Spring实例化源码解析之ConfigurationClassParser(三)
前言
上一章我们分析了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法的源码逻辑,其中核心逻辑do while中调用parser.parse(candidates)方法,解析candidates中的候选配置类。然后本章我们主要分析ConfigurationClassParser的parse方法到底做了什么。
parse
configCandidates在项目启动的时候只有我们的AopConfig类,也就是说这个parse方法其实就是解析启动类。
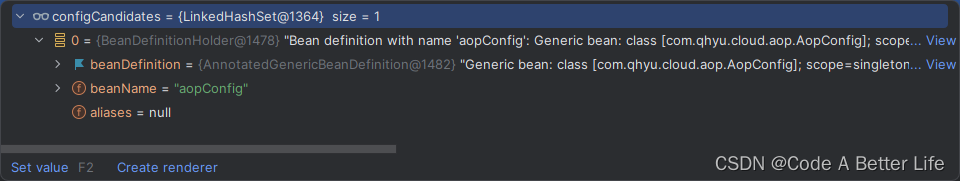
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();try {if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());}else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());}else {parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}}catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);}}this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();}
当前我的启动类是AopConfig,属于AnnotatedBeanDefinition,会进入到第一个if逻辑里。parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());第一个参数传入的元数据,第二个参数传入的是beanName。
private static final Predicate<String> DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER = className ->(className.startsWith("java.lang.annotation.") || className.startsWith("org.springframework.stereotype."));protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);}
processConfigurationClass方法传递了一个ConfigurationClass和一个Predicate,Predicate就是为了判断ClassName的,ConfigurationClass包含了元数据、beanName等信息。
processConfigurationClass
进入方法的第一个if用于判断是否包含@Condition注解,反正含义就是看这个候选配置类需不需要跳过,里面的其他逻辑就不关注了。下面其实就是核心逻辑了,我们继续拆解分析。
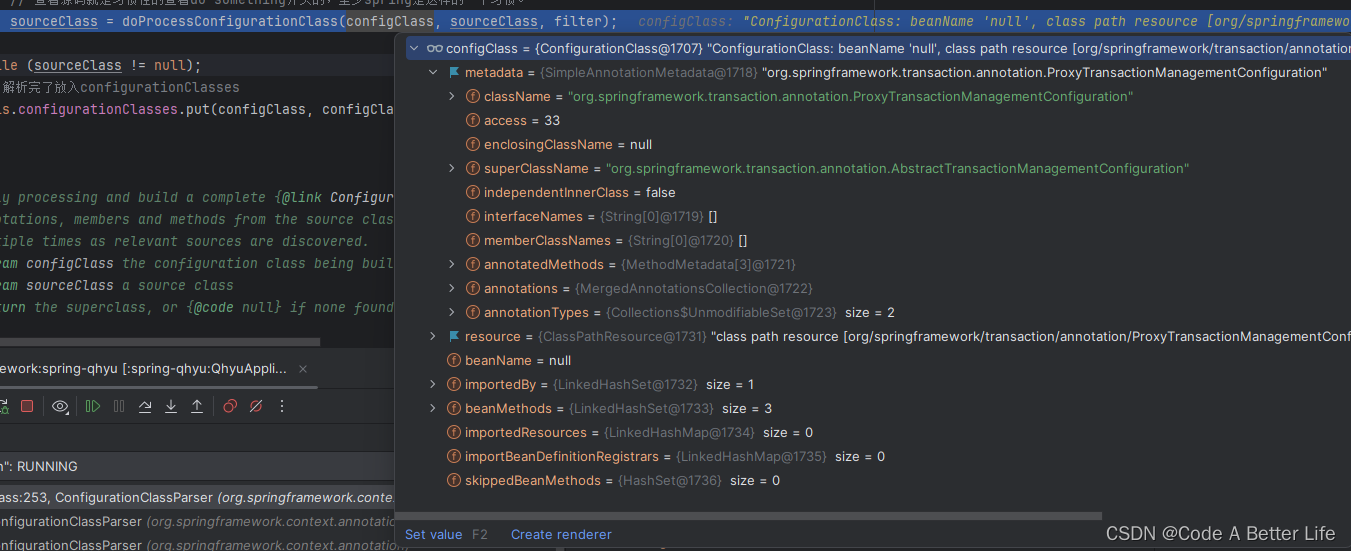
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {return;}// 查看这个配置类是不是存在了,如果存在就走下面的if逻辑ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);if (existingClass != null) {if (configClass.isImported()) {if (existingClass.isImported()) {existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);}// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.return;}else {// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);}}// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);// 此处使用了个do whiledo {// 查看源码就是习惯性的查看do something开头的,至少spring是这样的一个习惯。sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);}while (sourceClass != null);// 解析完了放入configurationClassesthis.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);}
existingClass是看配置类是不是已经解析过了,为什么启动的时候要判断是否存在,原因就是因为底下有个do while循环。这个方法后续会调用很多次。如果不存在会走底下的do while逻辑,就是本章的核心内容。这里会很绕,我尽量讲清楚。
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);还是可以单独拿出来描述一下:
方法的参数包括一个可为null的className和一个Predicate<String>类型的filter,还可能抛出IOException异常。
方法的执行逻辑如下:
1、首先,检查className是否为null或者经过filter筛选后返回true。如果是这种情况,直接返回预先设定的objectSourceClass对象。
2、如果className以"java"开头,表示该类是核心Java类型,将不使用ASM(Java字节码操作库)进行处理。此时,尝试加载该类,并使用ClassUtils.forName方法获取类的Class对象。如果加载失败,将抛出ClassNotFoundException异常并包装为NestedIOException。
3、如果以上条件都不满足,说明className表示的类不是核心Java类型,那么使用metadataReaderFactory(可能是一个元数据读取工厂)获取className对应的元数据读取器(MetadataReader),并将其传递给SourceClass的构造函数,创建一个新的SourceClass对象。
doProcessConfigurationClass
首先我的AopConfig有两个注解,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy和@ComponentScan(value = {“com.qhyu.cloud.**”}),当然我们的springboot项目一般都是约定大于配置的方式,不写这个ComponentScan注解。
下面是整个方法的源码和我的个人注释信息,我们这边还是先将源码整体放出来,然后再拆解分析。
