Linux migrate_type进一步探索
文章接着上回Linux migrate_type初步探索
1、物理页面添加到buddy系统
我们都知道物理内存一开始是由memblock进行分配管理,后面会切换到buddy系统管理。那么接下来我们看一下,memblock管理的物理页面是怎么添加到buddy系统中的。
start_kernel()
-> mm_init()
--> mem_init()
---> memblock_free_all()
----> free_low_memory_core_early()
1.1 free_low_memory_core_early()
static unsigned long __init free_low_memory_core_early(void)
{unsigned long count = 0;phys_addr_t start, end;u64 i;memblock_clear_hotplug(0, -1);// 处理预留内存for_each_reserved_mem_range(i, &start, &end)reserve_bootmem_region(start, end);/** We need to use NUMA_NO_NODE instead of NODE_DATA(0)->node_id* because in some case like Node0 doesn't have RAM installed* low ram will be on Node1*/// 遍历可释放物理内存区域,进行释放for_each_free_mem_range(i, NUMA_NO_NODE, MEMBLOCK_NONE, &start, &end,NULL)count += __free_memory_core(start, end);return count;
}static unsigned long __init __free_memory_core(phys_addr_t start,phys_addr_t end)
{unsigned long start_pfn = PFN_UP(start);unsigned long end_pfn = min_t(unsigned long,PFN_DOWN(end), max_low_pfn);if (start_pfn >= end_pfn)return 0;// 进行页面释放处理__free_pages_memory(start_pfn, end_pfn);return end_pfn - start_pfn;
}
1.2 __free_pages_memory()
static void __init __free_pages_memory(unsigned long start, unsigned long end)
{int order;while (start < end) {/*** 由于buddy系统最大能存放的页面order是MAX_ORDER - 1UL,所以这里要进行限制* __ffs()函数是用来根据start值计算出最合适的order值* __ffs()函数作用是求第start第一个位为1的位置,例如:start = 0x63300,* 说明该地址以0x100对齐,那么__ffs()返回值为8*/order = min(MAX_ORDER - 1UL, __ffs(start));// 如果发现order太大,实际没有那么多物理内存,则不断减小order,直至能包含为止while (start + (1UL << order) > end)order--;// 将页面释放到buddy系统memblock_free_pages(pfn_to_page(start), start, order);start += (1UL << order);}
}
1.3 memblock_free_pages()
void __init memblock_free_pages(struct page *page, unsigned long pfn,unsigned int order)
{if (early_page_uninitialised(pfn))return;// 调用内部接口释放页面__free_pages_core(page, order);
}void __free_pages_core(struct page *page, unsigned int order)
{unsigned int nr_pages = 1 << order;struct page *p = page;unsigned int loop;/** When initializing the memmap, __init_single_page() sets the refcount* of all pages to 1 ("allocated"/"not free"). We have to set the* refcount of all involved pages to 0.*/prefetchw(p);// 遍历当前order页面内所有page,并初始化for (loop = 0; loop < (nr_pages - 1); loop++, p++) {prefetchw(p + 1);// 清楚页面预留标记__ClearPageReserved(p);// 设置页面引用计数为0set_page_count(p, 0);}__ClearPageReserved(p);set_page_count(p, 0);atomic_long_add(nr_pages, &page_zone(page)->managed_pages);/** Bypass PCP and place fresh pages right to the tail, primarily* relevant for memory onlining.*/// 将页面释放到buddy系统中__free_pages_ok(page, order, FPI_TO_TAIL);
}static void __free_pages_ok(struct page *page, unsigned int order,fpi_t fpi_flags)
{unsigned long flags;int migratetype;unsigned long pfn = page_to_pfn(page);if (!free_pages_prepare(page, order, true))return;// 获取页面所在页块的迁移类型migratetype = get_pfnblock_migratetype(page, pfn);local_irq_save(flags);__count_vm_events(PGFREE, 1 << order);// 将页面放置在对应迁移类型对应order的管理链表上free_one_page(page_zone(page), page, pfn, order, migratetype,fpi_flags);local_irq_restore(flags);
}
这里就是物理内存从memblock转移到buddy系统的流程。
2、迁移类型fallback处理逻辑
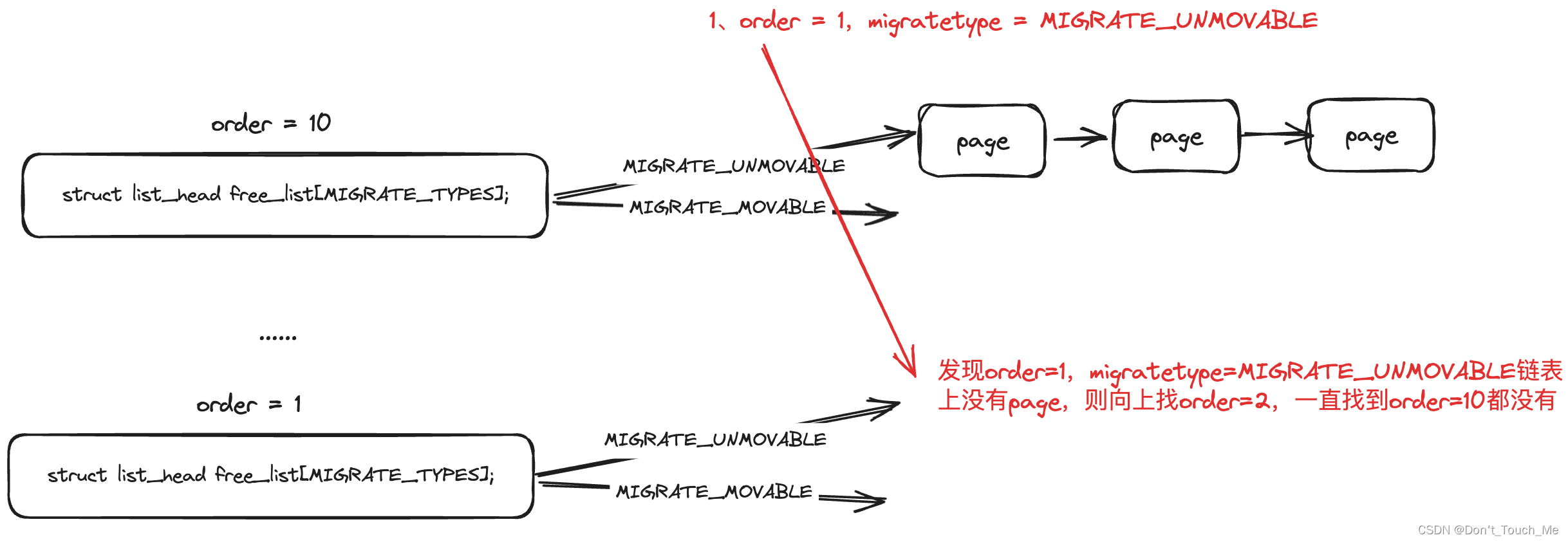
接下来我们再来看看一个新问题:一开始页块的迁移类型都是MIGRATE_MOVABLE,那对于MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE迁移类型的内存分配应该怎么处理呢?
2.1 原理图
我们都知道Linux内核内存分配接口alloc_pages(),那么我们就跟踪这个接口,看看是如何分配出MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE迁移类型的内存。
alloc_pages()
-> alloc_pages_node()
--> __alloc_pages_node()
---> __alloc_pages()
----> __alloc_pages_nodemask()
我们接下来仔细研究一下__alloc_pages_nodemask()实现:
2.2 __alloc_pages_nodemask()
/** This is the 'heart' of the zoned buddy allocator.*/
struct page *
__alloc_pages_nodemask(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int preferred_nid,nodemask_t *nodemask)
{struct page *page;// 第一次分配时,我们会从zone的low水线以上分配内存unsigned int alloc_flags = ALLOC_WMARK_LOW;gfp_t alloc_mask; /* The gfp_t that was actually used for allocation */struct alloc_context ac = { };/** There are several places where we assume that the order value is sane* so bail out early if the request is out of bound.*/// 如果order>=11时,buddy系统无法分配出内存,因此直接返回错误if (unlikely(order >= MAX_ORDER)) {WARN_ON_ONCE(!(gfp_mask & __GFP_NOWARN));return NULL;}gfp_mask &= gfp_allowed_mask;alloc_mask = gfp_mask;// 这里是根据gfp设置分配标识,以及确定优先从哪个zone里进行内存分配if (!prepare_alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order, preferred_nid, nodemask, &ac, &alloc_mask, &alloc_flags))return NULL;/** Forbid the first pass from falling back to types that fragment* memory until all local zones are considered.*/alloc_flags |= alloc_flags_nofragment(ac.preferred_zoneref->zone, gfp_mask);// 内存分配快速路径,我们今天只需要跟踪该函数实现就好了/* First allocation attempt */page = get_page_from_freelist(alloc_mask, order, alloc_flags, &ac);if (likely(page))goto out;/** Apply scoped allocation constraints. This is mainly about GFP_NOFS* resp. GFP_NOIO which has to be inherited for all allocation requests* from a particular context which has been marked by* memalloc_no{fs,io}_{save,restore}.*/alloc_mask = current_gfp_context(gfp_mask);ac.spread_dirty_pages = false;/** Restore the original nodemask if it was potentially replaced with* &cpuset_current_mems_allowed to optimize the fast-path attempt.*/ac.nodemask = nodemask;// 当快速路径无法分配出内存时,就会调用该函数,走慢速路径内存分配,这里会异步唤醒kswapd线程回收内存等操作page = __alloc_pages_slowpath(alloc_mask, order, &ac);out:if (memcg_kmem_enabled() && (gfp_mask & __GFP_ACCOUNT) && page &&unlikely(__memcg_kmem_charge_page(page, gfp_mask, order) != 0)) {__free_pages(page, order);page = NULL;}trace_mm_page_alloc(page, order, alloc_mask, ac.migratetype);return page;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__alloc_pages_nodemask);
2.3 get_page_from_freelist()
/** get_page_from_freelist goes through the zonelist trying to allocate* a page.*/
static struct page *
get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int alloc_flags,const struct alloc_context *ac)
