常用路径规划算法简介及python程序
目录
- 1、前言
- 2、D*算法
- 2.1简介
- 2.2优缺点
- 2.2.1 优点
- 2.2.2 缺点
- 2.3 python程序
- 3、A*算法
- 3.1 优缺点:
- 3.1.1 优点:
- 3.1.2 缺点:
- 3.2 python程序
- 4、人工势场算法
- 4.1优缺点
- 4.1.1优点:
- 4.1.2缺点:
- 4.2 python程序
- 5、Dijkstra算法
- 5.1优缺点
- 5.1.1优点:
- 5.1.2缺点:
- 5.2python程序
1、前言
在这篇博文中,我将为您介绍A算法、D算法、人工势场算法和Dijkstra算法等路径规划算法。我将详细解释它们的原理和优缺点,并展示一些学者编写的Python程序来演示它们的运行效果。通过阅读本文,您将对这些算法有一定的了解,并能够在实际应用中选择最适合的算法。
2、D*算法
2.1简介
D*规划算法是一种用于路径规划的增量式搜索算法。它可以在已知环境地图的情况下,根据实时的传感器信息和环境变化来动态更新路径规划结果。
D*规划算法的核心思想是通过不断地修正路径的代价值来逐步优化路径规划结果。它使用了两个重要的数据结构:状态图和代价图。状态图表示了地图中的各个位置以及它们之间的连接关系,而代价图则记录了每个位置到目标位置的代价值。
D*规划算法的基本流程如下:
- 初始化:设置起始位置和目标位置,并初始化状态图和代价图。
- 通过启发式函数计算起始位置到目标位置的估计代价值,并将起始位置加入到开放列表中。
- 进入循环,直到找到最优路径或者无法找到路径:
a. 选择开放列表中代价最小的位置作为当前位置。
b. 更新当前位置周围的邻居节点的代价值,并将其加入到开放列表中。
c. 如果目标位置的代价值发生变化,则重新计算路径。 - 根据最终的路径结果进行导航或执行其他操作。
D*规划算法具有较好的实时性能和适应性,可以应对环境变化和动态障碍物的情况。
2.2优缺点
2.2.1 优点
- 实时性:D*规划算法能够在运行时根据环境的变化实时更新路径信息,适用于动态环境中的路径规划问题。
- 高效性:D*规划算法通过增量式的更新方式,避免了对整个地图进行重新规划,从而减少了计算量,提高了路径规划的效率。
- 适应性:D*规划算法能够根据环境的变化自适应地调整路径,可以应对障碍物的移动或新增等情况。
2.2.2 缺点
- 初始规划开销较大:D*规划算法需要进行一次全局规划来初始化路径信息,这个过程可能会消耗较多的计算资源和时间。
- 对地图信息要求高:D*规划算法需要准确的环境地图信息,如果地图信息不准确或者不完整,可能会导致路径规划结果不理想。
- 对计算资源要求高:D*规划算法在实时更新路径信息时需要进行大量的计算,对计算资源要求较高。
2.3 python程序