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)throws IOException {// 如果这个候选配置类中有Component注解,走下面的逻辑if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {// Recursively process any member (nested) classes firstprocessMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);}// Process any @PropertySource annotationsfor (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {processPropertySource(propertySource);}else {logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");}}// Process any @ComponentScan annotations// 我们的AopConfig候选配置类就会走到下面这个逻辑Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);// componentScans不为空,第一个条件满足// sourceClass.getMetadata()不为null;通过Conditional注解来控制bean是否需要注册,控制被@Configuration标注的配置类是否需要被解析 第二个条件false,取反。if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately// 使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析// 这里面将会注册我们自己写的一些将被spring接管的类的BeanDefinition信息Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if neededfor (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();if (bdCand == null) {bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();}if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}}}}// Process any @Import annotationsprocessImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);// Process any @ImportResource annotationsAnnotationAttributes importResource =AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);if (importResource != null) {String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");for (String resource : resources) {String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);}}// Process individual @Bean methodsSet<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));}// Process default methods on interfacesprocessInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);// Process superclass, if anyif (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recursereturn sourceClass.getSuperClass();}}// No superclass -> processing is completereturn null;}
片段一
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {// Recursively process any member (nested) classes firstprocessMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);}
当前AopConfig启动类是没有Component注解的,不会进入这个逻辑。代码中的英文注释说的是首先递归处理任何成员(嵌套)类,也就是说如果@Component注解注释的类中没有内部类(嵌套类)也不会做任何处理。
片段二
// Process any @PropertySource annotationsfor (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {processPropertySource(propertySource);}else {logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");}}
直接看注释,处理任何被@PropertySource注解修饰的class
片段三
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations// 我们的AopConfig候选配置类就会走到下面这个逻辑Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);// componentScans不为空,第一个条件满足// sourceClass.getMetadata()不为null;通过Conditional注解来控制bean是否需要注册,控制被@Configuration标注的配置类是否需要被解析 第二个条件false,取反。if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately// 使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析// 这里面将会注册我们自己写的一些将被spring接管的类的BeanDefinition信息Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if neededfor (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();if (bdCand == null) {bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();}if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}}}}
处理任何被@ComponentScan注解修时的类,当然这里还包括@ComponentScans注解,componentScans属性会获取到注解的信息,如下图所示:
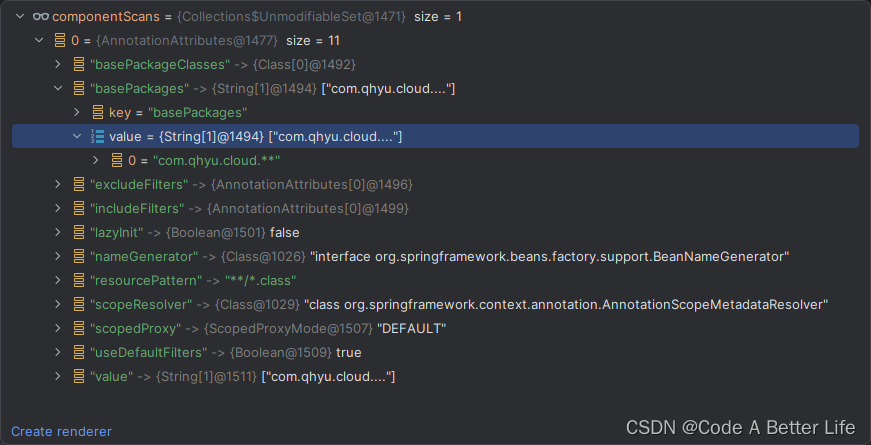
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN))
首先componentScans属性肯定不为空,所以第一个条件是ture,然后看是否应该跳过,当前AopConfig不存在Condition注解,返回false,此处取反,所以if条件返回true,进入if逻辑。
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately// 使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析// 这里面将会注册我们自己写的一些将被spring接管的类的BeanDefinition信息Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if neededfor (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();if (bdCand == null) {bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();}if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}}}
