertainty requires employing strategies and algorithms such as clock skew and clock synchronization algorithms to rectify inaccurate time.
In summary, time handling in distributed systems involves time synchronization, timestamp generation, propagation and comparison, event sequencing, and addressing time uncertainty. Through thoughtful design and the use of appropriate strategies, operations in distributed systems can proceed in a well-ordered, consistent, and reliable manner.
TrueTime API
The TrueTime API is a critical component of the Google Spanner database system, designed to provide highly accurate global time for solving issues of time uncertainty and consistency in distributed systems.
The TrueTime API aims to offer a globally trusted source of time to distributed systems, ensuring operations occur in a precisely ordered manner. It achieves this through the following:
1. GPS and atomic clocks : The TrueTime API utilizes Global Positioning System (GPS) and atomic clocks to obtain highly accurate time information. Each Spanner server node has its own GPS receiver and atomic clock, using the GPS receiver for time synchronization and the atomic clock to provide high-precision timestamps.
2. Clock uncertainty bounds : The TrueTime API provides a range of clock uncertainty that represents the trustworthiness of timestamps. This range consists of two values: a lower bound, representing a time after which an operation is guaranteed to have occurred, and an upper bound, indicating a time before which an operation likely occurred.
3. Gap between successive timestamps : TrueTime API calculates the gap between two consecutive timestamps. By measuring and analyzing this gap, an accurate range of clock uncertainty can be determined.
4. System time adjustment : TrueTime API can adjust system time to ensure clocks on different nodes remain synchronized. If a node’s clock is found to be inaccurate, TrueTime adjusts the system time to correct it.
The design approach of the TrueTime API leverages high-precision GPS and atomic clocks to provide a globally trusted time source. By combining clock uncertainty bounds and the calculation of timestamp gaps, it offers highly accurate global time to systems. This enables the Spanner database system to achieve strong consistency and reliable transactional processing across multiple data centers and regions.
Time Handling in Distributed Systems
In distributed systems, handling time is a critical step to ensure that operations among nodes are processed in the correct time order and maintain data consistency. Here are the main steps involved in time handling within a distributed system:
- Time synchronization: Firstly, to ensure that clocks across different nodes in the distributed system are consistent, time synchronization is conducted. Common methods include using Network Time Protocol (NTP) or Google’s TrueTime API to synchronize clocks across nodes. This ensures that all nodes operate with accurate time throughout the system.
- Timestamp generation: In a distributed system, to mark the occurrence order of events, timestamps are typically generated for each event. Timestamps can be unique identifiers that are incrementally increasing or values containing clock information. The generation of timestamps should ensure strict incrementality across different nodes in the system for proper time ordering of operations.
- Timestamp propagation and comparison: When nodes communicate with each other, timestamps are usually sent along with messages. The receiving node compares the received timestamp with its own timestamp to determine the order of the messages. If the received timestamp is earlier than its own timestamp, the node may delay processing the message or request a resend when needed.
- Event order maintenance: In distributed systems, maintaining the order of events often becomes necessary to ensure they are processed in the correct time order. By using distributed consensus protocols like Paxos, Raft, etc., events in the distributed system can be processed in a consistent order.
- Handling time uncertainty: In distributed systems, time uncertainty is inevitable due to factors such as network delays and clock inconsistencies. Dealing with time uncertainty requires strategies and algorithms, such as clock drift correction, clock synchronization algorithms, etc., to rectify inaccurate time.
To summarize, time handling in distributed systems primarily includes time synchronization, timestamp generation, timestamp propagation and comparison, event order maintenance, and handling time uncertainty. By designing the system appropriately and employing suitable time handling strategies, operations within a distributed system can be conducted orderly, consistently, and reliably.
相关文章:

时间不确定度在分布式系统中的说明
On the one hand 时间不确定度问题和影响在分布式系统中 说明 时钟不确定度(Clock Uncertainty)是指在分布式系统中,由于网络延迟、时钟漂移等因素导致系统中各个节点时钟的不同步现象。这种不同步可能会影响到分布式系统的一致性和正确性…...

