深入理解 Handler(java 层 + native 层)
文章目录
- 回顾
- 线程消息队列时怎样实现的
- 消息是怎么传递的?
- Handle 的延迟消息是怎么处理的?
- IdleHandler 的原理
- 主线程进入了 Looper 循环为什么没有 ANR?
- 消息屏障是什么?
回顾
之前学习过Handler相关的基础知识,今天再学习一下 Handler 更深层次的知识。
线程消息队列时怎样实现的
- 可以在子线程创建 Handler 么?- 主线程的 Looper 和 子线程的 Looper 有什么区别?- Handler Looper 和 MessageQueue 有什么关系?- MessageQueue 是怎么创建的?
- 可以在子线程创建 Handler 么?
在子线程创建 Handler 时会报一个 RuntimeException 让你调用 Looper.prepare()
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {mLooper = Looper.myLooper();if (mLooper == null) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't create handler inside thread " + Thread.currentThread()+ " that has not called Looper.prepare()");}mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;mCallback = callback;mAsynchronous = async;}
Looper.myLooper() 是从 ThreadLocal 中读取 Looper
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {return sThreadLocal.get();}
- Looper.prepare()
public static void prepare() {prepare(true);}private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");}sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));}
Looper.prepare() 呢,先从 sThreadLocal.get() 如果已经存在则抛出异常。如果没有 Looper 则创建一个 Looper 传入了 quitAllowed 参数,默认是 true ,quitAllowed 是什么意思的?quitAllowed 代表 Looper 是否可以退出,工作完成以后可以调用 Looper.quit() 退出,主线程创建的 Looper 可以看一下,创建的时候传入的是 false ,是不可以退出的,并且创建完会将 Looper 保存到一个静态变量里面,就可以随时获得主线程的 Looper。
- 可以在子线程创建 Handler 么?
- 可以,需要先创建 Looper
- 主线程的 Looper 和 子线程的 Looper 有什么区别?
- 上面讲的子线程创建 Looper quitAllowed 是true 主线程是 false;就是子线程的 Looper 可以退出,主线程不可以。
- 那么 Looper 创建的时候做了哪些事
// Looper 的构造函数private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);mThread = Thread.currentThread();}
Looper 在创建的时候 new MessageQueue(quitAllowed); 创建了消息队列
- new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
MessageQueue(boolean quitAllowed) {// 记录了是否可以退出mQuitAllowed = quitAllowed;// 调用了 nativeInit() 在 native 层去初始化mPtr = nativeInit();}
- Handler Looper 和 MessageQueue 有什么关系?
- 线程在创建 Handler 时需要创建 Looper ,创建 Looper 时创建了 MessageQueue (Handler 创建可以传入 Looper)多个 Handler 可以往同一个 Looper 发送 msg ,MessageQueue 发送消息时会根据 target 往对应的 Handler 中回调数据。
- 接下来看看 MessageQueue() 在 native 层做了哪些处理
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_os_MessageQueue.cpp -> android_os_MessageQueue_nativeInit
static jlong android_os_MessageQueue_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz) {NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = new NativeMessageQueue();if (!nativeMessageQueue) {jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Unable to allocate native queue");return 0;}nativeMessageQueue->incStrong(env);return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(nativeMessageQueue);
}
其主要创建了 NativeMessageQueue() 对象
- NativeMessageQueue
NativeMessageQueue::NativeMessageQueue() :mPollEnv(NULL), mPollObj(NULL), mExceptionObj(NULL) {// 先从当前线程的缓存中获取 Looper mLooper = Looper::getForThread();// 如果获取不到 则 new 一个 Looperif (mLooper == NULL) {mLooper = new Looper(false);// 然后设置到局部缓存中Looper::setForThread(mLooper);}
}
- Looper::getForThread(); 线程的局部缓存是什么呢?
sp<Looper> Looper::getForThread() {int result = pthread_once(& gTLSOnce, initTLSKey);LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(result != 0, "pthread_once failed");Looper* looper = (Looper*)pthread_getspecific(gTLSKey);return sp<Looper>::fromExisting(looper);
}
其实就是获取线程的 TLS ,叫 Thread Local Storage ,就是对线程内全部开放,其他线程无法访问。我记得之前好像学习 JVM 的内存分配的时候有涉及到。
- native 的 Looper 的创建
Looper::Looper(bool allowNonCallbacks) :... {mWakeEventFd = eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC);AutoMutex _l(mLock);rebuildEpollLocked();
}
首先根据 eventfd 创建了 mWakeEventFd ,这里是Android9 早起版本不是 mWakeEventFd 是管道,因为使用 mWakeEventFd 计数器比用管道的性能要好。管道需要写再读需要拷贝数据。(在android后期又对mWakeEventFd 的使用做了优化。)然后调用了 rebuildEpollLocked();
- rebuildEpollLocked();
void Looper::rebuildEpollLocked() {// Allocate the new epoll instance and register the WakeEventFd.// epoll_create1 创建了 epollmEpollFd.reset(epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC));// 创建了 createEpollEvent 事件设置了 mWakeEventFd ,监听可读事件epoll_event wakeEvent = createEpollEvent(EPOLLIN, WAKE_EVENT_FD_SEQ);int result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd.get(), EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeEventFd.get(), &wakeEvent);// ...
}
Looper 创建的时候会创建 mWakeEventFd ,并且去监听它的事件,那么数据是什么写到里面的呢?另外一个线程往当前线程消息队列中插入一条消息,然后会调用 wake() 函数 :调用完了 wake() 函数就会往 mWakeEventFd 里面写东西。
wake() 函数调用:可以看看java 层调用 Handler sendMessage 时,加入到 MessageQueue 后,会调用到下面代码,mPtr 是上面创建 MessageQueue时调用的 mPtr = nativeInit(); 返回的。
if (needWake) {nativeWake(mPtr);}
private native static void nativeWake(long ptr);
- 那么什么时候去读数据的呢?
