SpringBoot系列 启动流程
文章目录
- SpringApplication
- SpringApplication#run
- 启动流程
- BootstrapContext
- SpringApplicationRunListeners
- prepareEnvironment
- configureEnvironment
- configurePropertySources
- configureProfiles
- 上下文初始化
- prepareContext
- refreshContext
- prepareRefresh
- obtainFreshBeanFactory
- prepareBeanFactory
- postProcessBeanFactory
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
- registerBeanPostProcessors
- initMessageSource
- initApplicationEventMulticaster
- onRefresh
- registerListeners
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization
- finishRefresh
- destroyBeans
- cancelRefresh
- afterRefresh
- callRunners
以下面的启动类为例:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);}
}
下面逐步分析SpringBoot的启动流程
SpringApplication
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
SpringApplication#run
SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String…)方法包含了全部SpringBoot应用启动的流程,启动完毕之后会返回最终的应用上下文ConfigurableApplicationContext,通过这个上下文我们可以获取Spring中的所有配置,Bean信息等
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {long startTime = System.nanoTime();// 创建 BootstrapContextDefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;configureHeadlessProperty();// 加载spring.factories文件中的SpringApplicationRunListener实例SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);// 执行starting回调listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);// 打印Banner信息Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);// 使用ApplicationContextFactory创建ApplicationContext对象context = createApplicationContext();// 将配置的ApplicationStartup加到ApplicationContext中context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);// 初始化应用上下文prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);// 刷新应用上下文refreshContext(context);// 应用上下文刷新完毕之后的回调afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);if (this.logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);}// ApplicationRunListener的started回调listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);callRunners(context, applicationArguments);} catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}try {Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);} catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}return context;
}
启动流程
BootstrapContext
BootstrapContext是一个在Spring Boot和Spring Cloud中使用的引导上下文,它在应用程序启动期间以及环境后处理过程中扮演着重要角色。以下是BootstrapContext的主要作用:
- 早期启动阶段的作用
延迟访问高成本单例:在应用程序的早期启动阶段,BootstrapContext提供了对可能创建成本高昂的单例的延迟访问。这意味着,只有在需要时,这些单例才会被创建和初始化,从而优化了启动时间和资源使用。
共享单例:在ApplicationContext可用之前,BootstrapContext允许共享必要的单例对象。这对于需要在早期阶段就进行配置或初始化的组件特别有用。 - 配置加载与优先级
加载外部配置:BootstrapContext负责加载外部资源的配置属性,并解释本地外部配置文件(如bootstrap.yml或bootstrap.properties)中的属性。这些配置属性通常用于设置应用程序的基础设施,如服务发现、配置中心等。
配置优先级:默认情况下,bootstrap属性具有高优先级,并且无法被本地配置覆盖。这确保了基础设施相关的配置不会被意外地覆盖或修改。 - 应用程序上下文层级
作为Parent Context:在Spring Cloud中,BootstrapContext通常作为主应用程序上下文(main ApplicationContext)的父上下文。这意味着主上下文可以继承BootstrapContext中的属性和配置资源。
属性资源继承:主应用程序上下文可以从BootstrapContext中继承额外的属性资源和配置文件,从而简化了配置管理。 - 自定义与扩展
自定义配置:通过配置/META-INF/spring.factories文件中的org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration值,可以自定义BootstrapContext的行为和配置。这为开发人员提供了极大的灵活性和控制力。
添加属性资源:可以通过向BootstrapContext中添加PropertySourceLocator类型的bean来添加额外的属性资源。这允许开发人员从自定义的来源加载配置属性。 - 生命周期管理
监听启动事件:开发人员可以通过实现ApplicationListener接口来监听BootstrapContext的启动事件,从而执行自定义的初始化操作或配置任务。
关闭监听:在应用程序上下文关闭时,BootstrapContext也提供了相应的机制来执行清理操作或释放资源。
综上所述,BootstrapContext在Spring Boot和Spring Cloud应用程序中起到了至关重要的作用,它优化了启动过程、管理了配置优先级、支持了应用程序上下文的层级结构、提供了自定义和扩展的能力,并管理了生命周期事件。
private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();// List<BootstrapRegistryInitializer> bootstrapRegistryInitializersthis.bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));return bootstrapContext;
}
这个bootstrapRegistryInitializers就是在SpringApplication的构造方法里进行加载的

SpringApplicationRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners负责在Spring Boot应用程序启动的不同阶段广播消息,并传递给实现了ApplicationListener接口的监听器类,以执行自定义逻辑。
SpringApplicationRunListener是一个监听SpringApplication中run方法的接口,它在项目启动过程的各个阶段进行事件的发布。通过实现这个接口,开发者可以在应用程序启动的不同生命周期阶段插入自定义的逻辑。
SpringApplicationRunListeners类内部维护了一个SpringApplicationRunListener的集合,提供了与SpringApplicationRunListener接口一致的方法,方便统一遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener。
实例化:
SpringApplicationRunListeners的实例化发生在SpringApplication的run方法中。它通过调用getRunListeners方法,读取META-INF/spring.factories文件,获取SpringApplicationRunListener的子类(如EventPublishingRunListener)的Class信息,并通过反射API创建其实例。
生命周期方法
SpringApplicationRunListeners接口定义了多个回调方法,这些方法在Spring Boot应用程序启动的不同阶段被触发:
- starting():在Spring Boot应用程序开始启动时触发。此时,可以执行一些自定义的初始化操作。
- environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment):在环境准备好后触发。此时,应用程序上下文尚未创建,但环境已经配置好,允许监听器在此阶段对环境进行进一步的自定义配置。
- contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context):在应用程序上下文准备好后触发。此时,应用程序上下文已经创建并准备好,但尚未加载任何配置。
- contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context):在应用程序上下文加载完成后触发。此时,应用程序上下文已经被刷新,但尚未启动。
- started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context):在应用程序上下文刷新且应用启动时触发。此时,可以在CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunners唤醒前执行一些自定义操作。
- running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context):在应用程序已经启动并准备好后触发。此时,代表程序已经准备好处理请求。
- failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception):在应用程序启动失败时触发。此时,可以执行一些自定义的失败处理逻辑。
实现与应用
开发者可以通过实现SpringApplicationRunListeners接口,并在META-INF/spring.factories文件中注册自定义的SpringApplicationRunListener实现类,以在应用程序启动的不同阶段插入自定义逻辑。
例如,可以实现一个自定义的SpringApplicationRunListener,在starting()方法中打印一条消息,以指示应用程序已经开始启动。或者,在environmentPrepared()方法中,可以根据环境变量或配置文件中的设置来动态调整应用程序的配置。
注意事项
- 顺序性:由于SpringApplicationRunListeners的回调方法是在应用程序启动的不同阶段被触发的,因此它们的执行顺序是固定的。开发者需要确保在正确的阶段执行自定义逻辑。
- 异常处理:在实现SpringApplicationRunListeners的回调方法时,需要注意异常处理。如果某个方法抛出异常,可能会导致应用程序启动失败。因此,建议在方法中添加适当的异常处理逻辑。
综上所述,SpringApplicationRunListeners是Spring Boot框架中用于监听应用程序启动过程的重要组件。通过实现和注册自定义的SpringApplicationRunListener实现类,开发者可以在应用程序启动的不同阶段插入自定义逻辑,从而实现更灵活的应用程序配置和管理。
prepareEnvironment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// 创建ConfigurableEnvironmentConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();// 配置ConfigurableEnvironmentconfigureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);// 调用SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared回调listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");// 属性绑定bindToSpringApplication(environment);if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());}ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);return environment;
}
org.springframework.boot.ApplicationContextFactory是springboot2.4.0新加的一个策略接口,它定义了如何创建 ApplicationContext 实例的工厂方法。
configureEnvironment
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {if (this.addConversionService) {environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService());}configurePropertySources(environment, args);configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
configurePropertySources
org.springframework.core.env.PropertySources 是 Spring 框架中用于管理和保存属性配置的关键接口。它是多个 PropertySource 的集合,为应用程序提供了一个统一的配置属性源访问接口。以下是对 PropertySources 的详细解释:
PropertySources 接口扩展了 Iterable<PropertySource<?>>,意味着它可以遍历其中的 PropertySource 元素。每个 PropertySource 都代表了一个配置源,如系统环境变量、命令行参数、属性文件等。PropertySources 通过提供统一的方法来访问这些配置源中的属性。
虽然 PropertySources 本身是一个接口,没有直接定义获取属性的方法,但它通过其内部的 PropertySource 元素来间接提供这些功能。每个 PropertySource 都有一个 getProperty(String name) 方法,用于根据属性名获取属性值。此外,PropertySources 的实现类(如 MutablePropertySources)通常会提供一些方法来添加、删除或修改 PropertySource 元素。
属性源的加载顺序与优先级
在 Spring 应用程序中,PropertySources 中的属性源通常按照特定的顺序加载,并且具有不同的优先级。例如,Spring Boot 在启动时,会通过 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 装载 PropertySources,并往其中添加 environmentProperties 和 localProperties 等属性源。这些属性源的加载顺序和优先级决定了当存在多个相同名称的属性时,哪个属性值会被优先使用。
PropertySources 在 Spring 应用程序中广泛应用于配置属性的管理和访问。以下是一些常见的应用场景:
- 多配置文件支持:Spring Boot 支持通过 @PropertySource 或 @PropertySources 注解来加载多个配置文件,这些配置文件会被添加到 PropertySources 中。
- 系统环境变量与命令行参数:Spring 允许将系统环境变量和命令行参数作为属性源添加到 PropertySources 中,从而方便地在不同环境下配置应用程序。
- 自定义属性源:开发者可以通过实现 PropertySource 接口来创建自定义的属性源,并将其添加到 PropertySources 中,以满足特定的配置需求。
五、注意事项
- 属性名的唯一性:在 PropertySources 中,每个属性名应该是唯一的。如果存在多个相同名称的属性,那么优先级较高的属性源中的属性值将被优先使用。