{struct zoneref *z;struct zone *zone;struct pglist_data *last_pgdat_dirty_limit = NULL;bool no_fallback;retry:/** Scan zonelist, looking for a zone with enough free.* See also __cpuset_node_allowed() comment in kernel/cpuset.c.*/no_fallback = alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;z = ac->preferred_zoneref;// 优先从最优先的zone分配内存,若未分配到,降级到其他可分配内存的zonefor_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->highest_zoneidx,ac->nodemask) {struct page *page;unsigned long mark;if (cpusets_enabled() &&(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) &&!__cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_mask))continue;/** When allocating a page cache page for writing, we* want to get it from a node that is within its dirty* limit, such that no single node holds more than its* proportional share of globally allowed dirty pages.* The dirty limits take into account the node's* lowmem reserves and high watermark so that kswapd* should be able to balance it without having to* write pages from its LRU list.** XXX: For now, allow allocations to potentially* exceed the per-node dirty limit in the slowpath* (spread_dirty_pages unset) before going into reclaim,* which is important when on a NUMA setup the allowed* nodes are together not big enough to reach the* global limit. The proper fix for these situations* will require awareness of nodes in the* dirty-throttling and the flusher threads.*/if (ac->spread_dirty_pages) {if (last_pgdat_dirty_limit == zone->zone_pgdat)continue;if (!node_dirty_ok(zone->zone_pgdat)) {last_pgdat_dirty_limit = zone->zone_pgdat;continue;}}if (no_fallback && nr_online_nodes > 1 &&zone != ac->preferred_zoneref->zone) {int local_nid;/** If moving to a remote node, retry but allow* fragmenting fallbacks. Locality is more important* than fragmentation avoidance.*/local_nid = zone_to_nid(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone);if (zone_to_nid(zone) != local_nid) {alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;goto retry;}}mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);// 快速水线检查,查看当前zone是否可以分配出所需order大小的页面if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark,ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags,gfp_mask)) {int ret;#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT/** Watermark failed for this zone, but see if we can* grow this zone if it contains deferred pages.*/if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))goto try_this_zone;}
#endif/* Checked here to keep the fast path fast */BUILD_BUG_ON(ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS < NR_WMARK);if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS)goto try_this_zone;if (node_reclaim_mode == 0 ||!zone_allows_reclaim(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone))continue;// 尝试内存回收ret = node_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat, gfp_mask, order);switch (ret) {// 返回值为未进行回收扫描,则跳过该zonecase NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN:/* did not scan */continue;// 返回值为扫描但不能回收,则跳过该zonecase NODE_RECLAIM_FULL:/* scanned but unreclaimable */continue;default:/* did we reclaim enough */// 已经回收了一部分,检查水线是否满足,满足则使用该zone进行内存分配if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, mark,ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags))// 使用该zone进行内存分配goto try_this_zone;continue;}}try_this_zone:// 通过rmqueue从zone的buddy系统中分配页面page = rmqueue(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone, order,gfp_mask, alloc_flags, ac->migratetype);if (page) {// 分配到页面,进行一个处理prep_new_page(page, order, gfp_mask, alloc_flags);/** If this is a high-order atomic allocation then check* if the pageblock should be reserved for the future*/if (unlikely(order && (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER)))reserve_highatomic_pageblock(page, zone, order);// 返回分配到的页面return page;} else {
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT/* Try again if zone has deferred pages */if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))goto try_this_zone;}
#endif}}/** It's possible on a UMA machine to get through all zones that are* fragmented. If avoiding fragmentation, reset and try again.*/if (no_fallback) {alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;goto retry;}return NULL;
}
2.4 rmqueue()
/** Allocate a page from the given zone. Use pcplists for order-0 allocations.*/
static inline
struct page *rmqueue(struct zone *preferred_zone,struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,gfp_t gfp_flags, unsigned int alloc_flags,int migratetype)
{unsigned long flags;struct page *page;// 如果order为0,则从pcplist中分配,这样做是为了加快分配效率,这个在我之前的文章专门讲过,感兴趣的可以自己翻找一下if (likely(order == 0)) {/** MIGRATE_MOVABLE pcplist could have the pages on CMA area and* we need to skip it when CMA area isn't allowed.*/if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CMA) || alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA ||migratetype != MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {page = rmqueue_pcplist(preferred_zone, zone, gfp_flags,migratetype, alloc_flags);goto out;}}/** We most definitely don't want callers attempting to* allocate greater than order-1 page units with __GFP_NOFAIL.*/WARN_ON_ONCE((gfp_flags & __GFP_NOFAIL) && (order > 1));spin_lock_irqsave(&zone->lock, flags);do {page = NULL;/** order-0 request can reach here when the pcplist is skipped* due to non-CMA allocation context. HIGHATOMIC area is* reserved for high-order atomic allocation, so order-0* request should skip it.*/// 如果是中断上下文的内存分配,alloc_flags会带有ALLOC_HARDER标记,会走该分配路径if (order > 0 && alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER) {page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC);if (page)trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);}// 一般的内存分配,会走该路径if (!page)page = __rmqueue(zone, order, migratetype, alloc_flags);} while (page && check_new_pages(page, order));spin_unlock(&zone->lock);if (!page)goto failed;__mod_zone_freepage_state(zone, -(1 << order),get_pcppage_migratetype(page));__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1 << order);zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone);local_irq_restore(flags);out:/* Separate test+clear to avoid unnecessary atomics */if (test_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags)) {clear_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);wakeup_kswapd(zone, 0, 0, zone_idx(zone));}VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page && bad_range(zone, page), page);return page;failed:local_irq_restore(flags);return NULL;