在 Looper.loop() 里会从 Message 中获取 next() 的 message ,在调用 next() 函数时调用了 nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); 函数。调用到了 native 层 Looper::pollOnce
int Looper::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData) {int result = 0;for (;;) {//....result = pollInner(timeoutMillis);}
}
- 调用了 pollInner() 函数
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];// epoll_wait 等待有没有事件触发int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd.get(), eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);//...// 如果有事件了则在 for 循环中处理事件for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {const SequenceNumber seq = eventItems[i].data.u64;uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;if (seq == WAKE_EVENT_FD_SEQ) {if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {// 调用了 awoken(); 函数 awoken 就是把事件读出来 消化掉awoken();} } else {//...}}
}
- 架构图
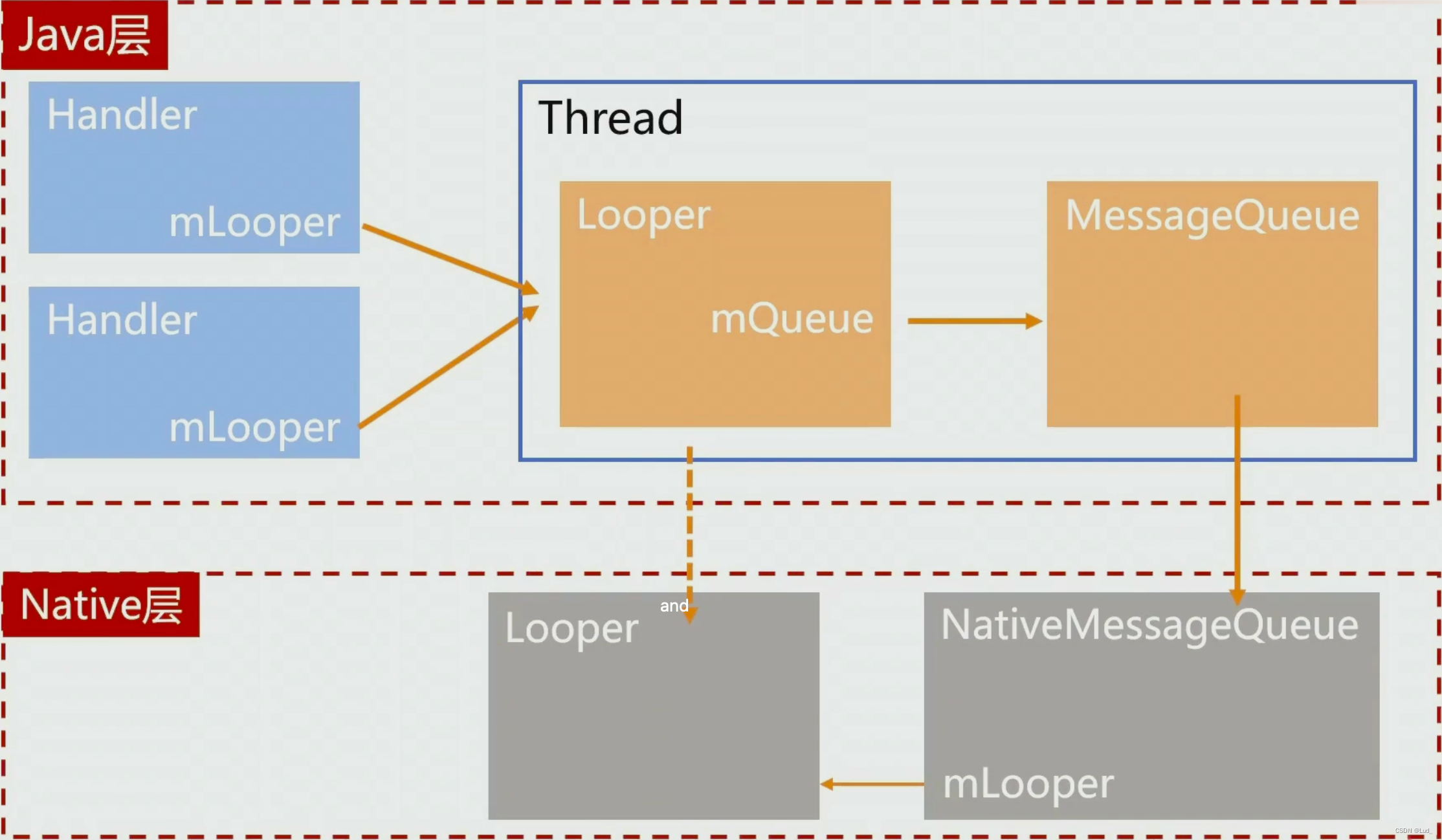
Handler 架构分为 java 层和 native 层,java 层开始,一个线程创建了 Looper 对应的创建了一个 MessageQueue , java 层的 MessageQueue 创建时对应创建了一个 native 层的 NativeMessageQueue 并且创建了一个 Looper ,也就是说 java 层的 Looper 和 MessageQueue 在 native 层也对应的有 Looper 和 MessageQueue。
- Handler Looper 和 MessageQueue 有什么关系?
- 一一对应的关系
- MessageQueue 是怎么创建的?
- java 层 Looper 创建的时候创建的 MessageQueue ,java 层MessageQueue 创建的时候会创建一个 native 层的 NativeMessageQueue,NativeMessageQueue 创建的时候会创建 Naive 层的 Looper ,Native 层的 Looper 创建的时候会创建一个可读的 epoll 。
消息是怎么传递的?
上面一段讲了 Handler 在 java 层和 native 层的架构,这回梳理一下消息是怎么传递呢。
- 消息循环过程是怎么样的?- 消息是怎么发送的?- 消息是怎么处理的?
- 从 java 层的 Looper.loop() 循环开始
public static void loop() {// 拿到 looper final Looper me = myLooper();// 拿到 MessageQueuefinal MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;for (;;) {// 取下一条消息Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {// 没有消息直接返回return;}// 调用消息的 target.dispatchMessage(msg);// target 就是对应的 Handlermsg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);// 回收消息msg.recycleUnchecked();}
loop() 中重点是 Message msg = queue.next(); 如何获取下一个消息和 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); 如何分发消息。

- msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); 分发 msg 比较简单
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {// 先以 msg 中的 callback 优先回调回去if (msg.callback != null) {handleCallback(msg);} else {// 然后再检查全局 mCallback if (mCallback != null) {// mCallback.handleMessage(msg) 返回 true 则不往下分发了。// 一些 hook 点就是通过反射 设置 mCallback 偷偷的更换 msg 然后返回 false if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {return;}}// 最后才调用 handleMessagehandleMessage(msg);}}
- Message msg = queue.next(); 怎么取消息
Message next() {int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; for (;;) {// 目的是阻塞线程,当其他线程发送一些特殊消息的时候会唤起阻塞// 第一次 nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0 所以第一次一定不会阻塞// 如果第一次下去之后没有消息了 nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1 了就需要一直等待了nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {Message prevMsg = null;// 取一条消息Message msg = mMessages;if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {do {prevMsg = msg;msg = msg.next;} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());}msg.next = null;// 标记成使用中msg.markInUse();// 然后返回消息return msg;// ... // No more messages.nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}}
}
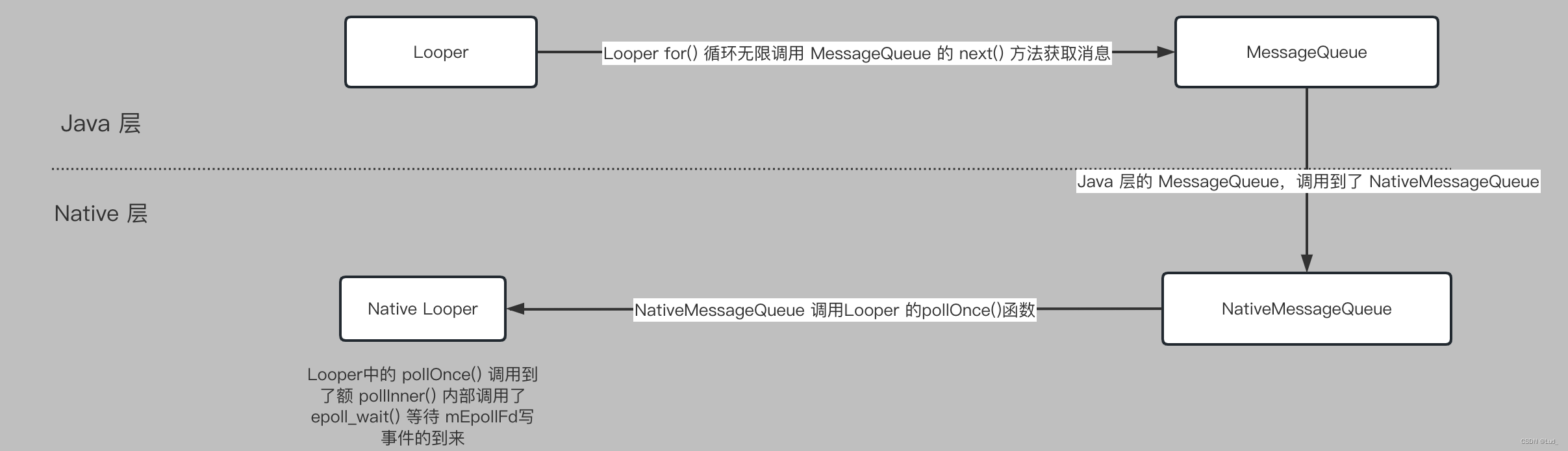
next() 方法这里主要看 nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); 方法,首次超时时间 nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0,所以一定不会阻塞,会去从队列中取消息,如果没有消息则把 nextPollTimeoutMillis 设置成 -1 ,下次 for() 循环会一直阻塞住。接下来看一下 nativePollOnce() 函数。
- nativePollOnce()
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativePollOnce(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,jlong ptr, jint timeoutMillis) {NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);nativeMessageQueue->pollOnce(env, obj, timeoutMillis);
}
android_os_MessageQueue_nativePollOnce() 调用了 NativeMessageQueue 的 pollOnce(env, obj, timeoutMillis);

void NativeMessageQueue::pollOnce(JNIEnv* env, jobject pollObj, int timeoutMillis) {mPollEnv = env;mPollObj = pollObj;mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);mPollObj = NULL;mPollEnv = NULL;// ...