这个循环,获取的AnnotaionAttributes就是我们的@ComponentScan(value = {“com.qhyu.cloud.**”})注解的信息。然后会调用使用this.componentScanParser ComponentScanAnnotationParser来解析,主要就是扫描我们定义的路径下的所有需要被Spring管理的bean,组装程BeanDefinitionHolder返回到scannedBeanDefinitions集合,同时这些bean的定义信息会被注入到bean工厂中,本章在此处不会深入的去分析里面的源码,将在下一章节进行分析。
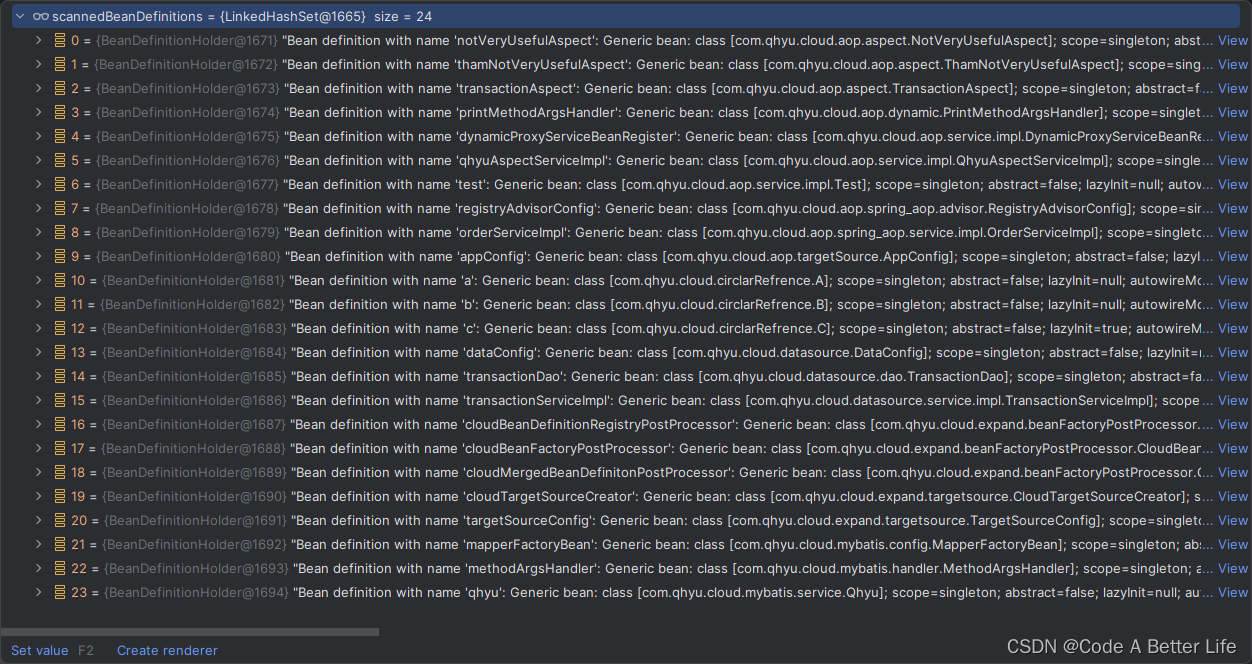
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());}
这段源码在之前已经分析过了,第二章节,如果发现我们scannedBeanDefinitions中还存在配置类,就继续解析,也就是把这些beanDefinition都注册到bean工厂中。
如果不是配置类或者处理完了配置类之后会继续往下走他的逻辑。
片段四
处理被@Import注解修时的类
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
比如我们的AopConfig不是有个@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解嘛,这个注解里面会有个@Import,所以AopConfig解析之后会执行configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata());代码,在ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的processConfigBeanDefinitions方法中this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);这行代码会读取出来进行注册。
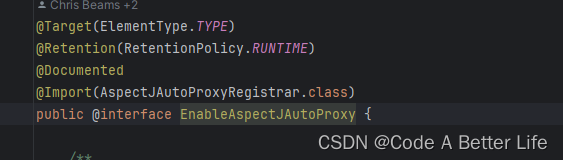
片段五
处理任何@ImportResource annotations
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");for (String resource : resources) {String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);}
}
片段六
处理各个@Bean的方法
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));}
片段七
处理接口上的默认方法
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
片段八
处理superclass,超类,如果有的话。可以发现这里面有个return,其他的片段都是返回的void,此处如果返回的话,外部的do while就会继续执行。
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recursereturn sourceClass.getSuperClass();}
}
整理流程梳理
方法的执行逻辑如下:
-
首先,检查配置类 configClass 是否被 @Component 注解标记。如果是,则递归处理任何成员类(嵌套类)。
-
处理任何 @PropertySource 注解。遍历配置类中的 @PropertySource 注解,如果当前环境实现了 ConfigurableEnvironment 接口,则进行属性源的处理。否则,记录日志,表明忽略该注解。
-
处理任何 @ComponentScan 注解。获取配置类中的 @ComponentScan 注解,如果存在且满足相关条件(componentScans 不为空,且配置类满足条件判断),则使用 componentScanParser 来解析注解,执行组件扫描操作,并注册相应的 BeanDefinition 信息。如果扫描到的定义中包含其他配置类,则递归解析这些配置类。
-
处理任何 @Import 注解。根据配置类中的 @Import 注解,获取需要导入的类,并进行处理。这些导入的类可以是其他配置类,也可以是其他普通的类。处理过程中,可能会继续递归解析导入的类。
-
处理任何 @ImportResource 注解。根据配置类中的 @ImportResource 注解,获取资源的位置和读取器类型,并进行处理。通常,这些资源是 XML 配置文件。解析过程中,可能会使用 BeanDefinitionReader 来读取并注册相关的 BeanDefinition。
-
处理配置类中的每个 @Bean 方法。获取配置类中所有的 @Bean 方法的元数据,并将其添加到 configClass 对象中。
-
处理接口的默认方法。如果配置类实现了接口,并且接口中定义了默认方法,则对这些默认方法进行处理。
-
处理父类(如果存在)。如果配置类有父类,并且父类不是 Java 核心类,也不在已知的父类列表中,则将父类添加到已知的父类列表中,并返回父类的注解元数据,以便进行递归处理。
-
如果没有父类,则处理完成,返回 null。
总结
本章主要分析了ConfigurationClassParser的parse方法的源码,其中设计到的ComponentScanAnnotationParser的parse方法我们没有深入分析,这里面涉及到的是将我们启动类目录或者@ComponentScan注解的basePackages目录下的我们需要交给容器管理的bean的定义信息注册将在下一章进行分析。
相关文章:

Spring实例化源码解析之ConfigurationClassParser(三)
前言 上一章我们分析了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法的源码逻辑,其中核心逻辑do while中调用parser.parse(candidates)方法,解析candidates中的候选配置类。然后本章我们主要分析ConfigurationClassParser的…...

在 Substance Painter中实现Unity Standard Shader
由于有需要在Substance Painter中显示什么样的效果,在Unity就要显示什么样的效果的需求,最近研究了几天,总算在Substance Painter中实现Unity standard的材质的渲染效果。具体效果如下: 在Unity中: Substance Painte…...

第二证券:个人开证券账户要开户费吗?
随着互联网和移动端东西的遍及,越来越多的人开端涉足股票投资,开立证券账户也成为一个热门话题。但是,许多初学者或许会有疑问,个人开证券账户是否需求支付开户费呢?这个问题的答案并不是那么简略,需求考虑…...
大厂面试-16道面试题
1 java集合类有哪些? List是有序的Collection,使用此接口能够精确的控制每个元素的插入位置,用户能根据索引访问List中元素。常用的实现List的类有LinkedList,ArrayList,Vector,Stack。 ArrayList是容量…...