}
2.5 __rmqueue()
/** Do the hard work of removing an element from the buddy allocator.* Call me with the zone->lock already held.*/
static __always_inline struct page *
__rmqueue(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order, int migratetype,unsigned int alloc_flags)
{struct page *page;#ifdef CONFIG_CMA/** Balance movable allocations between regular and CMA areas by* allocating from CMA when over half of the zone's free memory* is in the CMA area.*/// cma内存分配,这个我们暂时不进行讨论if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA &&zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES) >zone_page_state(zone, NR_FREE_PAGES) / 2) {page = __rmqueue_cma_fallback(zone, order);if (page)return page;}
#endif
retry:// 根据迁移类型从buddy对应迁移链表中分配对应order页面的内存page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, migratetype);if (unlikely(!page)) {if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA)page = __rmqueue_cma_fallback(zone, order);// 未分配到,则转移到fallback流程,我们的迁移类型转换就在这里if (!page && __rmqueue_fallback(zone, order, migratetype,alloc_flags))goto retry;}trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);return page;
}
2.6 __rmqueue_smallest()
假设我们要分配的页面的迁移类型是MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE,但是一开始所有内存都是MIGRATE_MOVABLE,这样子肯定是分配不出来内存的。
/** Go through the free lists for the given migratetype and remove* the smallest available page from the freelists*/
static __always_inline
struct page *__rmqueue_smallest(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,int migratetype)
{unsigned int current_order;struct free_area *area;struct page *page;/* Find a page of the appropriate size in the preferred list */// 根据当前请求的order和migratetype进行分配,如果当前order无法满足,则向上找,一直找到最大的MAX_ORDER - 1为止for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER; ++current_order) {// 先获取到对应的order数组链表area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);// 以migratetype作为下标,确定存放page的链表page = get_page_from_free_area(area, migratetype);// 如果page没有找到,说明order无法满足分配,则尝试更大的orderif (!page)continue;// 从page链表中删除pagedel_page_from_free_list(page, zone, current_order);// 进行buddy调整expand(zone, page, order, current_order, migratetype);set_pcppage_migratetype(page, migratetype);// 返回已分配到的pagereturn page;}return NULL;
}static inline struct page *get_page_from_free_area(struct free_area *area,int migratetype)
{// 根据迁移类型作为下标return list_first_entry_or_null(&area->free_list[migratetype],struct page, lru);
}
2.7 __rmqueue_fallback() 核心处理
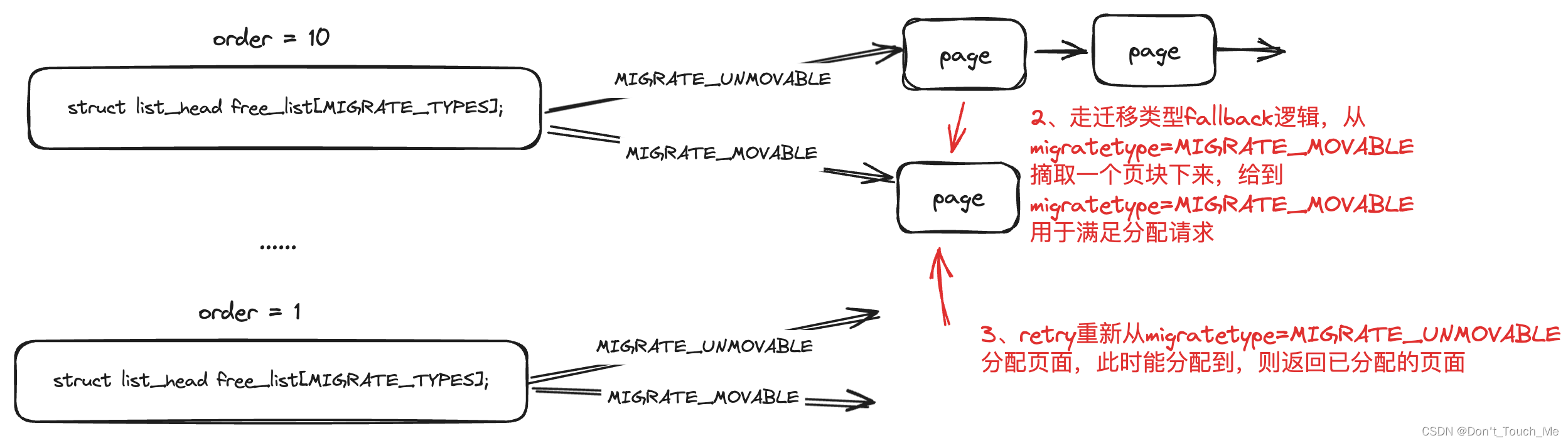
由于我们要分配的页面的迁移类型是MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE,但是一开始所有内存都是MIGRATE_MOVABLE,__rmqueue_smallest()无法分配出来内存,因此会走到__rmqueue_fallback()中进行处理。
/** Try finding a free buddy page on the fallback list and put it on the free* list of requested migratetype, possibly along with other pages from the same* block, depending on fragmentation avoidance heuristics. Returns true if* fallback was found so that __rmqueue_smallest() can grab it.** The use of signed ints for order and current_order is a deliberate* deviation from the rest of this file, to make the for loop* condition simpler.*/
static __always_inline bool
__rmqueue_fallback(struct zone *zone, int order, int start_migratetype,unsigned int alloc_flags)
{struct free_area *area;int current_order;int min_order = order;struct page *page;int fallback_mt;bool can_steal;/** Do not steal pages from freelists belonging to other pageblocks* i.e. orders < pageblock_order. If there are no local zones free,* the zonelists will be reiterated without ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT.*/// 一般的分配外面都会带有这个标记,为了减少页块内部碎片化if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT)min_order = pageblock_order;/** Find the largest available free page in the other list. This roughly* approximates finding the pageblock with the most free pages, which* would be too costly to do exactly.*/// 我们从最大order开始分配,这样对于一个页块只需要改变迁移类型就好,否则会导致一个MIGRATE_MOVABLE迁移类型的页块部分内存用于了MIGRATE_MOVABLE迁移类型的内存分配,导致页块内部碎片化,无法进行回收for (current_order = MAX_ORDER - 1; current_order >= min_order;--current_order) {area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);// 根据迁移类型查找是否可以从别的迁移类型中分配内存fallback_mt = find_suitable_fallback(area, current_order,start_migratetype, false, &can_steal);if (fallback_mt == -1)continue;/** We cannot steal all free pages from the pageblock and the* requested migratetype is movable. In that case it's better to* steal and split the smallest available page instead of the* largest available page, because even if the next movable* allocation falls back into a different pageblock than this* one, it won't cause permanent fragmentation.*/if (!can_steal && start_migratetype == MIGRATE_MOVABLE&& current_order > order)goto find_smallest;// 如果我们可以从别的迁移类型里偷到内存,则进行偷的处理goto do_steal;}return false;find_smallest:for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER;current_order++) {area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);fallback_mt = find_suitable_fallback(area, current_order,start_migratetype, false, &can_steal);if (fallback_mt != -1)break;}/** This should not happen - we already found a suitable fallback* when looking for the largest page.*/VM_BUG_ON(current_order == MAX_ORDER);do_steal:// 从可以偷的迁移类型里获取到内存page = get_page_from_free_area(area, fallback_mt);// 这里是将偷到的页块修改为分配请求需要的迁移类型steal_suitable_fallback(zone, page, alloc_flags, start_migratetype,can_steal);trace_mm_page_alloc_extfrag(page, order, current_order,start_migratetype, fallback_mt);return true;}
2.8 find_suitable_fallback()
查找一个合适的fallback迁移类型的页块。
/** Check whether there is a suitable fallback freepage with requested order.* If only_stealable is true, this function returns fallback_mt only if* we can steal other freepages all together. This would help to reduce* fragmentation due to mixed migratetype pages in one pageblock.*/
int find_suitable_fallback(struct free_area *area, unsigned int order,int migratetype, bool only_stealable, bool *can_steal)