- 属性值的类型转换:在获取属性值时,可能需要进行类型转换。Spring 提供了丰富的类型转换机制来支持这一需求。
- 安全性:在处理敏感配置信息时,需要注意保护这些信息的安全性,避免泄露给未经授权的用户或系统。
综上所述,org.springframework.core.env.PropertySources 是 Spring 框架中用于管理和保存属性配置的重要接口。通过理解和使用它,开发者可以更加灵活地配置和管理 Spring 应用程序中的属性信息。
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {// 所有配置属性MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();// 添加默认属性if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) { // 1// 添加到末尾DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources);}// 命令行的配置属性处理,即是否添加main方法的参数if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;if (sources.contains(name)) {PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));composite.addPropertySource(source);sources.replace(name, composite);} else {// 添加到末尾sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));}}
}
- 可以通过
SpringApplication#setDefaultProperties()进行设置
configureProfiles
上下文初始化
prepareContext
用于ApplicationContext的初始化操作,加载上下文的组件,执行一些生命周期回调等等
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {context.setEnvironment(environment);// 设置ApplicationContext的相关组件postProcessApplicationContext(context);// 执行ApplicationContextInitializer#initialize回调applyInitializers(context);// context准备完毕: 执行SpringApplicationRunListener#contextPrepared回调listeners.contextPrepared(context);bootstrapContext.close(context);if (this.logStartupInfo) {logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);logStartupProfileInfo(context);}// Add boot specific singleton beansConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);if (printedBanner != null) {beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);}if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);}}if (this.lazyInitialization) {context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());}// 添加PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor这个BeanFactoryPostProcessorcontext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));// Load the sourcesSet<Object> sources = getAllSources();Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");// 加载SpringApplication的sources对象数组的Bean信息load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));// context加载完毕: 执行SpringApplicationRunListener#contextLoaded回调listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
refreshContext
加载或刷新配置的持久化,这些配置可以来自 XML 文件、properties 文件、关心数据库等等。因为该方法是一个启动方法,如果失败了,它应该销毁已经创建的单例,以避免出现悬挂资源(dangling resources),换句话说,要么实例化所有的单例,要么一个也不实例化。
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
AbstractApplicationContext 是 ApplicationContext 的一个抽象实现类。和普通的 BeanFactory 不同的是,ApplicationContext 可以检测到它的内部 BeanFactory 中定义的特殊 Bean:自动完成 BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanPostProcessor、ApplicationListener 的注册。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");// Prepare this context for refreshing.prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);beanPostProcess.end();// Initialize message source for this context.initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context.initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them.registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event.finishRefresh();} catch (BeansException ex) {// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;} finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...resetCommonCaches();contextRefresh.end();}}
}
prepareRefresh
这里是做一些准备工作,包括设置开始时间、active 状态、PropertySources 的初始化等等
protected void prepareRefresh() {// Switch to active.this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();this.closed.set(false);this.active.set(true);// ...// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.initPropertySources();// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredPropertiesgetEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);} else {// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.this.applicationListeners.clear();this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);}// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,// to be published once the multicaster is available...this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
obtainFreshBeanFactory
告诉当前ApplicationContext的子类刷新内部的 BeanFactory,然后返回刷新后的 BeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {refreshBeanFactory();return getBeanFactory();
}
refreshBeanFactory是
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext的一个抽象方法,需要子类实现,直接的子类有2个,而refreshBeanFactory方法在两个里面都有实现