python程序如下:
"""D* grid planningauthor: Nirnay Roy"""
import mathfrom sys import maxsizeimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltshow_animation = Trueclass State:def __init__(self, x, y):self.x = xself.y = yself.parent = Noneself.state = "."self.t = "new" # tag for stateself.h = 0self.k = 0def cost(self, state):if self.state == "#" or state.state == "#":return maxsizereturn math.sqrt(math.pow((self.x - state.x), 2) +math.pow((self.y - state.y), 2))def set_state(self, state):""".: new#: obstaclee: oparent of current state*: closed states: current state"""if state not in ["s", ".", "#", "e", "*"]:returnself.state = stateclass Map:def __init__(self, row, col):self.row = rowself.col = colself.map = self.init_map()def init_map(self):map_list = []for i in range(self.row):tmp = []for j in range(self.col):tmp.append(State(i, j))map_list.append(tmp)return map_listdef get_neighbors(self, state):state_list = []for i in [-1, 0, 1]:for j in [-1, 0, 1]:if i == 0 and j == 0:continueif state.x + i < 0 or state.x + i >= self.row:continueif state.y + j < 0 or state.y + j >= self.col:continuestate_list.append(self.map[state.x + i][state.y + j])return state_listdef set_obstacle(self, point_list):for x, y in point_list:if x < 0 or x >= self.row or y < 0 or y >= self.col:continueself.map[x][y].set_state("#")class Dstar:def __init__(self, maps):self.map = mapsself.open_list = set()def process_state(self):x = self.min_state()if x is None:return -1k_old = self.get_kmin()self.remove(x)if k_old < x.h:for y in self.map.get_neighbors(x):if y.h <= k_old and x.h > y.h + x.cost(y):x.parent = yx.h = y.h + x.cost(y)elif k_old == x.h:for y in self.map.get_neighbors(x):if y.t == "new" or y.parent == x and y.h != x.h + x.cost(y) \or y.parent != x and y.h > x.h + x.cost(y):y.parent = xself.insert(y, x.h + x.cost(y))else:for y in self.map.get_neighbors(x):if y.t == "new" or y.parent == x and y.h != x.h + x.cost(y):y.parent = xself.insert(y, x.h + x.cost(y))else:if y.parent != x and y.h > x.h + x.cost(y):self.insert(y, x.h)else:if y.parent != x and x.h > y.h + x.cost(y) \and y.t == "close" and y.h > k_old:self.insert(y, y.h)return self.get_kmin()def min_state(self):if not self.open_list:return Nonemin_state = min(self.open_list, key=lambda x: x.k)return min_statedef get_kmin(self):if not self.open_list:return -1k_min = min([x.k for x in self.open_list])return k_mindef insert(self, state, h_new):if state.t == "new":state.k = h_newelif state.t == "open":state.k = min(state.k, h_new)elif state.t == "close":state.k = min(state.h, h_new)state.h = h_newstate.t = "open"self.open_list.add(state)def remove(self, state):if state.t == "open":state.t = "close"self.open_list.remove(state)def modify_cost(self, x):if x.t == "close":self.insert(x, x.parent.h + x.cost(x.parent))def run(self, start, end):rx = []ry = []self.insert(end, 0.0)while True:self.process_state()if start.t == "close":breakstart.set_state("s")s = starts = s.parents.set_state("e")tmp = startwhile tmp != end:tmp.set_state("*")rx.append(tmp.x)ry.append(tmp.y)if show_animation:plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")plt.pause(0.01)if tmp.parent.state == "#":self.modify(tmp)continuetmp = tmp.parenttmp.set_state("e")return rx, rydef modify(self, state):self.modify_cost(state)while True:k_min = self.process_state()if k_min >= state.h:breakdef main():m = Map(100, 100)ox, oy = [], []for i in range(-10, 60):ox.append(i)oy.append(-10)for i in range(-10, 60):ox.append(60)oy.append(i)for i in range(-10, 61):ox.append(i)oy.append(60)for i in range(-10, 61):ox.append(-10)oy.append(i)for i in range(-10, 40):ox.append(20)oy.append(i)for i in range(0, 40):ox.append(40)oy.append(60 - i)print([(i, j) for i, j in zip(ox, oy)])m.set_obstacle([(i, j) for i, j in zip(ox, oy)])start = [10, 10]goal = [50, 10]if show_animation:plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k")plt.plot(start[0], start[1], "og")plt.plot(goal[0], goal[1], "xb")plt.axis("equal")start = m.map[start[0]][start[1]]end = m.map[goal[0]][goal[1]]dstar = Dstar(m)rx, ry = dstar.run(start, end)if show_animation:plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':main()3、A*算法
A*算法是一种常用的启发式搜索算法,用于在图形结构中找到最短路径。它综合了广度优先搜索和贪婪最佳优先搜索的特点,通过评估函数来选择下一步要扩展的节点。
A*算法的原理如下:
首先,定义一个开放列表和一个关闭列表。开放列表用于存储待扩展的节点,关闭列表用于存储已经扩展过的节点。
将起始节点加入到开放列表中,并将其评估函数值设为0。
重复以下步骤直到找到目标节点或者开放列表为空:
a. 从开放列表中选择评估函数值最小的节点作为当前节点。
b. 将当前节点从开放列表中移除,并加入到关闭列表中。
c. 对当前节点的相邻节点进行遍历:
如果相邻节点已经在关闭列表中,则忽略。
如果相邻节点不在开放列表中,则将其加入到开放列表,并计算其评估函数值。
如果相邻节点已经在开放列表中,比较当前路径和之前路径的评估函数值,如果当前路径更优,则更新评估函数值和父节点。
如果开放列表为空,则表示无法找到目标节点,搜索失败。
3.1 优缺点:
3.1.1 优点:
可以保证找到最短路径,因为它综合了广度优先搜索和贪婪最佳优先搜索的特点。
在启发函数选择合适的情况下,可以高效地搜索大规模图形结构。
3.1.2 缺点:
启发函数的选择对算法的性能有很大影响,不同的启发函数可能导致不同的结果。
在某些情况下,A*算法可能会陷入局部最优解,无法找到全局最优解。
3.2 python程序