VMware vCenter 从6.7跨版本升级至7.0U3N
本文尝试使用 vCenter Server Appliance 管理界面 (VAMI) 进行对vCenter Server Appliance7应用进行小版本升级,从6.7.0.47000升级到7.0.3.01600(7.0U3N)。 一、升级前的准备工作 1、检查当前运行环境(当前为6.7.0.47000&#x…...
大麦订单生成器最新版 大麦订单一键生成截图
1.可以一键添加,生成的假订单没有水印,界面也很真实。 2.在软件中输入生成的信息,这是产品信息,选择生成的产品图像,最后生成它。 后台一键生成,独立后台管理 教程:解压源码,修改数…...

如何对Map集合的key进行大小写转换?
工具类: ToUpperCaseKeyMapUtil.java public class ToUpperCaseKeyMapUtil {//对单一的mappublic static <T> Map<String, T> toUpperCaseKeyMap(Map<String, T> map) {if (map ! null) {List<String> mapKeyList new ArrayList<>…...

将函数实现放到CPP报“无法解析的外部符号...”,系VS Bug
发现一个现象,就是项目中有一个类,如果将函数实现全部放到头文件中,编译不报错,如果将函数实现放到CPP中则始终提示“无法解析的外部符号...”,考虑到放到头文件中能正常编译运行,显然这里不符合“无法解析…...
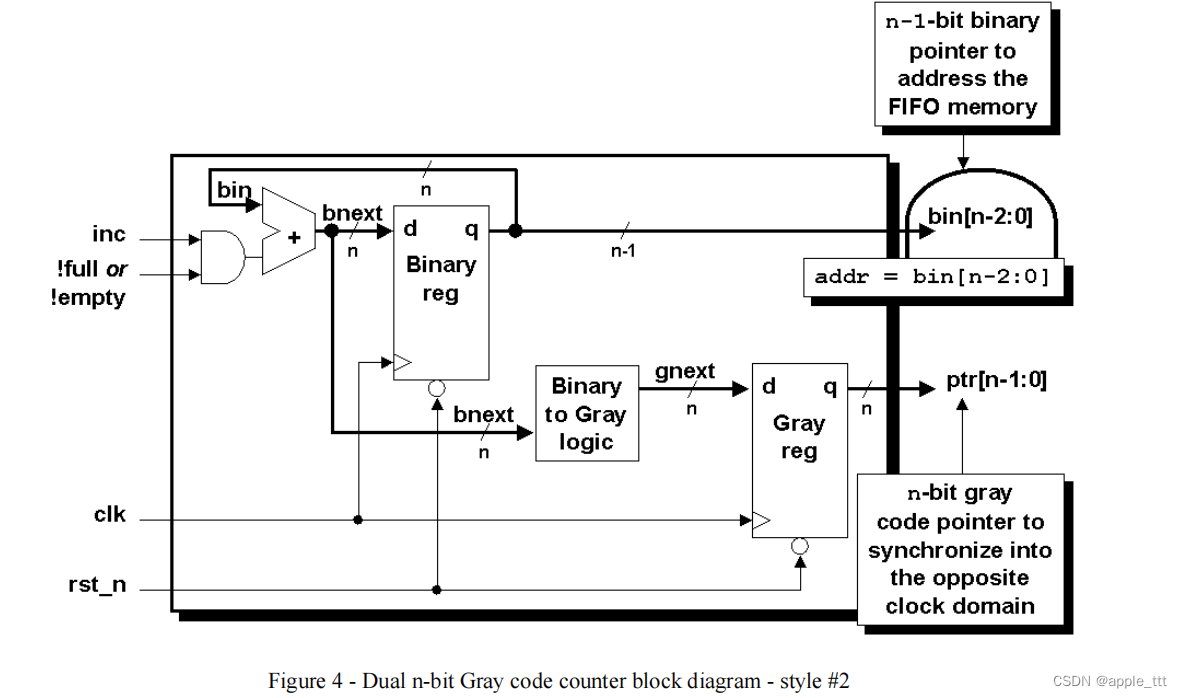
异步FIFO设计的仿真与综合技术(3)
概述 本文主体翻译自C. E. Cummings and S. Design, “Simulation and Synthesis Techniques for Asynchronous FIFO Design 一文,添加了笔者的个人理解与注释,文中蓝色部分为笔者注或意译。前文链接: 异步FIFO设计的仿真与综合技术…...

什么是区块链,解释区块链的原理和应用场景
1、什么是区块链,解释区块链的原理和应用场景。 区块链是一种分布式数据库,它由一系列按照时间顺序排列的数据块组成,并采用密码学方式保证不可篡改和不可伪造。区块链技术最初起源于比特币,作为比特币的底层技术,用于…...