一般来说基于WEB的系统的ApplicationContext的类型是org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,而它是AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext这个分支下的,所以我们先看它
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {if (hasBeanFactory()) {destroyBeans();closeBeanFactory();}try {// 创建BeanFactoryDefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);// 加载所有Bean定义信息,这里会根据不同的配置类型进行加载loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);this.beanFactory = beanFactory;} catch (IOException ex) {throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);}
}
loadBeanDefinitions将bean定义加载到给定的BeanFactory中,通常是通过委托给一个或多个BeanDefinitionReader完成的。

BeanDefinitionReader的继承体系如下:分别对应BeanDefinition存放的不同位置

prepareBeanFactory
配置 BeanFactory ,例如设置 context 的 class loader 和 post processor
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());if (!shouldIgnoreSpel) {beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));}beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationStartupAware.class);// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));}// Register default environment beans.if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());}if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());}if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());}if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME)) {beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME, getApplicationStartup());}
}
postProcessBeanFactory
对 BeanFactory 进行后处理,默认的实现为空,交给子类去扩展。可以对 beanFactory 进行想要的操作。比如 GenericWebApplicationContext 的实现如下:
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {if (this.servletContext != null) {beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext));beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);}WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors
实例化并且调用所有已注册的 BeanPostProcessor
initMessageSource
org.springframework.context.MessageSource是Spring框架中用于解析消息的顶层接口,它支持参数化和国际化信息。
MessageSource接口的主要功能是从资源文件中检索和解析消息。这些资源文件通常包含键值对,其中键是消息的标识符,值是实际要显示的字符串。通过MessageSource,开发者可以在代码中通过键来获取对应的消息值,从而实现了消息与代码的分离,提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。
MessageSource接口提供了多个重载的getMessage方法,用于获取消息。以下是几个常用的方法:
- String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String defaultMessage, Locale locale):根据指定的消息代码(code)、参数数组(args)、默认消息(defaultMessage)和语言环境(locale)来获取消息。如果找不到指定语言环境的消息,则使用默认消息。
- String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException:与上一个方法类似,但无法指定默认消息。如果找不到消息,会抛出NoSuchMessageException异常。
- String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException:使用MessageSourceResolvable对象来封装消息代码、参数和默认消息,然后根据指定的语言环境来获取消息。如果找不到消息,也会抛出NoSuchMessageException异常。
initApplicationEventMulticaster
初始化上下文中的事件机制
onRefresh
留给子类去实现,用于初始化其他特殊的 bean。比如 Spring Boot 中ServletWebServerApplicationContext 就是在这一步去创建的 web server
registerListeners
protected void registerListeners() {// Register statically specified listeners first.for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);}// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);}// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);}}
}
finishBeanFactoryInitialization
完成当前 context 的 beanFactory 的初始化,初始化剩下所有的不是懒加载的单例Bean对象
Bean的初始化都是通过BeanFactory#getBean进行的,也就是常说的将一个类型注册单例对象到容器并进行初始化
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {// Initialize conversion service for this context.// CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME => conversionServiceif (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {beanFactory.setConversionService(beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));}// Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));}// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {getBean(weaverAwareName);}// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.// 项目中自定义的所有Bean就是在此时进行实例化beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory定义的方法,在DefaultListableBeanFactory中实现:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {// ...// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...for (String beanName : beanNames) {// 先获取BeanDefinition信息RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);// 不是抽象类,并且是单例,且非懒加载if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {// 判断是否FactoryBean实例if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;boolean isEagerInit;if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,getAccessControlContext());} else {isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());}if (isEagerInit) {getBean(beanName);}}} else {getBean(beanName);}}}// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...for (String beanName : beanNames) {Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {StartupStep smartInitialize = getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize").tag("beanName", beanName);SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();return null;}, getAccessControlContext());} else {smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();}smartInitialize.end();}}
}
如果是SmartFactoryBean,则会根据一些条件判断是否要立即进行初始化,SmartFactoryBean#isEagerInit方法
如果是普通的FactoryBean,只有FactoryBean这个工厂Bean对象会被 Spring 容器初始化了,我们的FactoryBean对应的那个对象其实还没被初始化,要在第一次使用的时候,才会被初始化。
finishRefresh
完成当前 context 的 refresh 操作,调用 LifecycleProcessor 的 onRefresh 方法,发布 ContextRefreshedEvent 事件
protected void finishRefresh() {// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).clearResourceCaches();// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.initLifecycleProcessor();// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();// Publish the final event.publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage()) {LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);}
}
destroyBeans
内部调用的是
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#destroySingletons,用于出错时清除所有的单例对象
@Override
public void destroySingletons() {super.destroySingletons();updateManualSingletonNames(Set::clear, set -> !set.isEmpty());clearByTypeCache();
}// DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public void destroySingletons() {synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true;}String[] disposableBeanNames;synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet());}for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]);}this.containedBeanMap.clear();this.dependentBeanMap.clear();this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear();clearSingletonCache();
}// 清除三级缓存
protected void clearSingletonCache() {synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {this.singletonObjects.clear();this.singletonFactories.clear();this.earlySingletonObjects.clear();this.registeredSingletons.clear();this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = false;}
}
cancelRefresh
由于出现异常,需要取消上下文刷新操作
afterRefresh
afterRefresh是SpringApplication留给子类继承实现的一个方法,相当于一个回调
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
callRunners
这里会调用另外2个扩展点:ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner,此时上下文已经刷新完毕
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {context.getBeanProvider(Runner.class).orderedStream().forEach((runner) -> {if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);}if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);}});
}
相关文章:

SpringBoot系列 启动流程
文章目录 SpringApplicationSpringApplication#run 启动流程BootstrapContextSpringApplicationRunListenersprepareEnvironmentconfigureEnvironmentconfigurePropertySourcesconfigureProfiles 上下文初始化prepareContextrefreshContextprepareRefreshobtainFreshBeanFactor…...

vgg19提取特征
一般来说,大家使用VGG16,用的是第四列的网络架构,而使用VGG19,使用的就是第六列的网络架构。 使用vgg进行提取特征,在这个项目中,使用的就是每一块卷积层的第一层。 import torch.nn as nn from torchvis…...

Qt 中的 QChartView
深入理解 Qt 的 QChartView:图表展示与交互 QChartView 是 Qt Charts 模块中的一个核心类,它用于在 Qt 应用程序中显示图表,并支持多种用户交互方式。它继承自 QGraphicsView,通过封装 QChart,为用户提供了强大的图表…...

cheese安卓版纯本地离线文字识别插件
目的 cheese自动化平台是一款可以模拟鼠标和键盘操作的自动化工具。它可以帮助用户自动完成一些重复的、繁琐的任务,节省大量人工操作的时间。可以采用Vscode、IDEA编写,支持Java、Python、nodejs、GO、Rust、Lua。cheese也包含图色功能,识别…...

【C++】多肽
目录 一 多肽定义 1. 多肽的构成条件 1 例一 2 例二 2. 虚函数 3. 虚函数重写的两个意外 1 协变 2 析构函数的重写 二 关键字override 和 final 1. final 2.override 三 三重对比 1. 练习 四 多肽的原理 1. 多肽调用和普通调用 2.虚函数表 3. 分析 4. 原理 …...