python程序:
"""A* grid planningauthor: Atsushi Sakai(@Atsushi_twi)Nikos Kanargias (nkana@tee.gr)"""import mathimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltshow_animation = Trueclass AStarPlanner:def __init__(self, ox, oy, resolution, rr):"""Initialize grid map for a star planningox: x position list of Obstacles [m]oy: y position list of Obstacles [m]resolution: grid resolution [m]rr: robot radius[m]"""self.resolution = resolutionself.rr = rrself.min_x, self.min_y = 0, 0self.max_x, self.max_y = 0, 0self.obstacle_map = Noneself.x_width, self.y_width = 0, 0self.motion = self.get_motion_model()self.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy)class Node:def __init__(self, x, y, cost, parent_index):self.x = x # index of gridself.y = y # index of gridself.cost = costself.parent_index = parent_indexdef __str__(self):return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str(self.cost) + "," + str(self.parent_index)def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):"""A star path searchinput:s_x: start x position [m]s_y: start y position [m]gx: goal x position [m]gy: goal y position [m]output:rx: x position list of the final pathry: y position list of the final path"""start_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(sx, self.min_x),self.calc_xy_index(sy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)goal_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(gx, self.min_x),self.calc_xy_index(gy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()open_set[self.calc_grid_index(start_node)] = start_nodewhile True:if len(open_set) == 0:print("Open set is empty..")breakc_id = min(open_set,key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(goal_node,open_set[o]))current = open_set[c_id]# show graphif show_animation: # pragma: no coverplt.plot(self.calc_grid_position(current.x, self.min_x),self.calc_grid_position(current.y, self.min_y), "xc")# for stopping simulation with the esc key.plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:plt.pause(0.001)if current.x == goal_node.x and current.y == goal_node.y:print("Find goal")goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_indexgoal_node.cost = current.costbreak# Remove the item from the open setdel open_set[c_id]# Add it to the closed setclosed_set[c_id] = current# expand_grid search grid based on motion modelfor i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0],current.y + self.motion[i][1],current.cost + self.motion[i][2], c_id)n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)# If the node is not safe, do nothingif not self.verify_node(node):continueif n_id in closed_set:continueif n_id not in open_set:open_set[n_id] = node # discovered a new nodeelse:if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:# This path is the best until now. record itopen_set[n_id] = noderx, ry = self.calc_final_path(goal_node, closed_set)return rx, rydef calc_final_path(self, goal_node, closed_set):# generate final courserx, ry = [self.calc_grid_position(goal_node.x, self.min_x)], [self.calc_grid_position(goal_node.y, self.min_y)]parent_index = goal_node.parent_indexwhile parent_index != -1:n = closed_set[parent_index]rx.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.x, self.min_x))ry.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.y, self.min_y))parent_index = n.parent_indexreturn rx, ry@staticmethoddef calc_heuristic(n1, n2):w = 1.0 # weight of heuristicd = w * math.hypot(n1.x - n2.x, n1.y - n2.y)return ddef calc_grid_position(self, index, min_position):"""calc grid position:param index::param min_position::return:"""pos = index * self.resolution + min_positionreturn posdef calc_xy_index(self, position, min_pos):return round((position - min_pos) / self.resolution)def calc_grid_index(self, node):return (node.y - self.min_y) * self.x_width + (node.x - self.min_x)def verify_node(self, node):px = self.calc_grid_position(node.x, self.min_x)py = self.calc_grid_position(node.y, self.min_y)if px < self.min_x:return Falseelif py < self.min_y:return Falseelif px >= self.max_x:return Falseelif py >= self.max_y:return False# collision checkif self.obstacle_map[node.x][node.y]:return Falsereturn Truedef calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy):self.min_x = round(min(ox))self.min_y = round(min(oy))self.max_x = round(max(ox))self.max_y = round(max(oy))print("min_x:", self.min_x)print("min_y:", self.min_y)print("max_x:", self.max_x)print("max_y:", self.max_y)self.x_width = round((self.max_x - self.min_x) / self.resolution)self.y_width = round((self.max_y - self.min_y) / self.resolution)print("x_width:", self.x_width)print("y_width:", self.y_width)# obstacle map generationself.obstacle_map = [[False for _ in range(self.y_width)]for _ in range(self.x_width)]for ix in range(self.x_width):x = self.calc_grid_position(ix, self.min_x)for iy in range(self.y_width):y = self.calc_grid_position(iy, self.min_y)for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy):d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y)if d <= self.rr:self.obstacle_map[ix][iy] = Truebreak@staticmethoddef get_motion_model():# dx, dy, costmotion = [[1, 0, 1],[0, 1, 1],[-1, 0, 1],[0, -1, 1],[-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],[-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)],[1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],[1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]]return motiondef main():print(__file__ + " start!!")# start and goal positionsx = 10.0 # [m]sy = 10.0 # [m]gx = 50.0 # [m]gy = 50.0 # [m]grid_size = 2.0 # [m]robot_radius = 1.0 # [m]# set obstacle positionsox, oy = [], []for i in range(-10, 60):ox.append(i)oy.append(-10.0)for i in range(-10, 60):ox.append(60.0)oy.append(i)for i in range(-10, 61):ox.append(i)oy.append(60.0)for i in range(-10, 61):ox.append(-10.0)oy.append(i)for i in range(-10, 40):ox.append(20.0)oy.append(i)for i in range(0, 40):ox.append(40.0)oy.append(60.0 - i)if show_animation: # pragma: no coverplt.plot(ox, oy, ".k")plt.plot(sx, sy, "og")plt.plot(gx, gy, "xb")plt.grid(True)plt.axis("equal")a_star = AStarPlanner(ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius)rx, ry = a_star.planning(sx, sy, gx, gy)if show_animation: # pragma: no coverplt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")plt.pause(0.001)plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':main()4、人工势场算法
Potential Field based path planner是一种基于势场的路径规划算法,它模拟了物体在势场中的运动方式来寻找最优路径。该算法通过将环境划分为障碍物和目标区域,并为每个区域分配一个势能值,来引导机器人或其他移动物体避开障碍物并朝向目标。
该算法的原理如下:
- 定义势能场:将环境划分为障碍物和目标区域,并为每个区域分配一个势能值。通常情况下,障碍物区域的势能值较高,而目标区域的势能值较低。
- 计算合力:根据机器人当前位置和周围环境的势能值,计算合力。合力由两部分组成:引力和斥力。引力指向目标区域,斥力来自障碍物区域。
- 更新机器人位置:根据合力的方向和大小,更新机器人的位置。机器人会受到引力的吸引,同时受到斥力的排斥,从而朝着势能值较低的目标区域移动。
- 重复步骤2和3,直到机器人到达目标区域或无法找到可行路径。
4.1优缺点
4.1.1优点:
-
算法简单易实现:该算法的原理相对简单,容易理解和实现。
-
实时性较好:由于只需要计算当前位置周围的势能值和合力,因此算法具有较好的实时性能。
-
能够处理动态环境:由于势能场是根据当前环境计算的,因此可以适应动态环境的变化。
4.1.2缺点:
- 容易陷入局部最优:由于算法只考虑当前位置周围的势能值,可能会导致机器人陷入局部最优解,无法找到全局最优路径。
- 难以处理复杂环境:在存在大量障碍物或复杂形状的环境中,势能场的计算和更新可能变得复杂且耗时。
- 缺乏路径规划的优化策略:该算法主要通过势能场来引导机器人移动,缺乏对路径规划的优化策略,可能导致路径长度较长或不够平滑。
4.2 python程序