使用bert进行文本二分类
构建BERT(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)的训练网络可以使用PyTorch来实现。下面是一个简单的示例代码: import torch import torch.nn as nn from transformers import BertModel, BertTokenizer# Load BERT to…...

用Windows Installer CleanUp Utility 在windows server上面将软件卸载干净,比如SQLSERVER
这里写自定义目录标题 下载文件:Windows Installer CleanUp Utility。 通过以上工具可以将一个应用程序卸载干净。...

Java手写LinkedList和拓展
Java手写LinkedList和拓展 思维导图 #mermaid-svg-K0RTlFFvnikDRvqp {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-K0RTlFFvnikDRvqp .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-K0RTlFFvnikDRvqp .error-text{fill…...
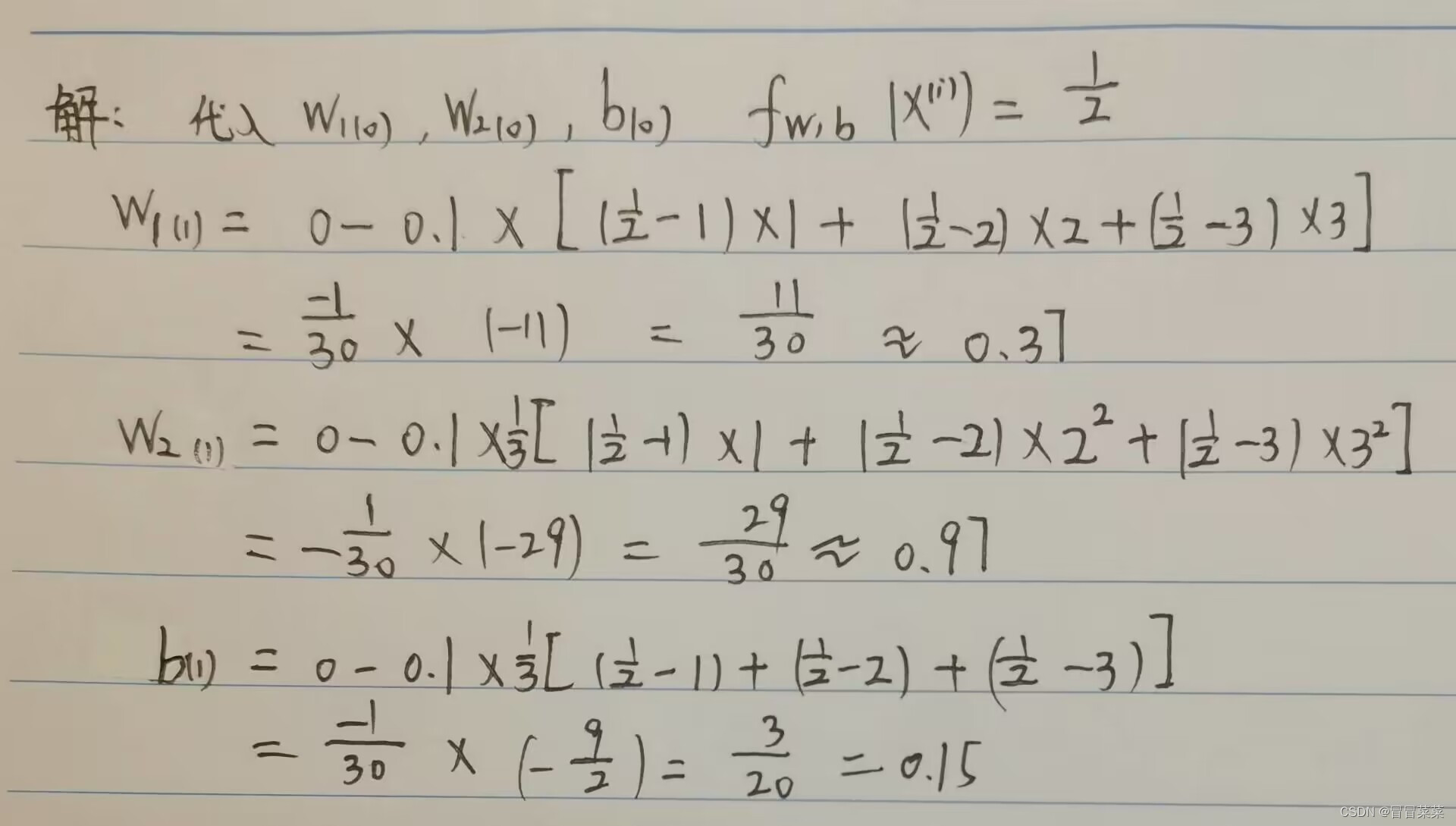
机器学习(14)---逻辑回归(含手写公式、推导过程和手写例题)
逻辑回归 一、逻辑回归概述二、模型、策略和优化(手写)三、w和b的梯度下降公式推导四、例题分析4.1 题目4.2 解答 一、逻辑回归概述 1. 逻辑回归也称作logistic回归分析,是一种广义的线性回归分析模型,属于机器学习中的监督学习。…...
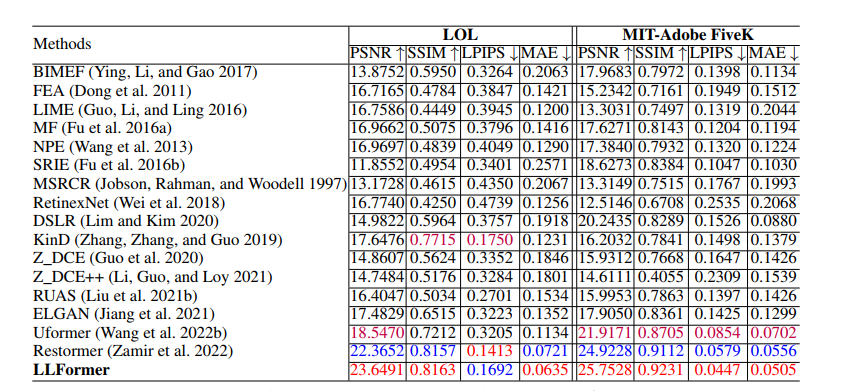
LLFormer 论文阅读笔记
Ultra-High-Definition Low-Light Image Enhancement: A Benchmark and Transformer-Based Method 这是南京大学在AAAI 2023发表的一篇AAAI2023 超高清图像暗图增强的工作。提出了一个超高清暗图增强数据集,提供了4K和8K的图片,同时提出了一个可用于暗图…...

