C++编程:实现一个跨平台安全的定时器Timer模块
文章目录
- 0. 概要
- 1. 设计目标
- 2. `SafeTimer` 类的实现
- 2.1 头文件 `safe_timer.h`
- 源文件 `safe_timer.cpp`
- 3. 工作流程图
- 4. 单元测试
0. 概要
对于C++应用编程,定时器模块是一个至关重要的组件。为了确保系统的可靠性和功能安全,我们需要设计一个高效、稳定的定时器。
本文将实现一个跨平台安全的C++ SafeTimer 定时器模块,并提供完整的gtest单元测试。
完整代码见 gitee_safe_timer
类似设计请参阅文章:C++编程: 线程池封装、任务异步执行以及任务延迟执行
1. 设计目标
目标是创建一个符合功能安全要求的定时器模块,具体包括以下几点:
- 线程安全:确保多线程环境下的安全性。
- 高可靠性:在异常情况下能够安全地停止定时器。
- 高可维护性:代码结构清晰,易于扩展和维护。
2. SafeTimer 类的实现
SafeTimer 类是我们实现的核心,它提供了单次触发(SingleShot)和重复触发(Repeat)两种定时功能,同时还支持暂停(Pause)和恢复(Resume)。以下是 SafeTimer 类的完整实现。
2.1 头文件 safe_timer.h
#ifndef SAFE_TIMER_H
#define SAFE_TIMER_H#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <string>
#include <thread>// 定义SafeTimer类,用于管理定时任务
class SafeTimer {public:// 构造函数,可以指定定时器的名称,默认为"SafeTimer"explicit SafeTimer(const std::string& name = "SafeTimer") noexcept;// 析构函数virtual ~SafeTimer() noexcept;// 禁止复制构造和赋值操作SafeTimer(const SafeTimer&) = delete;SafeTimer& operator=(const SafeTimer&) = delete;// 返回定时器的名称std::string GetName() const noexcept;// 返回定时器是否处于循环模式bool IsLoop() const noexcept;// 设置一个一次性定时任务template <typename Callable, typename... Arguments>bool SingleShot(uint64_t interval_in_millis, Callable&& func, Arguments&&... args);// 设置一个可重复的定时任务template <typename Callable, typename... Arguments>bool Repeat(uint64_t interval_in_millis, Callable&& func, Arguments&&... args);// 设置一个可重复的定时任务,可以选择是否立即执行一次template <typename Callable, typename... Arguments>bool Repeat(uint64_t interval_in_millis, bool call_func_immediately, Callable&& func, Arguments&&... args);// 取消当前的定时任务void Cancel() noexcept;// 暂停当前的定时任务bool Pause() noexcept;// 恢复已暂停的定时任务void Resume() noexcept;// 判断定时器是否处于空闲状态bool IsTimerIdle() const noexcept;private:// 启动定时任务的核心函数bool Start(uint64_t interval_in_millis, std::function<void()> callback, bool loop, bool callback_immediately = false);// 尝试使定时器过期,用于取消或暂停任务void TryExpire() noexcept;// 销毁线程资源void DestroyThread() noexcept;private:// 定时器的名称std::string name_;// 标记定时器是否为循环模式bool is_loop_;// 原子布尔类型,标记定时器是否已经过期std::atomic_bool is_expired_;// 原子布尔类型,标记是否尝试使定时器过期std::atomic_bool try_to_expire_;// 独占所有权的线程智能指针std::unique_ptr<std::thread> thread_;// 互斥锁,用于线程同步std::mutex mutex_;// 条件变量,用于线程间的通信std::condition_variable condition_;// 定时器启动时的时间点std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::steady_clock> start_time_;// 定时器结束时的时间点std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::steady_clock> end_time_;// 剩余任务时间(毫秒)uint64_t task_remain_time_ms_;// 回调函数,当定时器过期时调用std::function<void()> callback_;
};// 实现模板成员函数// 单次定时任务的实现
template <typename Callable, typename... Arguments>
bool SafeTimer::SingleShot(uint64_t interval_in_millis, Callable&& func, Arguments&&... args) {// 创建一个绑定的函数对象,用于延迟执行auto action = std::bind(std::forward<Callable>(func), std::forward<Arguments>(args)...);// 调用私有的Start函数,设置一次性任务return Start(interval_in_millis, action, false);
}// 循环定时任务的实现
template <typename Callable, typename... Arguments>
bool SafeTimer::Repeat(uint64_t interval_in_millis, Callable&& func, Arguments&&... args) {// 创建一个绑定的函数对象,用于延迟执行auto action = std::bind(std::forward<Callable>(func), std::forward<Arguments>(args)...);// 调用私有的Start函数,设置循环任务return Start(interval_in_millis, action, true);
}// 循环定时任务的实现,允许指定是否立即执行一次
template <typename Callable, typename... Arguments>
bool SafeTimer::Repeat(uint64_t interval_in_millis, bool call_func_immediately, Callable&& func, Arguments&&... args) {// 创建一个绑定的函数对象,用于延迟执行auto action = std::bind(std::forward<Callable>(func), std::forward<Arguments>(args)...);// 调用私有的Start函数,设置循环任务,可选择立即执行return Start(interval_in_millis, action, true, call_func_immediately);
}#endif // SAFE_TIMER_H
源文件 safe_timer.cpp
#include "safe_timer.h"
#include <iostream>SafeTimer::SafeTimer(const std::string& name) noexcept: name_(name), is_loop_(false), is_expired_(true), try_to_expire_(false), task_remain_time_ms_(0), callback_(nullptr) {}SafeTimer::~SafeTimer() noexcept {TryExpire();
}std::string SafeTimer::GetName() const noexcept {return name_;
}bool SafeTimer::IsLoop() const noexcept {return is_loop_;
}void SafeTimer::Cancel() noexcept {if (is_expired_ || try_to_expire_ || !thread_) {return;}TryExpire();
}bool SafeTimer::Pause() noexcept {if (is_expired_) {return false;}auto now = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();auto elapsed = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(now - start_time_).count();auto remaining = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time_ - now).count();if (remaining <= 0) {return false;}Cancel();task_remain_time_ms_ = static_cast<uint64_t>(remaining);return true;
}void SafeTimer::Resume() noexcept {if (task_remain_time_ms_ > 0 && callback_) {Start(task_remain_time_ms_, callback_, false, false);task_remain_time_ms_ = 0;}
}bool SafeTimer::IsTimerIdle() const noexcept {return is_expired_ && !try_to_expire_;
}bool SafeTimer::Start(uint64_t interval_in_millis, std::function<void()> callback, bool loop, bool callback_immediately) {if (!is_expired_ || try_to_expire_) {return false;}is_expired_ = false;is_loop_ = loop;DestroyThread();thread_ = std::make_unique<std::thread>([this, interval_in_millis, callback, callback_immediately]() {if (callback_immediately) {callback();}while (!try_to_expire_) {callback_ = callback;start_time_ = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();end_time_ = start_time_ + std::chrono::milliseconds(interval_in_millis);std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);condition_.wait_until(lock, end_time_);if (try_to_expire_) {break;}callback();if (!is_loop_) {break;}}is_expired_ = true;try_to_expire_ = false;});return true;
}void SafeTimer::TryExpire() noexcept {try_to_expire_ = true;DestroyThread();try_to_expire_ = false;
}void SafeTimer::DestroyThread() noexcept {if (thread_) {{std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);condition_.notify_all();}if (thread_->joinable()) {thread_->join();}thread_.reset();}
}
3. 工作流程图
这个流程图分别展示了 SingleShot 和 Repeat 的流程,同时包括了暂停、恢复和取消操作。
4. 单元测试
为了验证 SafeTimer 的功能,我们编写了一组单元测试,覆盖了定时器的各种使用场景,包括单次触发、重复触发、暂停、恢复和取消等功能。
#include <gmock/gmock.h>
#include <gtest/gtest.h>#include <chrono>
#include <thread>#include "safe_timer.h"class CallbackMock {public:MOCK_METHOD(void, CallbackMethod, ());
};class SafeTimerTest : public testing::Test {protected:CallbackMock callback_mock;void SetUp() override {// Do nothing now}void TearDown() override {// Do nothing now}
};TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, SingleShot) {SafeTimer timer("TestSingleShot");EXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(1);int time_ms = 100; // Delay time in millisecondsbool ret = timer.SingleShot(time_ms, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure executionstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(time_ms + 100));
}TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, RepeatWithParamCallImmediately) {SafeTimer timer("TestRepeatWithParamCallImmediately");int repeat_count = 3; // Number of times repeat should executeint time_ms = 200; // Delay time in millisecondsEXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(repeat_count);// Execute once immediatelyauto ret = timer.Repeat(time_ms, true, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure executionstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds((repeat_count - 1) * time_ms + 100));// Cancel previous timertimer.Cancel();EXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(repeat_count);// Do not execute immediatelyret = timer.Repeat(time_ms, false, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure executionstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(repeat_count * time_ms + 100));
}TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, RepeatWithoutParamCallImmediately) {SafeTimer timer("TestRepeatWithoutParamCallImmediately");int repeat_count = 3; // Number of times repeat should executeint time_ms = 500; // Delay time in millisecondsEXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(repeat_count);auto ret = timer.Repeat(time_ms, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure executionstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(repeat_count * time_ms + 100));
}TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, Cancel) {SafeTimer timer("Cancel");int repeat_count = 3; // Number of times repeat should executeint time_ms = 500; // Delay time in millisecondsEXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(repeat_count - 1);// Execute once immediatelyauto ret = timer.Repeat(time_ms, true, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for 100ms less to ensure cancel is called in timestd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds((repeat_count - 1) * time_ms - 100));timer.Cancel();
}// Test if cancelling immediately after timer creation causes any issues
// Expected: Cancelling immediately after timer creation should directly return and perform no operation
TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, CancelBeforeSingleShot) {SafeTimer timer("TestCancelBeforeSingleShot");EXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(1);timer.Cancel();int time_ms = 100; // Delay time in millisecondsauto ret = timer.SingleShot(time_ms, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure executionstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(time_ms + 100));
}// Test if cancelling immediately after creating a SingleShot timer causes any issues
// Expected: Properly cancel without issues
TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, CancelImmediatelyAfterSingleShot) {SafeTimer timer("TestCancelImmediatelyAfterSingleShot");EXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(0);int time_ms = 100; // Delay time in millisecondstimer.SingleShot(time_ms, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);timer.Cancel();// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure callback is not calledstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(time_ms + 100));
}TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, CancelAfterSingleShot) {SafeTimer timer("TestCancelAfterSingleShot");EXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(1);int time_ms = 100; // Delay time in millisecondsauto ret = timer.SingleShot(time_ms, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);EXPECT_TRUE(ret);// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure executionstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(time_ms + 100));timer.Cancel();
}TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, Pause) {SafeTimer timer("Pause");int repeat_count = 2; // Number of times repeat should executeint time_ms = 500; // Delay time in millisecondsEXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(repeat_count - 1);// Execute once immediatelytimer.Repeat(time_ms, true, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);// Sleep for 100ms less to ensure pause is called in timestd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds((repeat_count - 1) * time_ms - 100));auto ret = timer.Pause();EXPECT_TRUE(ret);
}TEST_F(SafeTimerTest, Resume) {SafeTimer timer("Resume");int repeat_count = 3; // Number of times repeat should executeint time_ms = 100; // Delay time in millisecondsEXPECT_CALL(callback_mock, CallbackMethod()).Times(repeat_count);// Execute once immediatelytimer.Repeat(time_ms, true, &CallbackMock::CallbackMethod, &callback_mock);int time_advance_pause = 50; // Time in milliseconds to pause in advance// Sleep for time_advance_pause ms less to ensure pause is called in timestd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds((repeat_count - 1) * time_ms - time_advance_pause));timer.Pause();timer.Resume();// Sleep for an additional 100ms to ensure timer execution is completedstd::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(time_advance_pause + 100));
}int main(int argc, char** argv) {testing::InitGoogleMock(&argc, argv);return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
以上代码是使用Google Test和Google Mock进行单元测试,以下是几项要点:
-
单次触发测试:
SingleShot测试了SafeTimer在设定的延时后只触发一次CallbackMethod。
-
重复触发测试:
RepeatWithParamCallImmediately测试了计时器立即执行并重复触发回调的功能。RepeatWithoutParamCallImmediately测试了计时器不立即执行,仅按照设定间隔重复触发回调的功能。
-
取消计时器测试:
Cancel测试了在计时器执行过程中取消操作是否有效。CancelBeforeSingleShot测试了在单次触发计时器创建后立即取消是否有效。CancelImmediatelyAfterSingleShot测试了在单次触发计时器执行前立即取消的效果。CancelAfterSingleShot测试了在单次触发计时器执行后再取消的效果。
-
暂停与恢复计时器测试:
Pause测试了暂停计时器的功能。Resume测试了暂停后恢复计时器的功能。
每个测试都使用EXPECT_CALL设置了预期的回调调用次数,并在适当的延时时间后检查回调是否按预期执行。
执行结果:
$ ./safe_timer_test
[==========] Running 9 tests from 1 test suite.
[----------] Global test environment set-up.
[----------] 9 tests from SafeTimerTest
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.SingleShot
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.SingleShot (200 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.RepeatWithParamCallImmediately
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.RepeatWithParamCallImmediately (1201 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.RepeatWithoutParamCallImmediately
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.RepeatWithoutParamCallImmediately (1600 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.Cancel
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.Cancel (900 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.CancelBeforeSingleShot
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.CancelBeforeSingleShot (200 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.CancelImmediatelyAfterSingleShot
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.CancelImmediatelyAfterSingleShot (201 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.CancelAfterSingleShot
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.CancelAfterSingleShot (200 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.Pause
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.Pause (400 ms)
[ RUN ] SafeTimerTest.Resume
[ OK ] SafeTimerTest.Resume (300 ms)
[----------] 9 tests from SafeTimerTest (5208 ms total)[----------] Global test environment tear-down
[==========] 9 tests from 1 test suite ran. (5208 ms total)
[ PASSED ] 9 tests.
相关文章:

C++编程:实现一个跨平台安全的定时器Timer模块
文章目录 0. 概要1. 设计目标2. SafeTimer 类的实现2.1 头文件 safe_timer.h源文件 safe_timer.cpp 3. 工作流程图4. 单元测试 0. 概要 对于C应用编程,定时器模块是一个至关重要的组件。为了确保系统的可靠性和功能安全,我们需要设计一个高效、稳定的定…...
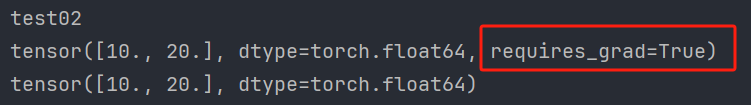
PyTorch的自动微分模块【含梯度基本数学原理详解】
文章目录 1、简介1.1、基本概念1.2、基本原理1.2.1、自动微分1.2.2、梯度1.2.3、梯度求导1.2.4、梯度下降法1.2.5、张量梯度举例 1.3、Autograd的高级功能 2、梯度基本计算2.1、单标量梯度2.2、单向量梯度的计算2.3、多标量梯度计算2.4、多向量梯度计算 3、控制梯度计算4、累计…...

AI 绘画|Midjourney设计Logo提示词
你是否已经看过许多别人分享的 MJ 咒语,却仍无法按照自己的想法画图?通过学习 MJ 的提示词逻辑后,你将能够更好地理解并创作自己的“咒语”。本文将详细拆解使用 MJ 设计 Logo 的逻辑,让你在阅读后即可轻松上手,制作出…...