"""Potential Field based path plannerauthor: Atsushi Sakai (@Atsushi_twi)"""from collections import deque
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# Parameters
KP = 5.0 # attractive potential gain
ETA = 100.0 # repulsive potential gain
AREA_WIDTH = 30.0 # potential area width [m]
# the number of previous positions used to check oscillations
OSCILLATIONS_DETECTION_LENGTH = 3show_animation = Truedef calc_potential_field(gx, gy, ox, oy, reso, rr, sx, sy):minx = min(min(ox), sx, gx) - AREA_WIDTH / 2.0miny = min(min(oy), sy, gy) - AREA_WIDTH / 2.0maxx = max(max(ox), sx, gx) + AREA_WIDTH / 2.0maxy = max(max(oy), sy, gy) + AREA_WIDTH / 2.0xw = int(round((maxx - minx) / reso))yw = int(round((maxy - miny) / reso))# calc each potentialpmap = [[0.0 for i in range(yw)] for i in range(xw)]for ix in range(xw):x = ix * reso + minxfor iy in range(yw):y = iy * reso + minyug = calc_attractive_potential(x, y, gx, gy)uo = calc_repulsive_potential(x, y, ox, oy, rr)uf = ug + uopmap[ix][iy] = ufreturn pmap, minx, minydef calc_attractive_potential(x, y, gx, gy):return 0.5 * KP * np.hypot(x - gx, y - gy)def calc_repulsive_potential(x, y, ox, oy, rr):# search nearest obstacleminid = -1dmin = float("inf")for i, _ in enumerate(ox):d = np.hypot(x - ox[i], y - oy[i])if dmin >= d:dmin = dminid = i# calc repulsive potentialdq = np.hypot(x - ox[minid], y - oy[minid])if dq <= rr:if dq <= 0.1:dq = 0.1return 0.5 * ETA * (1.0 / dq - 1.0 / rr) ** 2else:return 0.0def get_motion_model():# dx, dymotion = [[1, 0],[0, 1],[-1, 0],[0, -1],[-1, -1],[-1, 1],[1, -1],[1, 1]]return motiondef oscillations_detection(previous_ids, ix, iy):previous_ids.append((ix, iy))if (len(previous_ids) > OSCILLATIONS_DETECTION_LENGTH):previous_ids.popleft()# check if contains any duplicates by copying into a setprevious_ids_set = set()for index in previous_ids:if index in previous_ids_set:return Trueelse:previous_ids_set.add(index)return Falsedef potential_field_planning(sx, sy, gx, gy, ox, oy, reso, rr):# calc potential fieldpmap, minx, miny = calc_potential_field(gx, gy, ox, oy, reso, rr, sx, sy)# search pathd = np.hypot(sx - gx, sy - gy)ix = round((sx - minx) / reso)iy = round((sy - miny) / reso)gix = round((gx - minx) / reso)giy = round((gy - miny) / reso)if show_animation:draw_heatmap(pmap)# for stopping simulation with the esc key.plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])plt.plot(ix, iy, "*k")plt.plot(gix, giy, "*m")rx, ry = [sx], [sy]motion = get_motion_model()previous_ids = deque()while d >= reso:minp = float("inf")minix, miniy = -1, -1for i, _ in enumerate(motion):inx = int(ix + motion[i][0])iny = int(iy + motion[i][1])if inx >= len(pmap) or iny >= len(pmap[0]) or inx < 0 or iny < 0:p = float("inf") # outside areaprint("outside potential!")else:p = pmap[inx][iny]if minp > p:minp = pminix = inxminiy = inyix = minixiy = miniyxp = ix * reso + minxyp = iy * reso + minyd = np.hypot(gx - xp, gy - yp)rx.append(xp)ry.append(yp)if (oscillations_detection(previous_ids, ix, iy)):print("Oscillation detected at ({},{})!".format(ix, iy))breakif show_animation:plt.plot(ix, iy, ".r")plt.pause(0.01)print("Goal!!")return rx, rydef draw_heatmap(data):data = np.array(data).Tplt.pcolor(data, vmax=100.0, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)def main():print("potential_field_planning start")sx = 0.0 # start x position [m]sy = 10.0 # start y positon [m]gx = 30.0 # goal x position [m]gy = 30.0 # goal y position [m]grid_size = 0.5 # potential grid size [m]robot_radius = 50.0 # robot radius [m]ox = [15.0, 5.0, 20.0, 25.0] # obstacle x position list [m]oy = [25.0, 15.0, 26.0, 25.0] # obstacle y position list [m]if show_animation:plt.grid(True)plt.axis("equal")# path generation_, _ = potential_field_planning(sx, sy, gx, gy, ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius)if show_animation:plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':print(__file__ + " start!!")main()print(__file__ + " Done!!")5、Dijkstra算法
是一种用于解决单源最短路径问题的经典算法。它可以找到从一个起始节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。
Dijkstra算法的流程如下:
- 创建一个集合S,用于存放已经找到最短路径的节点。 初始化距离数组dist,将起始节点的距离设为0,其他节点的距离设为无穷大。
- 重复以下步骤,直到集合S包含所有节点:
a. 从距离数组dist中选择一个距离最小的节点u,将其加入集合S。
b. 对于节点u的每个邻居节点v,如果通过节点u到达节点v的路径比当前记录的最短路径更短,则更新距离数组dist中节点v的距离。 - 距离数组dist中记录的就是从起始节点到每个节点的最短路径。
5.1优缺点
5.1.1优点:
- 算法保证能够找到最短路径。
- 可以处理有向图和无向图。
- 可以处理带有负权边的图,但不能处理带有负权环的图。
5.1.2缺点:
-对于大规模图来说,算法的时间复杂度较高,为O(V^2),其中V是节点的数量。
-无法处理带有负权环的图,因为在每次迭代中,算法会选择当前距离最小的节点,而负权环会导致无限循环。
5.2python程序