JSP语法基础习题
目录 简答题:jsp中静态include和动态include的区别是什么? 简答题:jsp有哪些内置对象,作用分别是什么? 简答题:Request对象的主要方法有哪些? 代码题: 简答题:jsp中静态…...

vue类与样式的绑定列表渲染
目录 1.类与样式的绑定 1.1绑定 HTML class 1.2绑定数组 1.3绑定内联样式 绑定数组 2.列表渲染 2.1v-for 2.2v-for 与对象 2.3在 v-for 里使用范围值 1.类与样式的绑定 1.1绑定 HTML class 我们可以给 :class (v-bind:class 的缩写) 传递一个对象来动态切换 class…...
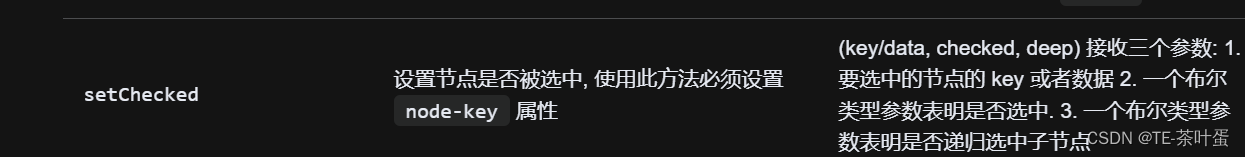
vue3+element-plus权限控制实现(el-tree父子级不关联情况处理)
文章目录 前言一、遇到的交互场景el-tree 中 check-strictly 属性 二、处理父级的半选中以及选中交互el-treecheck,check-change 事件编辑进来,父级的半选状态处理 总结 前言 在开发后台管理系统的时候,用户的权限控制是一个常见的需求。这里…...

js中事件委托和事件绑定之间的区别
聚沙成塔每天进步一点点 ⭐ 专栏简介⭐ 事件绑定(Event Binding)⭐事件委托(Event Delegation)⭐ 选择事件绑定或事件委托⭐ 写在最后 ⭐ 专栏简介 前端入门之旅:探索Web开发的奇妙世界 记得点击上方或者右侧链接订阅本…...