}
NativeMessageQueue::pollOnce() 函数调用了 Looper 的 pollOnce() 函数,并且带了一个超时时间。
int Looper::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData) {int result = 0;for (;;) {//...if (result != 0) { if (outFd != nullptr) *outFd = 0;if (outEvents != nullptr) *outEvents = 0;if (outData != nullptr) *outData = nullptr;return result;}result = pollInner(timeoutMillis);}
}
Looper::pollOnce() 首次的时候 result = 0 ,所以会调用 pollInner(timeoutMillis); 函数。
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {// ...struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];// 调用了 epoll_wait() 函数,这个函数是用来阻塞的,它返回只有几种情况// 第一种出错了,eventCount<0,第二种超时了 eventCount=0,第三种有事件传递进来 eventCount 就是事件个数int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd.get(), eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);// ...// 有事件返回以后则通过 for 循环处理事件for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {const SequenceNumber seq = eventItems[i].data.u64;uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;if (seq == WAKE_EVENT_FD_SEQ) {if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {// 如果事件满足条件,则调用 awoken() 来消费事件awoken();}} else {// ...}}//...return result;
}
当 Looper::pollInner() 返回了,就可以继续执行最上面的 next() 函数了,一直循环拿到下一个msg,就是不停的调用 nativePollOnce() 一直监听其他线程是否有发送事件进来,如果有事件,nativePollOnce() 就可以顺利执行下去,就可以拿下一个信息了。
- 那么怎么往消息队列里面发送消息呢?
一般使用的时候都是调用 Handler 的 sendMessage()
public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg){return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);}最后都会走到下面这个方法
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {MessageQueue queue = mQueue;if (queue == null) {return false;}return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);}
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {// Handler 设置给 targetmsg.target = this;if (mAsynchronous) {msg.setAsynchronous(true);}// 调用 MessageQueue 的 enqueueMessage 并传入 uptimeMillisreturn queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);}
- queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis); 重点代码如下
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {synchronized (this) {// 先将消息插入到消息队列中//...if (needWake) {// 然后调用 nativeWake(mPtr); 去将唤醒消息队列所在的线程nativeWake(mPtr);}}return true;}
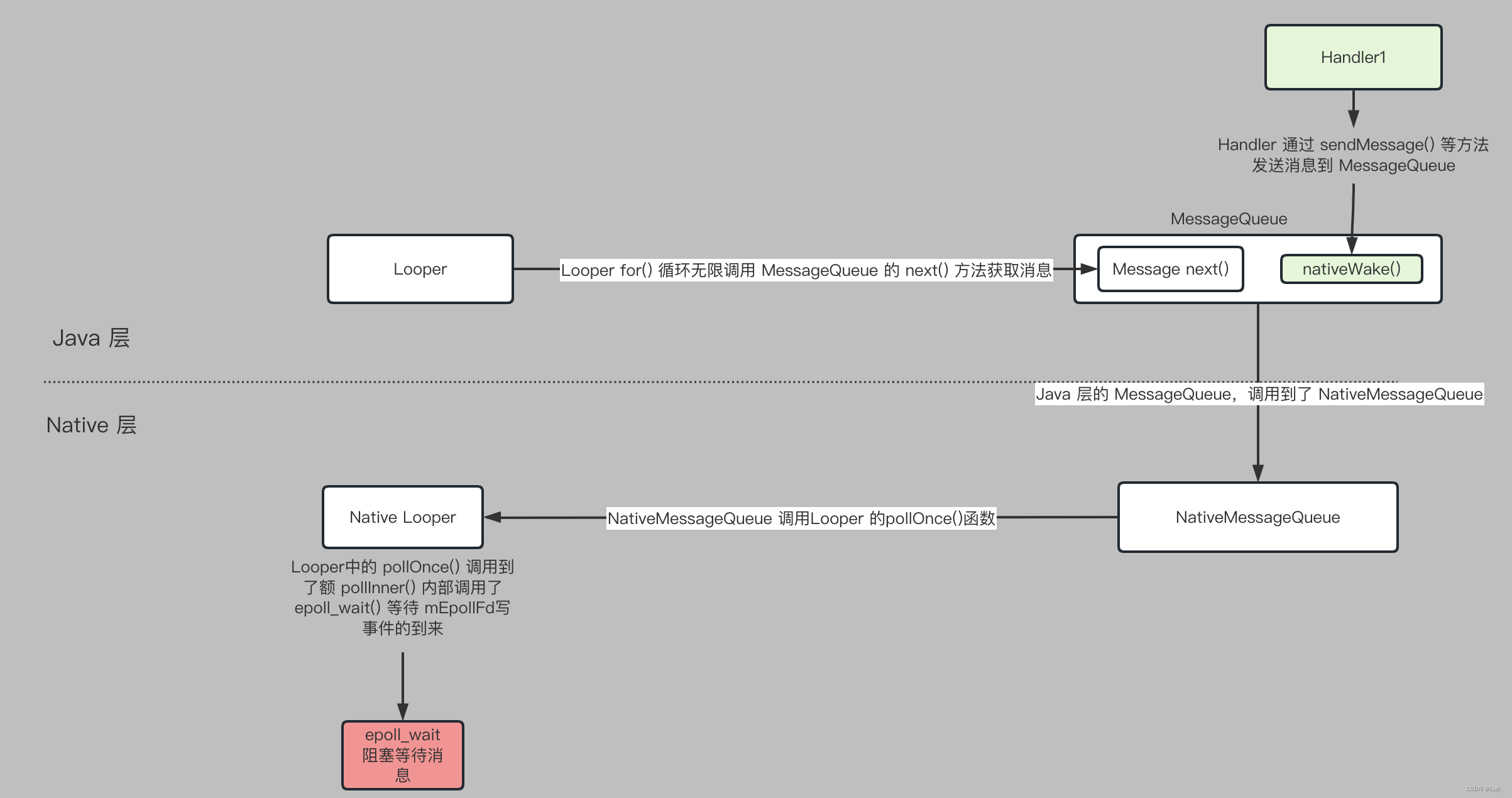
enqueueMessage() 首先将消息插入到消息队列,然后调用 nativeWake(mPtr); 唤醒消息队列所在的线程,这里重点看是如何唤醒的。
- nativeWake(mPtr);
static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativeWake(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong ptr) {NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);nativeMessageQueue->wake();
}
android_os_MessageQueue_nativeWake() 函数调用到了 NativeMessageQueue 的 wake() 函数。
void NativeMessageQueue::wake() {mLooper->wake();
}
最后又调用到了 Looper 的 mLooper->wake();
void Looper::wake() {
#if DEBUG_POLL_AND_WAKEALOGD("%p ~ wake", this);
#endifuint64_t inc = 1;ssize_t nWrite = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(write(mWakeEventFd.get(), &inc, sizeof(uint64_t)));
}
Looper::wake() 往 mWakeEventFd 里面的计数器写数,这样 epllo_wait() 的循环就可以收到可读事件了。
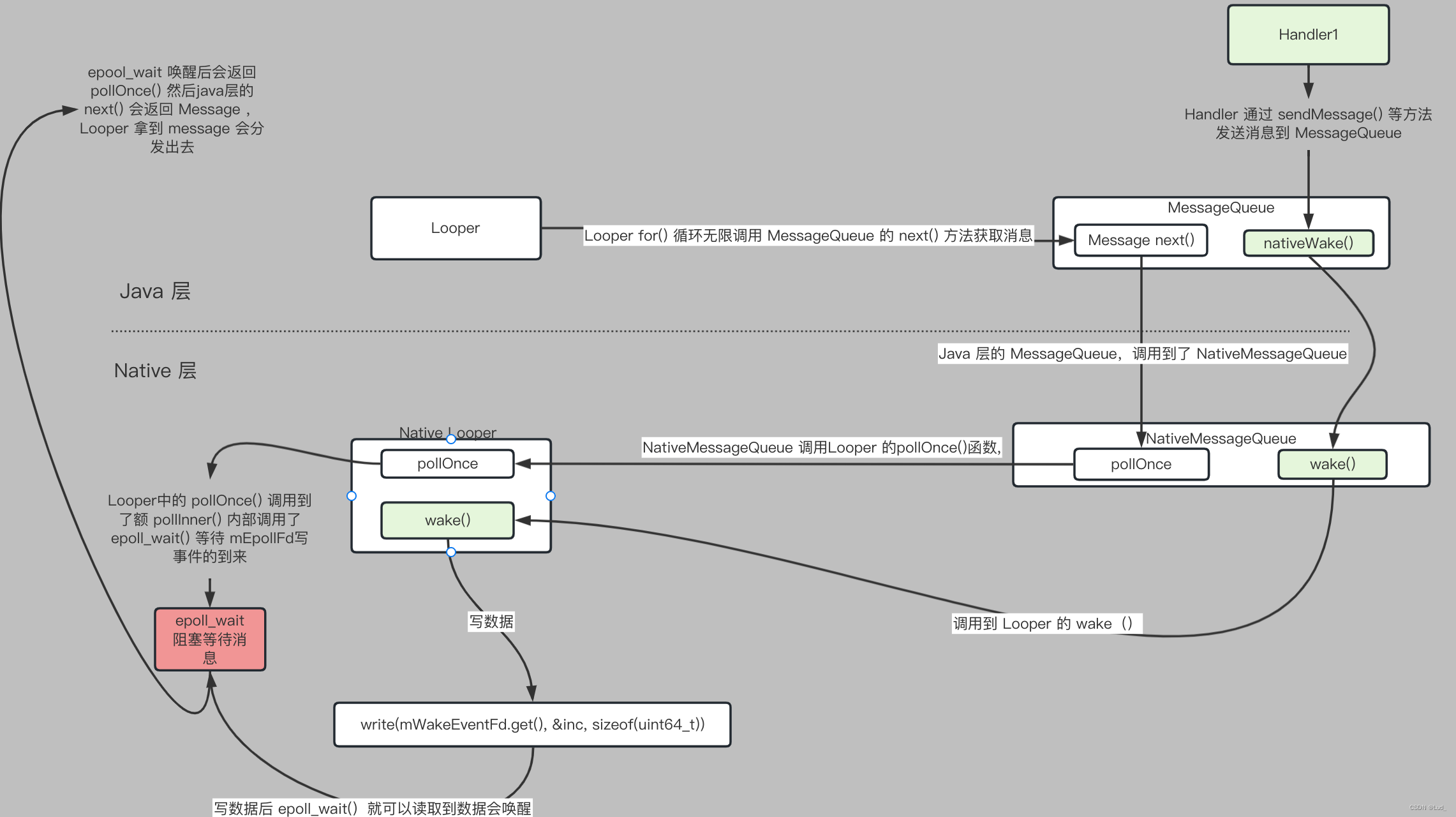
Handle 的延迟消息是怎么处理的?