{int i;int fallback_mt;if (area->nr_free == 0)return -1;// 先设置为不能偷*can_steal = false;for (i = 0;; i++) {// 从fallbacks数组里遍历fallback_mt = fallbacks[migratetype][i];if (fallback_mt == MIGRATE_TYPES)break;// 如果当前迁移类型没有内存,则换到下一个迁移类型if (free_area_empty(area, fallback_mt))continue;// 如果有内存,查看是否可以偷if (can_steal_fallback(order, migratetype))// 如果可以偷到话,设置为可偷*can_steal = true;if (!only_stealable)return fallback_mt;if (*can_steal)// 在能偷的前提下,将可偷的迁移类型返回return fallback_mt;}return -1;
}/** This array describes the order lists are fallen back to when* the free lists for the desirable migrate type are depleted*/
static int fallbacks[MIGRATE_TYPES][3] = {[MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE] = { MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE, MIGRATE_MOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },[MIGRATE_MOVABLE] = { MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE, MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },[MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE] = { MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE, MIGRATE_MOVABLE, MIGRATE_TYPES },
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA[MIGRATE_CMA] = { MIGRATE_TYPES }, /* Never used */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_ISOLATION[MIGRATE_ISOLATE] = { MIGRATE_TYPES }, /* Never used */
#endif
};
fallbacks是不同迁移类型内存不足时,可从哪个迁移类型中进行fallback操作,对于MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE迁移类型不足时,可以先MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE迁移类型中偷内存,如果MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE也没有内存的话,会进一步fallback到MIGRATE_MOVABLE迁移类型。因此对于我们一开始需要MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE类型的页面没有时,最终会fallback到MIGRATE_MOVABLE。
/** When we are falling back to another migratetype during allocation, try to* steal extra free pages from the same pageblocks to satisfy further* allocations, instead of polluting multiple pageblocks.** If we are stealing a relatively large buddy page, it is likely there will* be more free pages in the pageblock, so try to steal them all. For* reclaimable and unmovable allocations, we steal regardless of page size,* as fragmentation caused by those allocations polluting movable pageblocks* is worse than movable allocations stealing from unmovable and reclaimable* pageblocks.*/
static bool can_steal_fallback(unsigned int order, int start_mt)
{/** Leaving this order check is intended, although there is* relaxed order check in next check. The reason is that* we can actually steal whole pageblock if this condition met,* but, below check doesn't guarantee it and that is just heuristic* so could be changed anytime.*/// 如果我们偷的是一整个页块的大小,是允许的if (order >= pageblock_order)return true;if (order >= pageblock_order / 2 ||start_mt == MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE ||start_mt == MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE ||page_group_by_mobility_disabled)return true;return false;
}
can_steal_fallback()函数用来检查当前order大小页面是否可以从fallback的迁移类型中偷取,当我们偷取的内存是一整个页块时,页面偷取是可以的。
2.9 steal_suitable_fallback()
/** This function implements actual steal behaviour. If order is large enough,* we can steal whole pageblock. If not, we first move freepages in this* pageblock to our migratetype and determine how many already-allocated pages* are there in the pageblock with a compatible migratetype. If at least half* of pages are free or compatible, we can change migratetype of the pageblock* itself, so pages freed in the future will be put on the correct free list.*/
static void steal_suitable_fallback(struct zone *zone, struct page *page,unsigned int alloc_flags, int start_type, bool whole_block)
{unsigned int current_order = buddy_order(page);int free_pages, movable_pages, alike_pages;int old_block_type;// 获取当前page的迁移类型old_block_type = get_pageblock_migratetype(page);/** This can happen due to races and we want to prevent broken* highatomic accounting.*/if (is_migrate_highatomic(old_block_type))goto single_page;/* Take ownership for orders >= pageblock_order */// 如果我们是偷的一整个页块的话,进入该函数处理if (current_order >= pageblock_order) {// 修改当前page的所在页块的迁移类型,也就是从MIGRATE_MOVABLE变为MIGRATE_UNMOVABLEchange_pageblock_range(page, current_order, start_type);goto single_page;}/** Boost watermarks to increase reclaim pressure to reduce the* likelihood of future fallbacks. Wake kswapd now as the node* may be balanced overall and kswapd will not wake naturally.*/boost_watermark(zone);if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_KSWAPD)set_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);/* We are not allowed to try stealing from the whole block */if (!whole_block)goto single_page;free_pages = move_freepages_block(zone, page, start_type,&movable_pages);/** Determine how many pages are compatible with our allocation.* For movable allocation, it's the number of movable pages which* we just obtained. For other types it's a bit more tricky.*/if (start_type == MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {alike_pages = movable_pages;} else {/** If we are falling back a RECLAIMABLE or UNMOVABLE allocation* to MOVABLE pageblock, consider all non-movable pages as* compatible. If it's UNMOVABLE falling back to RECLAIMABLE or* vice versa, be conservative since we can't distinguish the* exact migratetype of non-movable pages.*/if (old_block_type == MIGRATE_MOVABLE)alike_pages = pageblock_nr_pages- (free_pages + movable_pages);elsealike_pages = 0;}/* moving whole block can fail due to zone boundary conditions */if (!free_pages)goto single_page;/** If a sufficient number of pages in the block are either free or of* comparable migratability as our allocation, claim the whole block.*/if (free_pages + alike_pages >= (1 << (pageblock_order-1)) ||page_group_by_mobility_disabled)set_pageblock_migratetype(page, start_type);return;single_page:// 并将页面迁移到对应的新的迁移类型所在的链表中move_to_free_list(page, zone, current_order, start_type);
}static void change_pageblock_range(struct page *pageblock_page,int start_order, int migratetype)
{int nr_pageblocks = 1 << (start_order - pageblock_order);while (nr_pageblocks--) {// 设置迁移类型set_pageblock_migratetype(pageblock_page, migratetype);pageblock_page += pageblock_nr_pages;}
}
将从fallback的迁移类型中获取到页面,并将页面放置到所需求的迁移类型后,会重新retry进行内存分配。
好了,这里对于migrate_type进一步探索就到这里了,感谢各位读者浏览!!!
预知后续如何,请看下个博文的分析。
相关文章:

Linux migrate_type进一步探索
文章接着上回Linux migrate_type初步探索 1、物理页面添加到buddy系统 我们都知道物理内存一开始是由memblock进行分配管理,后面会切换到buddy系统管理。那么接下来我们看一下,memblock管理的物理页面是怎么添加到buddy系统中的。 start_kernel() -&g…...

强化学习:时序差分法【Temporal Difference Methods】
强化学习笔记 主要基于b站西湖大学赵世钰老师的【强化学习的数学原理】课程,个人觉得赵老师的课件深入浅出,很适合入门. 第一章 强化学习基本概念 第二章 贝尔曼方程 第三章 贝尔曼最优方程 第四章 值迭代和策略迭代 第五章 强化学习实例分析:GridWorld…...
数据结构-二叉树-二叉搜索树
一、概念 二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者具有以下性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不为空,则左树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值。 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值。 它…...

Linux 磁盘管理命令df du dd
文章目录 3.Linux 磁盘管理命令3.1 df:显示报告文件系统磁盘使用信息案例练习 3.2 du:显示目录或者文件所占的磁盘空间案例练习 3.3 dd:磁盘操作案例练习 3.Linux 磁盘管理命令 3.1 df:显示报告文件系统磁盘使用信息 作用&#x…...

Leetcode 3138. Minimum Length of Anagram Concatenation
Leetcode 3138. Minimum Length of Anagram Concatenation 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3138. Minimum Length of Anagram Concatenation 1. 解题思路 这一题的话我们首先统计出来所有的字母出现的频率。 然后,我们只需要从头开始重新计数一下&…...
IT廉连看——UniApp——样式绑定
IT廉连看——UniApp——样式绑定 一、样式绑定 两种添加样式的方法: 1、第一种写法 写一个class属性,然后将css样式写在style中。 2、第二种写法 直接把style写在class后面 添加一些效果:字体大小 查看效果 证明这样添加样式是没有问题的…...