Android 11.0 系统system模块开启禁用adb push和adb pull传输文件功能
1.使用场景 在进行11.0的系统定制化开发中,在一些产品中由于一些开发的功能比较重要,防止技术点外泄在出货产品中,禁用 adb pull 和adb push等命令 来获取系统system下的jar 和apk 等文件,所以需要禁用这些命令 2.系统system模块开启禁用adb push和adb pull传输文件功能的…...

实战经验分享:如何通过HTTP代理解决频繁封IP问题
在网络爬虫和数据采集等应用中,频繁遇到目标网站封锁或限制IP的情况是非常常见的。为了解决这个问题,使用HTTP代理是一种有效的方法。本文将与您分享一些实战经验,帮助您通过HTTP代理解决频繁封IP问题,确保您的数据采集工作顺利进…...

通讯网关软件001——利用CommGate X2Access-U实现OPC UA数据转储Access
本文介绍利用CommGate X2ACCESS-U实现从OPC UA Server读取数据并同步转储至ACCESS数据库。CommGate X2ACCESS-U是宁波科安网信开发的网关软件,软件可以登录到网信智汇(http://wangxinzhihui.com)下载。 【案例】如下图所示,实现从OPC UA Server实时读取…...
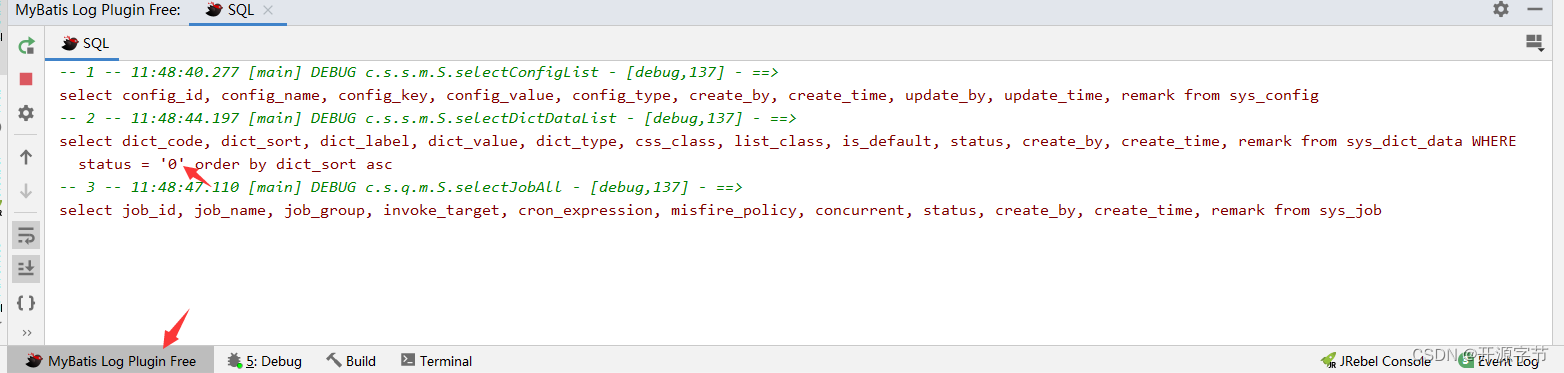
Mybatis sql参数自动填充
问题描述 在日常开发中,经常会遇到Mybatis sql语句的操作问题,由于Mybatis实现sql的动态拼接,开发过程中,为了验证sql是否书写正确,通常需要获取的控制台打印的sql语句来检查是否拼接正确。如下图所示: 那…...