- 发送延时消息一般从 Handler 发送消息开始,传入延迟的毫秒数。
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis){if (delayMillis < 0) {delayMillis = 0;}// 调用 sendMessageAtTime() 用当前时间 + 延迟时间 就是发送的时间return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);}
- sendMessageAtTime()
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {MessageQueue queue = mQueue;if (queue == null) {RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);return false;}return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);} private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {msg.target = this;if (mAsynchronous) {msg.setAsynchronous(true);}return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);}
调用了 MessageQueue 的 enqueueMessage() 传入了 msg 和 时间
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {synchronized (this) {//...msg.when = when;Message p = mMessages;boolean needWake;if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {// 消息队列是空 或者 when = 0 (调用 sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue 的时候 when = 0)// 或者比第一个时间还早 // 满足上面几个条件之一则插入到第一个节点msg.next = p;mMessages = msg;needWake = mBlocked;} else {needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();Message prev;for (;;) {// for 循环找到比第一个时间比它大的时间插入到它前面,就是按照时间从小到大排序prev = p;p = p.next;if (p == null || when < p.when) {break;}if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {needWake = false;}}msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.nextprev.next = msg;}if (needWake) {nativeWake(mPtr);}}return true;}
enqueueMessage() 就是按照时间为 Message 单链表做了个排序,所以延迟的意思就是先加入队列,到时间再处理消息。然后还是调用了 nativeWake(mPtr); 函数,上面代码将到了 调用完了 nativeWake(mPtr); 会写入事件,唤醒 native 层的 Looper 循环返回数据。先看一下 java 层的 loop
public static void loop() {final Looper me = myLooper();for (;;) {Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.return;}}
需要注意的是无消息或者消息未到时间的阻塞是在 queue.next(); 函数中 那么如果 msg == null 返回的 return 是出现异常了 loop() 停止了, 这是两个概念。 接下来看一下 queue.next();
Message next() {int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; for (;;) {// 目的是阻塞线程,当其他线程发送一些特殊消息的时候会唤起阻塞// 第一次 nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0 所以第一次一定不会阻塞// 如果第一次下去之后没有消息了 nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1 了就需要一直等待了nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();Message prevMsg = null;Message msg = mMessages;if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.do {prevMsg = msg;msg = msg.next;} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());}if (msg != null) {if (now < msg.when) {// 如果消息还没到时间,则 nextPollTimeoutMillis 等待时间设置成还差多少时间nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);} else {// 如果时间到了则返回 msgmBlocked = false;if (prevMsg != null) {prevMsg.next = msg.next;} else {mMessages = msg.next;}msg.next = null;msg.markInUse();return msg;}} else {// No more messages.nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}}
}
上面讲的时候说过,没有消息时 nativePollOnce() 会阻塞住,当 nativeWake() 发送后,会使得 nativePollOnce() 通过,会走下面的代码。首先 nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); 的 nextPollTimeoutMillis 参数是指睡眠多长时间,如果是 -1 则一直睡眠等待 wake() ,上面拿到 message 后如果到了时间则直接返回 msg ,如果还未到则计算一下还剩下多少时间赋值给 nextPollTimeoutMillis ,然后调用 nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); 睡眠等待时间到达。 下一次唤醒会把 msg 返回回去。
- 总结
延迟操作就是首先按照时间顺序插入消息队列中,然后通过 epoll_wait() 进行延迟阻塞,到时间了再返回消息。只不过延迟精度不一定很精确。而且如果处理消息太耗时,可能会让下一个消息延迟了。
IdleHandler 的原理
了解 IdleHandler 的作用以及调用方式了解 IdleHandler 有哪些使用场景熟悉 IdleHandler 的实现原理
/*** Callback interface for discovering when a thread is going to block* waiting for more messages.*/public static interface IdleHandler {/*** Called when the message queue has run out of messages and will now* wait for more. Return true to keep your idle handler active, false* to have it removed. This may be called if there are still messages* pending in the queue, but they are all scheduled to be dispatched* after the current time.*/boolean queueIdle();}
从上面注释来看,boolean queueIdle(); 回调的时机第一种是消息队列中没有了消息。第二种可能是消息队列中有消息,但是时间还未到执行它的时候。
- IdleHanlder 的用法
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new MessageQueue.IdleHandler() {@Overridepublic boolean queueIdle() {// 如果 return true; 就可以一直收到回调,如果 return false;就只能收到一次回调return true;}});
- MessageQueue 中 addIdleHandler() 函数
private final ArrayList<IdleHandler> mIdleHandlers = new ArrayList<IdleHandler>();public void addIdleHandler(@NonNull IdleHandler handler) {if (handler == null) {throw new NullPointerException("Can't add a null IdleHandler");}synchronized (this) {mIdleHandlers.add(handler);}}
addIdleHandler() 函数就是往 mIdleHandlers 数组中添加一个 handler ,那么 mIdleHandlers 的列表是什么时候调用的?
- mIdleHandlers 的列表是什么时候调用的?
在 Looper 的 loop() 函数中,上面讲过 loop() 会从 MessageQueue 中获取Message,然后去执行分发,然乎回收消息。那么MessageQueue是如何返回消息的?