LeNet实验 四分类 与 四分类变为多个二分类
目录 1. 划分二分类 2. 训练独立的二分类模型 3. 二分类预测结果代码 4. 二分类预测结果 5 改进训练模型 6 优化后 预测结果代码 7 优化后预测结果 8 训练四分类模型 9 预测结果代码 10 四分类结果识别 1. 划分二分类 可以根据不同的类别进行多个划分,以…...
【BUG】已解决:java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException
已解决:java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException 欢迎来到英杰社区https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/617804998 欢迎来到我的主页,我是博主英杰,211科班出身,就职于医疗科技公司,热衷分享知识,武汉城市开发…...

配置kali 的apt命令在线安装包的源为国内源
目录 一、安装VMware Tools 二、配置apt国内源 一、安装VMware Tools 点击安装 VMware Tools 后,会加载一个虚拟光驱,里面包含 VMware Tools 的安装包 鼠标右键单击 VMware Tools 的安装包,点击复制到 点击 主目录,再点击选择…...

JAVA 异步编程(线程安全)二
1、线程安全 线程安全是指你的代码所在的进程中有多个线程同时运行,而这些线程可能会同时运行这段代码,如果每次运行的代码结果和单线程运行的结果是一样的,且其他变量的值和预期的也是一样的,那么就是线程安全的。 一个类或者程序…...

Golang | Leetcode Golang题解之第260题只出现一次的数字III
题目: 题解: func singleNumber(nums []int) []int {xorSum : 0for _, num : range nums {xorSum ^ num}lsb : xorSum & -xorSumtype1, type2 : 0, 0for _, num : range nums {if num&lsb > 0 {type1 ^ num} else {type2 ^ num}}return []in…...

IDEA自带的Maven 3.9.x无法刷新http nexus私服
问题: 自建的私服,配置了域名,使用http协议,在IDEA中或本地Maven 3.9.x会出现报错,提示http被blocked,原因是Maven 3.8.1开始,Maven默认禁止使用HTTP仓库地址,只允许使用HTTPS仓库地…...

56、本地数据库迁移到阿里云
现有需求,本地数据库迁移到阿里云上。 库名xy102表 test01test02test01 test023条数据。1、登录阿里云界面创建免费试用ECS实列。 阿里云登录页 (aliyun.com)](https://account.aliyun.com/login/login.htm?oauth_callbackhttps%3A%2F%2Fusercenter2.aliyun.com%…...

新时代多目标优化【数学建模】领域的极致探索——数学规划模型
目录 例1 1.问题重述 2.基本模型 变量定义: 目标函数: 约束条件: 3.模型分析与假设 4.模型求解 5.LINGO代码实现 6.结果解释 编辑 7.敏感性分析 8.结果解释 例2 奶制品的销售计划 1.问题重述 编辑 2.基本模型 3.模…...

单例模式详解
文章目录 一、概述1.单例模式2.单例模式的特点3.单例模式的实现方法 二、单例模式的实现1. 饿汉式2. 懒汉式3. 双重校验锁4. 静态内部类5. 枚举 三、总结 一、概述 1.单例模式 单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种创建型设计模式,确保一个类…...