垃圾的flinkcdc
在 MySQL 中,创建表时使用反引号 将表名或字段名括起来的作用是: 保留字和关键字: 使用反引号可以避免使用MySQL的保留字和关键字作为表名或字段名时产生的冲突。比如,你可以创建一个名为 select 或 order 的表: sqlCopy Code C…...

关于视频号小店,常见问题解答,开店做店各方面详解
大家好,我是电商笨笨熊 视频号小店作为今年风口,一个新推出的项目,凭借着自身流量加用户群体的优势吸引了不少的电商玩家。 但对于很多玩家来说,视频号小店完全是一个新的项目、新的领域,因此也会存在很多的疑问&…...
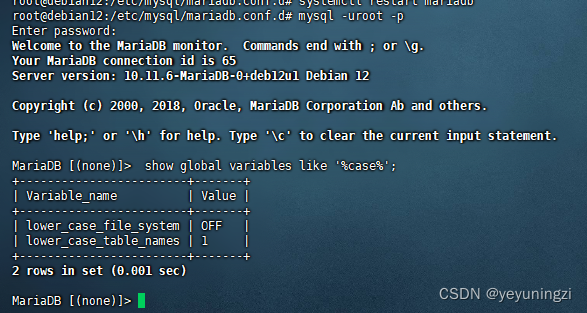
Debian mariadb 10.11设定表名 大小写不敏感方法
目录 问题表现:应用中查询 表提示 表不存在 处理步骤: 1、查询表名大小写敏感情况: show global variables like %case%; 2、修改mariadb 配置设置大小写 不敏感 mysql 配置大小写不敏感 mariadb 10.11设置表名大小写不敏感 /etc/mysq…...
常用六大加密软件排行榜|好用加密文件软件分享
为了保障数据安全,越来越多的企业开始使用文件加密软件。哪款加密软件适合企业哪些办公场景呢? 今天就给大家推荐一下文件加密软件排行榜的前六名: 1.域智盾 这款软件专为企业和政府机构设计,提供全面的文件保护解决方案。 点…...

百川2模型解读
简介 Baichuan 2是多语言大模型,目前开源了70亿和130亿参数规模的模型。在公开基准如MMLU、CMMLU、GSM8K和HumanEval上的评测,Baichuan 2达到或超过了其他同类开源模型,并在医学和法律等垂直领域表现优异。此外,官方还发布所有预…...
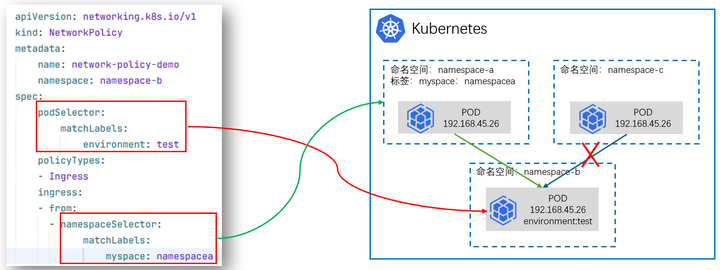
云原生专栏丨基于K8s集群网络策略的应用访问控制技术
在当今云计算时代,Kubernetes已经成为容器编排的事实标准,它为容器化应用提供了强大的自动化部署、扩展和管理能力。在Kubernetes集群中,网络策略(Network Policy)作为对Pod间通信进行控制的关键功能,对保障应用安全和隔离性起到了…...

MySQL 优化 - index_merge 导致查询偶发变慢
文章目录 前言问题描述原因分析总结 前言 今天遇到了一个有意思的问题,线上数据库 CPU 出现了偶发的抖动。定位到原因是一条查询语句偶发变慢造成的,随后通过调整表中的索引解决。 问题描述 下方是脱敏后的 SQL 语句: select oss_path f…...

SpringBoot自动连接数据库的解决方案
在一次学习设计模式的时候,沿用一个旧的boot项目,想着简单,就把数据库给关掉了,结果报错 Consider the following: If you want an embedded database (H2, HSQL or Derby), please put it on the classpath. 没有数据库的需…...

Docker-10 Docker Compose
一、前言 通过前面几篇文章的学习,我们可以通过Dockerfile文件让用户很方便的定义一个单独的应用容器。然而,在日常工作中,经常会碰到需要多个容器相互配合来完成某项任务的情况,或者开发一个Web应用,除了Web服务容器本身,还需要数据库服务容器、缓存容器,甚至还包括负…...

new mars3d.control.MapSplit({实现点击卷帘两侧添加不同图层弹出不同的popup
new mars3d.control.MapSplit({实现点击卷帘两侧添加不同图层弹出不同的popup效果: 左侧: 右侧: 说明:mars3d的3.7.12以上版本才支持该效果。 示例链接: 功能示例(Vue版) | Mars3D三维可视化平台 | 火星科技 相关代…...

数据库中虚拟表和临时表的区别?
虚拟表(Virtual Table)和临时表(Temporary Table)在数据库系统中都用于处理暂时性的数据存储需求,但它们的概念和用途有所不同: 虚拟表(通常是视图View): 虚拟表&#…...