Linux下Socket编程
1. Socket简介 Socket是什么? Socket是一种进程间通信的机制,通过它应用程序可以通过网络进行数据传输。Socket提供了一种跨平台的接口,使得同样的代码可以在不同的操作系统上运行。Socket类型 流式套接字(SOCK_STREAM࿰…...

Scrapy 爬虫的大模型支持
使用 Scrapy 时,你可以轻松使用大型语言模型 (LLM) 来自动化或增强你的 Web 解析。 有多种使用 LLM 来帮助进行 Web 抓取的方法。在本指南中,我们将在每个页面上调用一个 LLM,从中抽取我们定义的一组属性,而无需编写任何选择器或…...

数据仓库简介(一)
数据仓库概述 1. 什么是数据仓库? 数据仓库(Data Warehouse,简称 DW)是由 Bill Inmon 于 1990 年提出的一种用于数据分析和挖掘的系统。它的主要目标是通过分析和挖掘数据,为不同层级的决策提供支持,构成…...

Kafka和RabbitMQ区别
RabbitMQ的消息延迟是微秒级,Kafka是毫秒级(1毫秒1000微秒) 延迟消息是指生产者发送消息发送消息后,不能立刻被消费者消费,需要等待指定的时间后才可以被消费。 Kafka的单机呑吐量是十万级,RabbitMQ是万级…...

go-zero学习
go-zero官网: https://go-zero.dev/docs/tasks 好文: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_63629756/article/details/136599547 视频: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18JxUeyECg 微服务基础 根目录下,一个文件夹就是一个微服务。如果微…...
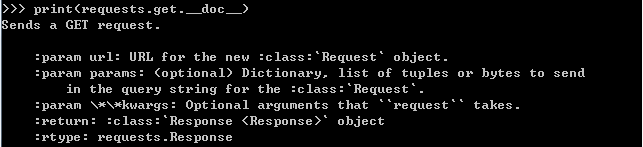
python如何查询函数
1、通用的帮助函数help() 使用help()函数来查看函数的帮助信息。 如: import requests help(requests) 会有类似如下输出: 2、查询函数信息 ★查看模块下的所有函数: dir(module_name) #module_name是要查询的函数名 如: i…...
)
计算机视觉与深度学习 | 从激光雷达数据中提取地面点和非地面点(附matlab代码)
===================================================== github:https://github.com/MichaelBeechan CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/u011344545 ===================================================== 激光雷达数据 使用velodyneFileReader函数从P...
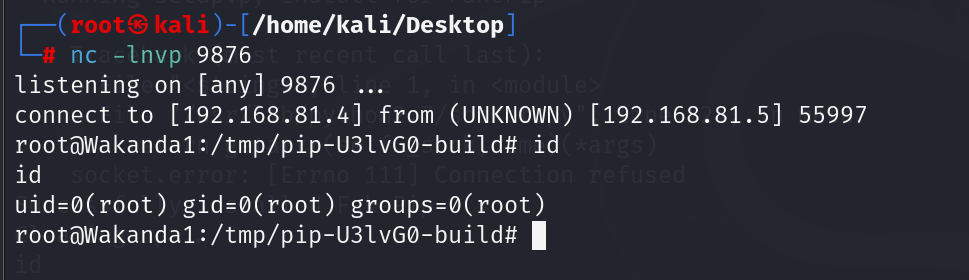
vulnhub-wakanda 1靶机
vulnhub:wakanda: 1 ~ VulnHub 导入靶机,放在kali同网段,扫描 靶机在192.168.81.5,扫描端口 四个端口,详细扫描一下 似乎没什么值得注意的,先看网站 就这一个页面,点按钮也没反应,扫…...

Bilibili视频如何保存到本地
Bilibili(哔哩哔哩)作为中国领先的视频分享平台之一,汇聚了大量的优质内容,从搞笑动画、综艺节目到专业教程,应有尽有。许多用户时常会遇到这样的需求:希望将视频保存到本地,方便离线观看或者保存珍藏。由于版权保护等…...

C++之多线程
前言 多线程和多进程是并发编程的两个核心概念,它们在现代计算中都非常重要,尤其是在需要处理大量数据、提高程序性能和响应能力的场景中。 多线程的重要性: 资源利用率:多线程可以在单个进程中同时执行多个任务,这可以更有效地利用CPU资源,特别是在多核处理器上。 性…...

《C++音频降噪秘籍:让声音纯净如初》
在音频处理领域,降噪是一项至关重要的任务。无论是录制音乐、语音通话还是音频后期制作,都需要有效地去除背景噪声,以获得清晰、纯净的音频效果。在 C中实现高效的音频降噪处理,可以为音频应用带来更高的质量和更好的用户体验。本…...

C(十)for循环 --- 黑神话情景
前言: "踏过三界宝刹,阅过四洲繁华。笑过五蕴痴缠,舍过六根牵挂。怕什么欲念不休,怕什么浪迹天涯。步履不停,便是得救之法。" 国际惯例,开篇先喝碗鸡汤。 今天,杰哥写的 for 循环相…...