搭建GraphQL服务
js版 GraphQL在 NodeJS 服务端中使用最多 安装graphql-yoga: npm install graphql-yoga 新建index.js: const {GraphQLServer} require("graphql-yoga")const server new GraphQLServer({ typeDefs: type Query { hello(name:String):String! …...

数据仓库介绍及应用场景
数据仓库(Data Warehouse)是一个用于存储、管理、检索和分析大量结构化数据的集中式数据库系统。与传统的事务处理数据库不同,数据仓库是为了支持决策支持系统(Decision Support Systems, DSS)和业务智能(B…...
 LeetCode 583. 两个字符串的删除操作 72. 编辑距离)
代码随想录算法训练营Day56 | 动态规划(16/17) LeetCode 583. 两个字符串的删除操作 72. 编辑距离
动态规划马上来到尾声了,当时还觉得动态规划内容很多,但是也这么过来了。 第一题 583. Delete Operation for Two Strings Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of steps required to make word1 and word2 the same. In on…...
HTML+CSS+JavaScript 大学生网页设计制作作业实例代码 200套静态响应式前端网页模板(全网最全,建议收藏)
目录 1.介绍2.这样的响应式页面这里有200套不同风格的 1.介绍 资源链接 📚web前端期末大作业 (200套) 集合 Web前端期末大作业通常是一个综合性的项目,旨在检验学生在HTML、CSS和JavaScript等前端技术方面的能力和理解。以下是一些可能的Web前端期末大…...

CFimagehost私人图床本地部署结合cpolar内网穿透实现公网访问
文章目录 1.前言2. CFImagehost网站搭建2.1 CFImagehost下载和安装2.2 CFImagehost网页测试2.3 cpolar的安装和注册 3.本地网页发布3.1 Cpolar临时数据隧道3.2 Cpolar稳定隧道(云端设置)3.3.Cpolar稳定隧道(本地设置) 4.公网访问测…...

uniapp瀑布流布局写法
首先我们要清楚瀑布流是什么? 瀑布流布局(Waterfall Flow Layout),也称为瀑布流式布局,是一种常见的网页或移动应用布局方式,特点是元素以不规则的方式排列,就像瀑布中的流水一样,每…...
蓝桥杯 题库 简单 每日十题 day8
01 扫雷 题目描述 在一个n行列的方格图上有一些位置有地雷,另外一些位置为空。 请为每个空位置标一个整数,表示周围八个相邻的方格中有多少个地雷。 输入描述 输入的第一行包含两个整数n,m。 第2行到第n1行每行包含m个整数,相邻整…...

Keepalived 高可用(附带配置实例,联动Nginx和LVS)
Keepalived 一、Keepalived相关知识点概述1.1 单服务的风险(单点故障问题)1.2 一个合格的集群应该具备的特性1.3 VRRP虚拟路由冗余协议1.4 健康检查1.5 ”脑裂“现象 二、Keepalived2.1 Keepalived是什么?2.2 Keepalived体系主要模块及其作用…...

第二证券:今年来港股回购金额超700亿港元 9月近200家公司获增持
本年以来,港股上市公司回购力度不断增强。据恒生指数公司计算,到9月15日,本年以来港股回购金额到达735亿港元,占去年全年总额的70%。该公司预测,2023年港股回购金额可能到达929亿港元,是前5年年度平均水平的…...

Autosar基础——RTE简介
AutoSAR文章目录 AUTomotive Open System Architecture Autosar-简介和历史发展 Autosar-软件架构 Autosar软件组件-Application Layer介绍和SWC(Software Component)类型 Autosar-Runnables(可运行实体) Autosar-OS配置 Autosar IOC机制(核间通信) Autosar实践-CANTp Auto…...

几个国内可用的强大的GPT工具
前言: 人工智能发布至今,过去了九个多月,已经成为了我们不管是工作还是生活中一个重要的辅助工具,大大提升了效率,作为一个人工智能的自然语言处理工具,它给各大行业的提供了一个巨大的生产工具,…...

《Python等级考试(1~6级)历届真题解析》专栏总目录
❤️ 专栏名称:《Python等级考试(1~6级)历届真题解析》 🌸 专栏介绍:中国电子学会《全国青少年软件编程等级考试》Python编程(1~6级)历届真题解析。 🚀 订阅专栏:订阅后可…...