Node.js -- mongoose
文章目录 1. 介绍2. mongoose 连接数据库3. 插入文件4. 字段类型5. 字段值验证6. 文档处理6.1 删除文档6.2 更新文档6.3 读取文档 7. 条件控制8. 个性化读取9. 代码模块化 1. 介绍 Mongoose是一个对象文档模型库,官网http://www.mongoosejs.net/ 方便使用代码操作mo…...
保持亮灯:监控工具如何确保 DevOps 中的高可用性
在快速发展的 DevOps 领域,保持高可用性 (HA) 至关重要。消费者期望应用程序具有全天候响应能力和可访问性。销售损失、客户愤怒和声誉受损都是停机的后果。为了使 DevOps 团队能够在问题升级为中断之前主动检测、排除故障并解决问题,监控工具成为这种情…...
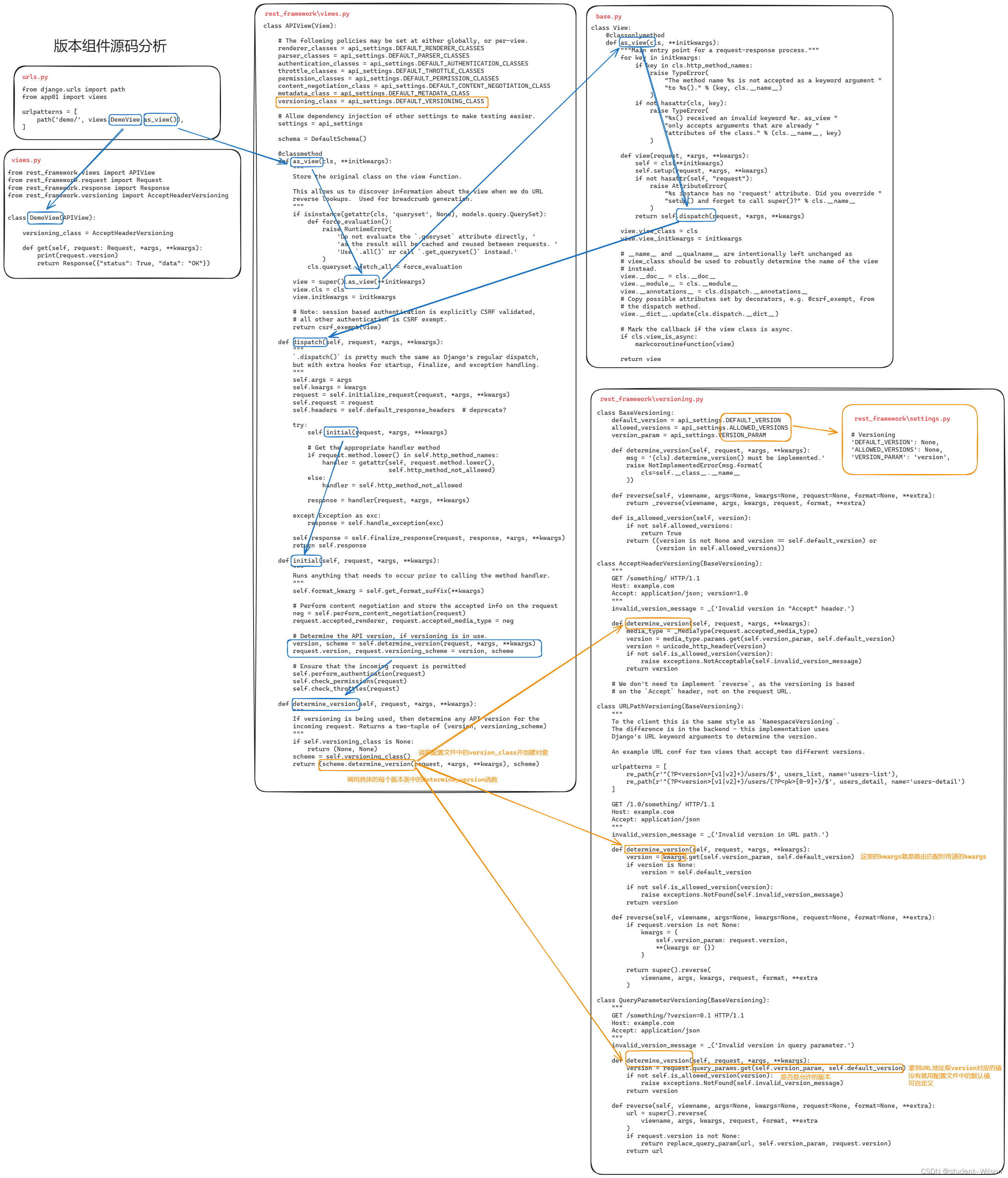
DRF版本组件源码分析
DRF版本组件源码分析 在restful规范中要去,后端的API中需要体现版本。 3.6.1 GET参数传递版本 from rest_framework.versioning import QueryParameterVersioning单视图应用 多视图应用 # settings.pyREST_FRAMEWORK {"VERSION_PARAM": "versi…...

未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?
编辑:陈萍萍的公主一点人工一点智能 未来机器人的大脑:如何用神经网络模拟器实现更智能的决策?RWM通过双自回归机制有效解决了复合误差、部分可观测性和随机动力学等关键挑战,在不依赖领域特定归纳偏见的条件下实现了卓越的预测准…...

挑战杯推荐项目
“人工智能”创意赛 - 智能艺术创作助手:借助大模型技术,开发能根据用户输入的主题、风格等要求,生成绘画、音乐、文学作品等多种形式艺术创作灵感或初稿的应用,帮助艺术家和创意爱好者激发创意、提高创作效率。 - 个性化梦境…...
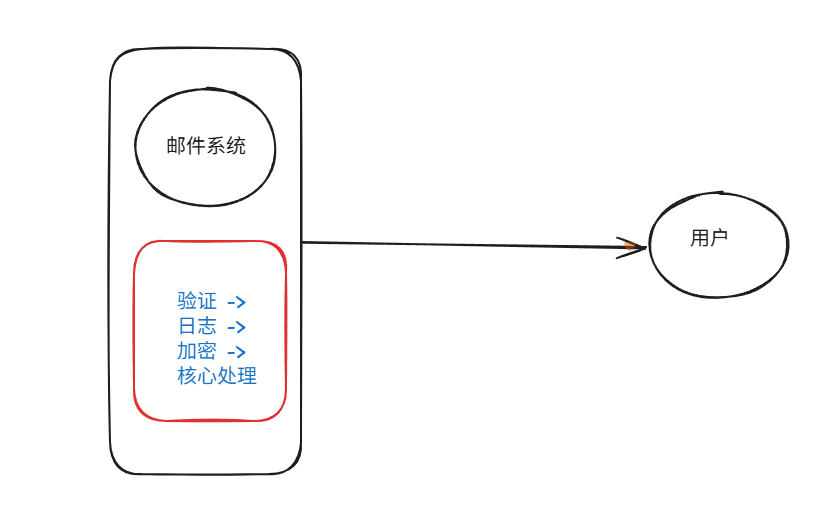
装饰模式(Decorator Pattern)重构java邮件发奖系统实战
前言 现在我们有个如下的需求,设计一个邮件发奖的小系统, 需求 1.数据验证 → 2. 敏感信息加密 → 3. 日志记录 → 4. 实际发送邮件 装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其…...
。】2022-5-15)
【根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。】2022-5-15
缘由根据当天日期输出明天的日期(需对闰年做判定)。日期类型结构体如下: struct data{ int year; int month; int day;};-编程语言-CSDN问答 struct mdata{ int year; int month; int day; }mdata; int 天数(int year, int month) {switch (month){case 1: case 3:…...