python程序:
"""Grid based Dijkstra planningauthor: Atsushi Sakai(@Atsushi_twi)"""import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mathshow_animation = Trueclass Dijkstra:def __init__(self, ox, oy, resolution, robot_radius):"""Initialize map for a star planningox: x position list of Obstacles [m]oy: y position list of Obstacles [m]resolution: grid resolution [m]rr: robot radius[m]"""self.min_x = Noneself.min_y = Noneself.max_x = Noneself.max_y = Noneself.x_width = Noneself.y_width = Noneself.obstacle_map = Noneself.resolution = resolutionself.robot_radius = robot_radiusself.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy)self.motion = self.get_motion_model()class Node:def __init__(self, x, y, cost, parent_index):self.x = x # index of gridself.y = y # index of gridself.cost = costself.parent_index = parent_index # index of previous Nodedef __str__(self):return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str(self.cost) + "," + str(self.parent_index)def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):"""dijkstra path searchinput:s_x: start x position [m]s_y: start y position [m]gx: goal x position [m]gx: goal x position [m]output:rx: x position list of the final pathry: y position list of the final path"""start_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(sx, self.min_x),self.calc_xy_index(sy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)goal_node = self.Node(self.calc_xy_index(gx, self.min_x),self.calc_xy_index(gy, self.min_y), 0.0, -1)open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()open_set[self.calc_index(start_node)] = start_nodewhile True:c_id = min(open_set, key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost)current = open_set[c_id]# show graphif show_animation: # pragma: no coverplt.plot(self.calc_position(current.x, self.min_x),self.calc_position(current.y, self.min_y), "xc")# for stopping simulation with the esc key.plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:plt.pause(0.001)if current.x == goal_node.x and current.y == goal_node.y:print("Find goal")goal_node.parent_index = current.parent_indexgoal_node.cost = current.costbreak# Remove the item from the open setdel open_set[c_id]# Add it to the closed setclosed_set[c_id] = current# expand search grid based on motion modelfor move_x, move_y, move_cost in self.motion:node = self.Node(current.x + move_x,current.y + move_y,current.cost + move_cost, c_id)n_id = self.calc_index(node)if n_id in closed_set:continueif not self.verify_node(node):continueif n_id not in open_set:open_set[n_id] = node # Discover a new nodeelse:if open_set[n_id].cost >= node.cost:# This path is the best until now. record it!open_set[n_id] = noderx, ry = self.calc_final_path(goal_node, closed_set)return rx, rydef calc_final_path(self, goal_node, closed_set):# generate final courserx, ry = [self.calc_position(goal_node.x, self.min_x)], [self.calc_position(goal_node.y, self.min_y)]parent_index = goal_node.parent_indexwhile parent_index != -1:n = closed_set[parent_index]rx.append(self.calc_position(n.x, self.min_x))ry.append(self.calc_position(n.y, self.min_y))parent_index = n.parent_indexreturn rx, rydef calc_position(self, index, minp):pos = index * self.resolution + minpreturn posdef calc_xy_index(self, position, minp):return round((position - minp) / self.resolution)def calc_index(self, node):return (node.y - self.min_y) * self.x_width + (node.x - self.min_x)def verify_node(self, node):px = self.calc_position(node.x, self.min_x)py = self.calc_position(node.y, self.min_y)if px < self.min_x:return Falseif py < self.min_y:return Falseif px >= self.max_x:return Falseif py >= self.max_y:return Falseif self.obstacle_map[node.x][node.y]:return Falsereturn Truedef calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy):self.min_x = round(min(ox))self.min_y = round(min(oy))self.max_x = round(max(ox))self.max_y = round(max(oy))print("min_x:", self.min_x)print("min_y:", self.min_y)print("max_x:", self.max_x)print("max_y:", self.max_y)self.x_width = round((self.max_x - self.min_x) / self.resolution)self.y_width = round((self.max_y - self.min_y) / self.resolution)print("x_width:", self.x_width)print("y_width:", self.y_width)# obstacle map generationself.obstacle_map = [[False for _ in range(self.y_width)]for _ in range(self.x_width)]for ix in range(self.x_width):x = self.calc_position(ix, self.min_x)for iy in range(self.y_width):y = self.calc_position(iy, self.min_y)for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy):d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y)if d <= self.robot_radius:self.obstacle_map[ix][iy] = Truebreak@staticmethoddef get_motion_model():# dx, dy, costmotion = [[1, 0, 1],[0, 1, 1],[-1, 0, 1],[0, -1, 1],[-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],[-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)],[1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],[1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]]return motiondef main():print(__file__ + " start!!")# start and goal positionsx = -5.0 # [m]sy = -5.0 # [m]gx = 50.0 # [m]gy = 50.0 # [m]grid_size = 2.0 # [m]robot_radius = 1.0 # [m]# set obstacle positionsox, oy = [], []for i in range(-10, 60):ox.append(i)oy.append(-10.0)for i in range(-10, 60):ox.append(60.0)oy.append(i)for i in range(-10, 61):ox.append(i)oy.append(60.0)for i in range(-10, 61):ox.append(-10.0)oy.append(i)for i in range(-10, 40):ox.append(20.0)oy.append(i)for i in range(0, 40):ox.append(40.0)oy.append(60.0 - i)if show_animation: # pragma: no coverplt.plot(ox, oy, ".k")plt.plot(sx, sy, "og")plt.plot(gx, gy, "xb")plt.grid(True)plt.axis("equal")dijkstra = Dijkstra(ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius)rx, ry = dijkstra.planning(sx, sy, gx, gy)if show_animation: # pragma: no coverplt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")plt.pause(0.01)plt.show()if __name__ == '__main__':main()说明:
接下来,根据生成的样本,生成道路地图的。输入参数包括采样点的x坐标和y坐标,机器人安全半径,以及占用栅格的KDTree二叉树。输出是一个表示道路地图的列表。
算法首先对采样点进行了KDTree的构建,以便进行高效的搜索。然后,遍历每个采样点,对其进行搜索和路径生成。对于每个采样点,通过查询KDTree获得与其最近的其他采样点,并检查路径是否可达。如果路径可达,则将相应的索引添加到边的ID列表中。如果边的ID数量达到了最大路径数N_KNN,则结束搜索。最后,将边的ID列表添加到道路地图中。
整个算法的流程是:构建KDTree -> 遍历采样点 -> 查询最近的其他采样点 -> 检查路径可达性 -> 添加边的ID到列表 -> 添加列表到道路地图。
该算法是迪杰斯特拉路径规划算法(Dijkstra Planning Algorithm),用于在给定的地图中寻找起点到目标点的最短路径。算法接受起点和目标点的坐标,以及可能的路径地图、样本坐标列表作为输入。
算法首先将起点节点和目标节点初始化为PNode对象,并将起点节点添加到open_set字典中。然后,进入循环,如果open_set为空,则表示找不到路径,打印提示信息并跳出循环。否则,从open_set中选择cost最小的节点作为当前节点,进行路径搜索的下一步。
在路径搜索的过程中,如果开启了动画展示(show_animation为True),则每次经过闭集中节点数量为偶数时会绘制当前节点,并监听esc键以停止模拟。如果当前节点的索引等于目标节点索引,则表示找到了目标节点,将目标节点的父节点索引设置为当前节点的父节点索引,并跳出循环。
接下来,将当前节点从open_set中删除,并将其添加到closed_set中。然后,根据运动模型,扩展搜索网格,计算当前节点与目标节点之间的距离,并创建一个新的PNode对象。如果新节点的索引已经在closed_set中,则跳过当前循环。否则,如果新节点的索引已经在open_set中,则比较新节点的cost与open_set中已有节点的cost,如果新节点的cost更小,则更新open_set中的节点的cost和父节点索引为新节点的cost和父节点索引。否则,将新节点添加到open_set中。
最后,如果没有找到路径(path_found为False),则返回空列表。否则,生成最终的路径坐标列表rx和ry。从目标节点开始,迭代找到每个节点的父节点,将节点的x和y坐标添加到rx和ry中。直到父节点索引为-1,表示到达起点。返回rx和ry作为最短路径的坐标列表。
总之,该算法使用迪杰斯特拉算法,在给定的路径地图中寻找起点到目标点的最短路径,并返回路径的坐标列表。
相关文章:

常用路径规划算法简介及python程序
目录 1、前言2、D*算法2.1简介2.2优缺点2.2.1 优点2.2.2 缺点 2.3 python程序 3、A*算法3.1 优缺点:3.1.1 优点:3.1.2 缺点: 3.2 python程序 4、人工势场算法4.1优缺点4.1.1优点:4.1.2缺点: 4.2 python程序 5、Dijkstr…...

计算x的对数math.log(x)math.log(x, a)math.log2(x)math.log10(x)
【小白从小学Python、C、Java】 【计算机等考500强证书考研】 【Python-数据分析】 计算x的对数 math.log(x) math.log(x, a) math.log2(x) math.log10(x) [太阳]选择题 以下说法错误的是() import math print("【执行】e math.exp(1)") e …...
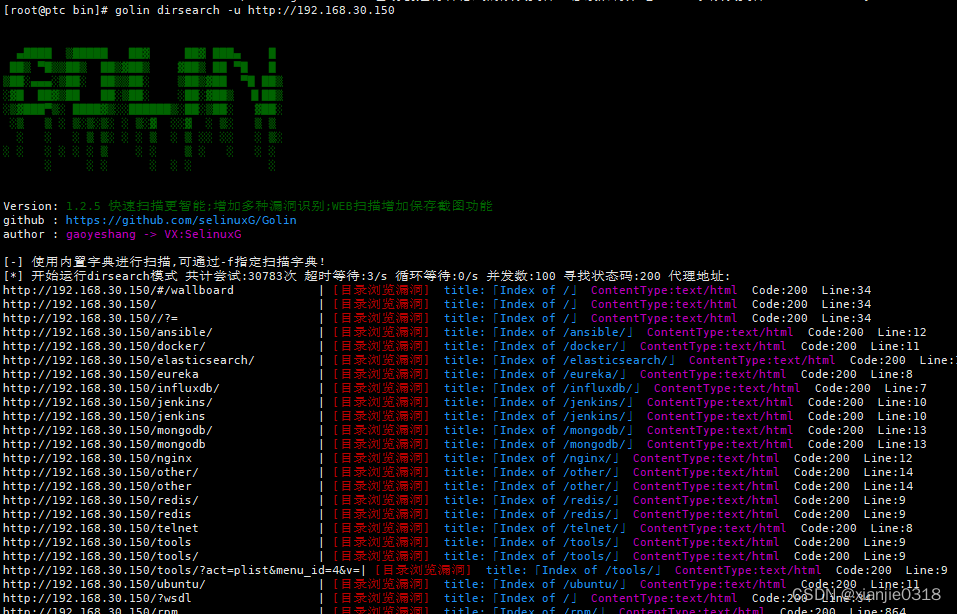
Golin 弱口令/漏洞/扫描/等保/基线核查的快速安全检查小工具
下载地址: 链接:https://pan.quark.cn/s/db6afba6de1f 主要功能 主机存活探测、漏洞扫描、子域名扫描、端口扫描、各类服务数据库爆破、poc扫描、xss扫描、webtitle探测、web指纹识别、web敏感信息泄露、web目录浏览、web文件下载、等保安全风险问题风险…...
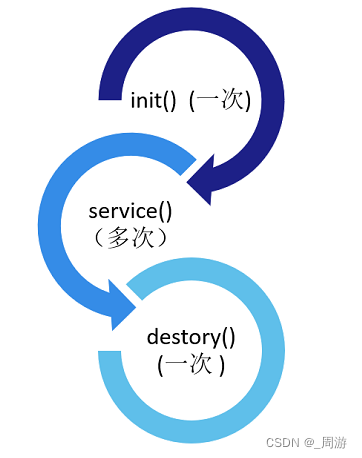
【JavaEE】_HttpServlet类
目录 1. init方法 2. destory方法 3. service方法 4. servlet生命周期 前文已经提及到:servlet是tomcat提供的,用于操作HTTP协议的一组API,可以将这组API理解为HTTP服务器的框架; 编写一个servlet程序,往往都要继…...
11-pytorch-使用自己的数据集测试
b站小土堆pytorch教程学习笔记 import torch import torchvision from PIL import Image from torch import nnimg_path ../imgs/dog.png imageImage.open(img_path) print(image) # imageimage.convert(RGB)transformtorchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.…...

数据安全之路:深入了解MySQL的行锁与表锁机制
欢迎来到我的博客,代码的世界里,每一行都是一个故事 数据安全之路:深入了解MySQL的行锁与表锁机制 前言基础innodb中锁与索引的关系如何避免表锁 前言 在当今数据密集的应用中,数据库锁成为了确保数据一致性和并发操作的关键工具…...