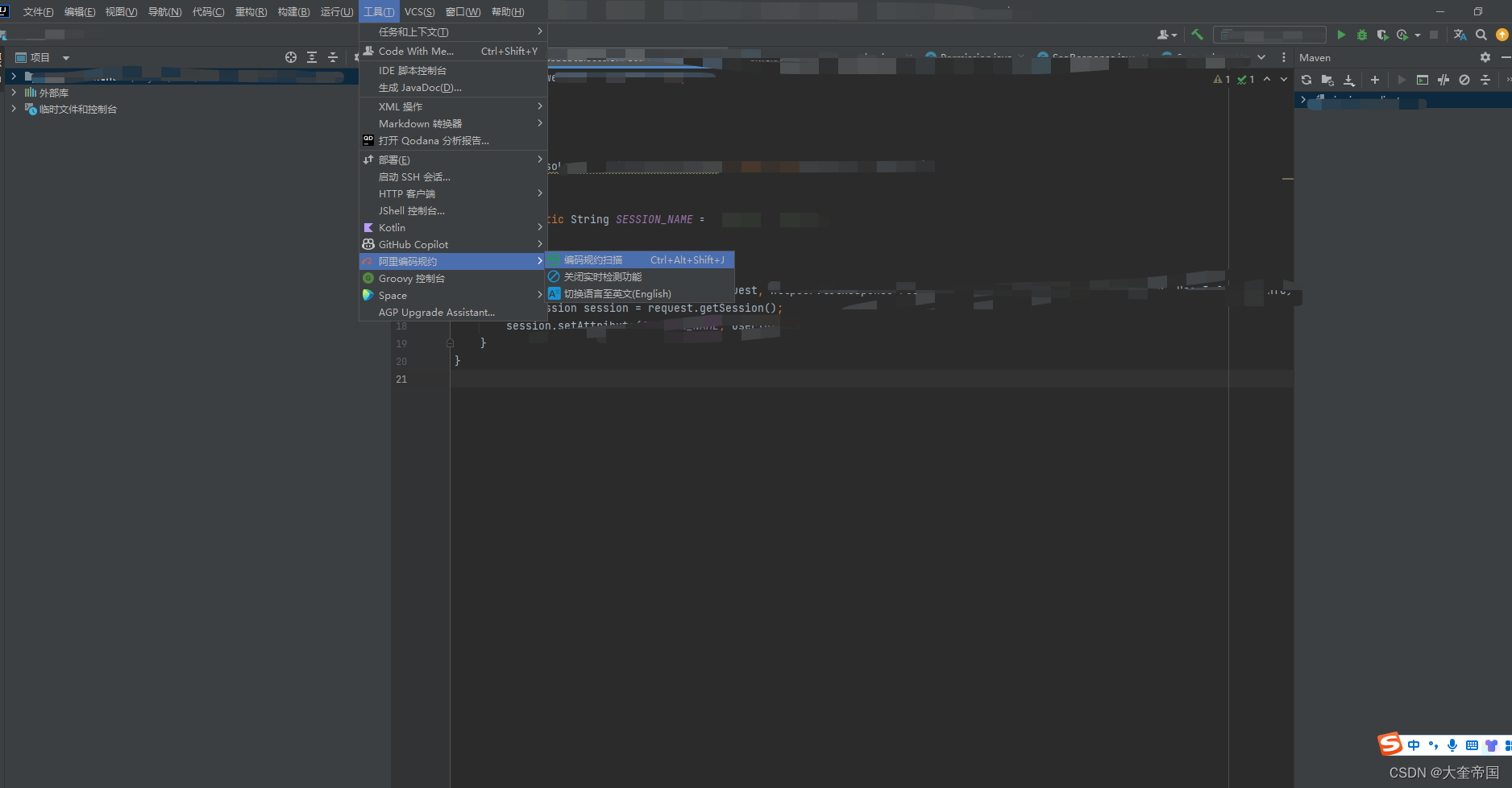
在IntelliJ IDEA 中安装阿里P3C以及使用指南
在IntelliJ IDEA 中安装阿里P3C以及使用指南 1.关于阿里p3c1.1说明1.2什么是P3C插件1.3p3c的作用是什么 2 如何在IDEA中安装p3c2.1 插件安装2.2 插件使用 3.参考连接 1.关于阿里p3c 1.1说明 代码规范检查插件P3C,是根据《阿里巴巴java开发手册(黄山版)》转化而成的…...
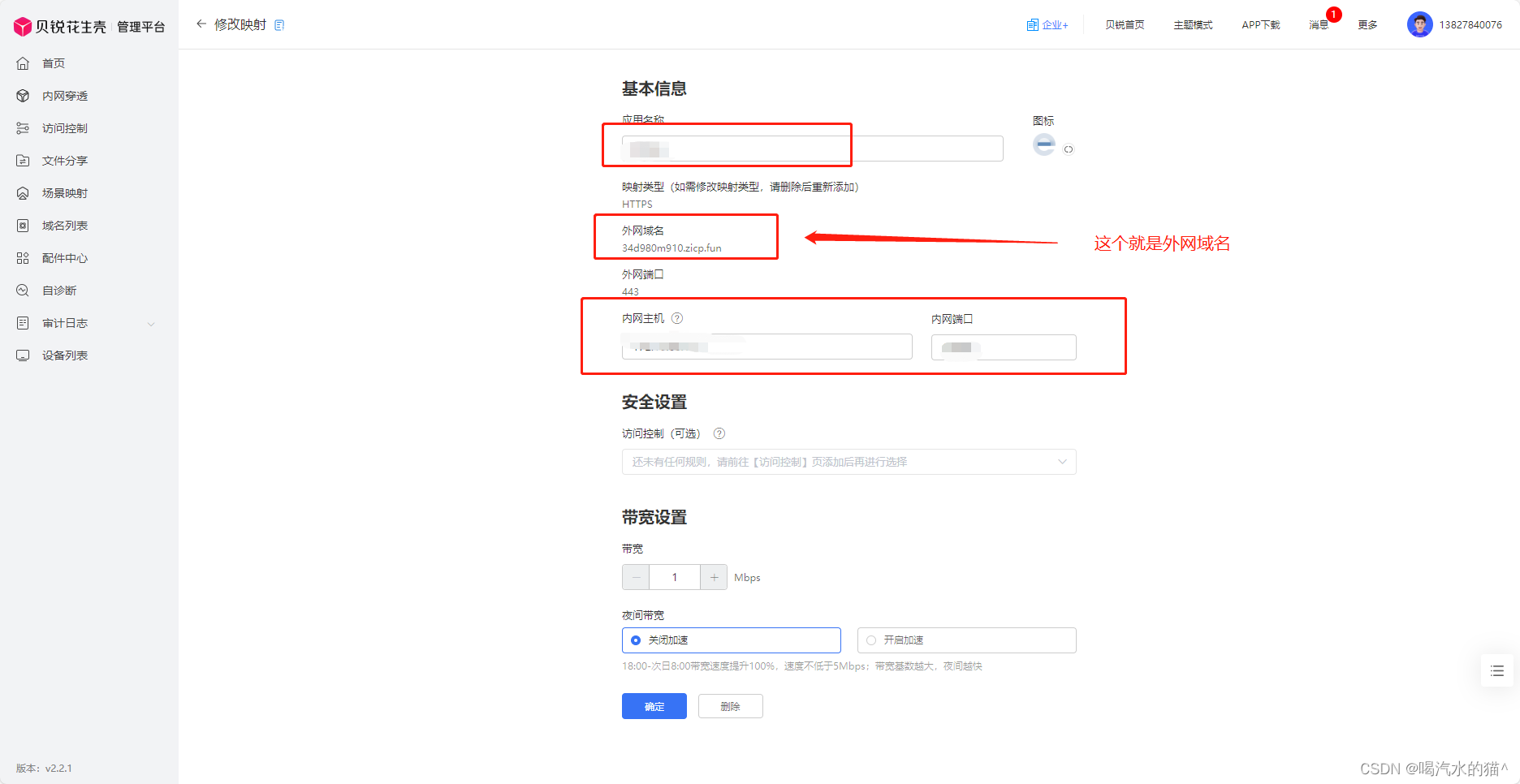
Java集成支付宝沙箱支付,详细教程(SpringBoot完整版)
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 一、开发前准备?二、使用步骤1、引入库2、配置在 application.yml 里面进行配置:3、alipay的java配置:AplipayConfig.java4、支付…...