记录一次docker报错无法访问文件夹,权限错误问题
记录一次docker报错无法访问文件夹,权限错误问题 1. 背景 使用docker安装photoview,为其分配了一个cache目录,用户其缓存数据。在运行过程中,扫描文件后显示如下错误 could not make album image cache directory: mkdir /app/c…...
 useEffect)
react crash course 2024(8) useEffect
引入 import { useEffect } from react; useEffect – React 中文文档useEffect 是一个 React Hook,它允许你 将组件与外部系统同步。 有些组件需要与网络、某些浏览器 API 或第三方库保持连接,当它们显示在页面上时。这些系统不受 React 控制࿰…...

GEE开发之Modis_NDWI数据分析和获取
GEE开发之Modis_NDWI数据分析和获取 0 数据介绍NDWI介绍MOD09GA介绍 1 NDWI天数据下载2 NDWI月数据下载3 NDWI年数据下载 前言:本文主要介绍Modis下的NDWI数据集的获取。归一化差异水指数 (NDWI) 对植被冠层液态水含量的变化很敏感。它来自近红外波段和第二个红外波…...
指令的指南)
在Ubuntu中设置开机自动运行(sudo)指令的指南
在Ubuntu系统中,有时需要在系统启动时自动执行某些命令,特别是需要 sudo权限的指令。为了实现这一功能,可以使用多种方法,包括编写Systemd服务、配置 rc.local文件或使用 cron任务计划。本文将详细介绍这些方法,并提供…...
《基于Apache Flink的流处理》笔记
思维导图 1-3 章 4-7章 8-11 章 参考资料 源码: https://github.com/streaming-with-flink 博客 https://flink.apache.org/bloghttps://www.ververica.com/blog 聚会及会议 https://flink-forward.orghttps://www.meetup.com/topics/apache-flink https://n…...
集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join)
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join 1、依赖1.1、依赖版本1.2、pom.xml 2、代码2.1、SqlSession 构造器2.2、MybatisPlus代码生成器2.3、获取 config.yml 配置2.3.1、config.yml2.3.2、项目配置类 2.4、ftl 模板2.4.1、…...

4. TypeScript 类型推断与类型组合
一、类型推断 (一) 什么是类型推断 TypeScript 的类型推断会根据变量、函数返回值、对象和数组的赋值和使用方式,自动确定它们的类型。 这一特性减少了显式类型注解的需要,在保持类型安全的同时简化了代码。通过分析上下文和初始值,TypeSc…...
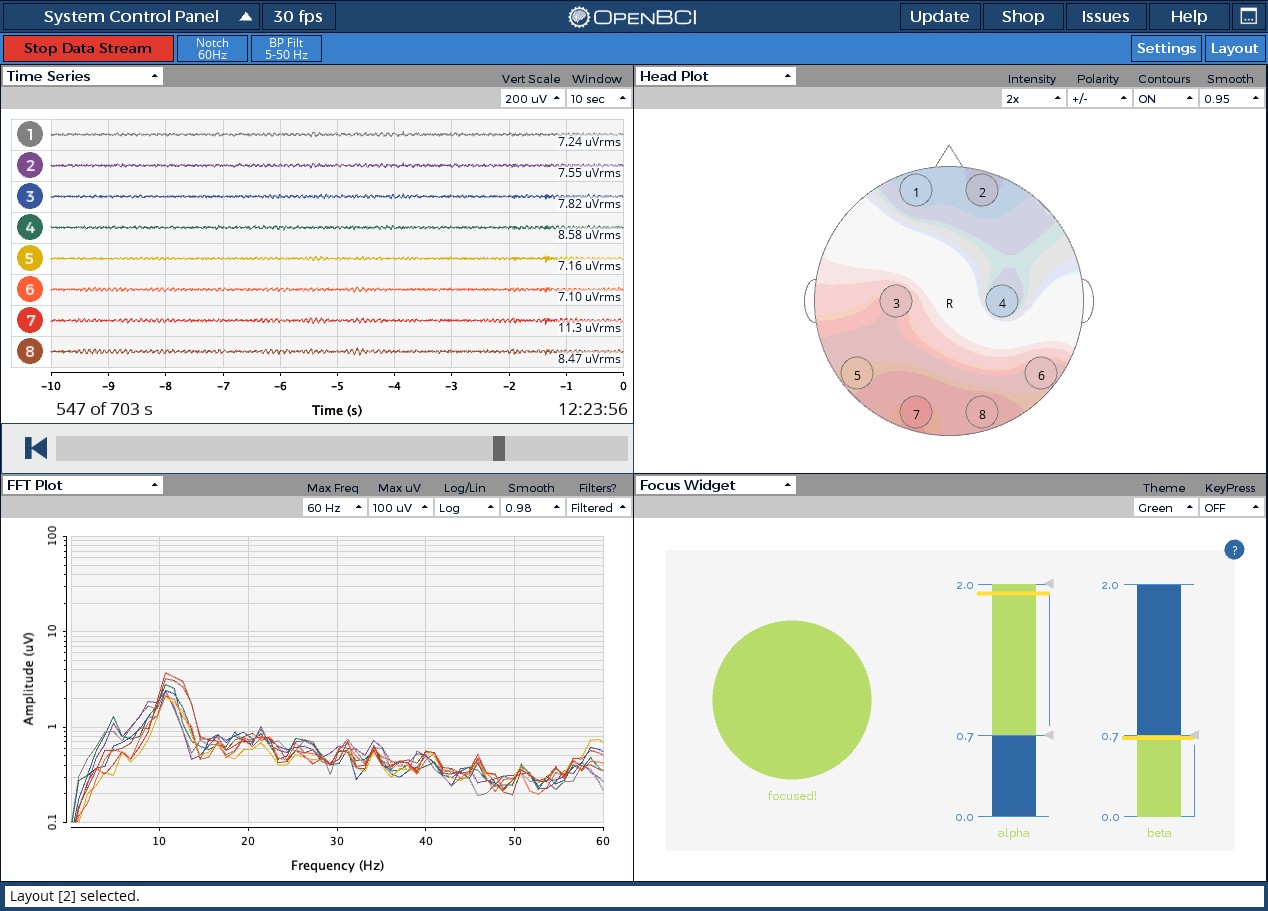
脑机新手指南(七):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(上)
一、OpenBCI_GUI 项目概述 (一)项目背景与目标 OpenBCI 是一个开源的脑电信号采集硬件平台,其配套的 OpenBCI_GUI 则是专为该硬件设计的图形化界面工具。对于研究人员、开发者和学生而言,首次接触 OpenBCI 设备时,往…...