WebGIS主流的客户端框架比较|OpenLayers|Leaflet|Cesium
实现 WebGIS 应用的主流前端框架主要包括 OpenLayers、Leaflet、Mapbox GL JS 和 Cesium 等。每个框架都有其独特的功能和优势,适合不同的应用场景。 WebGIS主流前端框架的优缺点 前 端 框架优点缺点OpenLayers较重量级的开源库,二维GIS功能最丰富全面…...

【LabVIEW作业篇 - 2】:分数判断、按钮控制while循环暂停、单击按钮获取book文本
文章目录 分数判断按钮控制while循环暂停按钮控制单个while循环暂停 按钮控制多个while循环暂停单击按钮获取book文本 分数判断 限定整型数值输入控件值得输入范围,范围在0-100之间,判断整型数值输入控件的输入值。 输入范围在0-59之间,显示…...
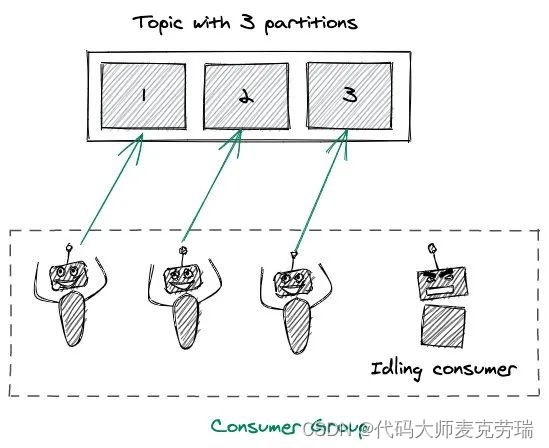
Kafka架构详解之分区Partition
目录 一、简介二、架构三、分区Partition1.分区概念2.Offsets(偏移量)和消息的顺序3.分区如何为Kafka提供扩展能力4.producer写入策略5.consumer消费机制 一、简介 Apache Kafka 是分布式发布 - 订阅消息系统,在 kafka 官网上对 kafka 的定义…...

SSM之Mybatis
SSM之Mybatis 一、MyBatis简介1、MyBatis特性2、MyBatis的下载3、MyBatis和其他持久化层技术对比 二、MyBatis框架搭建三、MyBatis基础功能1、MyBatis核心配置文件2、MyBatis映射文件3、MyBatis实现增删改查4、MyBatis获取参数值的两种方式5、MyBatis查询功能6、MyBatis自定义映…...

Python list comprehension (列表推导式 - 列表解析式 - 列表生成式)
Python list comprehension {列表推导式 - 列表解析式 - 列表生成式} 1. Python list comprehension (列表推导式 - 列表解析式 - 列表生成式)2. Example3. ExampleReferences Python 中的列表解析式并不是用来解决全新的问题,只是为解决已有问题提供新的语法。 列…...

2024年7月12日理发记录
上周五天气还算好,不太热,晚上下班打车回家后,将目的地设置成日常去的那个理发店。 下车走到门口,熟悉的托尼帅哥正在抽烟,他一眼看到了我,马上掐灭烟头,从怀里拿出口香糖,咀嚼起来&…...

几种常用排序算法
1 基本概念 排序是处理数据的一种最常见的操作,所谓排序就是将数据按某字段规律排列,所谓的字段就是数据节点的其中一个属性。比如一个班级的学生,其字段就有学号、姓名、班级、分数等等,我们既可以针对学号排序,也可…...

Spring3(代理模式 Spring1案例补充 Aop 面试题)
一、代理模式 在代理模式(Proxy Pattern)中,一个类代表另一个类的功能,这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式。 代理模式通过引入一个代理对象来控制对原对象的访问。代理对象在客户端和目标对象之间充当中介,负责将客户端…...