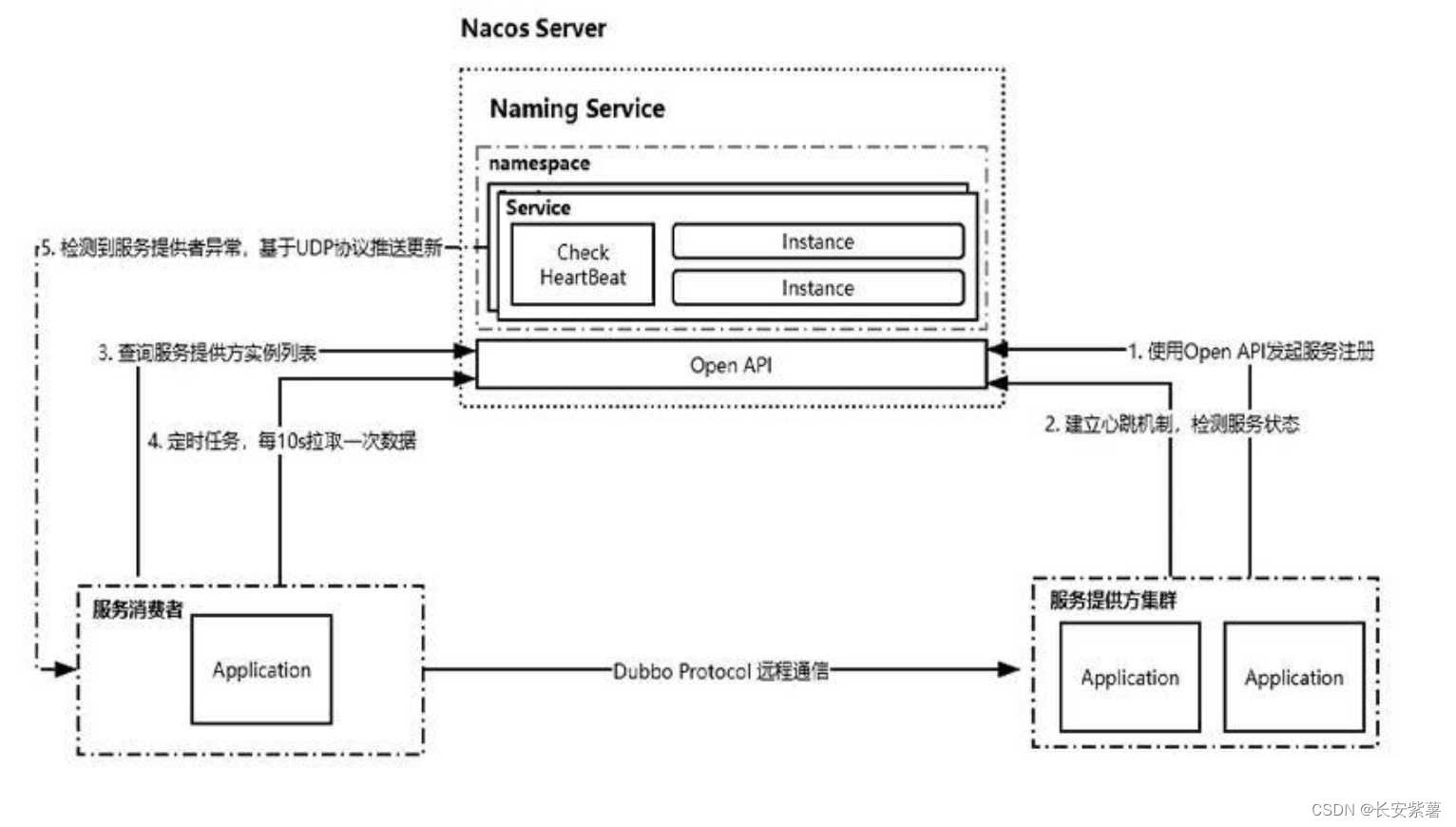
详解Nacos和Eureka的区别
文章目录 Eureka是什么Nacos是什么Nacos的实现原理 Nacos和Eureka的区别CAP理论连接方式服务异常剔除操作实例方式自我保护机制 Eureka是什么 Eureka 是Spring Cloud 微服务框架默认的也是推荐的服务注册中心, 由Netflix公司与2012将其开源出来,Eureka基于REST服务开发,主要用…...
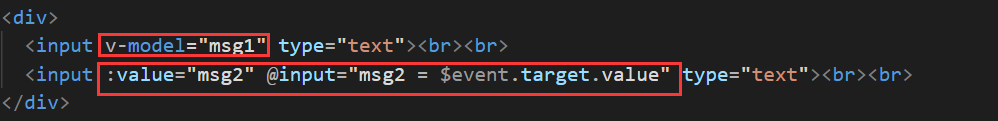
在Vue中实现组件间的通信(父子通信,非父子通信,通用通信)
在vue中实现组件间的通信 文章目录 在vue中实现组件间的通信1、组件通信1.1、不同的组件关系和组件通信方案分类1.2、组件通信的解决方案1.3、非父子通信- event bus事件总线 2、prop2.1、prop详解2.2、prop校验2.3、prop & data、单向数据流 3、v-mdoel原理 1、组件通信 …...