【深度学习】Pytorch 教程(十二):PyTorch数据结构:4、张量操作(3):张量修改操作(拆分、拓展、修改)
文章目录 一、前言二、实验环境三、PyTorch数据结构1、Tensor(张量)1. 维度(Dimensions)2. 数据类型(Data Types)3. GPU加速(GPU Acceleration) 2、张量的数学运算1. 向量运算2. 矩阵…...
适合新手博主站长使用的免费响应式WordPress博客主题JianYue
这款JianYue主题之所以命名为 JianYue,意思就是简单而不简约的。是根据Blogs主题优化而成,剔除了一些不必要的功能及排版,仅保留一种博客布局,让新手站长能够快速手上WordPress。可以说这款主题比较适合新手博主站长使用ÿ…...
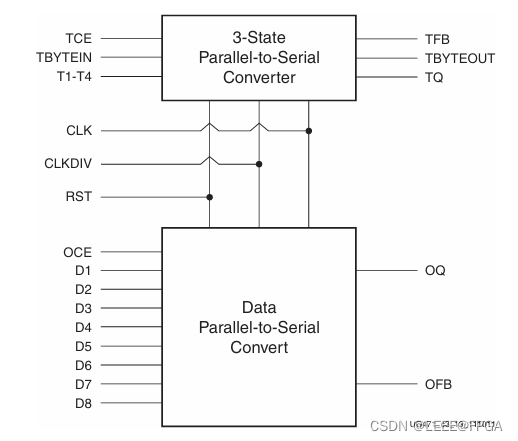
FPGA OSERDESE2
Output Parallel-to-Serial Logic Resources (OSERDESE2) OSERDESE2 在Xilinx 7 系列器件是一款专用的并行至串行转换器,具有特定的时钟和逻辑资源,旨在促进高速源同步接口的实现。每个OSERDESE2模块都包括一个专用的数据串行器和 3 状态控制。数据和 3 态串行器都可以在 SD…...

如何卸载Erlang以及RabbitMQ
参考以下两篇文章 https://blog.csdn.net/m0_49605579/article/details/130196536 Windows如何完全卸载RabbitMQ和Erlang_删除注册表hkey_local_machine\software\ericsson\erlang\e-CSDN博客 首先我是按照链接一的操作进行了卸载,但是Erlang的安装目录一直删除不…...
ros自定义action记录
文章目录 自定义action1. 定义action文件2. 修改 package.xml3. 修改 CMakeLists.txt4. 运行 catkin build5. simple_action_server.py6. simple_action_client.py 测试 自定义action ros 版本:kinetic 自定义test包的文件结构如下 |-- test | |-- CMakeLists.t…...

挑战30天学完Python:Day18 正则表达式
📘 Day 18 🎉 本系列为Python基础学习,原稿来源于 30-Days-Of-Python 英文项目,大奇主要是对其本地化翻译、逐条验证和补充,想通过30天完成正儿八经的系统化实践。此系列适合零基础同学,或仅了解Python一点…...
力扣● 343. 整数拆分 ● 96.不同的二叉搜索树
● 343. 整数拆分 想不到,要勇于看题解。 关键在于理解递推公式。 1、DP数组及其下标的含义:dp[i]是分解i这个数得到的最大的乘积。 2、DP数组如何初始化:dp[0]和dp[1]都没意义,所以直接不赋值,初始化dp[2]1即可。…...
游戏同步+游戏中的网络模块
原文链接:游戏开发入门(九)游戏同步技术_游戏数据同步机制流程怎么开发-CSDN博客 游戏开发入门(十)游戏中的网络模块_游戏开发组网-CSDN博客 3.同步技术的基本常识: a.同步给谁?某个用户&…...
【03】逆序数组
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 目录 一、逆序函数是什么? 二、逆序函数原码 1.直接逆序 2.创建临时数组逆序 三、结言 💥一、逆序函数是什么? 示例:输入1 4 …...
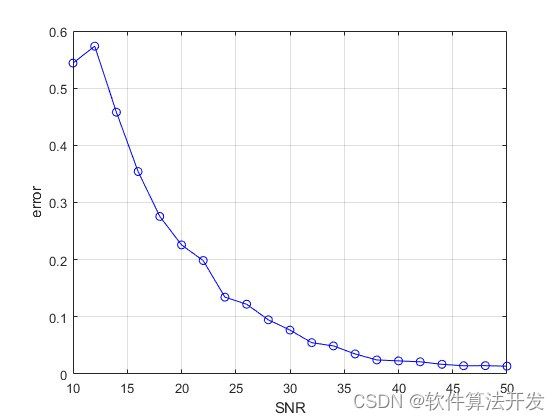
基于Prony算法的系统参数辨识matlab仿真
目录 1.程序功能描述 2.测试软件版本以及运行结果展示 3.核心程序 4.本算法原理 5.完整程序 1.程序功能描述 Prony算法是一种用于信号处理和系统辨识的经典方法,特别适用于线性时不变系统(LTI)的频率响应分析以及模拟复指数信号序列。其…...