ubuntu搭建nfs服务centos挂载访问
在Ubuntu上设置NFS服务器 在Ubuntu上,你可以使用apt包管理器来安装NFS服务器。打开终端并运行: sudo apt update sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server创建共享目录 创建一个目录用于共享,例如/shared: sudo mkdir /shared sud…...
第 86 场周赛:矩阵中的幻方、钥匙和房间、将数组拆分成斐波那契序列、猜猜这个单词
Q1、[中等] 矩阵中的幻方 1、题目描述 3 x 3 的幻方是一个填充有 从 1 到 9 的不同数字的 3 x 3 矩阵,其中每行,每列以及两条对角线上的各数之和都相等。 给定一个由整数组成的row x col 的 grid,其中有多少个 3 3 的 “幻方” 子矩阵&am…...

【学习笔记】深入理解Java虚拟机学习笔记——第4章 虚拟机性能监控,故障处理工具
第2章 虚拟机性能监控,故障处理工具 4.1 概述 略 4.2 基础故障处理工具 4.2.1 jps:虚拟机进程状况工具 命令:jps [options] [hostid] 功能:本地虚拟机进程显示进程ID(与ps相同),可同时显示主类&#x…...
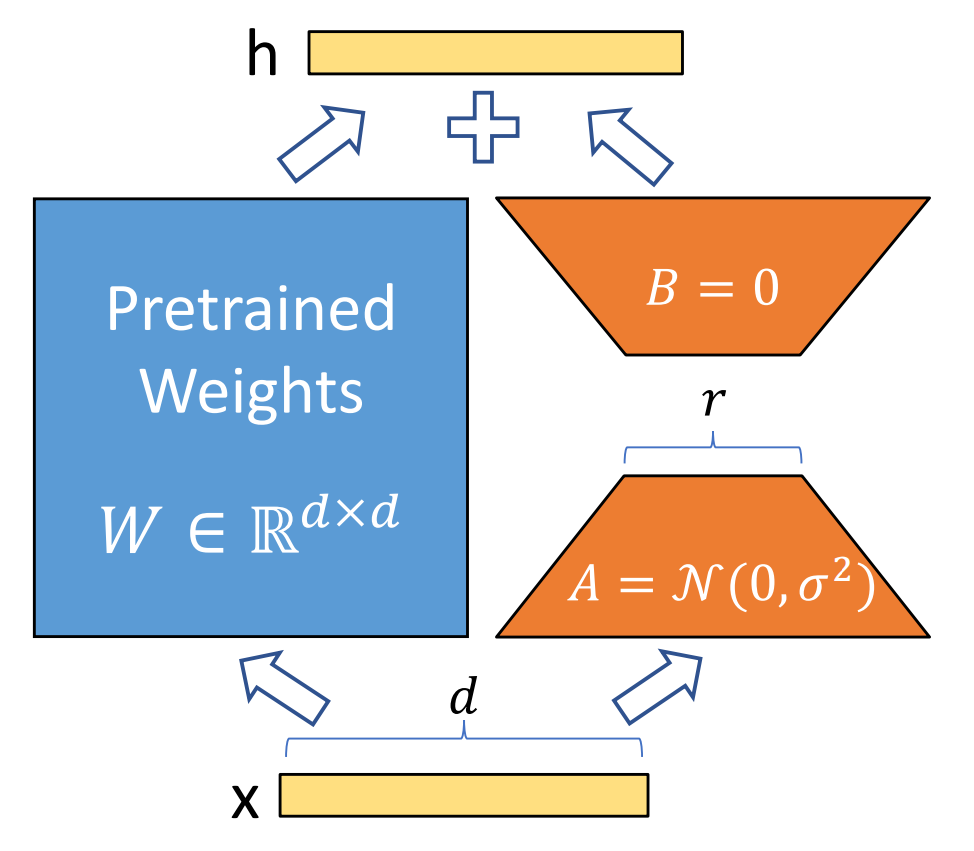
算法岗面试经验分享-大模型篇
文章目录 A 基础语言模型A.1 TransformerA.2 Bert B 大语言模型结构B.1 GPTB.2 LLamaB.3 ChatGLMB.4 Qwen C 大语言模型微调C.1 Fine-tuningC.2 Adapter-tuningC.3 Prefix-tuningC.4 P-tuningC.5 LoRA A 基础语言模型 A.1 Transformer (1)资源 论文&a…...

怎么让Comfyui导出的图像不包含工作流信息,
为了数据安全,让Comfyui导出的图像不包含工作流信息,导出的图像就不会拖到comfyui中加载出来工作流。 ComfyUI的目录下node.py 直接移除 pnginfo(推荐) 在 save_images 方法中,删除或注释掉所有与 metadata …...

解决:Android studio 编译后报错\app\src\main\cpp\CMakeLists.txt‘ to exist
现象: android studio报错: [CXX1409] D:\GitLab\xxxxx\app.cxx\Debug\3f3w4y1i\arm64-v8a\android_gradle_build.json : expected buildFiles file ‘D:\GitLab\xxxxx\app\src\main\cpp\CMakeLists.txt’ to exist 解决: 不要动CMakeLists.…...