- MessageQueue: next() 函数
Message next() {int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iterationint nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;for (;;) {// 阻塞用 有消息 或者超时 或者异常了 会往下走nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {// ... 获取 Message 逻辑省略// 如果没有获取到普通Message消息会往下获取 mIdleHandlers 中的数据// If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.// Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message// in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();}// 如果没有 IdleHandler 则直接跳过此次循环if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.mBlocked = true;continue;}if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];}// 将 mIdleHandlers 转换为数组mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);}// Run the idle handlers.// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.// 从 数组中获取 IdleHandler 数据for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handlerboolean keep = false;try {keep = idler.queueIdle();} catch (Throwable t) {Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);}// 如果 queueIdle() 返回的 false 则执行完了从列表中删除,也就是只执行一次if (!keep) {synchronized (this) {mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);}}}pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;}}
所以 nativePollOnce() 返回之后没有消息需要分发了,就开始处理 IdleHandler 中的数据了。
- framework 中用到了 IdleHandler 的地方
void scheduleGcIdler() {if (!mGcIdlerScheduled) {mGcIdlerScheduled = true;Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(mGcIdler);}mH.removeMessages(H.GC_WHEN_IDLE);}final class GcIdler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler {@Overridepublic final boolean queueIdle() {doGcIfNeeded();// 返回。false 只执行一次return false;}}在 ActivityThread 中添加进去了一个 mGcIdler 执行的时候会调用GC操作。
需要注意的是,如果 MessageQueue 中没有消息了,addIdleHandler 之后并不会触发 Idle 事件的执行,有时候需要往 MessageQueue 中 send 一条普通消息才可以。下面那条例子也是其中之一
- 之前的 Idle 都是异步的,下面这种情况是处理同步 Idle 的情况。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java
public void waitForIdleSync() {validateNotAppThread();Idler idler = new Idler(null);mMessageQueue.addIdleHandler(idler);mThread.getHandler().post(new EmptyRunnable());idler.waitForIdle();}
waitForIdleSync() 等待 Idle 执行返回,最后调用了idler.waitForIdle(); 等待
public void waitForIdle() {synchronized (this) {while (!mIdle) {try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {}}}}
调用了 wait(); 同步等待线程 mIdle 完成。直到 IdleHandler 的 queueIdle() 方法执行
public final boolean queueIdle() {if (mCallback != null) {mCallback.run();}synchronized (this) {mIdle = true;notifyAll();}return false;}
将mIdle = true; 再调用 notifyAll(); ,这样上面 wait() 的代码就可以执行下去了。我们自己开发的时候也可以使用这种方式。
- IdleHandler 适用场景
- 之前研究性能优化中的启动优化时,一些不必要立刻启动的项目可以放到 IdleHandler 中执行,或者 Activity onCreate() 以后一些可以在 UI 绘制等以后执行的,可以放在 IdleHandler 执行。
- 批量任务:任务密集,只关注最终结果(比如打开 App 收到一堆通知要刷新UI ,可以先汇总,等待UI绘制结束再统一刷新一次页面。)
主线程进入了 Looper 循环为什么没有 ANR?
了解 ANR 触发原理了解应用大致启动流程了解消息循环机制了解系统和应用通信流程
- ANR 是什么?
ANR 实际上是 AMS 在系统进程弹出来的一个 dialog
AMS 在发生 ANR 时会调用
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {mAppErrors.appNotResponding(proc, activity, parent, aboveSystem, annotation);}});
- mAppErrors.appNotResponding(proc, activity, parent, aboveSystem, annotation);
// Bring up the infamous App Not Responding dialogMessage msg = Message.obtain();msg.what = ActivityManagerService.SHOW_NOT_RESPONDING_UI_MSG;msg.obj = new AppNotRespondingDialog.Data(app, activity, aboveSystem);mService.mUiHandler.sendMessage(msg);
上面发送 mUiHandler 不是在 SystemServer 的主线程,其实是在子线程。(所以 UI 不一定是在主线程刷新,之前讲 UI 线程的时候提到过)
在 frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java 中会接收到 handleMessage 消息
final class UiHandler extends Handler {@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {switch (msg.what) {case SHOW_NOT_RESPONDING_UI_MSG: {mAppErrors.handleShowAnrUi(msg);ensureBootCompleted();} break;
在 mAppErrors.handleShowAnrUi(msg); 中会创建 diaog
dialogToShow = new AppNotRespondingDialog(mService, mContext, data);proc.anrDialog = dialogToShow;dialogToShow.show();
-
发生 ANR 的场景有哪些
Service TimeoutBroadcastQueue TimeoutContentProvider TimeoutInputDispatching Timeout (包括 Activity 输入等处理超时) -
那么 ANR 是怎么触发的呢?系统如何知道 ANR 了。
下面以 Service 为例
之前的文章 Android 深入理解 Service 的启动和绑定 有讲到过启动 service 的过程要经过下面的方法。
- ActiveService : realStartServiceLocked()
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),app.repProcState);
}
在调用 app.thread.scheduleCreateService() 之前,先调用了 bumpServiceExecutingLocked()
private final void bumpServiceExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean fg, String why) {boolean timeoutNeeded = true;long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();if (r.executeNesting == 0) {r.executeFg = fg;ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();if (stracker != null) {stracker.setExecuting(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), now);}if (r.app != null) {r.app.executingServices.add(r);r.app.execServicesFg |= fg;if (timeoutNeeded && r.app.executingServices.size() == 1) {scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);}}} else if (r.app != null && fg && !r.app.execServicesFg) {r.app.execServicesFg = true;if (timeoutNeeded) {scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);}}//...}
其内部调用了 scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
// static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG = 12;// How long we wait for a service to finish executing.static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT = 20*1000;// How long we wait for a service to finish executing.static final int SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT = SERVICE_TIMEOUT * 10;void scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(ProcessRecord proc) {if (proc.executingServices.size() == 0 || proc.thread == null) {return;}Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);msg.obj = proc;mAm.mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,proc.execServicesFg ? SERVICE_TIMEOUT : SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT);}
其实内部就是为 ActivityManagerService 的 handler 发送了一个延迟消息延迟时间就是 service 超时时间。发送的what = static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG = 12; 超时以后 AMS 接收到消息就会调用到 frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java ,再调用到了 mAm.mAnrHelper.appNotResponding(proc, anrMessage); 然后就弹出弹窗了。
-
那么如果 Service 正常启动了以后为什么没有弹窗呢?
之前文章讲过,Service 启动会回调到 ActivityThread 的 handleCreateService() -
handleCreateService()
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {// 这里面就是说的 IdleHanlder 的用处之一unscheduleGcIdler();LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);Service service = null;try {java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();service = packageInfo.getAppFactory().instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);} try {ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);context.setOuterContext(service);Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,ActivityManager.getService());service.onCreate();mServices.put(data.token, service);try {// 调用完了 service.onCreate(); 之后调用到了 AMS 的serviceDoneExecuting() ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);} catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();}} }
-
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
然后调用到了 serviceDoneExecutingLocked() -
重点:serviceDoneExecutingLocked 内部调用了下面方法
static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG = 12;mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r.app);
将同一个 what 属性的 ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG 从 Handler 移除掉,这样 ANR 的弹窗就不会弹出来了。
- 主线程的消息循环
public static void main(String[] args) {Looper.prepareMainLooper();// ... Looper.loop();}
原理上面已经讲过,loop() 循环 从 MeesageQueue 中读取数据,等等…,那么有几种情况会发送消息到主线程的 Hanlder 呢
1. 应用主线程发送消息2. 应用子线程发送消息3. binder 线程往主线程发送消息- 比如启动 AMS Service 都是通过 binder 线程发送到主线程去处理的
-
总结
为什么没有ANR:ANR是没有在规定时间内没有完成AMS的任务,和 loop() 循环没有啥必然联系AMS 的请求都是丢到应用端的 binder 线程去处理,然后再丢到发送消息去唤醒主线程处理。ANR 不是因为 for(;;) 而是主线程有耗时任务导致的 AMS 任务延迟导致的。比如上面启动 Service 的情况是先走的 service.onCreate() 然后去移除的 Handler 消息,所以 service onCreate() 不能有太耗时的操作。
消息屏障是什么?