创建第一个React项目
React脚手架 npx create-react-app react-demonpx是直接从互联网网上拉最新的脚手架进行创建react 运行React项目 npm start若想找到Webpack配置文件 npm ejectReact的基本使用 基本步骤 导入react和react-dom vue 创建react元素 渲染react元素到页面中导入 import React…...
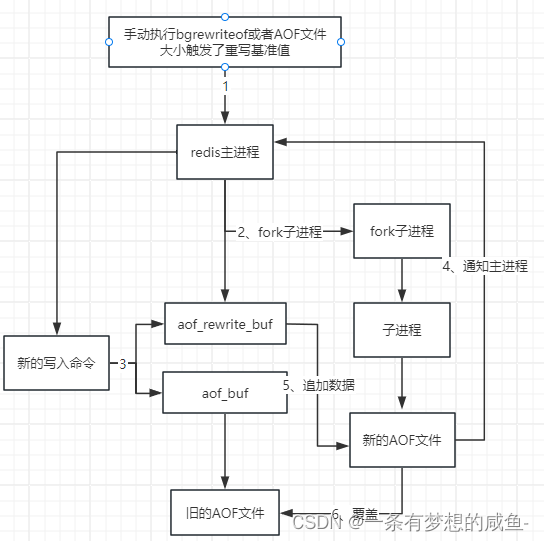
Redis篇之Redis持久化的实现
持久化即把数据保存到可以永久保存的存储设备当中(磁盘)。因为Redis是基于内存存储数据的,一旦redis实例当即数据将会全部丢失,所以需要有某些机制将内存中的数据持久化到磁盘以备发生宕机时能够进行恢复,这一过程就称…...
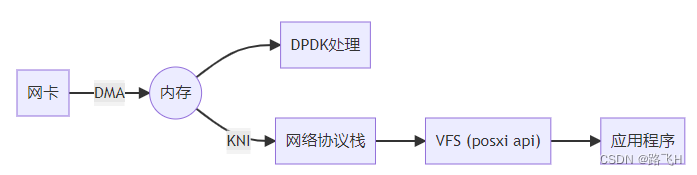
dpdk环境搭建和工作原理
文章目录 1、DPDK环境搭建1.1、环境搭建1.2、编译DPDK 2、DPDK工作原理 1、DPDK环境搭建 1.1、环境搭建 工具准备:VMware、ubuntu16.04。 (1)VMware添加两个网卡。桥接网卡作为 DPDK 运行的网卡,NAT 网卡作为 ssh 连接的网卡。 …...

接口测试实战--自动化测试流程
一、项目前期准备 常见项目软件架构: springMvc:tomcat里运行war包(在webapps目录下) springboot:java -jar xx.jar -xms(**) 运行参数 springCloud:k8s部署,使用kubectl create -f xx.yaml 接口自动化测试介入需越早越好,只要api定义好就可以编写自动化脚本; 某个…...

卡证检测矫正模型效果对比:不同光照与角度下的鲁棒性测试
卡证检测矫正模型效果对比:不同光照与角度下的鲁棒性测试 你有没有遇到过这样的场景?用手机拍身份证、银行卡或者驾驶证,想上传到某个App里,结果系统总是提示“图片不清晰”、“请摆正证件”或者“请避免反光”?这背后…...

造相-Z-Image-Turbo高可用架构:设计多节点负载均衡与故障转移方案
造相-Z-Image-Turbo高可用架构:设计多节点负载均衡与故障转移方案 当你的AI图像生成服务突然因为流量激增而卡顿,或者某个计算节点意外宕机导致用户排队等待时,那种感觉就像精心准备的晚宴突然停了电。对于“造相-Z-Image-Turbo”这类深度依…...
)
iOS设备上GoodNotes卡死自救指南:无需备份也能恢复笔记(附Filza详细操作)
iOS设备上GoodNotes卡死自救指南:无需备份也能恢复笔记 作为一名深度依赖GoodNotes进行日常记录的用户,我完全理解当应用突然卡死在初始化界面时的那种焦虑。上周我的iPad Pro突然遭遇这个问题,屏幕上永远停留在"准备自己的资料库&#…...

Janus-Pro-7B完整指南:统一多模态框架在Ollama中的部署与应用
Janus-Pro-7B完整指南:统一多模态框架在Ollama中的部署与应用 想找一个既能看懂图片,又能根据图片生成文字,甚至还能进行多轮对话的AI模型吗?Janus-Pro-7B可能就是你在找的那个“全能选手”。它不像传统模型那样,看图…...

Phi-3 Forest Lab零基础上手:向森林深处发送第一条讯息实操
Phi-3 Forest Lab零基础上手:向森林深处发送第一条讯息实操 1. 引言:从零开始,走进森林 想象一下,你有一个能理解你、能和你聊天、还能帮你解决各种问题的智能伙伴。它不需要强大的服务器,在你的个人电脑上就能流畅运…...

景区复购率低迷?全流程服务盘活留量|巨有科技
文旅行业复苏后,绝大多数景区都陷入了同一个运营怪圈:砸重金做营销、拓渠道抢新客,节假日客流爆满看似热闹,可游客离园之后,就彻底和景区断了联系,二次到访、多次复购的游客少之又少,老客留存率…...

wow-time时间操作说明
wow-time文件说明 项目地址:https://github.com/wow-iot3/wow_linux_eval本文件的功能主要用于处理时间操作,主要涉及时间信息获取(普通格式与cp56格式)、设置时间、格式转换、获取时间戳、获取毫秒数; 获取时间信息 int wow_time_get_cp56(C…...
_kaic)
weixin226基于微信小程序的新生报到系统的设计与实现ssm(文档+源码)_kaic
第5章 系统实现进入到这个环节,也就可以及时检查出前面设计的需求是否可靠了。一个设计良好的方案在运用于系统实现中,是会帮助系统编制人员节省时间,并提升开发效率的。所以在系统的编程阶段,也就是系统实现阶段,对于…...

从CSV到图表:sc-im处理数据的完整案例教程
从CSV到图表:sc-im处理数据的完整案例教程 【免费下载链接】sc-im sc-im - Spreadsheet Calculator Improvised -- An ncurses spreadsheet program for terminal 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/sc/sc-im sc-im是一款功能强大的终端电子表格程序…...

乙巳马年春联生成终端教育场景:AI对联创作比赛评分系统
乙巳马年春联生成终端教育场景:AI对联创作比赛评分系统 1. 引言:当传统文化遇见AI,一场别开生面的创作比赛 想象一下,在一所学校的礼堂里,学生们围坐在电脑前,他们不是在玩游戏,而是在参加一场…...