)
浏览器访问 AWS ECS 上部署的 Docker 容器(监听 80 端口)
✅ 一、ECS 服务配置 Dockerfile 确保监听 80 端口 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]或 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["python3", "-m", "http.server", "80"]任务定义(Task Definition&…...

在软件开发中正确使用MySQL日期时间类型的深度解析
在日常软件开发场景中,时间信息的存储是底层且核心的需求。从金融交易的精确记账时间、用户操作的行为日志,到供应链系统的物流节点时间戳,时间数据的准确性直接决定业务逻辑的可靠性。MySQL作为主流关系型数据库,其日期时间类型的…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...
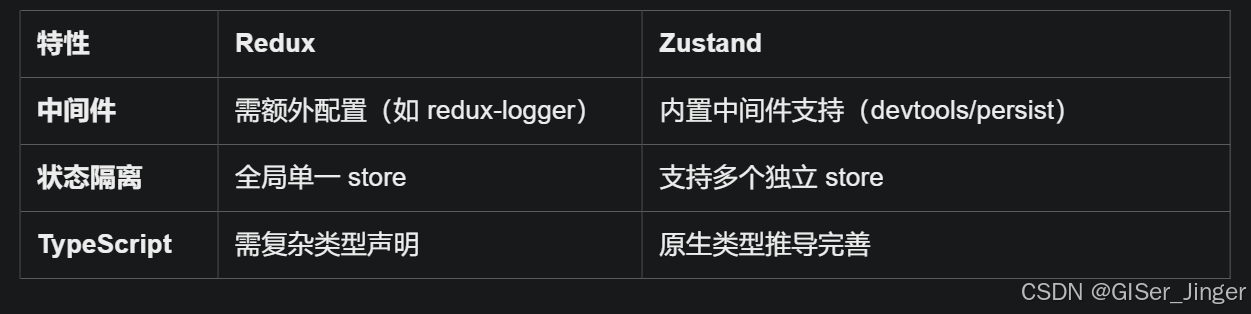
Zustand 状态管理库:极简而强大的解决方案
Zustand 是一个轻量级、快速和可扩展的状态管理库,特别适合 React 应用。它以简洁的 API 和高效的性能解决了 Redux 等状态管理方案中的繁琐问题。 核心优势对比 基本使用指南 1. 创建 Store // store.js import create from zustandconst useStore create((set)…...
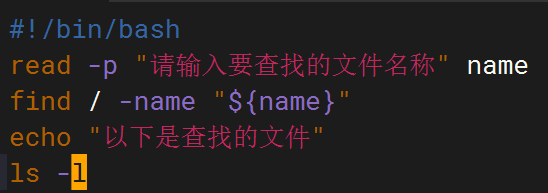
shell脚本--常见案例
1、自动备份文件或目录 2、批量重命名文件 3、查找并删除指定名称的文件: 4、批量删除文件 5、查找并替换文件内容 6、批量创建文件 7、创建文件夹并移动文件 8、在文件夹中查找文件...

376. Wiggle Subsequence
376. Wiggle Subsequence 代码 class Solution { public:int wiggleMaxLength(vector<int>& nums) {int n nums.size();int res 1;int prediff 0;int curdiff 0;for(int i 0;i < n-1;i){curdiff nums[i1] - nums[i];if( (prediff > 0 && curdif…...
cf2117E
原题链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/2117/problem/E 题目背景: 给定两个数组a,b,可以执行多次以下操作:选择 i (1 < i < n - 1),并设置 或,也可以在执行上述操作前执行一次删除任意 和 。求…...
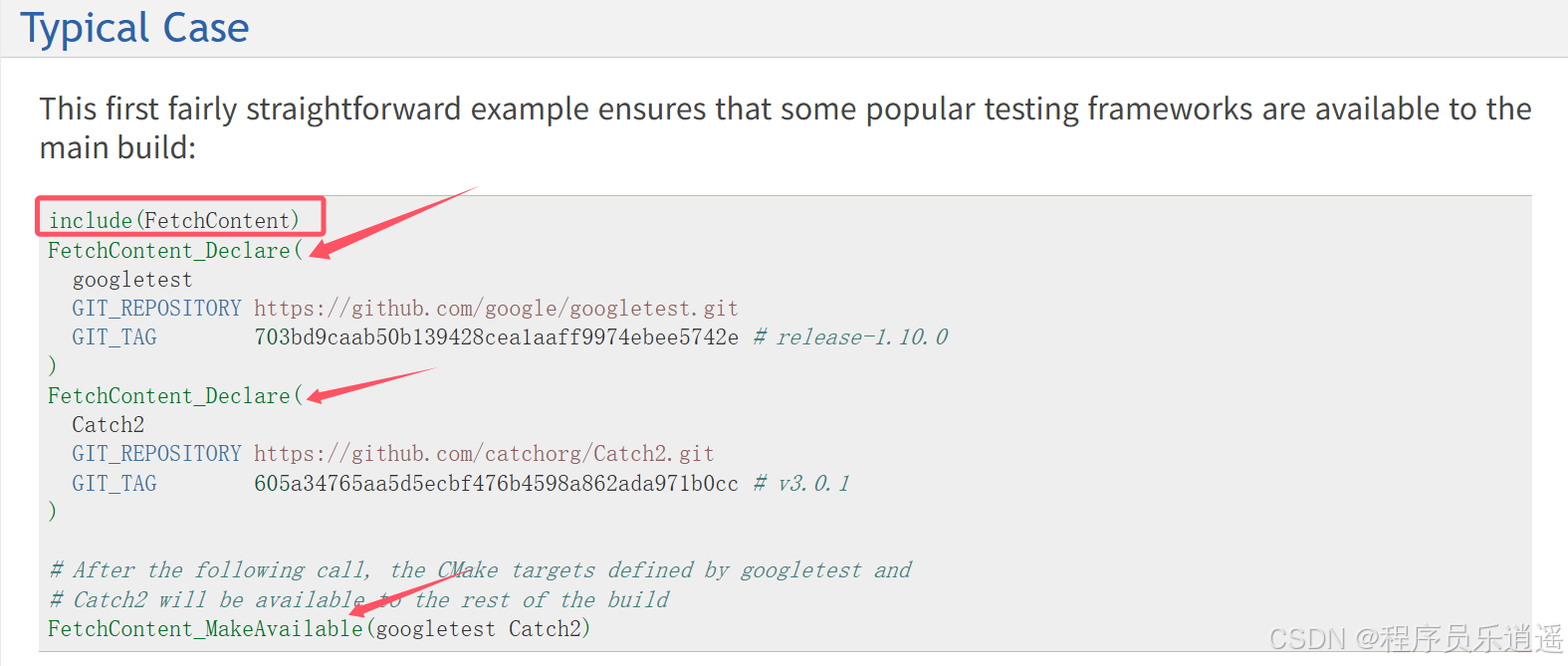
CMake 从 GitHub 下载第三方库并使用
有时我们希望直接使用 GitHub 上的开源库,而不想手动下载、编译和安装。 可以利用 CMake 提供的 FetchContent 模块来实现自动下载、构建和链接第三方库。 FetchContent 命令官方文档✅ 示例代码 我们将以 fmt 这个流行的格式化库为例,演示如何: 使用 FetchContent 从 GitH…...