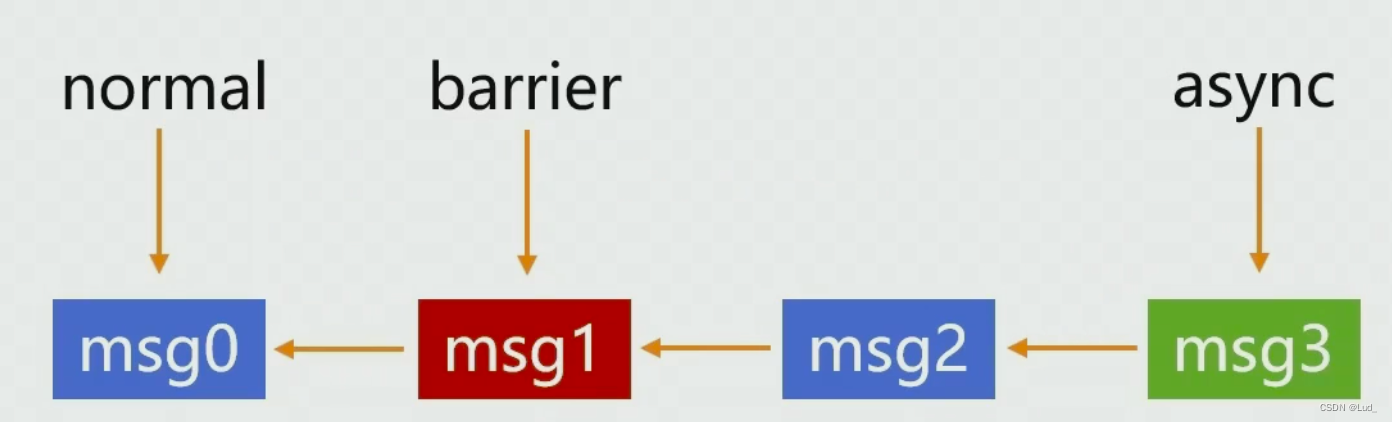
- 正常的消息队列分为几种消息,平时大多只用了普通消息,还有两种 一种是屏障消息,一种是异步消息。
- 屏障消息不是为了分发的,是为了阻塞普通消息的分发的
- 异步消息和普通消息的本质区别就是有一个异步的标志位,导致会有不同的处理。
- 如何发布一个屏障?
- frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java 中有一个函数 postSyncBarrier()
private int postSyncBarrier(long when) {synchronized (this) {final int token = mNextBarrierToken++;final Message msg = Message.obtain();msg.markInUse();msg.when = when;msg.arg1 = token;// 插入消息链表return token;}}
因为屏障消息不需要分发,所以不需要 target 也就是 Handler,后面会根据 target 是不是空来判断是不是屏障消息。并且它也会按照时间排序,不过它只会影响后面的消息。返回的 token 是用来后面撤销屏障用的。我们自己发送的消息 target 必须是有值的。
- 移除屏障的方法,需要通过 token
public void removeSyncBarrier(int token) {// Remove a sync barrier token from the queue.// If the queue is no longer stalled by a barrier then wake it.synchronized (this) {// 移除消息 ... // If the loop is quitting then it is already awake.// We can assume mPtr != 0 when mQuitting is false.if (needWake && !mQuitting) {nativeWake(mPtr);}}}
移除消息通过 token,移除后调用 nativeWake(mPtr); 函数唤醒 native_wait() 。唤醒以后会继续处理加入的普通消息。
- 屏障用在哪里了?
loop 获取消息是从 MessageQueue 中的 next() 函数,屏障消息也是如此
Message next() {final long ptr = mPtr;int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iterationint nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;for (;;) {nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);synchronized (this) {// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();Message prevMsg = null;Message msg = mMessages;// msg.target == null 就是屏障消息if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.do {// 如果是屏障消息则进入循环 一直往下查找有没有异步消息 如果有异步消息返回 没有则等待屏障的移除prevMsg = msg;msg = msg.next;} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());}if (msg != null) {// 处理返回消息return msg;} else {// No more messages.nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;}}nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;}}
next() 函数在获取 message 时,判断它是不是屏障消息,也就是 target == null ,如果是屏障消息则进行 do while() 循环,查找是否有异步消息要处理,如果有异步消息则返回异步消息,如果没异步消息,然后睡眠等待屏障的移除(需要其他线程唤醒,也就是上面的移除唤醒)。
- 插入消息也可能会唤醒线程
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {// 消息插入到了队列的头 如果休眠状态,需要唤醒// 如果普通消息,并且在屏障后面,则没有必要唤醒// 如果插入了最早的一条异步消息则需要唤醒if (needWake) {nativeWake(mPtr);}
}
- Android framework 哪里用到了屏障
主要是屏幕绘制的时候 ViewRootImpl 的 scheduleTraversals() 开始绘制之前发送了一个 postSyncBarrier()
void scheduleTraversals() {if (!mTraversalScheduled) {mTraversalScheduled = true;// 插入屏障 这样普通消息就会 block住。mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();// 然后等待 mTraversalRunnable 执行(下一个 vsync 信号到来)mChoreographer.postCallback(Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);}}
void doTraversal() {if (mTraversalScheduled) {mTraversalScheduled = false;mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);performTraversals();}}
doTraversal() 的时候移除消息,然后开始绘制了。目的是为了防止开始绘制因为普通消息延迟。
相关文章:

深入理解 Handler(java 层 + native 层)
文章目录回顾线程消息队列时怎样实现的消息是怎么传递的?Handle 的延迟消息是怎么处理的?IdleHandler 的原理主线程进入了 Looper 循环为什么没有 ANR?消息屏障是什么?回顾 之前学习过Handler相关的基础知识,今天再学…...
初步认识操作系统(Operator System)
操作系统一,冯诺依曼体系结构内存的重要作用二,操作系统的概念三,设计操作系统的目的三,操作系统在计算机体系中的定位四,操作系统是如何进行管理的一,冯诺依曼体系结构 在众多计算机相关的书籍中ÿ…...

Android—HTTPS部署自签名证书
一、生成自签名私有证书单向认证(只需要服务端证书) 生成server_ks.jks服务端密钥配置到服务端生成server.cer服务端证书配置到客户端 双向认证(还需要客户端证书,和信任证书) 生成client_ks.jks客户端密钥配置到客户…...
java基于springboot+vue微信小程序的学生健康管理
任何系统都要遵循系统设计的基本流程,本系统也不例外,同样需要经过市场调研,需求分析,概要设计,详细设计,编码,测试这些步骤,基于Java语言、微信小程序技术设计并实现了学生健康管理小程序。系统主要包括系统首页、个人中心、学生管理、健康档案管理、体检报告管理、健康评估管…...
金三银四丨黑蛋老师带你剖析-漏洞岗
作者丨黑蛋病毒岗之前我们简单看了看二进制逆向岗位和漏洞岗,今天我们来看一看病毒岗位,就单纯看二进制病毒岗位和漏洞岗位,其所需要的基础知识是差不多的,在Windows平台上,无非就是汇编,C语言,…...
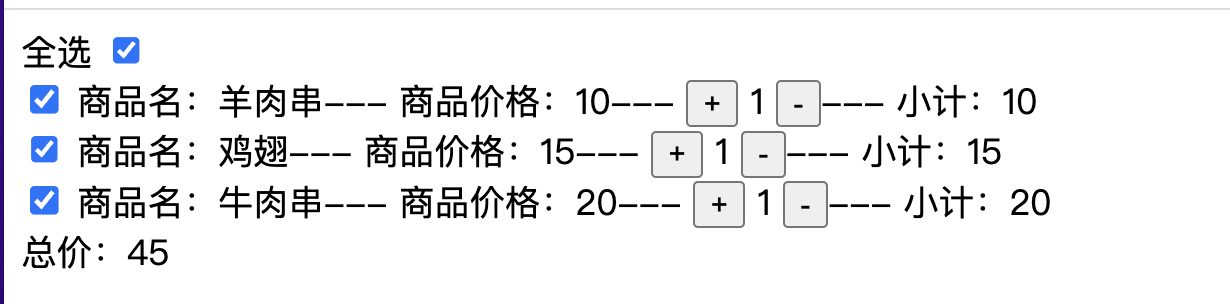
pinia实战 购物车(自定义插件实现pinia持久化)
目录 一、实例 二、需求 三. 代码解析 shop.vue shop.ts 四、持久化插件 插件介绍 持久化实现思路 一、实例 二、需求 单选全选功能,并且可以互相联动 小计功能 总计功能 商品加减,数量为零时不能在减 三. 代码解析 shop.vue 1.获取shop模块实…...