Ubuntu Cursor升级成v1.0
0. 当前版本低 使用当前 Cursor v0.50时 GitHub Copilot Chat 打不开,快捷键也不好用,当看到 Cursor 升级后,还是蛮高兴的 1. 下载 Cursor 下载地址:https://www.cursor.com/cn/downloads 点击下载 Linux (x64) ,…...
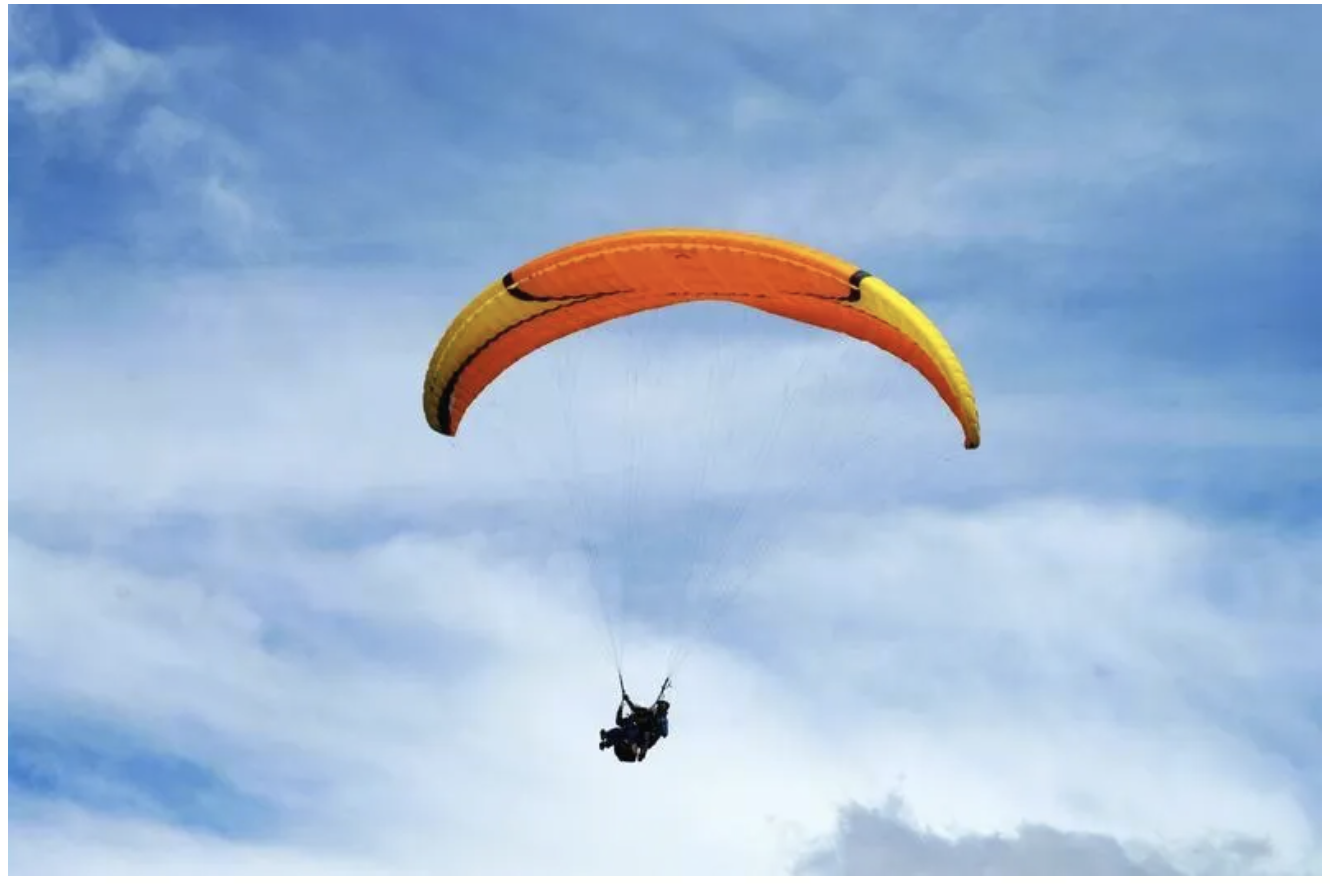