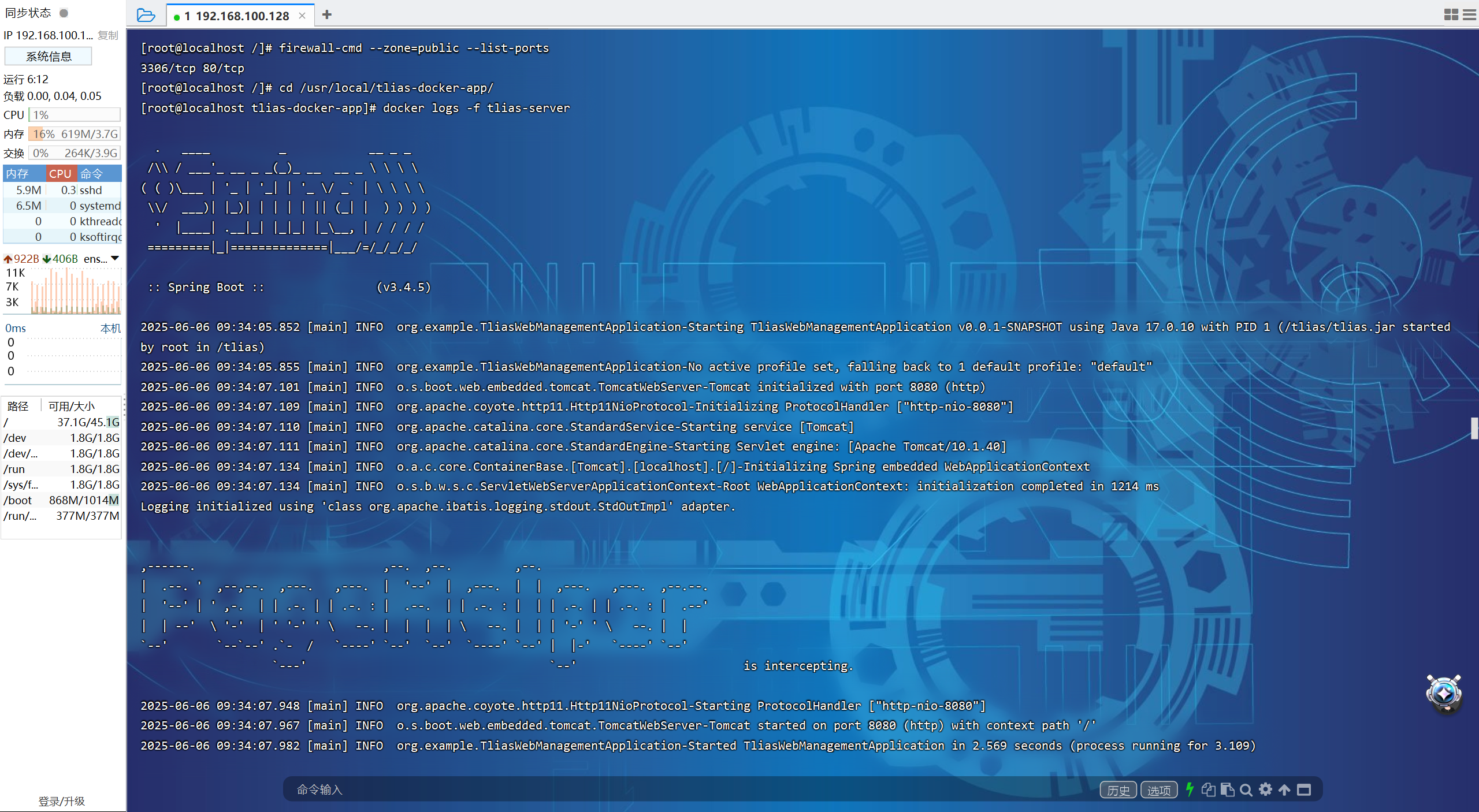
【JavaWeb】Docker项目部署
引言 之前学习了Linux操作系统的常见命令,在Linux上安装软件,以及如何在Linux上部署一个单体项目,大多数同学都会有相同的感受,那就是麻烦。 核心体现在三点: 命令太多了,记不住 软件安装包名字复杂&…...

Java 二维码
Java 二维码 **技术:**谷歌 ZXing 实现 首先添加依赖 <!-- 二维码依赖 --><dependency><groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId><artifactId>core</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><de…...