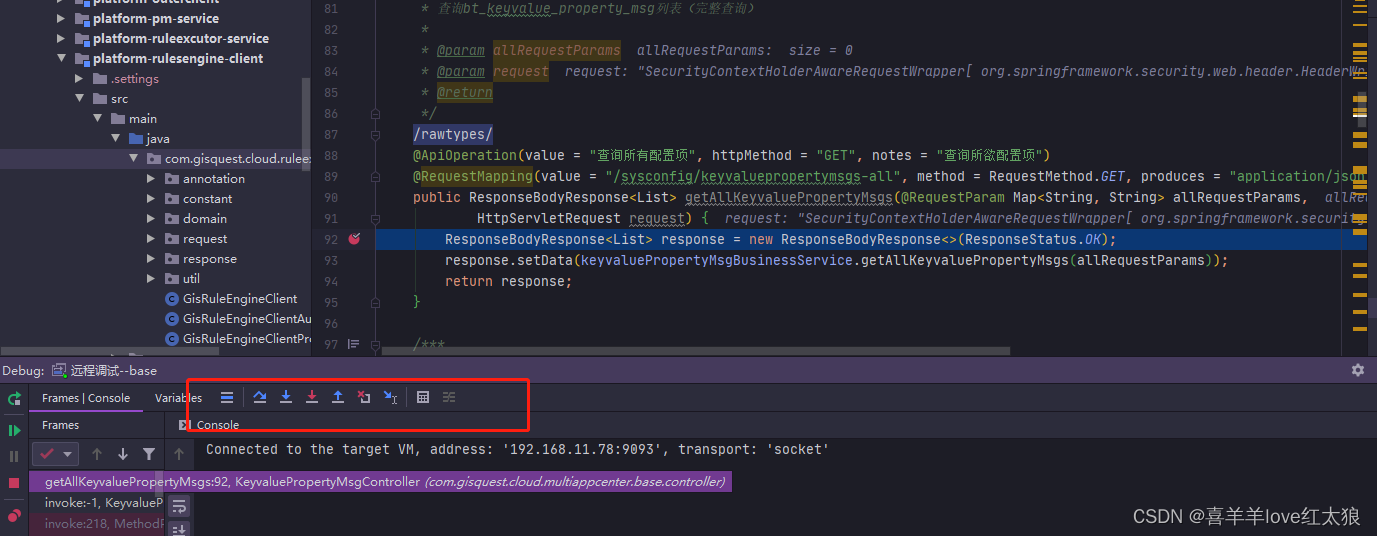
idea使用本地代码远程调试线上运行代码---linux环境
场景: 之前介绍过windows环境上,用idea进行远程调试那么在linux环境下实战一下 环境: linux 测试应用:使用docker部署的platform-multiappcenter-base-app-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar 应用 测试应用端口:19001 测试工具&…...
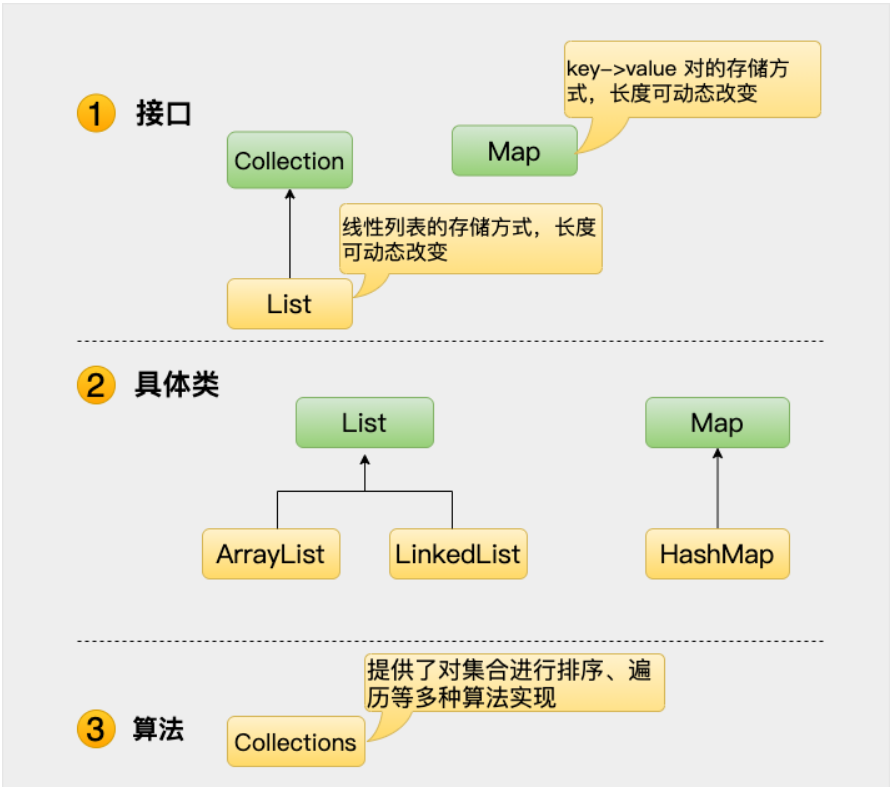
Java 基础面试题——集合
目录1.Java 有哪些常用容器(集合)?2.Collection 和 Collections 有什么区别?3.List、Set、Map 之间的区别是什么?4.HashMap 的长度为什么是 2 的 N 次方?源码中是如何保证的?5.HashMap 和 Hasht…...

编程思想、方法论和架构模式的应用
概要编程思想是指在编写代码时所采用的基本思维方式和方法论。分类编程思想分类:面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming,简称OOP):把数据和对数据的操作封装在一起,通过类和对象的概念实现模块化、可重…...
Vue|事件处理
事件处理1. 事件使用1.1 事件绑定1.2 事件参数2. 事件修饰符2.1 阻止默认事件2.2 阻止事件冒泡2.3 事件只允许触发一次2.4 事件捕获2.5 操作当前元素2.6 行为立即执行无需等待回调3. 键盘事件4. 本章小结4.1 事件使用小结4.2 事件修饰符小结4.3 键盘事件小结1. 事件使用 1.1 事…...
css书写方式
目录标题一、css是什么?二、css的书写方式1、行内样式【不推荐使用,太固定】2、页面样式(又叫内联样式)3、外联样式【店家推荐】4、import与link标签的区别一、css是什么? css(cascade style sheet)是用来装饰和装扮页…...
Python网络爬虫 学习笔记(2)BeaufitulSoup库
文章目录BeautifulSoup库的基本介绍HTML标签的获取和相关属性HTML文档的遍历prettify()方法使用BeautifulSoup库对HTML文件进行内容查找信息的标记的相关概念(非重点)find_all()方法(重点)综合实例:爬取软科2022中国大…...

JavaScript------内建对象
一、解构赋值 1、数组的解构 1.1、解构赋值 const arr ["孙悟空", "猪八戒", "沙和尚"];let a, b, c;[a, b, c] arr; // 等同于 [a, b, c] ["孙悟空", "猪八戒", "沙和尚"] 1.2、声明同时解构 let [d, e…...

React + Redux 处理异步请求
redux 处理异步请求 方式一:在 componentDidmount 中直接进⾏请求,在将数据同步到 redux 创建 Store 仓库 import {createStore } from redux;const defaultState = {banners: [] }const reducer =...
揭秘涨薪50%经验:从功能测试到自动化测试,我是如何蜕变的?
本人在今年互联网大环境如此严峻的情况下,作为一个刚毕业不到一年的初级测试,赶在“金三银四”依然拿到了一些面试机会,并且成功拿下4家公司的offer,其中不乏互联网大厂,而且最高总包给到了接近double(无炫…...
【论文速递】MMM2020 - 电子科技大学提出一种新颖的局部变换模块提升小样本分割泛化性能
【论文速递】MMM2020 - 电子科技大学提出一种新颖的局部变换模块提升小样本分割泛化性能 【论文原文】:A New Local Transformation Module for Few-shot Segmentation 【作者信息】:Yuwei Yang, Fanman Meng, Hongliang Li, Qingbo Wu,Xiaolong Xu an…...
)
补充前端面试题(二)
#$set数据变化视图不更新问题, 当在项目中直接设置数组的某一项的值,或者直接设置对象的某个属性值,这个时候,你会发现页面并没有更新。这是因为 Object.defineProperty()限制,监听不到变化。解决方式:this.$set(你要改…...