在软件开发中正确使用MySQL日期时间类型的深度解析
在日常软件开发场景中,时间信息的存储是底层且核心的需求。从金融交易的精确记账时间、用户操作的行为日志,到供应链系统的物流节点时间戳,时间数据的准确性直接决定业务逻辑的可靠性。MySQL作为主流关系型数据库,其日期时间类型的…...
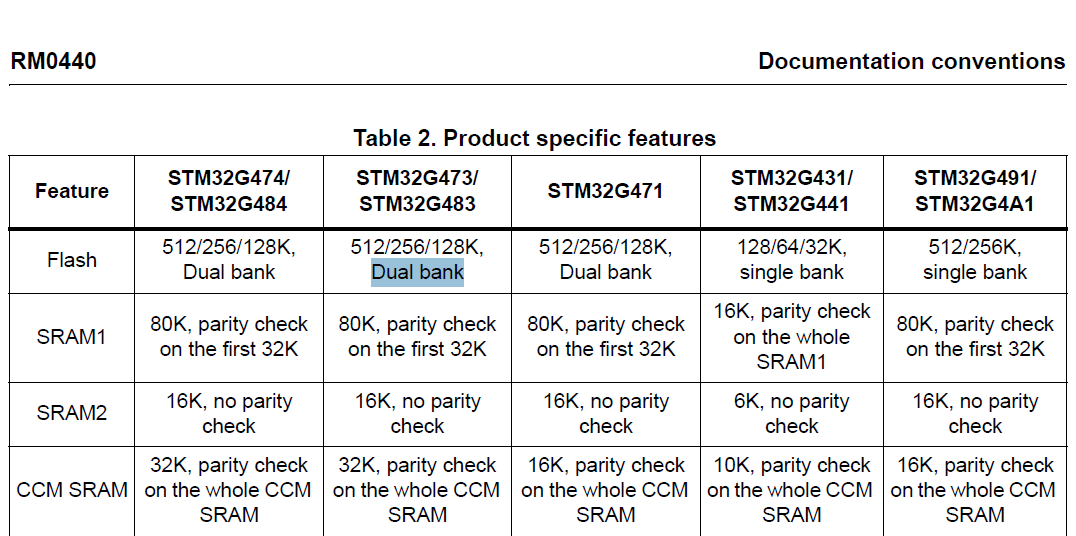
stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?
今天突然有人stm32G473的flash模式是单bank还是双bank?由于时间太久,我真忘记了。搜搜发现,还真有人和我一样。见下面的链接:https://shequ.stmicroelectronics.cn/forum.php?modviewthread&tid644563 根据STM32G4系列参考手…...
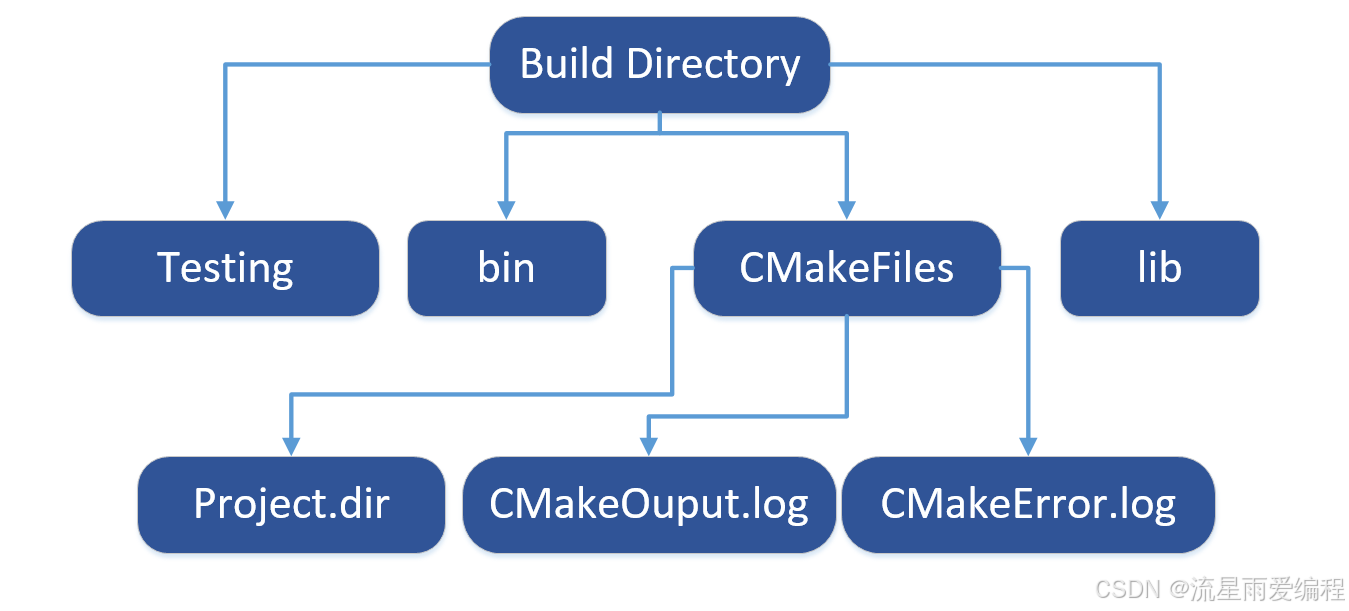
CMake基础:构建流程详解
目录 1.CMake构建过程的基本流程 2.CMake构建的具体步骤 2.1.创建构建目录 2.2.使用 CMake 生成构建文件 2.3.编译和构建 2.4.清理构建文件 2.5.重新配置和构建 3.跨平台构建示例 4.工具链与交叉编译 5.CMake构建后的项目结构解析 5.1.CMake构建后的目录结构 5.2.构…...
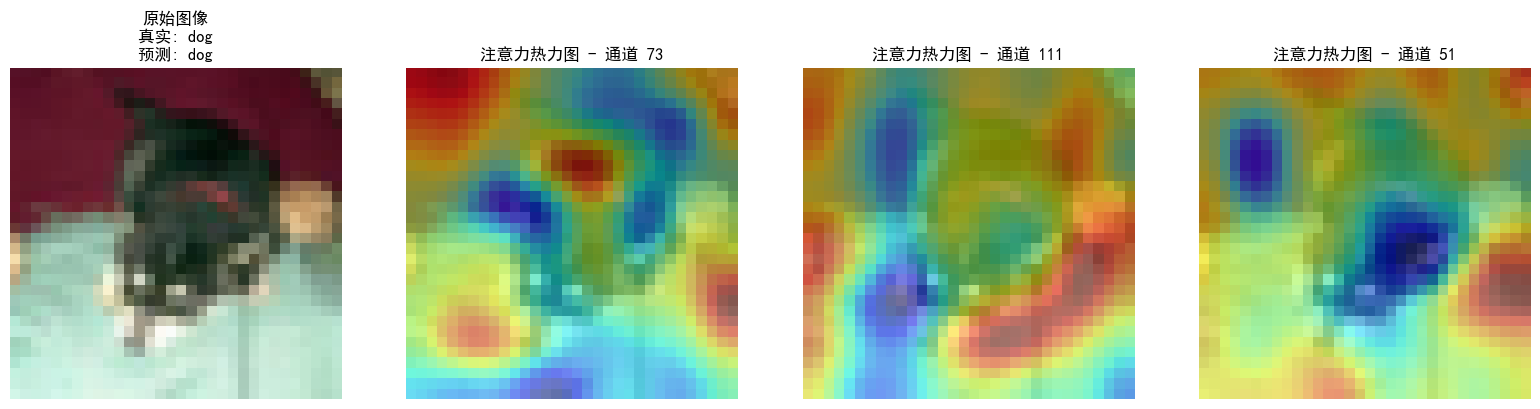
DAY 47
三、通道注意力 3.1 通道注意力的定义 # 新增:通道注意力模块(SE模块) class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):"""通道注意力模块(Squeeze-and-Excitation)"""def __init__(self, in_channels, reduction_rat…...