OpenLayers 可视化之热力图
注:当前使用的是 ol 5.3.0 版本,天地图使用的key请到天地图官网申请,并替换为自己的key 热力图(Heatmap)又叫热点图,是一种通过特殊高亮显示事物密度分布、变化趋势的数据可视化技术。采用颜色的深浅来显示…...
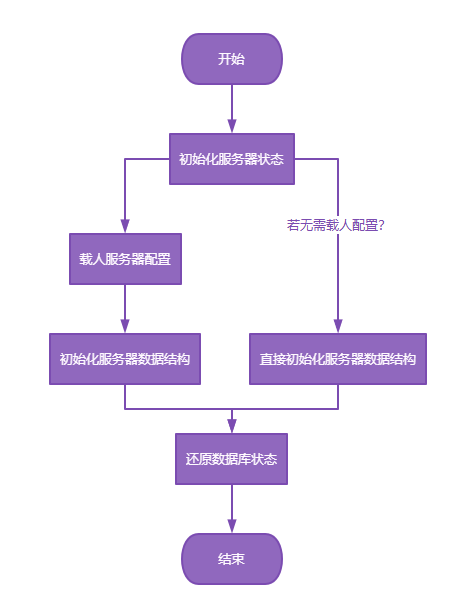
【Redis技术进阶之路】「原理分析系列开篇」分析客户端和服务端网络诵信交互实现(服务端执行命令请求的过程 - 初始化服务器)
服务端执行命令请求的过程 【专栏简介】【技术大纲】【专栏目标】【目标人群】1. Redis爱好者与社区成员2. 后端开发和系统架构师3. 计算机专业的本科生及研究生 初始化服务器1. 初始化服务器状态结构初始化RedisServer变量 2. 加载相关系统配置和用户配置参数定制化配置参数案…...

音视频——I2S 协议详解
I2S 协议详解 I2S (Inter-IC Sound) 协议是一种串行总线协议,专门用于在数字音频设备之间传输数字音频数据。它由飞利浦(Philips)公司开发,以其简单、高效和广泛的兼容性而闻名。 1. 信号线 I2S 协议通常使用三根或四根信号线&a…...
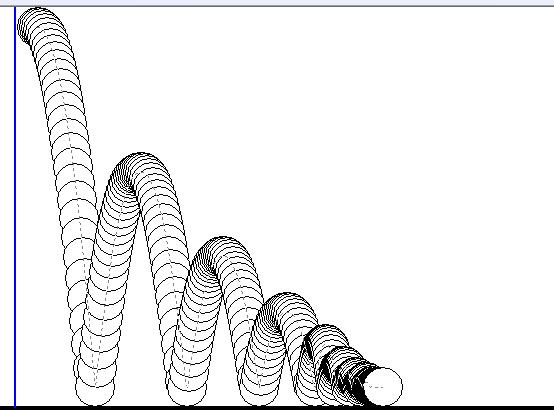
MFC 抛体运动模拟:常见问题解决与界面美化
在 MFC 中开发抛体运动模拟程序时,我们常遇到 轨迹残留、无效刷新、视觉单调、物理逻辑瑕疵 等问题。本文将针对这些痛点,详细解析原因并提供解决方案,同时兼顾界面美化,让模拟效果更专业、更高效。 问题一:历史轨迹与小球残影残留 现象 小球运动后,历史位置的 “残影”…...
免费数学几何作图web平台
光锐软件免费数学工具,maths,数学制图,数学作图,几何作图,几何,AR开发,AR教育,增强现实,软件公司,XR,MR,VR,虚拟仿真,虚拟现实,混合现实,教育科技产品,职业模拟培训,高保真VR场景,结构互动课件,元宇宙http://xaglare.c…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...

小木的算法日记-多叉树的递归/层序遍历
🌲 从二叉树到森林:一文彻底搞懂多叉树遍历的艺术 🚀 引言 你好,未来的算法大神! 在数据结构的世界里,“树”无疑是最核心、最迷人的概念之一。我们中的大多数人都是从 二叉树 开始入门的,它…...

计算机系统结构复习-名词解释2
1.定向:在某条指令产生计算结果之前,其他指令并不真正立即需要该计算结果,如果能够将该计算结果从其产生的地方直接送到其他指令中需要它的地方,那么就可以避免停顿。 2.多级存储层次:由若干个采用不同实现技术的存储…...
)
GitHub 常见高频问题与解决方案(实用手册)
1.Push 提示权限错误(Permission denied) 问题: Bash Permission denied (publickey) fatal: Could not read from remote repository. 原因: 没有配置 SSH key 或使用了 HTTPS 而没有权限…...

暴雨新专利解决服务器噪音与性能悖论
6月1日,我国首部数据中心绿色化评价方面国家标准《绿色数据中心评价》正式实施,为我国数据中心的绿色低碳建设提供了明确指引。《评价》首次将噪音控制纳入国家级绿色评价体系,要求从设计隔声结构到运维定期监测实现闭环管控,加速…...