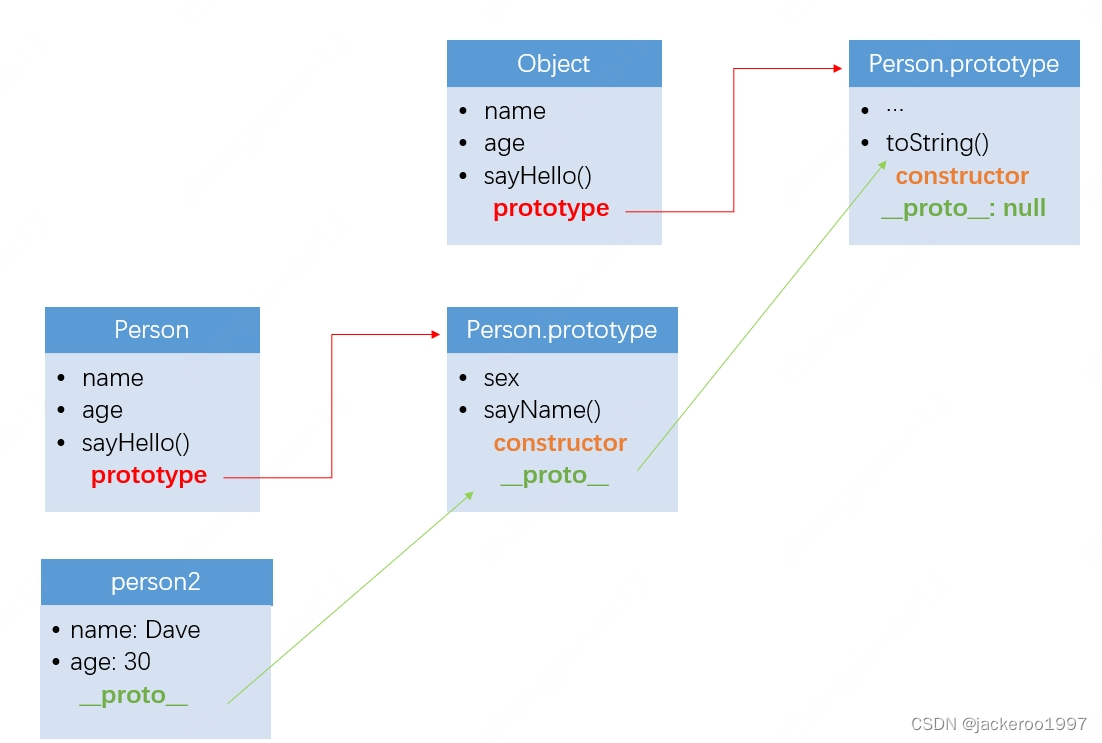
JavaScript原型、原型链、原型方法
文章目录原型和原型链prototype、 __ proto __ 、constructor原型链原型方法instanceOfhasOwnPropertyObject.create()、new Object()总结原型和原型链 prototype、 __ proto __ 、constructor 首先我们看下面一段代码 // 构造函数Personfunction Person(name, age) {this.na…...
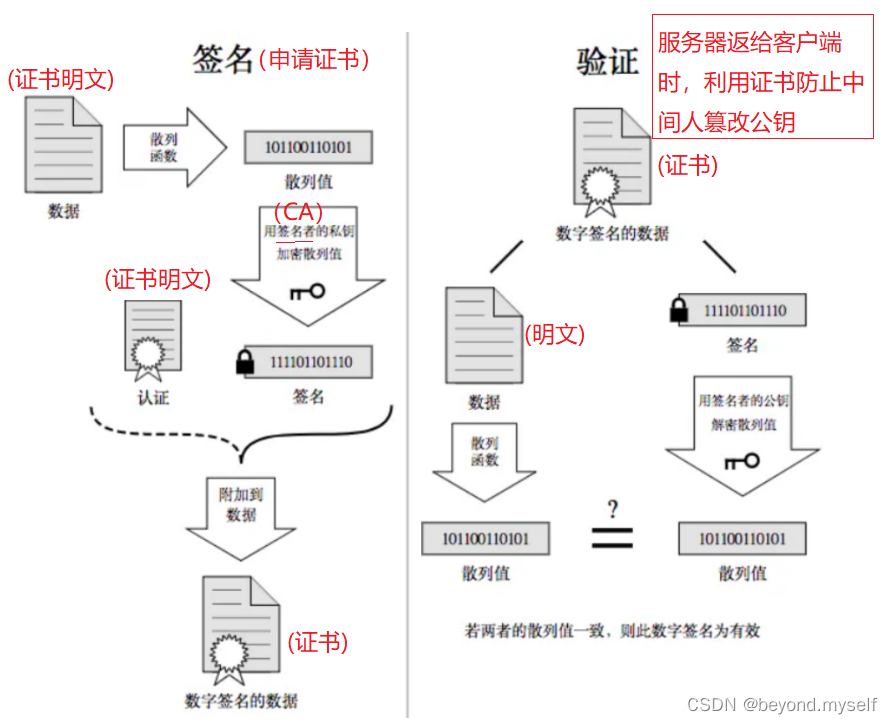
linux篇【14】:网络https协议
目录 一.HTTPS介绍 1.HTTPS 定义 2.HTTP与HTTPS (1)端口不同,是两套服务 (2)HTTP效率更高,HTTPS更安全 3.加密,解密,密钥 概念 4.为什么要加密? 5.常见的加密方式…...

1.9实验9:配置虚链路
1.4.4实验9:配置虚链路 实验目的(1) 实现OSPF 虚链路的配置 (2) 描述虚链路的作用 实验拓扑配置虚链路实验拓扑如图1-19所示。[1] 图1-19 配置虚链路 实验步骤...

Vim 调用外部命令学习笔记
Vim 外部命令集成完全指南 文章目录 Vim 外部命令集成完全指南核心概念理解命令语法解析语法对比 常用外部命令详解文本排序与去重文本筛选与搜索高级 grep 搜索技巧文本替换与编辑字符处理高级文本处理编程语言处理其他实用命令 范围操作示例指定行范围处理复合命令示例 实用技…...
观成科技:隐蔽隧道工具Ligolo-ng加密流量分析
1.工具介绍 Ligolo-ng是一款由go编写的高效隧道工具,该工具基于TUN接口实现其功能,利用反向TCP/TLS连接建立一条隐蔽的通信信道,支持使用Let’s Encrypt自动生成证书。Ligolo-ng的通信隐蔽性体现在其支持多种连接方式,适应复杂网…...
网络六边形受到攻击
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 抽象 现代智能交通系统 (ITS) 的一个关键要求是能够以安全、可靠和匿名的方式从互联车辆和移动设备收集地理参考数据。Nexagon 协议建立在 IETF 定位器/ID 分离协议 (…...
深入浅出Asp.Net Core MVC应用开发系列-AspNetCore中的日志记录
ASP.NET Core 是一个跨平台的开源框架,用于在 Windows、macOS 或 Linux 上生成基于云的新式 Web 应用。 ASP.NET Core 中的日志记录 .NET 通过 ILogger API 支持高性能结构化日志记录,以帮助监视应用程序行为和诊断问题。 可以通过配置不同的记录提供程…...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...
现代密码学 | 椭圆曲线密码学—附py代码
Elliptic Curve Cryptography 椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)是一种基于有限域上椭圆曲线数学特性的公钥加密技术。其核心原理涉及椭圆曲线的代数性质、离散对数问题以及有限域上的运算。 椭圆曲线密码学是多种数字签名算法的基础,例如椭圆曲线数字签…...

涂鸦T5AI手搓语音、emoji、otto机器人从入门到实战
“🤖手搓TuyaAI语音指令 😍秒变表情包大师,让萌系Otto机器人🔥玩出智能新花样!开整!” 🤖 Otto机器人 → 直接点明主体 手搓TuyaAI语音 → 强调 自主编程/自定义 语音控制(TuyaAI…...
Redis数据倾斜问题解决
Redis 数据倾斜问题解析与解决方案 什么是 Redis 数据倾斜 Redis 数据倾斜指的是在 Redis 集群中,部分节点存储的数据量或访问量远高于其他节点,导致这些节点负载过高,影响整体性能。 数据倾斜的主要表现 部分节点内存使用率远高于其他节…...
【分享】推荐一些办公小工具
1、PDF 在线转换 https://smallpdf.com/cn/pdf-tools 推荐理由:大部分的转换软件需要收费,要么功能不齐全,而开会员又用不了几次浪费钱,借用别人的又不安全。 这个网站它不需要登录或下载安装。而且提供的免费功能就能满足日常…...
uniapp 开发ios, xcode 提交app store connect 和 testflight内测
uniapp 中配置 配置manifest 文档:manifest.json 应用配置 | uni-app官网 hbuilderx中本地打包 下载IOS最新SDK 开发环境 | uni小程序SDK hbulderx 版本号:4.66 对应的sdk版本 4.66 两者必须一致 本地打包的资源导入到SDK 导入资源 | uni小程序SDK …...