pam_env.so模块配置解析
在PAM(Pluggable Authentication Modules)配置中, /etc/pam.d/su 文件相关配置含义如下: 配置解析 auth required pam_env.so1. 字段分解 字段值说明模块类型auth认证类模块,负责验证用户身份&am…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...

2021-03-15 iview一些问题
1.iview 在使用tree组件时,发现没有set类的方法,只有get,那么要改变tree值,只能遍历treeData,递归修改treeData的checked,发现无法更改,原因在于check模式下,子元素的勾选状态跟父节…...
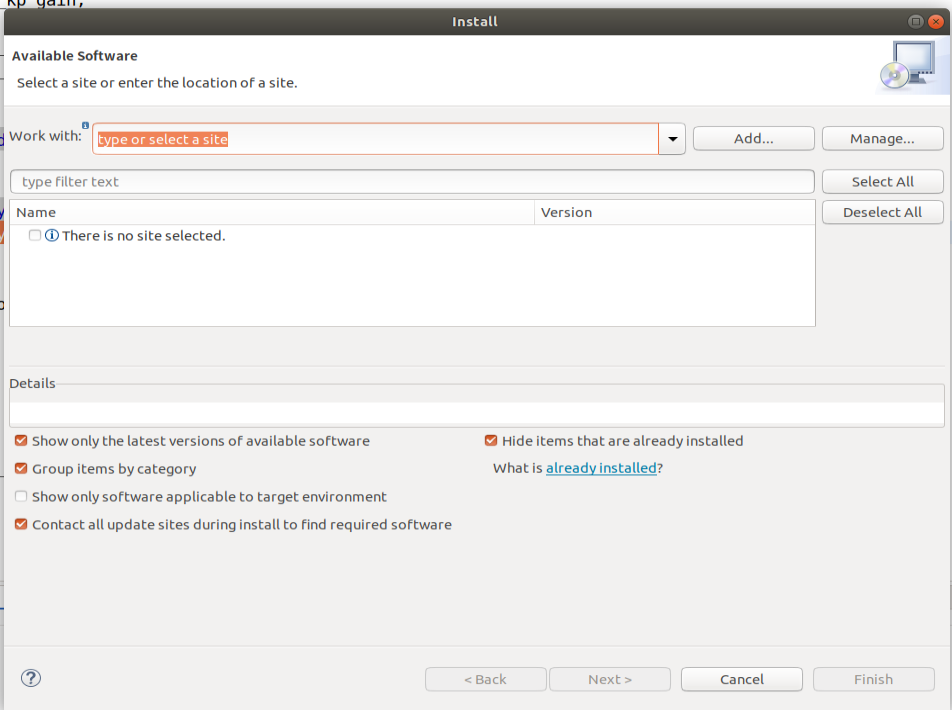
ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++
目录 文章目录 目录摘要1.修复过程摘要 本节主要解决ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++,无法导入ardupilot代码,会引起查看不方便的问题。如下图所示 1.修复过程 0.安装ubuntu 软件中自带的eclipse 1.打开eclipse—Help—install new software 2.在 Work with中…...