数学建模-滑翔伞伞翼面积的设计,运动状态计算和优化 !
我们考虑滑翔伞的伞翼面积设计问题以及运动状态描述。滑翔伞的性能主要取决于伞翼面积、气动特性以及飞行员的重量。我们的目标是建立数学模型来描述滑翔伞的运动状态,并优化伞翼面积的设计。 一、问题分析 滑翔伞在飞行过程中受到重力、升力和阻力的作用。升力和阻力与伞翼面…...
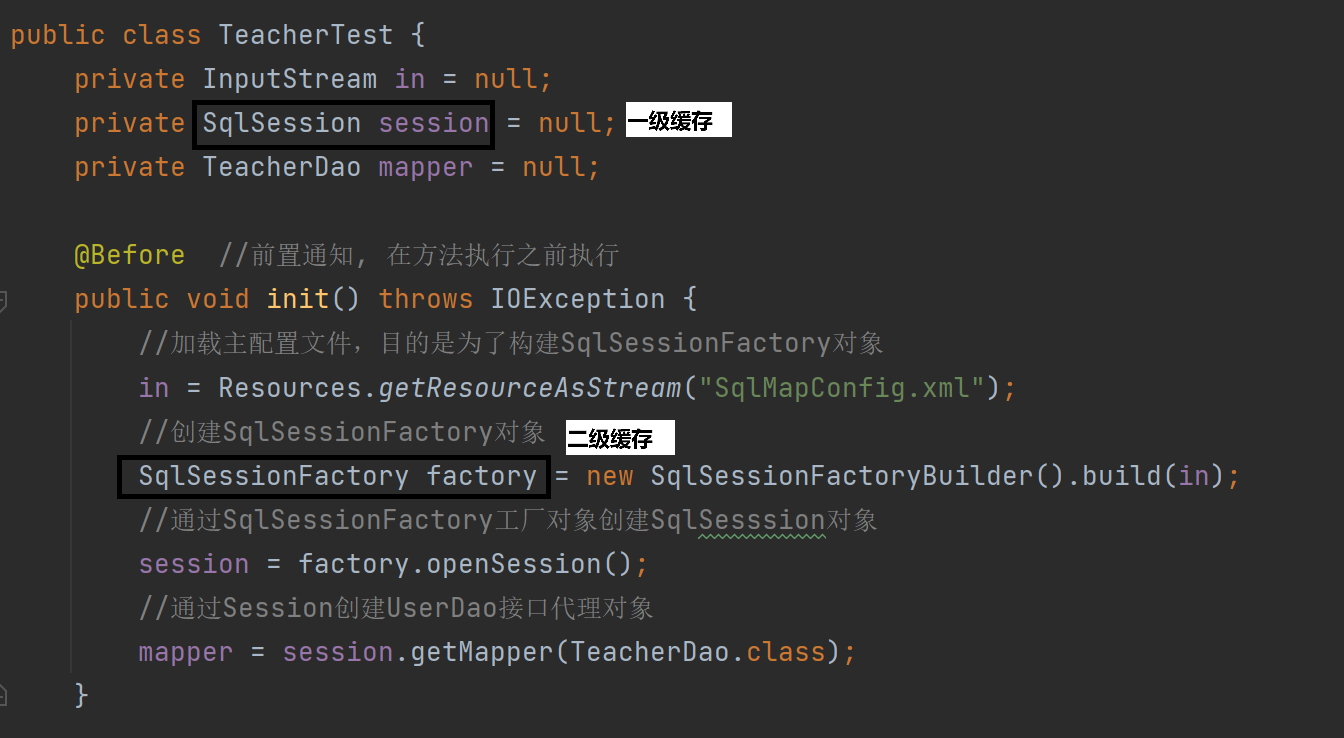
MyBatis中关于缓存的理解
MyBatis缓存 MyBatis系统当中默认定义两级缓存:一级缓存、二级缓存 默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启(sqlSession级别的缓存)二级缓存需要手动开启配置,需要局域namespace级别的缓存 一级缓存(本地缓存&#…...
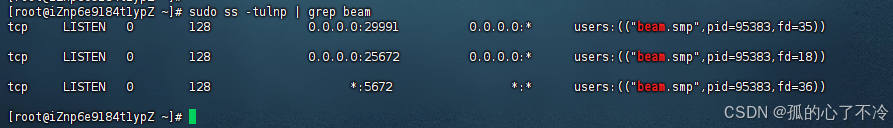
【Linux】Linux安装并配置RabbitMQ
目录 1. 安装 Erlang 2. 安装 RabbitMQ 2.1.添加 RabbitMQ 仓库 2.2.安装 RabbitMQ 3.配置 3.1.启动和管理服务 4. 访问管理界面 5.安装问题 6.修改密码 7.修改端口 7.1.找到文件 7.2.修改文件 1. 安装 Erlang 由于 RabbitMQ 是用 Erlang 编写的,需要先安…...

前端高频面试题2:浏览器/计算机网络
本专栏相关链接 前端高频面试题1:HTML/CSS 前端高频面试题2:浏览器/计算机网络 前端高频面试题3:JavaScript 1.什么是强缓存、协商缓存? 强缓存: 当浏览器请求资源时,首先检查本地缓存是否命中。如果命…...