UR 协作机器人「三剑客」:精密轻量担当(UR7e)、全能协作主力(UR12e)、重型任务专家(UR15)
UR协作机器人正以其卓越性能在现代制造业自动化中扮演重要角色。UR7e、UR12e和UR15通过创新技术和精准设计满足了不同行业的多样化需求。其中,UR15以其速度、精度及人工智能准备能力成为自动化领域的重要突破。UR7e和UR12e则在负载规格和市场定位上不断优化…...
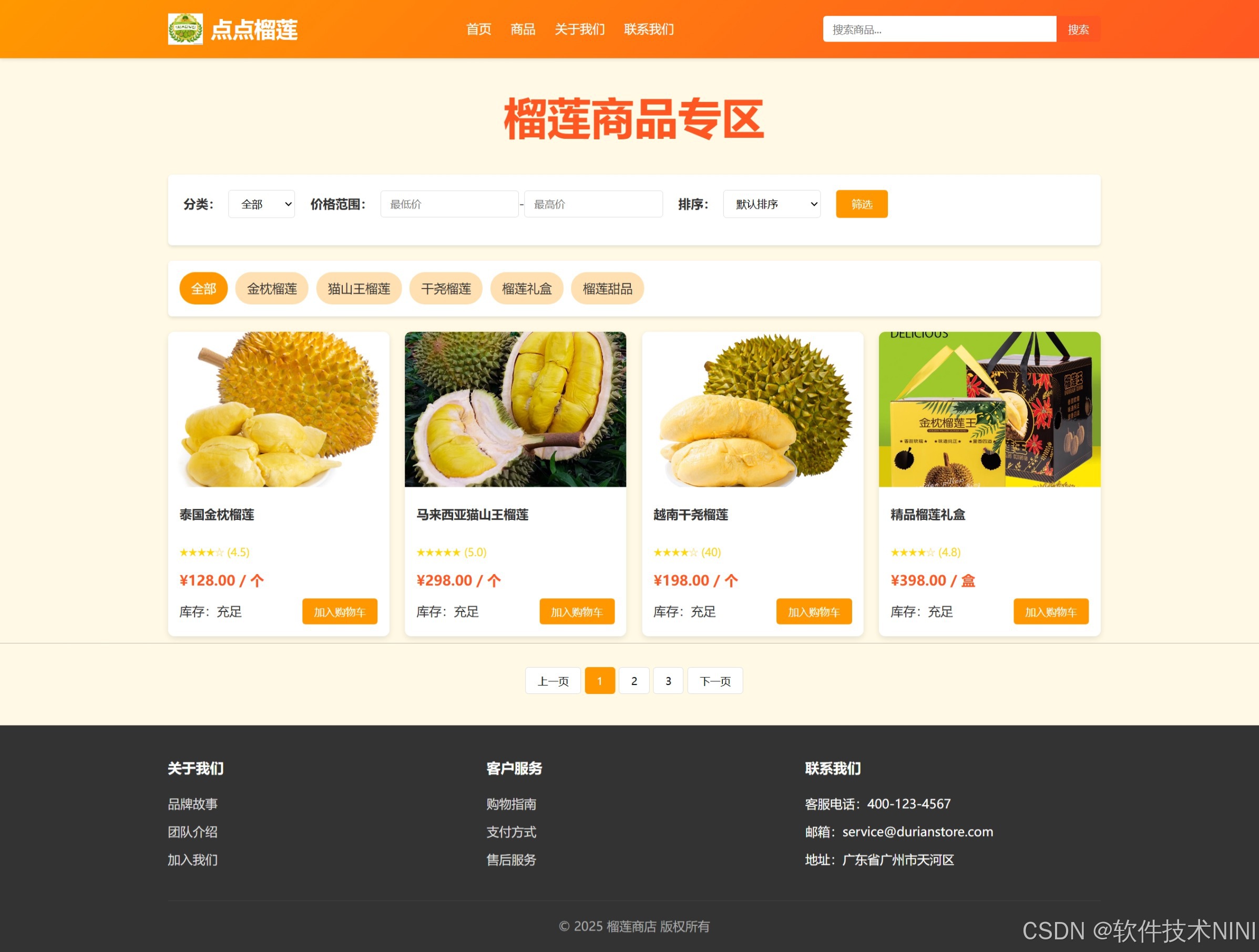
html css js网页制作成品——HTML+CSS榴莲商城网页设计(4页)附源码
目录 一、👨🎓网站题目 二、✍️网站描述 三、📚网站介绍 四、🌐网站效果 五、🪓 代码实现 🧱HTML 六、🥇 如何让学习不再盲目 七、🎁更多干货 一、👨…...
